Figure 1.
Study overview and establishment of serological pipeline
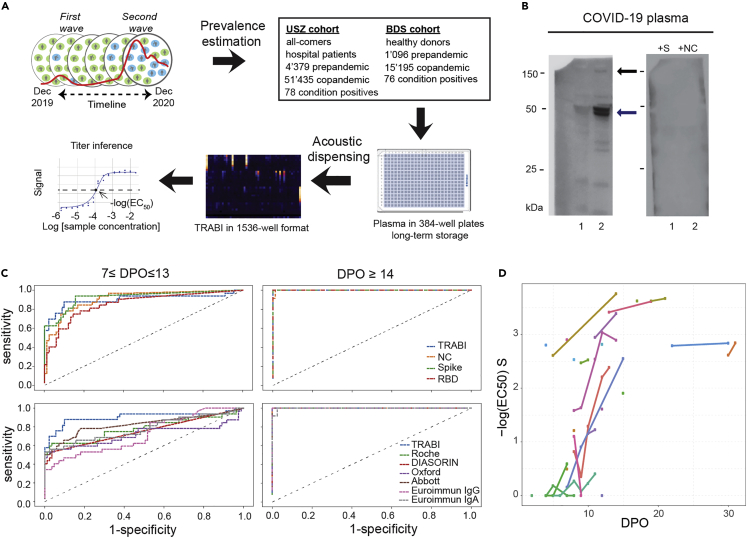
(A) To estimate the prevalence of CoV2 seropositivity in the population, prepandemic, and copandemic samples from two independent cohorts were analyzed by high-throughput microELISA (TRABI). IgG titers against S, RBD, and NC were determined and the -log(EC50) was inferred by regression analysis.
(B) Vero cells infected with CoV2 (lane 2), but not uninfected cells (lane 1), showed signals corresponding to S (black arrow) and NC (blue arrow, pointing at two bands) when immunoblotted with COVID-19 patient plasma. NC protein undergoes a proteolytic cleavage in SARS-CoV-infected VeroE6 cells, resulting in two distinct bands of around 46 and 43 kDa. We confirmed the identity of the two bands by probing with an anti-NC antibody (Sino Biologicals, data not shown). Spiking of COVID-19 patient plasma with recombinant S and NC led to the disappearance of all signals.
(C) Upper panel: Using 53 samples from confirmed patients with CoV2 and 83 prepandemic samples, we assessed the specificity-sensitivity relationship for all antigens individually and after combining all results into a single score (TRABI) using QDA-based posterior probability. Between 7 and 13 dpo, approximately 60% of samples were positive (posterior probability >0.5) at 100% specificity cutoff, whereas 100% sensitivity was reached at 14 dpo. Lower panel: COVID and prepandemic samples were used to assess the performance of TRABI, commercial tests (Roche, DiaSorin, Abbott, Euroimmun), and an assay developed at the Target Discovery Institute (Oxford). While all tests scored equally at ≥14 dpo, TRABI outperformed all other assays at ≤13 dpo.
(D) Time course of IgG response in 55 samples from 27 patients with COVID-19. IgG antibodies were reliably detectable at ≥13 dpo. Colors represent individual patients.