Abstract
Background:
Associations between candidate genetic variants and treatment outcomes of oxaliplatin, a drug commonly used for colorectal cancer patients, have been reported but not robustly established. This study aimed to validate previously reported prognostic and predictive genetic markers for oxaliplatin treatment outcomes and evaluate additional putative functional variants.
Methods:
Fifty-three SNPs were selected based on previous reports (40 SNPs) or putative function in candidate genes (13 SNPs). We used data from 1,502 patients with stage II–IV colorectal cancer who received primary adjuvant chemotherapy, 37% of whom received oxaliplatin treatment. Multivariable Cox proportional hazards models for overall survival and progression-free survival were applied separately in stage II–III and stage IV patients. For predictive SNPs, differential outcomes according to the type of chemotherapy (oxaliplatin-based vs. others) were evaluated using an interaction term. For prognostic SNPs, the association was assessed solely in patients with oxaliplatin-based treatment.
Results:
Twelve SNPs were predictive and/or prognostic at P < 0.05 with differential survival based on the type of treatment, in patients with stage II–III (GSTM5-rs11807, ERCC2-rs13181, ERCC2-rs1799793, ERCC5-rs2016073, XPC-rs2228000, P2RX7-rs208294, HMGB1-rs1360485) and in patients with stage IV (GSTM5-rs11807, MNAT1-rs3783819, MNAT1-rs4151330, CXCR1-rs2234671, VEGFA-rs833061, P2RX7-rs2234671). In addition, five novel putative functional SNPs were identified to be predictive (ATP8B3-rs7250872, P2RX7-rs2230911, RPA1-rs5030755, MGMT-rs12917, P2RX7-rs2227963).
Conclusions:
Some SNPs yielded prognostic and/or predictive associations significant at P < 0.05, however, none of the associations remained significant after correction for multiple testing.
Impact:
We did not robustly confirm previously reported SNPs despite some suggestive findings but identified further potential predictive SNPs, which warrant further investigation in well-powered studies.
Introduction
Oxaliplatin is a cytotoxic platinum-based chemotherapeutic drug that acts by forming DNA adducts and cross-links (1). It is frequently used in combination with fluoropyrimidines (FL; i.e., 5-fluorouracil/folinic acid or capecitabine) as a first-line chemotherapy treatment against colorectal cancer in stage III–IV and stage II with other risk factors, both adjuvant and metastatic settings, which has been shown to improve overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) compared with FL alone (2). However, the response rates to oxaliplatin are still less than 60% (3, 4), and oxaliplatin causes side effects, such as peripheral sensory neuropathy, resulting in dose-limiting toxicity (2, 5). These data emphasize the need for reliable biomarkers to predict the efficacy of oxaliplatin chemotherapy and improve clinical outcomes.
Tumor response to oxaliplatin efficacy is known to be multifactorial and depends on tumor mutations such as KRAS mutation (6–8), the interaction of oxaliplatin with tumor microenvironment and release of tumor protective cytokines (9), microRNAs characteristic of the tumor (10, 11). Treatment decision-making for individual patients could be improved by additional consideration of inherited patients' genetic variants. As resistance to platinum agents is partly attributed to enhanced tolerance to DNA adducts resulting from an increased DNA repair ability, genetic variations of DNA damage repair pathways could potentially influence the efficacy of oxaliplatin treatment in colorectal cancer patients (12, 13). The most frequently considered polymorphisms in relation to oxaliplatin efficacy were the synonymous substitution ERCC1-rs11615 and the missense variation ERCC2-rs13181, although the evidence is inconclusive to support clinical application (14, 15). Genetic mutations in glutathione-S-transferases (GST) involved in the drug detoxification process are also considered strong candidate predictors of oxaliplatin-based therapy effectiveness (16–18). Previous studies that focused on a common missense variant GSTP1-rs1695 yielded inconsistent results (19–21). Variants in other pathways, for example, drug transport, folate pathway, and VEGF and EGF pathways, immunogenic cell death pathway, enterocyte subtype-related genes, have also been studied without showing concrete evidence of influencing oxaliplatin efficacy (21–26).
However, the lack of success of previous studies does not demonstrate that the role of a patient's genetic variants in oxaliplatin efficacy is irrelevant. Previous studies have often been limited by small sample sizes, lack of adjustment for relevant covariates, multiple testing correction, and non-specific treatment definitions. Most studies assessed genetic variants only as prognostic markers, that is, association with outcome among patients with colorectal cancer who received a specified standard treatment such as adjuvant chemotherapy with oxaliplatin, but not as predictive markers, i.e., differential association with outcome according to the type of chemotherapy (e.g., with oxaliplatin versus without oxaliplatin). This study aimed to validate previously reported associations of prognostic and predictive genetic markers for oxaliplatin treatment outcome using a large independent patient with colorectal cancer sample and to evaluate further functional variants as potential prognostic/predictive markers.
Materials and Methods
Study population
We included patients recruited between 2003 and 2015 from an ongoing population-based case–control study (DACHS, colorectal cancer: chances for prevention through screening). Details of the study have been described previously (27, 28). Patients were eligible if they were at least 30 years of age at diagnosis, were proficient in German, had the mental and physical ability to participate in the study, and lived in the Rhine-Neckar-Odenwald region in Germany. At recruitment, extensive information on sociodemographic characteristics, medical history, and lifestyle factors was collected by trained interviewers using standardized questionnaires. Information on vital status, date, and cause of death were obtained from the local population registries and health authorities at 3-year, 5-year, and 10-year follow-up. About 3 years after diagnosis, we requested information on colorectal cancer treatment and recurrence from treating physicians. After 5 and 10 years, questionnaires were sent to the patients to obtain, among other items, information on recurrence status (re-appearance or metastases). If colorectal cancer recurrence was stated, the treating physician was contacted for validation and to obtain further details. For patients who died during follow-up or were lost to follow-up, recurrence history was obtained from the last attending physician. All patients gave their written informed consent. The ethics committees of the Medical Faculty of the University of Heidelberg and the State Medical Boards of Baden-Wuerttemberg and Rhineland-Palatinate approved the study.
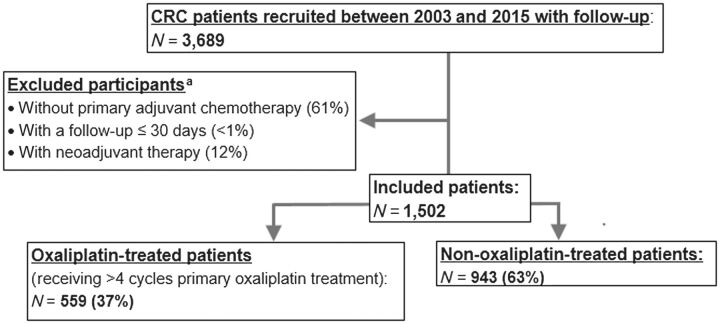
Figure 1 provides an overview of the inclusion of cases. Genotype and complete follow-up data (for either 3, 5, or 10 years) were available for a total of 3,689 histologically confirmed cases diagnosed between 2003 and 2014. We excluded patients who had not received adjuvant chemotherapy, received neoadjuvant chemotherapy, had an unknown start date of chemotherapy, or died within 30 days of the start of chemotherapy. Of patients treated with first-line adjuvant chemotherapy, we defined patients as having received oxaliplatin-based treatment if they received four or more cycles of oxaliplatin; otherwise, they were considered to have received non-oxaliplatin based treatment based on discussions with clinicians. When the number of cycles was not available, this was calculated using the difference between the start date and the end date of treatment divided by 28 days multiplied by two. Later-lines treatments were not considered in our analyses. In the current study, 1,502 patients with stage II–IV were included, of which 559 (37%) received four or more cycles of oxaliplatin.
Figure 1.
Inclusion of patients with CRC from the DACHS study. aThe number of participants and its percentage refers to patients with CRC recruited between 2003 and 2015 with follow-up (N = 3,689) and some of them were overlapped. CRC, colorectal cancer.
Genotyping, imputation, and SNP selection
DNA was extracted from blood samples (in 99.1% of participants) or buccal cells (in 0.9% of participants) using conventional methods. Details about genotyping and imputation for the DACHS population have been described in detail somewhere else (29). In short, genotyping was conducted using four different assays. For the included patients, genotype data were available from the whole-genome Illumina CytoSNP v12.2.1 assay (549 patients), Illumina Human OmniExpress Plus Exome (606 patients), and Infinium OncoArray-500K BeadChip (259 patients), performed in collaboration with the Genetics and Epidemiology of Colorectal Cancer Consortium, as well as the Illumina Global Screening Array (29 patients). Missing SNPs were imputed based on the Haplotype Reference Consortium v1.1 (http://www.haplotype-reference-consortium.org/). Genotyped/imputed SNPs were restricted based on minor allele frequency >5% and imputed SNPs additionally on imputation accuracy (R2 > 0.8).
Individual SNPs previously reported to be associated with the efficacy of oxaliplatin-based treatment in patients with colorectal cancer, 53 SNPs as prognostic and seven SNPs as predictive markers, were identified based on comprehensive literature research (Supplementary Table S1). Three pairs of previously reported SNPs were in high linkage disequilibrium (rs751402 and rs2016073, R2 = 0.99; rs1043953 and rs2228000, R2 = 0.82; rs973063; and rs3783819, R2 = 0.90). The SNPs with a lower P value, rs2016073, rs2228000, and rs3783819, were retained. Ten SNPs (rs1801133, rs8100856, rs366631, rs4124874, rs8192726, rs45608036, rs5030740, rs10817938, rs34116584, and rs2032582) were not genotyped or imputed and without proxy SNP (R2 > 0.8). Additional 13 common genetic variants with putative regulatory function (missense variants) of genes in the relevant pathways, for example, DNA repair system, Phase I/II metabolic enzymes, drug transport, folate pathway, and VEGF and EGF pathways, immunogenic cell death pathway, enterocyte subtype-related genes, which have not been studied for the association with oxaliplatin or studied without finding any association, were also identified (Table 1). In total, 53 candidate SNPs based on either previous reports (40 SNPs) or regulatory function in candidate genes (13 SNPs) were included in our analyses (Table 1).
Table 1.
Investigated SNPs based on previous reports and putative regulatory function.
| SNP | gsc37 (chr: position) | Pathway | Gene: Consequence/location | Proxy SNP (LD, R2) | EA/OA (Proxy SNP) | EAF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Previously reported SNPs (N = 40) | ||||||
| rs25487 | 19:44055726 | DNA repair system | XRCC1: Missense | C/T | 0.65 | |
| rs11615 | 19:45923653 | DNA repair system | ERCC1: Missense | G/A | 0.36 | |
| rs13181 | 19:45854919 | DNA repair system | ERCC2 (XPD): Missense | G/T | 0.37 | |
| rs1799793 | 19:45867259 | DNA repair system | ERCC2 (XPD): Missense | T/C | 0.36 | |
| rs238406 | 19:45868309 | DNA repair system | ERCC2 (XPD): Missense | T/G | 0.45 | |
| rs2016073 | 13:103497411 | DNA repair system | ERCC5: 2′UTR | G/A | 0.20 | |
| rs1047768 | 13:103504517 | DNA repair system | ERCC5: Missense | C/T | 0.58 | |
| rs17655 | 13:103528002 | DNA repair system | ERCC5: Missense | C/G | 0.23 | |
| rs2228000 | 3:14199887 | DNA repair system | XPC: Missense | A/G | 0.25 | |
| rs4151330 | 14:61371545 | DNA repair system | MNAT1: Intron | rs4899021 (R2 = 0.92) | G/A (G/T) | 0.36 |
| rs3783819 | 14:61316264 | DNA repair system | MNAT1: Intron | G/A | 0.60 | |
| rs3732183 | 2:47693959 | DNA repair system | MSH2: Intron | A/G | 0.23 | |
| rs1801516 | 11:108175462 | DNA repair system | ATM: Missense | A/G | 0.15 | |
| rs4937 | 16:57499902 | DNA repair system | POLR2C: Missense | T/C | 0.26 | |
| rs2233678 | 19:9945179 | DNA repair system | PIN1: 2KB Upstream Variant | C/G | 0.11 | |
| rs975351 | 1:116834105 | Drug transporter | Intergenic (Nearest gene, ATP1A1) | C/T | 0.41 | |
| rs2231142 | 4:89052323 | Drug transporter | ABCG2: Missense | T/G | 0.10 | |
| rs2622621 | 4:89030920 | Drug transporter | ABCG2: Intron | G/C | 0.34 | |
| rs2125739 | 6:43412865 | Drug transporter | ABCC10: Missense | C/T | 0.25 | |
| rs1045642 | 7:87138645 | Drug transporter | ABCB1 (MDR1, Pgp): Missense | G/A | 0.47 | |
| rs1128503 | 7:87179601 | Drug transporter | ABCB1 (MDR1, Pgp): Missense | G/A | 0.57 | |
| rs2273697 | 10:101563815 | Drug transporter | ABCC2: Missense | A/G | 0.22 | |
| rs1625649 | 10:131264931 | Drug transporter | MGMT: 5′UTR | A/C | 0.36 | |
| rs1642763 | 17:7557419 | Drug transporter | ATP1B2: G132G | A/G | 0.23 | |
| rs7249302 | 19:1808683 | Drug transporter | ATP8B3: Intron | T/C | 0.16 | |
| rs11807 | 1:110260742 | Phase I/II metabolic enzymes | GSTM5: 3′UTR | C/T | 0.19 | |
| rs1695 | 11:67352689 | Phase I/II metabolic enzymes | GSTP1: Missense | G/A | 0.31 | |
| rs1801131 | 1:11854476 | Folate pathway | MTHFR: Missense | G/T | 0.33 | |
| rs5275 | 1:186643058 | VEGF and EGF pathway | COX-2(PTGS2): 3′ UTR | G/A | 0.34 | |
| rs2234671 | 2:219029108 | VEGF and EGF pathway | CXCR1 (IL-8R1): Missense | G/C | 0.05 | |
| rs833061 | 6:43737486 | VEGF and EGF pathway | VEGFA: Promoter | T/C | 0.48 | |
| rs2227983 | 7:55229255 | VEGF and EGF pathway | EGFR: Missense | A/G | 0.26 | |
| rs1050305 | 9:75775235 | Immunogenic cell death pathway | LRP1: Missense | G/A | 0.09 | |
| rs1799986 | 12:57535266 | Immunogenic cell death pathway | LRP1: Missense | T/C | 0.16 | |
| rs11172113 | 12:57527283 | Immunogenic cell death pathway | LRP1: intron | C/T | 0.41 | |
| rs208294 | 12:121600253 | Immunogenic cell death pathway | P2RX7:Missense | C/T | 0.55 | |
| rs1718119 | 12:121615103 | Immunogenic cell death pathway | P2RX7:Missense | A/G | 0.40 | |
| rs1360485 | 13:31031884 | Immunogenic cell death pathway | HMGB1: 3′ UTR | C/T | 0.27 | |
| rs4939378 | 11:60266798 | Enterocyte subtype-related genes | MS4A12: Intron | A/G | 0.55 | |
| rs3812863 | 13:28545268 | Enterocyte subtype-related genes | CDX2: 2KB upstream variant | A/G | 0.60 | |
| Putative functional SNPs (N = 13)a | ||||||
