1. Introduction
Inborn errors of immunity (IEI) are a group of inherited disorders caused by damaging variants in genes essential for immunity. Cases in which a single gene causes disease provides fundamental insights into how a single protein’s function directly impacts specific components of the immune system. Patients with IEI may present clinically with primary immunodeficiency, autoinflammation, autoimmunity and/or malignancy. IEI research is a rapidly growing field, with the recent advances in genome sequencing leading to 485 currently known monogenetic defects that cause IEI (1).
Mucosal associated invariant T (MAIT) cells are a subset of unconventional T cells that are activated following engagement of their T cell receptor (TCR) with MR1, a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I-related molecule that presents vitamin B metabolite antigens (2). However, MAIT cells can also be activated in a TCR-independent manner via cytokines, namely interleukin (IL)-12 and IL-18 (3). MAIT cell effector responses mirror conventional T-helper (Th)1 and Th17 cytokine profiles (4), but can also engage in CD8 T cell-like cytotoxic responses via release of granzymes and perforin (5). Due to this broad activation and effector function potential, MAIT cells have been implicated as key immune players in defense against a range of bacterial and viral infections, in addition to a role in autoimmunity and cancer (6). Despite these insights, the proteins and cells essential to support MAIT cell frequency and function, and the implications for human immunity in the context of dysfunctional MAIT cells, are only just beginning to be uncovered. Recent reports of IEI that include MAIT cell immunophenotyping, and to a limited extent functional analysis, provide an ideal opportunity to discover the fundamental factors that govern MAIT cell biology.
2. IEI with disruptions to MAIT cell compartment
Here, we present a curated review of IEI in which MAIT cells have been assessed for frequency, phenotype and/or function ( Table 1 ). The most striking disruptions reported in IEI are cases that report a complete absence of MAIT cells ( Figure 1 ). Complete MAIT cell deficiency, along with an expansion of γδ T cells was observed in an individual with MR1 deficiency (29). This was the result of a homozygous point mutation in the antigen binding groove of MR1, rendering it unable to present antigen. This resulted in an immune system with a selective loss of MAIT cells. This individual’s infection history included Varicella zoster viral infection (complicated by secondary bacterial pneumonia and subsequent lung scarring) prolonged Campylobacter gastroenteritis with haematochezia (which was initially refractory to treatment), and extensive human papilloma virus (HPV)+ warts refractory to treatment. This case provided direct evidence for the importance of MAIT cells’ antigen-dependent role in controlling human bacterial infections, but also highlighted their antigen-independent role in controlling human viral infections, as had been suggested by previous mouse model (45) and observational human studies (46, 47).
Table 1.
Summary of inborn errors of immunity that have assessed MAIT cell frequency and/or function.
| Gene | Inheritance | Variant type | Gene function | Clinical presentation | Adult/pediatric | Cohort | MAIT cell frequency | MAIT cells defined by | MAIT cell phenotype | MAIT cell function | Other immune features | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADA2 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Enzyme (adenosine deaminase) | Autoinflammatory and immunodeficiency | Both | 10 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↓ Tregs, Vδ2, NKT, memory B, CD4+ and CD8+ memory T cells | (7) |
| AIRE | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Autoimmune regulator | APECED | Both | 8 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | Neutralizing autoantibodies against type I IFN and IL-22 | (8) |
| BCL10 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | TCR signaling | CID: respirators infections | Pediatric | 1 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | Absent memory B and T cells ↓ Tregs, NK, γδ T, and Tfh cells |
(9) |
| BTK | X-linked | Loss-of-function | Cell signaling (B cell) | XLA: bacterial infections, giardia, mycoplasma, and enteroviruses | Not provided | 4 | Decreased (circulating) | TRAV1-2 transcript | ND | ND | Absent circulating B cells ↓/absent serum Ig. |
(10) |
| CARMIL2 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Capping protein (cell structure and migration) | CID: bacterial, fungal, mycobacterial infections, viral warts, molluscum, and malignancy | Both | 6 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↑ naïve T cells ↓ Treg and memory B cells |
(11) |
| CD27 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Costimulatory molecule | EBV and lymphoproliferative conditions | Both | 10 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↑ CD8 T cells absent memory B cells |
(12) |
| CD28 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Costimulatory molecule | HPV-2 and HPV-4 driven by EV | Both | 3 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↑ naïve CD4+ T cells ↓ TCM cells and Tregs |
(13) |
