Abstract
Aims/hypothesis
Excess adiposity is differentially associated with increased risk of cardiometabolic disease in men and women, according to observational studies. Causal inference studies largely assume a linear relationship between BMI and cardiometabolic outcomes, which may not be the case. In this study, we investigated the shapes of the causal relationships between BMI and cardiometabolic diseases and risk factors. We further investigated sex differences within the causal framework.
Methods
To assess causal relationships between BMI and the outcomes, we used two-stage least-squares Mendelian randomisation (MR), with a polygenic risk score for BMI as the instrumental variable. To elucidate the shapes of the causal relationships, we used a non-linear MR fractional polynomial method, and used piecewise MR to investigate threshold relationships and confirm the shapes.
Results
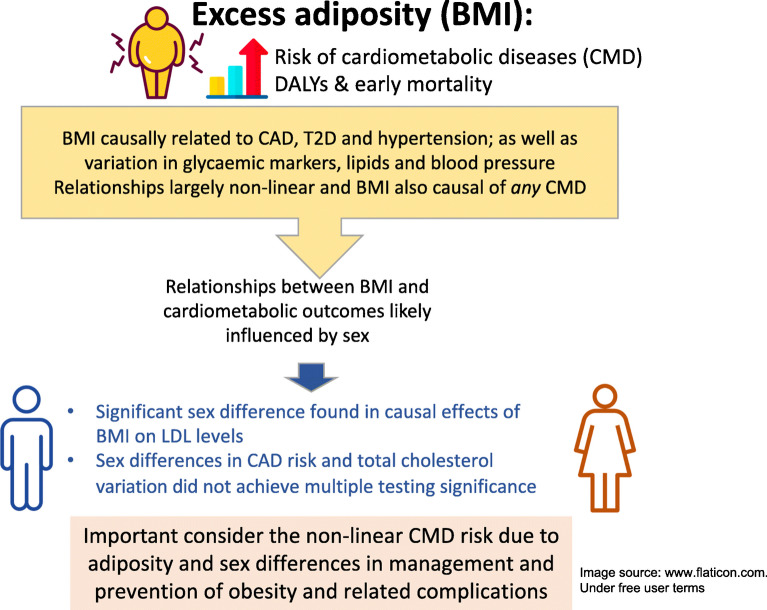
BMI was associated with type 2 diabetes (OR 3.10; 95% CI 2.73, 3.53), hypertension (OR 1.53; 95% CI 1.44, 1.62) and coronary artery disease (OR 1.20; 95% CI 1.08, 1.33), but not chronic kidney disease (OR 1.08; 95% CI 0.67, 1.72) or stroke (OR 1.08; 95% CI 0.92, 1.28). For cardiometabolic risk factors, BMI was positively associated with glucose, HbA1c, triacylglycerol levels and both systolic and diastolic BP. BMI had an inverse causal relationship with total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol. The data suggest a non-linear causal relationship between BMI and blood glucose levels, HbA1c and lipid fractions (p<0.001), more strongly in men than women. The piecewise MR results were consistent with the fractional polynomial results. The causal effect of BMI on coronary artery disease, total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol was different in men and women, but this sex difference was only significant for LDL-cholesterol after controlling for multiple testing (p<0.001). Further, the causal effect of BMI on coronary artery disease varied by menopause status in women.
Conclusions/interpretation
We describe the shapes of causal effects of BMI on cardiometabolic diseases and risk factors, and report sex differences in the causal effects of BMI on LDL-cholesterol. We found evidence of non-linearity in the causal effect of BMI on diseases and risk factor biomarkers. Reducing excess adiposity is highly beneficial for health, but there is greater need to consider biological sex in the management of adiposity.
Graphical abstract
Supplementary Information
The online version contains peer-reviewed but unedited supplementary material available at 10.1007/s00125-022-05811-5.
Keywords: Cardiometabolic, Causal, Mendelian randomisation, Obesity
Introduction
Cardiometabolic diseases (CMDs) are among the top ten causes of death and are associated with increased healthcare costs globally, making their relationship with adiposity a major public health concern [1–4]. Excess adiposity is associated with increased risk of CMDs, as well as increased risk of all-cause mortality [5–8]. The BMI category at lowest risk of early death is 20–25 kg/m2 in populations of European ancestry, with average health worsening significantly within the ‘overweight’ category, and deteriorating further as BMI increases [9]. Both observational studies and some causal inference studies suggest that BMI has a J-shaped relationship with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality [5, 10].
Observational studies often suffer from residual confounding and reverse causality, as do the relational shapes they describe. For example, the high mortality rate observed in some people with lower BMI (J-shaped relationship) is probably caused by the chronic disease cachexia [11]. While causal relationships between adiposity and CMDs have been determined previously, most studies assume these relationships are linear [12–15]. In addition, observational studies have shown that sex confers differential CMD risk profiles in men and women, but extensive investigation of such differences within a causal framework is lacking [16–19]. Therefore, understanding the nature of causal relationships between excess adiposity, CMDs and any sex differences therein may help to refine public health interventions [20].
Patterns of causal associations between excess adiposity and cardiometabolic outcomes remain understudied; given the shapes reported in observational studies, we hypothesised that adiposity has non-linear causal effects on cardiometabolic outcomes, with sex differences within this causal framework. The purpose of this study was to elucidate the nature of causal effects and explore the sex differences in the effects of BMI on CMDs (coronary artery disease [CAD], type 2 diabetes, chronic kidney disease [CKD], stroke and hypertension). We further extended these investigations to risk factor biomarkers: glycaemic markers (glucose, HbA1c), lipids (triacylglycerols, total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol and HDL-cholesterol), lipoprotein A (LPA), urea and BP.
Methods
Population
We used individual-level data from the UK Biobank, a cohort of approximately 500,000 participants of mixed ancestries assessed across 22 centres in the UK. For this study, we selected individuals of white European descent only (n=409,584). In summary, participants aged 40–69 years were enrolled between 2006 and 2010, and standard anthropometric measurements were taken, in addition to biological samples (urine, blood and saliva); socio-demographic, lifestyle and other health determining factors were recorded. The UK Biobank study received approval from the Multi-centre Research Ethics Committee (reference 16/NW/0274), and all participants gave informed consent [21]. Information about recruitment and data collection has been provided elsewhere [22]. The current analysis is based on application number 57232 to the UK Biobank resource. Use of UK Biobank data for the analysis described here was approved by the Swedish Ethics Approval Authority (application number 2021-03174).
Outcome variables
Disease outcomes
For each of the disease outcomes (type 2 diabetes, hypertension, stroke, CAD and CKD), information was obtained from ICD-9 (http://www.icd9data.com/2007/Volume1/default.htm) and ICD-10 (http://apps.who.int/classifications/icd10/browse/2016/en) diagnosis codes for both prevalent and incident disease, self-reported diagnoses, enrolment interview reports and self-reported medication data. We excluded participants whose reported age of type 2 diabetes diagnosis was 20 years old or less, as it was deemed to be probable type 1 diabetes. For cardiovascular disease (CAD, stroke and hypertension) and CKD, we additionally used information regarding surgical operations, plus interventional procedures related to each disease from OPCS4 codes (https://classbrowser.nhs.uk/#/), self-reported surgical procedures, and details of vascular diseases diagnosed by a doctor, which contained specific coding for each disease outcome. Additional information was obtained from medication data for both men and women, based on self-reported data collected at enrolment. Details of codes and data fields used for each disease are provided in electronic supplementary material (ESM) Table 1.
Disease-risk biomarkers
The disease-risk biomarkers that we included were glucose, HbA1c, triacylglycerols, cholesterol (total, HDL and LDL), urea and LPA, plus systolic BP (SBP) and diastolic BP (DBP). This information was obtained from the blood biochemistry categories of the UK Biobank, details of which are provided in ESM Table 2. For BP, we added 15 and 10 mmHg, respectively, to the values for SBP and DBP in participants taking BP medication [23].
Genetic data
Details of enrolment and genetic data handling have been extensively explained by Bycroft et al [22]. For this project, we used version 3 of the imputed genotypes data from the UK Biobank. We excluded SNPs and individuals with a genotype call rate <99%, SNPs with a Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium p value <1×10−10, those with an imputation score <80%, any duplicated SNPs, and SNPs with a minor allele frequency <0.01. Using quality control results provided by UK Biobank, we further excluded individuals deemed outliers for heterozygosity (indicating poor sample quality or contamination), those with sex ambiguity and aneuploidy, and one of any pair of related individuals (up to third-degree relatedness, kinship coefficient 0.0442–0.0882). After further exclusion of participants with missing anthropometric measurements or HbA1c beyond detectable ranges (>184 mmol/mol or 19%), our final sample comprised 333,582 individuals (ESM Fig. 1).
