Abstract
Background
Adverse outcome pathways (AOPs) are conceptual frameworks that organize knowledge about biological interactions and toxicity mechanisms. They present a sequence of events commencing with initial interaction(s) of a stressor, which defines the perturbation in a biological system (molecular initiating event, MIE), and a dependent series of key events (KEs), ending with an adverse outcome (AO). AOPs have recently become the subject of intense studies in a view to better understand the mechanisms of nanomaterial (NM) toxicity. Silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) are one of the most explored nanostructures and are extensively used in various application. This, in turn, has increased the potential for interactions of Ag NPs with environments, and toxicity to human health. The aim of this study was to construct a putative AOPs (pAOP) related to reproductive toxicity of Ag NPs, in order to lay the groundwork for a better comprehension of mechanisms affecting both undesired toxicity (against human cell) and expected toxicity (against microorganisms).
Methods
PubMed and Scopus were systematically searched for peer-reviewed studies examining reproductive toxicity potential of Ag NPs. The quality of selected studies was assessed through ToxRTool. Eventually, forty-eight studies published between 2005 and 2022 were selected to identify the mechanisms of Ag NPs impact on reproductive function in human male. The biological endpoints, measurements, and results were extracted from these studies. Where possible, endpoints were assigned to a potential KE and an AO using expert judgment. Then, KEs were classified at each major level of biological organization.
Results
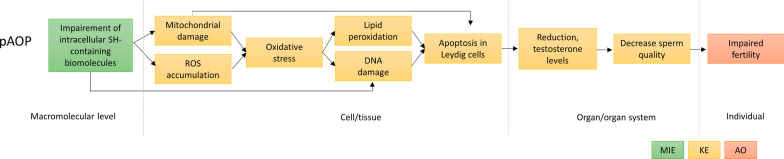
We identified the impairment of intracellular SH-containing biomolecules, which are major cellular antioxidants, as a putative MIE, with subsequent KEs defined as ROS accumulation, mitochondrial damage, DNA damage and lipid peroxidation, apoptosis, reduced production of reproductive hormones and reduced quality of sperm. These successive KEs may result in impaired male fertility (AO).
Conclusion
This research recapitulates and schematically represents complex literature data gathered from different biological levels and propose a pAOP related to the reproductive toxicity induced by AgNPs. The development of AOPs specific to NMs should be encouraged in order to provide new insights to gain a better understanding of NP toxicity.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12989-022-00511-9.
Keywords: Adverse outcome pathways, Silver nanoparticles, Reproductive toxicity, Molecular initiating event, Key events, Adverse outcome
Background
With respect to the European recommendation on the definition for nanomaterials (NMs), adopted in 2011 (Recommendation 2011/696/EU) and revised in 2022 (2022/C 229/01), NMs are materials with at least one dimension ranging between 1 and 100 nm, except those with a specific surface area by volume < 6 m2/cm3 [1]. Despite having the same composition as the corresponding bulk material, due to size effects, NPs display distinct characteristics. Among the NMs, Silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) are one of the most studied ones and they have been extensively used in various fields such as in food, cosmetic, textile, and medical industries [2–4]. Their high preference in such areas is generally attributed to their unique features differing from bulk materials, including optical, electrical, magnetic and antibacterial properties [5, 6]. Given that Ag NPs are incorporated into commercially available products primarily for antibacterial and antifungal purposes, their abundance in everyday products leads to concerns related to their health effects and the possible consequences of their dispersal in the environment [4, 5].
When taken up into the human body, the reactivity of NMs depends on complex physicochemical properties such as size, agglomeration state, dissolution kinetics, capping agent, surface charge, and specific surface area [7–9]. The small size and remarkably high surface area of NPs enhance their interaction with biomolecules, biological membranes, cells or tissues. The high surface area of metal- and metal-oxide based NPs such as copper, zinc oxide, silver, manganese oxide, and cerium oxide increases the potential that metal ions are released from these NPs as they dissolve [10, 11]. The so-called “Trojan-horse” mechanism, through which Ag NPs act as a vehicle that carries silver across the cell membrane followed by intra-cellular dissolution of Ag NPs to release Ag ions, has been proposed as one mechanism of Ag NP toxicity [12–14]. In the presence of molecular oxygen and protons, silver atoms on the surface of Ag NPs (Ag0) can be oxidized resulting in the release of Ag ions [15, 16]. Dissolution of Ag NPs to form Ag ions may lead to the formation of hydroxyl radicals [17]. The formation of hydroxyl radicals can go through a process similar to the Fenton reaction, in which Ag NPs act as a Fenton-like reagent reaction [Ag + H2O2 + H+ = Ag+ + •OH + H2O] [18, 19], thus contributing to the formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Still, Ag ion release cannot alone account for the observed toxic effects [20]. The toxicity mechanism for Ag NP could be related to their small size, the amount of released silver ions, or a combination of both [13, 21].
Released ions from Ag NPs bind to ligands, creating a mixture of metal ion-ligand complexes. Silver is a soft acid according to the Pearson (HSAB) acid–base theory, therefore it shows high affinity for soft bases, and among them, it is particularly affine for thiols [10, 22, 23]. Thiol groups of cysteine residues are crucial for many proteins to maintain their integrity and function [24, 25]. The most abundant thiolated molecules in human cells include some proteins, especially metallothioneins and Zn-finger proteins, and small molecules such as glutathione (GSH) [26–28]. These molecules play an important role in maintaining the oxidative balance [26], metal homeostasis and DNA integrity in cells [29]. Ag ions complexation with these thiol groups may induce protein misfolding, scavenge thiolated molecules, thereby hindering their function and impairing cellular antioxidant mechanisms [14, 30, 31]. Due to the complex nature of Ag NP exposure, there remains uncertainty and to some extent controversy, regarding the level to which each constituent —ion, ion-protein complex, particle— contributes to cellular toxicity.
Considering their presence in food additives, food packaging, in textiles such as clothing and bedding and in toothbrushes, hair straighteners, disinfectant sprays as cosmetic and hygiene products, the major routes of exposure of Ag NPs are dermal contact [32], ingestion [33], and inhalation [34]. According to European Commission Scientific Committees, the main target organs for Ag NP in the human body are the spleen, liver, and kidney, with less distribution to other organs [20]. In the aforementioned study from the European Commission Scientific Committees, tissue distribution of 20 nm, 80 nm, and 110 nm of Ag NPs were investigated in rats after single and repeated intravenous administration of 1 mL/animal (~ 25 µg/mL, approx. 0.1 mg/kg bw/d) by Lankveld et al. [35]. Following single exposure, highest silver concentrations per gram organ were found in spleen followed by liver for both 80 and 110 nm particles. In spleen, Ag NP concentrations were approxiately 20 fold lower for 20 nm particles compared to the larger particles. Concentration of 110 nm particles were found around 1600 ng per gram spleen. Ag NP concentrations in liver increased with particle size (169, 539 and 1077 ng/g liver for 20, 80 and 110 nm particles, respectively). In the other organs evaluated (kidney, heart, lungs, testes and brain) silver concentrations were much lower and comparable for all sizes [35].
There are studies that recorded high levels of silver accumulation in the brain and testicles [20, 33, 35–39], although the significance for toxicity is unknown [20]. In 2018, the Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS) of the European Commission recommended to collect information on the reproductive toxicity of Ag NPs [40]. The SCCS also noted the lack of information on systemic availability via the relevant uptake route(s) that would allow drawing conclusions on reproductive system toxicity [40]. Therefore, the potential toxicity mechanism of Ag NPs is a matter of great concern with regards to reproductive toxicity [41].
Exposure to nanoparticles may cause adverse effects on the reproductive function and fertility in adult males, including impact on reproductive cells, spermatogenesis, the seminiferous tubules, and testes [42]. In vitro studies show that Ag NPs cause the alteration of germ cells and somatic cells function mainly due to cell membrane peroxidation, oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage, DNA damage, and apoptosis [43–45]. Necrotic spermatogonial cells, degenerative alterations in the cellular architecture of testes and epididymis are reported in in vivo models [46, 47]. In some animal models, the accumulation of NPs in the testes is demonstrated [48, 49]. It is also reported that Ag NPs affect reproductive hormone levels such as testosterone and androgen hormones [47], sperm quantity and quality [46], which suggest potential consequences for male fecundity.
Likewise, in non-mammalian models, Ag NPs reproductive toxicity has been extensively studied. Ag NP considerably decrease reproductive potential in Caenorhabditis elegans [50]. Yan et al. prove the maternal transfer of Ag NPs to offsprings in Daphnia magna together with inhibition of the reproduction capability of F0 and F1 generations [51].
To support effective risk assessments of chemicals, The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) has introduced the Adverse Outcome Pathway (AOP) conceptual framework [52], which is designed to organize toxicological information, thereby assisting integrated approaches to testing and assessment strategies [52]. Considering the creation of non-animal testing approaches, emphasis has been placed on AOPs as a conceptual support for developing in vitro and in silico testing strategies [52]. This framework presents a sequence of events commencing with initial interaction(s) of a stressor, which defines the perturbation in a biological system (i.e., molecular initiating event, MIE), and then a dependent series of intermediate key events (KEs), ending up in an adverse outcome (AO) [52, 53]. KEs describe a toxicological response and are linked to one another by a Key Event Relationship (KER), which establishes one KE as upstream and one KE as downstream [52, 53]. The AOP-Wiki database [54] serves as the primary repository of qualitative information for the international AOP development effort.
Within AOP-Wiki, one AOP that describes reproductive failure due to Ag NP exposure is available, which is AOP207 [55]. It has been established on the non-mammalian model Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) by using a Bayesian network (BN) model [56]. The MIE of this AOP is oxidative stress through NADPH oxidase activity, reproduction failure is the outcome. PMK-1 (P38 MAPK) activation, HIF-1 activation, mitochondrial damage, DNA damage, and apoptosis are the described key events. Another AOP regarding reproductive toxicity of Ag NPs has been reported in zebrafish [57]. It describes that Ag NPs exposure causes oxidative stress, induces germ cells apoptosis via mitochondrial-dependent pathway, and ultimately impairs the reproduction in zebrafish [57]. Moreover, some reproductive failure-releated AOPs exist for other NPs such as graphene oxide and UV-activated Titanium dioxide NPs (TiO2 NPs). First, in AOP210 [58] the comprehensive mechanism of stress response to graphene oxide NPs is investigated in C. elegans using transcriptomics, metabolomics and lipidomics. Based on the results, the authors propose an AOP for oxidative stress leading to reproductive failure in C. elegans. This AOP includes the KEs increased oxidative stress, activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and activation of transcription factor DAF-16/FOXO, inhibition of WNT signaling, defect embryogenesis, with the AO being reproductive. In addition, in AOP208 [59], JAK/STAT and TGF-beta pathway activation leading the reproductive failure has been used to describe the mechanism by which UV-activated TiO2 NPs affect the reproductive function [60].
Anticipating Safety Issues at the Design Stage of NAno Product Development (ASINA) EU Horizon 2020 (H2020) project is developing a specific Safe by Design (SbD) Management Methodology, consistent with modern business management systems, to deliver SbD solutions and inform design decisions. Within this project, the investigation of toxicity mechanisms of antimicrobial NMs that born to exert a toxicity effect is pivotal to support their design and match safety requirements. The current literature is reviewed in order to identify major areas of concerns related to the toxicity of the NM categories under investigation, using an AOP-oriented approach. With this perspective, in the present study, the reproductive toxicity of Ag NPs toward male mammalian models has been reviewed and a putative testable AOP is proposed, since previous related work has only focused on non-mammalian models. Based on the existing literature, we evaluated the MIE, KEs and AOs related to the induction of reproductive failure. As a follow-up of the present investigation, we expect to compare the AOPs of different models, including identified toxicity thresholds, so as to propose the most promising design options (concentration, physicochemical features, stabilizing agents) able to guarantee a safe use of Ag NMs.
Methods
Literature search
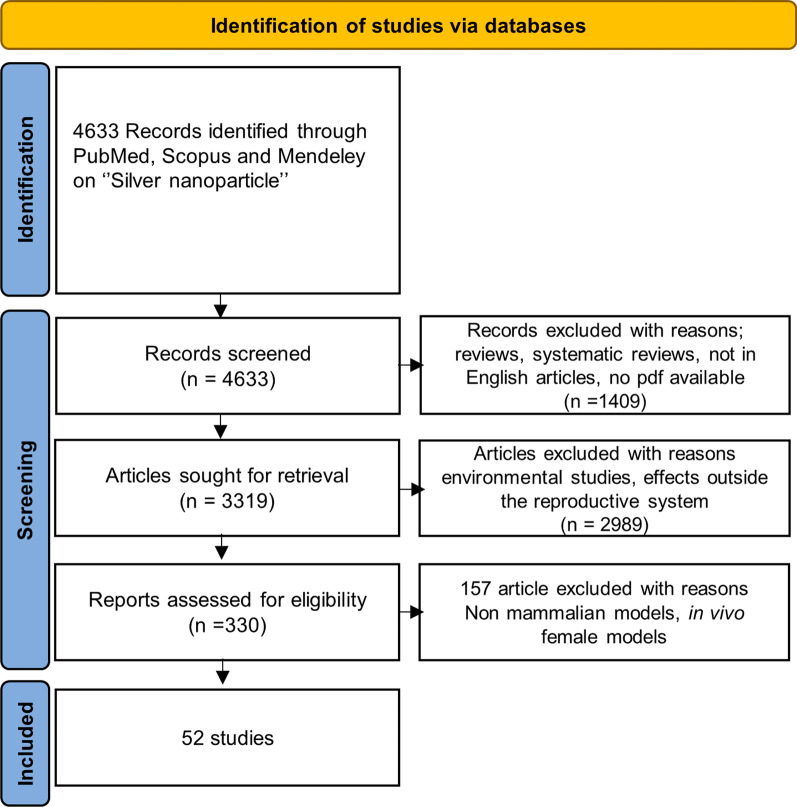
The searches for peer-reviewed research publications on the toxicity of Ag NPs were conducted in PubMed and Scopus and limited between 2007 and 2022 according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) recommendations [61]. The used search string was: (("silver"[MeSH Terms] OR "silver"[All Fields]) AND ("nanoparticles"[MeSH Terms] OR "nanoparticles"[All Fields]) AND ("toxic"[All Fields] OR "toxical"[All Fields] OR "toxically"[All Fields] OR "toxicant"[All Fields] OR "toxicities"[All Fields] OR "toxicity"[MeSH Subheading] OR "toxicity"[All Fields] OR "toxics"[All Fields]). In Scopus, the used keywords were: (silver AND nanoparticle AND toxicity). As shown in Fig. 1, a total of 4633 articles were identified. Among them, the articles not written in English, those that could not be accessed because they were either non-open access or because the main authors did not answer to our pdf request, as well as systematic reviews were excluded and this resulted in 3319 articles. Then, articles related to plant species or target organs outside of the reproductive system were eliminated. Finally, 330 articles were found to be related to reproductive toxicity of Ag NPs. Articles reporting data collected on in vivo female models, non-mammalian models such as drosophila, medaka, nematodes and zebrafish were further excluded. Finally, 52 articles were selected to identify how Ag NPs affect reproductive function in male in vivo and in vitro models.
Fig. 1.
Scheme of evaluation of the literature between 2007 and 2022
The articles were separated into two parts, in vivo and in vitro. While 44 studies were in vivo studies, 6 of them were in vitro studies. Two study comprises both in vivo and in vitro models; therefore, they were evaluated in both groups for the corresponding parts. That is, 46 in vivo data and 8 in vitro data were collected from 52 studies in total.
Quality assessment
Study quality, study design adequacy for their intended measures and the reliability of outcome were assessed in these 52 studies by using the Toxicological data Reliability Assessment Tool (ToxRTool) [62]. These studies were evaluated in terms of the nanoparticle identification (synthesis, characterization, p-chem informations) (group I), in vivo or in vitro test system characterization (animal source, age, body weight information, housing-feeding conditions, cell types, cultivation conditions) (group II), study design description (administration route, dose, frequency/duration of exposure etc.) (group III), study results documentation (endpoints, methods judgment) (group IV), and plausibility of study design and results (group V).
The studies were scored between 0 and 21 points or 0–18 points for in vivo and in vitro, respectively (reliable without restrictions, in vivo: 18–21 points, in vitro: 15–18 points; reliable with restrictions, in vivo: 13–17 points, in vitro: 11–14 points; not reliable, in vivo: < 13 points, in vitro < 11 points). Studies with a score of ≥ 13 (in vivo) and ≥ 11 (in vitro) points were classified as high quality.
Database analysis to identify potential KEs
The selected high quality studies were analyzed and reported in detail in our database as recommended by AOP-expert groups [53, 63, 64]. The physicochemical properties of the nanoparticles used in these articles (particle size, shape, surface area, surface charge, agglomeration status, surface coating, purity), characterization of the test organism used (animal sex, age, weight, cell type), route of administration, exposure dose and duration, methods, biological endpoints, and key results were reported separately for each article. The aim of this evaluation was to understand connection between p-chem properties and relevant key events and adverse outcomes, which would feed the ASINA SbD strategy.
Biological endpoints, measurements, methods were identified to define the standard strategy for nanoparticle reproductive toxicity evaluation and are listed in Table 1. The terminology used in the title of KEs were chosen according to the OECD guideline on AOP development [52]. All KEs were evaluated for three main criteria: credibility, measurability, and regulatory compliance. After that, KEs were classified at each major level of biological organization (molecular, cellular, tissue, organ, individual) and selected with respect to their potency to be measured in a relatively routine manner, in opposition to those that require highly specialized expertise or equipment. To establish the AOP frame, KEs that were reported as either transient or reversible were avoided.
Table 1.
Database summary of the analysis of 4 studies out of 48 selected studies
| Ag NP p-chem |
Experimental model and mode of exposure | Exposure dose, sampling time | Biological/toxicological Endpoints |
Actual measurements and methods | Result | Potential key event(s) (KE nr. from AOP-Wiki)a | Potential adverse outcomes (AOs) associated with the key event (AO nr. from AOP-Wikia | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Size: 50 nm Shape: Spherical Hydrodynamic size:113.4 ± 12.1 nm Zeta potential: − 12.30 ± 0.4 mV |
Adult male SD rats Oral gavage |
50 mg/kg bw, 3 months | Sperm Evaluation | Sperm Motility, Concentration, and Viability by eosin staining |
Increased sperm morphological abnormalities Decreased sperm concentrations motility and viability |
Decreased sperm quantity or quality in the adult, Decreased fertility (ID505, ID520) |
Impaired fertility (ID330, ID406) |
[46] | |
| Oxidative Status | GSH level, CAT activity and lipid peroxidation MDA content in testicular tissue by commercial kits |
Decreased CAT activity, Increased MDA content, Non-significant change in GSH level |
Decreased protection against oxidative stress, Occurance oxidative stress (ID210, ID1112, ID1249, ID1538, ID1869) Lipid Peroxidation (ID1445 or ID1511) |
Oxidative Damage (ID356) |
|||||
| Hormonal Assessment | Serum testosterone, LH and FSH by ELISA kit | Decreased testosterone, LH and FSH levels |
Reduction, testosterone level (ID1613, ID1689, ID1612) Reduced, Gonadotropins (ID1986) |
Decreased sperm quantity or quality in the adult, Decreased fertility (ID505, ID520) | |||||
| DNA damage | DNA strand breaks in testicular tissue by COMET assay | Increased DNA damage | Increased DNA damage (ID1194) | DNA Damage (ID1194) | |||||
| Histopathological Examination | Testis and Seminiferous tubules by Hematoxylin and Eosin (HE) staining |
Testis and Seminiferous tubules Histological alterations Necrotic spermatogonial cells |
Testicular atrophy (ID1506) |
Male reproductive tract malformations (ID348) Reduced, Reproductive Success (ID675) |
|||||
|
Size:45 nm PVP (< 1%) Zeta potential: − 20 mV |
New Zealand White male rabbits Intravenous |
5 mM AgNP solution (0.6 mg/kg bw) 2 months (weekly) |
Sperm Evaluation | Sperm Volume, Concentration, and Viability | Decreased sperm motility, concentration and volume | Decreased sperm quantity or quality in the adult, Decreased fertility (ID505, ID520) |
Impaired fertility (ID330, ID406) |
[88] | |
| Oxidative Status | MDA content, NO concentration, CAT and GPX Activity in sperm and blood samples by commercial kits |
Increased NO, and MDA content Decreased CAT activity, and GSH level |
Decreased protection against oxidative stress, Occurence oxidative stress (ID210, ID1112, ID1249, ID1538, ID1869) Lipid Peroxidation (ID1445 or ID1511) |
Oxidative Damage (ID356) |
|||||
|
Size:40 nm Shape: Spherical |
Adult male NMRI mice Oral gavage |
500 mg/kg bw with a time interval of 24 h for 35 days | Oxidative Status | Total antioxidant capacity and Lipid peroxidation parameters | Decrease in the total antioxidant capacity, Increased MDA content |
Decreased protection against oxidative stress, Occurence oxidative stress (ID210, ID1112, ID1249, ID1538, ID1869) Lipid Peroxidation (ID1445 or ID1511) |
Oxidative Damage (ID356) |
[98] | |
| Hormonal Assessment | Serum testosterone level by comercial kits | Decreased testosterone hormone | Reduction, testosterone level (ID1613, ID1689, ID1612) | Decreased sperm quantity or quality in the adult, Decreased fertility (ID505, ID520) | |||||
| Histological parameters | Testis, volume of interstitial tissue and seminiferous tubules | Decreased mean volume of testicular tissue and volume of seminiferous tubules Decreased sperm density, mean number of spermatocytes, mean number of Sertoli cells | Testicular atrophy (ID1506) |
Male reproductive tract malformations (ID348) Reduced, Reproductive Success (ID675) |
|||||
|
Size:100 nm Shape: Spherical SSA: 7.5329m2/g Zeta potential: − 18.9 mV |
Male Rats Sub dermal |
10 and 50 mg/kg bw, 7 and 28 days | Sperm Evaluation | Sperm motility, velocity by HE staining | Decreased sperm motility and velocity | Decreased sperm quantity or quality in the adult, Decreased fertility (ID505, ID520) | Impaired fertility | [47] | |
| Oxidative Status | MDA, GSH, CAT | Increased Lipid peroxidization, Decreased SOD, CAT, GSH and total thiols | Decreased protection against oxidative stress, Occurence oxidative stress (ID210, ID1112, ID1249, ID1538, ID1869) |
Oxidative Damage (ID356) |
|||||
| Hormonal Assessment | Testosterone, LH and FSH | Decreased testosterone, LH and FSH levels (dose dependent |
Reduction, testosterone level (ID1613, ID1689, ID1612) Reduced, Gonadotropins (ID1986) |
Decreased sperm quantity or quality in the adult, Decreased fertility (ID505, ID520) | |||||
| Histological parameters | Cellular achitecture of testes and epididymis | Degenerative alterations in the cellular architecture of testes and epididymis | Testicular atrophy (ID1506) |
Male reproductive tract malformations (ID348) Reduced, Reproductive Success (ID675) |
|||||
aAs several KEs and AOs are related to some of these cellular mechanisms, we indicate the title of only some of them, but the IDs of all of them are cited
Results and discussion
Quality assessment of the identified studies
The quality of 52 selected studies were assessed using ToxRTool. Four records were analysed as poor studies because of missing material characterization and/or usage of ultra-high concentrations or doses and/or no controls for biological endpoints have been included. Seven records were acceptable studies, with most quality criteria fulfilled but not strictly all. Finally, forty-one records were considered good studies, with all quality criteria fulfilled.
Overall, the 48 selected studies were classified as good and acceptable quality and these were later used in subsequent data evaluations.
Dataset evaluation
Datasets were created through our database containing a summary of the selected in vitro and in vivo studies. The in vitro datasets comprised studies performed on germ cells, Leydig, Sertoli cells or human semen. In these studies, the used cells were either commercial cell lines including mouse Sertoli cells (TM4 and 15P-1) or Leydig cells (TM3), or primary Sertoli cells (collected from 50 to 54 weeks-old Cobb-500 roosters), or C18–4 mouse spermatogonial stem cells established from type A spermatogonia isolated from 6-day-old mouse testes.
Among the in vivo studies, 17 studies used the oral route of exposure, i.e. Ag NPs were administered via oral gavage or through food/water, 13 used intraperitoneal injection, 9 used intravenous injection, 1 used subdermal, 1 intratracheal, and 1 intratesticular administration routes, which were mostly conducted in rats [25 studies], mice [15 studies] and rabbits [2 studies].
The dose ranges used in these studies were quite wide, for example in the 17 oral administration studies, 0.015 to 500 mg/kg/bw doses were applied. The dose was generally linked with those selected in previous studies. Some of the studies pointed that the investigated doses were in the range between the lowest observable adverse effect level (LOAEL) and a no observable adverse effect level (NOAEL) [46, 65], i.e., 125 mg/kg and 30 mg/kg, respectively, as suggested by a 90-day oral toxicity study, based on signs of liver toxicity [66].
In each study, the physicochemical properties of the used Ag NP was strictly reviewed, so that we could further identify the influence of these properties on the adverse outcome on the reproductive system. Ag NPs size range varied between 8.92 and 200 nm (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
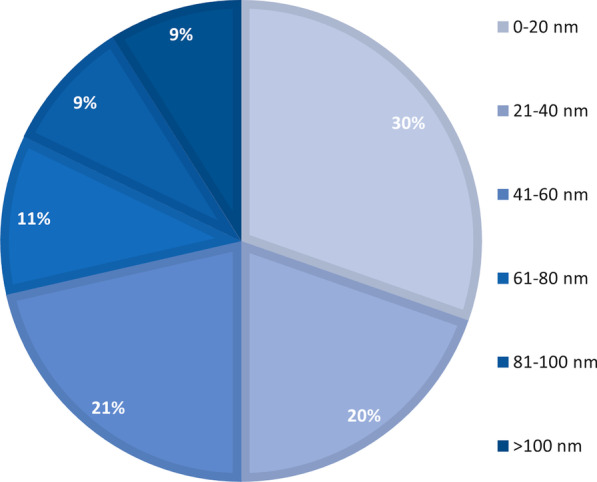
Size range of Ag NPs used for both in vivo and in vitro reproductive toxicity studies indicating the most prevalent size of Ag NPs (0–20 nm) employed for reproductive toxicity studies
Nine studies reported that the used Ag NPs were coated with polyvinyl pyrrolidone (PVP) or citrate. Moreover, some studies used Ag NPs produced via green method such as biogenic production in Bacillus funiculus, baker’s yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) or V. opulus L. fruit extract. The studied Ag NPs were mostly spherically-shaped.