| CD70 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Costimulatory ligand | EBV and lymphoproliferative conditions | Both | 7 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↑ γδ T cells ↓ memory B cells |
(12) |
| CDC42 | Dominant | Loss-of-function | GTP/GDP-binding protein (actin cytoskeleton) | Takenouchi Kosaki syndrome | Adult | 1 | Within normal range | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↑ memory T and naïve B cells ↓ B and NK cells |
(14) |
| CFTR | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Chloride channel | Cystic fibrosis | Adult | 41 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↑ γδ T cells ↓ NK cells |
(15) |
| CORO1A | Recessive | Loss-of-function | actin-regulating protein | SCID (leaky) | Pediatric | 1 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↓ naive T and NKT cells | (16) |
| CTPS1 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | DNA/RNA synthesis enzyme | Severe bacterial and viral infections | Pediatric | 7 | Decreased (circulating) | MR1 tetramer + surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↓ NKT, memory B and NK cells | (17) |
| DOCK8 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Guanine nucleotide exchange factor (cytoskeleton organization) | CID: recurrent viral, bacterial, and fungal infections, severe eczema, allergies, malignancy and autoimmunity | Both | 7 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↓ Tregs, total T, NKT and memory B cells ↑ total B cells ↓ IgM ↑ IgG, IgA and IgE |
(18) |
| GATA2 | Dominant | Loss-of-function | Transcription factor (hematopoiesis) | Complex disorder of hematopoiesis with variable extramedullary defects and myelodysplasia | Both | 4 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers CD8+ CD161+ Va7.2+ | ND | ND | ↓ monocytes, DC, B and NK cells | (19) |
| GINS1 | Recessive | (partial) Loss-of-function | DNA replication | craniofacial abnormalities, viral infections | Both | 3 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↓ NK cells and neutrophils ↑ IgA ↓ IgM and IgG |
(20) |
| IFNG | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Cytokine | MSMD | Pediatric | 2 | Within normal range | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↑ naive T cells ↓ NKT and CD27+ memory B cells |
(21) |
| IKZF2 | Dominant | Loss-of-function | Transcription factor (hematopoietic-specific) | CID: respiratory infections, thrush and mucosal ulcers, and chronic lymphadenopathy | Adult | 2 | Decreased (circulating and intestinal mucosa) | MR1 tetramer + surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | High CD69 | ND | ↑ activated T cells ↓ naïve CD8+ T cells ↓ IgG |
(22) |
| Recessive | Loss-of-function | CID: sinusitis, otitis media, lower respiratory tract infections, pneumonia | Adult | 1 | Absent | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | N/A | N/A | ↑ γδ ↓ CD4 T, B and NK cells Absent NKT ↓ IgG |
(23) | ||
| IL12RB1 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Cytokine receptor | MSMD | Not provided | 4 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↑ naïve T cells ↓ Th1 and Th17 cells |
(24) |
| IL12RB2 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Cytokine receptor | MSMD | Pediatric | 1 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↑ naïve T cells ↓ Th1 cells |
(25) |
| IL21R | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Cytokine receptor | CID: cryptosporidium infections | Both | 8 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↓ CD4+ T, cTfh, memory B, NK and myeloid-derived DC ↓ IgG |
(26) |
| IL23R | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Cytokine receptor | MSMD | Pediatric | 1 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↑ naïve T cells ↓ Th1 cells |
(25) |
| IL6ST | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Cytokine receptor | Hyper IgE Syndrome: staphylococcal lesions, candidiasis, severe allergy | Both | 12 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↑ naïve T cells ↓ TCM, CD8+ TEM, and Tfh cells |
(27) |
| MAGT1 | X-linked | Loss-of-function | Magnesium transporter | XMEN: EBV infection, lymphoma, viral infections, respiratory and GI infections | Both | 2 | Decreased (circulating) | Not defined | ND | ND | ↓ CD4 T, memory B, and NKT cells ↓ IgG |
(28) |
| MR1 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Metabolite antigen presentation | HPV warts, difficult to treat bacterial and viral infections | Adult | 1 | Absent | MR1 tetramer + surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | N/A | N/A | ↑ Vδ2+ cells | (29) |
| NFKB1 | Dominant | Loss-of-function | Transcription factor (NF-κB family) | CID: Mycobacterium genavense infection | Pediatric | 1 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+TCRαβ+Vα7.2+CD161+) | ND | ND | ↓ CD4 T, B, γδ T and NK cells ↓ IgG |
(30) |
| NFKB2 | Dominant | Loss-of-function | Transcription factor (NF-κB family) | Respiratory infections, pituitary dysfunction, and autoimmunity | Pediatric | 1 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD161+Va7.2+CD8+) | ND | ND | Disturbed B cell differentiation ↓ IgG ↓ Lymphocyte subsets |
(31) |
| PDCD1 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Immune-inhibitory receptor | Tuberculosis, autoimmunity, and hepatosplenomegaly | Pediatric | 1 | Decreased (circulating) | MR1 tetramer + surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ↓ IFN-γ production | ↑ CD4−CD8− T cells ↓ Vδ2+ and CD56hi NK cells |