Computing the BMI polygenic risk score
We used genome-wide association study (GWAS) summary statistics from the latest GIANT meta-analysis of BMI GWASs (excluding participants from the UK Biobank), and selected only genetic variants that were associated with BMI at a genome-wide significance level (p5×10−8): n=1560 SNPs [24]. Individual genetic data were obtained from the UK Biobank. A BMI polygenic risk score (PRS; PRSBMI) was calculated by weighting each SNP by its effect size from GWAS summary data and then summing these values for all SNPs for each individual in our sample. Prior to PRSBMI calculation, clumping restricted to r 2=0.2 and a 250 kb window was performed to ensure that only SNPs that are not in linkage disequilibrium were used. After this quality control step, there were 89 uncorrelated BMI SNPs available for use in generating the PRSBMI. All PRSBMI calculations were performed using PRSice-2 software [25]. To reduce the chances of horizontal pleiotropy between PRSBMI and the various diseases and risk factors, we selected BMI SNPs specific to each trait. This was done by excluding any SNPs that were associated with the respective trait at genome-wide significance from the BMI SNPs by comparing with GWAS summary data for the trait. We then computed a trait-specific PRSBMI (for instance, a PRSBMI for CAD analysis that used BMI SNPs that were not associated with CAD) for use in downstream analyses involving that specific trait.
Statistical analysis
Causal effect assessment
We used two-stage least-squares (2SLS) Mendelian randomisation (MR), with PRSBMI as the genetic instrumental variable, to estimate causal effects of BMI on cardiometabolic traits. Prior to analysis, BMI was transformed in the same way as in the discovery GWAS by Locke et al [24]. Specifically, the effects of age, age squared, smoking status, alcohol consumption, UK Biobank assessment centre and the Townsend Deprivation Index were regressed out separately for men and women. Residuals from each of the models, men and women, were then inverse normal-transformed to create a main exposure variable representing BMI.
In the first stage, the exposure was regressed on the PRSBMI in a linear model, adjusting for genotyping array and the first ten genetic principal components characterising the population substructure. Thereafter, fitted values were generated and used in the second stage of 2SLS, where logistic and linear regression models were used for binary and continuous traits respectively, with the fitted values as the exposure, adjusting for the same covariates as in the first stage. The regression coefficients of these fitted values in the second stage represent an estimate of the causal effect of BMI on the outcome [26]. We ran 2SLS models for each disease outcome and each biomarker, and also performed sex-stratified analyses.
Continuous outcomes were scaled so that the results represent a change in SD units of outcome per unit change in BMI. Cochran’s Q test was used to assess sex differences in the sex-stratified analysis. To estimate the causal effect of BMI on any CMD, we used both fixed and random effects meta-analysis, and considered the combined outcome as the likelihood of any CMD. We performed 15 main hypothesis tests (for the five disease outcomes and ten disease-risk biomarkers) and 30 sex-stratified tests; therefore, the Bonferroni-corrected significance level was set at p=0.001 (0.05/45).
Determining the shape of the causal relationships
To describe the shape of the causal relationships between BMI and each of the traits, we used a non-linear MR fractional polynomials method [27]. This involves calculating the local average causal effect (LACE) in quantiles of the exposure. These LACE estimates are then meta-regressed against the means of the exposure in each quantile, and tests of non-linearity are applied to test the null hypothesis that the resultant non-linear model is no different from a linear model. Given that stratifying directly on the exposure can lead to collider bias [27], we used two methods to construct these quantiles: the residual [27] and the doubly ranked [28] methods. In the residual method, the exposure is regressed on the genetic instrument, and the quantiles are derived from the residuals of this regression. While this ensures that the strata are independent from the genetic instrument, it has the caveat that it assumes homogeneity in the relationship between the genetic instrument and the exposure [28]. In the doubly ranked method this issue is addressed through a two-step process. First, individuals are categorised into pre-strata according to their level of the genetic instrument. Subsequently, within each of these pre-strata, individuals are ranked based on the level of the exposure. The final quantiles are then constructed by selecting individuals with equal ranks in the pre-strata, thus making the distribution of the genetic instrument similar across the final quantiles, while ensuring that the average level of the exposure is increasing across these final quantiles.
To obtain a deeper understanding of causal shapes, we also performed piecewise MR using the LACE estimates to investigate whether any of the relationships had a threshold effect and to confirm the results of the non-linearity tests. Unlike fractional polynomial MR, this method does not smooth over the different quantiles. Instead, it fits a linear model in each quantile, with the slope representing the LACE. For each trait, we also conducted sex-stratified analysis. All analyses were performed in R versions 3.6.2 and 4.3.2 (https://www.R-project.org/).
Sensitivity analyses
To address potential bias due to extreme values, varying incompleteness of phenotype data (e.g. LPA) and effects of factors such as menopause and waist–hip ratio, we performed several sensitivity analyses as follows: (1) using complete cases only; (2) excluding outliers of BMI, defined using Tukey’s lower and upper fences [29]; (3) including residuals from the first stage in the second stage (two-stage residual inclusion, 2SRI); (4) adjusting for lipid-lowering medication and waist–hip ratio; (5) excluding premenopausal or postmenopausal women, stratifying women by menopause status (self-reported or by age cut-point of 55 years), and stratifying both men and women by age; and (6) using a G-estimator method [30] to calculate causal estimates. All sensitivity analyses were also sex-stratified where applicable.
In 2SRI, the residuals are included as a control function to minimise bias of the standard 2SLS, especially when the effect measure is non-linear. The G-estimator gives a consistent estimate of the causal effect that varies the least. The causal effect estimates obtained using these methods should therefore not differ substantially from each other. We finally used two-sample MR to assess bidirectional causation.
Results
Participants’ characteristics are shown in Table 1. The dataset included slightly more women (n=179,522, 53.8%) than men (n=154,060, 46.2%). On average, women had slightly lower BMI (27.0±5.1 kg/m2) compared with men (27.8±4.2 kg/m2). There was no difference in the mean age, men 57.1±8.1 years, women 56.7±7.9 years. Men had higher baseline mean BP (SBP=145±19.4 mmHg; DBP=86.6±11.0 mmHg) compared with women (SBP=138±21.2 mmHg; DBP=82.4±11.1 mmHg), and a higher prevalence of CMDs (e.g., 67.4% in men vs 32.6% in women for CAD). Differences in anthropometric measures and disease prevalence persisted across age groups (ESM Figs 2 and 3).
Table 1.
Participant characteristics (n=333,582)
| Characteristic | Men | Women |
|---|---|---|
| Proportion | 46.2 | 53.8 |
| Age (years) | 57.1 (8.1) | 56.7 (7.9) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 27.8 (4.2) | 27.0 (5.1) |
| Townsend deprivation index | −1.59 (2.9) | −1.53 (3.0) |
| Smoking status | ||
| Never | 41.2 | 58.8 |
| Previous | 51.1 | 48.9 |
| Current | 53.7 | 46.3 |
| Alcohol intake status | ||
| Never | 24.7 | 75.3 |
| Previous | 43.0 | 57.0 |
| Current | 46.8 | 53.2 |
| Mortality | 60.0 | 40.0 |
| CMDs | ||
| CAD | 67.4 | 32.6 |
| Type 2 diabetes | 61.5 | 38.5 |
| Stroke | 61.3 | 38.7 |
| CKD | 55.2 | 44.8 |
| Hypertension | 53.7 | 46.3 |
| Biomarkers | ||
| SBP (mmHg) | 145.0 (19.4) | 138.0 (21.2) |
| DBP (mmHg) | 86.6 (11.0) | 82.4 (11.1) |
| Glucose (mmol/l) | 5.2 (1.4) | 5.1 (1.0) |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 36.3 (7.3) | 35.7 (5.7) |
| HbA1c (%) | 6.1 (1.9) | 6.0 (1.7) |
| Cholesterol (mmol/l) | 5.5 (1.1) | 5.9 (1.1) |
| HDL-cholesterol (mmol/l) | 1.3 (0.3) | 1.6 (0.4) |
| LDL-cholesterol (mmol/l) | 3.5 (0.9) | 3.6 (0.9) |
| Triacylglycerols (mmol/l) | 2.0 (1.2) | 1.6 (0.9) |
| LPA (mmol/l) | 43.4 (49.3) | 44.6 (49.5) |
| Urea (mmol/l) | 5.6 (1.4) | 5.3 (1.3) |
Continuous variables are presented as mean (SD) and categorical variables as percentages
In the 2SLS analyses, BMI was associated with type 2 diabetes (OR 3.10; 95% CI 2.73, 3.53; p=1.38×10−67), hypertension (OR 1.53; 95% CI 1.44, 1.62; p=8.92×10−44) and CAD (OR 1.20; 95% CI 1.08, 1.33; p=6.86×10−4), but not CKD (OR 1.08; 95% CI 0.67, 1.72; p=0.76) or stroke (OR=1.08; 95% CI 0.92, 1.28; p=0.34) (Table 2).
