Abstract
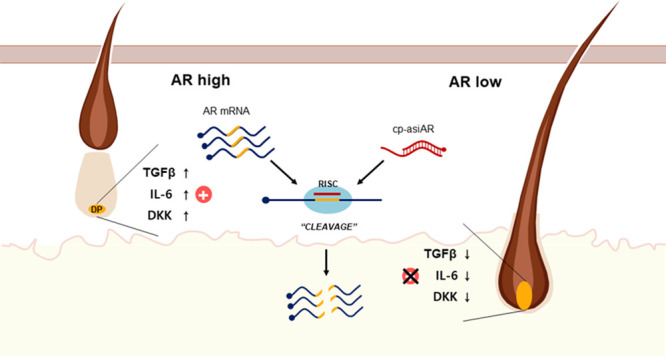
Asymmetric small interfering RNAs (asiRNAs) that mediate RNA interference have been investigated for therapeutic use in various tissues, including skin tissue. Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is caused by a combination of genetic factors, resulting in sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which binds to the androgen receptor (AR) to mediate a series of biomolecular changes leading to hair loss. This study aimed to evaluate the therapeutic potential of a cell-penetrating, AR-targeting asiRNA (cp-asiAR) for AGA treatment, which was designed to silence the AR gene. AGA mouse models were developed by stimulation with DHT, and ex vivo human scalp tissues were also used for analysis. Cp-asiAR-mediated changes in mRNA expression and protein levels of AR were assessed along with the examination of phenotypic improvements in mouse model of AGA. We also assessed downstream signaling associated with AR in primary human dermal papilla (DP) cells. Several cp-asiARs were screened for selecting the optimal sequence of AR using cell lines in vitro. A cholesterol-conjugated, chemically modified cp-asiAR candidate was optimized under passive uptake conditions in vitro. Intradermal cp-asiAR injection efficiently reduced mRNA and protein levels corresponding to AR in mouse models. Moreover, cp-asiAR injection promoted hair growth in mouse models with DHT-induced AGA. In ex vivo human hair follicle culture, the proportion of telogen hair decreased, and the mean hair bulb diameter increased in the cp-asiAR-treated group. In isolated primary human DP cells, AR expression was effectively downregulated by cp-asiAR. Furthermore, cp-asiAR attenuated DHT-mediated increases in interleukin-6, transforming growth factor-β1, and dickkopf-1 levels. No significant toxicity was observed in DP cells after cp-asiAR treatment. Cp-asiAR treatment showed effective downregulation of AR expression and prevention of DHT-mediated alterations in the hair cycle and hair diameter, indicating its potential as a novel therapeutic option for AGA.
Keywords: siRNA, androgenetic alopecia, androgen receptor, dihydrotestosterone, hair follicle, dermal papilla
1. Introduction
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological phenomenon in which a target gene is selectively silenced via sequence-specific gene suppression. RNAi is mediated by intracellular delivery of small interfering RNA (siRNA) that contains nucleotide sequences complementary to the target messenger RNA (mRNA). The binding of siRNA leads to cleavage and subsequent degradation of mRNA, and both processes are mediated by the cellular RNAi machinery. This highly specific method of gene silencing represents a potential target for the treatment of a wide range of medical conditions.1
Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is the most common form of hair loss in both men and women. Although the exact pathophysiology of AGA remains unknown, the key molecular process in the development of AGA involves the binding of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) to the androgen receptor (AR) present on the dermal papilla (DP) cells of genetically susceptible individuals. Because 5α-reductase is responsible for the conversion of free testosterone to DHT, systemic 5α-reductase inhibitors have long been used to treat AGA and are currently considered the standard treatment for AGA. However, orally administered 5α-reductase inhibitors demonstrate an increased risk of systemic adverse effects. Although these 5α-reductase inhibitors are generally well tolerated, patients with AGA are often reluctant to consume 5α-reductase inhibitors, owing to the distress associated with the possible adverse effects, such as sexual dysfunction and gynecomastia.2 Moreover, treatment of female AGA is complicated by the lack of indication for use of systemic 5α-reductase inhibitors in women. Therefore, there is substantial demands for a novel drug with a lower risk of systemic side effects to treat AGA. Minoxidil is currently the only FDA-approved topical agent for AGA. Although sufficient data are available supporting the clinical efficacy of topical minoxidil, its efficacy as monotherapy is seldom satisfactory in real world. Furthermore, minoxidil’s mechanism of action has not been fully elucidated, and whether minoxidil directly acts on the DHT- and AR-driven pathological mechanism of AGA remains unknown. Hence, novel therapeutic agents that affect AGA-induced alterations in hair biology are being extensively examined.
Theoretically, selective blockade of AR expression in the hair follicles could be a promising strategy for the treatment of AGA. Because this could be possible with the use of RNAi technology and considering that a siRNA structure called asymmetric siRNA (asiRNA) can significantly reduce the nonspecific effects observed with conventional siRNAs, we developed a cell-penetrating, AR-targeting asiRNA (cp-asiAR).3 In this study, we evaluated the therapeutic potential of cp-asiAR for AGA, which was designed specifically to silence AR gene expression in the hair follicle.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. In Vitro Validation of cp-asiRNA in T98G Cells
T98G cells were cultured at a density of 25,000 cells/well in 24 well plates. Cp-asiAR and nontargeting control (NTC; cp-asiRNA-targeting non-AR mRNA) were manufactured by OliX US, Inc. and dissolved in PBS (>1 mg/mL) for treatment. In the passive uptake experiment, the existing medium was replaced by a cp-asiAR-containing medium. After 24 h incubation with cp-asiAR, total RNA isolation, reverse transcription, and qPCR were performed as described in the quantitative polymerase chain reaction section below. Total protein was isolated for western blotting analysis after 48 h. Statistical significance was calculated using a t-test. In the siRNA sequence screening experiments, RNAiMAX was used for the transfection study following the manufacturer’s instruction (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA).
2.2. Cell Viability
Hair follicle dermal papilla cells (HFDPC) were obtained from Cell Applications (602t-05a) and cultivated in HFDPC Growth Medium (611-500; Cell Applications, CA) at 37 °C in a humidified incubator containing 5% CO2. All HFDPCs from the second to sixth passages of subcultures were used for the experiments. HFDPCs were seeded in a 6-well plate and then cultivated at 37 °C in a humidified incubator containing 5% CO2. After incubation overnight, the medium was replaced with Follicle Dermal Papilla Cell Basal medium (C-26500; PromoCell, Germany). After 24 h of culture, the cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of cp-asiAR. Next, 100 μL of EZ-Cytox (EZ-3000; DoGen, Korea) was added to each well, followed by incubation for 30 min at 37 °C. The samples were quantified by measuring optical density at 450 nm using an ELISA reader.
2.3. Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
Total RNA was extracted using the Blood/Cultured Cell Total RNA Mini Kit (FABRK001; Favorgen, Austria) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The RNA sample was then used for cDNA synthesis using RT&GO (RTRAG100; MPbio, Korea) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Next, qPCR amplification was performed using the LightCycler 480 Real-Time PCR system (Roche, Switzerland); all samples were run in triplicates. The qPCR thermal cycling setting was as follows: initial denaturation was performed at 95 °C for 10 min, followed by 45 cycles of amplification at 95 °C for 10 s, 60 °C for 10 s, and 72 °C for 10 s. Melting curve analysis was carried out using a standard program at 95 °C for 5 s, cooling to 65 °C for 1 min, followed by heating to 97 °C with five acquisitions per degree increase. The specific primer sets used for each gene were as follows:
Human AR (F: GGGGCTAGACTGCTCAACTG, R: GCCAAGTTTTGGCTGAAGAG).
Human GAPDH (F: GTTGTCATGGATGACCTTGG, R: CCCATCACCATCTTCCAGGA).
Human TUBA (F: GACCAAGCGTACCATCCA, R: CACGTTTGGCATACATCAGG).
Mouse AR (F: AGCCCATCTATTTCCACACAC, R: GAGGAATTTCCCCCAAGGCA).
Mouse RPL32 (F: CTGCCATCTGTTTTACGGCA, R: ATCAGGATCTGGCCCTTGAAC).
2.4. Western Blotting Analysis
Cells were lysed in RIPA buffer (EBA-1149; Elpis Biotech, Korea) supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (complete Mini, 11852700; Roche). Mouse skin biopsies were homogenized in RIPA buffer (R0278; Sigma-Aldrich, MO) supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (11836153001, Roche). Proteins in whole-cell lysates were resolved using sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. Subsequently, the membranes were probed with primary antibodies against AR (Sc7305; Santa Cruz, TX, or Ab133273; Abcam, UK), β-catenin (C9562; Cell Signaling, MA, USA), DKK-1 (Sc374574; Santa Cruz), IL-6 (ab6672; Abcam), TGF- β1 (Ab92486; Abcam), and β-actin (A5441; Sigma-Aldrich or Sc47778; Santa Cruz), followed by incubation with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (SeraCare, Milford, MA). Enhanced chemiluminescence was performed using ECL solution (SuperSignal West Pico Plus chemiluminescent substrate; Thermo Fisher Scientific).
2.5. Isolation and Culture of Human Hair Follicle Samples
After approval by the Institutional Review Board of Asan Medical Center (2020-0233), specimens were collected from the transitional zone of balding from the balding or nonbalding occipital scalps of twelve males and one female undergoing surgical excision of benign cutaneous tumors. Volunteers aged between 24 and 61 years were recruited. The Institutional Review Board at Asan medical center approved all of the procedures used in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from all volunteers. Tissue samples containing more than 80 hair follicles were cautiously dissected into single hair follicles (the anagen stage). Dissected hair follicles were cut individually into small pieces of approximately 2.5 mm in length from the bottom of the DP and then treated with the indicated concentration of reagents in Williams’ Medium E (W1878; Sigma-Aldrich) containing 1× antibiotic-antimycotic (15240062; Gibco, MA). They were incubated for 6 days at 37 °C in a humidified 5% CO2 incubator. Thereafter, the medium was refreshed 3 days after incubation.
2.6. Measurement of Human Hair Follicle Length and Diameter
On day 3 and 6 of incubation, the hair follicle length and diameter were measured. Photomicrographs of hair follicles were captured under a microscope (SMZ800N; Nikon, Japan), and the hair length and hair follicle diameter were analyzed using the HKBasic 3.7 software (Koptic, Korea).
2.7. In Vivo Efficacy of cp-asiAR in an AGA Mouse Model
To test AR knockdown, mice (n = 5 for each group) were injected with the indicated doses of cp-asiAR (0.125, 0.25, and 0.5 mg) via the dorsal back. For comparison, phosphate-buffered saline was used as a vehicle. All injection sites were 2 cm apart from each other to avoid interference. The skin was sampled using an 8 mm biopsy punch on the day of preparation. To test hair regrowth efficacy, mouse hair was shaved using a small animal clipper and they were subsequently treated with hair removal cream for one day (Day 0) before cp-asiAR injection. DHT was subcutaneously injected daily at a dose of 25 mg/kg during the experiment to mimic androgenetic hair loss condition. Cp-asiAR was injected on days 1, 8, and 15 at three sites on the mouse dorsal back. Flutamide, a known inhibitor of AR, was used as a reference and was subcutaneously injected daily at 100 mg/kg. The dorsal back of the mice was imaged every week to assess hair regrowth efficacy in the experimental group. At the end of the experiment, regrown hair was collected and measured to determine the microscale weight. The skin was sampled using an 8 mm biopsy punch on the day of preparation. For histological analysis, skin biopsy was fixed in formalin overnight, processed, and embedded in paraffin. Tissue sections (5 μm-thick) were stained with hematoxylin and eosin and observed under a light microscope. Hair follicles located in the dermis and subcutaneous layer were counted as presumptive telogen and anagen, respectively. Seven-week-old C57BL/6 mice were acclimated for 1 week in a mouse facility in OliX and used for tests. All studies were approved by Institutional Animal Care and Usage Committee (IACUC) in OliX.
2.8. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization of AR in Hair Follicles
Ex vivo human hair follicles were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 4–6 h and embedded in freezing medium (3801480; Leica). Ten-micron-thick frozen sections were post-fixed with 4% PFA, acetylated, and hybridized with the biotin-labeled AR riboprobe (1 ng/μL). Using streptavidin–HRP (Sp-3010-1; Vector Laboratories, CA) and tyramide amplification kit (B40932; Invitrogen), AR mRNA was detected under a fluorescence microscope. Fluorescence intensity in the DP was quantitated using the ImageJ software (v1.53, National Institutes of Health, MD). The DP area was identified using a bright field channel image.
Templates for AR riboprobes synthesis were generated by PCR using the T7 promoter-linked primer set (F: 5′-GCT TAA GCA GCT CCG CTG ACC-3′, R: 5′-CGA TGT TAA TAC GAC TCA CTA TAG GGT GAA GTC GCT TTC CTG GC-3′) from the AR cDNA construct. In vitro transcription with biotin labeling was performed following the manufacturer’s instruction (10881767001 and 11685597910; Roche).
2.9. Statistical Analysis
IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 22 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY) was used for statistical analysis. All statistical analyses were performed using Student’s t-test. Differences were considered statistically significant if p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Inhibition of AR Expression by cp-asiAR under In Vitro Conditions
To identify effective asiRNA candidates with the most potent target gene-silencing effects, we screened asiRNA library comprising 88 sequences designed to target the AR transcript. To evaluate AR silencing in vitro, asiRNAs were synthesized and transfected into human A549 cells with sufficient basal expression of AR and screened for mRNA knockdown efficacy. The most potent asiRNA was selected, which showed robust knockdown efficacy at mRNA and protein levels in independently repeated experiments (asiAR-072 and 72 in Table S1 and Figure S1, respectively). Chemical modifications were introduced to the selected asiRNA to generate the cell-penetrating asiRNA (cp-asiRNAs). The final candidate carried chemical modifications comprising cholesterol conjugation at the 3′-end of the passenger strand, phosphorothioate backbone modification, and 2′-O-methyl and fluoro-modification of the ribose sugar on both strands (Figure S2).
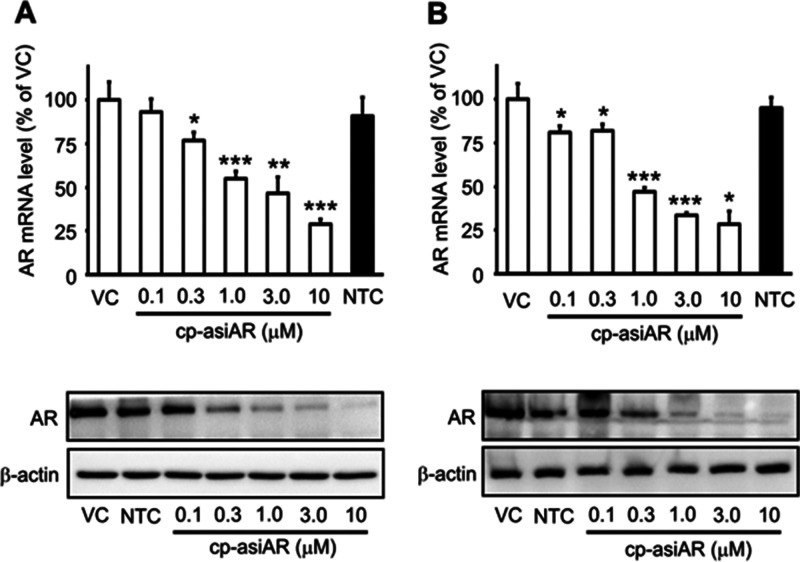
The resulting cp-asiAR showed dose-dependent reduction in mRNA and protein levels of AR without the aid of a transfection agent in human A549 cells (Figure 1A). AR nontargeting control cp-asiRNA did not reduce AR expression at a concentration of 10 μM. The IC50 value of AR mRNA knockdown was 0.732 μM (passive uptake, Figure S2). Knockdown efficacy was additionally validated in the independent AR-expressing human cell line T98G (Figure 1B). The IC50 value of AR mRNA knockdown was 0.735 μM.
Figure 1.
In vitro validation of the efficacy of cell-penetrating, AR-targeting asiRNA (cp-asiAR) knockdown. (A) A549 cells were treated with cp-asiARs at indicated concentrations by passive uptake. mRNA levels of AR observed 24 h after treatment were normalized using tubulin mRNA expression. AR mRNA levels relative to those of vehicle control (VC) are presented as mean and standard deviation (n = 6). AR protein levels at 48 h after treatment are shown below. β-actin protein level was considered as a loading control. (B) Knockdown efficacy was validated in T98G cells. Representative images are shown. NTC denotes nontargeting control siRNA treatment at a concentration of 10 μM. Statistical significance was calculated using a t-test with VC (*, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001).
3.2. Downregulation of AR Expression by Intradermal Injection of cp-asiAR in a Mouse Model
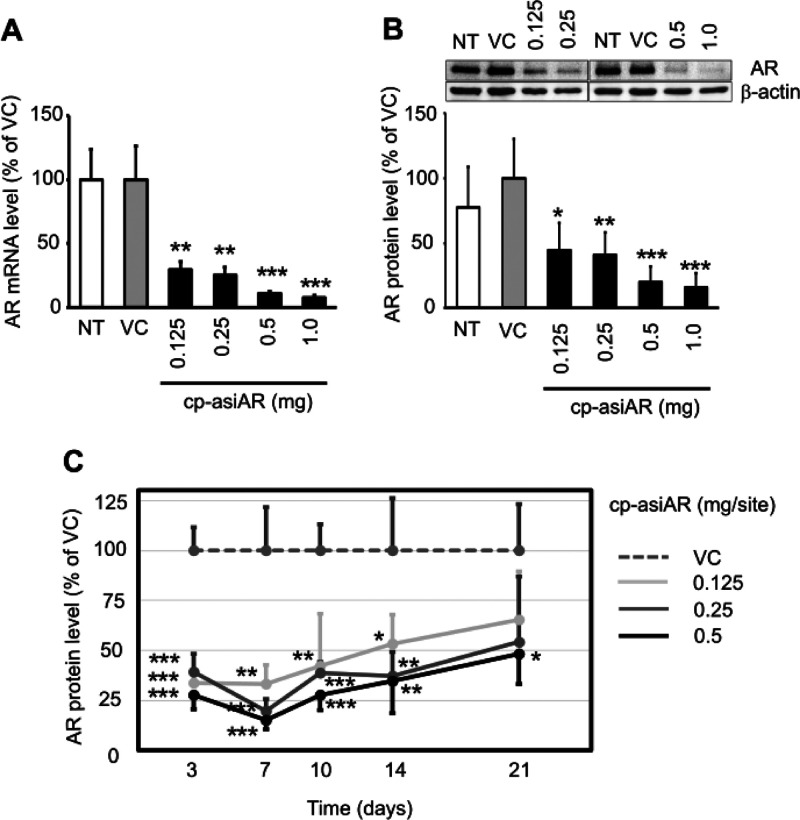
Next, we examined the knockdown efficacy of cp-asiAR in vivo. The AR gene-silencing efficacy of cp-asiAR was determined after intradermally injecting the mouse dorsal skin with different doses. Cp-asiAR was injected at four different doses from 0.125 to 1.0 mg into the mouse skin, and after 24 h, skin biopsy specimens were collected from the injection sites. Tissues were subjected to quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (RT-qPCR) analysis to assess the mRNA level of AR. The results showed a potent dose-dependent silencing effect on AR in the mouse dorsal skin (Figure 2A). We also analyzed the AR protein level in the tissue using western blotting. Similar to the mRNA level, the protein level was decreased to more than 50% in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 2B).
Figure 2.
In vivo validation of cp-asiAR KD efficacy. cp-asiAR was intradermally injected into the dorsal skin of mice, and the mRNA (A) or protein (B) level of AR in the injection site was measured after 24 h (n = 3). Protein level was quantitated using image analysis of western blotting (B, inset). RPL32 and β-actin were used as references for the relative mRNA and protein levels of AR, respectively. (C) cp-asiAR was injected at three doses, and skin biopsy was performed at the indicated times after injection. AR protein level normalized by β-actin was measured in the biopsy tissue. AR protein levels relative to the vehicle control are shown with the standard deviations (n = 4). Statistical significance was calculated using the t-test with the vehicle control (VC) (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001).
siRNA inhibits gene expression through the formation of RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). We tested the duration of the AR-silencing activity of cp-asiAR in mouse dorsal skin by measuring the AR protein level after injection. The silencing effect was maximal during the first week; however, AR expression recovered slowly. A single 0.5 mg injection of cp-asiAR significantly inhibited the AR protein level by more than 50% for up to 3 weeks. At lower doses (0.125 and 0.25 mg), the inhibition was significant for up to 2 weeks (Figures 2C and S3).
3.3. Therapeutic Efficacy of cp-asiAR in an AGA Mouse Model
To verify the therapeutic effect of cp-asiAR on AGA, the downregulation of the AR level was examined in an AGA mouse model. The model was established via daily treatment with low-dose DHT. Compared to normal mice, DHT-treated mice exhibited slow hair recovery on the shaved dorsal skin on day 21 after trimming (Figures 3A and S4). We compared hair regrowth ability between the groups treated with vehicle, cp-asiAR at three different doses, and flutamide (a known AR inhibitor). Weekly injection of cp-asiAR at all tested doses into the shaved dorsal skin of mice dramatically improved hair regrowth to a similar level as that in the flutamide-treated group (n = 5/group). We quantified the hair regrowth activity by measuring the weight of regrown hair. The weight of shaved hair increased significantly compared to that in the vehicle-treated group (Figure 3B). Image analysis of regrown hair area on day 15 also produced similar quantification results (Figure S5). To further characterize the hair cycle of the regrown hair, we performed hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining on dorsal skin sections. Analysis of skin histology showed distinguished hair follicles in the dermis (presumptive telogen) and in the subcutaneous layers (presumptive anagen). The ratio between presumptive anagen versus presumptive telogen hair follicles was significantly increased in all groups treated with cp-asiAR at all doses (Figures 3C and S6).
Figure 3.