(32) |
| RASGRP1 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Enzyme (catalyzes UTP to CTP) | EBV and lymphoproliferative conditions | Pediatric | 1 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↓ B, naïve CD4+ and CD8+ T, NK cells Absence of iNKT cells |
(33) |
| REL | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Transcription factor (NF-κB family) | CID: severe viral, bacterial, fungal, and parasitic diseases | Pediatric | 1 | Increased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | Normal IFN-γ production | ↑ Vδ1+ and ILC2 cells ↓ Tregs and NK cells |
(34) |
| RORC | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Transcription factor (nuclear hormone receptor) | Candidiasis and mycobacteriosis | Pediatric | 7 | Absent | MR1 tetramer + surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | N/A | N/A | Absent IL-17A/F-producing T cells (including NKT cells) | (35) |
| SAP | X-linked | Loss-of-function | Signaling adaptor molecule | XLP syndrome: lymphohystiocytosis and lymphomas | Both | 5 | Within normal range | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↓ NKT cells ↓ IgG |
(36) |
| SASH3 | X-linked | Loss-of-function | Adaptor protein (cell signaling) | CID: infections and refractory autoimmune cytopenias | Adult | 4 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↓ CD4+ T and NK cells | (37) |
| SH2D1A | X-linked | Loss-of-function | SLAM associated protein (SAP, signaling) | Susceptibility to EBV and lymphoproliferative conditions | Not provided | 5 | Within normal range | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | Normal ZBTB16 levels | ND | ↓ NKT, memory B and NK cells | (10) |
| SPPL2A | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Transmembrane protease | MSMD | Pediatric | 3 | Within normal range | Not defined | ND | ND | Absence of cDC2 cells | (38) |
| STAT3 | Dominant | Loss-of-function | Transcription factor (gene regulation) | Hyper IgE Syndrome: craniofacial abnormalities, bacterial infections, eczema, candidiasis, osteoporosis, coronary and cerebral aneurysms | Not provided | 23 | Decreased (circulating) | MR1 tetramer + surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | Normal RORγt and PLZF expression | ↓ IL-17A and IL-17F but normal IFNγ and TNF production | ↓ Th17, Tfh, NKT and memory B cells ↑ IgE |
(24) |
| STIM1 | Recessive | (partial) Loss-of-function | Ca2+-sensing | CID: late onset with inflammatory manifestations (psoriasis and colitis) | Both | 2 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | NKT cells absent | (39) |
| TBX21 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Transcription factor (lineage-defining) | MSMD | Pediatric | 1 | Decreased (circulating) | MR1 tetramer + surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | Impaired IFNγ production | ↓ CD4+ T, iNKT, Vδ2+ and NK cells | (40) |
| USP18 | Recessive | Loss-of-function (partial) | Negative regulator of type I IFN signaling | type I interferonopathy: autoinflammation and mycobacterial disease | Adult | 1 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | Impaired IL-12/IL-23 production by myeloid cells | (41) |
| XIAP | X-linked | Loss-of-function | Inhibitor-of-apoptosis protein | XLP syndrome: lymphohystiocytosis and lymphomas | Both | 16 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ↑ apoptosis after stimulation | ↓ IgG ↓ NKT cells |
(36) |
| ZAP70 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Protein tyrosine kinase (TCR signaling) | CID: infant onset with severe infections caused by varicella zoster virus and live vaccines | Pediatric | 1 | Absent | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | N/A | N/A | ↓ CD8+ T cells NKT cells absent |
(42) |
| ZNF341 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Transcription factor (STAT signaling) | Hyper IgE syndrome: candidiasis, staphylococcal infections, severe allergy | Both | 6 | Decreased (circulating) | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | ND | ↑ naïve CD4+ T cells ↓ TCM, memory B, ILC1, ILC2 and NK cells |
(43) |
| ZNFX1 | Recessive | Loss-of-function | Helicase | Mycobacterial disease | Both | 3 | Within normal range | Surrogate markers (CD3+CD161+Vα7.2+) | ND | Normal IFN-γ production | ↓ NK cells | (44) |
APECED, autoimmune polyendocrinopathy candidiasis ectodermal dystrophy; CID, combined immunodeficiency; DC, dendritic cell; EBV, Epstein–Barr virus; EV, epidermodysplasia verruciformis; HPV, human papillomavirus; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; ILC, innate lymphoid cell; MAIT, mucosal-associated invariant T; MSMD, mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial diseases; N/A, not applicable; ND, not determined; NK, natural killer; SCID, severe combined immunodeficiency; TCM, T central memory; TCR, T cell receptor; TEM, T effector memory; Tfh, T follicular helper; Tregs, regulatory T cell; XLA, X-linked agammaglobulinemia; XLP, X-linked lymphoproliferative; XMEN, X-linked immunodeficiency with magnesium defect, Epstein-Barr virus infection, and neoplasia. Clinical presentations in bold indicate name of disease/disorder.
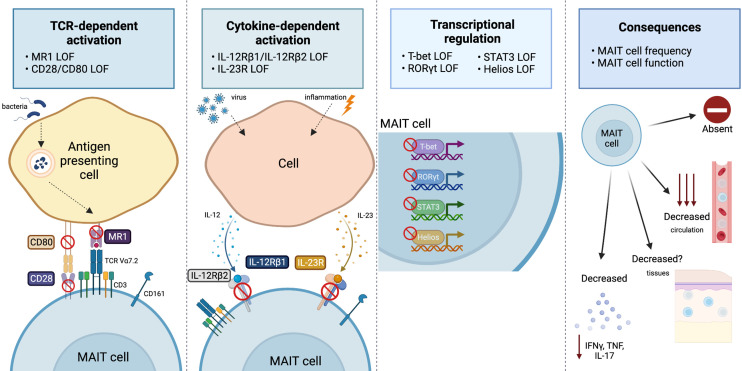
Figure 1.