Table 2.
Estimates of causal relationships between BMI and cardiometabolic outcomes using 2SLS MR in the UKB
| Combined | Men | Women | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | OR/β (95% CI) | p value | OR/β (95% CI) | p value | OR/β (95% CI) | p value |
| CMDs | ||||||
| CAD | 1.20 (1.08, 1.33) | 6.86 × 10−4 | 1.30 (1.15, 1.47) | 2.55 × 10−5 | 0.97 (0.81, 1.18) | 0.78 |
| Type 2 diabetes | 3.10 (2.73, 3.53) | 1.38 × 10−67 | 2.85 (2.43, 3.33) | 2.61 × 10−38 | 3.51 (2.84, 4.33) | 2.99 × 10−31 |
| Stroke | 1.08 (0.92, 1.28) | 0.34 | 1.14 (0.92, 1.40) | 0.23 | 1.00 (0.77, 1.30) | 0.98 |
| CKD | 1.08 (0.67, 1.72) | 0.76 | 1.13 (0.62, 2.06) | 0.69 | 0.99 (0.47, 2.06) | 0.97 |
| Hypertension | 1.53 (1.44, 1.62) | 8.92 × 10−44 | 1.50 (1.38, 1.63) | 1.49 × 10−22 | 1.55 (1.42, 1.70) | 9.28 × 10−23 |
| Biomarkers | ||||||
| DBP | 0.15 (0.12, 0.19) | 1.30 × 10−18 | 0.13 (0.09, 0.18) | 4.91 × 10−8 | 0.17 (0.12, 0.22) | 7.25 × 10−12 |
| SBP | 0.09 (0.06, 0.12) | 2.31 × 10−7 | 0.10 (0.06, 0.15) | 2.71 × 10−5 | 0.07 (0.03, 0.12) | 2.37 × 10−3 |
| Glucose | 0.16 (0.13, 0.20) | 4.90 × 10−24 | 0.18 (0.13, 0.23) | 6.76 × 10−12 | 0.15 (0.10, 0.20) | 7.77 × 10−9 |
| HbA1c | 0.22 (0.19, 0.26) | 2.30 × 10−34 | 0.23 (0.18, 0.28) | 3.85 × 10−18 | 0.22 (0.17, 0.27) | 4.09 × 10−18 |
| Cholesterol | −0.18 (−0.21, −0.14) | 1.37 × 10−24 | −0.23 (−0.28, −0.18) | 3.96 × 10−19 | −0.13 (−0.18, −0.08) | 5.13 × 10−8 |
| HDL-cholesterol | −0.26 (−0.30, −0.22) | 4.36 × 10−35 | −0.32 (−0.37, −0.26) | 3.66 × 10−28 | −0.25 (−0.31, −0.20) | 5.69 × 10−19 |
| LDL-cholesterol | −0.10 (−0.14, −0.07) | 9.59 × 10−10 | −0.17 (−0.21, −0.12) | 4.79 × 10−11 | −0.05 (−0.09, 0.00) | 0.05 |
| Triacylglycerols | 0.13 (0.09, 0.16) | 2.38 × 10−13 | 0.14 (0.09, 0.18) | 3.76 × 10−8 | 0.12 (0.07, 0.17) | 1.82 × 10−6 |
| LPA | 0.02 (−0.02, 0.05) | 0.31 | 0.01 (−0.05, 0.05) | 0.99 | 0.04 (−0.01, 0.09) | 0.16 |
| Urea | 0.05 (0.01, 0.08) | 0.01 | 0.02 (−0.03, 0.07) | 0.37 | 0.06 (0.02, 0.11) | 8.70 × 10−3 |
For disease-risk biomarkers (coefficients expressed in SD units), urea (β=0.05; 95% CI 0.01, 0.08; p=0.01) and LPA levels (β=0.02; 95% CI −0.02, 0.05, p=0.31) were not significantly associated with BMI, after correcting for multiple testing (p Bonferroni=0.001). A positive causal effect of BMI was observed for glucose (β=0.16; 95% CI 0.13, 0.20; p=4.90×10−24), HbA1c (β=0.22; 95% CI 0.19, 0.26, p=2.30×10−34), and triacylglycerol levels (β=0.13; 95% CI 0.09, 0.16, p=2.38×10−13). BMI had an inverse causal relationship with total cholesterol (β=−0.18; 95% CI −0.21, −0.14, p=1.37×10−24), LDL-cholesterol (β=−0.10; 95% CI −0.14, −0.07, p=9.59×10−10) and HDL-cholesterol (β=−0.26; 95% CI −0.30, −0.22, p=4.36×10−35). The effect of BMI on DBP variation (β=0.15; 95% CI 0.12, 0.19, p=1.30×10−18) was almost twice the effect on SBP variation (β=0.09; 95% CI 0.06, 0.12, p=2.31×10−7) (Table 2).
Sex-stratified analyses
As shown in Table 2, the causal effect of BMI on CAD in women was not statistically significant (OR=0.97; 95% CI 0.81, 1.18, p=0.78), but it was in men (OR=1.30; 95% CI 1.15, 1.47, p=2.55×10−5) (p value for sex difference=0.01; however, this was not significant after accounting for multiple testing, p<0.001, Table 3). No significant differences between sexes were observed for the causal effects of BMI on type 2 diabetes, stroke, hypertension or CKD.
Table 3.
Cochran’s Q test of the difference between men and women for causal effects of BMI on cardiometabolic traits
| Trait | Men vs all women | Men vs premenopausal women | Men vs postmenopausal women |
|---|---|---|---|
| CMDs | |||
| CAD | 0.011 | 0.115 | 0.006 |
| Type 2 diabetes | 0.121 | 0.325 | 0.541 |
| Stroke | 0.440 | 0.434 | 0.139 |
| CKD | 0.783 | 0.615 | 0.570 |
| Hypertension | 0.578 | 0.003 | 0.542 |
| Biomarkers | |||
| DBP | 0.333 | 0.083 | 0.710 |
| SBP | 0.369 | 0.102 | 0.157 |
| Glucose | 0.355 | 0.729 | 0.098 |
| HbA1c | 0.893 | 0.286 | 0.481 |
| Cholesterol | 0.005 | 0.001 | 0.067 |
| HDL-cholesterol | 0.111 | 0.913 | 0.009 |
| LDL-cholesterol | 5.94 × 10−4 | 2.31 × 10−4 | 0.032 |
| Triacylglycerols | 0.600 | 0.136 | 0.077 |
| LPA | 0.328 | 0.897 | 0.201 |
| Urea | 0.239 | 0.268 | 0.467 |
Of the biomarkers, LDL-cholesterol was not significantly associated with BMI in women (β=−0.05; 95% CI −0.09, 0.00, p=0.05), but it was in men (β=−0.17; 95% CI −0.21, −0.12, p=4.79×10−11), and this sex difference was significant even after adjusting for multiple testing (p Bonferroni=0.001). The causal effect of BMI on total cholesterol in men (β=−0.23; 95% CI −0.28, −0.18, p=3.96×10−19), was almost double the effect seen in women (β=−0.13, 95% CI −0.18, −0.08, p=5.13×10−8), but the sex difference did not persist after correcting for multiple testing (p Bonferroni=0.001). In men, urea was not significantly associated with BMI (β=0.02; 95% CI −0.03, 0.07, p=0.37); however, a positive association was observed in women (β=0.06; 95% CI 0.02, 0.11, p=8.70×10−3), although this was not significant after Bonferroni correction. BMI was associated with DBP in both men and women, but was associated with SBP in men only (Tables 2 and 3).