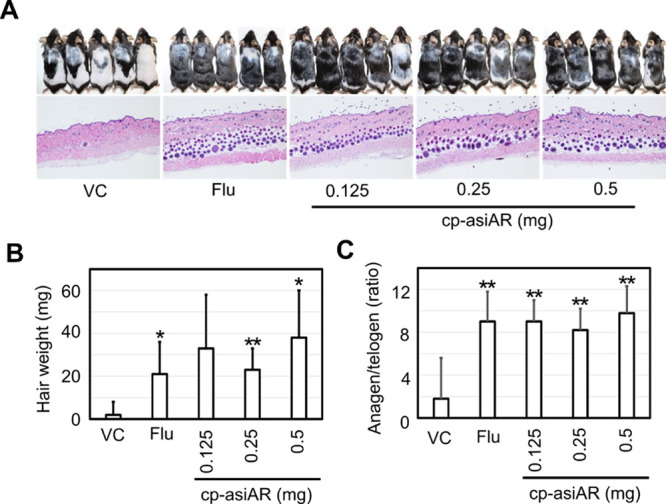
In vivo validation of cp-asiAR therapeutic efficacy in an AGA mouse model. (A) All mice were injected daily with DHT (25 mg/kg) during the entire experiment to mimic AGA-like hair loss conditions. They were injected intraperitoneally with flutamide (200 mg/kg) daily or intradermally at different doses of cp-asiAR on days 1, 8, and 15. On day 21, the mice were sacrificed, and hair regrowth was imaged (top, n = 5). The dorsal skin was isolated for histology and stained with H&E (bottom). Notable promotion of hair growth caused by cp-asiAR treatment at all tested doses was observed on day 21. (B) Regrown hair was shaved and weighed using a microscale. cp-asiAR treatment resulted in significant promotion of hair regrowth compared with the vehicle control. The mean and standard deviation are shown in the figure. (C) Presumptive anagen and telogen hair follicles were quantified from the H&E, and the ratio is presented as mean and standard deviation. Statistical significance was calculated using a t-test with the vehicle control (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).
We also verified the downregulation of AR protein levels in flutamide- and cp-asiAR-treated groups (Figure S7).
3.4. Therapeutic Efficacy of cp-asiAR in Human Hair Follicles
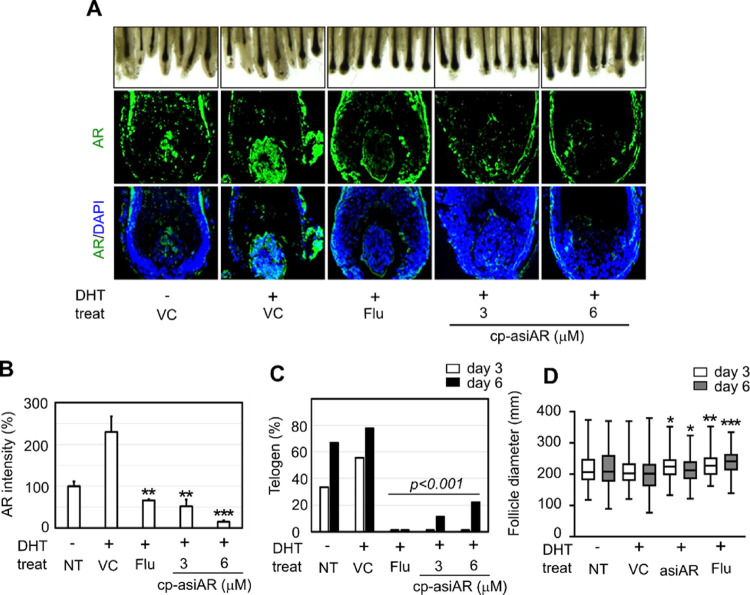
To validate the effect of cp-asiAR treatment in human skin, the hair cycle and hair bulb thickness were evaluated using ex vivo scalp tissues obtained from individuals with AGA. Hair follicles isolated from scalp tissue were allowed to undergo phase transition from anagen (plump or round bulb) to telogen (elongated bulb and papilla dissociation) ex vivo. DHT was added to the culture medium to mimic AR-rich AGA conditions; this was followed by co-treatment with cp-asiAR or flutamide. On day 6, a substantial increase in the proportion of telogen hair was observed in the vehicle- and DHT-treated groups (Figure 4A). Addition of 3 or 6 μM cp-asiAR in the culture medium successfully prevented transition to telogen. On day 3 and 6, little to no telogen hair was observed in the cp-asiAR- or flutamide-treated group (Figure 4C). In terms of hair follicle diameter, hair treated with only DHT was significantly thinner than that from the control on day 6. This change was significantly mitigated by treatment with either 12 μM cp-asiAR or 100 μM flutamide (Figure 4D).
Figure 4.
Ex vivo validation of cp-asiAR therapeutic efficacy in human hair follicles. Hair follicles were isolated from the human scalp and incubated with DHT (100 nM) to mimic AGA-like hair loss conditions. (A) Each group of hair follicles was co-treated with flutamide or cp-asiAR at the indicated doses and observed on days three and six after incubation (n = seven-nine/group). (Top) Images were obtained on day six, and telogen hair was identified based on morphological characteristics as described previously.4 Tapered, elongated bulb shape, and dissociation of very compact papilla were considered as the key features of telogen hair. (Bottom) Hair follicles from each group were isolated on day two after incubation. Frozen sections of the tissue were hybridized with the AR riboprobe to visualize the mRNA levels of AR in the hair follicle. (B) Fluorescence intensity in the DP area was analyzed using ImageJ, and the AR levels relative to the untreated control are presented as mean and standard deviation. Statistical significance was calculated using a t-test with the vehicle control (**, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001). (C) Telogen ratio in each treatment group was quantified based on the number of anagen and telogen hair follicles. Statistical significance was calculated using the Chi-square test with the vehicle control. (D) Effect of cp-asiAR on the hair follicle diameter following DHT treatment. A total of 130 hair follicles from 13 patients (8 with AGA and 5 without AGA) were collected, and the hair follicle diameter was measured on days three and six after incubation with the indicated treatment. Statistical significance was calculated using the t-test with the vehicle control of the same day (*, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01, ***, p < 0.001).
