Abstract
The standard therapies in lymphoma have predominantly focused on targeting tumor cells with less of a focus on the tumor microenvironment (TME), which plays a critical role in favoring tumor growth and survival. Such an approach may result in increasingly refractory disease with progressively reduced responses to subsequent treatments. To overcome this hurdle, targeting the TME has emerged as a new therapeutic strategy. The TME consists of T and B lymphocytes, tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), and other components. Understanding the TME can lead to a comprehensive approach to managing lymphoma, resulting in therapeutic strategies that target not only cancer cells, but also the supportive environment and thereby ultimately improve survival of lymphoma patients. Here, we review the normal function of different components of the TME, the impact of their aberrant behavior in B cell lymphoma and the current TME-direct therapeutic avenues.
Keywords: Tumor microenvironment, B-cell lymphoma, T cells, T follicular helper cells, T regulatory cells, Tumor-associated macrophages, Myeloid-derived suppressor cells, Cancer-associated fibroblasts
Introduction
The last two decades have seen numerous discoveries which have helped understand the biology of B cell lymphoma and lay the foundation for precision therapies. B cell lymphomas arise from the germinal center (GC), a dynamic structure that forms upon encounter of naïve B cells with a putative antigen [1], and may be secondary to i) genetic/epigenetic alterations in the GC B cells or ii) aberrant response of immune components of the microenvironment ultimately leading to lymphomagenesis [2]. Gene expression profiling (GEP) studies have divided diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) - the most common B cell lymphoma - into two main subgroups based on the cell of origin (COO): the activated B cell (ABC) and the germinal center B cell (GCB) subtypes [3]. More recently, two additional molecular classifications have used whole exome sequencing (WES) and structural genomic abnormalities to further subdivide DLBCL into several genetically defined subgroups [4, 5]. An additional layer of complexity includes the immune cells that infiltrate the tumor. A landmark study performed on tumor biopsies from 95 untreated patients with follicular lymphoma (FL) - the second most frequent B cell lymphoma - demonstrated significant enrichment of genes associated with macrophages in patients with unfavorable outcomes whereas the expression signature was enriched for genes linked to T-cells in those with a favorable outcome [6]. Additionally, we reported the prognostic value of memory CD4+ T-cells, which play a critical role in immune surveillance, and designed a prognostic risk model (BioFLIPI) to improve the identification of high-risk patients [7]. Similarly, the prognostic relevance of TME in DLBCL has been uncovered in two recent studies which have further deconvoluted the TME in several ecosystems [8, 9]. Part of the reason for an unfavorable TME may be linked to the mutation of genes directly or indirectly involved in the control of antigen presentation, including CREBBP [10], EP300 [11], EZH2 [12], and others [13]. However, many additional mechanisms may come into play to shape the immune response against tumors [14]. Here, we dissect the function of different immune components of the TME (Table 1), the impact of their aberrant expression in B cell lymphoma and novel therapeutic avenues (Tables 2 and 3).
Table 1.
Role and markers of the immune cells of the TME
| Immune cells | Role | Markers |
|---|---|---|
| Tfh cells |
- formation and maintenance of GCs - promote clonal selection and affinity maturation of GC B cells |
CD4+, CXCR5+, PD1+, ICOS+ |
| Treg cells |
- prevent autoimmunity by suppressing immune response activation and promoting tolerance towards self-antigens - suppress tumor immunity leading to immune escape |
CD4+, CD25+, FoxP3+, CD127- |
| Effector CD8+ T cells | Highly cytotoxic against transformed and virus-infected cells | CD8+, CD45RA+, CD45RO-, CCR7+, CD28+, IFN- γ+, IL-2+ |
| TAMs |
M1 – anti-tumorigenic M2 – pro-tumorigenic: i) suppress antitumor immunity by inhibiting the recruitment and activation of T cells; ii) serve as metastasis promoters |
M1: CD80+, CD86+, CD64+, CD16+, CD32+ M2: CD163+, CD206+, CD204+ |
| MDSCs | - enhance tumorigenesis by enhancing migratory capacity, autocrine growth factor-induced signaling and increasing levels of secretory molecules | HLA-DR-, CD14+, CD11b+, CD33+, S100A9+, |
| CAFs |
- enhance stiffening of ECM, angiogenesis, and cancer cell invasion - promote an immune suppressive TME |
PDGFRA+, PDGFRB+, FSP-1/S100A4+ and FAP+ |
| NK cells | - prevention of infection and tumor growth | CD56dim CD16bright (90%) CD56bright CD16dim (10%) |
| ILCs | - regulate tissue homeostasis, inflammation, tumor surveillance and tumorigenesis | CD45+, CD127+, CD161+/-, HLA-DR+, CD56+/-, CD11b-, CD11c+/-, CD19- |
Abbreviations: Tfh T follicular helper, Treg T regulatory, TAMs Tumor-associated macrophages, MDSCs Myeloid-derived suppressor cells, CAFs cancer-associated fibroblasts, ECM extracellular matrix, TME tumor microenvironment, PDGFRA platelet derived growth factor receptor α, PDGFRB platelet derived growth factor receptor β, FSP fibroblast specific protein 1, FAP fibroblast activation protein, NK Natural Killer, ILCs Innate lymphoid cells
Table 2.
Clinical trials including agents targeting the immune cells of the TME in B cell lymphomas
| Immune cells | Identifier | Study | Phase | Target | Agent |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tfh cells | NCT02376699 | A Phase 1, Open-label, Dose-escalation Study of SEA-CD40 in Adult Patients with Advanced Malignancies | I | CD40 | SEA-CD40 |
| Treg cells | NCT04855253 | Phase I/II Trial Using E7777 to Enhance Regulatory T-cell Depletion Prior to Tisagenlecleucel (Kymriah) Therapy for Relapsed/Refractory DLBCL | I/II | IL-2 | E7777 |
| NCT01919619 | A Pilot Study of Lenalidomide Alternating with Ipilimumab Post Allogeneic and Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation | II | CTLA-4 | Ipilimumab | |
| NCT04544059 | Lenalidomide Plus R-CHOP for CNS Relapse Prophylaxis in DLBCL | II | CD28 | Lenalidomide | |
| NCT05429 | A Phase 3, Single-Arm, Open-Label, Multicenter Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Tafasitamab Plus Lenalidomide in Participants with Relapsed or Refractory DLBCL | III | CD28 | Lenalidomide | |
| NCT04432402 | Efficacy and Safety of Lenalidomide in Combination with R-GemOx in First-line treatment of Elderly DLBCL | N/A | CD28 | Lenalidomide | |
| NCT04432402 | Duvelisib Exposure to Enhance Immune Profiles of T cells in Patients with DLBCL (DEEP T CELLS) | I | PI3K | Duvelisib | |
| NCT04849351 | A Multi-center, Single-arm, Open-label Clinical Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of HMPL-689 in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory MZL and FL | II | PI3K | Amdizalisib, HMPL-689 | |
| NCT03314922 | A Phase 1b, Open-Label, Dose-Escalation Study for the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of INCB050465 in Japanese Subjects with Previously Treated B-cell lymphoma (CITADEL-111) | I | PI3K | Parsaclisib | |
| NCT03919175 | A Phase 2 Study of Umbralisib and Rituximab as Initial Therapy for Patients with FL and MZL | II | PI3K | Umbralisib | |
| NCT02367040 | A Phase III, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Copanlisib in Combination with Rituximab in Patients with Relapsed iNHL – CHRONOS-3 | III | PI3K | Copanlisib (Aliqopa, BAY80-6946) | |
| NCT03884998 | A Phase 1 study of PI3Kα,δ Inhibitor Copanlisib in Combination with PD-1 Antagonist Nivolumab in Patients with Transformed CLL (Richter’s Transformation) or NHL | I | PI3K | Copanlisib (Aliqopa, BAY80-6946) | |
| Effector CD8+ T cells | NCT04566978 | A Pilot Study of 89Zr-DFO-REGN3767 Anti LAG-3 Antibody Positron Emission Tomography in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory DLBCL | I | LAG3 | 89Zr-DFO-REGN3767 |
| NCT05039658 | A Phase Ib, Open Label, Randomized, Multicenter Study of the Efficacy and Safety of IBI110 Single Agent and in Combination with Sintilimab for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory DLBCL | Ib | LAG3 | IBI110 | |
| NCT02061761 | A Phase 1/2a Dose Escalation and Cohort Expansion Study of the Safety, Tolerability, and Efficacy of Anti-LAG-3 Monoclonal Antibody (Relatlimab, BMS-968016) Administered Alone and in Combination with Anti-PD-1 Monoclonal Antibody (Nivolumab, BMS-936558) In relapsed or Refractory B-cell Malignancies | I/IIA | LAG3 | Relatlimab, BMS-896016 | |
| NCT05255601 | A Phase I/II study of the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics and Preliminary Efficacy of Relatlimab Plus Nivolumab in Pediatric and Young Adult Participants with Recurrent or Refractory Classical HL and NHL | I/II | LAG3 | Relatlimab, BMS-896016 | |
| NCT04767308 | A Single-center, Single-arm Exploratory Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of Fully Human Anti-CD5 Chimeric Antigen Receptor T cells (CT125A Cells) for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory CD5+ Hematopoietic Malignancies | I | CD5 | CD125A cells | |
| NCT01919619 | A Pilot Study of Lenalidomide Alternating with Ipilimumab Post Allogeneic and Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation | II | CTLA4 | Ipilimumab | |
| TAMs | NCT03530683 | A Phase1a/1b Dose-Escalation and Expansion Trial of TTI-622 in patients with Advanced Hematologic Malignancies, Including Lymphoma, Leukemia, and Multiple Myeloma | I | SIRPα | TTI-622 (SIRPα-IgG4 Fc) |
| NCT05507541 | Randomized Phase 2 Study with Safety Run-In of PD-1 Inhibitor and IgG4 SIRPα-Fc Fusion Protein (TTI-622) and PD-1 Inhibitor and IgG1 SIRPα-Fc Fusion Protein (TTI-621) in Relapsed DLBCL | II | SIRPα | TTI-622 (SIRPα-IgG4 Fc) | |
| NCT02953509 | A Phase 1b/2 Trial of Hu5F9-G4 in Combination with Rituximab or Rituximab + Chemotherapy in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory B-cell NHL | Ib/II | CD47 | Hu5F9-G4 | |
| NCT05626322 | A Phase 1b/2 Study of PF-07901801, a CD47 Blocking Agent, with Tafasitamab and Lenalidomide for Participants with Relapsed/Refractory DLBCL Not Eligible for Stem Cell Transplantation | II | CD47 | PF-07901801 | |
| NCT05025800 | A Phase I/II Open Label, Single Center, Study of the Combination of ALX148, Rituximab and Lenalidomide in Patients with Indolent and Aggressive B-cell NHL | I/II | CD47 | ALX148 | |
| NCT04806035 | A Phase 1b Multi-cohort Study of TG-1801 Alone in Combination with Ublituximab in Subjects with B-cell Lymphoma or CLL | I | CD47 | TG-1801 | |
| MDSCs | NCT03711604 | An Open Label, Compassionate Use Study of Tenalisib (RP6530) in Patients Currently Receiving Treatment on Tenalisib Trials in Hematological Malignancies | I/II | PI3K δ/γ | Tenalisib (RP6530) |
| NCT02916979 | A Pilot Trial Examining Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Checkpoint Immune Regulators’ Expression in Allogeneic Stem cell Transplant Recipients Using Myeloablative Busulfan and Fludarabine | I | Myeloablative Busulfan and Fludarabine | ||
| CAFs | NCT03155620 | NCI-COG Pediatric MATCH (Molecular Analysis for Therapy Choice Screening Protocol) | II | FGFR | JNJ-42756493 |
| NCT02465060 | Molecular Analysis for Therapy Choice (MATCH) | II | FGFR | JNJ-42756493 | |
| NK cells | NCT03056339 | Dose Escalation Study Phase I/II of Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived CAR-Engineered NK Cells in Conjunction with Lymphodepleting Chemotherapy in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory B-Lymphoid Malignancies | I/II | CD19 | iC9/CAR.19/IL15-Transfuced CB-NK Cells |
| NCT04052061 | Open-Label, Phase I Study of CD19 t-haNK in Subjects with DLBCL who have Received 2 or More Lines of Therapy and Are Ineligible for Transplant | I | CD19 | CD19 t-haNK | |
| NCT04074746 | Bispecific NK Engager AFM13 Combined with NK Cells for Patients with Recurrent of Refractory CD30 Positive HL or NHL | I/II | CD30 | AFM13 | |
| NCT02890758 | Phase I Trial of Universal Donor NK Cell Therapy in Combination with ALT-803 | I | IL-15 | ALT-803 | |
| NCT04609579 | A Phase 1 Open-label of Study SNX281 Given as Monotherapy and in Combination with a Checkpoint Inhibitor in Subjects with Advanced Solid Tumors and Lymphoma | I | STING protein | SNX281 | |
| NCT02727803 | Personalized NK Cell Therapy in CBT | II | Allogeneic Natural killer Cell Line NK-92 | ||
| NCT05472558 | Clinical Study of Cord Blood-Derived CAR-NK Cells Targeting CD19 in the Treatment of Refractory/Relapsed B-cell NHL | I | CD19 | CAR-NK cells | |
| NCT04639739 | Anti-CD19 CAR-NK Cell Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory B-cell NHL: a Multi-center, Uncontrolled Trial | I | CD19 | CAR-NK cells | |
| NCT04796688 | Safety and Efficacy of Universal Chimeric Antigen Receptor-modified AT19 Cells in Patients with CD19+ Relapsed/Refractory Hematological Malignancies: a Single-center, Open-label, Single-arm Clinical Study | I | CD19 | CAR-NK cells | |
| NCT05379647 | QN-019a as a Monotherapy and in Combination with Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibodies in Subjects with B-cell Malignancies | I | CD19 | QN-019a, CAR-NK cells |
Abbreviations: Tfh T follicular helper, Treg T regulatory, TAMs Tumor-associated macrophages, MDSCs Myeloid-derived suppressor cells, CAFs cancer-associated fibroblasts, NK Natural Killer, ILCs Innate lymphoid cells, DLBCL Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma, MZL Marginal Zone Lymphoma, FL Follicular Lymphoma, iNHL Indolent B-cell Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, HL Hodgkin Lymphoma, CLL Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
Table 3.