Effect of BMI on any cardiometabolic disease outcome
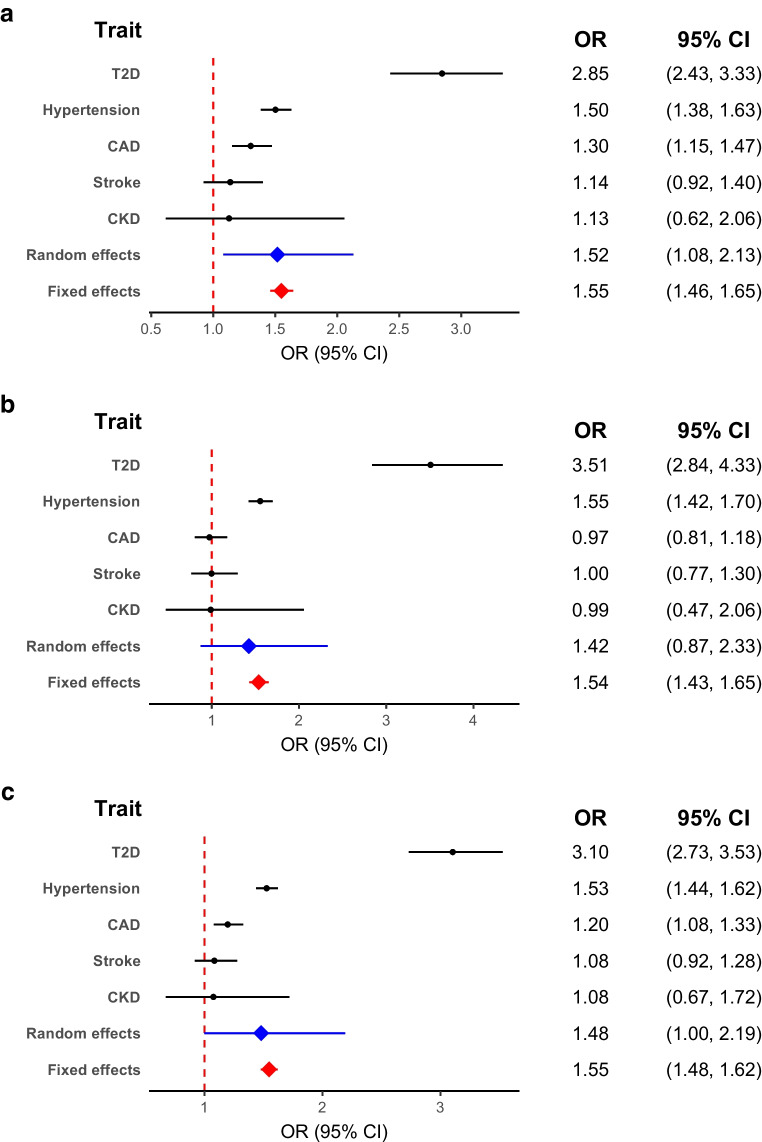
In combined meta-analysis of the causal effect sizes of BMI on CMD, BMI was significantly associated with increased causal odds of any CMD (fixed effects OR 1.55; 95% CI 1.48, 1.62; p=8.23×10−78; random effects OR 1.48; 95% CI 1.00, 2.19; p=0.05). In men, BMI was also causally linked to any CMD using both fixed and random effects, but in women this association was only significant when considering fixed effects (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Forest plots of a summary meta-analysis combining the causal effect estimates of BMI on CMDs in (a) men, (b) women, and (c) all participants. The common outcome in both fixed and random effect lines represents any CMD. T2D, type 2 diabetes
2SLS sensitivity analyses
In the combined analyses, results did not differ across the three methods used to estimate causal effects (2SLS, 2SRI and G-estimator) for any trait except BP, HbA1c and LPA levels, where use of the G-estimator gave larger effect sizes with wider 95% CIs (ESM Tables 3 and 4). Adjusting for lipid-lowering medication or waist–hip ratio did not materially change the results in either the main analysis or when excluding outliers for BMI (ESM Figs 4 and 5; ESM Tables 5 and 6).
A sex difference in effects of BMI on hypertension was observed when comparing men to premenopausal women, but this was not significant after accounting for multiple testing (p Bonferroni=0.001). Significant sex differences were observed for the relationship between BMI and LDL-cholesterol after multiple testing correction, but not when comparing men to postmenopausal women (ESM Table 7). In the age-stratified analyses (i.e., <55 years or 55 years and above), BMI was associated with CAD across all groups in men and in premenopausal (self-reported) women only. The causal effect of BMI was statistically significant in all groups for hypertension and type 2 diabetes, but not stroke or CKD (ESM Fig. 6 and ESM Table 8). Analyses performed to assess bidirectional causation did not yield results supporting such relationships. The association between SBP and BMI had a null effect size, while that between DBP and BMI suffered from horizontal pleiotropy (ESM Table 9).
Shapes of causal relationships
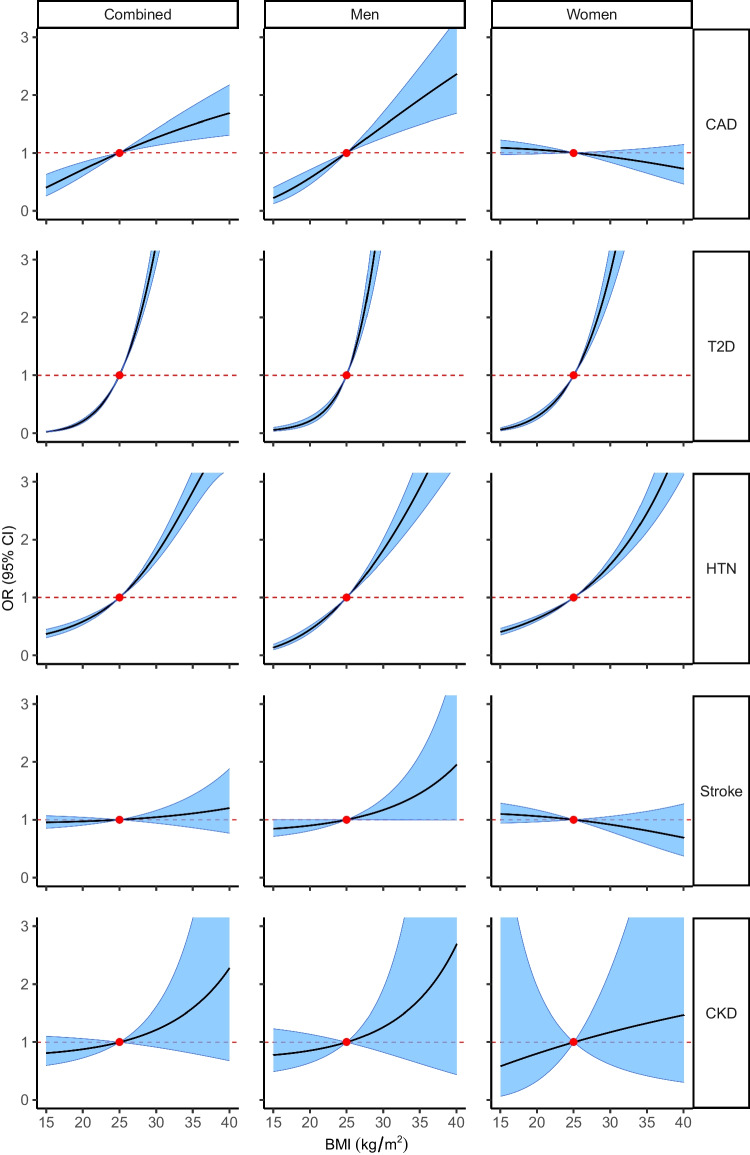
From the non-linear MR fractional polynomials (FP), there was evidence to support a non-linear causal effect of BMI on type 2 diabetes. A quadratic model (p Quadratic=9.45x10–5) and a fractional polynomial model (p FP=1.80x10–4) were both a better fit than a linear model. In sex-specific analyses, we found support for a non-linear relationship between BMI and type 2 diabetes only in men (p Quadratic and p FP <0.001). Nor was there evidence to suggest that BMI had a non-linear causal association with CKD in sex-stratified analyses (see Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
Plots showing the estimated shapes of the causal relationships between BMI and CMDs in combined and sex-specific analyses. Shape estimates are derived from the function of fractional polynomials based on the doubly ranked method that best fits the data. The solid black line represents the function curve, the blue band represents the 95% CI, the red dot represents the reference BMI of 25 kg/m2, and the dashed red line represents the null effect size. The plots have been cropped to depict estimated causal associations up to an OR of 3.0 for ease of comparison. HTN, hypertension; T2D, type 2 diabetes
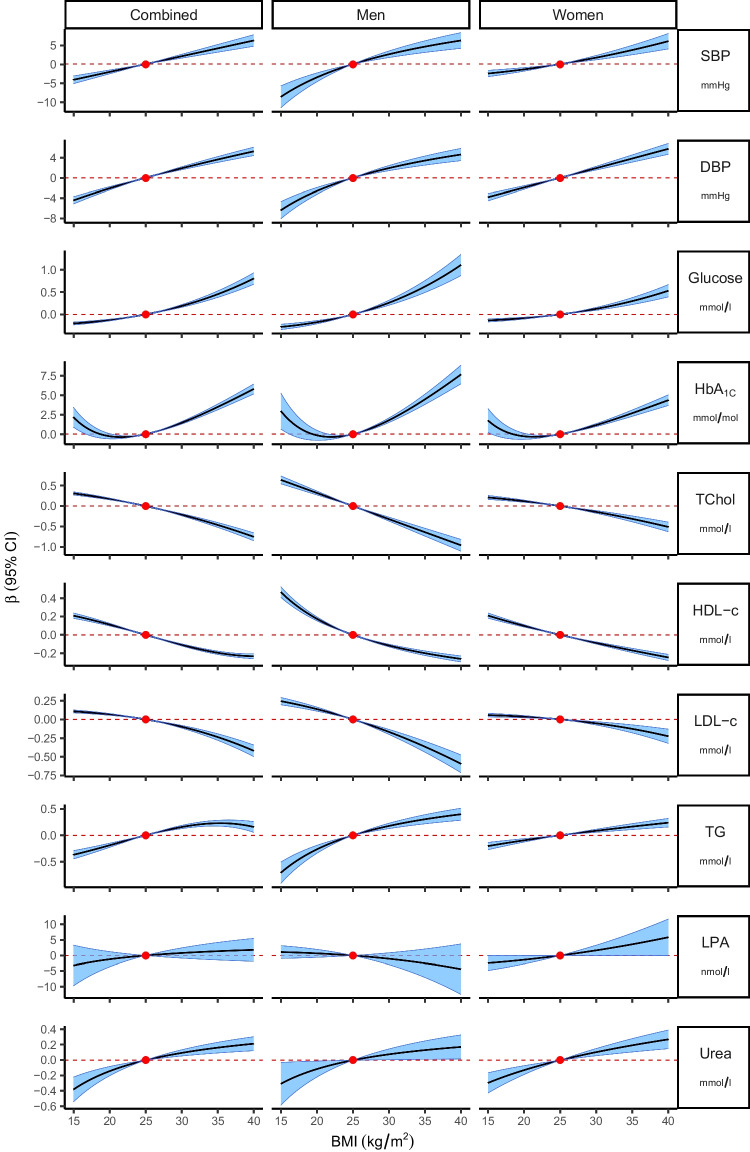
There was no statistically significant evidence to support a non-linear causal relationship between BMI and LPA, DBP, SBP and urea after correcting for multiple testing (p Bonferroni=0.001), but the results were significant for glycaemic and lipid biomarkers. When considering men and women separately, the data supported a non-linear causal association between BMI and HbA1c in each group; and a non-linear causal association between BMI and HDL-cholesterol and triacylglycerols only in men (see Table 4 and Fig. 3). The piecewise MR results were consistent with these results; however, interpretation of the plots can be difficult, especially at the tails of the effect estimate distribution, where the linear segments are unrestricted and thus extrapolate to the most extreme values (ESM Fig. 7).
Table 4.
Tests for shapes of causal relationships between BMI and cardiometabolic phenotypes derived from the residual and doubly ranked methods
| Outcome | Subset | p Q | p Quadratic | p FP | p FP degree | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Residual | Doubly ranked | Residual | Doubly ranked | Residual | Doubly ranked | Residual | Doubly ranked | ||
| CMDs | |||||||||
| CAD | Combined | 0.36 | 0.13 | 0.02 | 6.07×10–3 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.18 | 0.09 |
| Women | 0.00 | 0.13 | 0.28 | 0.04 | 0.43 | 0.29 | 0.44 | 0.11 | |
| Men | 0.44 | 0.59 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.11 | 0.83 | 0.92 | |
| T2D | Combined | 0.60 | 0.06 | 4.25×10–3 | 9.45×10–5 | 0.01 | 1.80×10–4 | 0.28 | 0.45 |
| Women | 0.02 | 0.75 | 0.08 | 0.22 | 0.17 | 0.20 | 0.10 | 0.93 | |
| Men | 0.73 | 8.80×10–4 | 0.02 | 5.47×10–6 | 0.05 | 5.53×10–5 | 0.21 | 0.03 | |
