Abstract
Stereoselective synthesis has been emerging as a resourceful tool because it enables the obtaining of compounds with biological interest and high enantiomeric purity. Flavonoids are natural products with several biological activities. Owing to their biological potential and aiming to achieve enantiomerically pure forms, several methodologies of stereoselective synthesis have been implemented. Those approaches encompass stereoselective chalcone epoxidation, Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation, Mitsunobu reaction, and the cycloaddition of 1,4-benzoquinone. Chiral auxiliaries, organo-, organometallic, and biocatalysis, as well as the chiral pool approach were also employed with the goal of obtaining chiral bioactive flavonoids with a high enantiomeric ratio. Additionally, the employment of the Diels–Alder reaction based on the stereodivergent reaction on a racemic mixture strategy or using catalyst complexes to synthesise pure enantiomers of flavonoids was reported. Furthermore, biomimetic pathways displayed another approach as illustrated by the asymmetric coupling of 2-hydroxychalcones driven by visible light. Recently, an asymmetric transfer hydrogen-dynamic kinetic resolution was also applied to synthesise (R,R)-cis-alcohols which, in turn, would be used as building blocks for the stereoselective synthesis of flavonoids.
Keywords: flavonoids, enantiomers, enantioselective synthesis, chiral
1. Introduction
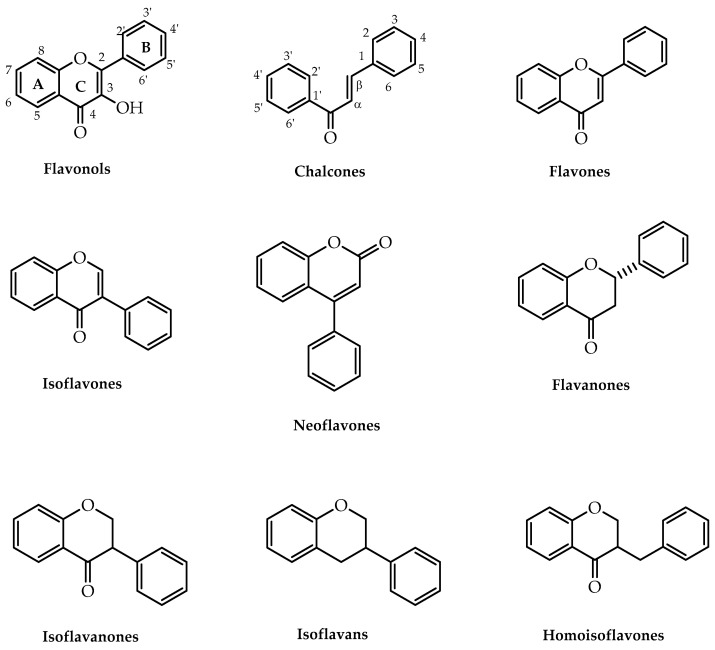
Flavonoids constitute a major group of polyphenolic compounds found in plants, fruits, vegetables, and nuts. They are associated with several roles in flora, namely, cell growth modulation and defence against extreme environmental conditions and oxidative stress. Moreover, they contribute to the perfume and colour in fruits and flowers, therefore promoting pollination [1,2]. In addition to flavonoids commonly found in terrestrial plants, some bioactive flavonoids can also be found in marine sources [3]. Structurally, flavonoids are composed of a 15-carbon scaffold with two aromatic rings (A and B) attached through a 3-carbon chain, which could be a heterocyclic ring denominated as a C ring. According to the degree of unsaturation and oxidation of the C ring and the position of the B ring, they can be categorised into different classes (Figure 1). In nature, this wide array of moieties is obtained through the combination of shikimate and acetate pathways under enzymatic transformation, with chalcones being the intermediates for the biosynthesis of the other classes of flavonoids [2,4].
Figure 1.
Main classes of flavonoids.
Flavonoids are well-known to possess a variety of biological activities with therapeutic interests such as antioxidant [5], antimalarial [6], anti-inflammatory [7,8], antiviral [9,10], antibacterial [11], antidiabetic [8], antifungal [12], and anticancer [1,13,14,15,16] potential. It is also reported that they protect the cardiovascular system from oxidative stress as a consequence of their ROS scavenger ability [17]. Moreover, flavonoids can be employed in the cosmetic field as protective agents against skin deterioration and hyperpigmentation attributable to UV irradiation [18]. They also contribute to improving elasticity and skin strength as well as averting the occurrence of dark spots because of their inhibitory activity towards elastases, collagenases, and tyrosinases [18].
In addition to these diverse medicinal features, these polyphenolic compounds can be used in the food industry as sweeteners and colouring agents in pastry products [19]. Furthermore, they can function as flavour enhancers and protect against lipid peroxidation in seed oils and biscuits, owing to their antioxidant effect [19]. Flavonoids can also be employed in the textile area to produce biocompatible fibres and to ameliorate their quality [18]. Additionally, these natural compounds can be incorporated in the dyeing process of fibres for the purpose of procuring more environmentally friendly manufacturing [18]. It has also been reported that flavonoids possess the capacity to restrain metal corrosion, which arouses interest from a metallurgical field perspective [20].
Considering the biological and industrial potential of natural flavonoids, several chemical methodologies have been developed to obtain nature-inspired flavonoids, as summarised in Table 1 [21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32].
Table 1.
Summary of synthetic methods for flavonoid classes.
| Flavonoids | Synthetic Approaches | References |
|---|---|---|
| Chalcones | Claisen–Schmidt reaction | [21,30,31] |
| Friedel–Crafts reaction | [21] | |
| Heck coupling | [32] | |
| Suzuki–Miyaura reaction | [62] | |
| Flavonols | Algar–Flynn–Oyamada reaction |
[21,34] |
| Karl von Auwers reaction | [60] | |
| Kostanecki methodology | [29] | |
| Flavanones | Intramolecular cyclisation of 2′-hydroxychalcones |
[36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43] |
| Flavones | Oxidative cyclisation of 2′-hydroxychalcones | [44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51] |
| Allan–Robinson reaction | [21,52] | |
| Baker–Venkataraman reaction |
[21,54] | |
| Kostanecki reaction | [55] | |
| Mentzer pyrone synthesis | [57] | |
| Suzuki–Miyaura reaction | [62] | |
| Isoflavones | Allan–Robinson reaction | [21,52] |
| Suzuki–Miyaura reaction | [62] | |
| Deoxybenzoin route | [22] | |
| Reductive cleavage of isoxazoles |
[23] | |
| Intramolecular ketene cycloaddition followed by decarboxylation | ||
| Rearrangement and cyclisation of chalcone epoxides |
[24] | |
| Rearrangement of flavanones | ||
| Wacker–Cook tandem conversion of α-methylene deoxybenzoins | [25] | |
| Cu(I)-mediated cyclisation of 3-(2-bromophenyl)-3-oxopropanol | [26] | |
| Neoflavones | Suzuki–Miyaura reaction | [62] |
| Pechmann reaction | [27] | |
| Perkin reaction | ||
| Wittig reaction of benzophenones | ||
| Metal-catalysed cross-coupling reactions such as Stille type | ||
| Direct arylation by the palladium-catalysed oxidative Heck coupling of arylboronic acids to coumarins |
[28] |
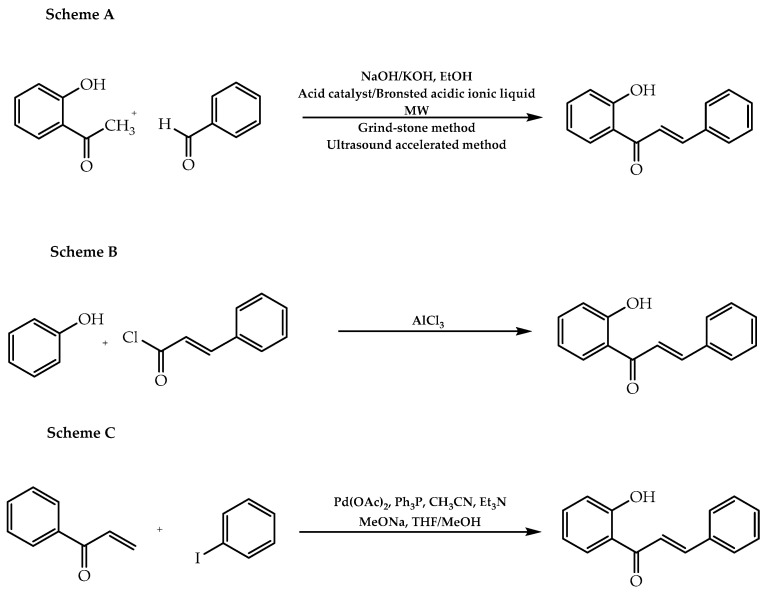
As in nature, 2′-hydroxychalcones can be intermediates for the synthesis of other classes of flavonoids, such as flavonols, flavones, and flavanones. Synthetically, they can be obtained via Claisen–Schmidt [21], Friedel–Crafts, and Heck coupling pathways [21] (Figure 2). Regarding the Claisen–Schmidt reaction, it comprises the reaction of an aromatic aldehyde and a substituted acetophenone under basic catalysis (Scheme A, Figure 2). This process can be improved with recourse to microwave and ultrasound [30,33], resulting in the enhancement of the yields and a reduction in the reaction time [31]. With respect to the Friedel–Crafts method, 2′-hydroxychalcones are originated from the condensation of (E)-3-phenylprop-2-enoyl chloride and phenols through AlCl3 catalysis [21] (Scheme B, Figure 2). In addition, the Heck coupling pathway is based on the combination of aryl α,β-unsaturated ketone and iodobenzene, culminating in the formation of the desired chalcone [32] (Scheme C, Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Synthetic methodologies of 2′-hidroxychalcones. Scheme A: Claisen–Schmidt reaction; Scheme B: Friedel–Crafts condensation; Scheme C: Heck coupling reaction.