| rs2228001 | 3:14187449 | DNA repair system | XPC: Missense | T/G | 0.59 | |
| rs2227999 | 3:14199908 | DNA repair system | XPC: Missense | T/C | 0.06 | |
| rs5030755 | 17:1782952 | DNA repair system | RPA1: Missense | G/A | 0.12 | |
| rs2308321 | 10:131565064 | Drug transporter | MGMT: Missense | G/A | 0.13 | |
| rs12917 | 10:131506283 | Drug transporter | MGMT: Missense | T/C | 0.13 | |
| rs8187710 | 10:101611294 | Drug transporter | ABCC2: Missense | rs146860861 (R2 = 0.88) | A/G (A/G) | 0.06 |
| rs7250872 | 19:1811603 | Drug transporter | ATP8B3: Missense | T/C | 0.30 | |
| rs1138272 | 11:67353579 | Phase I/II metabolic enzymes | GSTP1: Missense | T/C | 0.07 | |
| rs2227963 | 1:110257831 | Phase I/II metabolic enzymes | GSTM5: Missense | C/T | 0.08 | |
| rs17525809 | 12:121592689 | Immunogenic cell death pathway | P2RX7: Missense | C/T | 0.08 | |
| rs7958311 | 12:121605355 | Immunogenic cell death pathway | P2RX7:Missense | A/G | 0.24 | |
| rs2230911 | 12:121615131 | Immunogenic cell death pathway | P2RX7:Missense | G/C | 0.08 | |
| rs1805107 | 13:28537317 | Enterocyte subtype-related genes | CDX2: Missense | G/A | 0.18 | |
Abbreviations: ABCB1, ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 1; ABCC10, ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 10; ABCC2, ATP binding cassette subfamily C member 2; ABCG2, ATP binding cassette subfamily G member 2; ATM, ATM serine/threonine kinase; ATP1A1, ATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit alpha 1; ATP1B2, ATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit beta 2; ATP8B3, ATPase phospholipid transporting 8B3; COX-2, cytochrome c oxidase subunit 2; CXCR1, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 1; DNA, Deoxyribonucleic acid; EA, effect allele; EGF, DNA mismatch repair; EGFR, Epidermal growth factor receptor; ERCC1, excision repair cross-complementing group 1; ERCC2, ERCC excision repair 2; ERCC5, ERCC excision repair 5, endonuclease; GSTM5, glutathione S-transferase mu 5; GSTP1, glutathione S-transferase pi 1; HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; LD, Linkage disequilibrium; MGMT, O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase; MNAT1, MNAT1 component of CDK activating kinase; MSH2, mismatch repair protein Msh2; MTHFR, methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; OA, other allele; PIN1, peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase, NIMA-interacting 1; POLR2C, RNA polymerase II subunit C; PTGS2, prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1; P2RX7, purinergic receptor P2×7; RNA, Ribonucleic acid; RPA1, replication protein A1; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; XPC, XPC complex subunit, DNA damage recognition and repair factor; XPD, xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group C; XRCC1, X-ray repair cross complementing 1; VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor A.
aAdditional common genetic variants with putative regulatory function (non-synonymous coding variants, minor allele frequency > 5% in European population from ALFA) in the genes of previously identified variants in relevant pathways were also identified: XRCC1, XPD (ERCC2), ERCC1, XPG (ERCC5), XPC, POLR2C, MSH2, MGMT, MNAT1, PIN1, ATM, XPA, PIN1, and RPA1 in DNA repair system; GSTP1, GSTM5, UGT1A1, CYP2A6 in Phase I/II metabolic enzymes; ABCB1, ABCC2, ABCG2, ABCC10, ATP1A1, ATP1B2, ATP8B3 in Drug transfer; MTHFR and TYMS in Folate pathway; VEGFA, EGFR (HER-1), and CXCR1 (IL-8R1), and COX-2 (PTGS2) in VEGF and EGF pathway; P2RX7, LRP1, and HMGB1in Immunogenic cell death pathway; MS4A12 and CDX2 in Enterocyte subtype-related genes based on USCS Genome Browser on Human Feb. 2009 (GRC 37/hg19) Assembly (dbSNP release 151). Two pairs of SNPs, rs2308321 and rs2308327, rs17222723 and rs8187710 were in high linkage disequilibrium (R2 = 1.0, and 0.98, respectively), so only rs2308321 and rs8187710 were included in the analysis. And 33 SNPs (rs2227866, rs25489, rs9282564, rs2231137, rs61739534, rs45574836, rs72552099, rs143731390, rs4986892, rs17854972, rs2229059, rs1799782, rs35188899, rs201159454, rs10817938, rs9282564, rs143315534, rs1065411, rs5030740, rs4426527, rs1800127, rs34108076, rs34398639, rs2229278, rs34577247, rs11172123, rs28360447, rs763011660, rs61742222, rs2298552, rs2298553, rs77186314, and rs754463501) that were not genotyped or imputed and without proxy SNPs that were not genotyped or imputed and without proxy SNP (R2 > 0.8) were excluded.
Statistical analyses
Multivariable Cox proportional hazards models were used to test the 53 SNPs as predictive and prognostic markers for the two endpoints, OS and PFS. The SNPs were evaluated in allelic models, using genotypes and imputed genotype data as continuous variables coded as 0 to 2 alleles. Imputed data was in the format of genotype probabilities. The models were adjusted for age, sex, cancer location (proximal vs. distal), stage (only for stage II–III patients), liver resection (only for stage IV patients) for the analyses. The model was also stratified for grade (1–2 vs. 3–4), KRAS mutation (wild type vs. mutation), resection status (completely resected vs. not completely resected), array used for genotyping data to account for violation of proportional hazards assumption. Proximal cancer included cecum, ascending colon, and transverse colon, whereas distal cancer included descending colon, sigmoid colon, and rectum. KRAS mutation status was determined by Sanger sequencing as reported previously (30). Survival time for OS was defined as the time from the start of chemotherapy to the date of death (by any cause) or date of the last contact. Survival time for PFS was defined as the time from the start of chemotherapy to the date of recurrence, death (by any cause), or last contact.
An interaction term between SNPs and type of treatment was added to models based on all the patients with colorectal cancer to test predictive markers associated with differential survival according to the type of chemotherapy (oxaliplatin-based vs. others). Assessment for SNPs that are prognostic for oxaliplatin-based treatment outcomes was conducted solely in patients who received oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. All analyses were performed separately according to two UICC stage groups (II–III and IV) to allow for possible heterogeneity by stage (31).