| HTN | Combined | 0.73 | 2.17×10–3 | 0.83 | 0.06 | 1.00 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.03 |
| Women | 0.03 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.82 | 0.08 | 1.00 | 0.20 | 0.27 | |
| Men | 0.21 | 0.41 | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.23 | 0.02 | 0.27 | 0.78 | |
| Stroke | Combined | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.79 | 0.92 | 0.74 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Women | 0.51 | 0.12 | 0.55 | 0.11 | 0.70 | 0.38 | 0.54 | 0.32 | |
| Men | 0.75 | 0.44 | 0.34 | 0.18 | 0.44 | 0.32 | 0.85 | 0.60 | |
| CKD | Combined | 0.51 | 0.64 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.44 | 0.61 | 0.26 | 0.70 |
| Women | 0.00 | 0.61 | 0.01 | 0.83 | 4.68×10–3 | 0.90 | 1.00 | 0.95 | |
| Men | 0.00 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.51 | 0.01 | 0.64 | 0.06 | 0.61 | |
| Stroke | Combined | 0.10 | 0.02 | 0.79 | 0.92 | 0.74 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| Women | 0.51 | 0.12 | 0.55 | 0.11 | 0.70 | 0.38 | 0.54 | 0.32 | |
| Men | 0.75 | 0.44 | 0.34 | 0.18 | 0.44 | 0.32 | 0.85 | 0.60 | |
| Biomarkers | |||||||||
| DBP | Combined | 0.24 | 0.17 | 3.33×10–3 | 0.21 | 9.12×10–3 | 0.30 | 0.38 | 0.32 |
| Women | 0.40 | 0.13 | 0.31 | 0.99 | 0.46 | 1.00 | 0.34 | 0.46 | |
| Men | 0.24 | 0.70 | 1.12×10–3 | 0.11 | 1.36×10–3 | 0.11 | 0.61 | 0.98 | |
| SBP | Combined | 0.48 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 0.93 | 0.04 | 1.00 | 0.97 | 0.60 |
| Women | 0.22 | 0.41 | 0.56 | 0.66 | 0.60 | 0.82 | 0.90 | 0.38 | |
| Men | 0.48 | 0.64 | 0.02 | 0.22 | 9.36×10–3 | 0.21 | 0.96 | 0.99 | |
| Glucose | Combined | 0.24 | 9.04×10–4 | 2.17×10–5 | 1.40×10–5 | 2.16×10–4 | 3.46×10–5 | 0.02 | 0.18 |
| Women | 0.67 | 0.48 | 0.22 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.03 | 0.82 | 0.81 | |
| Men | 0.39 | 1.31×10–5 | 1.32×10–3 | 2.17×10–4 | 2.34×10–3 | 9.05×10–4 | 0.01 | 0.06 | |
| HBA1c | Combined | 1.38×10–4 | 6.68×10–10 | 9.54×10–10 | 4.12×10–12 | 7.25×10–8 | 7.46×10–11 | 3.27×10–3 | 1.86×10–3 |
| Women | 0.00 | 2.79×10–3 | 3.11×10–4 | 5.27×10–5 | 9.13×10–4 | 1.31×10–4 | 0.33 | 0.02 | |
| Men | 0.04 | 1.45×10–6 | 3.69×10–7 | 1.54×10–7 | 2.77×10–5 | 1.82×10–6 | 0.01 | 0.03 | |
| Total cholesterol | Combined | 5.68×10–5 | 0.02 | 2.50×10–10 | 6.73×10–3 | 3.42×10–8 | 7.98×10–3 | 6.75×10–3 | 0.59 |
| Women | 0.23 | 0.18 | 3.47×10–5 | 0.10 | 1.55×10–3 | 0.11 | 0.02 | 0.86 | |
| Men | 0.01 | 0.03 | 4.95×10–5 | 0.50 | 1.86×10–4 | 1.00 | 0.09 | 0.14 | |
| HDL-c | Combined | 0.02 | 9.06×10–5 | 7.04×10–8 | 1.63×10–6 | 1.82×10–6 | 1.83×10–5 | 0.03 | 9.04×10–3 |
| Women | 0.19 | 0.37 | 1.62×10–4 | 0.10 | 2.31×10–3 | 0.15 | 0.01 | 0.46 | |
| Men | 0.02 | 0.04 | 2.45×10–5 | 1.07×10–4 | 3.02×10–5 | 2.08×10–4 | 0.62 | 0.52 | |
| LDL-c | Combined | 7.94×10–4 | 5.17×10–6 | 2.56×10–13 | 7.76×10–6 | 2.78×10–5 | 4.00×10–5 | 9.00×10–9 | 0.21 |
| Women | 0.11 | 0.02 | 1.91×10–6 | 1.90×10–3 | 9.09×10–3 | 0.01 | 2.64×10–4 | 0.07 | |
| Men | 0.09 | 0.05 | 4.41×10–6 | 0.05 | 2.85×10–3 | 0.07 | 4.52×10–3 | 0.29 | |
| TG | Combined | 2.61×10–5 | 1.04×10–5 | 2.36×10–9 | 8.82×10–7 | 4.07×10–5 | 1.44×10–4 | 8.76×10–8 | 2.54×10–4 |
| Women | 0.34 | 0.48 | 2.36×10–3 | 0.34 | 0.05 | 0.48 | 1.24×10–3 | 0.45 | |
| Men | 0.12 | 3.02×10–3 | 3.34×10–7 | 6.37×10–5 | 1.16×10–3 | 8.84×10–4 | 8.05×10–4 | 0.08 | |
| LPA | Combined | 0.74 | 0.57 | 0.07 | 0.50 | 0.47 | 0.59 | 0.97 | 0.90 |
| Women | 0.74 | 0.68 | 0.51 | 0.65 | 0.60 | 0.68 | 0.86 | 0.84 | |
| Men | 0.75 | 0.16 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.55 | 0.40 | 0.16 | 0.24 | |
| Urea | Combined | 0.48 | 0.30 | 3.33×10–3 | 0.06 | 2.28×10–3 | 0.05 | 0.50 | 0.63 |
| Women | 0.96 | 0.03 | 0.43 | 0.47 | 0.23 | 0.45 | 0.75 | 0.96 | |
| Men | 0.13 | 0.34 | 1.43×10–3 | 0.10 | 0.04 | 0.19 | 0.05 | 0.30 | |
HDL-c HDL-cholesterol, HTN hypertension, LDL-c LDL-cholesterol, T2D type 2 diabetes, TG triacylglycerol
Fig. 3.
Plots showing the estimated shapes of the causal relationships between BMI and selected cardiometabolic biomarkers in combined and sex-specific analyses. Shape estimates are derived from the function of fractional polynomials based on the doubly ranked method that best fits the data. The solid black line represents the function curve, the blue band represents the 95% CI, the red dot represents the reference BMI of 25 kg/m2, and the red dashed line represents the null effect size. HDL-c, HDL-cholesterol; LDL-c, LDL-cholesterol; TChol, total cholesterol; TG, triacylglycerol
Discussion
In this study, we investigated the shapes of causal relationships between BMI, CMDs and biomarkers of disease risk. We further investigated sex differences within the causal framework, and estimated the causal effect of BMI on each CMD studied. The estimates from combined analyses showed that BMI is significantly associated with type 2 diabetes, CAD and hypertension, but not CKD or stroke; it is also associated with all assessed biomarkers except LPA and urea levels after controlling for multiple testing. In men, BMI associations mirrored those of the unstratified analyses, but BMI was not causally associated with CAD, LDL-cholesterol or SBP in women. BMI was causally associated with increased odds of any CMD in both sex-combined and sex-stratified analyses, when assuming fixed effects. When assuming random effects, the association in women was no longer significant. Sex differences persisted for causal effects of BMI on LDL-cholesterol only (with threefold attenuation of effect towards the null in women) after correcting for multiple testing. In investigations of non-linearity, after triangulation, the data support non-linear causal relationships between BMI and blood glucose levels, HbA1c and all tested lipid fractions. In sex-stratified analyses, triangulated evidence supported a non-linear association between BMI and type 2 diabetes, glucose, HDL-cholesterol and triacylglycerols only in men.