FDA-approved agents targeting the immune cells of the TME in B cell lymphomas
| Agent | Drug Category | Indication | Approval Year | Trials |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pembrolizumab | CPI | Adult and pediatric patients with refractory PMBCL | 2018 | KEYNOTE-170 (NCT02576990) |
| Lenalidomide | IMIDs | Previously treated FL and MZL | 2019 | AUGMENT (NCT01938001); MAGNIFY (NCT01996865) |
| Lenalidomide | IMIDs | ASCT-ineligible R/R DLBCL patients | 2020 | L-MIND (NCT02399085); RE-MIND (NCT04150328) |
| Umbralisib | PI3Ki | R/R MZL with at least one prior anti-CD20-based regimen; R/R FL with at least 3 prior lines of systemic therapy | 2021 | UTX-TGR-205 (NCT02793583) |
| Zanubrutinib | BTKi | R/R MZL with at least one anti-CD20-based regimen | 2021 | BGB-3111-241 (NCT03846427); BGB-3111-AU-003 (NCT02343120) |
Abbreviations: CPI checkpoint inhibitor, IMIDs immunomodulatory drugs, PI3Ki phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, BTKi Bruton Tyrosine Kinase inhibitor, PMBCL primary mediastinal large B cell lymphoma, FL Follicular Lymphoma, MZL Marginal Zone Lymphoma, DLBCL Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma, ASCT autologous stem cell transplant, R/R relapsed/refractory
T follicular helper cells
T follicular helper (Tfh) cells commonly reside inside the lymph nodes, tonsils, and spleen. They are defined by the expression of cell surface markers CD4, CXCR5, PD1, and ICOS, their master regulator being B cell lymphoma (BCL) 6 [15]. Tfh cells play a critical role in the formation and maintenance of GCs. Also, Tfh cells engage GC B cells to promote clonal selection and affinity maturation so that high-affinity B cells can be selected to exit the GC reaction and undergo terminal differentiation towards plasma cells or memory cells [15]. This mechanism is mediated through interaction between the co-stimulatory molecule CD40-ligand on the Tfh cells with CD40 on the B cells (Fig. 1) [15]. On the contrary, T follicular regulatory (Tfr) cells limit the output of the GC reaction counterbalancing Tfh function [1]. Of note, Tfh cells can convert to Tfr cells through FOXP3 activation in the late germinal center [16]. Several studies have shown an increased expression of Tfh CD4+PD1+ICOS+ cells [17] and/or CD4+CXCR5+Foxp3- [18] cells in diagnostic samples of malignant lymphoid disease compared to healthy controls. The same expression decreased or returned to normal at the end of effective treatment, but it increased in progressive disease [17]. It is possible that Tfh cells may contribute to lymphoma B cell survival via production of sCD40L which activates NF-kB pathway and in turn up-regulates c-FLIP and Bcl-xL [19, 20]. Increased expression of lymphoma-infiltrating Tfh cells was associated with high levels of IL-6, IL-21 [21], IL-4 [22], and CXCL13 [9] (Fig. 1). Conversely blocking these cytokines resulted in reduced infiltration of Tfh cells [21]. Additionally, the crosstalk between lymphoma B cells and Tfh cells increases the release of CCL17 and CCL22, which induces the preferential migration of regulatory T cells (Treg) and IL-4 producing CD4+ T cells, stimulating more chemokine release thus creating an immune suppressive TME that promotes tumor survival and growth [23, 24]. Another study divided Tfh cells into Tfr-like subsets (CD4+CD25+CXCR5+) and Tfh CD25- subset (CD4+CD25-CXCR5+) [25]. The difference between these two groups was associated with the higher expression of Blimp1, Foxp3, IL-10, TGF-β, and lower levels of IL-21 in Tfr-like CD25+ cells compared to Tfh CD25- cells [25]. This discovery is intriguing as it demonstrates the plasticity of the immune response and implies the possibility to leverage this characteristic as a therapeutic tool. Novel insights on the role of Tfh cells in immune evasion can usher in the opportunity for unexplored therapeutic targets [26]. In particular, identification of genetic mutations, cell markers and cytokine/chemokine signaling that impact Tfh cell function will help in improving our knowledge of the causative events that induce and/or sustain tumor development and growth. Thus, targeting these regulators may be a new approach to interrupting T cell support of lymphoma cells, which may complement other therapeutic approaches.
Fig. 1.
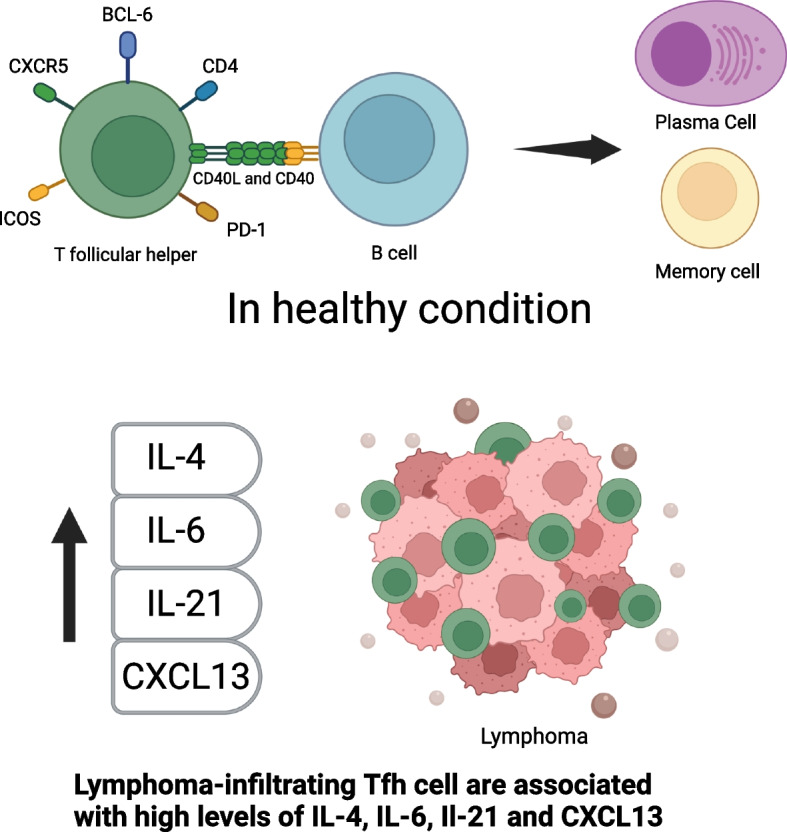
Role of T follicular helper (Tfh) cells in the normal germinal center and in lymphomagenesis
T regulatory cells
Treg cells are CD4+ T cells expressing high CD25 (IL-2Rα) and FoxP3, and low or not CD127 (IL-7R α) [27, 28]. They suppress immune response activation and promote tolerance towards self-antigens to prevent autoimmunity [29]. However, their function can also suppress tumor immunity leading to immune escape [30]. Nevertheless, the significance of tumor-infiltrating Treg cells remains elusive due to their heterogeneity and their expression of both co-inhibitory and co-stimulatory receptors [31]. Specifically, some studies have shown that Treg FOXP3+ cells display a tumor-protective effect [32, 33] in FL [34] and DLBCL [34, 35] by suppressing T-cell proliferation and IFN-γ production [31, 36], while others found that Treg cells co-expressing activating markers such as CTLA4 [37] and TIGIT [38] result in an enhanced suppressive property and are associated with poor prognosis [39]. It is possible that the prognostic impact of Treg cells is dependent on disease context, however more clarity is still needed. Therefore, in-depth phenotypic and functional characterization of Treg cells is mandatory to identify novel targets for therapy and in turn improve patient survival. These data suggest that targeting Treg cells could be beneficial due to their antitumor immunity, however, it might also lead to unwanted immune-mediated toxicities.
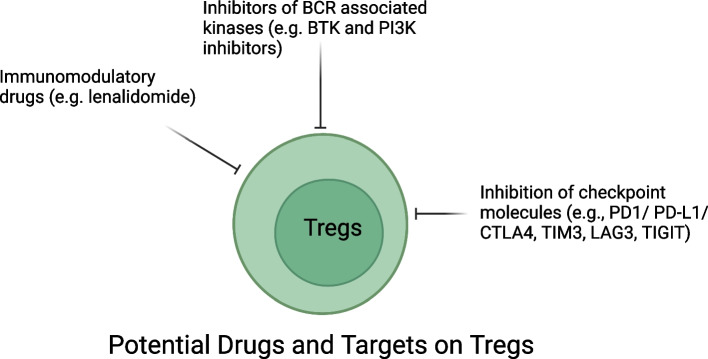
In the last decade several immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs) (e.g. lenalidomide) and targeting agents against B cell receptor (BCR) or intracellular kinases (e.g. BTK inhibitors and PI3K inhibitors) have been approved for hematologic malignancies [40]. Beside the tumor-specific effect, these molecules can also impact the immune components of the microenvironment (Fig. 2). For example, lenalidomide modulates Treg cells decreasing their suppressive function [41–43] and results in an enhanced anti-lymphoma activity. Similarly, PI3K inhibitors decrease the suppressive effect of Treg cells while enhancing CD8 T cell function [44–46]. The most recent therapeutic strategies targeting T cells include inhibition of checkpoint molecules such as PD1/PD-L1 and CTLA4 [47] or adoptive transfer of genetically engineered T cells [48]. Additional recently discovered immune checkpoint molecules that represent emerging targets for therapy are TIM3, LAG3 and TIGIT [49]. Blocking the negative T cell regulator CTLA4 reactivates immune response against the tumor in immunogenic cancers [50]. CTLA4 inhibition decreased Treg cells also in B cell lymphoma with a positive association of CD45RA-Treg ratio in responders vs non responders, however the antitumoral effects were quite modest [51]. PD1/PD-L1 inhibition prevents T cell exhaustion [52] and blocks the suppressive Treg activity [53]. Interestingly, inhibition of one checkpoint leads to compensatory increase of others. For example, blocking PD1 results in increase of LAG3 and CTLA4 [54]. On the contrary, combined inhibition of PD1 and LAG3 increased CD8 T cell cytotoxicity and decreased Treg cells [55]. Nevertheless, combination of two checkpoint blockades has shown modest activity in relapsed/refractory (R/R) B cell lymphoma [51, 56]. Similar to LAG3, TIM3 results in negative regulation of T cell response, ultimately leading to T cell exhaustion [57, 58], while its inhibition reduces tumor growth especially in combination with PD-1 blockade, but again the overall anti-tumor effect is modest [59]. TIGIT is also a negative regulator of T cells that can prevent immune response against tumor [60, 61]. As such it has attracted scientific attention as a novel target for therapy [62] and its use is under experimental evaluation. Given the tremendous potential of immune therapy, optimal methods to modulate Treg cells are needed in the future to achieve a balance between antitumor immunity and autoimmunity.
