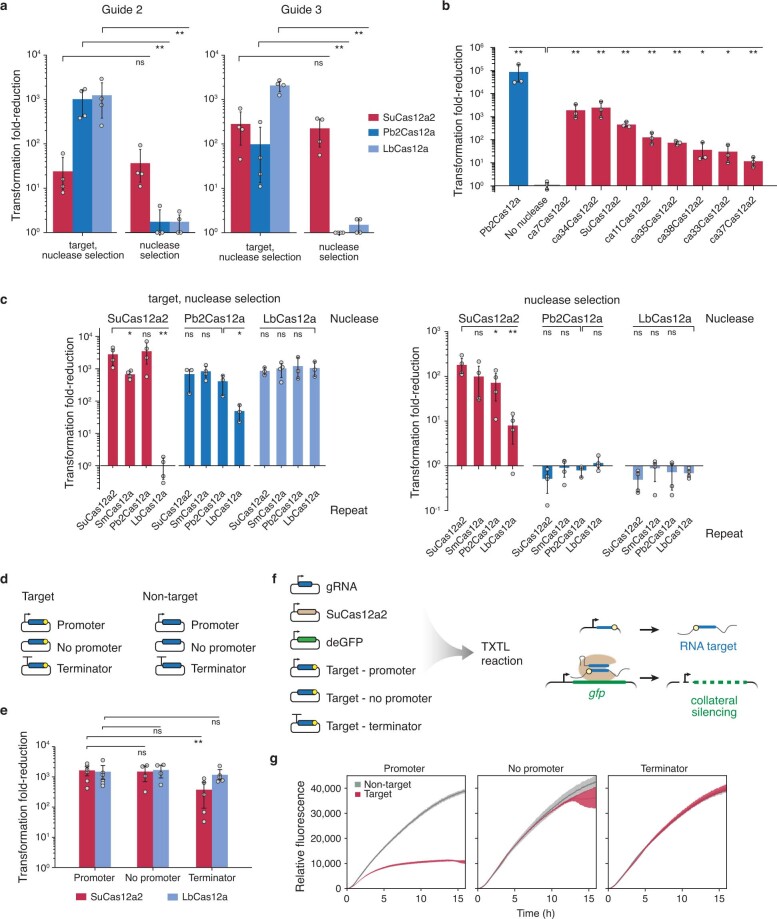
Extended Data Fig. 2. Cas12a2 can utilize Cas12a crRNA repeats and requires an RNA target in vivo.
a, Different guide:target pairs tested under antibiotic selection of the nuclease and target plasmids or only the nuclease plasmid. b, Reduction in plasmid transformation by Cas12a2 orthologues tested under antibiotic selection of the nuclease and target plasmids. c, Effect of swapping direct repeats associated with SuCas12a2 and Cas12a nucleases on plasmid transformation. The indicated nuclease, repeat-encoding crRNA, and target were subjected to the traditional (left) and modified (right) plasmid interference assay in E. coli. d, Diagram of the target and non-target plasmids used in the plasmid clearance assay shown in e. e, Impact of a promoter and a terminator upstream of the target site on plasmid clearance by SuCas12s2 and LbCas12a. f, Diagram of the cell-free TXTL reactions used to evaluate the impact of target expression on Cas12a2 collateral silencing shown in g. g, The effect of collateral silencing by SuCas12a2 in TXTL as a function of having a promoter, no promoter, or terminator upstream of the target expression site. Scatter plots represent averages of 4 technical replicates ± s.d. Unless stated otherwise, values are means ± s.d. of at least 3 independent experiments started from separate colonies. ns: p > 0.05, *: p < 0.05, **: p < 0.005 calculated with one-tailed Welch’s t-test.