Because of the small size of human hair follicles, we could not detect the repression of AR using RT-qPCR or western blotting. We thus used an in situ hybridization method to validate the knockdown efficacy of cp-asiAR in an ex vivo condition. Using an AR cRNA probe, we detected the mRNA expression of AR in tissue sections from vehicle- or cp-asiAR-treated hair follicles. The mRNA expression of AR was quantified using fluorescence in situ hybridization in the DP area. DHT treatment significantly increased AR mRNA expression in DP cell bodies to 230% of the control level, whereas co-treatment with cp-asiAR or flutamide decreased the expression level significantly to 15–50 or 66% of nontreat control, respectively. (Figure 4A,B).
3.5. AR Knockdown and Alterations in Downstream Signaling by cp-asiAR in Primary Human DP Cells
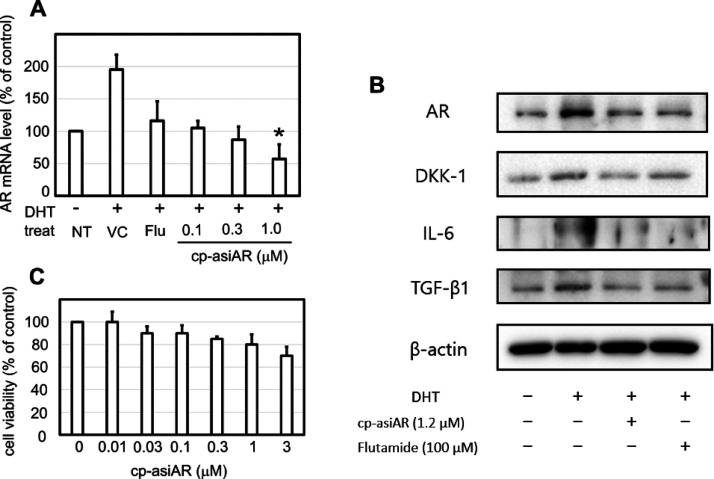
DP cells are known to induce inflammatory cytokine production in response to androgen, resulting in hair loss. Using commercially available primary DP cells or DP cells isolated directly from a patient’s scalp, we tested the knockdown efficacy of cp-asiAR on AR downstream signaling. DHT increased the mRNA expression of AR in primary DP cells by 2-fold, whereas co-treatment with cp-asiAR reduced AR mRNA expression in a dose-dependent manner (Figure 5A). Downregulation of AR protein expression was also demonstrated using western blotting (Figure 5B) and immunofluorescence staining (Figure S8). In addition, the expression levels of various proteins implicated in the development of AGA were assessed. The expression of dickkopf-1 (DKK-1), interleukin (IL)-6, and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1 showed a significant decrease at 48 h after co-treatment with cp-asiAR, compared to that after vehicle control treatment.
Figure 5.
AR knockdown and downstream signaling inhibition in human DP cells. Primary human DP cells were cultured and incubated with DHT to mimic AGA-like conditions. The cells were co-treated with flutamide or cp-asiAR at the indicated concentration. Statistical significance was calculated using the t-test with the vehicle control (*, p < 0.05). (A) The mRNA level of AR was measured using qPCR 24 h after treatment (n = 3). (B) Protein expression profile was obtained using western blotting 24 h after treatment. Treatment with cp-asiAR effectively downregulated the expression of AR, dickkopf-1 (DKK-1), interleukin (IL)-6, and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1. (C) Effects of cp-asiAR treatment on DP cell viability were tested using the modified MTT assay. No significant decrease in DP cell viability was observed.
To exclude the possibility that cp-asiAR-mediated toxicity inhibited AR signaling, DP cell viability was measured with different concentrations of cp-asiAR (Figure 5C). DP cell viability was not affected by cp-asiAR at all tested doses.
4. Discussion
In this study, we evaluated the potential of cp-asiAR for the treatment of AGA. We chose to employ RNAi because this technique enables a highly specific silencing of the expression of certain genes involved in the pathogenesis of a target disease.5 First, we demonstrated that cp-asiAR does not negatively affect DP cell viability and that local injection of cp-asiAR successfully silences AR expression in an animal model. Moreover, cutaneous injection of cp-asiAR promoted hair regrowth in DHT-treated mice. Our experiments using ex vivo human scalp tissue also showed that cp-asiAR treatment prevented the transition of hair follicles to the telogen phase in response to DHT stimulation. Consequently, treatment with cp-asiAR increased the hair diameter. Finally, silencing of AR using cp-asiAR not only successfully downregulated AR expression but also decreased the expression of IL-6, TGF-β1, and DKK-1.