Fig. 2.
Drugs targeting T regulatory (Treg) cells
Effector CD8+ T cells
Naïve CD8+ T cells differentiate into cytotoxic effector CD8+ T cells when encountering a cognate antigen [63]. Once the antigen has been eliminated, they undergo apoptosis or differentiate into memory T cells [64]. However, CD8+ T cells may become exhausted in the face of persistent antigen stimulation in infections or autoimmunity [65]. In addition, during tumorigenesis cancer cells secrete inhibitory factors to generate an immune suppressive tumor environment, thus, despite their important role in eliminating tumor cells, CD8+ cytotoxic T cells often become exhausted and eventually fail to control tumor development and progression [65]. Anergic or exhausted CD8+ T cells are defined as CD8+ CD28- CD57+ T cells with a reduced proliferation and cytotoxic effect (loss of IL-2, TNF-α, and IFN-γ production) [66]. Differential expression level of CD5 distinguishes different T cell activation and effector function, as CD5high CD8+ T cells are more active and abundant in the TME compared to CD5low CD8+ T cells. Since CD5 expression inversely correlates with PD1 expression, targeting CD5 may increase PD1 levels, which in turn would maximize the effect of anti-PD1 checkpoint blockade [67]. CD8+ T cells are also characterized by a sustained expression of inhibitory receptors such as PD1, CTLA4, and LAG3 [68]. Several studies have shown a favorable correlation between increased numbers of effector CD8+ T cells and good outcomes in FL [69, 70]. Specifically, increase of PD1+ CD8+ T cells associated with a favorable outcome in FL patients, while reduction of the same was observed in transformation [71]. By contrast, expression of LAG3 defines a subset of PD1+ CD8+ T cells which correlates with poor outcome in FL [72]. In line with these data, inhibition of LAG3 increases the proliferation and effector function of CD8+ T cells [73], suggesting that these immune checkpoint inhibitors can potentially augment antitumor immunity. Currently, there are several clinical trials investigating the efficacy of anti-LAG3 inhibitors alone or in combination with other immunotherapy in hematologic malignancies (NCT04566978, NCT05039658, NCT02061761, NCT05255601).
Tumor-associated macrophages
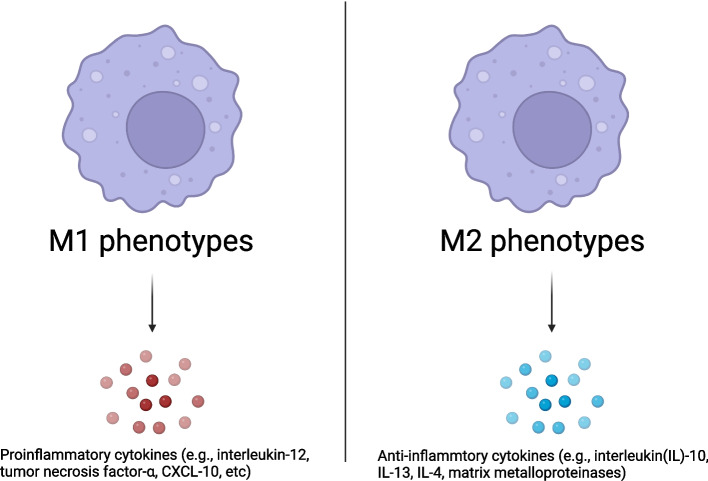
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) are one of the most critical immunosuppressive cell populations. TAMs suppress antitumor immunity and promote tumor progression by inhibiting the recruitment and activation of T cells via secreting cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors [74]. TAMs also serve as prominent metastasis promoters in the TME [75]. TAMs are classified into M1 and M2 phenotypes. In general, M1 macrophages are cytotoxic via secreting proinflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-12, tumor necrosis factor-α, CXCL-10) and are considered anti-tumorigenic, while M2 macrophages are pro-tumorigenic via secreting anti-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., IL-10, IL-13, IL-4, matrix metalloproteinases) [75] (Fig. 3). A study by Taskinen et al. showed that high expression of CD68+ (M1 marker) TAMs was associated with adverse outcome in chemotherapy-treated FL patients (P = 0.026), but those patients had a favorable prognosis (progression free survival [PFS] was not reached, p = 0.006) and overall survival (p = 0.006) compared to the control group [76]. However, an increased number of TAMs, particularly CD68+ macrophages, was correlated with an increased likelihood of relapse after autologous hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (P = 0.008) and shortened PFS (p = 0.03) in patients with classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma (HL) [77]. Along the same lines, elevated numbers of infiltrating CD163+ M2 macrophages were associated with increased angiogenic sprouting and poor prognosis in FL [78] and DLBCL [79]. Therefore, TAMs may exert either antitumor or protumor functions in different tumor types [80].
Fig. 3.
Macrophage polarization and specific cytokines release of M1 and M2 macrophages
Many clinical approaches targeting TAMs are still under investigation. Targeting the colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor (CSF1R) signaling pathway, which is essential for the recruitment, differentiation, and survival of TAMs, leads to their decrease in number and in immunosuppressive functions [81]. Targeting CSF1R caused abrogation of CD163+ TAMs in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), irrespective of the sensitivity to BTK inhibitors [82]. PLX3397 (pexidartinib), a CSF1R inhibitor, significantly reduced the viability of M2 macrophages, but it did not affect M1 macrophages in FL [83]. Also, inhibition of CSF1-CSF1R axis improved the efficacy of other immunotherapies, such as PD-1 or CTLA-4 blockades [84]. Another promising target is CD47 which is overexpressed in several B cell lymphomas, including DLBCL, FL and MCL [85]. The interaction between CD47 and SIRPα prevents cancer cells from being phagocytosed by macrophages and dendritic cells [86]. Chao et al. reported that anti-CD47 antibody reduced lymphoma burden, and the combination with rituximab had a synergist effect on promoting phagocytosis of lymphoma cells [85]. Notably, anti-CD47 antibodies robustly inhibited the dissemination of disease to secondary sites [87]. This correlated with a benefit in prognosis as extranodal lymphomas generally associate with a reduced response to therapy and a worse prognosis. CCL2/CCR2 is another essential signaling axis implicated in activating and mobilizing TAMs from the bone marrow to the site of inflammation in the TME [88]. Targeting CCL2-CCR2 might be a feasible immune intervention for lymphoma treatment. A study showed that CREBBP/EP300 mutation in DLBCL patients had higher CCL2 expression, and tumor progression was induced by TAMs throughout the FBXW7-NOTCH-CCL2/CSF1 axis [88]. Accordingly, CCR2 antagonist decreased tumor growth and dissemination of DLBCL cells, and increased survival in xenograft models [89]. Another study showed that the combination of CCR2 and immune checkpoint inhibitors reduces tumor growth in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas [90]. Lastly, microRNAs (miRNA) are secreted from tumor cells and could induce the recruitment and reprogramming of TAMs [91]. Recent studies have shown that overexpression of specific miRNAs (e.g., miR-33, miR-130, and miR-155) decreases tumor progression by shifting TAM from M2 to M1 phenotype [92, 93].
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) are a heterogeneous group of immature myeloid cells (IMC) which is pathologically activated in many conditions, including autoimmunity, infectious diseases, obesity, and pregnancy [94]. In physiological conditions, IMCs differentiate into mature monocytes, dendritic cells, and granulocytes, however the differentiation and maturation of IMCs are blocked in a pathological environment, which leads to the expansion of MDSCs (Fig. 4) [95]. MDSCs are further divided into two major subsets: polymorphonuclear (PMN)-MDSCs and monocytic (M)-MDSCs. They can be differentiated from their normal counterparts by high arginase-1 (Arg-1) and nitric oxide synthase-2 (NOS-2) expression, and high and persistent level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [94]. Also, PMN-MDSCs can be distinguished from neutrophils by their unique genomic profile [94], while M-MDSCs are different from TAMs based on their phenotype characterized by increased expression of F4/80 and M-CSF receptor, low expression of IRF8, low to intermediate expression of Ly6C and low or undetectable expression of S100A9 protein [94, 96]. MDSCs were shown to be higher at the time of diagnosis in Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients, especially in those with aggressive disease, compared to healthy control [97, 98]. Upregulated expression of MDSCs-related genes (e.g. ARG1, S100A12, and S100A8) was associated with inferior event-free survival compared to patients with low expression of these genes [99, 100]. Endoplasmic reticulum stress is the main regulator of the activation and suppressive function of MDSCs by promoting the expression of Arg-1 and NOS-2 [95]. Also, exosomes released by cancer cells accelerate the activation, expansion, and immunosuppression of MDSCs by transporting functional substances, such as miRNA, TGF- β, and PGE2 [95, 101].
Fig. 4.
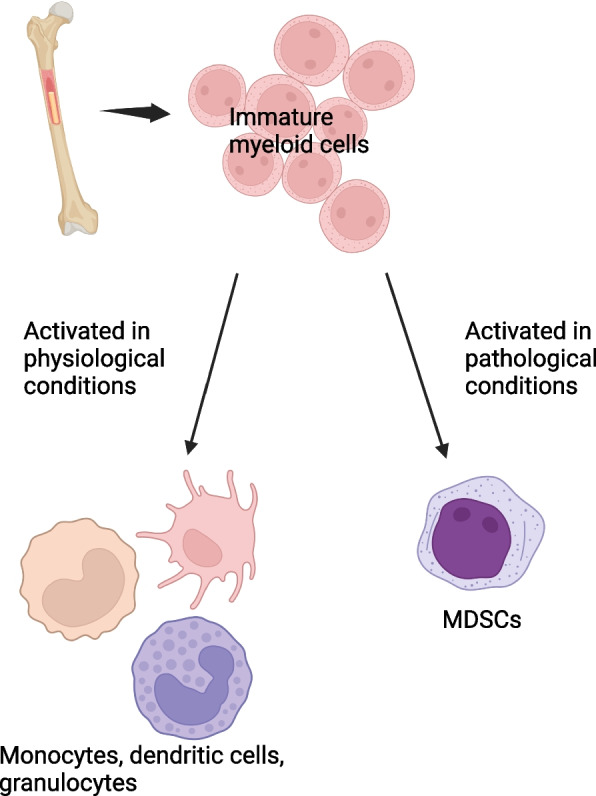
Myeloid differentiation in physiologic and pathologic conditions
Promising therapeutic strategies are reducing MDSCs accumulation in the TME as well as inducing functional repolarization of these cells. However, a complete deletion of myeloid cells would not be feasible as it may cause severe adverse effects, such as bacterial infections. An example of such a strategy is phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors (e.g. sildenafil) which reduce the immunosuppressive effect of MDSCs and enhance intratumoral T cell infiltration and activation through downregulation of Arg-1 and NOS-2 [102]. Antagomir, an antagonist of miR-30, showed to reduce MDSCs in B-cell lymphoma [103]. Histamine dihydrochloride (HDC) with IL-2 reduced MDSCs, but this anti-tumor mechanism is insufficiently understood [104]. The PI3Kδ/γ inhibitor RP6530 led to a significant inhibition of MDSCs and repolarized TAMs from M2 to M1-like phenotype in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) in vitro and in vivo [105]. In the future, targeting MDSCs may be a crucial point to improve the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy since it has been shown that MDSCs could inhibit CAR-T cell activation [106, 107].
Cancer-associated fibroblasts
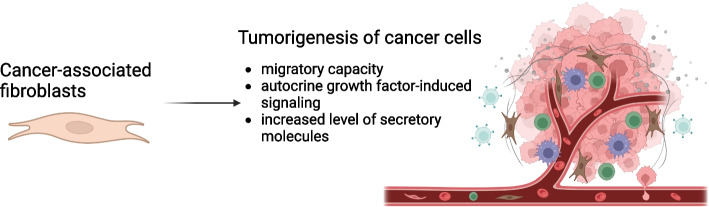
Fibroblasts are resting mesenchymal cells in the connective tissue, which become activated during wound healing by growth factors, such as TGF-β, platelet derived growth factor (PDGF) and IL-6 [108]. Once activated, fibroblasts generate cytokines and chemokines, recruit immune cells, and synthesize an extracellular matrix (ECM). However, normal activated fibroblasts are different from cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). CAFs exhibit enhanced migratory capacity, autocrine growth factor-induced signaling and increased levels of secretory molecules that enhance tumorigenesis (Fig. 5) [108]. This process might be a consequence of epigenetic changes promoting CAFs activation. Among the different molecular regulators released by CAFs, the CAF-derived stromal cell-derived factor 1 promotes tumor growth by inducing angiogenesis via the recruitment of endothelial progenitor cells into tumors [109]. CAFs also produce abundant VEGF, PDGFC, FGF2, osteopontin and secreted frizzled-related protein 2 to exacerbate the angiogenesis of neoplastic tissues [110]. Heat shock factor 1 (HSF1) may cause HSF1-driven pro-tumorigenic program in cancer cells [111]. Yes-associated protein 1 enhances stiffening of ECM, angiogenesis, and cancer cell invasion [112]. In general, CAFs promote an immune suppressive TME. The cytokines or chemokines secreted by CAFs may have direct or indirect implications for tumor immunity [110]. It is uncertain if CAFs are associated with immunosuppressive populations of B cells due to poorly defined markers for such cells [113]. Production of IL-4, IL-6, and IL-8 may induce immunosuppressive myeloid cell differentiation, while CXCL14 affects macrophages recruitment to the tumor. Additionally, CAFs modulate immunity through their acquisition of adhesion molecules (e.g., ICAM1), which serve as a docking platform for the immune cells [114].
Fig. 5.
Functions of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs)
Lymphoma B cells can trigger mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) differentiation into fibroblast reticular cells. Pandey et al. reported that stromal cells of FL-infiltrating lymph nodes and bone marrow overexpressed CXCL12, while IL-4-high FL-Tfh cells triggered CXCL12 upregulation [115], which further promotes FL B cell activation, migration and adhesion [115]. IL-8 promotes neutrophil survival, causing activation of stromal cells and promotion of malignant B-cell survival [116]. CCL2 is overexpressed by MSCs from FL bone marrow in comparison with those from healthy age-matched donors (HD-MSCs), and it is up-regulated in HD-MSCs after coculture with malignant B cells [117]. DLBCL stromal-1 gene signature is enriched in CAFs and its expression is inversely associated with DLBCL tumor stage. Thus, CAFs are hypothesized to aid in trapping malignant B cells in the lymph node preventing their spread to new anatomical locations. Among all the gene regulators, TGF-β is the main upstream regulator of the DLBCL stromal-1 gene signature [118]. TGF-β has been shown to cause apoptosis in mouse models of B cell lymphoma [119]. Although TGF-β could promote an immunosuppressive environment, it is also a potent negative regulator of B-cell survival, proliferation, activation, and differentiation [120].
Targeting CAFs could be a challenging task due to the lack of specific cell surface markers causing difficulty to precisely target CAFs without damaging the normal tissue. However, there are a few general approaches targeting CAFs: 1) targeting the chemokine and growth factor pathways to inhibit the activation of CAFs, 2) normalization of CAFs via all-transretinoic acid or calcipotriol, 3) depletion of CAFs by transgenic technologies or immunotherapies, 4) targeting CAF-derived ECM proteins and associated signaling to induce stromal depletion, 5) cellular therapies (such as oncolytic adenoviruses, TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand or type I interferon) [110].
Tumor-infiltrating natural killer cells
Natural killer (NK) cells are innate cytotoxic lymphocytes of the immune system, contributing to the prevention of infection and tumor growth [121]. NK cells can be divided into two subtypes: CD56dim CD16+ NK cells (a mature cytotoxic population) and CD56bright CD16- NK cells (an immature and mostly immunomodulatory population) [121]. For both populations the most important cell surface inhibitory receptors are i) the members’ killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) family and ii) the CD94/NKG2A heterodimer [122, 123]. In physiologic conditions, normal cells are spared by the NK cells due to the recognition of MHC Class I engaged with KIRs. By contrast, lack of “self-recognition” signals to the NK cells to attack abnormal cells, such as tumor cells which present downregulated antigen presentation molecules as immune evasion strategy (Fig. 6) [124].
Fig. 6.
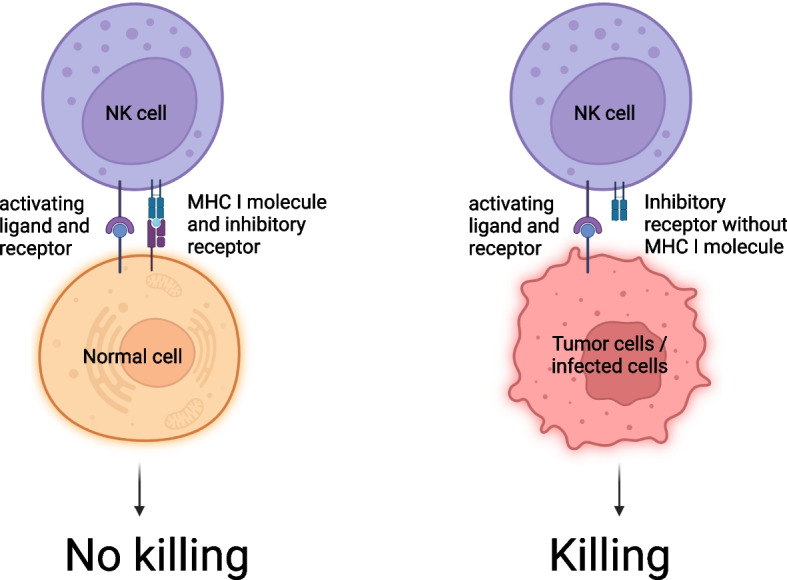
Role of natural killer (NK) cells in physiologic and pathologic conditions
The role of NK cells in tumor immunosurveillance is well established [125, 126]. Importantly, NK cells seem to prevent development of tumors including B cell lymphoma [127, 128]. Recent evidence has shown that tumor infiltrating NK cells unleashed cytotoxic T cells, ultimately resulting in tumor eradication [129]. In line with the role of NK cells in suppressing malignancies, several studies have demonstrated a survival advantage of tumor infiltration by NK cells [129–133]. Even though a direct correlation may be less clear due to the frequent co-expression of T cells, these studies support a critical role of NK cells in promoting antitumor immune response. Tumor immune escape includes mechanisms that prevent NK cell activation or recruitment. For examples, suppressive cytokines (e.g. TGF- β) [134, 135] and prostaglandin [136, 137] clearly suppress NK cell activation. TGF- β also induces differentiation of Treg cells, which in turn suppress NK cells [138, 139]. Additional escape mechanisms include engagement of inhibitory receptors. Besides expressing NK-cell inhibitory receptors, NK cells also express other immune checkpoint molecules (e.g., PD1, TIM3, TIGIT, SIRP α) [140–144]. For example, increased expression of PD1 on NK cells was observed in several tumors [145–148], including HL and DLBCL [148]. By contrast, the inhibitory ligand PDL1 was found on tumor cells and macrophages, thus favoring the PD1/PDL1 interaction which limits the anti-tumor effect of NK cells. Recent studies have shown that PD1 blockades disrupt the suppressive PD1/PDL1 axis, reactivating NK cells with clinical implication [148]. Blockade of other immune checkpoint molecules has also shown encouraging potential for NK cell-based immunotherapy [124]. TIGIT was associated with NK cell exhaustion. On the contrary, TIGIT blockade antibodies restored anti-tumor activity [149]. Monalizumab, a humanized antibody against NKG2A, unleashes NK and T cells, thus promoting an enhanced tumor immunity [150]. STING agonists, such as cyclic dinucleotides, enhance NK cell fitness and anti-tumor effect [130, 151]. Another approach to amplify NK cell function against tumor is using “NK cell engagers”: bi- or tri-specific antibodies that bind NK and tumor cells [152, 153]. Furthermore, FDA has recently approved the first NK cell-based immunotherapy, NK-92, for clinical testing [154, 155]. Of note, NK cells provide a safer chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineering platform compared to T cells [156]. Additionally, since they lack most of the KIRs, CAR-NK cells are less likely to become exhausted [157]. Several ongoing efforts have attempted to further potentiate and prolong NK-CAR potency by combining checkpoint inhibitor, cytokines and co-stimulatory signaling [157]. However, this promising off-the-shelf approach needs additional improvements to maximize its therapeutic efficacy.
Innate lymphoid cells
Innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) belong to the adaptive immune system and have a similar phenotype and function of T cells but differ from them for the lack of antigen receptors and clonal selection and expansion after stimulation [158]. ILCs are relatively rare (≤ 1% lymphocytes in mucosal tissues) [159] and can be distinguished in three main subsets: 1) type 1 ILCs include ILC1s and conventional NK cells [160, 161], express Tbx21, produce IFN-γ, and contribute to anti-viral and Th1 immunity [162]; 2) type 2 ILCs express Gata3, ROR α, TCF1 and Notch [163, 164], produce Th2 cell-associated cytokines (IL-4, IL-5, IL-9 and IL-13), and contribute to respond to Helminths infections and allergic diseases [165]; 3) type 3 ILCs express ROR γ t, present a different expression of T-bet [161, 166–168], produce IL-17A and IL-22, and participate in the homeostasis and mucosal defense and preservation of memory CD4 T cells [164, 169]. Notably, ILCs have a remarkable plasticity that allows them to acquire features of another ILCs subtype as required by changes in the TME. For examples, NK cells can switch to ILC1-like cells upon increase of TGF- β [135]. The existence of a continuous conversion from NK cells to ILC1s and vice versa is also plausible [170, 171]. Similarly, IL-12 has been shown to induce differentiation of ILC2s into ILC1 [172, 173] and ILC3s into ILC1s [173, 174]. ILCs also regulate tumor surveillance through a dynamic crosstalk with different immune components of the TME. Among ILCs, NK cells are the most active population as previously described. ILC2s can suppress immune response against tumor through IL-13-mediated enhancement of MDSCs expansion [174], alternatively they favor anti-tumor immunity through IL-5-mediated cooperation with DCs [175, 176]. ILC2s may potentiate the suppressive function of Treg through release of the growth factor AREG [177], or limit T cell activation through production of Arg1 [178]. ILC3s favor chronic inflammation, which in turn may promote tumor initiation [179, 180]. A group of ILC3s produce IL-17 and IL-22 [181, 182], which have been associated with poor prognosis in cancer patients [183, 184]. Collectively, these studies support the interplay between ILCs and the immune cells of the TME, which influence both innate and adaptive immune response against tumor. Future studies may be directed to investigating strategy blocking ILCs-myeloid or ILCs-Treg axes as a promising therapeutic strategy.
Lymphomas of the immune-privileged sites
The lymphomas of the immune-privileged sites include those arising from the central nervous system (PCNSL) and testes (PTL) [185]. Unlike other lymphomas, PCNSL and PTL are invisible to the immune system and have a suppression of anti-tumor T-cell response. Typically, they are localized diseases at presentation, even though they may be disseminated within the compartment (CNS-CNS, testis-testis) and between the compartments (CNS to testis) but rarely systemically, and have a poor prognosis [186, 187]. Constitutive activation of NF-kB via BCR (e.g. CD79B mutation) and toll-like receptor (e.g. MYD88 L265P mutation) is the canonical oncogenic pathway [188–190]. They share genetic features with classical ABC-DLBCL as well as with the recently defined molecular clusters MCD and C5 [4, 5]. However, the precise relationship between these classes remains to be elucidated. They present a high prevalence of genetic mutations causing loss of MHC class I and II expression [189, 191, 192]. Additionally, structural alterations at 9p24.1, which is the PD-L1 and PD-L2 locus, increase the abundance of transcriptional and translational expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2, further reinforcing immune evasion [189]. The predominant immune components of TME in these diseases are CD8+ cytotoxic T cells with a direct correlation between their number and outcome. Macrophages are also frequently identified, being an increased M1/M2 ratio associated with a better survival. Of note, PD1 and TIM3 appear to be concomitantly upregulated in CD8+ cytotoxic T cells and M2 macrophages with prognostic implications [193, 194]. However, further investigation is required to uncover the immune landscape of these diseases. The specific features of the lymphomas of the immune-privileged sites impact on treatment option. Especially, NF-kB/BTK inhibition has shown promise, with ibrutinib-based therapy being at the forefront of clinical investigation [195–197]. Additionally, checkpoint inhibition (e.g. nivolumab/pembrolizumab) has had an emerging role in the therapeutic armory [198].