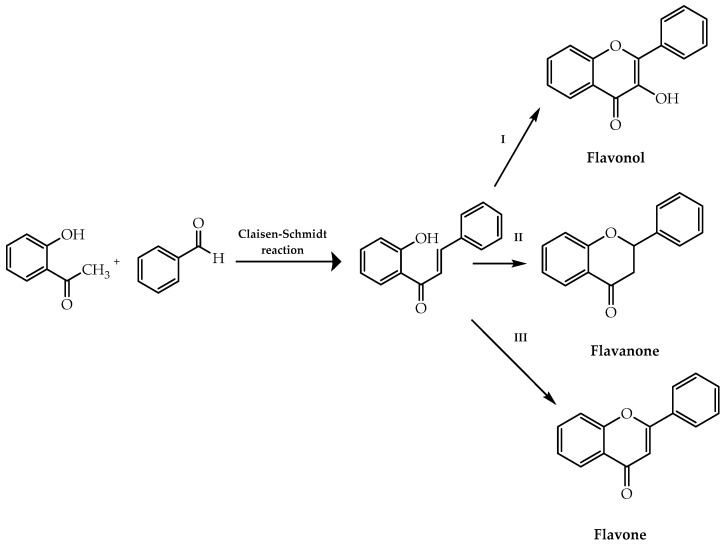
The Algar–Flynn–Oyamada methodology comprises the transformation of 2′-hydroxychalcones into flavonols (route I, Figure 3) through oxidative cyclisation mediated by hydrogen peroxide in alkaline medium [21,34,35]. The 2′-hydroxychalcones can also be building blocks for the synthesis of flavanones (route II, Figure 3) and flavones (route III, Figure 3). Considering the first class of flavonoids mentioned, they can be obtained through intramolecular cyclisation under acidic [36] or basic conditions [37], thermolysis [38], electrolysis [39], photolysis [40], microwave irradiation [41], a greener catalytic process [42], and palladium(II) catalysis [43]. Regarding flavones, these compounds can be synthesised through oxidative cyclisation under several reaction conditions such as classic I2-DMSO methodology [44] or using NH4I in a solvent-free environment [45]. There has also been reported the use of phenyliodinium acetate (PIDA) [46], selenium (IV) reagents under microwave irradiation [47], indium (III) halides in a gel-silica support system [48], CuI-mediated catalysis in the ionic liquid [bmim] [NTf2] as solvent [49], diphenyl disulfide at high temperatures [50], and oxalic acid-mediated catalysis [51] to obtain flavones via chalcones.
Figure 3.
Synthesis of flavonols, flavanones, and flavones using 2′-hydroxychalcones as building blocks.
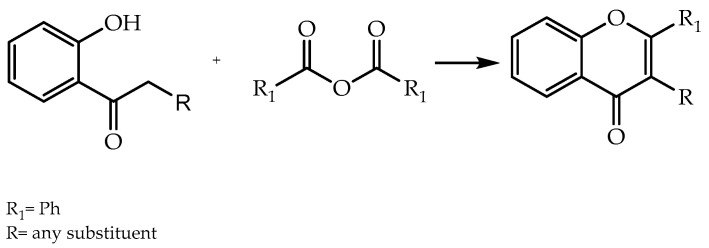
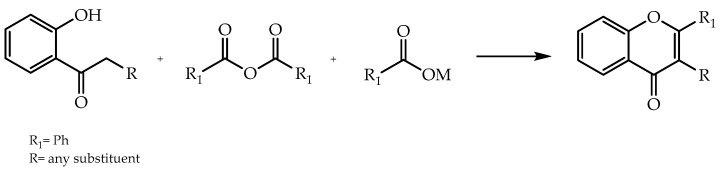
Alternatively, flavones can be obtained by other methods. The Allan–Robinson approach is established as a synthetic route to produce flavones and isoflavones from the condensation of o-hydroxyaryl ketones, aromatic acid anhydride, and the sodium salt of correlated aryl carboxylic acid anhydride [21,52] (Figure 4) [53].
Figure 4.
Synthesis of flavones and isoflavones by Allan–Robinson reaction.
The Baker–Venkataraman is another methodology implemented to produce intermediaries for the flavones’ synthesis [21], in which an α-acyloxy ketone is converted into β-diketones via basic catalysis and, subsequently, a cyclisation occurs to obtain the final flavone [54] (Figure 5).
Figure 5.
Synthesis of flavones by Baker–Venkataraman reaction.
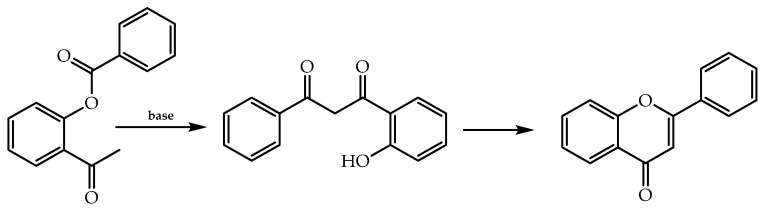
The Kostanecki method is another well-known reaction pathway to obtain flavonoids, namely flavones. It consists of the combination between a o-hydroxyaryl ketone, aromatic acid anhydrides, and their related salt [55] (Figure 6). There are several reports of the application of this process to synthesise flavonoids with biological activity, namely the work developed by DeMeyer et al. [56].
Figure 6.
Synthesis of flavones by Kostanecki reaction.
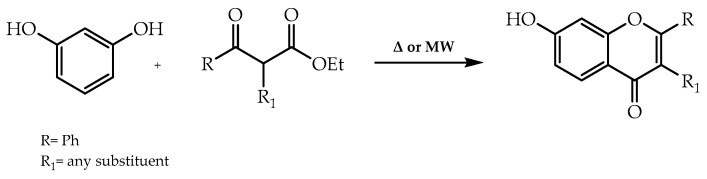
The Mentzer pyrone process encompasses the use of a phenol and a β-ketoester to synthesise flavone derivatives [57] without solvent and at high temperatures during a prolonged period of time or employing micro-wave irradiation [58] (Figure 7). A recent application of this strategy was employed by Pereira et al. [59] in the synthesis of flavones with antifouling activity [59].
Figure 7.
Synthesis of flavones by Mentzer reaction.
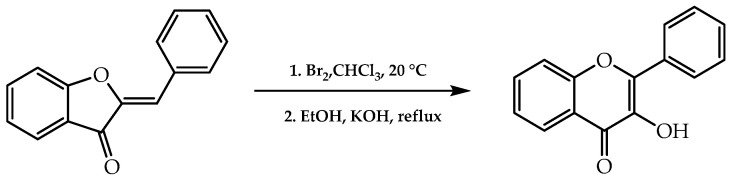
The Karl von Auwers method comprises a set of reactions which transforms aurones into flavonols [60] (Figure 8). These molecules are essential in plants to ensure protection against UV irradiation and metallic ions due to their chelating feature and free radical scavengers. As a result, flavonols could be employed as a vehicle of treatment for pathologies associated with oxidative stress [61].
Figure 8.
Synthesis of flavonols by Karl von Auwers approach.
The Suzuki–Miyaura approach has been latterly implemented in flavonoid moieties synthesis [62]. It involves a cross-coupling reaction between an organohalide and boronic acid/esters in the presence of a palladium complex [63]. Its application is generally associated with the formation of chalcones, flavones, isoflavones, and neoflavones because palladium input occurs in an sp2-hybridised carbon–halide bond [62]. Hurtová et al. [64] applied this methodology to synthesise derivatives of quercetin, luteolin, chrysin, and flavonoid boronates.
More information about the progress in the synthesis of flavonoids is reported in a recent revision [65]. Despite the presence of the stereogenic centre in many scaffolds of flavonoids, most of the synthetic strategies ignore the stereochemistry of their structures.
2. Stereoselective Synthesis of Flavonoids
Due to their biological activities and current concernment in attaining enantiomerically pure forms, chiral flavonoids are gaining attention in the scientific field [66]. The isolation of these natural compounds can be time-consuming and associated with a low yield, which accentuate even more the demand for the synthesis of enantiomerically pure forms of them [67].
A variety of methodologies to produce these bioactive compounds with high enantiomeric excess and purity have been reported. These approaches include separation processes, such as chiral chromatography [68,69,70,71,72], and stereoselective synthesis.
This revision complies with the research for synthetic routes of flavonoids with enantiomeric purity. For the purpose of supplementing this requirement, several methodologies have been developed.
2.1. Stereoselective Chalcone Epoxidation Approach
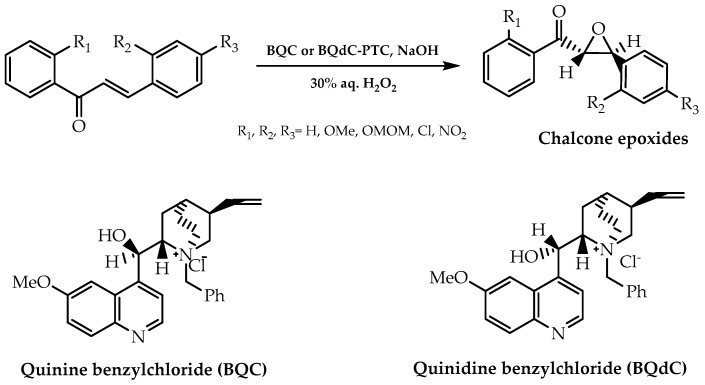
As previously mentioned, chalcones play a major role as intermediaries for the synthesis of the various groups of flavonoids and, as a result, an asymmetric synthetic process was developed considering chalcones as building blocks. This procedure consisted of the asymmetric epoxidation of chalcones, giving rise to the respective epoxides and their later use as chirons for the synthesis of other flavonoids [73]. In 1976, the use of quinine benzylchloride and quinidine benzylchloride as chiral phase-transfer catalysts in the epoxidation of α,β-unsatured ketones was reported [74] (Figure 9), allowing the application of this method in the synthesis of chalcone epoxides. However, the resulting enantiomeric excess was low, therefore leading to investigations with the aim of improving enantioselectivity [74].
Figure 9.
Chalcone epoxides synthesis using BQC and BQdC as phase-transfer catalysts.
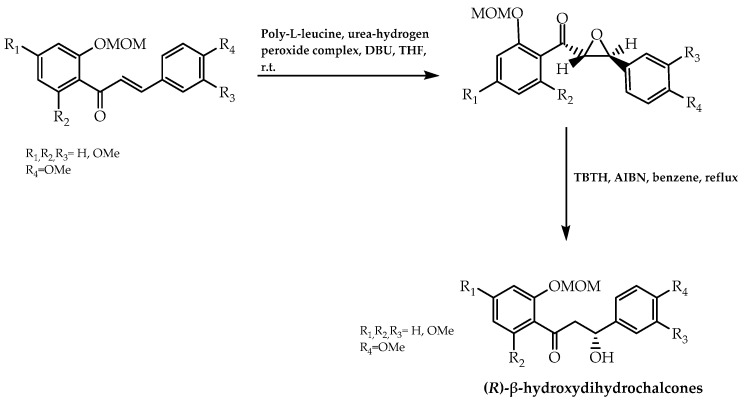
The turning point in this synthetic process arose from the implementation of three reaction components developed by Juliá et al. [75], comprising alkaline hydrogen peroxide, an organic solvent (carbon tetrachloride or toluene), and polymeric L- or D-alanine [75]. This synthetic process was later refined in a two-phase non-aqueous system in order to achieve higher enantiomeric purity [76]. Taking this into account, Nel et al. [77] proceeded to synthesise a series of enantiomeric (S)- and (R)-2′-methoxymethyl-β-hydroxydihydrochalcones (Figure 10), presenting some of them as an enantiomeric excess value in a range between 84% and 91%. These compounds constitute a resourceful tool in the industry, namely as sweeteners in candies and mouthwashes. Moreover, they assume a function of attracting insects in order to promote pollination in flora [77].
Figure 10.
Hydroxydihydrochalcones synthesis via chalcone asymmetric epoxidation in a two-phase non-aqueous system and catalysed by poly-amino acids.
2.2. Sharpless Asymmetric Dihydroxylation, Mitsunobu Reaction, and Cycloaddition of 1,4-Benzoquinone
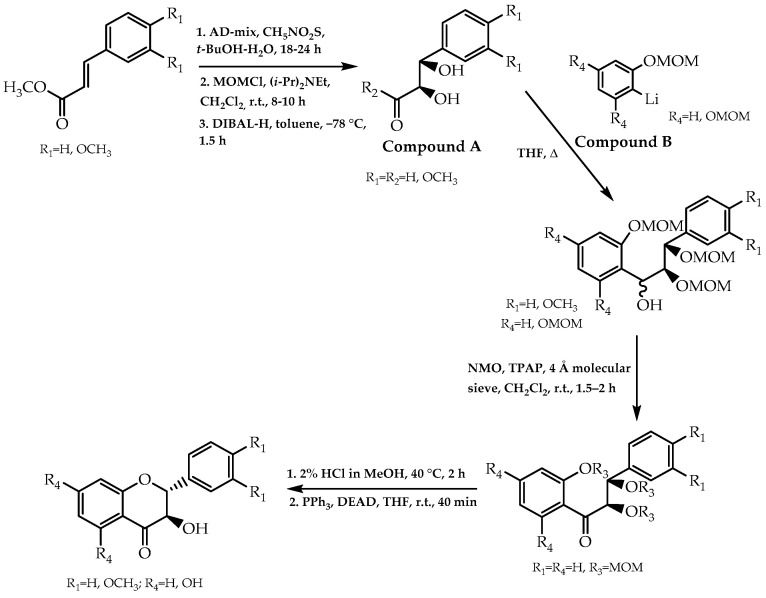
In 2000, the combination of the Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation and Mitsunobu reaction was applied to obtain pure enantiomeric 3-hydroxyflavanones, resulting in a novel approach to synthesise this flavonoid class. The first reaction phase consisted of the formation of the (2R,3S)-diols (compound A, Figure 11) via Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation using AD-mix with an outstanding enantiomeric excess of 99%. The synthesis of the enantiomerically pure 3-hydroxyflavanones in the final phase was based on the intramolecular Mitsunobu pathway as verified in the configuration of the stereogenic centre (Figure 11). This methodology was also used to obtain (2R,3R)-3′,4′-O-dimethyltaxifolin, which is a derivative of a 3-hydroxyflavanone with a protective role in the hepatic system [78].
Figure 11.
Stereoselective synthesis of 3-hydroxyflavanones based on the combination of Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation and Mitsunobu reaction.
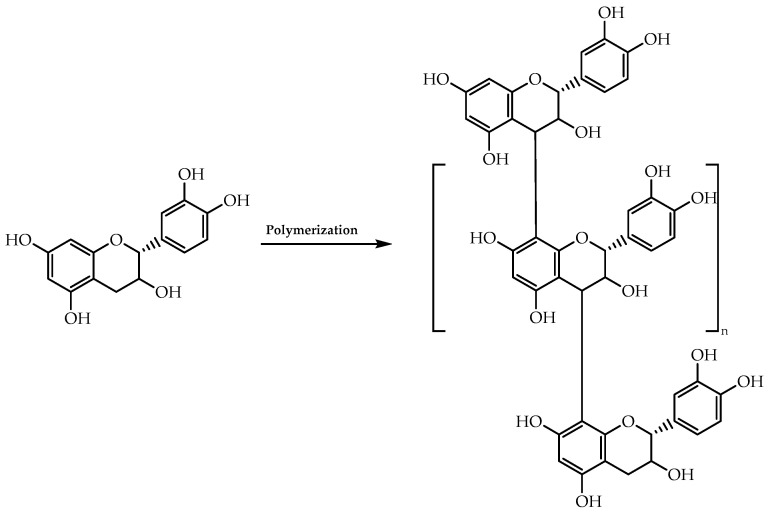
The applicability of Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation extends to the synthesis of flavan-3-ols and isoflavonoid derivatives. Van Rensburg et al. [79] employed this methodology to synthesise polyoxygenated diarylpropan-1,2-diols from retro-chalcones, which would be then used to obtain the chiral flavan-3-ol scaffold [79]. These chiral moieties arouse interest in many fields, namely as building blocks of condensed tannins polymers (Figure 12), which have been receiving attention for the development of eco-friendly food packaging, owing to their chemical properties [80].
Figure 12.
General structural feature of a natural condensed tannin composed of chiral flavan-3-ols.
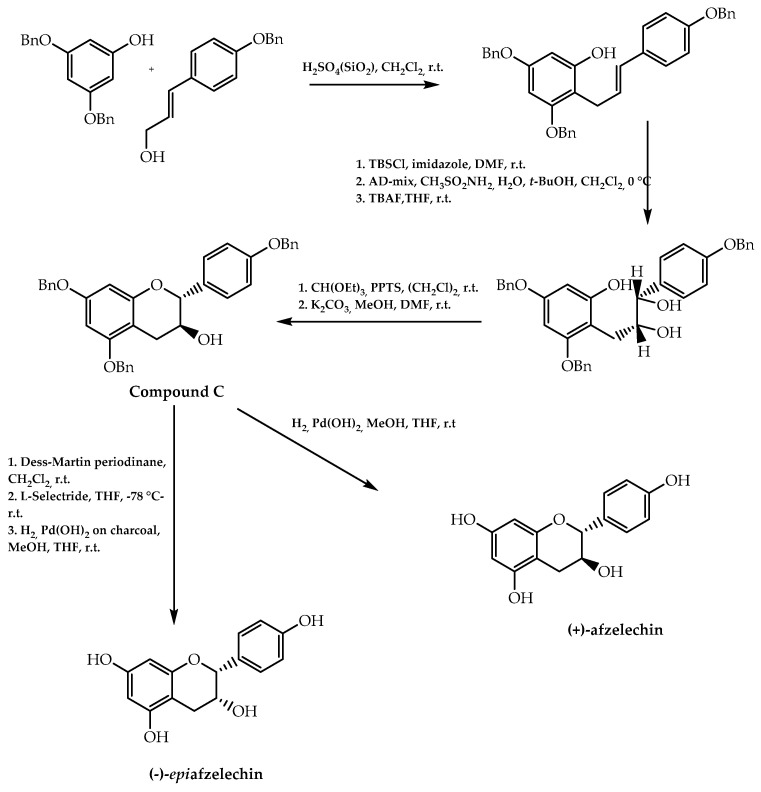
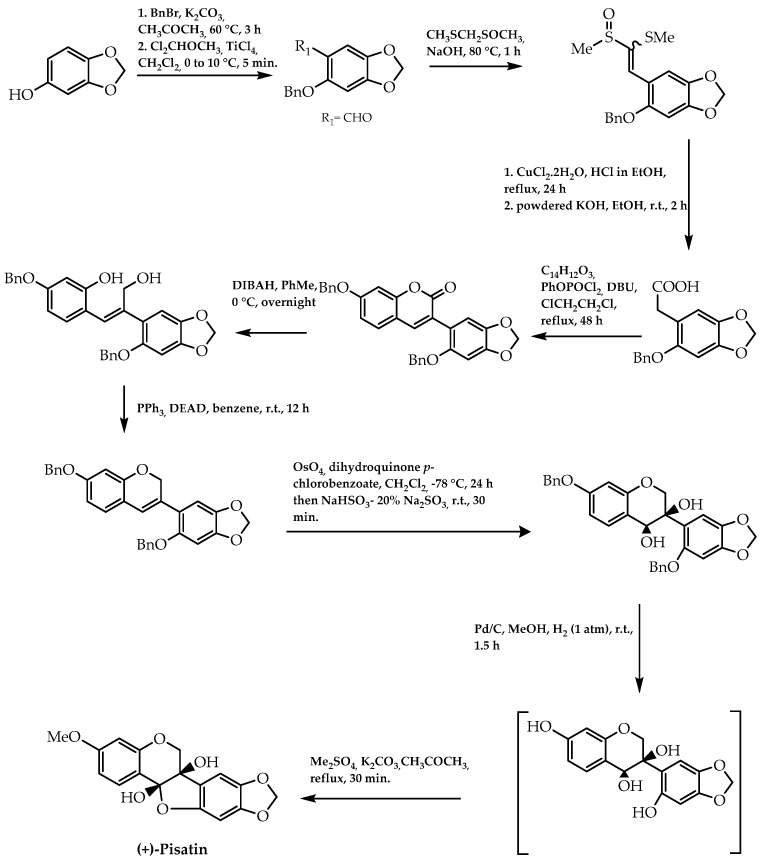
This approach was also extended for the synthesis of (+)-afzelechin and (-)-epiafzelechin by Wan et al. [81] with the aim of obtaining analogues of epigallocatechin-3-gallate with a cancer-preventive effect. These flavan-3-ols were stereoselectivity synthesised through the establishment of the stereogenic centres in the flavanol intermediate (compound C, Figure 13) by Sharpless dihydroxylation [81]. Moreover, (+)-pisatin, a natural isoflavonoid with a protective effect against microbial infections, was synthesised encompassing a Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation in one of the mechanism steps, resulting in an enantiomeric excess of 94% [82] (reaction phase 7, Figure 14).
Figure 13.
(+)-Afzelechin and (−)-epiafzelechin synthesis.
Figure 14.
(+)-Pisatin synthesis.
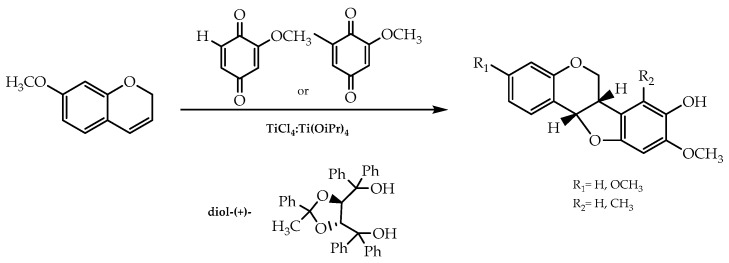
Furthermore, it was reported that isoflavonoid derivatives could also be obtained in an enantiomerically pure form via the cycloaddition of 1,4-benzoquinone and 2H-chromenes catalysed by a Ti-TADDOLate complex, which was demonstrated by Engler et al. [83]. They applied this procedure to synthesise pterocarpans with 75% and 80% of enantiomeric excess in light of their relevance as antifungal and antibacterial agents [83] (Figure 15).
Figure 15.
Pterocarpans obtained by cycloaddition via Ti-TADDOLate complex catalysis.
