A 57-year-old male with history of deceased-donor kidney transplant 3 years ago presented to the hospital with 3 days of nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. His immunosuppressive regimen was mycophenolate, tacrolimus, and prednisone. The patient’s roommate had been hospitalized with COVID-19 20 days prior but had since returned home. Six days prior, while asymptomatic, the patient had tested negative for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in a nasopharyngeal specimen.
He endorsed chills but denied cough, dyspnea, dysgeusia, myalgia, headache, or history of travel. He had a fever of 103.5°F and tachycardia to 110 but no hypoxia. He did not appear to be in significant distress. He had bibasilar crackles on lung exam and a normal abdominal exam.
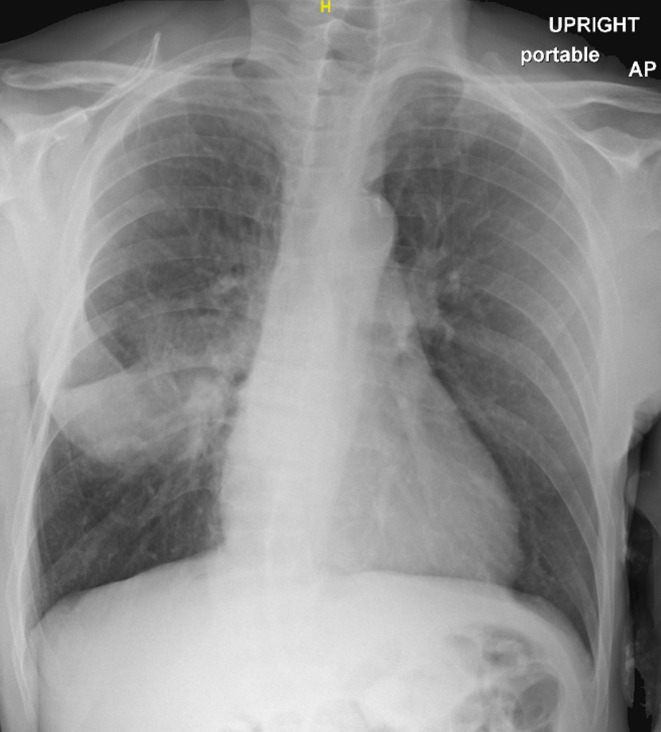
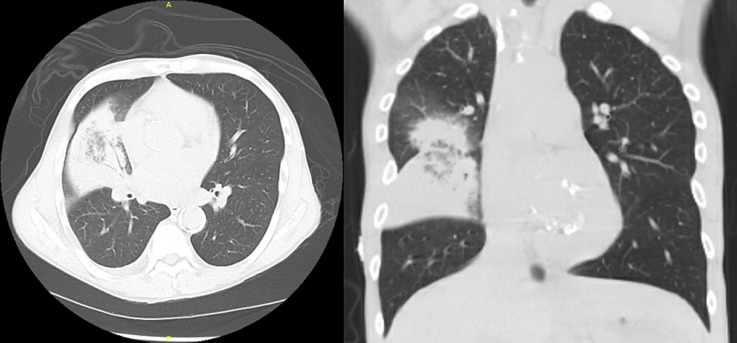
Laboratory testing revealed leukocytosis (12.6/μL with 87% neutrophils), lymphopenia (0.8/μL), thrombocytopenia (122/μL), hyponatremia (127 mEq/L), and a mildly elevated creatinine (1.87 mg/dL, baseline: 1.3-1.5 mg/dL). Chest radiograph ( Figure 1) and computed tomography (CT) ( Figure 2) showed a dense right middle lobe pneumonia. Repeat SARS-CoV-2 PCR, respiratory pathogen panel (both in a nasopharyngeal specimen), and Clostridium difficile toxin PCR in the stool were all negative. He was admitted to the inpatient transplant service for further care.
FIGURE 1.
Radiograph of the chest showing airspace disease in the right middle lobe
FIGURE 2.
Computed tomography of the chest, axial, and coronal views, showing right middle lobe consolidation with air bronchograms
1. QUESTIONS
-
1Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient’s symptoms, laboratory results, and imaging findings?
-
aAn intracellular bacterium
-
bA mold
-
cA parasite
-
dA virus
-
eA yeast
-
a
-
2Which of the following tests should be the preferred next step towards diagnosis?
-
aPathogen-specific antibodies in the serum
-
bPCR in an oropharyngeal specimen
-
cSerum β-D-glucan
-
dSerum galactomannan
-
eUrinary antigen
-
a
-
3Which of the following is appropriate treatment for this infection?
-
aAzithromycin
-
bHydroxychloroquine
-
cRemdesivir
-
dVoriconazole
-
eAzithromycin and hydroxychloroquine
-
a
-
4Which of the following cognitive biases likely affected the initial diagnostic approach to this case?
-
aAvailability bias
-
bDunning-Kruger effect
-
cGambler’s fallacy
-
dBlind obedience
-
eAll the above
-
a