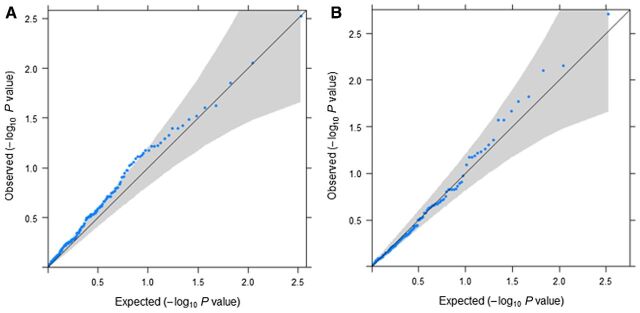
We adjusted for multiple testing by using Bonferroni corrected P value of 4.7 × 10–4 (P = 0.05 divided by the number of tests done, 53 SNPs* 2 endpoints). Quantile–quantile (Q–Q) plots were employed to appraise the expected distributions under the null hypothesis against the distributions of the observed test statistics of the 53 SNPs tested (Fig. 2). They describe the P values obtained from association tests plotted against those which would be expected solely by chance. P values that deviate from the identity line (x = y) at the tail of the distribution would indicate deviation from the null hypothesis. We assessed the study power to evaluate predictive/prognostic SNPs of treatment by calculating detectable effect sizes for OS and PFS given the power of 85% and a type I error of 4.7 × 10–4 and 0.05 (Supplementary Table S2).
Figure 2.
Q–Q plots showing P values obtained from tests on the associations between type of treatment (oxaliplatin vs. non-oxaliplatin based treatment) and 53 SNPs as predictive and prognostic factors for two endpoints (OS, PFS) in patients with stage II–III (A), and patients with stage IV (B). It shows P values (blue dots) with 95% CI (gray area). The solid lines represent the identity line (x = y). OX, oxaliplatin treatment.
The statistical analyses were carried out using R version 3.6.0 (www.R-project.org) and the R packages “survival” and “powerSurEpi.”
Results
The main characteristics of the study population overall and according to the two stage groups (stage II–III and stage IV) are shown in Table 2. The mean age of the patients with colorectal cancer was 66 years (SD: 10 years), and 40% of them were female.
Table 2.
Patient characteristics of the DACHS study sample.
| Stage II–III colorectal cancer patients | Stage IV colorectal cancer patients | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All stage (II–IV colorectal cancer patients) (N = 1,502) | Patients who received OX-based treatment (N = 402) | Patients who received non-OX-based treatment (N = 634) | Patients who received OX-based treatment (N = 157) | Patients who received non-OX based treatment (N = 309) | |
| Age (years) | |||||
| Mean (SD) | 65.8 (10.4) | 61.8 (9.60) | 68.7 (9.91) | 62.0 (11.4) | 67.1 (9.73) |
| Sex (female) | |||||
| Number (%) | 587 (39.1%) | 147 (36.6%) | 272 (42.9%) | 58 (36.9%) | 110 (35.6%) |
| Stage, number (%) | |||||
| Stage II | 179 (11.9%) | 32 (8.0%) | 147 (23.2%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Stage III | 857 (57.1%) | 370 (92.0%) | 487 (76.8%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Stage IV | 466 (31.0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 157 (100%) | 309 (100%) |
| Grade (grade 3–4), number (%) | |||||
| Grade 1–2 | 971 (64.6%) | 272 (67.7%) | 432 (68.1%) | 101 (64.3%) | 166 (53.7%) |
| Grade 3–4 | 472 (31.4%) | 122 (30.3%) | 180 (28.4%) | 48 (30.6%) | 122 (39.5%) |
| Unknown | 59 (3.9%) | 8 (2.0%) | 22 (3.5%) | 8 (5.1%) | 21 (6.8%) |
| CRC site (distal) | |||||
| Number (%) | 1,016 (68%) | 247 (61.4%) | 436 (68.8%) | 113 (72.0%) | 195 (63.1%) |
| CRC site (rectum) | |||||
| Number (%) | 420 (28%) | 59 (15%) | 232 (36%) | 46 (29%) | 83 (27%) |
| Resection status of the primary colorectal lesion, number (%) | |||||
| Completely resected | 1,292 (86%) | 383 (95.3%) | 601 (94.8%) | 110 (70.1%) | 198 (64.1%) |
| Not completely resected | 100 (6.7%) | 8 (2.0%) | 14 (2.2%) | 23 (14.6%) | 55 (17.8%) |
| Unknown | 110 (7.3%) | 11 (2.7%) | 19 (3.0%) | 24 (15.3%) | 56 (18.1%) |
| Liver resection (yes) | |||||
| No | NA | NA | NA | 77 (49.0%) | 171 (55.3%) |
| Yes | NA | NA | NA | 46 (29.3%) | 80 (25.9%) |
| Unknown | NA | NA | NA | 34 (21.7%) | 58 (18.8%) |
| KRAS mutation, number (%) | |||||
| Wild type | 540 (36.0%) | 132 (32.8%) | 254 (40.1%) | 48 (30.6%) | 106 (34.3%) |
| Mutation | 284 (18.9%) | 71 (17.7%) | 140 (22.1%) | 23 (14.6%) | 50 (16.2%) |
| Unknown | 678 (45.1%) | 199 (49.5%) | 240 (37.9%) | 86 (54.8%) | 153 (49.5%) |
| Death | |||||
| Number (%) | 754 (50.2%) | 103 (25.6%) | 253 (39.9%) | 126 (80.3%) | 272 (88.0%) |
| Time to death (month) | |||||
| Medium (SD) | 54.9 (39.9) | 60.6 (34.7) | 62.2 (39.8) | 31.4 (25.5) | 23.5 (27.8) |
| Recurrence-free event | |||||
| Number (%) | 820 (54.6%) | 124 (30.8%) | 287 (45.3%) | 132 (84.1%) | 277 (89.6%) |
| Time to event (month) | |||||
| Medium (SD) | 36.5 (37.1) | 48.8 (31.4) | 55.8 (41.5) | 21.9 (19.8) | 16.2 (22.9) |
Abbreviations: N, number; NA, not applicable.
We found some significant SNP associations at P < 0.05, none of which remained statistically significant after multiple testing corrections. These includes five predictive SNPs, GSTM5-rs11807, ERCC2-rs13181, ERCC2-rs1799793, ERCC5-rs2016073, HMGB1-rs1360485, which showed differential survival for oxaliplatin compared with non-oxaliplatin treated patients (Pinteraction = 0.026 for OS and PFS, Pinteraction = 0.041 for OS, Pinteraction = 0.016 for OS, Pinteraction = 0.032 for PFS, Pinteraction = 0.025 for PFS, respectively; Table 3; Supplementary Table S3). Two of the SNPs are also prognostic, GSTM5-rs11807-C, and ERCC5-rs2016073-G, which were associated with worse survival in the patients who received oxaliplatin. Two more SNPs were only prognostic. XPC-rs2228000-A was associated with improved PFS in patients who received oxaliplatin, whereas P2RX7-rs208294-C was associated with worse OS and PFS. In addition, three putative functional SNPs were identified to be associated with oxaliplatin at P < 0.05 in patients with stage II–III colorectal cancer. P2RX7-rs2230911-G was prognostic and predictive, showing improved OS in patients who received oxaliplatin, whereas two SNPs, MGMT-rs12917-T and RPA1- rs5030755-G, were only predictive (Table 3; Supplementary Table S3).
