Abstract
Glycosylation of proteins is a post-translational process where oligosaccharides are attached to proteins, potentially altering their folding, epitope availability, and immune recognition. In Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus-type 2 (PRRSV-2), positive selection pressure acts on amino acid sites potentially associated with immune escape through glycan shielding. Here, we describe the patterns of potential N-glycosylation sites over time and across different phylogenetic lineages of PRRSV-2 to better understand how these may contribute to patterns of coexistence and emergence of different lineages. We screened 19,179 PRRSV GP5 sequences (2004–2021) in silico for potential N-glycosylated sites. The emergence of novel combinations of N-glycosylated sites coincided with past PRRSV epidemics in the U.S. For lineage L1A, glycosylation at residues 32, 33, 44, 51, and 57 first appeared in 2012, but represented >62% of all L1A sequences by 2015, coinciding with the emergence of the L1A 1-7-4 strain that increased in prevalence from 8 to 86% of all L1A sequences from 2012 to 2015. The L1C 1-4-4 strain that emerged in 2020 also had a distinct N-glycosylation pattern (residues 32, 33, 44, and 51). From 2020 to 2021, this pattern was responsible for 44–47% of the L1C sequences, contrasting to <5% in years prior. Our findings support the hypothesis that antigenic evolution contributes to the sequential dominance of different PRRSV strains and that N-glycosylation patterns may partially account for antigenic differences amongst strains. Further studies on glycosylation and its effect on PRRSV GP5 folding are needed to further understand how glycosylation patterns shape PRRSV occurrence.
Keywords: glycosylation, PRRSV, multi-strain dynamics, epidemiology, emergence
1. Introduction
Glycosylation of proteins is a common post-translational process in which oligosaccharides are added to specific portions of proteins [1]. These additions may impact several biological functions of proteins, including folding and indirectly modulating interactions between polypeptide chains by “masking” or “exposing” particular portions of the peptides [1,2], which, from an immunological standpoint, may modify how certain epitopes are recognized by hosts. Several types of glycosylation have been described, but the most commonly studied is N-linked glycosylation, which may occur when a specific set or sequon of amino acids (Asn-Xxx-Thr/Ser) occur in a protein [3].
The impact that glycosylation may have on human infections has been investigated under the context of several viruses’ envelope glycoproteins [4]. The interactions between glycosylated viral proteins and cellular receptors have been shown to influence viral entry in host cells by viral hepatitis [5], while N-linked glycosylation is thought to be a key component of HIV evasion from humoral immunity [6,7]. More recently, changes in the glycosylation patterns of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein have been associated with the emergence of new variants of interest [8].
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus-type 2 (PRRSV-2), which is an RNA virus in the Betaarterivirus genus and Arteriviridae family (PRRSV-2), is the costliest disease affecting the U.S. swine herd, with annual losses estimated to be greater than USD 650 million dollars [9]. PRRSV-2 is genetically diverse, with numerous lineages and sub-lineages described [10,11,12]. The emergence of different strains of PRRSV-2 is thought to be at least partially driven by immunological processes [12,13]. N-glycosylation is relevant to this topic because it has the potential to modify how the virus is recognized by the host immune system. The prototype VR2332 strain GP5 protein contains at least three N-glycosylation sites that are thought to be important for virus assembly and entry into host cells [14]. The main envelope protein, GP5, is a transmembrane protein that contains the Principle Neutralizing Epitope (located roughly between residues 35 and 51), which is flanked by hypervariable regions 1 and 2 (residues 32–39 and 57–61, respectively) (Figure 1) [12,15,16,17]. Residues in the hypervariable positions are frequently reported to be glycosylated [18,19] and are often under positive selection pressure [11,20]. Animals infected with PRRSV strains with distinct glycosylation patterns had different neutralizing antibody production profiles, suggesting that the presence or absence of specific glycosylation may alter the immunogenicity of the virus [19]. Even though macro-evolutionary and multi-strain dynamics of PRRSV are hypothesized to be at least partially immune-driven [12,21], little can be found describing glycosylation patterns on PRRSV over time [22], which could partially explain the emergence and turnover of PRRSV strains.
