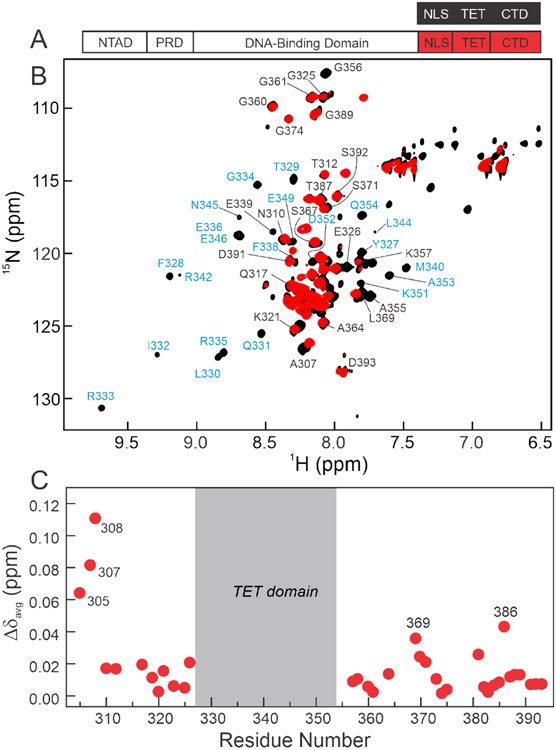
Figure 2.
A. Schematic representation of the isolated p53(304-393) peptide (top) and segmentally 15N-labeled full-length p53 (bottom, labeled at 304-393 through intein splicing) used for NMR experiments. B. 800MHz 1H-15N TROSY-HSQC spectra of isolated 15N/2H p53(304-393) peptide (black) and 15N/2H segmentally labeled tetrameric p53 (15N(304-393)-p53, red). Resonances appearing in the center of the spectra arise from the disordered NLS and CTD residues, while more dispersed cross-peaks in the spectrum of the p53(304-393) peptide correspond to the folded TET domain. Assignments labeled in black were obtained from triple resonance spectra of p53(304-393); assignments labeled in blue were mapped from published data for the isolated TET domain.55 Resonances of the TET domain residues are unobservable in segmentally labeled full-length p53 and do not give observable connectivities in triple resonance spectra of the p53(304-393) peptide. Cross peaks of residues 389 and 391-393 are split due to isomerism of Pro390. All samples were in 20mM Tris, pH7.0, 150mM NaCl, 5% D2O, and 2mM DTT and NMR spectra were acquired at 25°C. C. Weighted average 1H, 15N chemical shift differences between isolated p53(304-393) peptide and the full-length segmentally labeled p53 tetramer. Resonances of residues 305, 307, and 308 are shifted due to their proximity to the intein splice site. Residues in the CTD that exhibit significant chemical shift changes between spectra of 15N(304-393)-p53 and the p53(304-393) peptide are labeled. Weighted average chemical shift differences were calculated using the equation: