Abstract
Background and Aims
Cytokine profiles of peripheral blood and other bodily fluids provide diagnostic indicators for assessing inflammatory processes. Menstrual effluent may provide a noninvasive source of biological material for monitoring cytokine levels in blood and in endometrial tissues. This pilot study investigated the potential of measuring cytokines in menstrual effluent, and compared the cytokine profiles of menstrual versus peripheral blood.
Methods
Seven healthy donors (aged ≥18 and ≤45 years) collected menstrual effluent on day 2 of menses. Matched peripheral blood samples were collected by venous blood draw on the same day. Levels of 62 cytokines were measured in all samples by 62‐plex Luminex assay.
Results
Peripheral blood and menstrual effluent cytokine profiles were tenuously correlated (r 2 = 0.26, p < 0.0001), with higher levels detected in menstrual effluent for 48/62 cytokines. Thirty five cytokines were significantly elevated in menstrual effluent compared to peripheral blood samples (IL‐8, CCL2, CCL4, LIF, IL‐1RA, IL‐6, IL‐1β, HGF, CCL3, FGF‐2, TNF‐α, VEGF‐A, IL‐1α, CXCL1, IL‐9, IL‐10, EGF, CXCL5, CSF3, EOTAXIN, TGF‐α, TRAIL, CXCL10, VEGF‐D, IL‐12P40, CXCL9, IL‐18 RESISTIN, IL‐22, IL‐21, CSF1, IFN‐γ, IL‐17A, CXCL12, IL‐12p70). Two cytokines (LEPTIN, CSF2) were expressed at significantly lower levels in menstrual effluent compared to peripheral blood. Linear regression of individual cytokines found low predictive power (linear regression p > 0.05) for 53/62 cytokines in menstrual effluent versus peripheral blood. Levels of TGF‐β (r 2 = 0.87, p = 0.002) and CCL7 (r 2 = 0.63, p = 0.033) were significantly positively correlated between matched menstrual and peripheral blood samples.
Conclusion
In this group of study participants, the cytokine profile of menstrual effluent was quantitatively distinct from peripheral blood, and also characterized by higher levels of inflammatory signaling. This pattern of comparative menstrual blood cytokine profiles points to a need for further studies to evaluate the relationship between peripheral and menstrual blood cytokines in broader populations including both healthy and diseased states.
Keywords: chemokine, cytokine, endometriosis, endometrium, inflammation, menstrual blood, TGF‐β
Abbreviations
- CCL7
CC motif chemokine ligand 7
- TGF‐β
transforming growth factor beta
1. INTRODUCTION
Cytokines are a broad category of small, nonstructural proteins that participate in regulation of inflammatory and immune responses. These proteins are pleiotropic intercellular messengers, and have diverse proinflammatory, anti‐inflammatory, chemo‐attractive, or hematopoietic colony‐stimulating functions. 1 Cytokine secretion patterns provide insight into the biology of tissue homeostasis in health and disease, and multiplexed cytokine assays are widely used for quantification and analysis of diagnostic biomarkers in clinical research and medical practice. While peripheral blood is the most commonly studied fluid for cytokine analysis across a range of health conditions, cytokine profiles in other fluid samples, such as cerebral spinal fluid, saliva, urine, semen, or tears provide a unique perspective into the cellular signaling specific to these tissues. 2
Menstrual effluent is a complex fluid comprised of blood, vaginal secretions, and endometrial cells. Absence of implantation triggers menstruation via hormonal signaling to induce ischemia, apoptosis, necrosis, and shedding of cellular debris from the uterine wall as menstrual effluent. 3 In both healthy and endometriotic women, laparoscopic and endometrial sampling from peritoneal and endometrial tissues identified clinically relevant alterations in inflammatory signaling compared to healthy controls. 4 However, utility of these approaches is limited by the surgically invasive specimen sampling methods. Menstrual effluent is a readily accessible source of endometrial cytokines, which can be passively collected and does not require invasive sampling procedures. However, to date, only limited evaluations of cytokines in menstrual blood have been reported in healthy women. 5 , 6
Recent studies have demonstrated that menstrual blood may be a comparable alternative to systemic blood for monitoring common biomarkers such as HbA1c, cholesterol, follicle stimulating hormone, lipoproteins, and high sensitivity C‐reactive protein. 7 , 8 N‐acetyl‐b‐d‐glucosamine and myeloperoxidase activities in menstrual effluent from patients with endometriosis show positive correlation with peripheral blood measurements, and are significantly elevated compared to control subjects. 9 In women with menorrhagia, menstrual effluent has increased levels of tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF‐α) and reduced levels of vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF‐A), matrix metalloproteinase‐2 (MMP‐2) and metalloproteinase‐9 (MMP‐9). 10 Meanwhile, combined interleukin‐6 (IL‐6)/interleukin‐1 beta (IL‐1β) or TNF‐α/IL‐6 measurements in menstrual effluent demonstrate high sensitivity or specificity for detection of chronic endometritis when both cytokines exceed cutoff values. 11 Thus, while menstrual effluent is rich in inflammatory markers specific to endometrial tissues and provides insights into menstrual cycle physiology, our understanding of cytokine profiles of menstrual effluent in healthy women remains limited.
In the present study, we characterized the peripheral and menstrual effluent profile of 62 cytokines in 7 women via a Luminex Magnetic assay. The primary goal of our study was to compare the cytokine profiles of peripheral and menstrual effluent samples, and to evaluate potential correlates between these samples.
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
2.1. Subjects and sample collection
This was a prospective observational study of 7 self‐reported healthy reproductive‐aged women randomly selected from a cohort previously described in Naseri et al. 8 The sample size for this pilot was based on the number of matching menstrual and venous blood samples available for analysis at the time of the study. Exclusion criteria included being younger than 18 years of age, older than 45 years, postmenopausal, not menstruating regularly, and uncomfortable with or clinically unable to use a menstrual cup for menstrual effluent collection. Participants were given a study kit containing a menstrual cup (Diva International Inc.) and two blood collection tubes. Serum separator tubes and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) plasma collection tubes were used for sample preparation. Participants were instructed to contact study staff on the first day of their period, being the first day with actual flow. That day, participants were instructed to stop intake of food after midnight. On the second day of their period participants were instructed to use the menstrual cup for 3 h, starting at the time they woke up in the morning, and then immediately pour the collected menstrual effluent into the designated blood collection tubes. The second day was chosen due to convenience and because the second day of menstruation for most participants was found to be the day with the heaviest flow of menstrual effluent. Participants were instructed to present at the study site on the same day of menstrual sample collection to provide a corresponding venous blood draw. Both samples were spun down and frozen at −80°C.
2.2. Luminex cytokine analysis
All assays were performed by the Human Immune Monitoring Center at Stanford University. Human 62‐plex Procarta kits (Thermo Fisher Scientific) were used according to the manufacturer's recommendations with modifications as described below. Beads were added to a 96 well plate and washed in a Biotek ELx405 washer. Samples were added to the plate containing the mixed antibody‐linked beads and incubated at room temperature for 1 h followed by overnight incubation at 4°C with shaking at 500–600 rpm. Following the overnight incubation plates were washed in a Biotek ELx405 washer and then biotinylated detection antibody was added for 75 min at room temperature with shaking. Plate was washed as above, and streptavidin‐PE was added. After incubation for 30 min at room temperature, washes were performed as described above. Reading buffer was added to the wells. Each sample was measured in duplicate. Plates were read using a Luminex 200 or a FM3D FlexMap instrument with a lower bound of 50 beads per sample per cytokine. Custom Assay Chex control beads by Radix BioSolutions were added to all wells for assay quality control (Radix BioSolutions). To reduce potential variability, all laboratory experimental work was carried out on the same sample plate, and cytokine measurements for each sample were interpolated against a standard curve.
2.3. Statistical analysis
Luminex data was acquired with Xponent software and reports were generated using Masterplex QT‐4/Mirai Bio/Hitachi software and analyzed with Excel and Prism. Statistical tests, n‐ and p‐values are all located in the figures and/or legends. Significance was defined as p < 0.05. No statistical methods were used to predetermine sample size. Nonparametric comparison between menstrual and peripheral blood samples was performed by Wilcoxon matched‐pairs signed rank test. Multiple comparisons method: Two‐stage linear step‐up procedure of Benjamini, Kireger and Yekutieli, at desired false discovery rate (FDR) (Q) = 5%. Linear regression among the 62 cytokines was used to identify cytokines that are nominally correlated between peripheral and menstrual samples (linear regression p < 0.05). Robustness of linear correlation was tested by measuring if correlations remained significant after removal of any single datapoint.
3. RESULTS
Menstrual and peripheral blood samples from 7 subjects were analyzed via 62‐plex human immuno‐assay to investigate the relative cytokine levels of both samples. Overall, menstrual samples contained a higher inflammatory profile compared to peripheral blood, and the cytokine profiles of peripheral and menstrual effluent were significantly positively correlated (r 2 = 0.26, p < 0.001), Figure 1. The highest levels of cytokines for both samples were interleukin‐1 receptor antagonist (IL1‐RA), resistin, soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (S‐VCAM‐1), plasminogen activator inhibitor‐1 (PAI‐1), soluble intercellular adhesion molecule‐1 (siCAM‐1), and C‐X‐C motif chemokine 5 (CXCL5) (Table 1). A total of 77% (48/62) of cytokines measured had higher mean levels detected in menstrual compared to peripheral blood.
Figure 1.
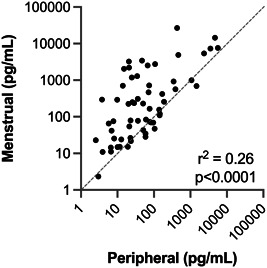
Correlation of mean peripheral and menstrual effluent cytokine profiles. Mean levels of 62 cytokines in systemic versus menstrual effluent samples from n = 7 subjects shown on a log‐log scale. Linear regression values r 2 = 0.26, p < 0.0001. Gray dashed line indicates the equality line for a 1:1 correlation. For 48/62 cytokines, mean menstrual effluent levels are above the equality line
Table 1.
Expression levels of cytokines in peripheral and menstrual effluent
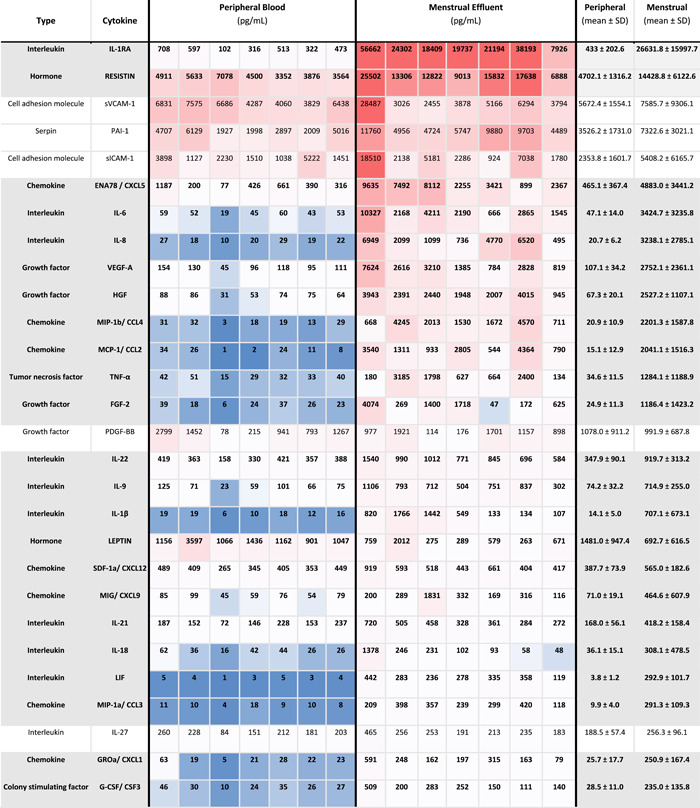
|
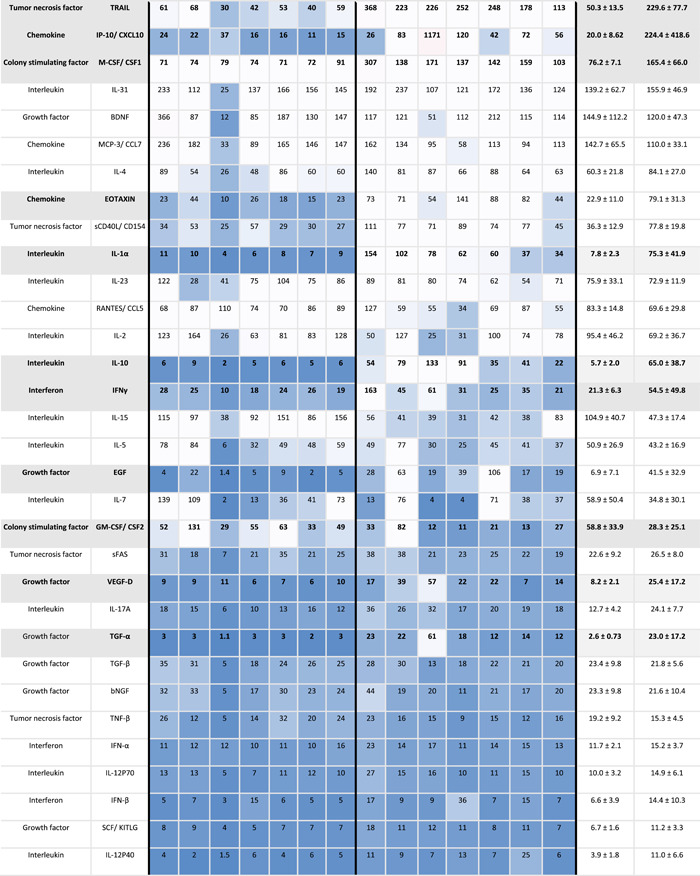
|
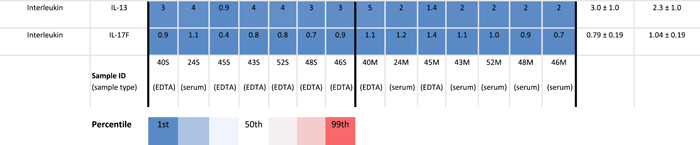
|
Note: Mean cytokines measurements in pg/ml ±SD in peripheral and menstrual effluent shown for n = 7 subjects, on a 1–99th percentile Blue‐Red color scale. Serum and plasma sample identification provided for each specimen (bottom row).
To further evaluate differences between the two types of fluid samples, menstrual effluent cytokine levels were normalized against peripheral blood levels from each subject. Thirty five cytokines were significantly elevated in menstrual effluent compared to peripheral samples (IL‐8, CCL2, CCL4, LIF, IL‐1RA, IL‐6, IL‐1β, HGF, CCL3, FGF‐2, TNF‐α, VEGF‐A, IL‐1α, CXCL1, IL‐9, IL‐10, EGF, CXCL5, CSF3, EOTAXIN, TGF‐α, TRAIL, CXCL10, VEGF‐D, IL‐12P40, CXCL9, IL‐18 RESISTIN, IL‐22, IL‐21, CSF1, IFN‐γ, IL‐17A, CXCL12, IL‐12p70) (Figure 2 and Table 2). Il‐8, CCL2, and CCL4 had approximately 100‐fold higher expression levels in menstrual samples, likely reflecting the recruitment of monocytes, neutrophils and various lymphocytes to endometrial tissues during induction of menstrual flow. Two cytokines (LEPTIN, CSF2) were significantly lower in menstrual effluent samples compared to serum.
Figure 2.
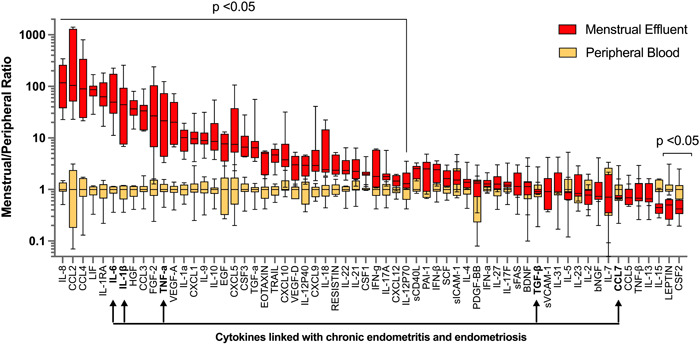
Fold change in cytokine levels in menstrual versus peripheral blood samples.
Menstrual levels of each cytokine were normalized to the systemic blood levels of each patient. Graph depicts median and min/max for normalized menstrual and systemic blood levels for each cytokine. Differences between groups were tested by Wilcoxon matched‐pairs signed rank test. Multiple comparisons method: two‐stage linear step‐up procedure of Benjamini, Kireger and Yekutieli, at desired false discovery rate (q) = 5%. FDR‐adjusted p‐values are depicted. Arrows indicate cytokines in endometrial tissues that are associated with chronic endometritis and endometriosis. FDR, false discovery rate
Table 2.
Differentially expressed cytokines in menstrual effluent
| Cytokine | Mean menstrual/peripheral ratio (SD) | Adjusted p‐value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Higher in menstrual effluent vs. peripheral blood | |||
| Chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 2 | CCL2 | 481.6 (606.5) | 0.020 |
| Chemokine (C‐C motif) ligands 4 | CCL4 | 212.1 (278.9) | 0.020 |
| Interleukin 8 | IL‐8 | 150.1 (115.7) | 0.020 |
| Leukemia inhibitory factor | LIF | 87.1 (43.0) | 0.020 |
| Interleukin 6 | IL‐6 | 85.3 (81.2) | 0.020 |
| Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist | IL‐1RA | 77.2 (56.2) | 0.020 |
| Interleukin 1β | IL‐1β | 67.3 (88.6) | 0.020 |
| Fibroblast growth factor 2 | FGF2 | 66.1 (84.8) | 0.032 |
| Tumor necrosis factor alpha | TNF‐α | 44.1 (44.3) | 0.020 |
| Hepatocyte growth factor | HGF | 40.6 (21.5) | 0.020 |
| Chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 3 | CCL3 | 36.2 (26.2) | 0.020 |
| Vascular endothelial growth factor A | VEGF‐A | 28.5 (21.1) | 0.020 |
| Chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 5 | CXCL5 | 24.5 (37.8) | 0.020 |
| Interleukin 10 | IL‐10 | 15.3 (17.8) | 0.020 |
| Transforming growth factor alpha | TGF‐α | 13.2 (18.8) | 0.020 |
| chemokine (C‐X‐C motif) ligand 1 | CXCL1 | 12.0 (8.4) | 0.020 |
| Interleukin 9 | IL‐9 | 12.0 (8.9) | 0.020 |
| Interleukin 1 alpha | IL‐1α | 10.1 (5.3) | 0.020 |
| Colony‐stimulating factor 3 | CSF3 | 9.9 (8.3) | 0.020 |
| Chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 9 | CXCL9 | 8.7 (14.2) | 0.020 |
| Chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 10 | CXCL10 | 8.2 (10.6) | 0.032 |
| Epidermal growth factor | EGF | 8.1 (3.9) | 0.032 |
| Interleukin‐18 | IL‐18 | 7.5 (8.0) | 0.020 |
| TNF‐related apoptosis‐inducing ligand | TRAIL | 4.9 (1.9) | 0.020 |
| Eotaxin | EOTAXIN | 4.0 (1.7) | 0.032 |
| RESISTIN | RESISTIN | 3.2 (1.5) | 0.020 |
| Interleukin‐12 subunit beta | IL‐12P40 | 3.1 (1.4) | 0.020 |
| Vascular endothelial growth factor D | VEGF‐D | 3.0 (1.6) | 0.020 |
| Interleukin‐22 | IL‐22 | 2.9 (1.7) | 0.020 |
| Interleukin‐21 | IL‐21 | 2.9 (1.8) | 0.045 |
| Interferon gamma | IFN‐γ | 2.7 (2.2) | 0.020 |
| Interleukin‐17A | IL‐17A | 2.2 (1.6) | 0.032 |
| Colony stimulating factor 1 | CSF1 | 2.2 (1.0) | 0.032 |
| Interleukin‐12 | IL‐12P70 | 1.6 (0.9) | 0.045 |
| Chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 12 | CXCL12 | 1.5 (0.4) | 0.032 |
| Lower in menstrual effluent vs. peripheral blood | |||
| Colony stimulating factor 2 | CSF2 | 0.4 (0.2) | 0.020 |
| LEPTIN | LEPTIN | 0.4 (0.2) | 0.020 |
Note: Name, fold change in menstrual/peripheral blood expression levels, and FDR‐adjusted p‐value for differences between menstrual and peripheral blood expression.
Abbreviations: FDR, false discovery rates; IFN, interferons; IL, interleukin; TGF, transforming growth factor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor.
To further investigate the relationship between peripheral and menstrual effluent cytokine profiles, we performed linear regression for peripheral versus menstrual effluent measurements of each cytokine. Nine cytokines (Table 3) were nominally correlated between peripheral and menstrual samples (linear regression p < 0.05). To reduce the likelihood of false positive results due to low sample size, we performed outlier analysis to test if linear correlations were still significant after removal of any single datapoint. Following this screen, two cytokines, TGF‐β and CCL7, remained significantly correlated between menstrual and peripheral blood samples (Figure 3). For the other 53/62 cytokines analyzed, there was no correlation between menstrual and peripheral blood levels, indicating that menstrual effluent contains a distinct and elevated cytokine profile that cannot be readily predicted from peripheral blood measurements in healthy subjects.
Table 3.
Correlation between cytokines in peripheral and menstrual effluent
| Cytokine | Nominal correlation | Outlier analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r 2 | p‐value | r 2 | p‐value | ||
| Transforming growth factor beta | TGF‐β | 0.87 | 0.002 | 0.82 | 0.013 |
| Chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 7 | CCL7 | 0.63 | 0.033 | 0.66 | 0.0497 |
| Interleukin 5 | IL‐5 | 0.63 | 0.033 | 0.60 | 0.07 |
| Colony‐stimulating factor 2 | CSF2 | 0.87 | 0.002 | 0.20 | 0.37 |
| Leptin | 0.86 | 0.003 | 0.00 | 0.99 | |
| Transforming growth factor alpha | TGF‐α | 0.81 | 0.005 | 0.21 | 0.36 |
| Chemokine (C‐X‐C motif) ligand 1 | CXCL1 | 0.78 | 0.009 | 0.47 | 0.53 |
| C‐X‐C motif chemokine ligand 10 | CXCL10 | 0.73 | 0.014 | 0.09 | 0.57 |
| Interferon beta | IFN‐β | 0.72 | 0.015 | 0.05 | 0.68 |
Note: Name, linear regression r 2 values, and slope p‐values for cytokine expression levels measured in peripheral versus menstrual effluent. Outlier analysis shows correlation after removal of the single most significant datapoint. Bold values are statitistically significantly different.
Abbreviations: IFN, interferons; IL, interleukin; TGF, transforming growth factor.
Figure 3.
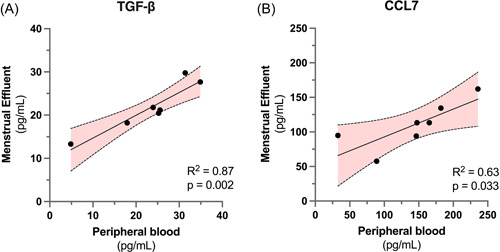
Menstrual and peripheral blood measurements of TGF‐β and CCL7 levels are significantly correlated.
Linear correlation and 95% confidence interval for (A) TGF‐β (r 2 = 0.87, p = 0.002) and (B) CCL7 (r 2 = 0.63, p = 0.033) measurements in menstrual vs peripheral blood samples for n = 7 subjects. Elevated levels of TGF‐β and CCL7 have been previously implicated in endometrial inflammatory disorders. TGF, transforming growth factor
4. DISCUSSION
We measured levels of 62 clinically‐relevant cytokines in menstrual and peripheral blood from 7 healthy subjects. In these healthy subjects, the cytokine profile of menstrual effluent was only moderately correlated with values that were obtained peripheral blood draws, revealing a unique, menstrual pattern of physiological inflammatory signaling. Normal menstruation is an inflammatory process, featuring intercellular signaling between endometrial cells, neutrophils and macrophages. 12 Many of the highly‐expressed cytokines in menstrual effluent have distinct physiological roles in endometrial and menstrual health, including regulation of leukocyte recruitment, regulation of chronic inflammation, and promotion of endometrial repair via stimulation of angiogenic growth factor secretion (Table 4). These results demonstrate the feasibility of measuring diverse cytokines in menstrual effluent and highlight the potential clinical utility of menstrual effluent as a unique and noninvasive source of biological material for investigations into inflammatory processes relevant to female reproductive health.
Table 4.
Description of 10 most‐differentially expressed cytokines in menstrual versus venous blood samples
| Cytokine | Type | Functions | Refs. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chemokine (C‐C motif) ligand 2 | CCL2 | Chemokine |
|
1 , 13 |
| Chemokine (C‐C motif) ligands 4 | CCL4 | Chemokine |
|
14 , 15 |
| Interleukin 8 | IL‐8 | Interleukin |
|
1 , 16 |
| Leukemia inhibitory factor | LIF | Interleukin |
|
17 , 18 |
| Interleukin 6 | IL‐6 | Interleukin |
|
19 |
| Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist | IL‐1RA | Interleukin |
|
20 |
| Interleukin 1β | IL‐1β | Interleukin |
|
20 , 21 |
| Fibroblast growth factor 2 | FGF2 | Growth Factor |
|
22 , 23 |
| Tumor necrosis factor alpha | TNF‐α | Tumor Necrosis factor |
|
1 |
Our study offers an exploratory glimpse into the comparative inflammatory profiles of peripheral blood and menstrual effluent. The results create a snapshot view of inflammation at a single timepoint during the menstrual cycle, allowing direct comparison of data from menstrual and peripheral samples. Further studies should investigate the temporal profile of cytokines expression levels throughout the menstrual cycle, as distinct populations of cytokines may be differentially regulated in menstrual versus peripheral blood at different times during menstruation. Menstruation typically lasts 4 days, and the relationship between cytokine profiles of menstrual and peripheral blood may change over the course of the menstrual cycle.
Our small sample size is a key limitation to the interpretations facilitated by this study. Factors such as aging‐related changes in fecundity may influence the cytokine profile of menstrual effluent and could not be evaluated in the present study due to the limited number of participants. However inter‐individual differences in cytokine profiles are reported to be strikingly low, 6 and we observed similarly low levels of inter‐sample variability in our data. We performed FDR correction on statistical analyses to account for multiple comparisons testing.
A second limitation of this study is that the health status of participants was self‐reported, and medical records were not assessed to confirm absence of intrauterine conditions such as endometriosis and endometritis. Further studies on menstrual effluent may benefit from including an infectious screen to minimize potential interference from infection. A third potential limitation of this study is the use of both plasma and serum samples for cytokine analysis. Although we did not note any confounding effect on cytokine levels from blood collection in serum‐separator versus EDTA‐coated tubes (Table 1), the low number of subjects in this pilot study does not allow for robust evaluation of potential effects of serum versus plasma blood collection tubes on cytokine measurements. Consequent to these limiting factors, our analyses likely under‐represent the number of differentially expressed cytokines, as well as the number of cytokines with significant correlations between peripheral and menstrual samples. Fourth, our study represents an observational profile of cytokine signaling in healthy subjects, and does not enable functional inference as to the physiological significance of differential cytokine expression. Differences in cytokine stability in peripheral versus menstrual effluent may confound physiological differences of cytokine expression in endometrial tissues versus systemic circulation. Further research should investigate these relationships among a broader population, and explore menstrual effluent cytokine profiles in both healthy and diseased states.
Our findings expand upon the initial reports of Guterstam et al, who compared peripheral and menstrual effluent profiles of 20 cytokines measured on day 1 of menstrual flow. 6 Measures of fold‐change between menstrual and peripheral blood samples are highly consistent for the 13 cytokines that were measured in both studies. Our findings corroborate significantly increased levels of IL‐6, IL‐8, TNF‐α, IFN‐γ, VEGF, IL‐1β, MIP‐1a/CCL3, CXCL10, IL‐18, IL‐12p70, and IL‐10, and identify an additional 24 cytokines with differential expression in menstrual effluent. Together these reports support the replicability of comparative cytokine measurements in menstrual effluent in relation to peripheral blood measures.
Additionally, we uncovered two cytokines in menstrual effluent whose levels may be reliably predicted from peripheral blood analysis: TGF‐β and MCP‐3/CCL7. Testing menstrual effluent for levels of IL‐1β, IL‐6, TNF‐α, as well as TGF‐β and CCL7 may provide clinicians insights into fertility conditions associated with elevated levels of these cytokines. TGF‐β is a multifunctional growth factor that controls proliferation, differentiation, and chemotaxis. 1 It is highly expressed in whole blood by multiple cell types, 24 and in human uterine tissues throughout the menstrual cycle. 25 Peripheral blood levels of TGF‐β have been investigated as biomarkers of diabetic retinopathy, 26 intraperitoneal adhesions, 27 , 28 and lupus nephritis. 29 , 30 In the endometrium, TGF‐β regulates vascular maturation, and increased TGFB1 expression is associated with recurrent pregnancy loss and with decreased menstrual bleeding. 31 , 32 Dysregulation of TGF‐β signaling is also implicated in reproductive health conditions such as polycystic ovaries, 33 and endometrial cancer. 34
CCL7 (also known as MCP‐3), is a chemokine for monocytes, and other leukocytes. 35 Elevated levels of CCL7 are present in laparoscopic aspiration samples from adults with endometriosis, 36 and uterine CCL7 production has been associated with leukocyte chemotaxis in cervical ripening, 37 and with preterm delivery. 38 Serum and plasma levels of CCL7 have been proposed as biomarkers of atherosclerosis, 39 systemic sclerosis, 40 and severity of COVID‐19 infection. 41 Elevated plasma levels of both TGF‐β and CCL7 have also been associated with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. 42 Larger follow‐up studies should evaluate the predictive power of TGF‐β and CCL7 in menstrual effluent compared to peripheral blood samples, and explore the potential utility of noninvasive menstrual effluent sampling as a diagnostic measure for different health conditions.