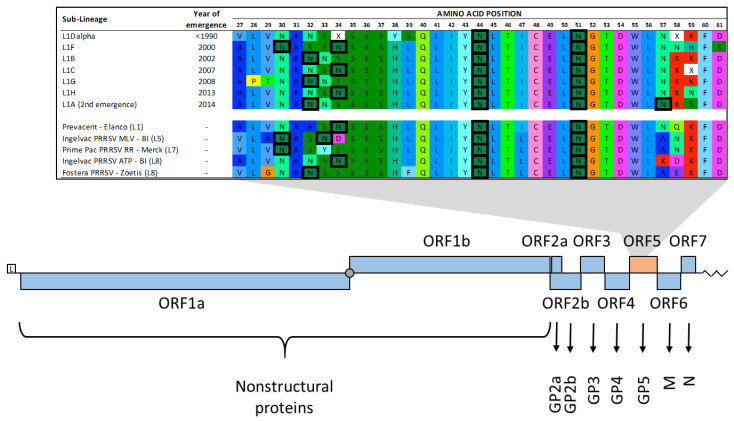
Figure 1.
Amino acid sites within the ectodomain of GP5 with potential N-glycosylation highlighted in hyper-variable regions 1 (sites 32–39) and 2 (sites 57–61) in the ORF5 portion of the genome (top). Displayed examples of potential N-glycosylation are shown on the consensus sequences of sub-lineages of PRRSV that dominated the PRRSV landscape, ordered according to their year of emergence and on vaccine sequences [12]. PRRSV genome organization and expression (bottom): L—leader sequence (5’ UTR); filled circle—ORF 1a and 1b ribosomal frameshift site; zigzag line—3’s UTR and poly(A) tail. For additional detailed illustrations on the PRRSV genome, please refer to [23,24,25,26]. Figures partially adapted from [12,23].
2. Materials and Methods
To explore the potential N-glycosylation of PRRSV in the U.S. over time, we analyzed data from the University of Minnesota Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory from 2004 to 2021, comprised of 19,179 PRRSV ORF5 sequences (which encode the GP5 protein). ORF5 sequences were translated to amino acids using AliView [27]. Sequons in the translated amino acid sequence were identified using a custom-built script coded in Stata 15 [28]-code is available in Supplementary File S1. Our code identified sequons with the pattern Asn-Xxx-(Thr/Ser), where the middle position could be any amino acid except proline, since a sequon consisting of Asn-Pro-(Thr/Ser) is not adequate for an N-glycosylation to occur [29]. Sequences were then summarized according to which residues were potentially N-glycosylated. Specific N-glycosylated residues were referred to by the position of the initial asparagine within the GP5 protein. Sequences were stratified according to the year collected and to which phylogenetic lineage or sub-lineage they belonged [10,11,12,30]. To visualize phylogenetic relationships, a time-scaled phylogenetic (ML; GTR + G) tree was constructed for 500 randomly selected sequences using Mega and TimeTree [31,32] and illustrated using Microreact [33]. Figures illustrating the percentage of sequences according to their potential N-glycosylation pattern per year per (sub-)lineage were constructed using Stata 15 [28]. Glycosylation patterns that occurred in <5% of the sequences of a given lineage or sub-lineage were grouped into “other patterns”.