Potential molecular initiating events
Two mechanisms involved in the toxicity of Ag NPs have been proposed. First, silver ions are formed and released, mediated by the oxidation of the metallic silver core, inducing the formation of ROS [67]. Second, silver ions interaction with enzymes and proteins containing thiol groups, such as metallothioneins or zinc-finger proteins, affect cellular processes such as cellular respiration and antioxidant defense system, possibly resulting in cell death [13, 14, 30, 68, 69]. Silver ions, indeed, are soft acid according to the HSAB principle, consequently they show high affinity towards soft bases and among them silver is highly affine for biomolecules containing thiols. However, it is important to go one-step back and explore the link between the oxidative stress and Ag NP dissolution to understand via which mechanism Ag NPs induce oxidative stress, in order to identify molecular initiating event(s).
Ag NP dissolution mechanisms are well described [10, 17, 70, 71]. The release of ions from Ag NPs has been shown to be an oxidation involving dissolved oxygen and protons. The reaction stoichiometry is as shown in the Eq. (1) [19].
| 1 |
Dissolution of Ag NPs to form Ag ions may accompany the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide under acidic conditions leading to the formation of hydroxyl radicals [17]. The formation of hydroxyl radicals can go through a process similar to the Fenton reaction, in which Ag NPs act as a Fenton-like reagent [17]. Under neutral and alkaline conditions, the reaction of Ag NPs with H2O2 generates oxygen instead of °OH radical [19]. The pH of the environment plays a role in the Ag NPs dissolution, as illustrated by Eq. (2) [71].
| 2 |
The ability of generating radicals has been reported across a variety of metal and metal oxide NPs, such as copper nanoparticles, zinc oxide nanoparticles, Ag NPs [72–74]. Previous reports using electron spin resonance (ESR) coupled with spin trapping and spin labeling prove that free radicals are derived from the surface of Ag NPs [75, 76].
Inorganic NPs preferably enter into the cells via endocytosis [77]. Endocytosis can be categorized into phagocytosis and pinocytosis [78]. The uptake of larger particles (> 500 nm) is usually associated with phagocytosis. Pinocytosis can be classified into clathrin mediated endocytosis (CME) and caveolae mediated endocytosis (79). The internalization of nanoparticles with particles size < 200 nm usually proceeds by CME. Smaller nanoparticles (< 50 nm) undergo caveolae mediated endocytosis [80]. The uptake of NPs can be influenced by factors such as the physicochemical properties of NPs and cell types [81]. In cells exposed to AgNPs, the NPs are observed in early endosomes originating from membrane invagination [82, 83], which then fuse into late endosomes and ultimately to lysosomes. It is also supposed that AgNPs may directly cross the membrane to reach the cytoplasm, possibly by direct membrane translocation (81). The exact mechanisms mediating the penetration of AgNPs through the membrane still remain to be elucidated. Whatever the route of internalization, the local environment around Ag NPs drastically changes. In the favor of low lysosomal pH, Ag NPs undergo intracellular dissolution, leading to Ag(I) species [12, 22]. This behavior is related to the so-called “Trojan horse” mechanism and leads to high Ag(I) concentrations in cellular compartments that Ag ions would otherwise not reach. Intracellular Ag(I) is a chemically reactive form of silver and shows remarkable affinity to zinc-finger domains of proteins, thiol-containing enzymes and molecules, mainly GSH and metallothioneins. Binding to these ligands leads to the subsequent formation of intracellular Ag(I)-thiolate complexes [30, 84, 85]. Such interaction affects the native domain structure of these proteins, which plays a role in maintaining the cellular homeostasis and antioxidant systems. As a consequence, it will influence their biological functions [14, 69, 84–86].
Due to the abovementioned mechanisms, since a MIE describes an initial point of interaction between stressors and the biomolecule, we propose that the impairment of intracellular SH-containing biomolecules can be defined as a MIE of the pAOP described here. Indeed, the release of Ag(I) in solution, the consequent production of ROS together with the thiol-Ag ion complexation would activate such MIE and lead to a chain of intracellular consequences ultimately leading to reproductive toxicity.
In our MIE evaluations, we reviewed AOP207 [55], examining the reproductive toxicity of Ag NPs in worms. This AOP focuses on identifying potential MIEs on Ag NPs induced reproductive toxicity in C. elegans (Table 2) and is still under development. The authors examine the question of how Ag NPs cause ROS production in C. elegans. They state that ROS can be formed on the surface of nanomaterials or that following the NP internalization endosomes are formed and ROS are produced by NADPH oxidase. They examine whether ROS arise directly from Ag NPs or indirectly through the action of NADPH oxidase. Finally, they identify NADPH oxidase as MIE, and reproduction failure as the outcome in C. elegans. However, any general correlation between the findings from C. elegans and in vitro and in vivo mammalian studies on the toxicity of Ag NPs is lacking [87].
Table 2.
Male reproductive system AOPs on AOP-Wiki
| AOP ID: | Title | KE | AO | Taxonomic Applicability | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 | PPARα activation in utero leading to impaired fertility in males |
MIE: Activation, PPARα KE1: Decrease, Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (STAR) KE2: Reduction, Cholesterol transport in mitochondria KE3: Reduction, Testosterone synthesis in Leydig cells KE4: Reduction, Testosterone level KE5: Decrease, Translocator protein (TSPO) |
Impaired, Fertility Malformation, Male reproductive tract |
Rattus norvegicus Homo sapiens Mus musculus |
[138] |
| 64 | Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) Mediated Adult Leydig Cell Dysfunction Leading to Decreased Male Fertility |
MIE: Glucocorticoid Receptor Agonist, Activation KE1: Repressed expression of steroidogenic enzymes KE2: Increased apoptosis, decreased number of adult Leydig Cells KE3: Reduction, Testosterone synthesis in Leydig cells KE4: Reduction, testosterone level KE5: Decreased sperm quantity or quality in the adult, Decreased fertility |
Impaired, Fertility | Rattus norvegicus | [151] |
| 207 | NADPH oxidase and P38 MAPK activation leading to reproductive failure in Caenorhabditis elegans |
MIE: Activation, NADPH Oxidase KE1: ROS formation KE2: Increase, Oxidative Stress/Activation, PMK-1 P38 MAPK KE3: Activation, HIF-1 KE4: Increased, DNA Damage-Repair KE5: Damaging, Mitochondria KE6: Apoptosis |
Reproductive failure | Caenorhabditis elegans | [55] |
| 208 | Janus kinase (JAK)/Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) and Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta pathways activation leading to reproductive failure |
KE1: Activation, JAK/STAT pathway KE2: Activation, TGF-beta pathway |
Reproductive failure | Caenorhabditis elegans | [59] |
| 322 | Alkylation of DNA leading to reduced sperm count |
MIE: Alkylation, DNA KE1: Inadequate DNA repair KE2: Increase, DNA strand breaks KE3: Increase, Apoptosis |
Reduce, Sperm count | No information | [122] |
| 323 | PPAR alpha Agonism Impairs Fish Reproduction |
MIE: Activation, PPARα KE1: Decreased, cholesterol KE2: Decreased, 11KT KE3: Impaired, Spermatogenesis KE4: impaired, Fertility |
No information | Teleost fish | [152] |
| 444 | Ionizing radiation leads to reduced reproduction in Eisenia fetida via reduced spermatogenesis and cocoon hatchability |
MIE: Deposition of Energy MIE: Increase in reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) MIE: Increase, DNA damage KE1: Increased, Oxidative Stress KE2: Increase, Apoptosis KE3: Decreased spermatogenesis KE4: Decrease, Fecundity KE5: Decrease, Reproduction |
Decrease, Population growth rate | No information | [153] |
Identification and selection of key events
AOP-Wiki was screened to identify already-existing KEs that could describe the biological events reported in the 48 selected studies. The result of this analysis and screening is reported in Additional file 1, an extract of which, reduced to the analysis of 4 articles, is presented in Table 1.
Disruption of SH-containing molecules (MIE), such as glutathione, can cause oxidative stress through disruption of the antioxidant system, as described in the section above. In our database, the most reported biological events is Ag NPs exposure triggering oxidative stress, which is described in 22 out of the 48 articles at both cellular and tissue level. It has been shown that accumulation of Ag NPs led to cell depletion from the molecular antioxidant GSH [47, 88–90], and decreased super oxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities [38, 47, 90–92], altered enzymatic oxidative defense system in male reproductive system [38, 46, 47, 90, 93, 94] and lead to increased ROS levels in human sperm [95], in mouse Sertoli cells (15P-1) [96], in somatic Leydig (TM3) and Sertoli (TM4) cells [44, 97] which eventually caused oxidative stress.
In addition, mitochondrial damage due to the impairment of metallothioneins (MIE) would result in oxidative stress by inhibition of electron transfer chain enzymes and perturbation of antioxidant system. Thus, it would increase mitochondrial ROS production, which may lead to mitochondrial damage including damage to respiratory chain and its membrane permeability. It has been shown that Ag NPs within the intracellular space has the potential to cause mitochondrial dysfunction by the depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane [97, 99]. Wang et al. reported damaged mitochondria in the testis upon Ag NP exposure to Balb/c mice [100]. These findings support the hypothesis in the biological plausibility perspective that Ag NPs interact with the thiol groups of the biomolecules, causing disruptions in the antioxidant system and thus triggering oxidative stress.
In addition to outlining the evidence supported by biological plausibility, there is also empirical evidence supporting this association in AOP-Wiki. AOP17 [101] has proposed a MIE similar to ours as the binding of electrophilic chemicals to SH(thiol)-group of proteins and/or to seleno-proteins, generating neurotoxicity. It is stated in AOP17 that soft metals like mercury binding to thiol/sulfhydryl/SH/SeH-groups results in structural modifications affecting the catalytic capacity of enzymes, and thereby reducing their capacity to neutralize ROS [102]. The relationship of this MIE and oxidative stress is classified as moderate in quantitative manner. The same could occur with Ag ions. Therefore, it can be assumed that impairment of SH-containing molecules like glutathione and metallothioneins can lead to both mitochondrial damage (KE1a) and ROS production (KE1b), eventually resulting in oxidative stress (KE2) as shown in Fig. 3.
Fig. 3.
Proposed putative AOP: impairment of intracellular SH-containing biomolecules leading to impaired fertility
Lipid peroxidation following Ag NP exposure has also been identified in our database. Lipid peroxidation byproducts including malondialdehyde (MDA), and thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) have been shown to be significantly increased in serum, testicular tissue or in reproductive cells exposed to Ag NPs [46, 96, 98, 103, 104]. ROS-mediated lipid peroxidation is shown in at least two studies out of the 48 studies [38, 88]. Collodel et al. [88] confirmed the correlation between excessive radical generation, lipid peroxidation, and damage to the sperm membrane. Evidence supporting the KER between oxidative stress and lipid peroxidation was also provided by AOP-Wiki and the relation (KER ID:1727) is classified as high by weight of evidence and quantitative understanding. Therefore, it can be postulated that oxidative stress leads to lipid peroxidation, as reported in Fig. 3.
Ag NPs induced DNA damage is reported in some of the evaluated studies in in vitro germ cells, somatic cells [95, 105] and in in vivo sperm samples and testicular tissues [46, 89, 92, 93, 106–109]. It is well accepted that spermatozoa are extremely sensitive to the damaging effects of ROS due to the polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) in their cell membranes and due to the lack of adequate DNA repair mechanisms [41, 110]. Reactive oxygen species induce intracellular oxidative burden by fostering the peroxidation of lipids. The sequence of events involves lipid peroxidation, loss of membrane integrity with increased permeability, reduced sperm motility, structural DNA damage and apoptosis [41]. According to AshaRani et al. and Carlson et al., ROS formation/oxidative stress was suggested to be a key event in DNA damage induction [99, 111].
Apoptosis is a widely observed response to Ag NP exposure, which is frequently reported through measurements of apoptosis-related proteins at the cellular level, or the tissue level with histopathological observations. At the cellular level, Ag NPs induce apoptosis in the mouse germ cell line C18-4 [112], in the mouse male-derived Sertoli cell line TM4 [97]. It is also suggested that accumulated ROS lead to apoptosis as downstream event in somatic Leydig and Sertoli cells [44]. Ag NPs induce expression of autophagy-related genes and activate signaling molecules involved in apoptosis [44]. Ntera2 cells (NT2, human testicular embryonic carcinoma cell line) are affected by Ag NPs which cause DNA strand breaks, reduce the cell proliferation and trigger apoptosis and necrosis [107].
Moreover, several in vivo studies demonstrate alterations in apoptosis-related gene expressions, increased ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 expressions (90, 93, 100, 113, 114) and mitochondria-dependent intrinsic apoptotic pathway in testes [93, 113]. An extensive gene expression analysis conducted on 383 genes by microarray shows great changes in apoptosis-related genes and proteins (caspase3 and Myc). This analysis shows apoptosis-related changes of testis morphology and sperm production, with the evidence of apoptotic nuclei in spermatogonia and spermatocytes in the testis [93, 100].
The histopathology assessment of tubular cross-sections of seminiferous tubules provides evidence of increased number of apoptotic germ cells such as spermatogonia, spermatocytes and spermatids and somatic Leydig cells.
[39, 115]. Testicular sections in rats treated with Ag NPs show decrease and disturbance in the spermatogenic cells arrangements, atrophied seminiferous tubules with degenerative Sertoli cell, and depletion in Leydig cells [89]. In addition, other studies using different target systems such as liver [31], colon [116], and endothelial cells [117] show that Ag NPs cause apoptosis in a p53-dependent process involving ROS and the c-Jun N-terminal kinase cascade, or via the IKK/NF-κB pathway. These results suggest the appropriateness of the KE ‘apoptosis’. Moreover, it is widely recognized that if cells fail to handle oxidative stress, then apoptosis will be triggered through downstream signaling pathways [118–121]. Therefore, we chose to define apoptosis as a downstream event of mitochondrial damage, DNA damage and lipid peroxidation in the pAOP that we propose (KE4).
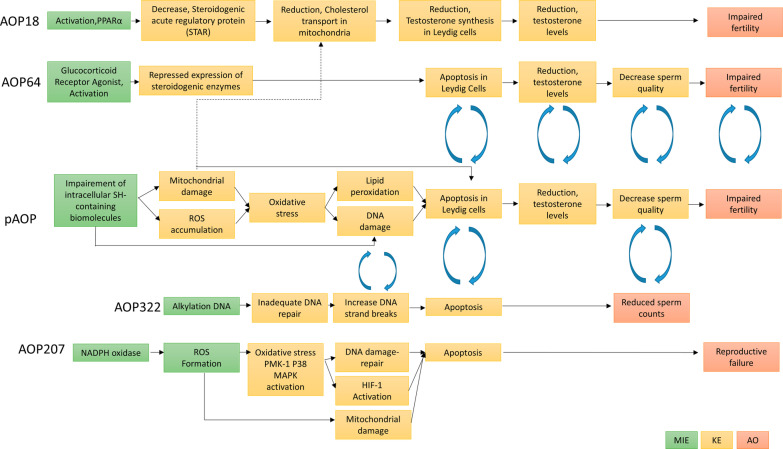
In AOP-Wiki, apoptosis, DNA damage, and sperm count relation was evaluated in AOP 322 [122] (Fig. 4). In this network, DNA alkylation (MIE) cause subsequent KEs as inadequate DNA repair, increased DNA strand breaks, increased apoptosis, and reduced sperm counts (Table 2). This AOP 322 is still under development, however, it provides a key sub-network that is possibly relevant to our pAOPs (Fig. 4). The AOP examining the reproductive toxicity of Ag NPs in worms [55] classified PMK-1 (P38 MAPK) activation, HIF-1 activation, mitochondrial damage, DNA damage, and apoptosis as KEs (Fig. 4). The authors performed correlation analysis between each KE on their AOPs and it has been proved that there is significant positive correlations between the exposure concentration of Ag NPs, ROS formation, the expression of bli-3 (NADPH oxidase), and mitochondrial damage. The most significant negative correlations were observed between the concentration of Ag NPs, reproduction and DNA repair gene expressions in C. elegans [56]. Our in vivo and in vitro data analysis is in good agreement with this AOP framework developed by Jeong et al., which has similar KEs as in our proposed pAOP on mammalian models.
Fig. 4.
Putative AOP (pAOP) on Ag NPs reproductive toxicity relations with already existing AOPs, AOP18 [138] PPARα activation in utero leading to impaired fertility in males, AOP64 [151] Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) Mediated Adult Leydig Cell Dysfunction Leading to Decreased Male Fertility, AOP207 [55] NADPH oxidase and P38 MAPK activation leading to reproductive failure in Caenorhabditis elegans
Significant alterations of serum and intratesticular testosterone levels was observed upon Ag NPs exposure, as reported in a number of studies from our database [46, 47, 91, 92, 114, 123]. According to Attia et al. the significant decrease in the level of serum testosterone could be related with the adverse effects of Ag NPs in Leydig cells [91]. Circulating testosterone levels depend on the steroidogenic capacity of individual Leydig cells and the total number of Leydig cells per testis [124]. Leydig cell apoptosis causes the decrease in their number in the testis, which in turn affects testosterone level as shown in some studies [39, 125, 126] and further impact the spermatogenesis [127]. Therefore, the relationship between apoptosis of Leydig cells and alterations of serum and intratesticular testosterone levels is consistent with established biological knowledge.
On the other hand, there are studies showing that low testosterone levels are associated with impaired cholesterol transport in damaged mitochondria of Leydig cells [128, 129]. Mitochondrial steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR) or translocator protein (TSPO) are responsible for cholesterol transport from the outer to the inner mitochondrial membrane [130]. In the inner membrane, cholesterol is converted into the Pregnenolone by CYP11a1 [130]. Afterwards, 3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydorgenase (Hsd3b), 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydorgenase (Hsd17b), and CYP17A1 transform pregnenolone to testosterone [125, 130]. In our database, steroidogenesis perturbation by Ag NPs were shown in some reproductive toxicology studies. Garcia et al. [131] reported no change in the expression level of StAR after Ag NP administration although they detected increased Cyp11a1 and Hsd3b1 expression levels in CD1 mice. Increases in these two enzymes involved in the steroid biosynthetic pathway were consistent with observed increases in serum and intratesticular testosterone in this study. By contrast, Dziendzikowska et al. [132] reported decreased expression level of StAR, Cyp11a1, Hsd3b1 and Hsd17b3 in Wistar rats treated with Ag NPs. They also found a decreased plasma and testicular testosterone concentration after Ag NP treatment, which was correlated with decreased expression level of the aforementioned proteins. Similar to these results, in an in vitro study, Zhang et al. [105] showed inhibited StAR, Hsd3b1, and Hsd17b transcription in TM3 cells. They stated that decreased expression of Hsd3b1, and Hsd17b may be partially due to the reduced levels of StAR, which negatively affected testosterone production in TM3 cells [44]. When no modulation of StAR mRNA expression is observed, the author’s hypothesis is that it might be due to post-translational modifications that regulate StAR activity [39]. In fact, regulation of StAR gene expression is a complex process involving the interaction of a number of post-transcriptional mechanisms that govern mRNA and protein expression, as well as multiple signaling pathways that coordinate the cooperation of various hormones and transcriptional machinery (133, 134). These post-translational modifications to StAR (reviewed in [134]), may serve to enhance its stability or its ability to interact with other proteins necessary for cholesterol transport. On the other hand, as suggested by Dziendzikowska et al. [135], impaired steroidogenesis is probably resulting from the interactions of Ag ions with the thiol groups present in the inner mitochondrial membrane [136, 137]. This concurs well with the MIE in the putative AOP that we propose.
In AOP-Wiki, impairment of steroidogenesis was investigated regarding its role in reproductive toxicity, and we identified AOP18 [138] that describes the AO impaired fertility following a MIE that is Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor alpha (PPARα) activation in Leydig cells [139]. The development of this AOP relies on evidence collected from rodent models and incorporates human mechanistic and epidemiological data. The pathway comprises the activation of PPARα, followed by the disruption of cholesterol transport in mitochondria, impairment of hormonal balance which leads to malformation of the reproductive tract in males. PPARα is a transcription factor belonging to the nuclear receptor family, which also contains steroid and thyroid hormone receptors [140]. PPARs play an essential role in the metabolic regulation of lipids, particularly cholesterol, linking lipid metabolism with effects on reproduction. The effects of PPARα action on the reproductive system, as reported in AOP18, stem from limited experimental data showing associations between activation of this receptor and disruption of steroidogenesis [141, 142]. However, the major uncertainty in this AOP is the functional relationship between PPARα activation (i.e., the MIE) and cholesterol transport reduction [143]. Data gaps is defined as lacking of complete/pathway driven studies to investigate the effects of PPARs and their role in male reproductive development. On the other hand, in their evidence assessment, the authors found a moderate relation between cholesterol transport in mitochondria and testosterone synthesis. It is stated that decreasing the amount of cholesterol inside the mitochondria (e.g., by decreasing the expression of enzymes like StAR or TSOP) will result in a diminished amount of substrate for hormone (testosterone) synthesis. These results offer compelling evidence for the alteration of testosterone level in our pAOP. Therefore, we can assume that apoptosis in Leydig cells or its mitochondrial damage may lead to the endpoint of testosterone level reduction that we define as KE5 in our pAOP.
In our database, after intravenous injection or oral route administration, Ag NPs are shown to accumulate in the testes and are found in spermatids and ejaculated sperms, which suggests the likelihood that Ag NPs could pass through the blood-testis barrier (BTB) and eventually could impair the endocrine and reproductive functions [33, 37, 48, 49, 66, 144–146]. Arisha et al. showed increased Ag NPs levels in testes, reduced expression of tight junction proteins (occludin, claudin-11, and tight junction protein 1) resulting in BTB permeability increase [113]. They correlated these results with significantly reduced mRNA expression of hypothalamic GnRH1, testicular AR, and serum levels of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH) and testosterone concentrations. The authors conclude that decreased testosterone level, mainly due to unbalanced sexual hormones signaling and testicular damage, affects spermatogenesis. In a very recent study investigating steroidogenesis in rat hippocampus upon exposure to Ag NPs, the alterations in expression of Star, Hsd3b3, and Hsd17b1 genes, involved in steroid metabolism, is shown [135]. Any interference with the normal functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary–testicular axis can lead to reduced fertility, and if this interference persists, infertility could develop. Although these events do not occur in the reproductive organ itself but rather in the associated endocrine system, they contribute to Ag-NP reproductive toxicity and are complementary to all the other tested endpoints. Still, we chose not to include them in the current pAOP, which is focused exclusively on the male reproductive organ.
Sperm characteristics have a great importance in the prediction of fertility. Twenty-four out of the 48 identified studies analyzed sperm parameters after exposure to Ag NPs, including sperm morphology, viability, motility, and DNA damage. Upon Ag NP exposure, abnormal sperm morphology, decreased sperm viability and motility, increased sperm DNA damage were reported in a number of studies [46, 88, 90, 92, 100, 103, 123, 147]. Gromadzka-Ostrowska et al. [148] observed a decrease in the number of epididymal spermatozoa after 28 days in Wistar rats treated with a single injection of 20 nm AgNPs. The production of sperm requires a complex interaction between Sertoli, Leydig and germ cells. Any defect of these cells may prevent normal sperm production. In fact, the epididymis is necessary for post-testicular sperm maturation as it provides the milieu required for spermatozoa to gain the ability for fertilization (149). During the transit through the epididymis segments, the sperm released from the lumen of seminiferous tubules undergoes maturation and acquires motility and the ability to fertilize oocytes [149]. Cavallin et al. [108] showed reduced sperm storage and reduced sperm transit time after Ag NPs exposure to rats. This is explained as altered serum concentrations of testosterone, which could stimulate the contraction of the smooth muscle of the epididymis; as a result these increased contractions could contribute to the observed decrease in sperm transit time (108). Moreover, studies mostly emphasize that inadequate hormonal level may provoke low sperm quality and quantity [150]. In the AOP-Wiki database, the reduction of testosterone level is defined as an upstream event of decreased sperm quality. Therefore, we assigned decreased sperm quality and quantity (KE6) as a downstream event of reduction, testosterone level (KE5). When no modulation of StAR mRNA expression is observed, the authors hypothesis is that it might be due to post-translational modifications that regulate StAR activity (41). At the organ level, in vivo histopathological analysis of testis was conducted in 27 studies out of 48. Testis index and histological structure of testicular tissues, morphology, seminiferous tubule area, circumference, diameter and tubular degeneration/atrophy were the most studied parameters. A prominent atrophy of seminiferous tubules, thinning of the tubule wall, disorganization and vacuolization of germinal epithelium, and loss of spermatogenic cells in testis tissue of rats and mice exposed to Ag NPs are reported [47, 90, 93, 97]. In the interstitial tissue, Leydig cells are highly affected, presenting disrupted plasma membrane on extensive areas, with loss of cell organelles [93]. Shehata et al. showed significant reduction in the area, circumference and mean diameter of seminiferous tubules in Ag NP exposed rats [46]. These results suggest that Ag NPs may affect the testicular structure and decrease reproductive success.
As a summary, impairment of intracellular SH-containing biomolecules may lead to mitochondrial damage and ROS accumulation (KE1) and lead to oxidative stress (KE2) which further provoke DNA damage and Lipid peroxidation (KE3). Intracellular perturbations may lead to apoptosis in Leydig cells. At the organ/organ system level, these perturbations result in altered testosterone level (KE5) and decreased sperm quality (KE6). All these biological events, which emerged from our literature analysis, lead to the pAOP framework shown in Fig. 3.
Network of AOPs
Then, the pAOPs presented in Fig. 3 was used to tentatively build a network of AOPs for reproductive toxicity. MIEs and KEs involved in male reproduction impairment-related AOPs were extracted from AOP-Wiki and are listed in the Table 2.