Conclusion
The crosstalk between malignant B cells and immune cells in the lymphoma TME is highly complicated and might be affected by often interconnected intrinsic and/or extrinsic mechanisms which ultimately can lead to immune escape. This notion suggests the need to adopt a more comprehensive therapeutic strategy that does not limit its focus to tumor cells but that considers a global approach including the TME. Targeting the TME has long been considered a promising strategy, but much more work is needed to identify novel prognostic and predictive targets. Stratification of the patients for precision medicine as well as monitoring of immune response remain unmet clinical needs. Several advancements have been made towards this direction, such as the recent development of liquid biopsy that monitors circulating tumor DNA and immune components [199] or immune-imaging tools [200–202] to assess the efficacy of immunotherapy. The horizon of B cell lymphoma allows for a glimpse of a therapeutic strategy that considers the tumor in its whole, and maybe such an approach might be able to overcome the current clinical hurdles and rescue the still high therapeutic failures.
Abbreviations
- GC
Germinal center
- GEP
Gene expression profiling
- DLBCL
Diffuse large B cell lymphoma
- COO
Cell of origin
- ABC
Activated B cell
- GCB
Germinal center B cell
- WES
Whole exome sequencing
- FL
Follicular lymphoma
- Tfh
T follicular helper
- BCL6
B cell lymphoma 6
- Tfr
T follicular regulatory
- IMiDs
Immunomodulatory drugs
- TAMs
Tumor-associated macrophages
- PFS
Progression free survival
- CSF1R
Colony-stimulating factor-1 receptor
- miRNA
microRNAs
- MDSCs
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells
- IMC
Immature myeloid cells
- PMN
Polymorphonuclear
- Arg-1
Arginase-1
- NOS-2
Nitric oxide synthase-2
- PDGF
Platelet derived growth factor
- ECM
Extracellular matrix
- CAFs
Cancer-associated fibroblasts
- HSF1
Heat shock factor 1
- HD-MSCs
Healthy age-matched donors
- HL
Hodgkin lymphoma
- NK
Natural killer
- CAR
Chimeric antigen receptor
- ILC
Innate lymphoid cells
- PCNSL
Primary central nervous system lymphoma
- PTL
Primary testis lymphoma
- BCR
B cell receptor
Authors’ contributions
WLN and PM reviewed the literature, designed, and wrote the manuscript; SMA revised the paper. All the authors approved it.
Funding
This article did not receive any specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sector.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant affiliation or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript. No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Mesin L, Ersching J, Victora GD. Germinal center B cell dynamics. Immunity. 2016;45:471–482. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Basso K, Dalla-Favera R. Germinal centres and B cell lymphomagenesis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15:172–184. doi: 10.1038/nri3814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Alizadeh AA, Eisen MB, Davis RE, Ma C, Lossos IS, Rosenwald A, et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature. 2000;403:503–511. doi: 10.1038/35000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chapuy B, Stewart C, Dunford AJ, Kim J, Kamburov A, Redd RA, et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat Med. 2018;24:679–690. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0016-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Schmitz R, Wright GW, Huang DW, Johnson CA, Phelan JD, Wang JQ, et al. Genetics and pathogenesis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:1396–1407. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1801445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dave SS, Wright G, Tan B, Rosenwald A, Gascoyne RD, Chan WC, et al. Prediction of survival in follicular lymphoma based on molecular features of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:2159–2169. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa041869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mondello P, Fama A, Larson MC, Feldman AL, Villasboas JC, Yang ZZ, et al. Lack of intrafollicular memory CD4 + T cells is predictive of early clinical failure in newly diagnosed follicular lymphoma. Blood Cancer J. 2021;11:130. doi: 10.1038/s41408-021-00521-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kotlov N, Bagaev A, Revuelta MV, Phillip JM, Cacciapuoti MT, Antysheva Z, et al. Clinical and biological subtypes of B-cell lymphoma revealed by microenvironmental signatures. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:1468–1489. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Steen CB, Luca BA, Esfahani MS, Azizi A, Sworder BJ, Nabet BY, et al. The landscape of tumor cell states and ecosystems in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2021;39(10):1422–1437. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.08.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Mondello P, Tadros S, Teater M, Fontan L, Chang AY, Jain N, et al. Selective inhibition of HDAC3 targets synthetic vulnerabilities and activates immune surveillance in lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2020;10:440–459. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-19-0116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Meyer SN, Scuoppo C, Vlasevska S, Bal E, Holmes AB, Holloman M, et al. Unique and shared epigenetic programs of the CREBBP and EP300 acetyltransferases in germinal center B cells reveal targetable dependencies in lymphoma. Immunity Cell Press. 2019;51:535–547.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.08.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ennishi D, Takata K, Béguelin W, Duns G, Mottok A, Farinha P, et al. Molecular and genetic characterization of MHC deficiency identifies ezh2 as therapeutic target for enhancing immune recognition. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:546–563. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-18-1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mondello P, Ansell SM, Nowakowski GS. Immune epigenetic crosstalk between malignant B cells and the tumor microenvironment in B cell lymphoma. Front Genet. 2022;13:826594. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.826594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mondello P, Ansell SM. PHOENIX rises: genomic-based therapies for diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2021;39:1570–1572. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.10.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Crotty S. T follicular helper cell differentiation, function, and roles in disease. Immunity. 2014;41:529–542. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jacobsen JT, Hu W, Castro TBR, Solem S, Galante A, Lin Z, et al. Expression of Foxp3 by T follicular helper cells in end-stage germinal centers. Science. 2021;373:eabe5146. doi: 10.1126/science.abe5146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhou DM, Xu YX, Zhang LY, Sun Y, Wang ZY, Yuan YQ, et al. The role of follicular T helper cells in patients with malignant lymphoid disease. Hematology. 2017;22:412–418. doi: 10.1080/10245332.2017.1300623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cha Z, Gu H, Zang Y, Wang Z, Li J, Huang W, et al. The prevalence and function of CD4+CXCR5+Foxp3+ follicular regulatory T cells in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;61:132–139. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.05.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mintz MA, Cyster JG. T follicular helper cells in germinal center B cell selection and lymphomagenesis. Immunol Rev. 2020;296:48–61. doi: 10.1111/imr.12860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Travert M, Ame-Thomas P, Pangault C, Morizot A, Micheau O, Semana G, et al. CD40 ligand protects from TRAIL-induced apoptosis in follicular lymphomas through NF-κB activation and up-regulation of c-FLIP and Bcl-xL. J Immunol. 2008;181:1001–1011. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.2.1001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Brady MT, Hilchey SP, Hyrien O, Spence SA, Bernstein SH. Mesenchymal stromal cells support the viability and differentiation of follicular lymphoma-infiltrating follicular helper T-cells. PLoS One. 2014;9:e97597. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Calvo KR, Dabir B, Kovach A, Devor C, Bandle R, Bond A, et al. IL-4 protein expression and basal activation of Erk in vivo in follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2008;112:3818–3826. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-02-138933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rawal S, Chu F, Zhang M, Park HJ, Nattamai D, Kannan S, et al. Cross talk between follicular Th cells and tumor cells in human follicular lymphoma promotes immune evasion in the tumor microenvironment. J Immunol. 2013;190:6681–6693. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1201363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Pangault C, Amé-Thomas P, Ruminy P, Rossille D, Caron G, Baia M, et al. Follicular lymphoma cell niche: identification of a preeminent IL-4-dependent T(FH)-B cell axis. Leukemia. 2010;24:2080–2089. doi: 10.1038/leu.2010.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ma X, Zha J, He J, Chen L, Huang J, Wu W, et al. T follicular helper cell-mediated IL-21 production suppresses FOXP3 expression of T follicular regulatory-like cells in diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients. Hum Immunol. 2020;81:452–459. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2020.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Han G, Deng Q, Marques-Piubelli ML, Dai E, Dang M, Ma MCJ, et al. Follicular lymphoma microenvironment characteristics associated with tumor cell mutations and MHC class II expression. Blood Cancer Discov. 2022;3:428–443. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-21-0075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chaudhry A, Rudensky AY. Control of inflammation by integration of environmental cues by regulatory T cells. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:939–944. doi: 10.1172/JCI57175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:986–992. doi: 10.1038/ni904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Josefowicz SZ, Lu LF, Rudensky AY. Regulatory T cells: mechanisms of differentiation and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012;30:531–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.25.022106.141623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Facciabene A, Motz GT, Coukos G. T-regulatory cells: key players in tumor immune escape and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2012;72:2162–2171. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yang ZZ, Novak AJ, Stenson MJ, Witzig TE, Ansell SM. Intratumoral CD4+CD25+ regulatory T-cell-mediated suppression of infiltrating CD4+ T cells in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2006;107:3639–3646. doi: 10.1182/blood-2005-08-3376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Carreras J, Lopez-Guillermo A, Fox BC, Colomo L, Martinez A, Roncador G, et al. High numbers of tumor-infiltrating FOXP3-positive regulatory T cells are associated with improved overall survival in follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2006;108:2957–2964. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-018218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wahlin BE, Aggarwal M, Montes-Moreno S, Gonzalez LF, Roncador G, Sanchez-Verde L, et al. A unifying microenvironment model in follicular lymphoma: outcome is predicted by programmed death-1-positive, regulatory, cytotoxic, and helper T cells and macrophages. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:637–650. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tzankov A, Meier C, Hirschmann P, Went P, Pileri SA, Dirnhofer S. Correlation of high numbers of intratumoral FOXP3+ regulatory T cells with improved survival in germinal center-like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, follicular lymphoma and classical Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Haematologica. 2008;93:193–200. doi: 10.3324/haematol.11702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lee NR, Song EK, Jang KY, Choi HN, Moon WS, Kwon K, et al. Prognostic impact of tumor infiltrating FOXP3 positive regulatory T cells in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma at diagnosis. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008;49:247–256. doi: 10.1080/10428190701824536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yang ZZ, Novak AJ, Ziesmer SC, Witzig TE, Ansell SM. Attenuation of CD8+ T-cell function by CD4+CD25 + regulatory T cells in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2006;66:10145–10152. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Nakayama S, Yokote T, Akioka T, Hiraoka N, Nishiwaki U, Miyoshi T, et al. Infiltration of effector regulatory T cells predicts poor prognosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified. Blood Adv. 2017;1:486–493. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2016000885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Yang ZZ, Kim HJ, Wu H, Jalali S, Tang X, Krull JE, et al. TIGIT expression is associated with T-cell suppression and exhaustion and predicts clinical outcome and anti-PD-1 response in follicular lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26:5217–5231. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-0558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Tang X, Yang Z-Z, Kim HJ, Anagnostou T, Yu Y, Wu X, et al. Phenotype, function, and clinical significance of CD26+ and CD161+Tregs in splenic marginal zone lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2022;28:4322–4335. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-0977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Profitós-Pelejà N, Santos JC, Marín-Niebla A, Roué G, Ribeiro ML. Regulation of B-cell receptor signaling and its therapeutic relevance in aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Cancers (Basel) 2022;14:860. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ramsay AG, Clear AJ, Kelly G, Fatah R, Matthews J, MacDougall F, et al. Follicular lymphoma cells induce T-cell immunologic synapse dysfunction that can be repaired with lenalidomide: implications for the tumor microenvironment and immunotherapy. Blood. 2009;114:4713–4720. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-04-217687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pandiyan P, Younes SA, Ribeiro SP, Talla A, McDonald D, Bhaskaran N, et al. Mucosal regulatory T cells and T helper 17 cells in HIV-associated immune activation. Front Immunol. 2016;7:228. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Grygorowicz MA, Borycka IS, Nowak E, Paszkiewicz-Kozik E, Rymkiewicz G, Błachnio K, et al. Lenalidomide potentiates CD4+CD25+Treg-related suppression of lymphoma B-cell proliferation. Clin Exp Med. 2017;17:193–207. doi: 10.1007/s10238-016-0411-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tarantelli C, Argnani L, Zinzani PL, Bertoni F. PI3Kδ Inhibitors as Immunomodulatory Agents for the Treatment of Lymphoma Patients. Cancers (Basel) 2021;13:5535. doi: 10.3390/cancers13215535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Carnevalli LS, Sinclair C, Taylor MA, Gutierrez PM, Langdon S, Coenen-Stass AML, et al. PI3Kα/δ inhibition promotes anti-tumor immunity through direct enhancement of effector CD8+ T-cell activity 11 medical and health sciences 1107 immunology. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6:1–14. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0457-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Jin H, Zhou Y, Wang L. The mechanism of rapamycin in promoting asthmatic regulatory T cell differentiation and function. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2021;50:621–626. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2021-0173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Fife BT, Bluestone JA. Control of peripheral T-cell tolerance and autoimmunity via the CTLA-4 and PD-1 pathways. Immunol Rev. 2008;224:166–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00662.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Larson RC, Maus M, v. Recent advances and discoveries in the mechanisms and functions of CAR T cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2021;21:145–161. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-00323-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bejarano L, Jordāo MJC, Joyce JA. Therapeutic targeting of the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:933–959. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sobhani N, Tardiel-Cyril DR, Davtyan A, Generali D, Roudi R, Li Y. CTLA-4 in regulatory T cells for cancer immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel) 2021;13:1440. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Tuscano JM, Maverakis E, Groshen S, Tsao-Wei D, Luxardi G, Merleev AA, et al. A phase I study of the combination of rituximab and ipilimumab in patients with relapsed/ refractory B-cell lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:7004–7013. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wei SC, Levine JH, Cogdill AP, Zhao Y, Anang NAAS, Andrews MC, et al. Distinct cellular mechanisms underlie anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 checkpoint blockade. Cell. 2017;170:1120–1133. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.07.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Gong J, Chehrazi-Raffle A, Reddi S, Salgia R. Development of PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors as a form of cancer immunotherapy: a comprehensive review of registration trials and future considerations. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6:8. doi: 10.1186/s40425-018-0316-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Huang RY, Francois A, McGray AR, Miliotto A, Odunsi K. Compensatory upregulation of PD-1, LAG-3, and CTLA-4 limits the efficacy of single-agent checkpoint blockade in metastatic ovarian cancer. Oncoimmunology. 2017;6:e1249561. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1249561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Huang RY, Eppolito C, Lele S, Shrikant P, Matsuzaki J, Odunsi K. LAG3 and PD1 co-inhibitory molecules collaborate to limit CD8+ T cell signaling and dampen antitumor immunity in a murine ovarian cancer model. Oncotarget. 2015;6:27359–27377. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ansell SM, Hurvitz SA, Koenig PA, LaPlant BR, Kabat BF, Fernando D, et al. Phase I study of ipilimumab, an anti-CTLA-4 monoclonal antibody, in patients with relapsed and refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15:6446–6453. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zhu C, Anderson AC, Schubart A, Xiong H, Imitola J, Khoury SJ, et al. The Tim-3 ligand galectin-9 negatively regulates T helper type 1 immunity. Nat Immunol. 2005;6:1245–1253. doi: 10.1038/ni1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kang CW, Dutta A, Chang LY, Mahalingam J, Lin YC, Chiang JM, et al. Apoptosis of tumor infiltrating effector TIM-3+CD8+ T cells in colon cancer. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15659. doi: 10.1038/srep15659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Hahn AW, Gill DM, Pal SK, Agarwal N. The future of immune checkpoint cancer therapy after PD-1 and CTLA-4. Immunotherapy. 2017;9:681–692. doi: 10.2217/imt-2017-0024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yu X, Harden K, Gonzalez LC, Francesco M, Chiang E, Irving B, et al. The surface protein TIGIT suppresses T cell activation by promoting the generation of mature immunoregulatory dendritic cells. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:48–57. doi: 10.1038/ni.1674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Johnston RJ, Comps-Agrar L, Hackney J, Yu X, Huseni M, Yang Y, et al. The Immunoreceptor TIGIT regulates antitumor and antiviral CD8+ T cell effector function. Cancer Cell. 2014;26:923–937. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2014.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Harjunpää H, Guillerey C. TIGIT as an emerging immune checkpoint. Clin Exp Immunol. 2020;200:108–119. doi: 10.1111/cei.13407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Kaech SM, Ahmed R. Memory CD8+ T cell differentiation: initial antigen encounter triggers a developmental program in naïve cells. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:415–422. doi: 10.1038/87720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Youngblood B, Hale JS, Kissick HT, Ahn E, Xu X, Wieland A, et al. Effector CD8 T cells dedifferentiate into long-lived memory cells. Nature. 2017;552:404–409. doi: 10.1038/nature25144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Collier JL, Weiss SA, Pauken KE, Sen DR, Sharpe AH. Not-so-opposite ends of the spectrum: CD8+ T cell dysfunction across chronic infection, cancer and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol. 2021;22:809–819. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00949-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Strioga M, Pasukoniene V, Characiejus D. CD8+ CD28- and CD8+ CD57+ T cells and their role in health and disease. Immunology. 2011;134:17–32. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2011.03470.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Alotaibi F, Vincent M, Min WP, Koropatnick J. Reduced CD5 on CD8+ T cells in tumors but not lymphoid organs is associated with increased activation and effector function. Front Immunol. 2021;11:584937. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.584937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Blank CU, Haining WN, Held W, Hogan PG, Kallies A, Lugli E, et al. Defining ‘T cell exhaustion’. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19:665–674. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0221-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Wahlin BE, Sander B, Christensson B, Kimby E. CD8+ T-cell content in diagnostic lymph nodes measured by flow cytometry is a predictor of survival in follicular lymphoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:338–397. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-1734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Alvaro T, Lejeune M, Salvadó M-T, Lopez C, Jaén J, Bosch R, et al. Immunohistochemical patterns of reactive microenvironment are associated with clinicobiologic behavior in follicular lymphoma patients. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:5350–5357. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.06.4766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Carreras J, Lopez-Guillermo A, Roncador G, Villamor N, Colomo L, Martinez A, et al. High numbers of tumor-infiltrating programmed cell death 1-positive regulatory lymphocytes are associated with improved overall survival in follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1470–1476. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.0513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Yang ZZ, Kim HJ, Villasboas JC, Chen YP, Price-Troska TP, Jalali S, et al. Expression of LAG-3 defines exhaustion of intratumoral PD-1 + T cells and correlates with poor outcome in follicular lymphoma. Oncotarget. 2017;8:61425–61439. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.18251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Grosso JF, Kelleher CC, Harris TJ, Maris CH, Hipkiss EL, de Marzo A, et al. LAG-3 regulates CD8+ T cell accumulation and effector function in murine self- and tumor-tolerance systems. J Clin Investig. 2007;117:3383–3392. doi: 10.1172/JCI31184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Pathria P, Louis TL, Varner JA. Targeting tumor-associated macrophages in Cancer. Trends Immunol. 2019;40:310–327. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2019.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Lin Y, Xu J, Lan H. Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor metastasis: biological roles and clinical therapeutic applications. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:76. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0760-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Taskinen M, Karjalainen-Lindsberg M-L, Nyman H, Eerola L-M, Leppä S. A high tumor-associated macrophage content predicts favorable outcome in follicular lymphoma patients treated with rituximab and cyclophosphamide-doxorubicin-vincristine-prednisone. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:5784–5789. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Steidl C, Lee T, Shah SP, Farinha P, Han G, Nayar T, et al. Tumor-associated macrophages and survival in classic Hodgkin’s lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:875–885. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0905680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Clear AJ, Lee AM, Calaminici M, Ramsay AG, Morris KJ, Hallam S, et al. Increased angiogenic sprouting in poor prognosis FL is associated with elevated numbers of CD163+ macrophages within the immediate sprouting microenvironment. Blood. 2010;115:5053–5056. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-11-253260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Shen L, Li H, Shi Y, Wang D, Gong J, Xun J, et al. M2 tumour-associated macrophages contribute to tumour progression via legumain remodelling the extracellular matrix in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30347. doi: 10.1038/srep30347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Wu K, Lin K, Li X, Yuan X, Xu P, Ni P, et al. Redefining tumor-associated macrophage subpopulations and functions in the tumor microenvironment. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1731. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Petty AJ, Yang Y. Tumor-associated macrophages in hematologic malignancies: new insights and targeted therapies. Cells. 2019;8:1526. doi: 10.3390/cells8121526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Papin A, Tessoulin B, Bellanger C, Moreau A, le Bris Y, Maisonneuve H, et al. CSF1R and BTK inhibitions as novel strategies to disrupt the dialog between mantle cell lymphoma and macrophages. Leukemia. 2019;33(2442):2453. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0463-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Valero JG, Matas-Céspedes A, Arenas F, Rodriguez V, Carreras J, Serrat N, et al. The receptor of the colony-stimulating factor-1 (CSF-1R) is a novel prognostic factor and therapeutic target in follicular lymphoma. Leukemia. 2021;35:2635–2649. doi: 10.1038/s41375-021-01201-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.DeNardo DG, Ruffell B. Macrophages as regulators of tumour immunity and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2019;19:369–382. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0127-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Chao MP, Alizadeh AA, Tang C, Myklebust JH, Varghese B, Gill S, et al. Anti-CD47 antibody synergizes with rituximab to promote phagocytosis and eradicate non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cell. 2010;142:699–713. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Eladl E, Tremblay-Lemay R, Rastgoo N, Musani R, Chen W, Liu A, et al. Role of CD47 in hematological malignancies. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:96. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00930-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Chao MP, Tang C, Pachynski RK, Chin R, Majeti R, Weissman IL. Extranodal dissemination of non-Hodgkin lymphoma requires CD47 and is inhibited by anti-CD47 antibody therapy. Blood. 2011;118:4890–4901. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-338020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Huang YH, Cai K, Xu PP, Wang L, Huang CX, Fang Y, et al. CREBBP/EP300 mutations promoted tumor progression in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma through altering tumor-associated macrophage polarization via FBXW7-NOTCH-CCL2/CSF1 axis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6:10. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00437-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Yan-Li L, Hu Q-Q, Wen Z-F, Li Q, Zhai Z-M. CCR2 expression promotes diffuse large B lymphoma cell survival and invasion. Lab Investig. Lab Invest. 2022;102:1377–88. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35851856/. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 90.Wu X, Singh R, Hsu DK, Zhou Y, Yu S, Han D, et al. A small molecule CCR2 antagonist depletes tumor macrophages and synergizes with anti–PD-1 in a murine model of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL) J Investig Dermatol. 2020;140:1390–1400. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2019.11.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ludwig N, Rubenich DS, Zaręba Ł, Siewiera J, Pieper J, Braganhol E, et al. Potential roles of tumor cell-and stroma cell-derived small extracellular vesicles in promoting a pro-angiogenic tumor microenvironment. Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:3599. doi: 10.3390/cancers12123599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Poles WA, Nishi EE, de Oliveira MB, Eugênio AIP, de Andrade TA, Campos AHFM, et al. Targeting the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages and modulating mir-155 expression might be a new approach to treat diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019;68:269–282. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-2273-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Moradi-Chaleshtori M, Bandehpour M, Soudi S, Mohammadi-Yeganeh S, Hashemi SM. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of anti-tumoral effect of M1 phenotype induction in macrophages by miR-130 and miR-33 containing exosomes. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2021;70:1323–1339. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02762-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Gabrilovich DI, Bronte V, Chen SH, Colombo MP, Ochoa A, Ostrand-Rosenberg S, et al. The terminology issue for myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Res. 2007;67:425. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Tian X, Shen H, Li Z, Wang T, Wang S. Tumor-derived exosomes, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, and tumor microenvironment. J Hematol Oncol. 