2.3. Chiral Auxliaries Approach
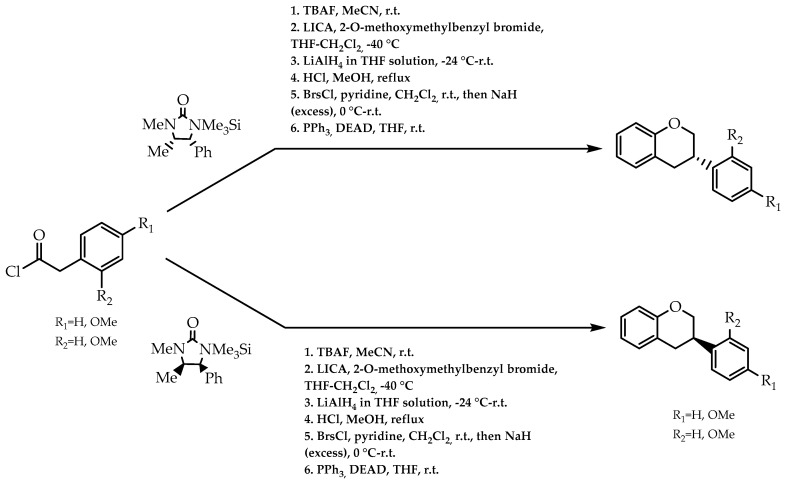
Isoflavans are a group of isoflavonoids with a variety of biological effects [84]. Since these compounds belong to a series of molecules where stereogenic centres are confined in 2, 3, and 4 positions, the development of enantioselective pathways to achieve enantiomeric pure moieties at position 3 could unfold stereoselective routes to other similar structures. Regarding this, Versteeg et al. [85] attempted to obtain isoflavans through a stereoselective α-benzylation of phenyl acetic acid derivatives, using (4S,5R)-(+)- and (4R,5S)-(-)-imidazolidin-2-ones as chiral auxiliaries (Figure 16). The implementation of this protocol brought an excellent outcome, with an array of enantiomeric excess between 94% and 99% and a chiral synthetic route for the 3-phenylchroman moiety [85].
Figure 16.
Enantioselective synthesis of isoflavans using imidazolidin-2-ones as chiral auxiliaries.
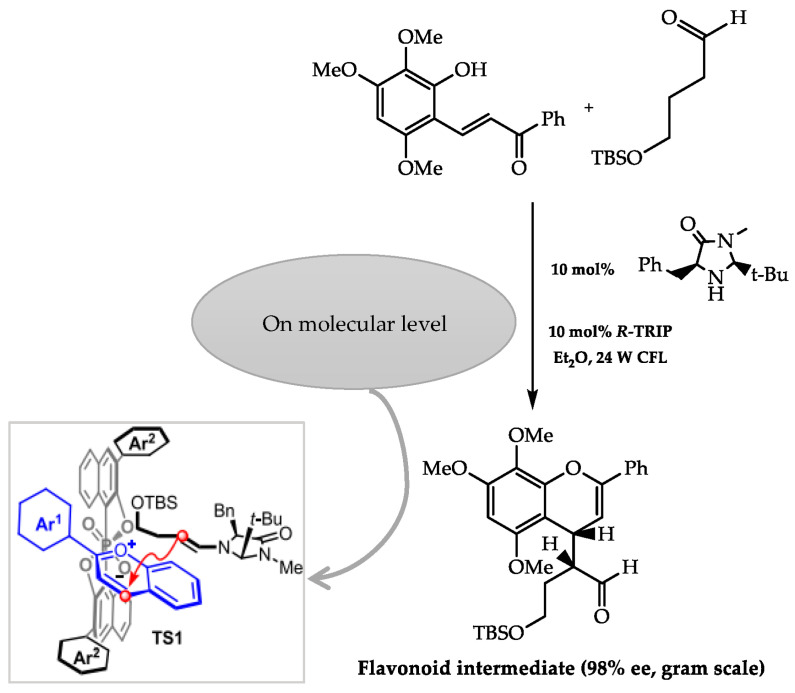
In addition, imidazolidinones were also relevant as chiral auxiliaries in the total synthesis of ent-fissistigmatin C. This molecule structure embodies a fragment of a flavonoid and another of the sesquiterpenoid linked through carbon 4 and carbon 1″, which establishes the generation of two stereogenic centres in the natural compound. Xu et al. [86] developed a strategy to obtain fissistigmatin-C based on the reaction of a 2-hydroxychalcone and an aliphatic aldehyde [86]. In this reaction step, the flavonoid formed from the coupling of the two compounds previously mentioned was synthesised via a collaborative catalytic action of a chiral imidazolidine, (R)-TRIP, and visible light (Figure 17). On the molecular level, (R)-TRIP facilitated the attack of the enamine of the imidazolidinone in the si face by alleviating the steric hindrance, culminating with the formation of the flavonoid intermediate with 98% of the enantiomeric excess [86] (Figure 17).
Figure 17.
Stereoselective synthesis of flavonoid intermediate in ent-fissistigmatin-C synthesis (adapted from Xu et al.) [86].
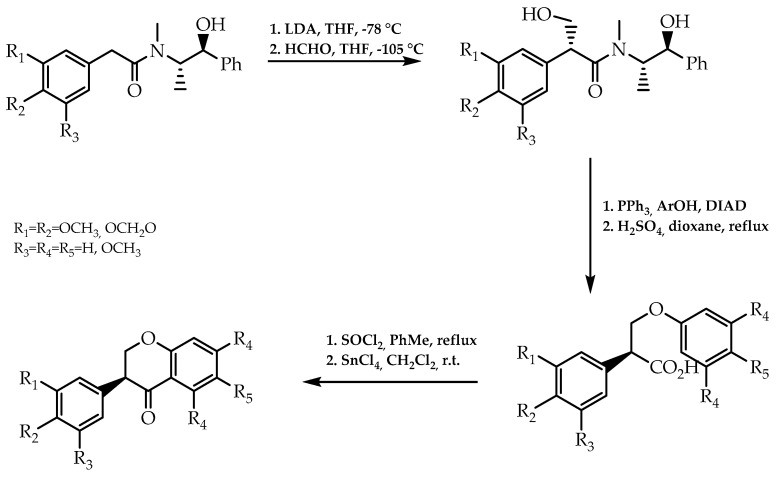
Considering the bioactive potential of isoflavanones as antifungal and antibacterial agents, in 2000, an enantioselective synthesis of isoflavanones was reported by Vicario et al. [87]. They resorted an asymmetric aldol reaction between (S,S)-(+)-pseudoephedrine arylacetamides and formaldehyde to introduce chirality in the intended compound. Subsequently, it was given the synthesis of the B ring via aryl ether formation and the displacement of the chiral auxiliary, culminating in the formation of the desired isoflavanones through Friedel, Crafts acylation (Figure 18). The chiral analysis by liquid chromatography showed that only one enantiomeric form was synthesised, boosting this methodology as an effective approach to obtain isoflavanones with a high degree of enantiomeric purity [87].
Figure 18.
Enantioselective synthesis of isoflavanones using (S,S)-(+)-pseudoephedrine as chiral auxiliary.
2.4. Organocatalysis
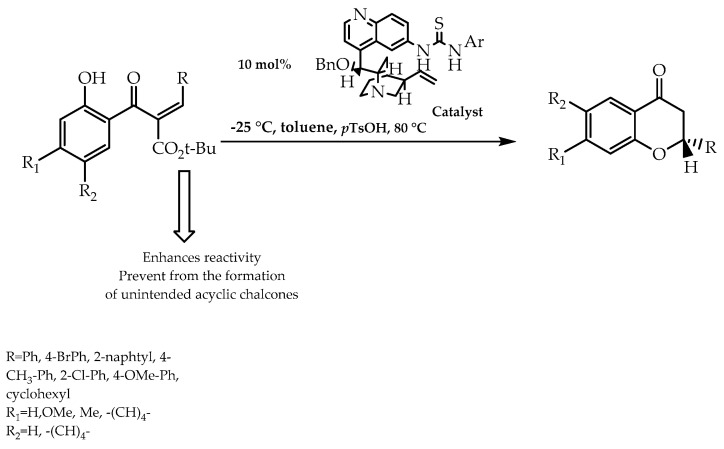
Flavonoids can also be obtained through organocatalytic asymmetric processes with the aim of acquiring enantiomeric pure forms of these natural compounds. Biddle et al. [88] proposed an asymmetric synthesis of flavanones based on the intramolecular conjugated addition of α-substituted chalcones, using thiourea compounds as catalysts (Figure 19). The application of this methodology culminated in the synthesis of the flavanone scaffold with 94% of enantiomeric excess [88].
Figure 19.
Enantioselective flavanones synthesis via chiral quinine-thiourea catalysis.
In 2010, a research team elaborated a deracemization methodology catalysed by alkaloid derivatives to obtain α-substituted ketones [89]. This process encompassed hydrogen fluoride as a proton supplier for the formation of the ammonium cation stemming from the alkaloids’ derivatives. This one, in turn, was responsible for the protonation of the silyl enolate intermediate previously synthesised, giving the desired products. Furthermore, it was proposed that the anion generated as a consequence of the protonation of the amine promoted the catalytic process, therefore enhancing the enantioselective transformation. In order to demonstrate the postulate, and bearing in mind the extent of the biological properties of flavonoids, they employed this strategy in the deracemization of homoisoflavones, resulting in the respective enantiomers with 78% and 81% of enantiomeric excess, and turning this process into a viable route to obtain enantiomeric pure forms of this flavonoid group [89] (Figure 20).