Some AOPs listed in this table are already discussed in the previous section. We observed that these AOPs share at least one common KE with our pAOPs. For example, oxidative stress, apoptosis, reduction of testosterone levels, decreased sperm quality events are shared by AOP 64, 207, 444. In Fig. 4, we interconnected these events with our pAOPs. While individual AOPs are likely to be activated by a limited number of reprotoxic compounds, interconnected AOPs that are linked by common KEs of single AOPs are likely to represent more realistic descriptions of the complexity of disease pathophysiology [154].
The AOP network reported in Fig. 4 also shows the potential knowledge gaps in internal associations between KEs. Complete/pathway driven studies investigating the effects of impairment of SH-containing biomolecules and their role in male reproductive development are lacking. For establishing a solid quantitative linkage, mode of action framework analysis for reproductive toxicity is needed. This figure also could serve as a candidate list of MIE that could provide clues for experimental verifications for future studies.
Experimental methods for assessing the KEs
As suggested by Halappanavar et al. [63], AOPs can be used as a tool in the design of testing strategies to support the safety assessment of nanomaterials. In this regard, our database identified the various in vitro endpoints, methods and assays used to measure the KEs in this pAOP (Table 3).
Table 3.
Summary information of the biological endpoints measured in the reproductive system toxicology
| KE | Biological events/measurement | Methods | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell viability | MTT, MTS, LDH, CCK-8 assay | [96, 97, 105, 107, 112] | |
| Oxidative stress | ROS Production | H2DCFDA | [95, 97, 105] |
|
Lipid peroxidation, MDA content In testicular tissue and cells |
ELISA, Western Blot, qRT-PCR | [89, 90, 94, 96, 98, 109] | |
|
Enzymatic/non-enzymatic antioxidants GPX, CAT, SOD, TBARS, TAOC, GSH in Sperm, Seminal Plasma, and Blood, serum, testicular tissue homogenate and in vitro cells |
ELISA, Western Blot, qRT-PCR | [46, 88, 89, 96, 104, 155] | |
| DNA damage |
DNA Strand breaks, In cells and the testis tissue |
Comet Assay, DNA microarray analysis, DNA fragmentation |
[46, 88, 89, 96, 107, 109] |
| Mitochondrial damage | Cell metabolic activity | MTT assay | [112] |
| Mitochondrial membrane potential | Quantitative method uses a tetraphenylphosphonium ion (TPP+)-sensitive electrode, or by fluorimetric methods | [97] | |
| Apoptosis, in germ Sertoli and Leydig cell | P53, BAX, bcl-2 gene expressions or cell apoptosis | Western Blot, qPCR, TUNEL Assay Flow Cytometry | [90, 93, 97, 112, 113, 166] |
| Reproductive hormone levels |
Hormonal Assessment Serum Testosterone, LH and FSH, P450scc, StAR, Hsd3b, and Cyp17a1 gene expression |
Radioimmunoassay [167], ELISA, qRT-PCR, chemiluminescent protein immunoassay | [46, 89, 91, 98, 100, 132, 174] |
| Sperm evaluations | Morphology, Motility, Concentration, Count, Viability, Plasma membrane intergrity | Eosin/nigrosine staining, hemocytometer, Microscope | [46, 92, 95, 103, 146, 166, 175] |
| Acrosome status | Fluorescence assessment (eg.chlortetracycline fluorescence assay) | [65, 146, 175] | |
| Sperm DNA integrity | Toluidine blue staining, Aniline blue staining, Acridine orange staining Eosin–nigrosine-staining | [38, 90, 103, 123, 148] | |
| Sperm DNA damage | Comet assay | [109, 148] | |
| The mitochondrial activity | Activity of cytochrome c oxidase | [65, 108] | |
| Spermatogenesis |
The transcript expression of Gnrh1, Ar, Cyp11a1, Hsd3b1, Hsd17b3, Srd5a1, Cyp19a1, Star by qPCR Intratesticular steroid metabolism enzyme protein level aromatase (Aro) and 5α-reductase type 1 (Srd5a1) measurements |
[108, 132] | |
| Determination of silver concentration in organs | ICPMS, UV/vis proton spectrophotometery | [38, 114, 176] | |
| Histopathological Examination |
The seminiferous tubules area, circumference, and diameter, Testis index and histological structure of testicular tissues |
Hematoxylin and Eosin light microscope Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) | [46, 100, 103, 123] |
In studies examining oxidative stress, the intracellular level of ROS has often been evaluated using a fluorescent probe such as H2-DCF-DA [95, 97, 105]. MDA content in ELISA methods can be used to detect lipid peroxidation, which is one of the main indicators of oxidative stress [90, 94, 98]. With commercial kits, GSH levels and total antioxidant capacities can be measured, as well as analyzed at the level of antioxidant biomolecules and enzymes such as CAT, SOD [96, 104, 155]. GSH and GSSG levels can also be determined biochemically via high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), capillary electrophoresis or microplates. Gene expressions of the antioxidant defense system can be measured by RT-qPCR. Mitochondrial dysfunction can be measured by colorimetric assays such as 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), through assessment of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP), mitochondrial ATP production, cytochrome c release, or mitochondrial DNA damage [97].
Although in the articles from our database DNA damage is evaluated using the comet assay, micronucleus assay and DNA fragmentation, a roadmap for testing DNA damage caused by nanomaterials was recently proposed by Elespuru et al. [156]. It includes the use of an in vitro gene mutation assay (OECD TG476 [157], HPRT or TG490 [158], mouse lymphoma TK ± assay) and a chromosomal damage assay (OECD TG487 [159] in vitro micronucleus assay or TG473 [160] chromosomal aberration assay). Eventually, optional assays are proposed, both in vitro (comet assay) and in vivo (comet assay, OECD TG489 [161]; transgenic rodent gene mutation assay TG488 [162]; erythrocyte micronucleus assay, TG474 [163]; bone marrow chromosomal aberration test, TG 475 [164]). Other non-guideline test methods to measure the DNA damage also exist although they are not discussed in the roadmap by Elespuru et al. [156]. For instance the detection of DNA repair proteins such as H2AX, 53BP1 or XRCC2 can be used, or high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) coupled to tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) that quantifies very low levels of oxidative lesions to DNA [165].
In articles in our database, apoptosis was evaluated by western blot, qPCR, TUNEL Assay or Flow Cytometry [93, 97, 112, 166]. Other methods can also be used, including annexin V-FITC probes, with analysis of the relative percentage of Annexin V-FITC-positive/PI-negative cells by flow cytometry. The alteration of procaspases 7 and 3, Caspase-3 and caspase-9 activity, as well as the cleavage of the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) can be determined by western blotting or RT-PCR.
The OECD TG 456 [167] is a validated test guideline for in vitro screening of the effect of chemicals on steroidogenesis, specifically the production of 17ß-estradiol (E2) and testosterone. In vitro testosterone synthesis in Leydig cells can be measured by P450scc, StAR, Hsd3b, and Cyp17a1 gene expression or indirectly by testosterone radioimmunoassay or analytical methods such as LC–MS or by isotope-dilution gas chromatography–mass spectrometry in serum [168, 169]. Sperm assessment includes the evaluation of sperm count and concentration (hemocytometer, automated image-based system), morphology and motility (microscope, automated image-based system) and viability (for example propidium iodide staining of necrotic cells, TUNEL assay staining apoptotic cells). Sperm DNA damage can be evaluated by Acridine orange assay. The principle of the assay is sperm DNA binds to the AO dye by acid denaturation. AO binding to intact DNA is visualized as green and damaged DNA as red by a microscope or flow cytometer [170]. Models that can be used as alternatives to animal experimentation for assessing this putative AOP on male reproductive function, i.e., in vitro models of Leydig cells, Sertoli cells, Sertoli-germ cell cocultures, as well as methods to prepare testicular organ and tissue culture systems can be found in the Database Service on Alternative Methods to animal experimentation (DB-ALM) [171]. Data generated by alternative methods or in vivo testing can be integrated in quantitative AOPs and can be validated for future studies.
Another purpose of our research in developing this pAOP was to observe how physicochemical properties of NPs influence the key events and their relationships. From the selected articles that were analysed, we identified Ag NP size, agglomeration state, surface coating and tendency to dissolve as key physico-chemical parameters that could influence their toxicity (Additional file 1). However, it is difficult to reach a definite conclusion, as the physicochemical characterization of Ag NPs in the considered articles is too diverse and sometimes lacks precision. It seems clear from these studies that controlling ion release could diminish the hazard potential of Ag NPs with respect to SbD approaches [22]. Therefore, it is highly recommended to analyze Ag ion release systematically in the published articles. Since ion release is higher when the nanoparticle is smaller and when the nanoparticle surface is uncoated or coated with a ligand that tends to desorb, we consider that both the size and surface coating are important parameters that influence Ag NP hazard potential, as previously suggested in studies related to other organs [14, 172, 173].
Conclusion
This review discusses the effects of Ag NPs on male reproductive system in the concept of AOPs. By reviewing the existing literature, a putative AOP framework was constructed, where the MIE is identified as the impairment of intracellular SH-containing biomolecules, with subsequent key events that are mitochondrial damage, ROS accumulation, DNA damage and lipid peroxidation, apoptosis, reduction of reproductive hormones production and sperm quality. These successive key events may result in impaired male fertility (AO). This AOP study summarizes complex data from different biological levels in the literature. It could serve to predict male fertility impairment caused by some NMs using the proposed methods of KE evaluation. Moreover, since the use of the AOP approach is emerging in the nanotoxicology community, proposing some putative AOPs like this one and linking AOPs as networks would help increasing the improvement of mechanistic understanding of pathways interactions involved in various reproductive disorders. Finally, it should be considered that among the factors contributing to the global population decline we are foreseeing, the fertility outcomes related to the decrease in testosterone level and semen quality and quantity, also induced by environmental pollutants, are of pivotal importance. Thus, more efforts should be devoted in the future to better characterize the risk of using new potential endocrine disrupting compounds, as well as to guarantee the better strategies to develop safer and more environmentally sustainable Ag-based materials.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. List of the 48 studies selected for the putative AOP construction.
Abbreviations
- Ag NPs
Silver nanoparticles
- AO
Adverse outcome
- AOP
Adverse outcome pathway
- ASINA
Anticipating Safety Issues at the Design Stage of NAno Product Development
- BTB
Blood-testis barrier
- CAT
Catalase
- ESR
Electron spin resonance
- FSH
Follicle-stimulating hormone
- GSH
Glutathione
- HPLC
High performance liquid chromatography
- Hsd17b
17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydorgenase
- Hsd3b
3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydorgenase
- KE
Key event
- KER
Key Event Relationship
- LH
Luteinizing hormone
- MDA
Malondialdehyde
- MIE
Molecular initiating event
- MMP
Mitochondrial membrane potential
- MTT
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- NM
Nanomaterial
- NP
Nanoparticle
- nm
Nanometer
- OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
- pAOP
Putative Adverse Outcome Pathway
- PARP
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase
- PPARα
Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor alpha
- PUFA
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- PVP
Polyvinyl pyrrolidone
- ROS
Reactive oxygen species
- SbD
Safe by Design
- SOD
Super oxide dismutase
- StAR
Steroidogenic acute regulatory protein
- TBARS
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances
- TM3
Leydig cells
- TM4
Sertoli cells
- ToxRTool
Toxicological data Reliability Assessment Tool
- TSPO
Translocator protein
Author contributions
Conceptualization: MC, PM, AC. Funding acquisition: AC, PM, MC. Data curation, Formal analysis: OK. Writing—original draft: OK, MC. Writing—review and editing: OK, PM, AC, MC. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This work has received funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Grant Agreement no. 862444, ASINA (Anticipating Safety Issues at the Design Stage of NAno Product Development).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Definition - Nanomaterials - Environment - European Commission. https://ec.europa.eu/environment/chemicals/nanotech/faq/definition_en.htm.
- 2.Prabhu S, Poulose EK. Silver nanoparticles: mechanism of antimicrobial action, synthesis, medical applications, and toxicity effects. Int Nano Lett. 2012;2(1):1–10. doi: 10.1186/2228-5326-2-32. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yoshida Y, Churei H, Takeuch Y, Wada T, Uo M, Izumi Y, et al. Novel antibacterial mouthguard material manufactured using silver-nanoparticle-embedded ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer masterbatch. Dent Mater J. 2018;37(3):437–444. doi: 10.4012/DMJ.2017-226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.ANSES. Exposure to silver nanoparticles | Anses—Agence nationale de sécurité sanitaire de l’alimentation, de l’environnement et du travail. https://www.anses.fr/en/content/exposure-silver-nanoparticles. 2018.