Overview of the range and consequences of MAIT cell activation and signaling pathways disrupted by IEI. MAIT cells can be stimulated via TCR-dependent activation, where microbial-derived vitamin B metabolites are presented on MR1 and recognized by the MAIT cell TCR Vα7.2. Disruptions to MR1 or costimulatory molecules (CD28/CD80) has been shown to impact the MAIT cell compartment. MAIT cells are also activated by viral or inflammatory conditions in which cells produce IL-12 or IL-23 in response. Cases in which IL-12Rβ1, IL-12Rβ2, or IL-23R are deficient alters the MAIT cells compartment. The transcription factors T-bet, RORγT, STAT3 and Helios all play a vital role for MAIT cell development and/or effector function, and cases in which they are deficient report alterations to the MAIT cell compartment. Ultimately, all these pathway disruptions can cause varying consequences to the MAIT cell compartment, that includes: an absence or reduction in MAIT cells in circulation (it is unknown whether this is also the case at tissue sites) or a reduction in pro-inflammatory cytokine production (IFNγ, TNF, or IL-17). Figure created with BioRender.com.
Absence of MAIT cells was also reported in seven individuals with RORγT deficiency (35), along with a lack of Th17 and natural killer T (NKT) cells in these patients, who presented with common features of candidiasis and mycobacterial disease. MAIT cells were also reportedly absent in a ZAP70-deficient patient who initially presented with CD8+ T cell lymphopenia and severe viral infections (42). These examples highlight the exceptionally rare instances of individuals with a deficiency of a protein essential for either MAIT cell development or peripheral maintenance. The immunological phenotype and clinical presentation of those with a MAIT cell deficiency were varied, but all involved disturbances to the T cell compartment and frequent, severe, or difficult to treat infections.
By far the most common observation reported across IEI describe a decrease in the proportion (or total number) of circulating MAIT cells. Reduced frequencies of circulating MAIT cells have been reported for a range of different IEI that have a diverse clinical and/or immunological presentation, including: combined immunodeficiency (CID), X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA), Mendelian susceptibility to mycobacterial diseases (MSMD), X-linked immunodeficiency with magnesium defect, Epstein-Barr virus infection, and neoplasia (XMEN), and X-linked lymphoproliferative (XLP) syndrome. The majority of which are characterized by altered T and/or B cell compartments. Genes with variants related to a decrease in MAIT cells can range from: costimulatory receptors (e.g. CD28) (12, 13), cell structure proteins (e.g. CARMIL2/RLTPR) (11, 16, 18), cytokine receptors (e.g. IL12RB1/IL12RB2) (24–27), DNA replication proteins (e.g. GINS1) (17, 20) and transcription factors (e.g. TBX21) (19, 22, 30, 31, 40, 43) (see Table 1 for full list).
Interestingly, a single case report described an expansion of MAIT cells in a child with c-Rel deficiency presenting with a history of severe viral, bacterial, fungal, and parasitic infections (34). Vδ1 and innate-lymphoid cells (ILC) were also expanded, and reduced frequencies of natural killer (NK) and regulatory T cells (Tregs), compared to pediatric healthy controls. However, with only a single case, it is difficult to interpret whether this MAIT cell expansion is attributable to the specific IEI, or simply individual variation. Of the IEI studies that measured and reported MAIT cell frequency, six have described frequencies of MAIT cells within a normal range in their patient cohorts (10, 14, 21, 36, 38, 44). Together, these reports demonstrate that reduced frequency of MAIT cells is a common, but not a universal, observation in IEI.
MAIT cell frequency is also impacted by loss-of-function variants in IKZF2, which encodes the T cell transcriptional regulator Helios. Helios deficiency can present as dominant or recessive CID with varying severity. A heterozygous IKZF2 variant was reported in a proband and her father presenting with mild CID characterized by recurrent upper respiratory infections, mucosal ulcers, and chronic lymphadenopathy (22). The immune phenotype was chronic activation and proinflammatory cytokine production by both effector and regulatory T cells, but immune subset frequencies largely remained intact. A homozygous IKZF2 variant in a single case presented with a more severe CID characterized by recurrent lower respiratory tract infections, leading to multiple pneumonias requiring hospitalization (23). The immune phenotype was more pronounced, with reductions in: CD4+ T, B, and NK cells and an absence of NKT cells. Even with differing presentations, both studies reported a decrease or absence of MAIT cells due to the IKZF2 variants. Together, this demonstrates that MAIT cells are particularly susceptible to changes in Helios function, compared to other immune cell subsets.
The Helios deficiency study by Hetemäki et al. (22) extended beyond the typical circulating MAIT cell enumeration to measure tissue resident MAIT cells. MAIT cells are mucosal associated as their name suggests, with a large proportion populating mucosal sites. It is not well understood whether the MAIT cell circulating frequency reflects that of their tissue-associated counterparts. Colon and duodenal biopsies were examined from two individuals with Helios deficiency and a decrease in MAIT cell frequency was observed in all tissues examined when compared to healthy donor tissue (22). Therefore, this reduction in tissue associated MAIT cells suggests a global decrease of MAIT cells, rather than a redistribution to the tissues.
Establishing whether reported changes in frequency are due directly to the inborn error itself, a result of a secondary effect of the IEI on other immune components that interact with MAIT cells, or simply the result of MAIT cells responding to a clinical history of repeated episodes of prolonged infection and inflammation, is challenging. Thus, we will next discuss the strict considerations for reporting on MAIT cells in the context of IEI.