Figure 20.
Deracemization of homoisoflavones with silyl enolate formation and subsequent enantioselective protonation.
2.5. Organometallic Catalysis
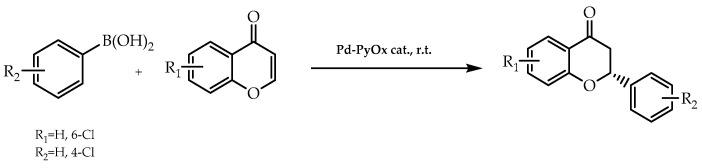
In addition to the enantiomeric pure flavonoids mediated by organocatalysis, organometallic compounds were also employed to promote the stereoselective synthesis of this natural compound. Due to their major interest in obtaining these compounds in the enantiomerically pure form, Lestini et al. [90] focused on the conjugate addition of chromones and arylboronic acids via palladium(II)-pyridinooxazoline catalysis to achieve their goal. For the purpose of enhancing the efficiency of the methodology, they undertook the catalytic process in palladium-nanoreactors with the aim of resulting in a catalytic stability increment. Then, they functionalised pyridinooxazoline with an acrylate monomer, which, in turn, was linked to palladium(II) trifluoroacetate and, subsequently, integrated in the nanoparticle, where the enantioselective synthesis of flavanones occurred. The final products were obtained within a range of from 79% to 84% of enantiomeric excess, highlighting the scientific relevance of this method regarding the enantioselective synthesis of natural bioactive compounds with antitumor, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities [90] (Figure 21).
Figure 21.
Enantioselective synthesis of flavanones by Pd-PyOx catalysis.
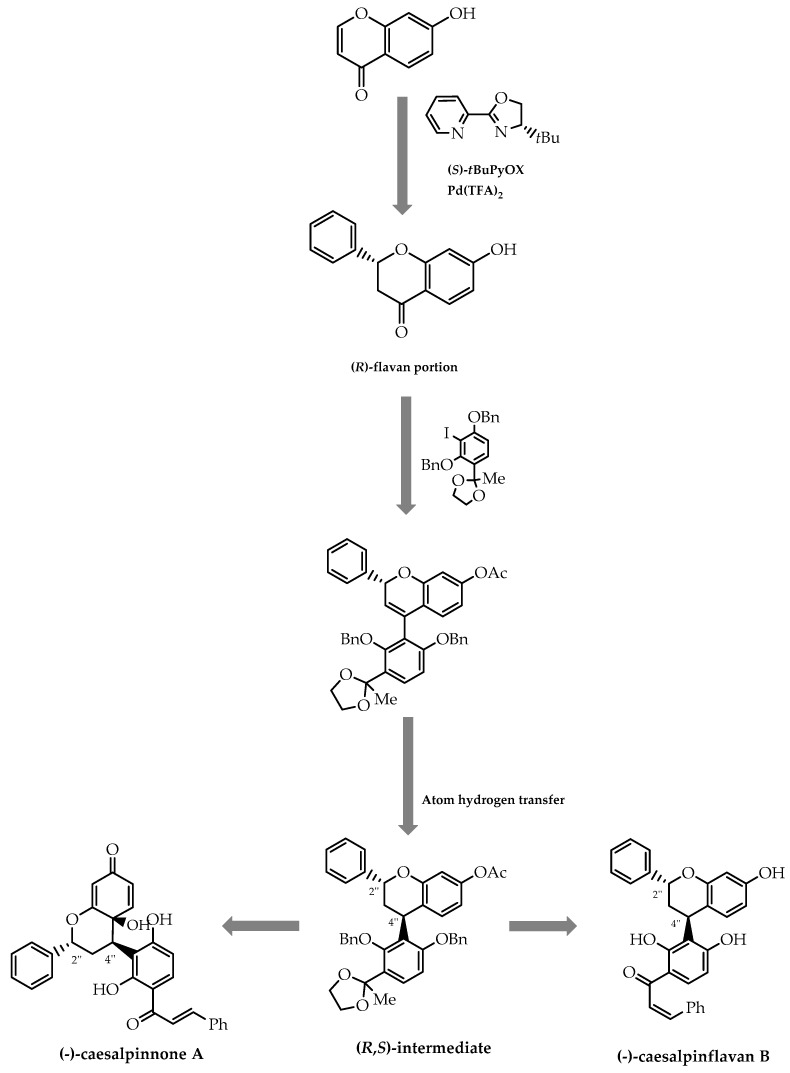
Furthermore, a similar process previously developed by Stoltz et al. [91] was employed by Timmerman et al. [92] in the stereoselective synthesis of (-)-caesalpinnone A and (-)-caesalpinflavan: two natural flavonoids with cytotoxic activity against several cancer cell lines [92]. Aiming to accomplish the aforementioned, they proceeded to use the palladium-catalysed conjugation addition methodology to create the sterogenic centre in the flavan portion of caesalpinnone A and caesalpinflavan B [92] (Figure 22). Subsequently, they established the chirality of C4″ in light of the work developed by Shenvi et al. [93], using a hydrogen atom transfer method to reduce the C3″-C4″ bond (Figure 22), resulting in the synthesis of the chiral intermediates of flavan-chalcone hybrids with high enantiomeric excess [92].
Figure 22.
Schematic representation of the stereoselective synthesis of (−)-caesalpinnone A and (−)-caesalpinflavan B via conjugate addition catalysed by Pd-PyOx and atom transfer hydrogen.
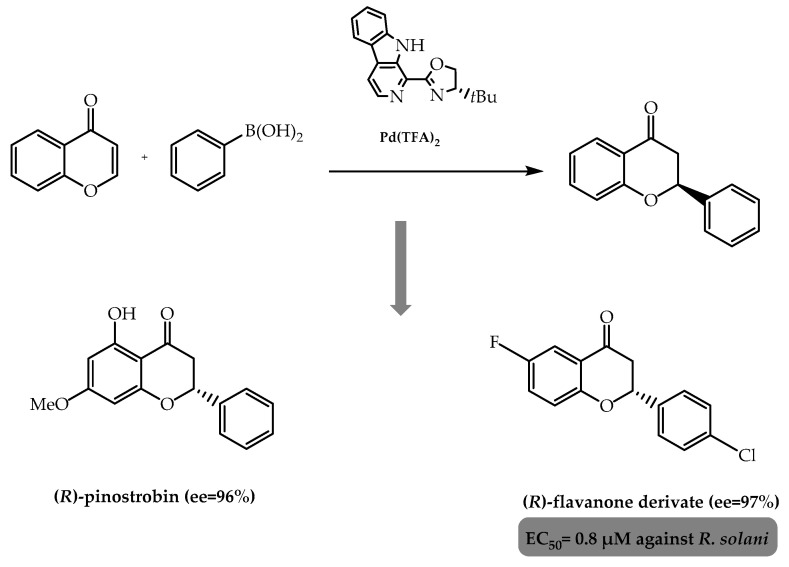
Moreover, in 2021, Yang et al. [94] focused on improving the palladium catalytic system used in the conjugate addition of arylboronic acids and chromones mentioned above with the goal of obtaining new chiral agrochemicals based on the flavanone scaffold. They successfully unravelled a synthetic route using a palladium-carboline (Pd-CarOx) (Figure 23) to obtain a library of chiral flavanones, in which some of them were synthesised with an enantiomeric excess of 84% to 97%. Subsequently, they established a structure–activity relationship pattern, culminating in the synthesis of (R)-pinostrobin through a mild reaction pathway as well as the attainment of the enantiomer R of a novel antifungal flavanone-derivative as a promising lead compound [94] (Figure 23).
Figure 23.
Enantioselective synthesis of flavanones through conjugate addition between chromones and arylboronic acids using Pd-CarOx complex as catalyst.
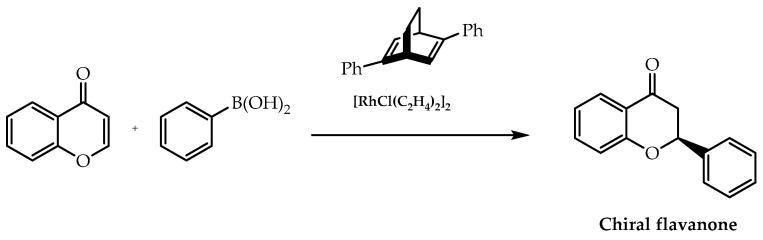
Additionally, this enantioselective reaction can also be employed using rhodium catalyst complexes. He et al. [95] applied this metallic element with a chiral diene to catalyse the enantioselective synthesis of flavanones via the 1,4-addition of arylboronic acids (Figure 24), resulting in products obtained with enantiomeric excess higher than 97% [95].