Causal associations between excess adiposity and cardiometabolic health have been reported previously, with results that are largely consistent with ours [13, 14, 31]. In our analysis, BMI was inversely associated with all cholesterol types and directly associated with triacylglycerol levels. This may reflect dyslipidaemic obesity, characterised by high levels of triacylglycerols and NEFAs, decreased HDL-cholesterol with HDL dysfunction (a shift towards proinflammation and altered reverse cholesterol transport), and normal or slightly increased LDL-cholesterol, attributed to altered metabolism favouring hypertriglyceridaemia [32]. One study assessed sex differences for causal effects of BMI in leading causes of death including cardiometabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, CAD and stroke [15]. In that study, BMI was causally related to the three diseases in men and women; the relationship with type 2 diabetes, but not CAD or stroke, varied by sex. In our study, BMI was not associated with stroke, and sex differences in type 2 diabetes were not replicated; the inconsistent findings between these studies may reflect our decision not to use sex-specific SNP effect estimates.
We found that BMI was associated with CAD in men but not all women. While some reasons for such findings may include weak instruments or violations of MR assumptions (conditional restriction), the ‘weak instrument test’ was not suggestive of weak instruments in our case (statistic=3015.08, p<2×10−16), and the Durbin–Wu–Hausman test supported the instrumental variable analysis as more consistent (p=1.04×10−6) than the ordinary least-squares regression. It is possible that a BMI PRS that is weighted using effect sizes from combined GWASs may not fully capture general adiposity in women, or that general adiposity itself is a poor predictor of CAD in all women. However, when women were grouped by menopause status, BMI was found to be significantly associated with CAD in premenopausal women only. This possibly points to detrimental effects of excess adiposity, which nullify the ‘protective effects’ of sex hormones [33]. In this cohort, premenopausal women with obesity had more than twice the prevalence of CAD compared with their non-obese counterparts (ESM Table 10). The null association observed in postmenopausal women may reflect dampened effects of general adiposity (or the presence of other competing/stronger risk factors) on CAD risk in this group. In two prospective studies of postmenopausal women, central or truncal obesity was associated with CAD/cardiovascular disease risk, but not general adiposity [34, 35]. We did not investigate different adiposity phenotypes, and the relationship between such phenotypes and CAD warrants further investigation within a causal framework.
Sexual dimorphism in lipid metabolism and the pathophysiology of CMDs is well-established [36–38]. For example, obesity tends to peak about 10 years earlier in men (50–54 years) compared with women (60–64 years). Even at the same BMI and age or fitness levels, men have a worse cardiometabolic health profile despite women having higher fat mass and lower skeletal muscle mass [9, 36, 38, 39]. Women tend to store excess lipids in subcutaneous adipose tissue (which is considered to be protective against CMDs), especially in the gluteal–femoral region, while in men excess fat is more centrally distributed in the visceral adipose tissue (which increases risk of CMDs). These differences are diminished when perturbations in oestrogen levels occur, as in the menopause (low levels) or when taking oral contraceptives (supraphysiological levels) [38, 40].
While the observed sex differences do not stand after correcting for multiple testing, except for LDL-cholesterol, they are worth considering given the documented role of sexual dimorphism in energy homeostasis and cardiometabolic health. Further, despite mixed results from studies, sexual dimorphism may have implications for weight loss interventions in men and women with different levels of metabolic health [41–45]. Complications during pregnancy, such as gestational diabetes and pre-eclampsia, confer additional risk for CMDs in women. Furthermore, from our results, excess adiposity appears to be detrimental to women both pre- and post menopause, while men have a higher burden of CMD at an earlier age compared with women of similar BMI. Such differences may have clinical implications. For men, screening for CMD at an earlier age and at a lower BMI threshold could identify people predisposed to CMD earlier, who would benefit from timely interventions. In women, targeted screening for CMD should take into consideration obesity in premenopausal women.