Table 3.
SNPs nominally associated at P < 0.05 with OS and PFS as prognostic and/or predictive markers in patients with stage II–III colorectal cancer.
| Patients who received OX-based treatment | Patients who received non-OX-based treatment | Interaction terma | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene - SNP - effect allele | HR (95% CI) | P | HR (95% CI) | P | P | Endpoint |
| Previously reported SNPs | ||||||
| GSTM5 - rs11807 - C | 1.48 (1.02–2.15) | 0.037 | 0.93 (0.73–1.18) | 0.542 | 0.026 | OS |
| GSTM5 - rs11807 - C | 1.52 (1.05–2.20) | 0.028 | 0.91 (0.69–1.21) | 0.522 | 0.026 | PFS |
| ERCC2 - rs13181 - G | 1.17 (0.87–1.58) | 0.295 | 0.80 (0.64–0.97) | 0.022 | 0.041 | OS |
| ERCC2 - rs1799793 - T | 1.32 (0.97–1.79) | 0.080 | 0.81 (0.66–1.00) | 0.048 | 0.016 | OS |
| ERCC5 - rs2016073 - G | 1.48 (1.02–2.14) | 0.038 | 0.95 (0.71–1.27) | 0.720 | 0.032 | PFS |
| XPC - rs2228000 - A | 0.63 (0.42–0.96) | 0.031 | 1.08 (0.84–1.39) | 0.555 | 0.059 | PFS |
| P2RX7 - rs208294 - C | 1.36 (1.01–1.83) | 0.045 | 1.07 (0.88–1.30) | 0.516 | 0.427 | OS |
| P2RX7 - rs208294 - C | 1.63 (1.19–2.24) | 0.002 | 1.00 (0.8–1.26) | 0.983 | 0.096 | PFS |
| HMGB1 - rs1360485 - C | 0.71 (0.48–1.03) | 0.071 | 1.17 (0.92–1.48) | 0.192 | 0.025 | PFS |
| Putative functional SNPs | ||||||
| MGMT - rs12917 - T | 1.37 (0.91–2.07) | 0.131 | 0.71 (0.52–0.96) | 0.029 | 0.012 | OS |
| RPA1 - rs5030755 - G | 1.27 (0.76–2.11) | 0.364 | 0.65 (0.42–1.00) | 0.053 | 0.015 | PFS |
| P2RX7 - rs2230911 - G | 0.42 (0.18–0.97) | 0.043 | 1.42 (0.97–2.06) | 0.069 | 0.006 | OS |
Note: Significant P value marked in bold. The models were adjusted for age, sex, cancer location (proximal vs. distal), and stage for the analyses. The model was also stratified for grade (1–2 vs. 3–4), KRAS mutation (wild type vs. mutation), resection status (completely resected vs. not completely resected), array used for genotyping data to account for violation of proportional hazards assumption.
Abbreviations: ERCC2, ERCC excision repair 2; ERCC5, ERCC excision repair 5, XPC, XPC complex subunit; GSTM5, glutathione S-transferase mu 5; HMGB1, high mobility group box 1; MGMT, O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase; P2RX7, purinergic receptor P2×7; RPA1, replication protein A1.
aInteraction term between SNP and the type of chemotherapy (oxaliplatin-based vs. others).
In patients with stage IV (mCRC), six previously reported SNPs were associated with oxaliplatin treatment at P < 0.05 in our data. Two of them, MNAT1-rs4151330-G and VEGFA-rs833061-T, were both predictive and prognostic (Pinteraction = 0.042 and 0.002, respectively), were associated with better PFS among patients who received oxaliplatin (Table 4; Supplementary Table S4). We also found two predictive SNPs, CXCR1-rs2234671-G (Pinteraction = 0.023 for OS and Pinteraction = 0.030 for PFS, respectively) and P2RX7-rs208294-C (Pinteraction = 0.036 for OS), and two prognostic SNPs, GSTM5-rs11807-C and MNAT1-rs4151330-G, which were associated with worse survival in patients who received oxaliplatin. In addition, two putative functional SNPs showed associations at P < 0.05. ATP8B3-rs7250872-T was both predictive and prognostic at P < 0.01, associated with worse survival in oxaliplatin-treated patients. Another putative SNP, P2RX7-rs208294-C, was only predictive, showing better OS in the patients who received oxaliplatin versus those that did not (Table 4; Supplementary Table S4).
Table 4.
SNPs nominally associated at P < 0.05 with OS and PFS as prognostic and/or predictive markers in patients with mCRC (stage IV).
| Patients who received OX-based treatment | Patients who received non-OX-based treatment | Interaction terma | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene - SNP - effect allele | HR (95% CI) | P | HR (95% CI) | P | P | Endpoint |
| Previously reported SNPs | ||||||
| GSTM5 - rs11807 - C | 1.80 (1.02–3.18) | 0.044 | 0.86 (0.63–1.20) | 0.381 | 0.084 | OS |
| MNAT1 - rs3783819 - G | 1.56 (1.05–2.32) | 0.028 | 0.98 (0.78–1.25) | 0.901 | 0.153 | OS |
| MNAT1 - rs3783819 - G | 1.80 (1.12–2.88) | 0.014 | 0.87 (0.68–1.11) | 0.266 | 0.109 | PFS |
| MNAT1 - rs4151330 - G | 0.60 (0.40–0.92) | 0.018 | 1.02 (0.80–1.30) | 0.893 | 0.192 | OS |
| MNAT1 - rs4151330 - G | 0.52 (0.31–0.86) | 0.012 | 1.20 (0.93–1.56) | 0.158 | 0.042 | PFS |
| CXCR1 - rs2234671 - G | 0.55 (0.19–1.62) | 0.279 | 1.46 (0.90–2.36) | 0.127 | 0.023 | OS |
| CXCR1 - rs2234671 - G | 0.41 (0.13–1.36) | 0.146 | 1.25 (0.73–2.13) | 0.422 | 0.030 | PFS |
| VEGFA - rs833061 - T | 0.60 (0.40–0.91) | 0.015 | 1.14 (0.90–1.45) | 0.270 | 0.002 | PFS |
| P2RX7 - rs208294 - C | 0.80 (0.56–1.16) | 0.236 | 1.01 (0.78–1.32) | 0.936 | 0.036 | OS |
| Putative functional SNPs | ||||||
| ATP8B3 - rs7250872 - T | 2.24 (1.36–3.69) | 0.002 | 0.97 (0.72–1.30) | 0.826 | 0.007 | OS |
| ATP8B3 - rs7250872 - T | 1.91 (1.14–3.18) | 0.013 | 1.26 (0.92–1.71) | 0.148 | 0.398 | PFS |
| P2RX7 - rs17525809 - C | 0.87 (0.41–1.84) | 0.708 | 1.43 (0.92–2.23) | 0.112 | 0.025 | OS |
Note: Significant P value marked in bold. The models were adjusted for age, sex, cancer location (proximal vs. distal), and liver resection for the analyses. The model was also stratified for grade (1–2 vs. 3–4), KRAS mutation (wild-type vs. mutation), resection status (completely resected vs. not completely resected), array used for genotyping data to account for violation of proportional hazards assumption.