Given that AR is a pivotal receptor in the pathogenesis of AGA, local downregulation of AR expression can be an important strategy to treat AGA. Systemic inhibition of AR activity was found to be effective in AGA treatment in previous clinical trials, but adverse effect limited the use of systemic anti-androgen therapy.6 In contrast, local injection of cp-asiAR makes it possible to maintain a high drug concentration in the dermis of the bald area with minimal drug concentration in the plasma and, hence, can be considered a treatment modality that is both effective and safe. The stability test performed using low concentrations of RNase showed gradual degradation of cp-asiAR within 16 h (Figure S9). Rapid degradation of cp-asiAR in the plasma would minimize the systemic effect of the treatment. Consistently, pharmacokinetic analysis showed highly enriched cp-asiRNA in the skin for up to seven days but a negligible amount of cp-asiAR in the plasma, liver, and kidney (Table S2). Although RNAi is a powerful treatment strategy with highly specific binding to a particular nucleotide sequence, some off-target effects have been observed in previous studies.7 Owing to the nature of in vitro and ex vivo studies, we were not able to assess the risk of off-target effects of cp-asiAR in detail. However, our observation that cp-asiAR did not impair DP cell viability supported the ability of cp-asiAR to specifically inhibit AR without critical off-target effects, which could potentially jeopardize cell viability.
Hair miniaturization, which is a characteristic feature of AGA, is known to be associated with an alteration in the hair cycle. Shorter anagen cycles coupled with an increased proportion of telogen hair characterize AGA-affected hair.8 The only FDA-approved topical drug for AGA, minoxidil, is considered to function via either induction of anagen or prolongation of the anagen hair cycle.9 We found that with changes in the hair cycle, AGA was successfully prevented by treatment with cp-asiAR. The hair diameter may serve as an indirect measure of the hair cycle because telogen hair is thinner than anagen hair. In this study, significantly longer hair diameter was observed after treatment with cp-asiAR. Moreover, actual promotion of hair growth by local injection of cp-asiAR was observed in DHT-induced mice. The promotion of hair growth has been widely used as an important indicator of the therapeutic efficacy of drugs against AGA.10 Collectively, these findings suggest that the specific downregulation of AR by cp-asiAR can effectively inhibit DHT-induced changes in the hair.
The exact molecular mechanism involved in AGA remains unknown. However, previous research has elucidated the role of some key molecules, including TGF-β1, IL-6, and DKK-1.11 These three molecules have been identified as androgen-inducible mediators involved in the pathogenesis of AGA. More specifically, TGF-β1 has been associated with the induction of catagen, while IL-6 and DKK-1 are known to inhibit hair elongation and eventual regression of hair follicles.12 Changes in the expression of these molecules have been used widely as surrogate markers of AGA treatment. Thus, the decreased expression of TGF-β1, IL-6, and DKK-1 following treatment with cp-asiAR observed in this study indicates successful blockade of androgen-triggered biological responses, providing a molecular basis for the mechanism of cp-asiAR-mediated AGA treatment.
Although we have shown that cp-asiAR can prevent DHT-induced AGA in both in vivo and ex vivo tissues, certain obstacles remain to be overcome before cp-asiAR can be used clinically. First, the induction of AGA solely relied on DHT exposure. Despite the crucial role of DHT in the development of AGA, other factors such as DP cell senescence also contribute to AGA.13 In fact, the serum levels of DHT and other androgens decrease with age, but the prevalence of AGA is much higher in the elderly than in the young population. Thus, inhibition of DHT-induced changes in hair biology by cp-asiAR may not be sufficient for treating AGA. Second, local injection of cp-asiAR requires multiple injections to cover the entire bald area. Thus, it is subject to general side effects of local intradermal injection, such as bleeding, bruising, focal infection, and pain. In addition, bolus injection may lead to uneven therapeutic response in the injected area. To avoid such problems, using a microneedle for injection can be considered. Other possible routes of administration together with the optimal concentration of cp-asiAR, which can effectively treat AGA while minimizing side effects, need to be explored. Therefore, future studies, including clinical trials, are warranted to evaluate, in detail, the efficacy and safety of cp-asiAR in the treatment of AGA.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that treatment with the AR gene-targeting cp-asiRNA effectively downregulated AR expression, as well as its downstream signals implicated in AGA. We have observed substantial promotion of hair regrowth after local intradermal injection of cp-asiRNA in our animal study. Ex vivo experiments using human scalp hair cultures revealed that cp-asiRNA could prevent DHT-induced changes in the hair cycle and hair diameter, which are key features of AGA. Therefore, local cp-asiAR administration could be used as a novel therapeutic option for AGA.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Medical Device Development Fund grant funded by the Korean government (the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety) (Project Number: 1711137939, RS-2020-KD000025).
Glossary
Abbreviations
- AGA
androgenetic alopecia
- AR
androgen receptor
- DHT
dihydrotestosterone
- DKK-1
dickkopf-1
- DP
dermal papilla
- HFDPC
hair follicle dermal papilla cell
- IL
interleukin
- KD
knockdown
- PFA
paraformaldehyde
- qPCR
quantitative polymerase chain reaction
- RNA
ribonucleic acid
- TGF-β1
transforming growth factor-β1
Supporting Information Available
The Supporting Information is available free of charge at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00510.