3. Results and Discussion
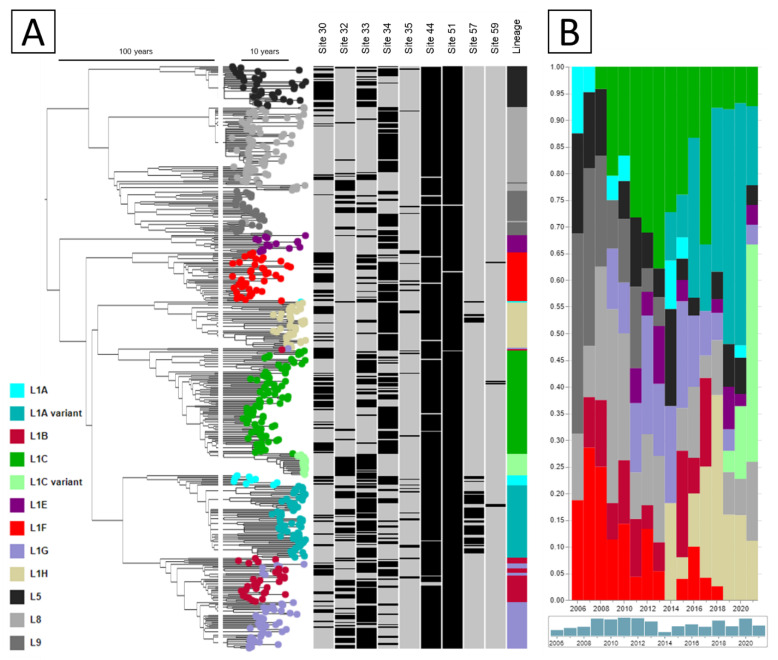
Potential N-glycosylation of nine residues was identified (residues 30, 32, 33, 34, 35, 44, 51, 57, and 59), with different combinations of glycosylated sites being prevalent over time (Figure 2A). Even though the glycosylation pattern of a sequence is not necessarily lineage-defining, the emergence of certain constellations of potential N-glycosylations coincides with past PRRSV epidemics in the U.S., as can be seen in Figure 3 for L1A, L1C, and L1H. Each of these lineages had been present at low frequencies for some time (Figure 2B), but a rapid increase in frequency was associated with a novel glycosylation pattern. For L1A, sequences glycosylated at sites 32, 33, 44, 51, and 57 first appeared in 2012, and by 2014 it represented more than 40% of all L1A sequences identified, reaching a peak of 62% of all L1A sequences identified in 2015. This coincides with the emergence of the L1A 1-7-4 virus [11], which was a widely recognized event of clinical significance in the industry [34].
Figure 2.
(A) Time-scaled phylogenetic tree of 500 randomly selected sequences illustrating if each sequence was potentially N-glycosylated (black) or not (gray) at each residue site in which glycosylation was identified. (B) Fraction of sequences belonging to each lineage identified in each year.
Figure 3.
Percentage of sequences identified in each year according to their pattern of potentially N-glycosylated sites across lineages and sub-lineages. Each graph corresponds to a sub-lineage (specified on top of the graph), followed by the total number of sequences of that sub-lineage identified in each year.
The emergence of the L1C 1-4-4 variant [35] in 2020 can also be observed from a glycosylation pattern perspective. This virus’s glycosylation pattern (at residues 32, 33, 44, and 51) was circulating since at least 2007, though represented only a small percentage of sequences (Figure 3-L1C). In 2020 and 2021, this pattern was observed in 44 and 47% of the L1C sequences identified in those years. More generally, the prevalence of different patterns in L1C appears to be wave-like, with different patterns prevalent at various points in time. Other lineages also display a change in the relative frequency of occurrence of glycosylation patterns over time, but those are harder to trace back to well-defined PRRSV epidemics. Glycosylation patterns are not solely responsible for the emergence of new strains, as evidenced by the fact that the pattern associated with the L1C-1-4-4 variant was present in this lineage since at least 2007. However, in a dynamic landscape of cross-immunity elicited by natural occurrence of PRRSV, diverse immunization practices through live virus exposure, and vaccination, the relative fitness of viruses with specific glycosylation patterns may change over time.
One limitation of this study is that we are only reporting sites that are potentially N-glycosylated. No spectrometric and biochemical studies were performed to evaluate if these sites are indeed glycosylated. Another limitation is that we used secondary data to conduct the analysis. The UMN VDL dataset is based upon sequencing requested by clients, introducing geographical biases (data comes from more than nine states, but 82% of the sequences are from the Midwest U.S.) and potential biases in PRRSV detection associated with reasons for sequencing (such as atypical clinical presentation). However, we believe the breadth of data available from the UMN VDL more than likely offsets this limitation. Finally, as an observational study, we cannot assess causality (is a given glycosylation pattern the cause of frequency increases for a given strain or is it just a hitchhiker present in a successful strain?). However, experimental studies show that glycosylation may play a role in protein folding [36], immune evasion [18] and recognition of epitopes and subsequent neutralization by the immune system [22], which supports the hypothesis that glycosylation pattern may be a relevant aspect when it comes to understanding the sequential dominance of different PRRSV strains in the field.