3. Considerations for MAIT cell frequency reporting for individuals with IEI
There is no standardized method for reporting MAIT cell frequency, with variation in how they are reported and how they are identified/defined. The most common (and accessible) method for MAIT cell identification is via expression of surrogate surface markers: TCR-Vα7.2 and CD161 (10). However, it is more accurate to define MAIT cells using MR1 tetramers loaded with 5-OP-RU (48). TCR-Vα7.2+ and CD161++ cells overlap 96% with MR1-tetramer+ cells in circulation. While it is an appropriate method for identifying MAIT cells (49), it is important to consider if the IEI impacts expression of CD161, in which case MR1 tetramers should be used for identification instead.
A major issue in reporting circulating MAIT cell frequency in humans is that no standardized frequency or number values have been established. Also, MAIT cell markers/tetramers are not typically included in standard clinical T cell panels. Thus, studies either establish their own standard values, with reference to an internal healthy control group, or patient values are compared to the typical 1–5% of circulating T cells reference range set by earlier studies of MAIT cells (4, 10, 49). Importantly, this simplified reference range does not consider variation of circulating MAIT cells present in different healthy control populations. Previous studies report MAIT cell frequency is significantly impacted by both age and sex (50, 51). MAIT cells steadily increase and peak at 20–29 years of age, before progressively declining during aging (49). Thus, it is important for IEI studies to compare to an age-matched MAIT cell value for each patient, either internally or referencing external age-matched values, to confidently report any alterations to normal frequency.
Another consideration when interpreting data on MAIT cells is the infection status of the patient at the time of analysis. MAIT cells have been shown to dynamically change in frequency during an acute infection (52) with studies in mice suggesting they accumulate and expand at the tissue site of infection (45, 53). Thus, an active infection could cause a decrease in circulating MAIT cells that may be unrelated to the underlying genetic defect. In addition, the use of corticosteroids to treat asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease have also been shown to impact MAIT cell frequency (54, 55). Therefore, detailed clinical history, list of current medications, and the current infection status at the time of sampling should be provided. A more definitive approach to assess circulating MAIT cell frequency is to measure multiple samples over time. This would provide important insight into the stability of any observed change in MAIT cell frequency. This approach would also control for any infection-induced fluctuations when functionally assessing T cell (including MAIT cell) activation, proliferation, and cytotoxicity markers. As these would also be expected to alter with varying infection status.
Examination of tissue biopsies (particularly from areas of inflammation or infection), although challenging to obtain, would also address the question of MAIT cell kinetics in IEI. By directly examining MAIT cell frequency at tissue sites, it could then be correlated back to the proportion of circulating cells. This would provide an understanding of the relationship between circulating and tissue-resident MAIT cell populations, and if disturbances in MAIT cell frequency are directly attributable to the underlying IEI, rather than a consequence of increased inflammation/infection-induced tissue-homing.
4. Limited MAIT cell functional analysis in IEI
A less explored aspect of MAIT cells in IEI is the potential changes in their ability to respond to stimuli. MAIT cells can be activated via TCR-dependent or TCR-independent stimulation (2, 3). Factors that control or influence these separate activation pathways in MAIT cells could be elucidated by studying the functional response of MAIT cells from IEI patients.
Several studies have examined interferon (IFN)γ production by MAIT cells in IEI. MAIT cells from a PD-1 deficient patient produced less IFNγ in response to bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) + IL-12 stimulation (32). Also, MAIT cells from a T-bet deficient patient produced less IFNγ in response to phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)/ionomycin stimulation (40). However, in addition to IFNγ, MAIT cells can also produce proinflammatory cytokines TNF and IL-17A, as well as cytotoxic granules and perforin, that should be considered when undertaking functional analysis (4).
The most comprehensive functional analysis of MAIT cells in IEI was in individuals with STAT3 loss-of-function (n = 5–7) (24). STAT3-deficient MAIT cells produced normal levels of IFNγ, TNF and granzyme B when stimulated with PMA/ionomycin. However, they showed impaired IL-17A production under these conditions. In addition, STAT3-deficient MAIT cells were unable to produce IL-17A or IL-17F in Th17 culture conditions, suggesting a direct role for STAT3 regulating IL17A/IL17F transcription in MAIT cells. These functional results mirror what was observed for the functional dysregulation of STAT3-deficient CD4+ (Th17) T cells in the same individuals. These observations highlight the importance of assessing polyfunctionality of MAIT cell responses to stimuli in IEI, as it may provide fundamental insights into the key proteins required for differing MAIT cell effector functions.
5. Conclusion
MAIT cells are a particularly interesting immune subset to study in IEI. Given the signaling, activation, and functional pathways shared with NKT, γδ, CD8+ and Th17 T cells, it is not surprising that MAIT cells are often at the intersection of various immune cell effector responses across innate and adaptive immunity. However, it is important when contributing to, and assessing, the literature on MAIT cells in IEI that certain key factors are taken into consideration. It is essential to understand how MAIT cells are defined, and the comparative healthy reference ranges, to make informed interpretations of the impact of IEI on MAIT cell biology. Finally, the infection status at the time of sampling can also impact the strength of conclusions of these studies. In conclusion, MAIT cells are understudied yet play a unique role in human immunity, at the intersection of innate and adaptive responses. Understanding MAIT cells in the context of IEI provides an opportunity to understand their role and potential to contribute to immune dysregulation in IEI.