Abbreviations: ATP8B3, ATPase phospholipid transporting 8B3; CXCR1, C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 1; GSTM5, glutathione S-transferase mu 5; MNAT1, MNAT1 component of CDK activating kinase; P2RX7, purinergic receptor P2×7; VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor A.
aInteraction term between SNP and the type of chemotherapy (oxaliplatin-based vs. others).
Limited power was observed to detect a small effect size of predictive/prognostic SNPs of treatment, particularly with the less common SNPs (Supplementary Table S2).
Discussion
Using a large independent sample of 1,502 patients with colorectal cancer, we found associations at P < 0.05 for several of the SNPs previously reported to be predictive or prognostic, but none remained significant after accounting for multiple testing. Our results suggest that many previous findings linking genetic variants and oxaliplatin on colorectal cancer survival might have been false-positive associations due to small sample sizes (range from 37 to 1,028, with 50% less than 150), failure to correct for multiple testing, and limited adjustment for relevant covariates.
Our study tested the SNPs as a predictive marker, indicating the likelihood of benefit from an oxaliplatin treatment compared with other treatments, and as a prognostic marker, indicating the patient's clinical outcome after standard oxaliplatin treatment. Our data replicated 12 previously reported SNPs to be predictive and/or prognostic at P < 0.05. Of these, six were in genes related to the DNA repair system. Two variants in ERCC2, rs13181-G and rs1799793-T, were found to be associated with differential OS in patients with stage II–III, with worse OS among patients who received oxaliplatin-based treatment but not otherwise. Previous studies have reported rs13181-GG and rs1799793-AA genotype to be associated with worse survival in patients with oxaliplatin-treated mCRC (32–34). Our study also found that XPC-rs2228000-A was associated with better PFS in patients with stage II–III colorectal cancer after oxaliplatin-based treatment, whereas ERCC5-rs2016073-G showed poorer PFS. These findings were not consistent with those of previous studies, which reported a longer disease-free survival associated with the rs2228000-C allele in 718 Korean patients with colorectal cancer after oxaliplatin-based treatment (35) and an improved tumor response associated with rs2016073-G in 83 Chinese subjects with advanced colorectal cancer (36). To interpret the inconsistent results, ethnic heterogeneity should be considered. Unlike the previous study population on these SNPs (Asians), our study was conducted in Caucasians. Ethnicity was not a study sample inclusion criteria in our study population, DACHS, and patients' information on ethnicity was not available. However, data collection by face-to-face interview meant that the patients were restricted to German speakers. On the basis of other population-based studies in the same region of Germany, less than 4% of study participants could have been non-Caucasians. Finally, in our study, two variants in MNAT1, rs3783819-G, and rs4151330-G were associated with oxaliplatin efficacy. Rs3783819-G was prognostic with worse survival in patients with mCRC who received oxaliplatin, whereas rs4151330-G was also found to be both predictive and prognostic for better survival. We previously reported two SNPs to be predictive in a smaller sample of 623 patients with II–IV stage colorectal cancer (37). However, we did not find any evidence to support a predictive role of the widely studied SNP, ERCC1-rs11615, in association with oxaliplatin.
The variant rs11807 in GSTM5, a GST family member involved in drug detoxification, showed the most consistently significant result across the two tumor stage groups. Rs11807-C was predictive and prognostic for patients with stage II–III colorectal cancer with worse OS and PFS after oxaliplatin-based treatment and also predictive for mCRC. The rs11807 C allele was shown to be associated with higher gene expression in colon tissue (38). We previously reported this SNP to be prognostic for poorer OS in a smaller sample of 201 patients with II–IV stage colorectal cancer (39). However, we found no association with the widely studied SNP, GSTP1-rs1695, in relation to oxaliplatin.
Previous studies assessed rs833061 in the promoter region of VEGFA, an angiogenesis inhibitor, predominantly as a predictor of the effectiveness of bevacizumab-containing therapy (40, 41). One study reported a lower response rate and worse PFS and OS for rs833061-TC/CC compared with TT genotype in 128 patients with mCRC who received FOLFOX4 (24). This is in line with our data that indicated rs833061-T to be a prognostic and predictive marker for mCRC patients with improved PFS in oxaliplatin-treated patients. Our study also found rs2234671-G in CXCR1, an encoding gene for IL8 receptors, to be associated with differential OS and PFS in the patients with mCRC, whereby outcome was improved after oxaliplatin-based treatment. This is in line with a previous report of rs2234671-GG genotype associated with a better response rate in 132 patients with mCRC receiving oxaliplatin-based therapy with bevacizumab (42). In contrast, rs2234671-GG genotype was associated with a decreased time to progression compared with GC genotype in another study of 105 patients with mCRC treated with oxaliplatin without bevacizumab (23).
Oxaliplatin has been known to be an immunogenic cell death inducer, which influences its efficacy (43, 44). Immunogenic cell death is induced by the ability to activate endoplasmic reticulum stress, which causes the release of damage-associated molecular patterns from dying tumor cells and the subsequent activation of pattern recognition receptors of the host innate immune cells (45). We found that rs208294-C in P2RX7 (pattern recognition receptors—encoding gene) and rs1360485-C in HMGB1 (damage-associated molecular patterns—encoding gene) were predictive for better OS in mCRC, respectively, better PFS in patients with stage II–III after oxaliplatin-based treatment. These SNPs were previously reported to be predictive for worse outcomes in 648 patients with mCRC (25). Furthermore, we found two newly tested functional SNPs in P2RX7, rs2230911-G and rs17525809-C, to be predictive in patients with stage II–III, respectively, in patients with mCRC associated with oxaliplatin treatment. Rs2230911-CG genotype has been associated with higher expression of P2RX7 than CC genotype in colon tissues (38). Rs17525809-TC was shown to be associated with higher expression of the gene than TT genotype although imprecisely estimated (i.e., wide confidence intervals; ref. 38).
In addition, three more functional SNPs, RPA1-rs5030755, MGMT-rs12917, and ATP8B3-rs7250872, were newly identified at P < 0.01. The RPA1-rs5030755-G-allele was predictive for worse PFS in patients with stage II–III colorectal cancer after oxaliplatin-based treatment. Indeed higher RPA1 expression has been associated with decreased oxaliplatin sensitivity in colon cancer cells (46). RPA1 expression was higher in rs5030755-AG than AA genotype in colon tissue although imprecisely estimated (38). Our study also found MGMT-rs12917-T to be predictive for worse OS in stage II–III CRC patients who received oxaliplatin. Rs12917-CT genotype has been associated with lower expression of MGMT than CC genotype (38), which may affect DNA damage repair capacity. Rs7250872-T, associated with higher gene ATP8B3 expression (38), was predictive and prognostic for poorer survival in mCRC patients who received oxaliplatin in our data.
The main challenge to validate the previously reported significant SNP associations was the heterogeneity of study design and patient sample. We used the criterion of four completed cycles of adjuvant first-line oxaliplatin to define patients as having received adjuvant first-line oxaliplatin treatment, whereas, in previous studies, various definitions of chemotherapy treatment were used. Moreover, our study tested candidate SNPs both as prognostic and predictive markers, unlike most previous studies, which assessed only prognostic associations. Predictive markers provide information on the likelihood of benefit from a specific treatment (compared with another treatment), which could be used for individualized treatment decision-making. In contrast, prognostic markers provide information about the patient's survival after standard treatment but do not predict the response to treatment. Considering oxaliplatin is not used alone, but in association with FL and other chemotherapeutic drugs, prognostic evidence from patients who received a combination of FL and oxaliplatin provides only limited information specifically on oxaliplatin as a treatment option. Finally, most of the previously identified SNPs were evaluated in patients with a certain stage of disease only (metastatic or nonmetastatic). We assessed the selected SNPs separately in both groups of patients according to the stage.