- 5.Marambio-Jones C, Hoek EMV. A review of the antibacterial effects of silver nanomaterials and potential implications for human health and the environment. J Nanoparticle Res. 2010;12(5):1531–1551. doi: 10.1007/S11051-010-9900-Y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nakamura S, Sato M, Sato Y, Ando N, Takayama T, Fujita M, et al. Synthesis and application of silver nanoparticles (Ag NPs) for the prevention of infection in healthcare workers. Vol. 20, International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Silva RM, Anderson DS, Franzi LM, Peake JL, Edwards PC, Van Winkle LS, et al. Pulmonary effects of silver nanoparticle size, coating, and dose over time upon intratracheal instillation. Toxicol Sci. 2015;144(1):151–162. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Anderson DS, Silva RM, Lee D, Edwards PC, Sharmah A, Guo T, et al. Persistence of silver nanoparticles in the rat lung: influence of dose, size, and chemical composition. Nanotoxicology. 2015;9(5):591–602. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2014.958116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Batista D, Pascoal C, Cássio F. How do physicochemical properties influence the toxicity of silver nanoparticles on freshwater decomposers of plant litter in streams? Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2017;140:148–155. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.02.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Liu J, Sonshine DA, Shervani S, Hurt RH. Controlled release of biologically active silver from nanosilver surfaces. ACS Nano. 2010;4(11):6903–6913. doi: 10.1021/nn102272n. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Peretyazhko TS, Zhang Q, Colvin VL. Size-controlled dissolution of silver nanoparticles at neutral and acidic pH conditions: kinetics and size changes. Environ Sci Technol. 2014;48(20):11954–11961. doi: 10.1021/ES5023202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hsiao IL, Hsieh YK, Wang CF, Chen IC, Huang YJ. Trojan-Horse mechanism in the cellular uptake of silver nanoparticles verified by direct intra- and extracellular silver speciation analysis. Environ Sci Technol. 2015;49(6):3813–3821. doi: 10.1021/ES504705P. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Beer C, Foldbjerg R, Hayashi Y, Sutherland DS, Autrup H. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles—nanoparticle or silver ion? Toxicol Lett. 2012;208(3):286–292. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2011.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bobyk L, Tarantini A, Beal D, Veronesi G, Kieffer I, Motellier S, et al. Toxicity and chemical transformation of silver nanoparticles in A549 lung cells: dose-rate-dependent genotoxic impact. Environ Sci Nano. 2021;8(3):806–821. doi: 10.1039/D0EN00533A. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Reidy B, Haase A, Luch A, Dawson KA, Lynch I. Mechanisms of silver nanoparticle release, transformation and toxicity: a critical review of current knowledge and recommendations for future studies and applications. Materials. 2013;6(6):2295–2350. doi: 10.3390/MA6062295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.McShan D, Ray PC, Yu H. Molecular toxicity mechanism of nanosilver. J Food Drug Anal. 2014;22(1):116–127. doi: 10.1016/j.jfda.2014.01.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.He W, Zhou YT, Wamer WG, Boudreau MD, Yin JJ. Mechanisms of the pH dependent generation of hydroxyl radicals and oxygen induced by Ag nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2012;33(30):7547–7555. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.06.076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.He D, Miller CJ, Waite TD. Fenton-like zero-valent silver nanoparticle-mediated hydroxyl radical production. J Catal. 2014;317:198–205. doi: 10.1016/j.jcat.2014.06.016. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Liu J, Hurt RH. Ion release kinetics and particle persistence in aqueous nano-silver colloids. Environ Sci Technol. 2010;44(6):2169–2175. doi: 10.1021/es9035557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.European Commission. Nanosilver: safety, health and environmental effects and role in antimicrobial resistance, Final Opinion Health Effects of Exposure to nanosilver. http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/emerging/members_wg/index_en.htm. 2014. 10.2772/76851.
- 21.Rohde MM, Snyder CM, Sloop J, Solst SR, Donati GL, Spitz DR, et al. The mechanism of cell death induced by silver nanoparticles is distinct from silver cations. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2021;18(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12989-021-00430-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Marchioni M, Jouneau PH, Chevallet M, Michaud-Soret I, Deniaud A. Silver nanoparticle fate in mammals: bridging in vitro and in vivo studies. Coord Chem Rev. 2018;364:118–136. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2018.03.008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Barngrover BM, Aikens CM. Incremental binding energies of Gold(I) and Silver(I) thiolate clusters. J Phys Chem A. 2011;115(42):11818–11823. doi: 10.1021/JP2061893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hogg PJ. Disulfide bonds as switches for protein function. Trends Biochem Sci. 2003;28(4):210–214. doi: 10.1016/S0968-0004(03)00057-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Go YM, Chandler JD, Jones DP. The cysteine proteome. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;84:227–245. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.03.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ulrich K, Jakob U. The role of thiols in antioxidant systems. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019;140:14–27. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.05.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Coyle P, Philcox JC, Carey LC, Rofe AM. Metallothionein: the multipurpose protein. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002;59(4):627–647. doi: 10.1007/S00018-002-8454-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hübner C, Haase H. Interactions of zinc- and redox-signaling pathways. Redox Biol. 2021;41:101916. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Xiong Y, Uys JD, Tew KD, Townsend DM. S-glutathionylation: from molecular mechanisms to health outcomes. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(1):233. doi: 10.1089/ARS.2010.3540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jiang HS, Zhang Y, Lu ZW, Lebrun R, Gontero B, Li W. Interaction between silver nanoparticles and two dehydrogenases: role of thiol groups. Small. 2019;15(27):1900860. doi: 10.1002/smll.201900860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Piao MJ, Kang KA, Lee IK, Kim HS, Kim S, Choi JY, et al. Silver nanoparticles induce oxidative cell damage in human liver cells through inhibition of reduced glutathione and induction of mitochondria-involved apoptosis. Toxicol Lett. 2011;201(1):92–100. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2010.12.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.George R, Merten S, Wang TT, Kennedy P, Maitz P. In vivo analysis of dermal and systemic absorption of silver nanoparticles through healthy human skin. Australas J Dermatol. 2014;55(3):185–190. doi: 10.1111/ajd.12101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.van der Zande M, Vandebriel RJ, Van Doren E, Kramer E, Herrera Rivera Z, Serrano-Rojero CS, et al. Distribution, elimination, and toxicity of silver nanoparticles and silver ions in rats after 28-day oral exposure. ACS Nano. 2012;6(8):7427–7442. doi: 10.1021/nn302649p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sung JH, Ji JH, Park JD, Yoon JU, Kim DS, Jeon KS, et al. Subchronic inhalation toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol Sci. 2009;108(2):452–461. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfn246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lankveld DPK, Oomen AG, Krystek P, Neigh A, Troost-de Jong A, Noorlander CW, et al. The kinetics of the tissue distribution of silver nanoparticles of different sizes. Biomaterials. 2010;31(32):8350–8361. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.07.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Antsiferova AA, Kopaeva MY, Kochkin VN, Kashkarov PK. Kinetics of silver accumulation in tissues of laboratory mice after long-term oral administration of silver nanoparticles. Nanomaterials. 2021;11(12):3204. doi: 10.3390/nano11123204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Arslan NP, Keles ON, Gonul-Baltaci N. Effect of titanium dioxide and silver nanoparticles on mitochondrial dynamics in mouse testis tissue. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022;200(4):1650–1658. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02763-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rezazadeh-Reyhani Z, Razi M, Malekinejad H, Sadrkhanlou R. Cytotoxic effect of nanosilver particles on testicular tissue: evidence for biochemical stress and Hsp70-2 protein expression. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2015;40(2):626–638. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2015.08.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Garcia TX, Costa GMJ, França LR, Hofmann MC. Sub-acute intravenous administration of silver nanoparticles in male mice alters Leydig cell function and testosterone levels. Reprod Toxicol. 2014;45:59–70. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2014.01.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.European Commission. Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety SCCS Opinion on Colloidal Silver (nano). http://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/experts/declarations/sccs_en.htm. 2018.
- 41.Alahmar A. Role of oxidative stress in male infertility: an updated review. J Hum Reprod Sci. 2019;12(1):4. doi: 10.4103/jhrs.JHRS_150_18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Brohi RD, Wang L, Talpur HS, Wu D, Khan FA, Bhattarai D, et al. Toxicity of nanoparticles on the reproductive system in animal models: a review. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:606. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Habas K, Brinkworth MH, Anderson D. Silver nanoparticle-mediated cellular responses in isolated primary Sertoli cells in vitro. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018;116:182–188. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.04.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gurunathan S, Zhang XF, Choi YJ, Han JW, Kim E, Park JH, et al. Differential nanoreprotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in male somatic cells and spermatogonial stem cells. Int J Nanomed. 2015;10:1335. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S76062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Braydich-Stolle LK, Lucas B, Schrand A, Murdock RC, Lee T, Schlager JJ, et al. Silver nanoparticles disrupt GDNF/Fyn kinase signaling in spermatogonial stem cells. Toxicol Sci. 2010;116(2):577–589. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfq148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Shehata AM, Salem FMS, El-Saied EM, Abd El-Rahman SS, Mahmoud MY, Noshy PA. Zinc nanoparticles ameliorate the reproductive toxicity induced by silver nanoparticles in male rats. Int J Nanomed. 2021;16:2555–2568. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S307189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Olugbodi JO, David O, Oketa EN, Lawal B, Okoli BJ, Mtunzi F. Silver nanoparticles stimulates spermatogenesis impairments and hematological alterations in testis and epididymis of male rats. Molecules. 2020;25(5):1063. doi: 10.3390/molecules25051063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wang Z, Qu G, Su L, Wang L, Yang Z, Jiang J, et al. Evaluation of the biological fate and the transport through biological barriers of nanosilver in mice. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19(37):6691–6697. doi: 10.2174/1381612811319370012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kim YS, Kim JS, Cho HS, Rha DS, Kim JM, Park JD, et al. Twenty-eight-day oral toxicity, genotoxicity, and gender-related tissue distribution of silver nanoparticles in sprague-dawley rats. Inhal Toxicol. 2008;20(6):575–583. doi: 10.1080/08958370701874663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Roh JY, Sang JS, Yi J, Park K, Kyu HC, Ryu DY, et al. Ecotoxicity of silver nanoparticles on the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans using functional ecotoxicogenomics. Environ Sci Technol. 2009;43(10):3933–3940. doi: 10.1021/es803477u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yan N, Tsim SMJ, He X, Tang BZ, Wang WX. Direct visualization and quantification of maternal transfer of silver nanoparticles in Zooplankton. Environ Sci Technol. 2020;54(17):10763–10771. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.0c03228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.OECD. Users’ Handbook supplement to the Guidance Document for developing and assessing Adverse Outcome Pathways | OECD Series on Adverse Outcome Pathways | OECD iLibrary. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/users-handbook-supplement-to-the-guidance-document-for-developing-and-assessing-adverse-outcome-pathways_5jlv1m9d1g32-en. 2014.
- 53.Halappanavar S, Ede JD, Shatkin JA, Krug HF. A systematic process for identifying key events for advancing the development of nanomaterial relevant adverse outcome pathways. NanoImpact. 2019;15(February):100178. doi: 10.1016/j.impact.2019.100178. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.AOP-Wiki. Adverse Outcome Pathway Wiki. https://aopwiki.org/.
- 55.AOP-Wiki. AOP207: NADPH oxidase and P38 MAPK activation leading to reproductive failure in Caenorhabditis elegans. https://aopwiki.org/aops/207.
- 56.Jeong J, Song T, Chatterjee N, Choi I, Cha YK, Choi J. Developing adverse outcome pathways on silver nanoparticle-induced reproductive toxicity via oxidative stress in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans using a Bayesian network model. Nanotoxicology. 2018;12(10):1182–1197. doi: 10.1080/17435390.2018.1529835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ma YB, Lu CJ, Junaid M, Jia PP, Yang L, Zhang JH, et al. Potential adverse outcome pathway (AOP) of silver nanoparticles mediated reproductive toxicity in zebrafish. Chemosphere. 2018;207:320–328. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.AOP-Wiki. AOP210: activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and Forkhead box O (FOXO) and reduction of WNT pathways leading to reproductive failure: Integrated multi-OMICS approach for AOP building. https://aopwiki.org/aops/210.
- 59.AOP-Wiki. AOP208:Janus kinase (JAK)/Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) and Transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta pathways activation leading to reproductive failure. https://aopwiki.org/aops/208.