5. CONCLUSION
This observational study expands upon recent endeavors to elucidate the biomarker profiles of peripheral vs menstrual effluent samples. Menstrual effluent contains a unique inflammatory profile that reflects the inflammatory state of endometrial tissues, and is distinctly different from the cytokine signature found in peripheral blood. Further study is needed to establish how various cytokines are correlated between menstrual and peripheral blood across different health conditions, such as endometriosis, endometritis, polycystic ovary syndrome, and recurrent pregnancy loss. Our preliminary results suggest that menstrual effluent can be utilized as a noninvasive option for monitoring uterine inflammatory and fertility signaling. These measures provide a baseline for further comparisons with menstrual cytokine measures in health and disease.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Sara Naseri: investigation; methodology; writing—review & editing. Yael Rosenberg‐Hasson: formal analysis; investigation; writing—original draft. Holden T. Maecker: investigation. Maria I. Avrutsky: formal analysis; visualization; writing—original draft; Writing—review & editing. Paul D. Blumenthal: conceptualization; funding acquisition; resources; writing—review & editing.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
S. Naseri and M. Avrutsky are employed by Qurasense Inc., which develops laboratory tests for analyzing menstrual blood. Funding sources and financial relationships had no role in study design, collection, analysis, or interpretation of data.
ETHICS STATEMENT
The study was approved by the Stanford Institutional Review Board (IRB‐35817). Interested women completed a telephone screening to assess eligibility and willingness to participate, and all participants signed consent forms.
TRANSPARENCY STATEMENT
The lead author Paul D. Blumenthal affirms that this manuscript is an honest, accurate, and transparent account of the study being reported; that no important aspects of the study have been omitted; and that any discrepancies from the study as planned (and, if relevant, registered) have been explained.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This study was internally funded by the Section of Family Planning Services and Research in the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecolgy at Stanford University School of Medicine.
Naseri S, Rosenberg‐Hasson Y, Maecker HT, Avrutsky MI, Blumenthal PD. A cross‐sectional study comparing the inflammatory profile of menstrual effluent vs. peripheral blood. Health Sci Rep. 2023;6:e1038. 10.1002/hsr2.1038
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data underlying this article are available in the article and in its online Supporting Information Material.
REFERENCES
- 1. Chauhan P, Nair A, Patidar A, Dandapat J, Sarkar A, Saha B. A primer on cytokines. Cytokine. 2021;145:155458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Liu C, Chu D, Kalantar‐Zadeh K, George J, Young HA, Liu G. Cytokines: from clinical significance to quantification. Adv Sci. 2021;8(15):2004433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Yang H, Zhou B, Prinz M, Siegel D. Proteomic analysis of menstrual blood. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics: MCP. 2012;11(10):1024‐1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Kyama CM, Overbergh L, Debrock S, et al. Increased peritoneal and endometrial gene expression of biologically relevant cytokines and growth factors during the menstrual phase in women with endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 2006;85(6):1667‐1675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Gargiulo AR, Fichorova RN, Politch JA, Hill JA, Anderson DJ. Detection of implantation‐related cytokines in cervicovaginal secretions and peripheral blood of fertile women during ovulatory menstrual cycles. Fertil Steril. 2004;82(Suppl 3):1226‐1234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Crona Guterstam Y, Strunz B, Ivarsson MA, et al. The cytokine profile of menstrual blood. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2021;100(2):339‐346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Naseri S, Brewster RCL, Blumenthal PD. Novel use of menstrual blood for monitoring glycaemic control in patients with diabetes: a proof‐of‐concept study. BMJ Sexual & Reproductive Health. 2022;48(2):123‐127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Naseri S, Lerma K, Blumenthal P. Comparative assessment of serum versus menstrual blood for diagnostic purposes: a pilot study. J Clin Lab Med. 2019;4(2). 10.16966/2572-9578.130 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9. da Silva CM, Vilaça Belo A, Passos Andrade S, et al. Identification of local angiogenic and inflammatory markers in the menstrual blood of women with endometriosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2014;68(7):899‐904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Malik S, Day K, Perrault I, Charnock‐Jones DS, Smith SK. Reduced levels of VEGF‐A and MMP‐2 and MMP‐9 activity and increased TNF‐α in menstrual endometrium and effluent in women with menorrhagia. Hum Reprod. 2006;21(8):2158‐2166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Tortorella C, Piazzolla G, Matteo M, et al. Interleukin‐6, interleukin‐1β, and tumor necrosis factor α in menstrual effluents as biomarkers of chronic endometritis. Fertil Steril. 2014;101(1):242‐247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Evans J, Salamonsen LA. Inflammation, leukocytes and menstruation. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2012;13(4):277‐288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Dahm‐Kähler P, Ghahremani M, Lind AK, Sundfeldt K, Brännström M. Monocyte chemotactic protein‐1 (MCP‐1), its receptor, and macrophages in the perifollicular stroma during the human ovulatory process. Fertil Steril. 2009;91(1):231‐239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Lee D, Shin KJ, Kim DW, et al. CCL4 enhances preosteoclast migration and its receptor CCR5 downregulation by RANKL promotes osteoclastogenesis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(5):495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Kitaya K, Nakayama T, Okubo T, Kuroboshi H, Fushiki S, Honjo H. Expression of macrophage inflammatory Protein‐1β in human endometrium: its role in endometrial recruitment of natural killer cells. J Clin Endocr. 2003;88(4):1809‐1814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Maybin JA, Hirani N, Jabbour HN, Critchley HOD. Novel roles for hypoxia and prostaglandin E2 in the regulation of IL‐8 during endometrial repair. Am J Pathol. 2011;178(3):1245‐1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Nicola NA, Babon JJ. Leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF). Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015;26(5):533‐544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Salleh N, Giribabu N. Leukemia inhibitory factor: roles in embryo implantation and in nonhormonal contraception. Sci World J. 2014;2014:1‐10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Tanaka T, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T. IL‐6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol. 2014;6(10):a016295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Dinarello CA. The IL‐1 family of cytokines and receptors in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2019;15(10):612‐632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Gonçalves GA, Invitti AL, Parreira RM, Kopelman A, Schor E, Girão MJBC. p27(kip1) overexpression regulates IL‐1β in the microenvironment of stem cells and eutopic endometriosis co‐cultures. Cytokine. 2017;89:229‐234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Benington L, Rajan G, Locher C, Lim LY. Fibroblast growth factor 2‐A review of stabilisation approaches for clinical applications. Pharmaceutics. 2020;12(6):508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Paiva P, Hannan NJ, Hincks C, et al. Human chorionic gonadotrophin regulates FGF2 and other cytokines produced by human endometrial epithelial cells, providing a mechanism for enhancing endometrial receptivity. Hum Reprod. 2011;26(5):1153‐1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Morikawa M, Derynck R, Miyazono K. TGF‐β and the TGF‐β family: context‐dependent roles in cell and tissue physiology. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol. 2016;8(5):a021873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Chegini N, Zhao Y, Williams RS, Flanders KC. Human uterine tissue throughout the menstrual cycle expresses transforming growth factor‐beta 1 (TGF beta 1), TGF beta 2, TGF beta 3, and TGF beta type II receptor messenger ribonucleic acid and protein and contains [125I]TGF beta 1‐binding sites. Endocrinology. 1994;135(1):439‐449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Bonfiglio V, Platania CBM, Lazzara F, et al. TGF‐β serum levels in diabetic retinopathy patients and the role of Anti‐VEGF therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(24):9558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Torres K, Pietrzyk Ł, Plewa Z, et al. TGF‐β and inflammatory blood markers in prediction of intraperitoneal adhesions. Adv Med Sci. 2018;63(2):220‐223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Eren EC, Basım P. Role of peripheral inflammatory biomarkers, transforming growth factor‐beta and interleukin 6 in predicting peritoneal adhesions following repeat cesarean delivery. Ir J Med Sci. 2022;191(6):2697‐2704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Rashad NM, El‐Shabrawy RM, Said D, El‐Shabrawy SM, Emad G. Serum levels of transforming growth factor beta‐1 (TGF‐β1) as an early no invasive marker for diagnosis of lupus nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Egypt J Immunol. 2019;26(1):31‐42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Jin T, Almehed K, Carlsten H, Forsblad‐d'Elia H. Decreased serum levels of TGF‐β1 are associated with renal damage in female patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2012;21(3):310‐318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Lu Q, Sun D, Shivhare SB, et al. Transforming growth factor (TGF) β and endometrial vascular maturation. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:640065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Maybin JA, Boswell L, Young VJ, Duncan WC, Critchley HOD. Reduced transforming growth Factor‐β activity in the endometrium of women with heavy menstrual bleeding. J Clin Endocr Metab. 2017;102(4):1299‐1308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Kristensen SG, Kumar A, Kalra B, et al. Quantitative differences in TGF‐β family members measured in small antral follicle fluids from women with or without PCO. J Clin Endocr Metab. 2019;104(12):6371‐6384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Zakrzewski PK. Canonical TGFβ signaling and its contribution to endometrial cancer development and Progression‐Underestimated target of anticancer strategies. J Clin Med. 2021;10(17):3900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Tsou CL, Peters W, Si Y, et al. Critical roles for CCR2 and MCP‐3 in monocyte mobilization from bone marrow and recruitment to inflammatory sites. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(4):902‐909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Bailey AP, Hill AS, Beste MT, et al. Comparison of cytokines in the peritoneal fluid and conditioned medium of adolescents and adults with and without endometriosis. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2021;85(3):e13347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Takemura M, et al. Cyclic mechanical stretch augments both interleukin‐8 and monocyte chemotactic protein‐3 production in the cultured human uterine cervical fibroblast cells. Mol Hum Reprod. 2004;10(8):573‐580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Jacobsson B, Holst RM, Andersson B, Hagberg H. Monocyte chemotactic protein‐2 and ‐3 in amniotic fluid: relationship to microbial invasion of the amniotic cavity, intra‐amniotic inflammation and preterm delivery. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2005;84(6):566‐571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Waśkiel‐Burnat A, Niemczyk A, Blicharz L, et al. Chemokine C‐C motif ligand 7 (CCL7), a biomarker of atherosclerosis, is associated with the severity of alopecia areata: a preliminary study. J Clin Med. 2021;10(22):5418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Yanaba K, Komura K, Kodera M, et al. Serum levels of monocyte chemotactic protein‐3/CCL7 are raised in patients with systemic sclerosis: association with extent of skin sclerosis and severity of pulmonary fibrosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2006;65(1):124‐126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Yang Y, Shen C, Li J, et al. Plasma IP‐10 and MCP‐3 levels are highly associated with disease severity and predict the progression of COVID‐19. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020;146(1):119‐127.e4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Lee KS, Chung JH, Lee KH, et al. Plasma levels of monocyte chemotactic protein 3 and beta‐nerve growth factor increase with amnestic mild cognitive impairment. Cell Mol Immunol. 2009;6(2):143‐147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data underlying this article are available in the article and in its online Supporting Information Material.