In this paper we reported trends of occurrence of potential N-glycosylation in PRRS viruses obtained from the University of Minnesota Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory for different PRRSV lineages over different years. Protein glycosylation has been implicated in many aspects of adaptive immune response [37]. As such, the wealth of historical data available for PRRSV, with thousands of PRRSV ORF5 sequences available, should not be understated. Further exploration of glycosylation patterns, how they affect PRRSV GP5 folding, and experimental studies could help better understand how glycosylation patterns shape PRRSV occurrence and how that can be leveraged to improve PRRSV control.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the industry partners who contributed to data in this analysis, particularly to veterinarians and systems that submitted samples for PRRSV diagnosis to the University of Minnesota Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/vaccines10122021/s1, The Stata code used to detect sequons on the genetic data can be found on Supplementary File S1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.A.D.P. and K.V.; methodology, I.A.D.P. and K.V.; software, I.A.D.P.; validation, I.A.D.P. and K.V.; formal analysis, I.A.D.P.; investigation, I.A.D.P.; resources, K.V. and A.R.; data curation, I.A.D.P.; writing—original draft preparation, I.A.D.P.; writing—review and editing, I.A.D.P., D.N.M., N.P., J.P.B., D.S., A.R. and K.V.; visualization, I.A.D.P. and K.V.; supervision, K.V.; project administration, K.V.; funding acquisition, K.V. and D.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available the University of Minnesota Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory. Restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding Statement
This project was supported by the USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture, by the joint NIFA-NSF-NIH-BBSRC Ecology and Evolution of Infectious Disease award 2019-67015-29918 and BB/T004401/1 and by the USDA NIFA Critical Agricultural Research and Extension program 2022-68008-37146.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Lisowska E. The role of glycosylation in protein antigenic properties. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2002 59:445–455. doi: 10.1007/s00018-002-8437-3. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11964123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Reily C., Stewart T.J., Renfrow M.B., Novak J. Glycosylation in health and disease. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019 15:346–366. doi: 10.1038/s41581-019-0129-4. Available online: http://www.nature.com/articles/s41581-019-0129-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Price J.L., Powers D.L., Powers E.T., Kelly J.W. Glycosylation of the enhanced aromatic sequon is similarly stabilizing in three distinct reverse turn contexts. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011 108:14127–14132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1105880108. Available online: https://pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.1105880108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Watanabe Y., Bowden T.A., Wilson I.A., Crispin M. Exploitation of glycosylation in enveloped virus pathobiology. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2019 1863:1480–1497. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2019.05.012. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0304416519301333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gruszewska E., Grytczuk A., Chrostek L. Glycosylation in viral hepatitis. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2021 1865:129997. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2021.129997. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0304416521001562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stewart-Jones G.B., Soto C., Lemmin T., Chuang G.-Y., Druz A., Kong R., Thomas P.V., Wagh K., Zhou T., Behrens A.-J., et al. Trimeric HIV-1-Env Structures Define Glycan Shields from Clades A, B, and G. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Cell. 2016 165:813–826. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.010. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0092867416304019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Crispin M., Ward A.B., Wilson I.A. Structure and Immune Recognition of the HIV Glycan Shield. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2018 47:499–523. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biophys-060414-034156. Available online: https://www.annualreviews.org/doi/10.1146/annurev-biophys-060414-034156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Watanabe Y., Allen J.D., Wrapp D., McLellan J.S., Crispin M. Site-specific glycan analysis of the SARS-CoV-2 spike. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Science. 2020 369:330–333. doi: 10.1126/science.abb9983. Available online: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/science.abb9983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Holtkamp D.J., Kliebenstein J.B., Neumann E.J., Zimmerman J.J., Rotto H.F., Yoder T.K., Wang C., Yeske P.E., Mowrer C.L., Haley C.A. Assessment of the economic impact of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus on United States pork producers. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];J. Swine Health Prod. 2013 21:72–84. Available online: http://www.aasv.org/shap/issues/v21n2/v21n2p72.html. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shi M., Lam T.T.-Y., Hon C.-C., Hui R.K.-H., Faaberg K.S., Wennblom T., Murtaugh M.P., Stadejek T., Leung F.C.-C. Molecular epidemiology of PRRSV: A phylogenetic perspective. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Virus Res. 2010 154:7–17. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.08.014. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0168170210002911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Paploski I.A.D., Corzo C., Rovira A., Murtaugh M.P., Sanhueza J.M., Vilalta C., Schroeder D.C., VanderWaal K. Temporal Dynamics of Co-circulating Lineages of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2019;10:2486. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Paploski I., Pamornchainavakul N., Makau D., Rovira A., Corzo C., Schroeder D., Cheeran M., Doeschl-Wilson A., Kao R., Lycett S., et al. Phylogenetic Structure and Sequential Dominance of Sub-Lineages of PRRSV Type-2 Lineage 1 in the United States. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Vaccines. 2021 9:608. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9060608. Available online: https://www.mdpi.com/2076-393X/9/6/608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kwon T., Yoo S.J., Lee D.-U., Sunwoo S.Y., Je S.H., Park J.W., Kim M.-H., Park C.-K., Lyoo Y.S. Differential evolution of antigenic regions of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus 1 before and after vaccine introduction. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Virus Res. 2018 260:12–19. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2018.11.004. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0168170218304337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Li J., Tao S., Orlando R., Murtaugh M.P. N-glycosylation profiling of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus envelope glycoprotein 5. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Virology. 2015 478:86–98. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2015.02.013. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0042682215000598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen J., Liu T., Zhu C.-G., Jin Y.-F., Zhang Y.-Z. Genetic Variation of Chinese PRRSV Strains Based on ORF5 Sequence. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Biochem. Genet. 2006 44:421–431. doi: 10.1007/s10528-006-9039-9. Available online: http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s10528-006-9039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Key K.F., Haqshenas G., Guenette D.K., Swenson S.L., Toth T.E., Meng X.-J. Genetic variation and phylogenetic analyses of the ORF5 gene of acute porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus isolates. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Veter-Microbiol. 2001 83:249–263. doi: 10.1016/S0378-1135(01)00427-8. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0378113501004278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Larochelle R., D’Allaire S., Magar R. Molecular epidemiology of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) in Québec. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Virus Res. 2003 96:3–14. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1702(03)00168-0. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0168170203001680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wei Z., Lin T., Sun L., Li Y., Wang X., Gao F., Liu R., Chen C., Tong G., Yuan S. N-Linked Glycosylation of GP5 of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Is Critically Important for Virus Replication In Vivo. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];J. Virol. 2012 86:9941–9951. doi: 10.1128/JVI.07067-11. Available online: https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/JVI.07067-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Faaberg K.S., Hocker J.D., Erdman M.M., Harris D.H., Nelson E.A., Torremorell M., Plagemann P.G. Neutralizing Antibody Responses of Pigs Infected with Natural GP5 N-Glycan Mutants of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Viral Immunol. 2006 19:294–304. doi: 10.1089/vim.2006.19.294. Available online: https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/10.1089/vim.2006.19.294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chen N., Trible B.R., Kerrigan M.A., Tian K., Rowland R.R. ORF5 of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus (PRRSV) is a target of diversifying selection as infection progresses from acute infection to virus rebound. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016 40:167–175. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.03.002. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1567134816300727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Makau D.N., Lycett S., Michalska-Smith M., Paploski I.A.D., Cheeran M.C.-J., Craft M.E., Kao R.R., Schroeder D.C., Doeschl-Wilson A., VanderWaal K. Ecological and evolutionary dynamics of multi-strain RNA viruses. [(accessed on 20 November 2022)];Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2022 6:1414–1422. doi: 10.1038/s41559-022-01860-6. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41559-022-01860-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Rupasinghe R., Lee K., Liu X., Gauger P.C., Zhang J., Martínez-López B. Molecular Evolution of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Field Strains from Two Swine Production Systems in the Midwestern United States from 2001 to 2020. [(accessed on 20 November 2022)];Microbiol. Spectr. 2022 10:e02634-21. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02634-21. Available online: https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/spectrum.02634-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.ICTV Family: Arteriviridae. ICTV Ninth Report. 2009. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)]. 2009 Taxonomy Release. Available online: https://ictv.global/report_9th/RNApos/Nidovirales/Arteriviridae.