Figure 24.
Asymmetric 1,4-addition of arylboronic acids catalysed by rhodium-chiral diene complex.
2.6. Biocatalysis
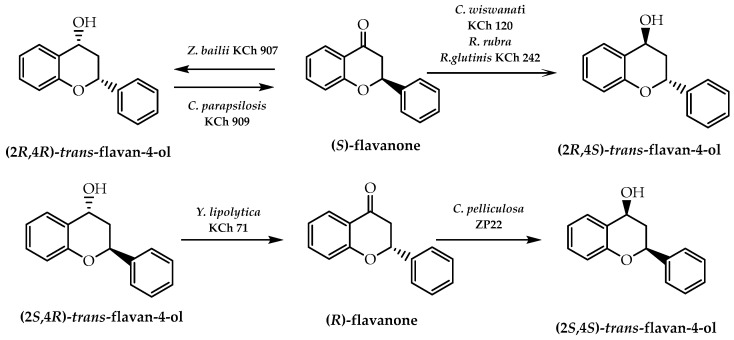
Biocatalysis presents as a resourceful tool to obtain compounds with structural complexity and several stereogenic centres. In contrast to the conventional chemical synthetic pathway, it can be performed under non-hazardous conditions and foremost enantiomeric excess [96], which makes this type of catalysis an appealing tool for the stereoselective synthesis of natural compounds, including flavonoids. In 2014, Janeczko et al. [97] synthesised chiral flavanones and cis/trans-flavan-4-ols, which were subject to different yeast strains. This methodology enabled the obtaining of the (2R,4S)-trans-flavan-4-ol from the reduction of (S)-flavanone by C. wiswanati KCh 120, R. rubra, and R. glutinis KCh 242 with 92%, 99%, and 98% of enantiomeric excess, respectively [97] (Figure 25). From the reduction of the same chiral flavanone, they were also able to produce (2R,4R)-cis-flavan-4-ol with an enantiomeric excess of 61%, using Z. bailii KCh 907, and (2S,4S)-cis-flavan-4-ol was obtained through an (R)-flavanone reduction by C.pelliculosa ZP22 with an enantiomeric excess of 75% [97] (Figure 25). On the other hand, (S)-flavanone and (R)-flavanone were obtained through the oxidation of (2R,4R)-cis-flavan-4-ol and (2S,4R)-trans-flavan-4-ol by C.parapsilosis KCh 909 and Y. lipolytica KCh 71 with enantiomeric excesses of 93% and 85%, respectively [97] (Figure 25).
Figure 25.
Enantioselective synthesis of flavanones and cis/trans-flavan-4-ols through biocatalysis using yeast strains.
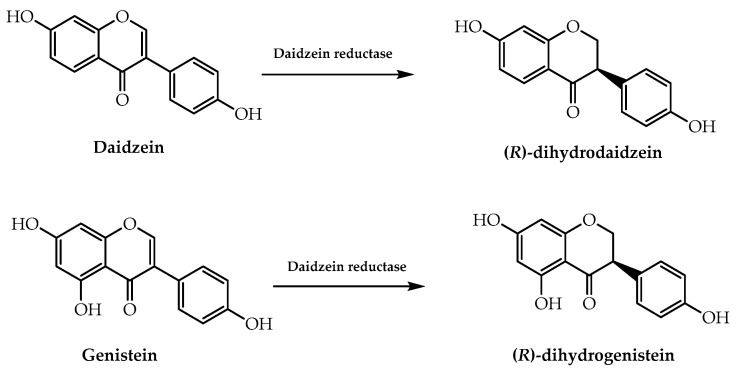
In light of the therapeutic effect of isoflavones and their derivatives in menopausal disorders and estrogenic-related osteoporosis, Kawada et al. [98] proceeded to evaluate the enzymatic parameters of daidzein reductase, which is intervenient in the conversion of daidzein in the human intestine. According to their results related to enantioselectivity, a highly purified form of the enzyme from Eggerthella sp. YY7918 was able to synthesise (R)-dihydrodaidzein (Figure 26), disclosing a methodology to obtain enantiomeric pure forms of (R)-dihydroisoflavones [98]. Furthermore, they applied this process to another substrate, genistein, enabling them to produce the corresponding (R)-dihydroisoflavone [98] (Figure 26).
Figure 26.
Enantioselective synthesis of (R)-dihydrodaidzein and (R)-dihydrogenistein by daidzein reductase from Eggerthella sp. YY7918.
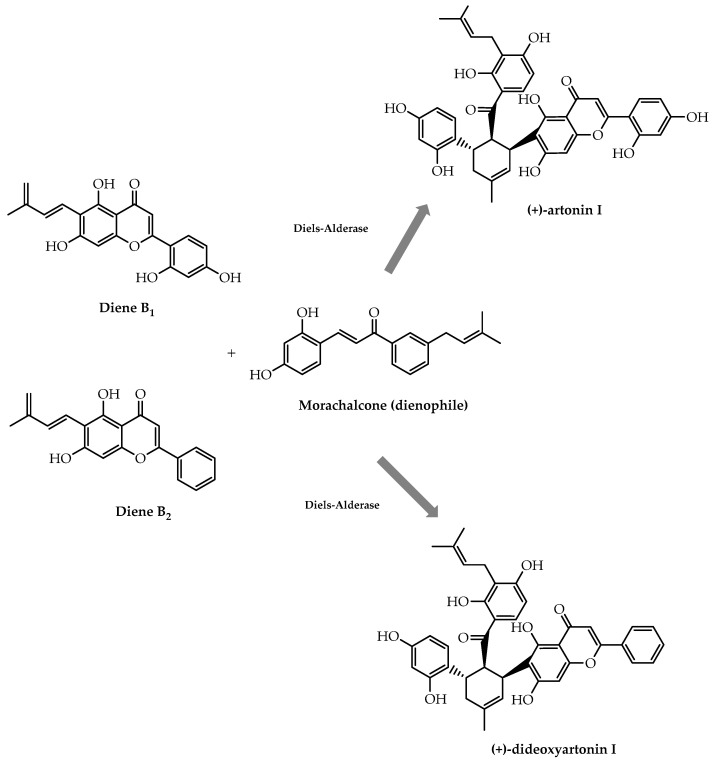
Another example of the application of biocatalysis to produce enantiomeric pure forms of flavonoids was the employment of a Diels–Alderase to synthesise artonin I, a natural flavonoid with positive effects on Staphylococcus aureus multidrug-resistant strains [99]. This enzyme was responsible for the catalysis of the Diels–Alder reaction between morachalcone and the dienes B1/B2 to give (+)-artonin I and (+)-dideoxyartonin I (Figure 27) with an enantiomeric excess of 99% and higher than 99%, respectively [99].
Figure 27.
Chemoenzymatic stereoselective synthesis of (+)-artonin I and (+)-dideoxyartonin I.