2019;12:84. doi: 10.1186/s13045-019-0772-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Kumar V, Patel S, Tcyganov E, Gabrilovich DI. The nature of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 2016;37:208–220. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2016.01.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Romano A, Parrinello NL, Vetro C, Forte S, Chiarenza A, Figuera A, et al. Circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells correlate with clinical outcome in Hodgkin lymphoma patients treated up-front with a risk-adapted strategy. Br J Haematol. 2015;168:689–700. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Marini O, Spina C, Mimiola E, Cassaro A, Malerba G, Todeschini G, et al. Identification of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (G-MDSCs) in the peripheral blood of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients. Oncotarget. 2016;7:27676–27688. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Azzaoui I, Uhel F, Rossille D, Pangault C, Dulong J, le Priol J, et al. T-cell defect in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas involves expansion of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Blood. 2016;128:1081–1092. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-08-662783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Tadmor T, Fell R, Polliack A, Attias D. Absolute monocytosis at diagnosis correlates with survival in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma-possible link with monocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Hematol Oncol. 2013;31:65–71. doi: 10.1002/hon.2019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Ren WH, Zhang XR, Li WB, Feng Q, Feng HJ, Tong Y, et al. Exosomal miRNA-107 induces myeloid-derived suppressor cell expansion in gastric cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:4023–4040. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S198886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Serafini P, Meckel K, Kelso M, Noonan K, Califano J, Koch W, et al. Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition augments endogenous antitumor immunity by reducing myeloid-derived suppressor cell function. J Exp Med. 2006;203:2691–2702. doi: 10.1084/jem.20061104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Xu Z, Ji J, Xu J, Li D, Shi G, Liu F, et al. MiR-30a increases MDSC differentiation and immunosuppressive function by targeting SOCS3 in mice with B-cell lymphoma. FEBS J. 2017;284:2410–2424. doi: 10.1111/febs.14133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Grauers Wiktorin H, Nilsson MS, Kiffin R, Sander FE, Lenox B, Rydström A, et al. Histamine targets myeloid-derived suppressor cells and improves the anti-tumor efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint blockade. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019;68:163–174. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-2253-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Locatelli SL, Careddu G, Serio S, Consonni FM, Maeda A, Viswanadha S, et al. Targeting cancer cells and tumor microenvironment in preclinical and clinical models of Hodgkin lymphoma using the dual PI3Kd/G inhibitor RP6530. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:1098–1112. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Cherkassky L, Morello A, Villena-Vargas J, Feng Y, Dimitrov DS, Jones DR, et al. Human CAR T cells with cell-intrinsic PD-1 checkpoint blockade resist tumor-mediated inhibition. J Clin Investig. 2016;126:3130–3144. doi: 10.1172/JCI83092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Burga RA, Thorn M, Point GR, Guha P, Nguyen CT, Licata LA, et al. Liver myeloid-derived suppressor cells expand in response to liver metastases in mice and inhibit the anti-tumor efficacy of anti-CEA CAR-T. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2015;64:817–829. doi: 10.1007/s00262-015-1692-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Kalluri R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:582–598. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Orimo A, Gupta PB, Sgroi DC, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Delaunay T, Naeem R, et al. Stromal fibroblasts present in invasive human breast carcinomas promote tumor growth and angiogenesis through elevated SDF-1/CXCL12 secretion. Cell. 2005;121:335–348. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.02.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Chen X, Song E. Turning foes to friends: targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019;18:99–115. doi: 10.1038/s41573-018-0004-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Scherz-Shouval R, Santagata S, Mendillo ML, Sholl LM, Ben-Aharon I, Beck AH, et al. The reprogramming of tumor stroma by HSF1 is a potent enabler of malignancy. Cell. 2014;158:564–578. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Calvo F, Ege N, Grande-Garcia A, Hooper S, Jenkins RP, Chaudhry SI, et al. Mechanotransduction and YAP-dependent matrix remodelling is required for the generation and maintenance of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Cell Biol. 2013;15:637–646. doi: 10.1038/ncb2756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Sarvaria A, Madrigal JA, Saudemont A. B cell regulation in cancer and anti-tumor immunity. Cell Mol Immunol. 2017;14:662–674. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2017.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Powell DW, Mifflin RC, Valentich JD, Crowe SE, Saada JI, West AB. Myofibroblasts. I. Paracrine cells important in health and disease. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 1999;277:C1–C9. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1999.277.1.C1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Pandey S, Mourcin F, Marchand T, Nayar S, Guirriec M, Pangault C, et al. IL-4/CXCL12 loop is a key regulator of lymphoid stroma function in follicular lymphoma. Blood. 2017;129:2507–2518. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-08-737239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Grégoire M, Guilloton F, Pangault C, Mourcin F, Sok P, Latour M, et al. Neutrophils trigger a NF-ΚB dependent polarization of tumorsupportive stromal cells in germinal center B-cell lymphomas. Oncotarget. 2015;6:16471–16487. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Guilloton F, Caron G, Ménard C, Pangault C, Amé-Thomas P, Dulong J, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells orchestrate follicular lymphoma cell niche through the CCL2-dependent recruitment and polarization of monocytes. Blood. 2012;119:2556–2567. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-08-370908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Haro M, Orsulic S. A paradoxical correlation of cancer-associated fibroblasts with survival outcomes in B-cell lymphomas and carcinomas. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2018;6:98. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2018.00098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Stelling A, Hashwah H, Bertram K, Manz MG, Tzankov A, Müller A. The tumor suppressive TGF-b/SMAD1/S1PR2 signaling axis is recurrently inactivated in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2018;131:2235–2246. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-10-810630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Sanjabi S, Oh SA, Li MO. Regulation of the immune response by TGF-β: from conception to autoimmunity and infection. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2017;9:a0222236. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:503–510. doi: 10.1038/ni1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Harel-Bellan A, Quillet A, Marchiol C, DeMars R, Tursz T, Fradelizi D. Natural killer susceptibility of human cells may be regulated by genes in the HLA region on chromosome 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986;83:5688–5692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.McWilliams EM, Mele JM, Cheney C, Timmerman EA, Fiazuddin F, Strattan EJ, et al. Therapeutic CD94/NKG2A blockade improves natural killer cell dysfunction in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Oncoimmunology. 2016;5:e1226720. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1226720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Wolf NK, Kissiov DU, Raulet DH. Roles of natural killer cells in immunity to cancer, and applications to immunotherapy. Nat Rev Immun. 2022:1–16 https://www.nature.com/articles/s41577-022-00732-1. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 125.Kärre K, Ljunggren HG, Piontek G, Kiessling R. Selective rejection of H-2-deficient lymphoma variants suggests alternative immune defence strategy. Nature. 1986;319:675–678. doi: 10.1038/319675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Seaman WE, Sleisenger M, Eriksson E, Koo GC. Depletion of natural killer cells in mice by monoclonal antibody to NK-1.1. Reduction in host defense against malignancy without loss of cellular or humoral immunity. J Immunol. 1987;138:4539–4544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Street SEA, Hayakawa Y, Zhan Y, Lew AM, MacGregor D, Jamieson AM, et al. Innate immune surveillance of spontaneous B cell lymphomas by natural killer cells and γδ T cells. J Exp Med. 2004;199:879–884. doi: 10.1084/jem.20031981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Smyth MJ, Crowe NY, Godfrey DI. NK cells and NKT cells collaborate in host protection from methylcholanthrene-induced fibrosarcoma. Int Immunol. 2001;13:459–463. doi: 10.1093/intimm/13.4.459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Bonavita E, Bromley CP, Jonsson G, Pelly VS, Sahoo S, Walwyn-Brown K, et al. Antagonistic inflammatory phenotypes dictate tumor fate and response to immune checkpoint blockade. Immunity. 2020;53:1215–1229. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.10.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Marcus A, Mao AJ, Lensink-Vasan M, Wang LA, Vance RE, Raulet DH. Tumor-derived cGAMP triggers a STING-mediated interferon response in non-tumor cells to activate the NK cell response. Immunity. 2018;49:754–763. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.09.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Varn FS, Wang Y, Mullins DW, Fiering S, Cheng C. Systematic pan-cancer analysis reveals immune cell interactions in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2017;77:1271–1282. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Cózar B, Greppi M, Carpentier S, Narni-Mancinelli E, Chiossone L, Vivier E. Tumor-infiltrating natural killer cells. Cancer Discov. 2021;11:34–44. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Cursons J, Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes F, Foroutan M, Anderson A, Hollande F, Hediyeh-Zadeh S, et al. A gene signature predicting natural killer cell infiltration and improved survival in melanoma patients. Cancer Immunol Res. 2019;7:1162–1174. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Castriconi R, Cantoni C, della Chiesa M, Vitale M, Marcenaro E, Conte R, et al. Transforming growth factor β1 inhibits expression of NKP30 and NKG2d receptors: consequences for the NK-mediated killing of dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:4120–4125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0730640100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Gao Y, Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes F, Bald T, Ng SS, Young A, Ngiow SF, et al. Tumor immunoevasion by the conversion of effector NK cells into type 1 innate lymphoid cells. Nat Immunol. 2017;18:1004–1015. doi: 10.1038/ni.3800. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Zelenay S, van der Veen AG, Böttcher JP, Snelgrove KJ, Rogers N, Acton SE, et al. Cyclooxygenase-dependent tumor growth through evasion of immunity. Cell. 2015;162:1257–1270. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Young A, Ngiow SF, Gao Y, Patch AM, Barkauskas DS, Messaoudene M, et al. A2AR adenosine signaling suppresses natural killer cell maturation in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2018;78:1003–1016. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2826. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Ghiringhelli F, Ménard C, Martin F, Zitvogel L. The role of regulatory T cells in the control of natural killer cells: relevance during tumor progression. Immunol Rev. 2006;214:229–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2006.00445.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Kerdiles Y, Ugolini S, Vivier E. T cell regulation of natural killer cells. J Exp Med. 2013;210:1065–1068. doi: 10.1084/jem.20130960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Stanietsky N, Simic H, Arapovic J, Toporik A, Levy O, Novik A, et al. The interaction of TIGIT with PVR and PVRL2 inhibits human NK cell cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:17858–17863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0903474106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Chan CJ, Martinet L, Gilfillan S, Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes F, Chow MT, Town L, et al. The receptors CD96 and CD226 oppose each other in the regulation of natural killer cell functions. Nat Immunol. 2014;15:531–538. doi: 10.1038/ni.2850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Hsu J, Hodgins JJ, Marathe M, Nicolai CJ, Bourgeois-Daigneault MC, Trevino TN, et al. Contribution of NK cells to immunotherapy mediated by PD-1/PD-L1 blockade. J Clin Investig. 2018;128:4654–4668. doi: 10.1172/JCI99317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Concha-Benavente F, Kansy B, Moskovitz J, Moy J, Chandran U, Ferris RL. PD-L1 mediates dysfunction in activated PD-1 þ NK cells in head and neck cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Res. 2018;6:1548–1560. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Deuse T, Hu X, Agbor-Enoh S, Jang MK, Alawi M, Saygi C, et al. The SIRPα-CD47 immune checkpoint in NK cells. J Exp Med. 2021;218:e20200839. doi: 10.1084/jem.20200839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Benson DM, Bakan CE, Mishra A, Hofmeister CC, Efebera Y, Becknell B, et al. The PD-1/PD-L1 axis modulates the natural killer cell versus multiple myeloma effect: a therapeutic target for CT-011, a novel monoclonal anti-PD-1 antibody. Blood. 2010;116:2286–2294. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-02-271874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Beldi-Ferchiou A, Lambert M, Dogniaux S, Vély F, Vivier E, Olive D, et al. PD-1 mediates functional exhaustion of activated NK cells in patients with Kaposi sarcoma. Oncotarget. 2016;7:72961–72977. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Liu Y, Cheng Y, Xu Y, Wang Z, Du X, Li C, et al. Increased expression of programmed cell death protein 1 on NK cells inhibits NK-cell-mediated anti-tumor function and indicates poor prognosis in digestive cancers. Oncogene. 2017;36:6143–6153. doi: 10.1038/onc.2017.209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Vari F, Arpon D, Keane C, Hertzberg MS, Talaulikar D, Jain S, et al. Immune evasion via PD-1/PD-L1 on NK cells and monocyte/macrophages is more prominent in Hodgkin lymphoma than DLBCL. Blood. 