- 24.Tarbes S.M., Del Portillo H.A., Montoya M., Fraile L. Key Gaps in the Knowledge of the Porcine Respiratory Reproductive Syndrome Virus (PRRSV) Front. Veter-Sci. 2019;6:38. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2019.00038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kappes M.A. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Structural Protein of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus, the Replicase Nonstructural Protein 2. Iowa State University, Digital Repository; Ames, Spain: 2014. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)]. Available online: https://lib.dr.iastate.edu/etd/14184/ [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sandri G. PRRSV Sequencing and Its Use in Practice. 2018. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)]. Available online: https://www.pig333.com/articles/prrsv-sequencing-and-its-use-in-practice_13422/
- 27.Larsson A. AliView: A fast and lightweight alignment viewer and editor for large datasets. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Bioinformatics. 2014 30:3276–3278. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu531. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/bioinformatics/article-lookup/doi/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.StataCorp . Stata Statistical Software: Release 15. StataCorp LLC; College Station, TX, USA: 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Taguchi Y., Yamasaki T., Ishikawa M., Kawasaki Y., Yukimura R., Mitani M., Hirata K., Kohda D. The structure of an archaeal oligosaccharyltransferase provides insight into the strict exclusion of proline from the N-glycosylation sequon. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Commun. Biol. 2021 4:941. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02473-8. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-021-02473-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Shi M., Lam T.T., Hon C.C., Murtaugh M.P., Davies P.R., Hui R.K., Li J., Wong L.T., Yip C.W., Jiang J.W., et al. Phylogeny-Based Evolutionary, Demographical, and Geographical Dissection of North American Type 2 Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Viruses. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];J. Virol. 2010 84:8700–8711. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02551-09. Available online: http://jvi.asm.org/cgi/doi/10.1128/JVI.02551-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kumar S., Stecher G., Tamura K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016 33:1870–1874. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msw054. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27004904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sagulenko P., Puller V., Neher R.A. TreeTime: Maximum-likelihood phylodynamic analysis. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Virus Evol. 2018 4:vex042. doi: 10.1093/ve/vex042. Available online: http://academic.oup.com/ve/article/doi/10.1093/vex042/4794731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Argimón S., AbuDahab K., Goater R.J.E., Fedosejev A., Bhai J., Glasner C., Feil E.J., Holden M.T.G., Yeats C.A., Grundmann H., et al. Microreact: Visualizing and sharing data for genomic epidemiology and phylogeography. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Microb. Genom. 2016 2:e000093. doi: 10.1099/mgen.0.000093. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28348833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wang X., Marthaler D., Rovira A., Rossow S., Murtaugh M.P. Emergence of a virulent porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in vaccinated herds in the United States. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Virus Res. 2015 210:34–41. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.07.004. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26169029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kikuti M., Paploski I.A.D., Pamornchainavakul N., Picasso-Risso C., Schwartz M., Yeske P., Leuwerke B., Bruner L., Murray D., Roggow B.D., et al. Emergence of a New Lineage 1C Variant of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus 2 in the United States. Front. Veter- Sci. 2021;8:1–10. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.752938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shental-Bechor D., Levy Y. Effect of glycosylation on protein folding: A close look at thermodynamic stabilization. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2008 105:8256–8261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0801340105. Available online: https://pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.0801340105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wolfert M., Boons G.-J. Adaptive immune activation: Glycosylation does matter. [(accessed on 19 August 2022)];Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013 9:776–784. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1403. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24231619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available the University of Minnesota Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory. Restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for this study.