One limitation of this study is that we were not able to examine tumor response to oxaliplatin treatment using metrics based on tumor sizes, such as early tumor shrinkage and depth of response which have been known to be potential clinical endpoints in metastatic colorectal cancer (47). However, OS and PFS are widely used end-points to predict long-term survival in prospective studies. Despite the large sample size used in our analysis, limited power to detect small effect size should be considered when interpreting the outcomes (Supplementary Table S2). We cannot exclude that modest effects of some SNP associations may have remained undetected due to limited power, particularly for the less common variants. For the same reason, we were not able to test rare variants or consider the heterogeneity of treatment in the non-oxaliplatin-treated patients. The Q–Q plot of P values obtained from the tests in stage II–III indicated some P value inflation (λ = 1.28; Fig. 2A). As this is an observational study, patients were not randomized into treatment groups. Even though we adjusted for multiple covariables that could differ between the treatment groups, there might still be residual differences unaccounted for.
In conclusion, we were not able to robustly validate the previously reported genetic variants associated with survival outcomes in relation to oxaliplatin treatment despite replication of some associations at P < 0.05. The suggestive findings for several novel putative functional variants indicate that predictive markers could be identified. Further investigations and validation in well-powered studies are warranted to establish the clinical utility of the associated genetic variants.
Authors' Disclosures
P. Seibold reports grants from German Research Council and German Federal Ministry of Education and Research during the conduct of the study. H. Brenner reports grants from German Research Council and German Federal Ministry of Education and Research during the conduct of the study. J. Chang-Claude reports grants from Federal Ministry of Education and Researchology during the conduct of the study. No disclosures were reported by the other authors.
Supplementary Material
Table S1 shows SNPs previously reported to be associated with oxaliplatin treatment. Table S2 presents detectable effect sizes at 85% power and type I error of 0.05 and 4.7 x 10-4 (corresponding to Bonferroni corrected p-value) for all endpoints based on minor allele frequency of genetic variants. Table S3-4 shows SNP associations with first-line oxaliplatin treatment for all endpoints in stage II-III CRC patients (Table S3) and mCRC patients (Table S4).
Acknowledgments
The DACHS study was supported by grants from the German Research Council (BR 1704/6-1, BR1704/6-3, BR 1704/6-4, BR 1704/6-6, CH 117/1-1, BR 1704/17-1, and HO 5117/2-1) and the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (01KH0404, 01ER0814, 01ER0815, and 01GL1712). GECCO was supported by the NCI, NIH, and US Department of Health and Human Services, grant numbers U01 CA137088 and R01 CA059045.
The costs of publication of this article were defrayed in part by the payment of page charges. This article must therefore be hereby marked advertisement in accordance with 18 U.S.C. Section 1734 solely to indicate this fact.
Footnotes
Note: Supplementary data for this article are available at Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention Online (http://cebp.aacrjournals.org/).
Authors' Contributions
H.A. Park: Formal analysis, validation, writing–original draft, project administration, writing–review and editing, literature search. P. Seibold: Writing–review and editing, literature search. D. Edelmann: Methodology. A. Benner: Methodology. F. Canzian: Methodology, writing–review and editing. E. Alwers: Writing–review and editing. L. Jansen: Data curation. M. Schneider: Writing–review and editing. M. Hoffmeister: Data curation, funding acquisition, writing–review and editing. H. Brenner: Data curation, funding acquisition, writing–review and editing. J. Chang-Claude: Conceptualization, resources, data curation, supervision, funding acquisition, methodology, project administration, writing–review and editing.
References
- 1. Faivre S, Chan D, Salinas R, Woynarowska B, Woynarowski JM. DNA strand breaks and apoptosis induced by oxaliplatin in cancer cells. Biochem Pharmacol 2003;66:225–37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Andre T, Boni C, Mounedji-Boudiaf L, Navarro M, Tabernero J, Hickish T, et al. Oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and leucovorin as adjuvant treatment for colon cancer. N Engl J Med 2004;350:2343–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Saltz LB, Clarke S, Diaz-Rubio E, Scheithauer W, Figer A, Wong R, et al. Bevacizumab in combination with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized phase III study. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:2013–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Douillard JY, Siena S, Cassidy J, Tabernero J, Burkes R, Barugel M, et al. Randomized, phase III trial of panitumumab with infusional fluorouracil, leucovorin, and oxaliplatin (FOLFOX4) versus FOLFOX4 alone as first-line treatment in patients with previously untreated metastatic colorectal cancer: the PRIME study. J Clin Oncol 2010;28:4697–705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Ibrahim A, Hirschfeld S, Cohen MH, Griebel DJ, Williams GA, Pazdur R. FDA drug approval summaries: oxaliplatin. Oncologist 2004;9:8–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Lin YL, Liau JY, Yu SC, Ou DL, Lin LI, Tseng LH, et al. KRAS mutation is a predictor of oxaliplatin sensitivity in colon cancer cells. PLoS One 2012;7:e50701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Orlandi A, Di Salvatore M, Bagalà C, Basso M, Strippoli A, Plastino F, et al. ERCC1 induction after oxaliplatin exposure may depend on KRAS mutational status in colorectal cancer cell line: in vitro veritas. J Cancer 2015;6:70–81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Basso M, Strippoli A, Orlandi A, Martini M, Calegari MA, Schinzari G, et al. KRAS mutational status affects oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy independently from basal mRNA ERCC-1 expression in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer 2013;108:115–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Gu J, Li Z, Zhou J, Sun Z, Bai C. Response prediction to oxaliplatin plus 5-fluorouracil chemotherapy in patients with colorectal cancer using a four-protein immunohistochemical model. Oncol Lett 2019;18:2091–101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Sun C, Wang FJ, Zhang HG, Xu XZ, Jia RC, Yao L, et al. miR-34a mediates oxaliplatin resistance of colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting macroautophagy via transforming growth factor-β/Smad4 pathway. World J Gastroenterol 2017;23:1816–27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Zhou Y, Wan G, Spizzo R, Ivan C, Mathur R, Hu X, et al. miR-203 induces oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer cells by negatively regulating ATM kinase. Mol Oncol 2014;8:83–92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Martin L, Hamilton T, Schilder R. Platinum resistance: the role of DNA repair pathways. Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:1291–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Sharma RA, Dianov GL. Targeting base excision repair to improve cancer therapies. Mol Aspects Med 2007;28:345–74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Kap EJ, Popanda O, Chang-Claude J. Nucleotide excision repair and response and survival to chemotherapy in colorectal cancer patients. Pharmacogenomics 2016;17:755–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Yin M, Yan J, Martinez-Balibrea E, Graziano F, Lenz HJ, Kim HJ, et al. ERCC1 and ERCC2 polymorphisms predict clinical outcomes of oxaliplatin-based chemotherapies in gastric and colorectal cancer: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res 2011;17:1632–40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Watson MA, Stewart RK, Smith GB, Massey TE, Bell DA. Human glutathione S-transferase P1 polymorphisms: relationship to lung tissue enzyme activity and population frequency distribution. Carcinogenesis 1998;19:275–80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Lévi F, Metzger G, Massari C, Milano G. Oxaliplatin: pharmacokinetics and chronopharmacological aspects. Clin Pharmacokinet 2000;38:1–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Townsend DM, Tew KD. The role of glutathione-S-transferase in anti-cancer drug resistance. Oncogene 2003;22:7369–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Li HY, Ge X, Huang GM, Li KY, Zhao JQ, Yu XM, et al. GSTP1, ERCC1 and ERCC2 polymorphisms, expression and clinical outcome of oxaliplatin-based adjuvant chemotherapy in colorectal cancer in Chinese population. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2012;13:3465–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Stoehlmacher J, Park DJ, Zhang W, Groshen S, Tsao-Wei DD, Yu MC, et al. Association between glutathione S-transferase P1, T1, and M1 genetic polymorphism and survival of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2002;94:936–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Kap EJ, Richter S, Rudolph A, Jansen L, Ulrich A, Hoffmeister M, et al. Genetic variants in the glutathione S-transferase genes and survival in colorectal cancer patients after chemotherapy and differences according to treatment with oxaliplatin. Pharmacogenet Genomics 2014;24:340–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Etienne-Grimaldi MC, Milano G, Maindrault-Goebel F, Chibaudel B, Formento JL, Francoual M, et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene polymorphisms and FOLFOX response in colorectal cancer patients. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2010;69:58–66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Zhang W, Stoehlmacher J, Park DJ, Yang D, Borchard E, Gil J, et al. Gene polymorphisms of epidermal growth factor receptor and its downstream effector, interleukin-8, predict oxaliplatin efficacy in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer 2005;5:124–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Chen MH, Tzeng CH, Chen PM, Lin JK, Lin TC, Chen WS, et al. VEGF -460T → C polymorphism and its association with VEGF expression and outcome to FOLFOX-4 treatment in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Pharmacogenomics J 2011;11:227–36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Arai H, Xiao Y, Loupakis F, Kawanishi N, Wang J, Battaglin F, et al. Immunogenic cell death pathway polymorphisms for predicting oxaliplatin efficacy in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Immunother Cancer 2020;8:e001714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Suenaga M, Schirripa M, Cao S, Zhang W, Cremolini C, Lonardi S, et al. Clinical significance of enterocyte-specific gene polymorphisms as candidate markers of oxaliplatin-based treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer. Pharmacogenomics J 2021;21:285–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Brenner H, Chang-Claude J, Seiler CM, Rickert A, Hoffmeister M. Protection from colorectal cancer after colonoscopy: a population-based, case-control study. Ann Intern Med 2011;154:22–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Brenner H, Chang-Claude J, Jansen L, Knebel P, Stock C, Hoffmeister M. Reduced risk of colorectal cancer up to 10 years after screening, surveillance, or diagnostic colonoscopy. Gastroenterology 2014;146:709–17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Weigl K, Chang-Claude J, Hsu L, Hoffmeister M, Brenner H. Establishing a valid approach for estimating familial risk of cancer explained by common genetic variants. Int J Cancer 2020;146:68–75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Jia M, Jansen L, Walter V, Tagscherer K, Roth W, Herpel E, et al. No association of CpG island methylator phenotype and colorectal cancer survival: population-based study. Br J Cancer 2016;115:1359–66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Puppa G, Sonzogni A, Colombari R, Pelosi G. TNM staging system of colorectal carcinoma: a critical appraisal of challenging issues. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2010;134:837–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Gan Y, Li XR, Chen DJ, Wu JH. Association between polymorphisms of XRCC1 Arg399Gln and XPD Lys751Gln genes and prognosis of colorectal cancer in a Chinese population. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2012;13:5721–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Stoehlmacher J, Park DJ, Zhang W, Yang D, Groshen S, Zahedy S, et al. A multivariate analysis of genomic polymorphisms: prediction of clinical outcome to 5-FU/oxaliplatin combination chemotherapy in refractory colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 2004;91:344–54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Liu Z, Kong J, Kong Y, Cai F, Xu X, Liu J, et al. Association of XPD Asp312Asn polymorphism and response to oxaliplatin-based first-line chemotherapy and survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Adv Clin Exp Med 2019;28:1459–68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Sun K, Gong A, Liang P. Predictive impact of genetic polymorphisms in DNA repair genes on susceptibility and therapeutic outcomes to colorectal cancer patients. Tumour Biol 2015;36:1549–59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Chen J, Xie F, Chen K, Wang D, Jiang H, Li J, et al. ERCC5 promoter polymorphisms at -763 and +25 predict the response to oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol Ther 2009;8:1424–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Kap EJ, Seibold P, Richter S, Scherer D, Habermann N, Balavarca Y, et al. Genetic variants in DNA repair genes as potential predictive markers for oxaliplatin chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. Pharmacogenomics J 2015;15:505–12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. GTEx Consortium. Human genomics. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) pilot analysis: multitissue gene regulation in humans. Science 2015;348:648–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Kap EJ, Seibold P, Scherer D, Habermann N, Balavarca Y, Jansen L, et al. SNPs in transporter and metabolizing genes as predictive markers for oxaliplatin treatment in colorectal cancer patients. Int J Cancer 2016;138:2993–3001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Sohn BS, Park SJ, Kim JE, Kim KP, Hong YS, Suh C, et al. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway and outcomes of patients treated with first-line cytotoxic chemotherapy combined with bevacizumab for advanced colorectal cancer. Oncology 2014;87:280–92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Loupakis F, Cremolini C, Yang D, Salvatore L, Zhang W, Wakatsuki T, et al. Prospective validation of candidate SNPs of VEGF/VEGFR pathway in metastatic colorectal cancer patients treated with first-line FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab. PLoS One 2013;8:e66774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Gerger A, El-Khoueiry A, Zhang W, Yang D, Singh H, Bohanes P, et al. Pharmacogenetic angiogenesis profiling for first-line Bevacizumab plus oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2011;17:5783–92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Zitvogel L. Immunogenic cell death in cancer therapy. Annu Rev Immunol 2013;31:51–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Tesniere A, Schlemmer F, Boige V, Kepp O, Martins I, Ghiringhelli F, et al. Immunogenic death of colon cancer cells treated with oxaliplatin. Oncogene 2010;29:482–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Galluzzi L, Buqué A, Kepp O, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G. Immunogenic cell death in cancer and infectious disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2017;17:97–111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Li S, Xu K, Gu D, He L, Xie L, Chen Z, et al. Genetic variants in RPA1 associated with the response to oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. J Gastroenterol 2019;54:939–49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Heinemann V, Stintzing S, Modest DP, Giessen-Jung C, Michl M, Mansmann UR. Early tumour shrinkage (ETS) and depth of response (DpR) in the treatment of patients with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Eur J Cancer 2015;51:1927–36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1 shows SNPs previously reported to be associated with oxaliplatin treatment. Table S2 presents detectable effect sizes at 85% power and type I error of 0.05 and 4.7 x 10-4 (corresponding to Bonferroni corrected p-value) for all endpoints based on minor allele frequency of genetic variants. Table S3-4 shows SNP associations with first-line oxaliplatin treatment for all endpoints in stage II-III CRC patients (Table S3) and mCRC patients (Table S4).