Detailed data on cp-asiRNA including stability; pharmacokinetic profile; and its AR knockdown efficacy demonstrated in vitro and in vivo (PDF)
Author Contributions
The manuscript was written through contributions of all authors. All authors have given approval to the final version of the manuscript. Conceptualization: D.K.L, C.H.W.; Methodology: C.H.W., D.K.; Data curation: H.K.Y., S.H.H, J.H.P.; Formal analysis: I.J.M., H.K.Y., D.K., S.W.H.; Investigation: H.K.Y., D.K., S.W.H., M.E.C., H.C.; Writing – original draft: I.J.M., H.K.Y., D.K.; Writing – review and editing: I.J.M., D.K., D.K.L., C.H.W., Project administration: D.K.L., C.H.W. I.J.M., H.K.Y., D.K. contributed equally to this work as first authors.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Supplementary Material
References
- a Dorsett Y.; Tuschl T. siRNAs: applications in functional genomics and potential as therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 318–329. 10.1038/nrd1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Reich S. J.; Fosnot J.; Kuroki A.; Tang W.; Yang X.; Maguire A. M.; Bennett J.; Tolentino M. J. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) targeting VEGF effectively inhibits ocular neovascularization in a mouse model. Mol. Vis. 2003, 9, 210–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; c Hwang J.; Chang C.; Kim J. H.; Oh C. T.; Lee H. N.; Lee C.; Oh D.; Lee C.; Kim B.; Hong S. W.; Lee D. K. Development of Cell-Penetrating Asymmetric Interfering RNA Targeting Connective Tissue Growth Factor. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 2305–2313. 10.1016/j.jid.2016.06.626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trost L.; Saitz T. R.; Hellstrom W. J. G. Side Effects of 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review. Sex. Med. Rev. 2013, 1, 24–41. 10.1002/smrj.3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Chang C. I.; Yoo J. W.; Hong S. W.; Lee S. E.; Kang H. S.; Sun X.; Rogoff H. A.; Ban C.; Kim S.; Li C. J.; Lee D. K. Asymmetric shorter-duplex siRNA structures trigger efficient gene silencing with reduced nonspecific effects. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 725–732. 10.1038/mt.2008.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Hong S. W.; Park J. H.; Yun S.; Lee C. H.; Shin C.; Lee D. K. Effect of the guide strand 3’-end structure on the gene-silencing potency of asymmetric siRNA. Biochem. J. 2014, 461, 427–434. 10.1042/bj20140407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh J. W.; Kloepper J.; Langan E. A.; Kim Y.; Yeo J.; Kim M. J.; Hsi T.-C.; Rose C.; Yoon G. S.; Lee S.-J.; Seykora J.; Kim J. C.; Sung Y. K.; Kim M.; Paus R.; Plikus M. V. A Guide to Studying Human Hair Follicle Cycling In Vivo. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 34–44. 10.1038/JID.2015.354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Lee M. Y.; Wang H. Z.; White T. W.; Brooks T.; Pittman A.; Halai H.; Petrova A.; Xu D.; Hart S. L.; Kinsler V. A.; di W. L. Allele-Specific Small Interfering RNA Corrects Aberrant Cellular Phenotype in Keratitis-Ichthyosis-Deafness Syndrome Keratinocytes. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2020, 140, 1035–1044.e7. 10.1016/j.jid.2019.09.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Sun B. K.; Tsao H. Small RNAs in development and disease. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2008, 59, 725–737. 10.1016/j.jaad.2008.08.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Paradisi R.; Porcu E.; Fabbri R.; Seracchioli R.; Battaglia C.; Venturoli S. Prospective cohort study on the effects and tolerability of flutamide in patients with female pattern hair loss. Ann. Pharmacother. 2011, 45, 469–475. 10.1345/aph.1P600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Wysowski D. K.; Fourcroy J. L. Flutamide hepatotoxicity. J. Urol. 1996, 155, 209–212. 10.1016/S0022-5347(01)66596-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bobbin M. L.; Rossi J. J. RNA Interference (RNAi)-Based Therapeutics: Delivering on the Promise?. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 56, 103–122. 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010715-103633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Whiting D. Scalp biopsy as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in androgenetic alopecia. Dermatol. Ther. 1998, 8, 24–33. [Google Scholar]; b Whiting D. A. Possible mechanisms of miniaturization during androgenetic alopecia or pattern hair loss. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2001, 45, S81–S86. 10.1067/mjd.2001.117428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen E. A.; Dunlap F. E.; Funicella T.; Koperski J. A.; Swinehart J. M.; Tschen E. H.; Trancik R. J. A randomized clinical trial of 5% topical minoxidil versus 2% topical minoxidil and placebo in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia in men. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 47, 377–385. 10.1067/mjd.2002.124088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Shin H. S.; Park S. Y.; Hwang E. S.; Lee D. G.; Mavlonov G. T.; Yi T. H. Ginsenoside F2 reduces hair loss by controlling apoptosis through the sterol regulatory element-binding protein cleavage activating protein and transforming growth factor-β pathways in a dihydrotestosterone-induced mouse model. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 755–763. 10.1248/bpb.b13-00771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Park W.-S.; Lee C.-H.; Lee B.-G.; Chang I.-S. The extract of Thujae occidentalis semen inhibited 5α-reductase and androchronogenetic alopecia of B6CBAF1/j hybrid mouse. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2003, 31, 91–98. 10.1016/S0923-1811(02)00146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lolli F.; Pallotti F.; Rossi A.; Fortuna M. C.; Caro G.; Lenzi A.; Sansone A.; Lombardo F. Androgenetic alopecia: a review. Endocrine 2017, 57, 9–17. 10.1007/s12020-017-1280-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- a Foitzik K.; Lindner G.; Mueller-Roever S.; Maurer M.; Botchkareva N.; Botchkarev V.; Handjiski B.; Metz M.; Hibino T.; Soma T.; Paolo Dotto G.; Paus R. Control of murine hair follicle regression (catagen) by TGF-beta1 in vivo. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 752–760. 10.1096/fasebj.14.5.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; b Kwack M. H.; Ahn J. S.; Kim M. K.; Kim J. C.; Sung Y. K. Dihydrotestosterone-inducible IL-6 inhibits elongation of human hair shafts by suppressing matrix cell proliferation and promotes regression of hair follicles in mice. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 43–49. 10.1038/jid.2011.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton J. H.; Hannen R. F.; Bahta A. W.; Farjo N.; Farjo B.; Philpott M. P. Oxidative stress-associated senescence in dermal papilla cells of men with androgenetic alopecia. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1244–1252. 10.1038/jid.2015.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.