Non-linear MR has been previously used to assess causal relationships (e.g., the effect of alcohol on cardiovascular disease [46] or BMI on socioeconomic status [47]), but there is a dearth of literature on the nature of the causal effects of BMI on cardiometabolic health between the sexes. In one study focused on CKD, BMI was found to be causally associated with CKD using summary data MR, with evidence of non-linearity in the UK Biobank using the residual method [48]. We found no such association in our analyses using the doubly ranked method. This may be partly explained by our selection of CKD cases, which was more detailed than the previous study (ESM Table 1). Determining the shapes of causal associations may help estimate the relative benefits of interventions at different levels of exposure. For instance, lowering BMI from 40 to 25 kg/m2 would result in an approximately twofold decrease in the causal risk of type 2 diabetes (Fig. 2). Use of causal estimates could therefore provide a powerful tool for public health decision-making.
Causal inference studies using MR attempt to give an unbiased estimate of a causal effect of a given exposure on an outcome of interest, provided that the assumptions of MR are not violated, and the instruments explain sufficient variance in the exposures and/or outcomes of interest. To mitigate potential bias, we specifically used SNPs generated from GWASs that did not overlap with the UK Biobank, as the latter dataset was used in our primary analyses. We also performed sensitivity analyses to assess whether the results would change, and chose SNPs unrelated to each specific outcome to mitigate chances of horizontal pleiotropy. Although other problems of MR, such as canalisation, cannot be formally assessed, we believe that the estimates provided in this study offer a glimpse into the differences in causal effects of BMI on CMD between men and women, supporting further investigation.
Strengths
In this study, we used MR, which offers a powerful alternative to assess causal relationships between exposures and outcomes of interest [49]. Conventional MR methods assume a linear relationship to estimate the population-averaged causal effect; however, we tested those linear assumptions to offer better insights for formulating public health policies and interventions [50]. Further, we used both residual and doubly-ranked non-linear MR and piece-wise linear MR to triangulate the evidence. We also had the advantage of a large sample size from the UK Biobank.
Weaknesses
We used BMI as our sole measure of adiposity. BMI does not account for differential adiposity, nor is it a reliable measure of relative adiposity across different populations or ethnicities, making it hard to generalise the findings. However, BMI has been shown to be a reliable population-level measure for assessing general adiposity. MR faces challenges of horizontal pleiotropy and canalisation. While there is no formal method to test the latter, we selected BMI SNPs that were not associated with each respective outcome assessed, hence reducing the chances of horizontal pleiotropy. We also could not rule out methodological limitations, in that there may be other shapes, unavailable to us, that better fit these data. The field of MR is evolving quickly, and it may be that analyses need to be updated if and when there are fundamental changes in state-of-the-art in MR methods.
Conclusion
In this analysis, BMI was found to be causally associated with increased risk of type 2 diabetes, CAD and hypertension, but not stroke or CKD, and was also associated with variation in disease-risk biomarkers, except LPA and urea. Further, BMI was causally associated with any CMD when considering fixed effects, in combined and sex-stratified analyses. We found evidence in support of a non-linear causal relationship between BMI and glycaemic and lipid biomarkers, except LPA. The adverse consequences of BMI on CAD risk are similar in men and premenopausal women. However, although BMI continues to confer increased CAD risk in men, it seems to be no longer a strong risk factor in postmenopausal women. These results further our understanding of the complex nature of the causal relationships between BMI and CMD. It also highlights the role of sex in CAD and lipid and glucose homeostasis in the context of causal risk conferred by excess adiposity, and underscores the need for consideration of sex in the management of excess adiposity. Finally, reducing excess adiposity remains highly beneficial in improving energy and lipid metabolism, as well as reducing the risk of CMD.
Supplementary Information
(PDF 846 kb)
Acknowledgments
Authors’ relationships and activities
PWF is currently Director of Translational Medicine at the Novo Nordisk Foundation, Copenhagen, Denmark. The authors declare that there are no relationships or activities that might bias, or be perceived to bias, their work.
Contribution statement
PMM and PWF were responsible for the conception and design of the study, and data interpretation; PMM analysed the data and drafted the manuscript. JFT, NT and DC prepared the data. PWF, JFT, NT, DC, GNG, NA-P, HP-M and HF interpreted the data and critically revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version. PMM, PWF and NG are guarantors of this work.
Abbreviations
- 2SLS
Two-stage least-squares
- 2SRI
Two-stage residual inclusion
- CAD
Coronary artery disease
- CKD
Chronic kidney disease
- CMD
Cardiometabolic disease
- DBP
Diastolic blood pressure
- GWAS
Genome-wide association study
- LACE
Local average causal effect
- LPA
Lipoprotein A
- MR
Mendelian randomisation
- PRS
Polygenic risk score
- SBP
Systolic blood pressure
Funding
Open access funding provided by Lund University. This manuscript is part of the Stratification of Obesity Phenotypes to Optimize Future Obesity Therapy (SOPHIA) project. SOPHIA has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking under grant agreement number 875534. This Joint Undertaking receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program, EFPIA and T1D Exchange, the JDRF and the Obesity Action Coalition. Further funding was provided by the European Commission (ERC-2015-CoG–681742 NASCENT), the Swedish Research Council (Distinguished Young Researcher Award) and the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research (LUDC-IRC, 15-0067).
Data availability
Individual-level data used in this study is available upon application to the UK Biobank. GWAS data used to compute polygenic risk scores are available at https://portals.broadinstitute.org/collaboration/giant/index.php/GIANT_consortium_data_files#GWAS_Anthropometric_2014_Height_Summary_Statistics
Footnotes
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Change history
2/20/2024
Editor’s note: Readers are alerted that the authors have discovered a problem with a previously published statistical method used in this study and are currently reanalysing their data. Appropriate editorial action will be taken once the reanalysis has been completed.