2018;131:1809–1819. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-07-796342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Zhang Q, Bi J, Zheng X, Chen Y, Wang H, Wu W, et al. Blockade of the checkpoint receptor TIGIT prevents NK cell exhaustion and elicits potent anti-tumor immunity. Nat Immunol. 2018;19:723–732. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.André P, Denis C, Soulas C, Bourbon-Caillet C, Lopez J, Arnoux T, et al. Anti-NKG2A mAb is a checkpoint inhibitor that promotes anti-tumor immunity by unleashing both T and NK cells. Cell. 2018;175:1731–1743. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.McWhirter SM, Barbalat R, Monroe KM, Fontana MF, Hyodo M, Joncker NT, et al. A host type I interferon response is induced by cytosolic sensing of the bacterial second messenger cyclic-di-GMP. J Exp Med. 2009;206:1899–1911. doi: 10.1084/jem.20082874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Gauthier L, Morel A, Anceriz N, Rossi B, Blanchard-Alvarez A, Grondin G, et al. Multifunctional natural killer cell engagers targeting NKp46 trigger protective tumor immunity. Cell. 2019;177:1701–1713. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.04.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Sarhan D, Brandt L, Felices M, Guldevall K, Lenvik T, Hinderlie P, et al. 161533 TriKE stimulates NK-cell function to overcome myeloid-derived suppressor cells in MDS. Blood Adv. 2018;2:1459–1460. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2017012369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Chang YH, Connolly J, Shimasaki N, Mimura K, Kono K, Campana D. A chimeric receptor with NKG2D specificity enhances natural killer cell activation and killing of tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2013;73:1777–1786. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Parihar R, Rivas C, Huynh M, Omer B, Lapteva N, Metelitsa LS, et al. NK cells expressing a chimeric activating receptor eliminate MDSCs and rescue impaired CAR-T cell activity against solid tumors. Cancer. Immunol Res. 2019;7:363–375. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Klingemann H. Are natural killer cells superior CAR drivers? Oncoimmunology. 2014;3:e28147. doi: 10.4161/onci.28147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Laskowski TJ, Biederstädt A, Rezvani K. Natural killer cells in antitumour adoptive cell immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2022;22:557–575. doi: 10.1038/s41568-022-00491-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Eberl G, Colonna M, Santo JPD, McKenzie ANJ. Innate lymphoid cells: a new paradigm in immunology. Science. 2015;348:aaa6566. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa6566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Tait Wojno ED, Beamer CA. Isolation and identification of innate lymphoid cells (ILCs) for immunotoxicity testing. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1803:353–370. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8549-4_21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Diefenbach A, Colonna M, Koyasu S. Development, differentiation, and diversity of innate lymphoid cells. Immunity. 2014;41:354–365. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.09.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.McKenzie ANJ, Spits H, Eberl G. Innate lymphoid cells in inflammation and immunity. Immunity. 2014;41:366–374. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.09.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Bernink JH, Peters CP, Munneke M, te Velde AA, Meijer SL, Weijer K, et al. Human type 1 innate lymphoid cells accumulate in inflamed mucosal tissues. Nat Immunol. 2013;14(14):221–229. doi: 10.1038/ni.2534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Mackay LK, Kallies A. Transcriptional regulation of tissue-resident lymphocytes. Trends Immunol. 2017;38:94–103. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2016.11.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Tait Wojno ED, Artis D. Emerging concepts and future challenges in innate lymphoid cell biology. J Exp Med. 2016;213:2229–2248. doi: 10.1084/jem.20160525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Licona-Limón P, Kim LK, Palm NW, Flavell RA. TH2, allergy and group 2 innate lymphoid cells. Nat Immunol. 2013;14:536–542. doi: 10.1038/ni.2617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Hwang YY, McKenzie ANJ. Innate lymphoid cells in immunity and disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2013;785:9–26. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-6217-0_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Huntington ND, Carpentier S, Vivier E, Belz GT. Innate lymphoid cells: parallel checkpoints and coordinate interactions with T cells. Curr Opin Immunol. 2016;38:86–93. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2015.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Mjösberg J, Bernink J, Peters C, Spits H. Transcriptional control of innate lymphoid cells. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42:1916–1923. doi: 10.1002/eji.201242639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Klose CSN, Artis D. Innate lymphoid cells as regulators of immunity, inflammation and tissue homeostasis. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:765–774. doi: 10.1038/ni.3489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Klose CSN, Flach M, Möhle L, Rogell L, Hoyler T, Ebert K, et al. Differentiation of type 1 ILCs from a common progenitor to all helper-like innate lymphoid cell lineages. Cell. 2014;157:340–356. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.03.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Constantinides MG, McDonald BD, Verhoef PA, Bendelac A. A committed precursor to innate lymphoid cells. Nature. 2014;508:397–401. doi: 10.1038/nature13047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Bal SM, Bernink JH, Nagasawa M, Groot J, Shikhagaie MM, Golebski K, et al. IL-1β, IL-4 and IL-12 control the fate of group 2 innate lymphoid cells in human airway inflammation in the lungs. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:636–645. doi: 10.1038/ni.3444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Ohne Y, Silver JS, Thompson-Snipes LA, Collet MA, Blanck JP, Cantarel BL, et al. IL-1 is a critical regulator of group 2 innate lymphoid cell function and plasticity. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:646–655. doi: 10.1038/ni.3447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Trabanelli S, Chevalier MF, Martinez-Usatorre A, Gomez-Cadena A, Salomé B, Lecciso M, et al. Tumour-derived PGD2 and NKp30-B7H6 engagement drives an immunosuppressive ILC2-MDSC axis. Nat Commun. 2017;8:593. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00678-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Ikutani M, Yanagibashi T, Ogasawara M, Tsuneyama K, Yamamoto S, Hattori Y, et al. Identification of innate IL-5–producing cells and their role in lung eosinophil regulation and antitumor immunity. J Immunol. 2012;188:703–713. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1101270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Saranchova I, Han J, Huang H, Fenninger F, Choi KB, Munro L, et al. Discovery of a metastatic immune escape mechanism initiated by the loss of expression of the tumour biomarker Interleukin-33. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30555. doi: 10.1038/srep30555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Zaiss DMW, Gause WC, Osborne LC, Artis D. Emerging functions of amphiregulin in orchestrating immunity, inflammation, and tissue repair. Immunity. 2015;42:216–226. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.01.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Bando JK, Nussbaum JC, Liang H-E, Locksley RM. Type 2 innate lymphoid cells constitutively express arginase-I in the naïve and inflamed lung. J Leukoc Biol. 2013;94:877–884. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0213084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Fuchs A, Vermi W, Lee JS, Lonardi S, Gilfillan S, Newberry RD, et al. Intraepithelial type 1 innate lymphoid cells are a unique subset of il-12- and il-15-responsive ifn-γ-producing cells. Immunity. 2013;38:769–781. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.02.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Bernink JH, Krabbendam L, Germar K, de Jong E, Gronke K, Kofoed-Nielsen M, et al. Interleukin-12 and -23 control plasticity of Cd127+ group 1 and group 3 innate lymphoid cells in the intestinal Lamina Propria. Immunity. 2015;43:146–160. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Pearson C, Thornton EE, McKenzie B, Schaupp AL, Huskens N, Griseri T, et al. ILC3 GM-CSF production and mobilisation orchestrate acute intestinal inflammation. Elife. 2016;5:e10066. doi: 10.7554/eLife.10066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Griseri T, Arnold IC, Pearson C, Krausgruber T, Schiering C, Franchini F, et al. Granulocyte macrophage Colony-stimulating factor-activated eosinophils promote Interleukin-23 driven chronic colitis. Immunity. 2015;43:187–199. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.07.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Liu J, Duan Y, Cheng X, Chen X, Xie W, Long H, et al. IL-17 is associated with poor prognosis and promotes angiogenesis via stimulating VEGF production of cancer cells in colorectal carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;407:348–354. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.03.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Mlecnik B, Fredriksen T, Mauger S, Bindea G, et al. Clinical impact of different classes of infiltrating T cytotoxic and helper cells (Th1, Th2, Treg, Th17) in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71:1263–1271. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.King RL, Goodlad JR, Calaminici M, Dotlic S, Montes-Moreno S, Oschlies I, et al. Lymphomas arising in immune-privileged sites: insights into biology, diagnosis, and pathogenesis. Virchows Arch. 2020;476:647–665. doi: 10.1007/s00428-019-02698-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Kridel R, Telio D, Villa D, Sehn LH, Gerrie AS, Shenkier T, et al. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with testicular involvement: outcome and risk of CNS relapse in the rituximab era. Br J Haematol. 2017;176:210–221. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Bromberg JEC, Issa S, Bakunina K, Minnema MC, Seute T, Durian M, et al. Rituximab in patients with primary CNS lymphoma (HOVON 105/ALLG NHL 24): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 intergroup study. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:216–228. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30747-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Radke J, Ishaque N, Koll R, Gu Z, Schumann E, Sieverling L, et al. The genomic and transcriptional landscape of primary central nervous system lymphoma. Nat Commun. 2022;13:1–20. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-30050-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Chapuy B, Roemer MGM, Stewart C, Tan Y, Abo RP, Zhang L, et al. Targetable genetic features of primary testicular and primary central nervous system lymphomas. Blood. 2016;127:869–881. doi: 10.1182/blood-2015-10-673236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Ngo VN, Young RM, Schmitz R, Jhavar S, Xiao W, Lim K-H, et al. Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma. Nature. 2011;470:115–119. doi: 10.1038/nature09671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Challa-Malladi M, Lieu YK, Califano O, Holmes A, Bhagat G, Murty V, et al. Combined genetic inactivation of Beta2-microglobulin and CD58 reveals frequent escape from immune recognition in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2011;20:728. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.11.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Steidl C, Shah SP, Woolcock BW, Rui L, Kawahara M, Farinha P, et al. MHC class II transactivator CIITA is a recurrent gene fusion partner in lymphoid cancers. Nature. 2011;471:377–381. doi: 10.1038/nature09754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Marcelis L, Antoranz A, Delsupehe AM, Biesemans P, Ferreiro JF, Debackere K, et al. In-depth characterization of the tumor microenvironment in central nervous system lymphoma reveals implications for immune-checkpoint therapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020;69:1751–1766. doi: 10.1007/s00262-020-02575-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Guo J, Tang Q. Recent updates on chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021;28:1075–1087. doi: 10.1038/s41417-020-00259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Mondello P, Brea EJ, de Stanchina E, Toska E, Chang AY, Fennell M, et al. Panobinostat acts synergistically with ibrutinib in diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells with MyD88 L265 mutations. JCI Insight. 2017;2:e90196. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.90196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Grommes C, Pastore A, Palaskas N, Tang SS, Campos C, Schartz D, et al. Ibrutinib unmasks critical role of Bruton tyrosine kinase in primary CNS lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:1018–1029. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Lionakis MS, Dunleavy K, Roschewski M, Widemann BC, Butman JA, Schmitz R, et al. Inhibition of B cell receptor signaling by Ibrutinib in primary CNS lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 2017;31:833–843.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.04.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Mondello P, Mian M, Bertoni F. Primary central nervous system lymphoma: novel precision therapies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2019;141:139–145. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2019.06.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Nabet BY, Esfahani MS, Moding EJ, Hamilton EG, Chabon JJ, Rizvi H, et al. Noninvasive early identification of therapeutic benefit from immune checkpoint inhibition. Cell. 2020;183:363–376. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Tavaré R, Escuin-Ordinas H, Mok S, McCracken MN, Zettlitz KA, Salazar FB, et al. An effective immuno-PET imaging method to monitor CD8-dependent responses to immunotherapy. Cancer Res. 2016;76:73–82. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Farwell MD, Gamache RF, Babazada H, Hellmann MD, Harding JJ, Korn R, et al. CD8-targeted PET imaging of tumor-infiltrating T cells in patients with Cancer: a phase i first-in-humans study of 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C, a radiolabeled anti-CD8 Minibody. J Nucl Med. 2022;63:720–726. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.121.262485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Gosmann D, Russelli L, Weber WA, Schwaiger M, Krackhardt AM, D’Alessandria C. Promise and challenges of clinical non-invasive T-cell tracking in the era of cancer immunotherapy. EJNMMI Res. 2022;12:5. doi: 10.1186/s13550-022-00877-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.