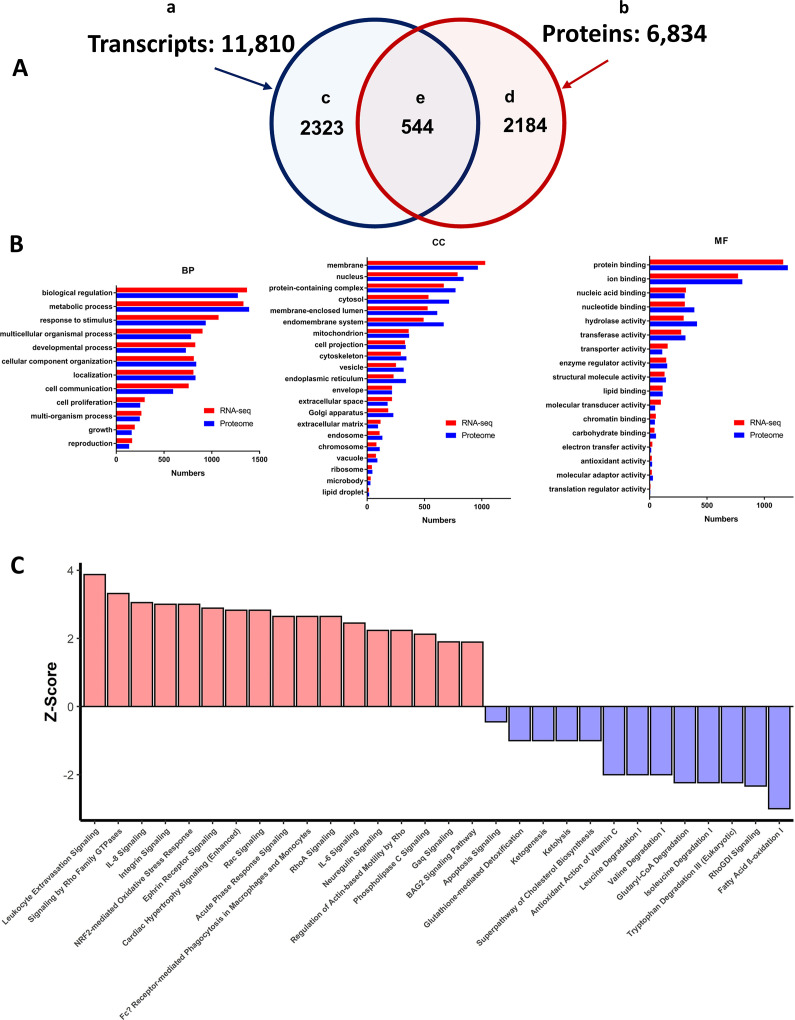
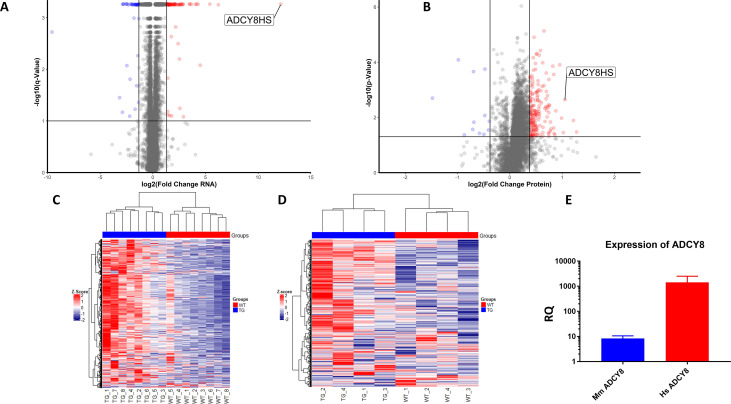
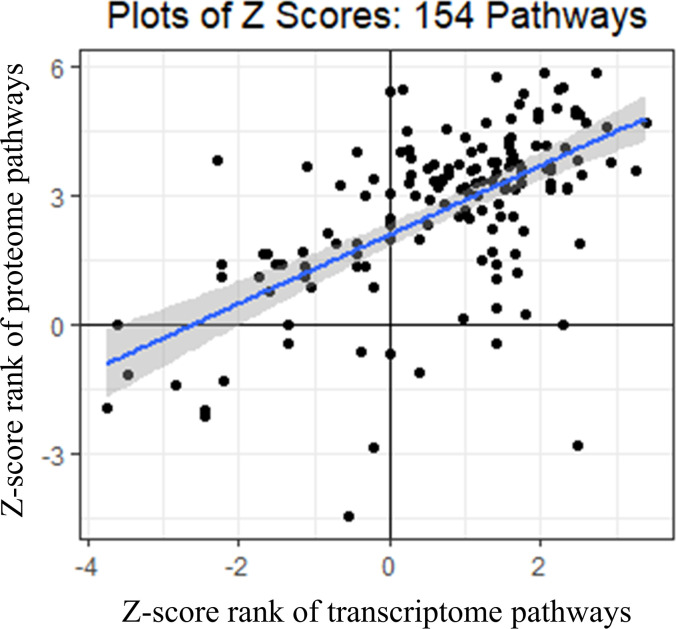
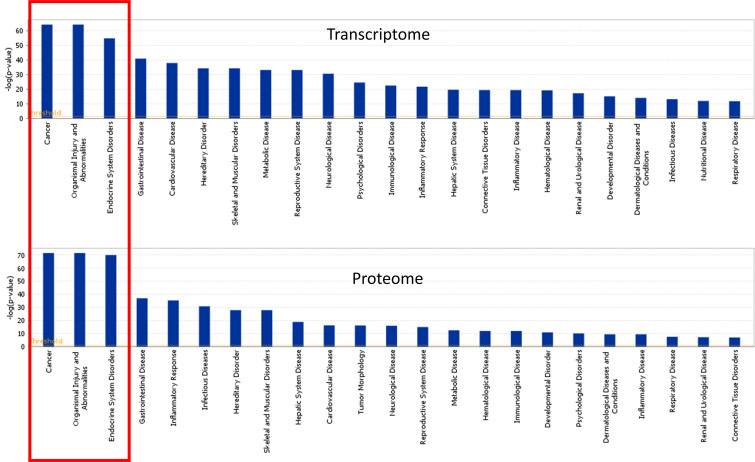
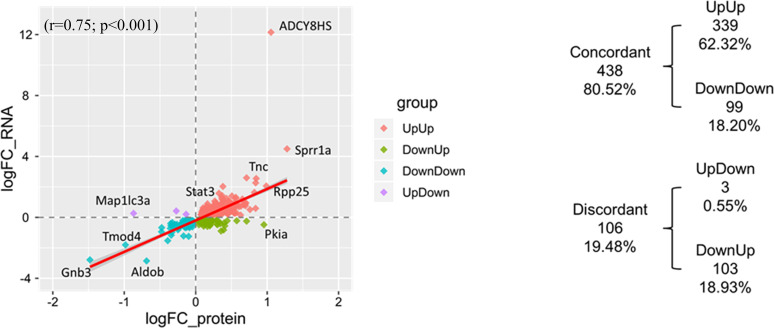
Figure 10. Summary of LV transcriptome and proteome analysis of TGAC8 and WT.
(A) Schematic of the total number of transcripts (subset ‘a’ – 11,810), and proteins (subset ‘b’ 6834), identified in LV lysates, the number of transcripts (subset ‘c’ 2323), and proteins (subset ‘d’ 2184), that differed by genotype, and number of identified transcripts and proteins that both differed by genotype (subset ‘e’ - 544). (B) WEBGESTALT analysis of the 2323 transcripts (Panel A subset ‘c’) and 2184 proteins (Panel A subset ‘d’) that significantly differed by genotype. Biological Processes (BP), Cell Compartment (CC), Molecular Functions (MF). (C) Top canonical signaling pathways differing in enrichment (-log10(pvalue) >1.3) and activation status by genotype in IPA analysis of transcripts and proteins.