Change history
7/1/2024
A Correction to this paper has been published: 10.1007/s00125-024-06168-7
References
- 1.Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO et al (2020) Global burden of cardiovascular diseases and risk factors, 1990–2019: update from the GBD 2019 study. J Am Coll Cardiol 76(25):2982–3021. 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.11.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bommer C, Sagalova V, Heesemann E et al (2018) Global economic burden of diabetes in adults: projections from 2015 to 2030. Diabetes Care 41(5):963. 10.2337/dc17-1962 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.American Heart Association (2017) Cardiovascular disease: a costly burden for america projections through 2035. AHA, Washington, DC
- 4.WHO (2021) The top 10 causes of death. Available from https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death. Accessed 8 November 2021
- 5.Sun YQ, Burgess S, Staley JR et al (2019) Body mass index and all cause mortality in HUNT and UK Biobank studies: linear and non-linear mendelian randomisation analyses. BMJ 364:l1042. 10.1136/bmj.l1042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kivimäki M, Kuosma E, Ferrie JE et al (2017) Overweight, obesity, and risk of cardiometabolic multimorbidity: pooled analysis of individual-level data for 120 813 adults from 16 cohort studies from the USA and Europe. Lancet Public Health 2(6):e277–e285. 10.1016/S2468-2667(17)30074-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Blüher M (2019) Obesity: global epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Endocrinol 15(5):288–298. 10.1038/s41574-019-0176-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Berrington de Gonzalez A, Hartge P, Cerhan JR et al (2010) Body-mass index and mortality among 1.46 million white adults. N Engl J Med 363(23):2211–2219. 10.1056/NEJMoa1000367 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.GBD 2015 Obesity Collaborators, Afshin A, Forouzanfar MH et al, (2017) Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N Engl J Med 377(1):13–27. 10.1056/NEJMoa1614362 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Bhaskaran K, Dos-Santos-Silva I, Leon DA, Douglas IJ, Smeeth L (2018) Association of BMI with overall and cause-specific mortality: a population-based cohort study of 3.6 million adults in the UK. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 6(12):944–953. 10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30288-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Fraser A, Lawlor DA, Howe LD (2016) Nonlinear exposure-outcome associations and public health policy. JAMA 315(12):1286–1287. 10.1001/jama.2015.18023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fall T, Hägg S, Mägi R et al (2013) The role of adiposity in cardiometabolic traits: a Mendelian randomization analysis. PLoS Med 10(6):e1001474. 10.1371/journal.pmed.1001474 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Emdin CA, Khera AV, Natarajan P et al (2017) Genetic association of waist-to-hip ratio with cardiometabolic traits, type 2 diabetes, and coronary heart disease. JAMA 317(6):626–634. 10.1001/jama.2016.21042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dale CE, Fatemifar G, Palmer TM et al (2017) Causal associations of adiposity and body fat distribution with coronary heart disease, stroke subtypes, and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a mendelian randomization analysis. Circulation 135(24):2373–2388. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.026560 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Censin JC, Peters SAE, Bovijn J et al (2019) Causal relationships between obesity and the leading causes of death in women and men. PLoS Genet 15(10):e1008405. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008405 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Motiejūnaitė J, Akiyama E, Cohen-Solal A et al (2020) The association of long-term outcome and biological sex in patients with acute heart failure from different geographic regions. Eur Heart J 41(13):1357–1364. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa071 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lew J, Sanghavi M, Ayers CR et al (2017) Sex-based differences in cardiometabolic biomarkers. Circulation 135(6):544–555. 10.1161/circulationaha.116.023005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gerdts E, Regitz-Zagrosek V (2019) Sex differences in cardiometabolic disorders. Nat Med 25(11):1657–1666. 10.1038/s41591-019-0643-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Faulkner JL, Belin de Chantemèle EJ (2019) Sex hormones, aging and cardiometabolic syndrome. Biol Sex Differ 10(1):30. 10.1186/s13293-019-0246-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chokshi DA, El-Sayed AM, Stine NW (2015) J-shaped curves and public health. JAMA 314(13):1339–1340. 10.1001/jama.2015.9566 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.UK Biobank (2021) UK Biobank research ethics approval Available from https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/learn-more-about-uk-biobank/about-us/ethics. Accessed 12 November 2021
- 22.Bycroft C, Freeman C, Petkova D et al (2018) The UK biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 562(7726):203–209. 10.1038/s41586-018-0579-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tobin MD, Sheehan NA, Scurrah KJ, Burton PR (2005) Adjusting for treatment effects in studies of quantitative traits: antihypertensive therapy and systolic blood pressure. Stat Med 24(19):2911–2935. 10.1002/sim.2165 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Locke AE, Kahali B, Berndt SI et al (2015) Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature 518(7538):197–206. 10.1038/nature14177 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Choi SW, O'Reilly PF (2019) PRSice-2: polygenic risk score software for biobank-scale data. GigaScience 8(7):giz082. 10.1093/gigascience/giz082 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Burgess S, Small DS, Thompson SG (2017) A review of instrumental variable estimators for Mendelian randomization. Stat Methods Med Res 26(5):2333–2355. 10.1177/0962280215597579 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Staley JR, Burgess S (2017) Semiparametric methods for estimation of a nonlinear exposure-outcome relationship using instrumental variables with application to Mendelian randomization. Genet Epidemiol 41(4):341–352. 10.1002/gepi.22041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tian H, Mason AM, Liu C, Burgess S (2023) Relaxing parametric assumptions for non-linear Mendelian randomization using a doubly-ranked stratification method. PLOS Genet 19:e1010823 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Tukey JW (1977) Exploratory data analysis. Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Reading, Mass [Google Scholar]
- 30.Naimi AI, Cole SR, Kennedy EH (2016) An introduction to g methods. Int J Epidemiol 46(2):756–762. 10.1093/ije/dyw323 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Riaz H, Khan MS, Siddiqi TJ et al (2018) Association between obesity and cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of mendelian randomization studies. JAMA Netw Open 1(7):e183788. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.3788 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Klop B, Elte JWF, Cabezas MC (2013) Dyslipidemia in obesity: mechanisms and potential targets. Nutrients 5(4):1218–1240. 10.3390/nu5041218 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Manrique-Acevedo C, Chinnakotla B, Padilla J, Martinez-Lemus LA, Gozal D (2020) Obesity and cardiovascular disease in women. Int J Obes 44(6):1210–1226. 10.1038/s41366-020-0548-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Cho JH, Kim HL, Kim MA et al (2019) Association between obesity type and obstructive coronary artery disease in stable symptomatic postmenopausal women: data from the KoRean wOmen'S chest pain rEgistry (KoROSE). Menopause 26(11):1272–1276. 10.1097/gme.0000000000001392 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chen GC, Arthur R, Iyengar NM et al (2019) Association between regional body fat and cardiovascular disease risk among postmenopausal women with normal body mass index. Eur Heart J 40(34):2849–2855. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz391 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mauvais-Jarvis F (2015) Sex differences in metabolic homeostasis, diabetes, and obesity. Biol Sex Differ 6(1):14. 10.1186/s13293-015-0033-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Koutsari C, Basu R, Rizza RA, Nair KS, Khosla S, Jensen MD (2011) Nonoxidative free fatty acid disposal is greater in young women than men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96(2):541–547. 10.1210/jc.2010-1651 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Goossens GH, Jocken JWE, Blaak EE (2021) Sexual dimorphism in cardiometabolic health: the role of adipose tissue, muscle and liver. Nat Rev Endocrinol 17(1):47–66. 10.1038/s41574-020-00431-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Schorr M, Dichtel LE, Gerweck AV et al (2018) Sex differences in body composition and association with cardiometabolic risk. Biol Sex Differ 9(1):28. 10.1186/s13293-018-0189-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lumish HS, O’Reilly M, Reilly MP (2020) Sex differences in genomic drivers of adipose distribution and related cardiometabolic disorders. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 40(1):45–60. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313154 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Williams RL, Wood LG, Collins CE, Callister R (2015) Effectiveness of weight loss interventions--is there a difference between men and women: a systematic review. Obes Rev 16(2):171–186. 10.1111/obr.12241 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mongraw-Chaffin ML, Peters SAE, Huxley RR, Woodward M (2015) The sex-specific association between BMI and coronary heart disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 95 cohorts with 1·2 million participants. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 3(6):437–449. 10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00086-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Gasteyger C, Larsen TM, Vercruysse F, Pedersen D, Toubro S, Astrup A (2009) Visceral fat loss induced by a low-calorie diet: a direct comparison between women and men. Diabetes Obes Metab 11(6):596–602. 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2008.01025.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cooper AJ, Gupta SR, Moustafa AF, Chao AM (2021) Sex/gender differences in obesity prevalence, comorbidities, and treatment. Curr Obes Rep 10(4):458–466. 10.1007/s13679-021-00453-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Christensen P, Meinert Larsen T, Westerterp-Plantenga M et al (2018) Men and women respond differently to rapid weight loss: Metabolic outcomes of a multi-centre intervention study after a low-energy diet in 2500 overweight, individuals with pre-diabetes (PREVIEW). Diabetes Obes Metab 20(12):2840–2851. 10.1111/dom.13466 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Silverwood RJ, Holmes MV, Dale CE et al (2014) Testing for non-linear causal effects using a binary genotype in a Mendelian randomization study: application to alcohol and cardiovascular traits. Int J Epidemiol 43(6):1781–1790. 10.1093/ije/dyu187 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Howe LD, Kanayalal R, Harrison S et al (2020) Effects of body mass index on relationship status, social contact and socio-economic position: Mendelian randomization and within-sibling study in UK Biobank. Int J Epidemiol 49(4):1173–1184. 10.1093/ije/dyz240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zheng J, Zhang Y, Rasheed H et al (2021) Trans-ethnic Mendelian-randomization study reveals causal relationships between cardiometabolic factors and chronic kidney disease. Int J Epidemiol. 10.1093/ije/dyab203 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 49.Didelez V, Sheehan N (2007) Mendelian randomization as an instrumental variable approach to causal inference. Stat Methods Med Res 16(4):309–330. 10.1177/0962280206077743 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Burgess S, Davies NM, Thompson SG, Consortium EP-I (2014) Instrumental variable analysis with a nonlinear exposure-outcome relationship. Epidemiology 25(6):877–885. 10.1097/EDE.0000000000000161 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(PDF 846 kb)
Data Availability Statement
Individual-level data used in this study is available upon application to the UK Biobank. GWAS data used to compute polygenic risk scores are available at https://portals.broadinstitute.org/collaboration/giant/index.php/GIANT_consortium_data_files#GWAS_Anthropometric_2014_Height_Summary_Statistics