Figure 1. Isolation and characterization of EBV gH/gL-specific mAbs.
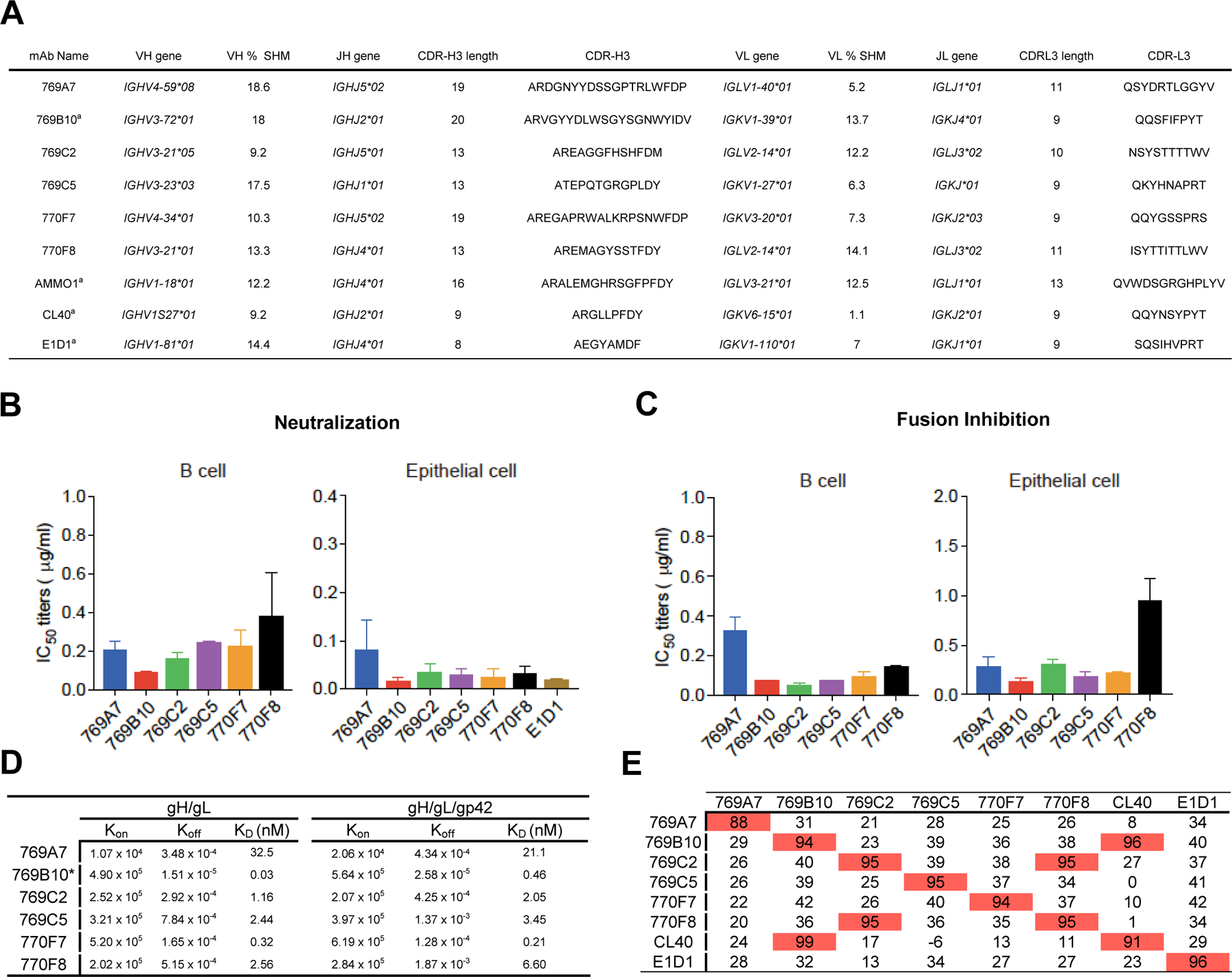
(A) EBV gH/gL-specific B cells were isolated from two convalescent donor samples. Immunoglobulin gene assignments, and antibody characteristics are shown for isolated antibodies, and previously described EBV gH/gL-targeting antibodies for reference.
(B) Antibody neutralization of EBV infection of Raji B cells and SVKCR2 epithelial cells.
(C) Inhibition of B cell and epithelial cell fusion by isolated mAbs.
(D) Octet Biolayer interferometry antibody-antigen affinity measurements using EBV gH/gL (left) and gH/gL/gp42 (right) antigens. The association, dissociation rates, and KD values are shown for antibodies. 769B10 values were previously described (Bu et al., 2019).
(E) Antibody competition profile using previously described antibodies (mAbs E1D1, CL40, 769B10) as competitors. Antibodies noted in the left column were first bound to gH/gL, followed by binding to a second antibody noted in the top row, with percent competition indicated.