Author contributions
LJH: conceptualization, writing - original draft preparation. VLB: conceptualization, writing - reviewing and editing. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
LJH is supported by a National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (NHMRC) Investigator Grant (2007884) and a Jack Brockhoff Foundation Early Career Research Grants (JBF 4847-2021). VLB is supported by Sir Clive McPherson Family Research Fellowship and DW Keir Fellowship.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
- 1. Tangye SG, Al-Herz W, Bousfiha A, Cunningham-Rundles C, Franco JL, Holland SM, et al. Human inborn errors of immunity: 2022 update on the classification from the international union of immunological societies expert committee. J Clin Immunol (2022) 42:1473–507. doi: 10.1007/s10875-022-01289-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Kjer-Nielsen L, Patel O, Corbett AJ, Le Nours J, Meehan B, Liu L. Et al. MR1 presents microbial vitamin b metabolites to MAIT cells. Nature. (2012) 491(7426):717–23. doi: 10.1038/nature11605 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Ussher JE, Bilton M, Attwod E, Shadwell J, Richardson R, de Lara C, et al. CD161++ CD8+ T cells, including the MAIT cell subset, are specifically activated by IL-12+IL-18 in a TCR-independent manner. Eur J Immunol (2014) 44(1):195–203. doi: 10.1002/eji.201343509 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Dusseaux M, Martin E, Serriari N, Péguillet I, Premel V, Louis D, et al. Human MAIT cells are xenobiotic-resistant, tissue-targeted, CD161hi IL-17-secreting T cells. Blood. (2011) 117(4):1250–9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-08-303339 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Kurioka A, Ussher JE, Cosgrove C, Clough C, Fergusson JR, Smith K, et al. MAIT cells are licensed through granzyme exchange to kill bacterially sensitized targets. Mucosal Immunol (2015) 8(2):429–40. doi: 10.1038/mi.2014.81 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Howson LJ, Salio M, Cerundolo V. MR1-restricted mucosal-associated invariant T cells and their activation during infectious disease. Front Immunol (2015) 6:303. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00303 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Yap JY, Moens L, Lin MW, Kane A, Kelleher A, Toong C, et al. Intrinsic defects in b cell development and differentiation, T cell exhaustion and altered unconventional T cell generation characterize human adenosine deaminase type 2 deficiency. J Clin Immunol (2021) 41(8):1915–35. doi: 10.1007/s10875-021-01141-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Kaleviste E, Rühlemann M, Kärner J, Haljasmägi L, Tserel L, Org E, et al. 22 paucity in APECED is associated with mucosal and microbial alterations in oral cavity. Front Immunol (2020) 11:838. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00838 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Garcia-Solis B, Van Den Rym A, Pérez-Caraballo JJ, Al-Ayoubi A, Alazami AM, Lorenzo L, et al. Clinical and immunological features of human BCL10 deficiency. Front Immunol (2021) 12:786572. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.786572 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Martin E, Treiner E, Duban L, Guerri L, Laude H, Toly C, et al. Stepwise development of MAIT cells in mouse and human. PloS Biol (2009) 7(3):e54. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000054 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Wang Y, Ma CS, Ling Y, Bousfiha A, Camcioglu Y, Jacquot S, et al. Dual T cell- and b cell-intrinsic deficiency in humans with biallelic RLTPR mutations. J Exp Med (2016) 213(11):2413–35. doi: 10.1084/jem.20160576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Ghosh S, Köstel Bal S, Edwards ESJ, Pillay B, Jiménez Heredia R, Erol Cipe F, et al. Extended clinical and immunological phenotype and transplant outcome in CD27 and CD70 deficiency. Blood. (2020) 136(23):2638–55. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020006738 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Béziat V, Rapaport F, Hu J, Titeux M, Bonnet des Claustres M, Bourgey M, et al. Humans with inherited T cell CD28 deficiency are susceptible to skin papillomaviruses but are otherwise healthy. Cell. (2021) 184(14):3812–28.e30. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Bucciol G, Pillay B, Casas-Martin J, Delafontaine S, Proesmans M, Lorent N, et al. Systemic inflammation and myelofibrosis in a patient with takenouchi-kosaki syndrome due to CDC42 Tyr64Cys mutation. J Clin Immunol (2020) 40(4):567–70. doi: 10.1007/s10875-020-00742-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Smith DJ, Hill GR, Bell SC, Reid DW. Reduced mucosal associated invariant T-cells are associated with increased disease severity and pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. PloS One (2014) 9(10):e109891. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109891 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Moshous D, Martin E, Carpentier W, Lim A, Callebaut I, Canioni D, et al. Whole-exome sequencing identifies coronin-1A deficiency in 3 siblings with immunodeficiency and EBV-associated b-cell lymphoproliferation. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2013) 131(6):1594–603. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.01.042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Martin E, Minet N, Boschat AC, Sanquer S, Sobrino S, Lenoir C, et al. Impaired lymphocyte function and differentiation in CTPS1-deficient patients result from a hypomorphic homozygous mutation. JCI Insight (2020) 5(5):e133880. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.133880 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Pillay BA, Avery DT, Smart JM, Cole T, Choo S, Chan D, et al. Hematopoietic stem cell transplant effectively rescues lymphocyte differentiation and function in DOCK8-deficient patients. JCI Insight (2019) 5(11):e127527. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.127527 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Dickinson RE, Milne P, Jardine L, Zandi S, Swierczek SI, McGovern N, et al. The evolution of cellular deficiency in GATA2 mutation. Blood. (2014) 123(6):863–74. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-07-517151 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Cottineau J, Kottemann MC, Lach FP, Kang YH, Vély F, Deenick EK, et al. Inherited GINS1 deficiency underlies growth retardation along with neutropenia and NK cell deficiency. J Clin Invest. (2017) 127(5):1991–2006. doi: 10.1172/JCI90727 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Kerner G, Rosain J, Guérin A, Al-Khabaz A, Oleaga-Quintas C, Rapaport F, et al. Inherited human IFN-γ deficiency underlies mycobacterial disease. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130(6):3158–71. doi: 10.1172/JCI135460 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Hetemäki I, Kaustio M, Kinnunen M, Heikkilä N, Keskitalo S, Nowlan K, et al. Loss-of-function mutation in IKZF2 leads to immunodeficiency with dysregulated germinal center reactions and reduction of MAIT cells. Sci Immunol (2021) 6(65):eabe3454. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abe3454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Shahin T, Kuehn HS, Shoeb MR, Gawriyski L, Giuliani S, Repiscak P, et al. Germline biallelic mutation affecting the transcription factor Helios causes pleiotropic defects of immunity. Sci Immunol (2021) 6(65):eabe3981. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abe3981 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Wilson RP, Ives ML, Rao G, Lau A, Payne K, Kobayashi M, et al. STAT3 is a critical cell-intrinsic regulator of human unconventional T cell numbers and function. J Exp Med (2015) 212(6):855–64. doi: 10.1084/jem.20141992 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Martínez-Barricarte R, Markle JG, Ma CS, Deenick EK, Ramírez-Alejo N, Mele F, et al. Human IFN-γ immunity to mycobacteria is governed by both IL-12 and IL-23. Sci Immunol (2018) 3(30):eaau6759. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aau6759 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Cagdas D, Mayr D, Baris S, Worley L, Langley DB, Metin A, et al. Genomic spectrum and phenotypic heterogeneity of human IL-21 receptor deficiency. J Clin Immunol (2021) 41(6):1272–90. doi: 10.1007/s10875-021-01031-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Béziat V, Tavernier SJ, Chen YH, Ma CS, Materna M, Laurence A, et al. Dominant-negative mutations in human IL6ST underlie hyper-IgE syndrome. J Exp Med (2020) 217(6):e20191804. doi: 10.1084/jem.20191804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Klinken EM, Gray PE, Pillay B, Worley L, Edwards ESJ, Payne K, et al. Diversity of XMEN disease: Description of 2 novel variants and analysis of the lymphocyte phenotype. J Clin Immunol (2020) 40(2):299–309. doi: 10.1007/s10875-019-00732-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Howson LJ, Awad W, von Borstel A, Lim HJ, McWilliam HEG, Sandoval-Romero ML, et al. Absence of mucosal-associated invariant T cells in a person with a homozygous point mutation in MR1. Sci Immunol (2020) 5(49). doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abc9492 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Gonzalez-Granado LI, Ruiz-García R, Blas-Espada J, Moreno-Villares JM, Germán-Diaz M, López-Nevado M, et al. Acquired and innate immunity impairment and severe disseminated mycobacterium genavense infection in a patient with a NF-κB1 deficiency. Front Immunol (2018) 9:3148. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03148 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Klemann C, Camacho-Ordonez N, Yang L, Eskandarian Z, Rojas-Restrepo JL, Frede N, et al. Clinical and immunological phenotype of patients with primary immunodeficiency due to damaging mutations in NFKB2. Front Immunol (2019) 10:297. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00297 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Ogishi M, Yang R, Aytekin C, Langlais D, Bourgey M, Khan T, et al. Inherited PD-1 deficiency underlies tuberculosis and autoimmunity in a child. Nat Med (2021) 27(9):1646–54. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01388-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Winter S, Martin E, Boutboul D, Lenoir C, Boudjemaa S, Petit A, et al. Loss of RASGRP1 in humans impairs T-cell expansion leading to Epstein-Barr virus susceptibility. EMBO Mol Med (2018) 10(2):188–99. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201708292 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Lévy R, Langlais D, Béziat V, Rapaport F, Rao G, Lazarov T, et al. Inherited human c-rel deficiency disrupts myeloid and lymphoid immunity to multiple infectious agents. J Clin Invest (2021) 131(17). doi: 10.1172/JCI150143 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Okada S, Markle JG, Deenick EK, Mele F, Averbuch D, Lagos M, et al. IMMUNODEFICIENCIES. impairment of immunity to candida and mycobacterium in humans with bi-allelic RORC mutations. Science. (2015) 349(6248):606–13. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa4282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Rigaud S, Fondanèche MC, Lambert N, Pasquier B, Mateo V, Soulas P, et al. XIAP deficiency in humans causes an X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Nature. (2006) 444(7115):110–4. doi: 10.1038/nature05257 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Delmonte OM, Bergerson JRE, Kawai T, Kuehn HS, McDermott DH, Cortese I, et al. SASH3 variants cause a novel form of X-linked combined immunodeficiency with immune dysregulation. Blood. (2021) 138(12):1019–33. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020008629 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Kong XF, Martinez-Barricarte R, Kennedy J, Mele F, Lazarov T, Deenick EK, et al. Disruption of an antimycobacterial circuit between dendritic and helper T cells in human SPPL2a deficiency. Nat Immunol (2018) 19(9):973–85. doi: 10.1038/s41590-018-0178-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Schaballie H, Rodriguez R, Martin E, Moens L, Frans G, Lenoir C, et al. A novel hypomorphic mutation in STIM1 results in a late-onset immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2015) 136(3):816–9.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.03.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Yang R, Mele F, Worley L, Langlais D, Rosain J, Benhsaien I, et al. Human T-bet governs innate and innate-like adaptive IFN-γ immunity against mycobacteria. Cell. (2020) 183(7):1826–47.e31. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.046 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Martin-Fernandez M, Buta S, Le Voyer T, Li Z, Dynesen LT, Vuillier F, et al. A partial form of inherited human USP18 deficiency underlies infection and inflammation. J Exp Med (2022) 219(4). doi: 10.1084/jem.20211273 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Hauck F, Blumenthal B, Fuchs S, Lenoir C, Martin E, Speckmann C, et al. SYK expression endows human ZAP70-deficient CD8 T cells with residual TCR signaling. Clin Immunol (2015) 161(2):103–9. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2015.07.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Béziat V, Li J, Lin JX, Ma CS, Li P, Bousfiha A, et al. A recessive form of hyper-IgE syndrome by disruption of ZNF341-dependent STAT3 transcription and activity. Sci Immunol (2018) 3(24):eaat4956. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aat4956 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Le Voyer T, Neehus AL, Yang R, Ogishi M, Rosain J, Alroqi F, et al. Inherited deficiency of stress granule ZNFX1 in patients with monocytosis and mycobacterial disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2021) 118(15). doi: 10.1073/pnas.2102804118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. van Wilgenburg B, Loh L, Chen Z, Pediongco TJ, Wang H, Shi M, et al. MAIT cells contribute to protection against lethal influenza infection in vivo. Nat Commun (2018) 9(1):4706. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07207-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. van Wilgenburg B, Scherwitzl I, Hutchinson EC, Leng T, Kurioka A, Kulicke C, et al. MAIT cells are activated during human viral infections. Nat Commun (2016) 7:11653. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11653 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Flament H, Rouland M, Beaudoin L, Toubal A, Bertrand L, Lebourgeois S, et al. Outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection is linked to MAIT cell activation and cytotoxicity. Nat Immunol (2021) 22(3):322–35. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00870-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Corbett AJ, Eckle SB, Birkinshaw RW, Liu L, Patel O, Mahony J, et al. T-Cell activation by transitory neo-antigens derived from distinct microbial pathways. Nature. (2014) 509(7500):361–5. doi: 10.1038/nature13160 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Gherardin NA, Souter MN, Koay HF, Mangas KM, Seemann T, Stinear TP, et al. Human blood MAIT cell subsets defined using MR1 tetramers. Immunol Cell Biol (2018) 96(5):507–25. doi: 10.1111/imcb.12021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Novak J, Dobrovolny J, Novakova L, Kozak T. The decrease in number and change in phenotype of mucosal-associated invariant T cells in the elderly and differences in men and women of reproductive age. Scand J Immunol (2014) 80(4):271–5. doi: 10.1111/sji.12193 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Lee OJ, Cho YN, Kee SJ, Kim MJ, Jin HM, Lee SJ, et al. Circulating mucosal-associated invariant T cell levels and their cytokine levels in healthy adults. Exp Gerontol. (2014) 49:47–54. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2013.11.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Howson LJ, Napolitani G, Shepherd D, Ghadbane H, Kurupati P, Preciado-Llanes L, et al. MAIT cell clonal expansion and TCR repertoire shaping in human volunteers challenged with salmonella paratyphi a. Nat Commun (2018) 9(1):253. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02540-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Wang H, D'Souza C, Lim XY, Kostenko L, Pediongco TJ, Eckle SBG, et al. MAIT cells protect against pulmonary legionella longbeachae infection. Nat Commun (2018) 9(1):3350. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05202-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Hinks TS, Zhou X, Staples KJ, Dimitrov BD, Manta A, Petrossian T, et al. Innate and adaptive T cells in asthmatic patients: Relationship to severity and disease mechanisms. J Allergy Clin Immunol (2015) 136(2):323–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.01.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Hinks TS, Wallington JC, Williams AP, Djukanović R, Staples KJ, Wilkinson TM. Steroid-induced deficiency of mucosal-associated invariant T cells in the chronic obstructive pulmonary disease lung. implications for nontypeable haemophilus influenzae infection. Am J Respir Crit Care Med (2016) 194(10):1208–18. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201601-0002OC [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]