- 60.Kim H, Jeong J, Chatterjee N, Roca CP, Yoon D, Kim S, et al. JAK/STAT and TGF-ß activation as potential adverse outcome pathway of TiO2NPs phototoxicity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):1–12. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17495-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Schneider K, Schwarz M, Burkholder I, Kopp-Schneider A, Edler L, Kinsner-Ovaskainen A, et al. “ToxRTool”, a new tool to assess the reliability of toxicological data. Toxicol Lett. 2009;189(2):138–144. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2009.05.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Halappanavar S, Van Den Brule S, Nymark P, Gaté L, Seidel C, Valentino S, et al. Adverse outcome pathways as a tool for the design of testing strategies to support the safety assessment of emerging advanced materials at the nanoscale. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2020;17(1):1–24. doi: 10.1186/s12989-020-00344-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Murugadoss S. A strategy towards the generation of testable adverse outcome pathways for nanomaterials. Altex. 2021 doi: 10.14573/altex.2102191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Mathias FT, Romano RM, Kizys MML, Kasamatsu T, Giannocco G, Chiamolera MI, et al. Daily exposure to silver nanoparticles during prepubertal development decreases adult sperm and reproductive parameters. Nanotoxicology. 2015;9(1):64–70. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2014.889237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kim YS, Song MY, Park JD, Song KS, Ryu HR, Chung YH, et al. Subchronic oral toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2010;7(1):1–11. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-7-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Cunningham B, Engstrom AE, Harper BJ, Harper SL, Mackiewicz MR. Silver nanoparticles stable to oxidation and silver ion release show size-dependent toxicity in vivo. Nanomaterials. 2021 doi: 10.3390/NANO11061516/S1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Ratte HT. Bioaccumulation and toxicity of silver compounds: a review. Environ Toxicol Chem. 1999;18(1):89–108. doi: 10.1002/etc.5620180112. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Gordon O, Vig Slenters T, Brunetto PS, Villaruz AE, Sturdevant DE, Otto M, et al. Silver coordination polymers for prevention of implant infection: thiol interaction, impact on respiratory chain enzymes, and hydroxyl radical induction. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010;54(10):4208–4218. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01830-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Loza K, Diendorf J, Sengstock C, Ruiz-Gonzalez L, Gonzalez-Calbet JM, Vallet-Regi M, et al. The dissolution and biological effects of silver nanoparticles in biological media. J Mater Chem B. 2014;2(12):1634. doi: 10.1039/c3tb21569e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pallavicini P, Preti L, De VL, Dacarro G, Diaz Fernandez YA, Merli D, et al. Fast dissolution of silver nanoparticles at physiological pH. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2020;563:177–188. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.12.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Shi M, Kwon HS, Peng Z, Elder A, Yang H. Effects of surface chemistry on the generation of reactive oxygen species by copper nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2012;6(3):2157–2164. doi: 10.1021/NN300445D. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Jose GP, Santra S, Mandal SK, Sengupta TK. Singlet oxygen mediated DNA degradation by copper nanoparticles: potential towards cytotoxic effect on cancer cells. J Nanobiotechnol. 2011;9(1):1–8. doi: 10.1186/1477-3155-9-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Xia T, Kovochich M, Liong M, Mädler L, Gilbert B, Shi H, et al. Comparison of the mechanism of toxicity of zinc oxide and cerium oxide nanoparticles based on dissolution and oxidative stress properties. ACS Nano. 2008;2(10):2121–2134. doi: 10.1021/nn800511k. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Kim JS, Kuk E, Yu KN, Kim JH, Park SJ, Lee HJ, et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2007;3(1):95–101. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2006.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Park MVDZ, Neigh AM, Vermeulen JP, de la Fonteyne LJJ, Verharen HW, Briedé JJ, et al. The effect of particle size on the cytotoxicity, inflammation, developmental toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 2011;32(36):9810–9817. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.08.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Oh N, Park JH. Endocytosis and exocytosis of nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Int J Nanomed. 2014;9(Supplement 1):51–63. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S26592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Mazumdar S, Chitkara D, Mittal A. Exploration and insights into the cellular internalization and intracellular fate of amphiphilic polymeric nanocarriers. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2021;11(4):903–924. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Prietl B, Meindl C, Roblegg E, Pieber TR, Lanzer G, Fröhlich E. Nano-sized and micro-sized polystyrene particles affect phagocyte function. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2014;30(1):1–16. doi: 10.1007/S10565-013-9265-Y/TABLES/3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Chakraborty A, Jana NR. Clathrin to lipid raft-endocytosis via controlled surface chemistry and efficient perinuclear targeting of nanoparticle. J Phys Chem Lett. 2015;6(18):3688–3697. doi: 10.1021/ACS.JPCLETT.5B01739/SUPPL_FILE/JZ5B01739_LIVESLIDES.MP4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Wu M, Guo H, Liu L, Liu Y, Xie L. Size-dependent cellular uptake and localization profiles of silver nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed. 2019;14:4247. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S201107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Milić M, Leitinger G, Pavičić I, Zebić Avdičević M, Dobrović S, Goessler W, et al. Cellular uptake and toxicity effects of silver nanoparticles in mammalian kidney cells. J Appl Toxicol. 2015;35(6):581–592. doi: 10.1002/JAT.3081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Zhang XF, Shen W, Gurunathan S. Silver nanoparticle-mediated cellular responses in various cell lines: an in vitro model. Int J Mol Sci. 2016 doi: 10.3390/IJMS17101603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Kluska K, Peris-Díaz MD, Płonka D, Moysa A, Dadlez M, Deniaud A, et al. Formation of highly stable multinuclear AgnSn clusters in zinc fingers disrupts their structure and function. Chem Commun. 2020;56(9):1329–1332. doi: 10.1039/C9CC09418K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Liu W, Worms I, Slaveykova VI. Interaction of silver nanoparticles with antioxidant enzymes. Environ Sci Nano. 2020;7(5):1507–1517. doi: 10.1039/C9EN01284B. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Käkinen A, Ding F, Chen P, Mortimer M, Kahru A, Ke PC. Interaction of firefly luciferase and silver nanoparticles and its impact on enzyme activity. Nanotechnology. 2013;24(34):345101. doi: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/34/345101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Lim D, Roh JY, Eom HJ, Choi JY, Hyun J, Choi J. Oxidative stress-related PMK-1 P38 MAPK activation as a mechanism for toxicity of silver nanoparticles to reproduction in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2012;31(3):585–592. doi: 10.1002/etc.1706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Giulia C, Simona M, Elena M, Daniela C, Lucia M, Anna Ida F, et al. Oxidative and/or inflammatory thrust induced by silver nanoparticles in rabbits: effect of vitamin E or NSAID administration on semen parameters. Mediat Inflamm. 2020;2020:1–15. doi: 10.1155/2020/6664062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Altwaijry N, El-Masry TA, Alotaibi B, Tousson E, Saleh A. Therapeutic effects of rocket seeds (Eruca sativa L.) against testicular toxicity and oxidative stress caused by silver nanoparticles injection in rats. Environ Toxicol. 2020;35(9):952–960. doi: 10.1002/tox.22931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Abu-Taweel GM, Albetran HM, Al-Mutary MG, Ahmad M, Low IM. Alleviation of silver nanoparticle-induced sexual behavior and testicular parameters dysfunction in male mice by yttrium oxide nanoparticles. Toxicol Rep. 2021;8:1121–1130. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2021.05.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Attia AA. Evaluation of the testicular alterations induced by silver nanoparticles in male mice: biochemical, histological and ultrastructural studies. Res J Pharm Biol Chem Sci. 2014;5(4):1558–1589. [Google Scholar]
- 92.Moradi-Sardareh H, Basir HRG, Hassan ZM, Davoudi M, Amidi F, Paknejad M. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles on different tissues of Balb/C mice. Life Sci. 2018;211:81–90. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.09.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Bidian C, Filip GA, David L, Florea A, Moldovan B, Robu DP, et al. The impact of silver nanoparticles phytosynthesized with Viburnum opulus L. extract on the ultrastrastructure and cell death in the testis of offspring rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021;150:112053. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Lopes IMD, de Oliveira IM, Bargi-Souza P, Cavallin MD, Kolc CSM, Khalil NM, et al. Effects of silver nanoparticle exposure to the testicular antioxidant system during the prepubertal rat stage. Chem Res Toxicol. 2019;32(6):986–994. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.8b00281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Wang E, Huang Y, Du Q, Sun Y. Silver nanoparticle induced toxicity to human sperm by increasing ROS(reactive oxygen species) production and DNA damage. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2017;52:193–199. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2017.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Zapór L. Effects of silver nanoparticles of different sizes on cytotoxicity and oxygen metabolism disorders in both reproductive and respiratory system cells. Arch Environ Prot. 2016;42(4):32–47. doi: 10.1515/aep-2016-0038. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Han JW, Jeong JK, Gurunathan S, Choi YJ, Das J, Kwon DN, et al. Male- and female-derived somatic and germ cell-specific toxicity of silver nanoparticles in mouse. Nanotoxicology. 2016;10(3):361–373. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2015.1073396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Shariatzadeh SMA, Miri SA, Cheraghi E. The protective effect of Kombucha against silver nanoparticles-induced toxicity on testicular tissue in NMRI mice. Andrologia. 2021;53(3):1–10. doi: 10.1111/and.13982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Carlson C, Hussain SM, Schrand AM, Braydich-Stolle LK, Hess KL, Jones RL, et al. Unique cellular interaction of silver nanoparticles: size-dependent generation of reactive oxygen species. J Phys Chem B. 2008;112(43):13608–13619. doi: 10.1021/JP712087M. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Wang E, Huang Y, Du Q, Sun Y. Alterations in reproductive parameters and gene expression in Balb/c mice testes after exposure to silver nanoparticles. Andrologia. 2021;53(1):1–9. doi: 10.1111/and.13841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.AOP-Wiki. AOP17:Binding of electrophilic chemicals to SH(thiol)-group of proteins and /or to seleno-proteins involved in protection against oxidative stress during brain development leads to impairment of learning and memory. https://aopwiki.org/aops/17.
- 102.Spiller HA. Rethinking mercury: the role of selenium in the pathophysiology of mercury toxicity. Clin Toxicol. 2017;56(5):313–326. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2017.1400555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Elsharkawy EE, Abd El-Nasser M, Kamaly HF. Silver nanoparticles testicular toxicity in rat. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2019 doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2019.103194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Hassanpour H, Mirshokraei P, Khalili Sadrabad E, Esmailian Dehkordi A, Layeghi S, Afzali A, et al. In vitro effect of nanosilver on gene expression of superoxide dismutases and nitric oxide synthases in chicken sertoli cells. Animal. 2014;9(2):295–300. doi: 10.1017/S1751731114002262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Zhang XF, Choi YJ, Han JW, Kim E, Park JH, Gurunathan S, et al. Differential nanoreprotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in male somatic cells and spermatogonial stem cells. Int J Nanomed. 2015;10:1335–1357. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S76062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Asare N, Duale N, Slagsvold HH, Lindeman B, Olsen AK, Gromadzka-Ostrowska J, et al. Genotoxicity and gene expression modulation of silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mice. Nanotoxicology. 2016;10(3):312–321. doi: 10.3109/17435390.2015.1071443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Asare N, Instanes C, Sandberg W, Refsnes M, Schwarze P, Kruszewski M, et al. Cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of silver nanoparticles in testicular cells. Toxicology. 2012;291(1–3):65–72. doi: 10.1016/J.TOX.2011.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Cavallin MD, Wilk R, Oliveira IM, Cardoso NCS, Khalil NM, Oliveira CA, et al. The hypothalamic-pituitary-testicular axis and the testicular function are modulated after silver nanoparticle exposure. Toxicol Res (Camb) 2018;7(1):102–116. doi: 10.1039/c7tx00236j. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Mohamed HRH. Studies on the genotoxicity behavior of silver nanoparticles in the presence of heavy metal cadmium chloride in mice. J Nanomater. 2016 doi: 10.1155/2016/5283162. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Agarwal A, Virk G, Ong C, du Plessis SS. Effect of oxidative stress on male reproduction. World J Mens Health. 2014;32(1):1. doi: 10.5534/WJMH.2014.32.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.AshaRani PV, Low Kah Mun G, Hande MP, Valiyaveettil S. Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human cells. ACS Nano. 2009;3(2):279–290. doi: 10.1021/nn800596w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Braydich-Stolle L, Hussain S, Schlager J, Hofmann MC. In vitro cytotoxicity of nanoparticles in mammalian germline stem cells. Toxicol Sci. 2005;88(2):412–419. doi: 10.1093/TOXSCI/KFI256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Arisha AH, Ahmed MM, Kamel MA, Attia YA, Hussein MMA. Morin ameliorates the testicular apoptosis, oxidative stress, and impact on blood–testis barrier induced by photo-extracellularly synthesized silver nanoparticles. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2019;26(28):28749–28762. doi: 10.1007/s11356-019-06066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.de Brito JLM, de Lima VN, Ansa DO, Moya SE, Morais PC, de Azevedo RB, et al. Acute reproductive toxicology after intratesticular injection of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in Wistar rats. Nanotoxicology. 2020;14(7):893–907. doi: 10.1080/17435390.2020.1774812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Thakur M, Gupta H, Singh D, Mohanty IR, Maheswari U, Vanage G, et al. Histopathological and ultra structural effects of nanoparticles on rat testis following 90 days (Chronic study) of repeated oral administration. J Nanobiotechnol. 2014;12(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12951-014-0042-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Satapathy SR, Mohapatra P, Preet R, Das D, Sarkar B, Choudhuri T, et al. Silver-based nanoparticles induce apoptosis in human colon cancer cells mediated through p53. Nanomedicine (Lond) 2013;8(8):1307–1322. doi: 10.2217/NNM.12.176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Shi J, Sun X, Lin Y, Zou X, Li Z, Liao Y, et al. Endothelial cell injury and dysfunction induced by silver nanoparticles through oxidative stress via IKK/NF-κB pathways. Biomaterials. 2014;35(24):6657–6666. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.04.093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Wang X, Sharma RK, Sikka SC, Thomas AJ, Falcone T, Agarwal A. Oxidative stress is associated with increased apoptosis leading to spermatozoa DNA damage in patients with male factor infertility. Fertil Steril. 2003;80(3):531–535. doi: 10.1016/S0015-0282(03)00756-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Muratori M, Tamburrino L, Marchiani S, Cambi M, Olivito B, Azzari C, et al. Investigation on the origin of sperm DNA fragmentation: role of apoptosis. Immaturity Oxid Stress Mol Med. 2015;21(1):109–122. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2014.00158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Evans EPP, Scholten JTM, Mzyk A, Reyes-San-Martin C, Llumbet AE, Hamoh T, et al. Male subfertility and oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2021;46:102071. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Cheng X, Zhang W, Ji Y, Meng J, Guo H, Liu J, et al. Revealing silver cytotoxicity using Au nanorods/Ag shell nanostructures: disrupting cell membrane and causing apoptosis through oxidative damage. RSC Adv. 2013;3(7):2296. doi: 10.1039/c2ra23131j. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 122.AOP-Wiki. AOP322: alkylation of DNA leading to reduced sperm count. https://aopwiki.org/aops/322.
- 123.Fathi N, Hoseinipanah SM, Alizadeh Z, Assari MJ, Moghimbeigi A, Mortazavi M, et al. The effect of silver nanoparticles on the reproductive system of adult male rats: a morphological, histological and DNA integrity study. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2018;28(3):299–305. doi: 10.17219/acem/81607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Zirkin BR, Papadopoulos V. Leydig cells: formation, function, and regulation†. Biol Reprod. 2018;99(1):101–111. doi: 10.1093/biolre/ioy059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Baki ME, Miresmaili SM, Pourentezari M, Amraii E, Yousefi V, Spenani HR, et al. Effects of silver nano-particles on sperm parameters, number of Leydig cells and sex hormones in rats. Iran J Reprod Med. 2014;12(2):139–144. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Park TJ, Song KY, Sohn SH, Lim IK. Marked inhibition of testosterone biosynthesis by the hepatotoxin nodularin due to apoptosis of Leydig cells. Mol Carcinog. 2002;34(3):151–163. doi: 10.1002/mc.10059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Orazizadeh M, Khorsandi L, Absalan F, Hashemitabar M, Daneshi E. Effect of beta-carotene on titanium oxide nanoparticles-induced testicular toxicity in mice. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2014;31(5):561–568. doi: 10.1007/s10815-014-0184-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Korytowski W, Pilat A, Schmitt JC, Girotti AW. Deleterious cholesterol hydroperoxide trafficking in steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) protein-expressing MA-10 Leydig cells: implications for oxidative stress-impaired steroidogenesis. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(16):11509–11519. doi: 10.1074/JBC.M113.452151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Tong MH, Christenson LK, Song WC. Aberrant cholesterol transport and impaired steroidogenesis in Leydig cells lacking estrogen sulfotransferase. Endocrinology. 2004;145(5):2487–2497. doi: 10.1210/EN.2003-1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Papadopoulos V, Miller WL. Role of mitochondria in steroidogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;26(6):771–790. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2012.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Valerio-García RC, Carbajal-Hernández AL, Martínez-Ruíz EB, Jarquín-Díaz VH, Haro-Pérez C, Martínez-Jerónimo F. Exposure to silver nanoparticles produces oxidative stress and affects macromolecular and metabolic biomarkers in the goodeid fish Chapalichthys pardalis. Sci Total Environ. 2017;583:308–318. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Dziendzikowska K, Krawczyńska A, Oczkowski M, Królikowski T, Brzóska K, Lankoff A, et al. Progressive effects of silver nanoparticles on hormonal regulation of reproduction in male rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2016;313:35–46. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2016.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Manna PR, Kero J, Tena-Sempere M, Pakarinen P, Stocco DM, Huhtaniemi IT. Assessment of mechanisms of thyroid hormone action in mouse Leydig cells: regulation of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein, steroidogenesis, and luteinizing hormone receptor function. Endocrinology. 2001;142(1):319–331. doi: 10.1210/ENDO.142.1.7900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Manna PR, Dyson MT, Stocco DM. Regulation of the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein gene expression: present and future perspectives. Mol Hum Reprod. 2009;15(6):321. doi: 10.1093/MOLEHR/GAP025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Dziendzikowska K, Wilczak J, Grodzicki W, Gromadzka-Ostrowska J, Węsierska M, Kruszewski M. Coating-dependent neurotoxicity of silver nanoparticles—an in vivo study on hippocampal oxidative stress and neurosteroids. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1365. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Hadrup N, Loeschner K, Mortensen A, Sharma AK, Qvortrup K, Larsen EH, et al. The similar neurotoxic effects of nanoparticulate and ionic silver in vivo and in vitro. Neurotoxicology. 2012;33(3):416–423. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2012.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.De Matteis V, Malvindi MA, Galeone A, Brunetti V, De Luca E, Kote S, et al. Negligible particle-specific toxicity mechanism of silver nanoparticles: the role of Ag+ ion release in the cytosol. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med. 2015;11(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/j.nano.2014.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.AOP-Wiki. AOP18: PPARα activation in utero leading to impaired fertility in males. https://aopwiki.org/aops/18.
- 139.Nepelska M, Odum J, Munn S. Adverse outcome pathway: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α activation and reproductive toxicity—development and application in assessment of endocrine disruptors/reproductive toxicants. Appl Vitr Toxicol. 2017;3(3):234–249. doi: 10.1089/aivt.2017.0004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Huang JC. The Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in the development and physiology of gametes and preimplantation embryos. PPAR Res. 2008 doi: 10.1155/2008/732303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Corton JC, Lapinskas PJ. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: mediators of phthalate ester-induced effects in the male reproductive tract? Toxicol Sci. 2005;83(1):4–17. doi: 10.1093/TOXSCI/KFI011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Corton JC, Cunningham ML, Hummer BT, Lau C, Meek B, Peters JM, et al. Mode of action framework analysis for receptor-mediated toxicity: the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα) as a case study. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014;44(1):1–49. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2013.835784. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Shipley JM, Waxman DJ. Simultaneous, bidirectional inhibitory crosstalk between PPAR and STAT5b. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004;199(3):275–284. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2003.12.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Park EJ, Bae E, Yi J, Kim Y, Choi K, Lee SH, et al. Repeated-dose toxicity and inflammatory responses in mice by oral administration of silver nanoparticles. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2010;30(2):162–168. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2010.05.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Lee J, Kim Y, Song K, Ryu H, Sung J, Park J, et al. Biopersistence of silver nanoparticles in tissues from Sprague-Dawley rats. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2013;10:1. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-10-36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Castellini C, Ruggeri S, Mattioli S, Bernardini G, Macchioni L, Moretti E, et al. Long-term effects of silver nanoparticles on reproductive activity of rabbit buck. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2014;60(3):143–150. doi: 10.3109/19396368.2014.891163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Sleiman HK, Romano RM, De OCA, Romano MA. Effects of prepubertal exposure to silver nanoparticles on reproductive parameters in adult male wistar rats. J Toxicol Environ Health Part A. 2013;76(17):1023–1032. doi: 10.1080/15287394.2013.831723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Gromadzka-Ostrowska J, Dziendzikowska K, Lankoff A, Dobrzyńska M, Instanes C, Brunborg G, et al. Silver nanoparticles effects on epididymal sperm in rats. Toxicol Lett. 2012;214(3):251–258. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2012.08.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.James ER, Carrell DT, Aston KI, Jenkins TG, Yeste M, Salas-Huetos A. The role of the epididymis and the contribution of epididymosomes to mammalian reproduction. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(15):1–17. doi: 10.3390/IJMS21155377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Iftikhar M, Noureen A, Uzair M, Jabeen F, Abdel Daim M, Cappello T. Perspectives of nanoparticles in male infertility: evidence for induced abnormalities in sperm production. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(4):1758. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18041758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.AOP-Wiki. AOP64:Glucocorticoid Receptor (GR) mediated adult Leydig cell dysfunction leading to decreased male fertility. https://aopwiki.org/aops/64.
- 152.AOP-Wiki. AOP323:PPARalpha Agonism impairs fish reproduction. https://aopwiki.org/aops/323.
- 153.AOP-Wiki. AOP444:Ionizing radiation leads to reduced reproduction in Eisenia fetida via reduced spermatogenesis and cocoon hatchability. https://aopwiki.org/aops/444.
- 154.Spinu N, Bal-Price A, Cronin MTD, Enoch SJ, Madden JC, Worth AP. Development and analysis of an adverse outcome pathway network for human neurotoxicity. Arch Toxicol. 2019;93(10):2759–2772. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02551-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Coccini T. Gene expression changes in rat liver and testes after lung instillation of a low dose of silver nanoparticles. J Nanomed Nanotechnol. 2014;05:05. doi: 10.4172/2157-7439.1000227. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Elespuru R, Pfuhler S, Aardema MJ, Chen T, Doak SH, Doherty A, et al. Genotoxicity assessment of nanomaterials: recommendations on best practices, assays, and methods. Toxicol Sci. 2018;164(2):391–416. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfy100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.OECD. Test No. 476: in vitro mammalian cell gene mutation tests using the Hprt and xprt genes. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-476-in-vitro-mammalian-cell-gene-mutation-tests-using-the-hprt-and-xprt-genes_9789264264809-en. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. OECD; 2016. (OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4). 10.1787/9789264264809-en.
- 158.OECD. Test No. 490: in vitro mammalian cell gene mutation tests using the thymidine kinase gene. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-490-in-vitro-mammalian-cell-gene-mutation-tests-using-the-thymidine-kinase-gene_9789264264908-en. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. OECD; 2016. (OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4). 10.1787/9789264264908-en.
- 159.OECD. Test No. 487: in vitro mammalian cell micronucleus test. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-487-in-vitro-mammalian-cell-micronucleus-test_9789264264861-en. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. OECD; 2016. (OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4). 10.1787/9789264264861-en.
- 160.OECD. Test No. 473: in vitro mammalian chromosomal aberration test. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-473-in-vitro-mammalian-chromosomal-aberration-test_9789264264649-en. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. OECD; 2016. (OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4). 10.1787/9789264264649-en.
- 161.OECD. Test No. 489: in vivo mammalian alkaline comet assay. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-489-in-vivo-mammalian-alkaline-comet-assay_9789264264885-en. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. OECD; 2016. (OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4). 10.1787/9789264264885-en.
- 162.OECD. Test No. 488: transgenic rodent somatic and germ cell gene mutation assays. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-488-transgenic-rodent-somatic-and-germ-cell-gene-mutation-assays_9789264203907-en. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. OECD; 2022. (OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4). 10.1787/9789264203907-en.
- 163.OECD. Test No. 474: mammalian erythrocyte micronucleus test. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-474-mammalian-erythrocyte-micronucleus-test_9789264224292-en. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. OECD; 2014. 10.1787/9789264224292-en.
- 164.OECD. Test No. 475: Mammalian Bone Marrow Chromosomal Aberration Test. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals. OECD Publishing; 2014.
- 165.Ravanat JL, Breton J, Douki T, Gasparutto D, Grand A, Rachidi W, et al. Radiation-mediated formation of complex damage to DNA: a chemical aspect overview. Br J Radiol. 2014;87:1035. doi: 10.1259/BJR.20130715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Zhang XF, Gurunathan S, Kim JH. Effects of silver nanoparticles on neonatal testis development in mice. Int J Nanomed. 2015;10:6243–6256. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S90733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.OECD. Test No. 456: H295R steroidogenesis assay. https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/environment/test-no-456-h295r-steroidogenesis-assay_9789264122642-en. OECD; 2022. p. 1–10. (OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Section 4). 10.1787/9789264122642-en.
- 168.Taieb J, Mathian B, Millot F, Patricot MC, Mathieu E, Queyrel N, et al. Testosterone measured by 10 immunoassays and by isotope-dilution gas chromatography-mass spectrometry in sera from 116 men, women, and children. Clin Chem. 2003;49(8):1381–1395. doi: 10.1373/49.8.1381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Paduch DA, Brannigan RE, Fuchs EF, Kim ED, Marmar JL, Sandlow JI. The laboratory diagnosis of testosterone deficiency. Urology. 2014;83(5):980–988. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2013.12.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Panner Selvam MK, Agarwal A. A systematic review on sperm DNA fragmentation in male factor infertility: laboratory assessment. 2019;16(1):65–76. 10.1016/J.AJU.2017.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 171.ECVAM. EURL ECVAM database on alternative methods to animal experimentation (DB-ALM) | EU Science Hub. https://ec.europa.eu/jrc/en/scientific-tool/database-alternative-methods-animal-experimentation.
- 172.Gliga AR, Skoglund S, Odnevall Wallinder I, Fadeel B, Karlsson HL. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: the role of cellular uptake, agglomeration and Ag release. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014;11(1):11. doi: 10.1186/1743-8977-11-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Hamilton RF, Buckingham S, Holian A. The effect of size on Ag nanosphere toxicity in macrophage cell models and lung epithelial cell lines is dependent on particle dissolution. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4):6815–6830. doi: 10.3390/IJMS15046815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Lafuente D, Garcia T, Blanco J, Sánchez DJ, Sirvent JJ, Domingo JL, et al. Effects of oral exposure to silver nanoparticles on the sperm of rats. Reprod Toxicol. 2016;60:133–139. doi: 10.1016/j.reprotox.2016.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Miresmaeili SM, Halvaei I, Fesahat F, Fallah A, Nikonahad N, Taherinejad M. Evaluating the role of silver nanoparticles on acrosomal reaction and spermatogenic cells in rat. Iran J Reprod Med. 2013;11(5):423–430. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Pourali P, Nouri M, Ameri F, Heidari T, Kheirkhahan N, Arabzadeh S, et al. Histopathological study of the maternal exposure to the biologically produced silver nanoparticles on different organs of the offspring. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020;393(5):867–878. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01796-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. List of the 48 studies selected for the putative AOP construction.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.