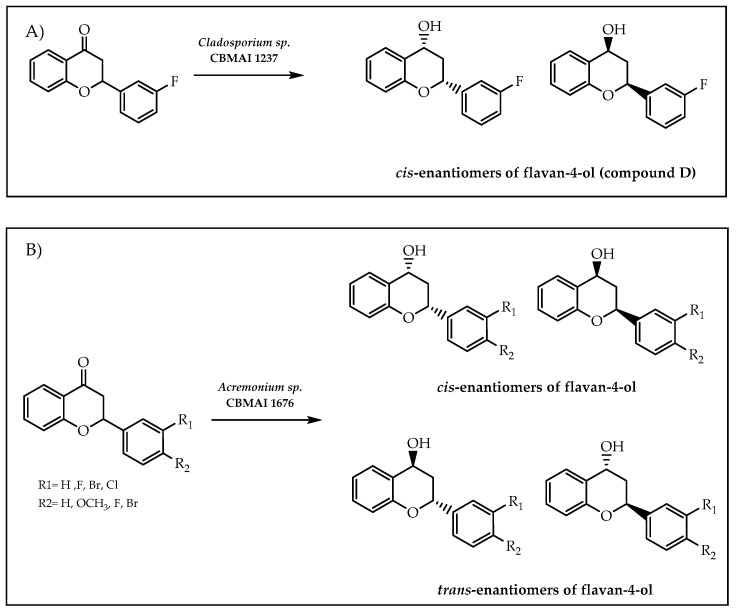
In 2021, de Matos et al. [100] reported the utilisation of strains of marine-derived fungi in order to proceed to the stereoselective reduction of flavanones, culminating in the formation of chiral flavan-4-ols (Figure 28). Pursuant to preliminary results, Acremonium sp. CBMAI 1676 and Cladosporium sp. CBMAI 1237 were the strains which demonstrated promising results in terms of yield and enantioselectivity and, subsequently, were employed in further studies [100]. From the application of the aforementioned strains, the formation of the cis-enantiomers of flavan-4-ol (compound D, scheme A, Figure 28) with an enantiomeric excess of 64% from the activity of Cladosporium sp. CBMAI 1237 was highlighted [100]. Additionally, it is also relevant to denote that the synthesis of cis and trans-enantiomers of the products formed from all flavanones occurred with an enantiomeric excess in a range of 77% to 97% and superior to 95%, respectively, in Acremonium sp. CBMAI 1676 [100] (scheme B, Figure 28). As a result, the methodology developed by de Matos et al. [100] enabled the synthesising of halogenated flavanols, particularly brominated flavan-4-ols [100].
Figure 28.
Synthesis of cis/trans-enantiomers of flavan-4-ols using marine-derived fungi. (A) Compound D synthesis by Cladosporium sp. CBMAI 1237; (B) Cis and trans-enantiomers of flavan-4-ol synthesis by Acremonium sp. CBMAI 1676.
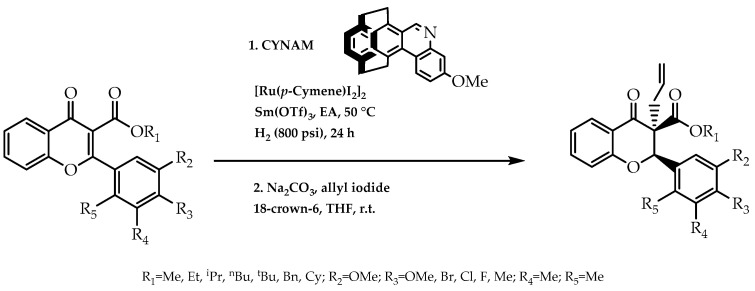
As a consequence of the medicinal relevance of chiral flavanones, Zhu et al. [101] were inspired by a biomimetic asymmetric reduction in NAD(P)H-dependent to synthesise the enantiomeric forms of these flavonoids. They proceeded to elaborate on the chiral [2.2]paracyclophane-based NAD(P)H models (CYNAMs), in which, after reaction conditions’ optimisation, one of the models was applied to obtain enantiomeric tetrasubstituted alkene flavanones (Figure 29), culminating in the formation of most chiral forms in an enantiomeric excess array between 90% and 99% [101]. With this methodology, they were able to reinforce the importance of biocatalysis and the respective cofactors to enable the stereoselective synthesis of flavonoids with higher enantiomeric purity.
Figure 29.
Biomimetic synthesis of chiral flavanones mediated by CYNAM model.
2.7. Chiral Pool Methodology
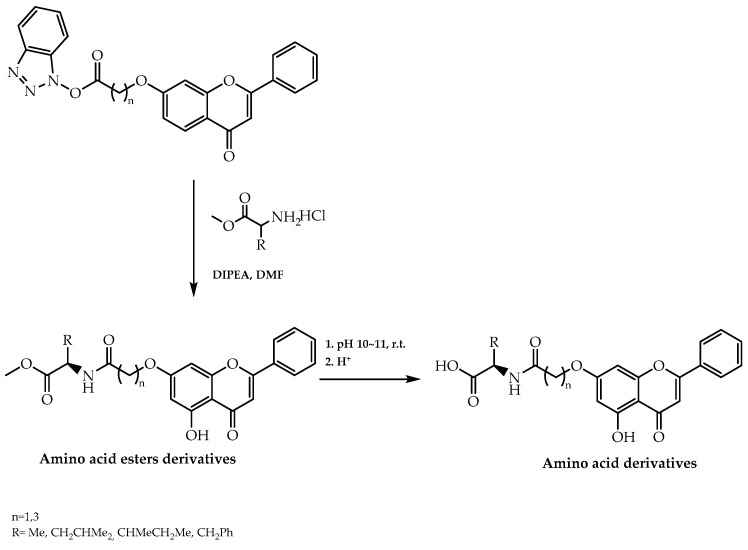
Another approach to achieve highly enantiomerically pure forms of chiral derivatives of flavonoids is through the chiral pool strategy. This method was employed with the aim of synthesising flavonoids with antitumor activity [66]. Chrysin is a natural flavone well-known for its chemopreventive and apoptosis inducer role in several cancer malign forms [102]. Based on the therapeutic relevance of this flavonoid as well as the increasing effect of amino acids in selectivity, Song et al. [102] proceeded to introduce alanine, leucine, isoleucine, and phenylalanine to synthesise the corresponding chrysin amino acid derivatives (Figure 30). As a result of that, an enhancement in the anticancer effect displayed by the obtained products was verified [102], highlighting the importance of chirality in the therapeutic effect of this flavonoid. Moreover, it was also reported that N-[4-(5-hydroxy-4-oxo-2-phenyl-4H-chromen-7-yloxy)butyryl]-L-isoleucine methyl ester demonstrated the most potent inhibitory effect on human gastric carcinoma MGC-803 cells among the synthetic-obtained derivatives and positive control cisplatin, with an IC50 value of 3.78 µmol/L [102].
Figure 30.
Synthesis of amino acid and amino acid esters derivatives of chrysin by chiral pool approach.
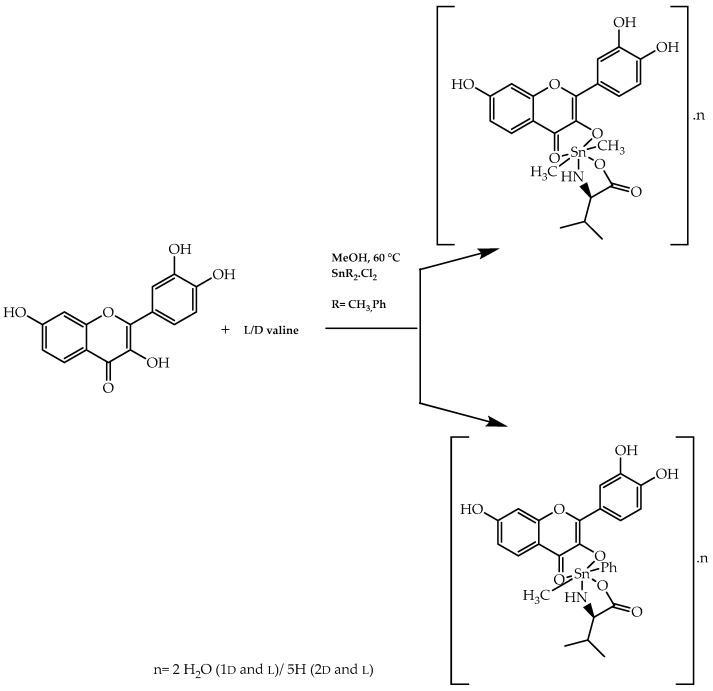
Another illustration of the employment of amino acids in obtaining the flavonoid-related compounds with anticancer activity is the methodology developed by Parveen et al. [103]. They synthesised chiral complexes composed of quercetin, L/D-valine, and organotin (IV), aiming to achieve a synergetic effect from these three components (Figure 31). From further cytotoxic studies carried out in HeLa (cervix), MCF7 (breast cancer), Hep-G2 (liver cancer), and MIA-Pa-Ca-2 (pancreatic cancer), it was possible to verify that the majority of the L-enantiomers of the complexes showed values of GI50 lower than 10 µg/mL, outlining their potential in chemotherapy [103]. Additionally, molecular docking studies revealed that the configuration was a preponderant factor in the interaction between the target and L-valine-quercetin diorganotin (IV) complexes and, as a consequence, it corroborated the role of chirality on the pharmacological effect demonstrated by these synthesised compounds [103].
Figure 31.
Synthesis of L/D-valine-quercetin diorganotin (IV).
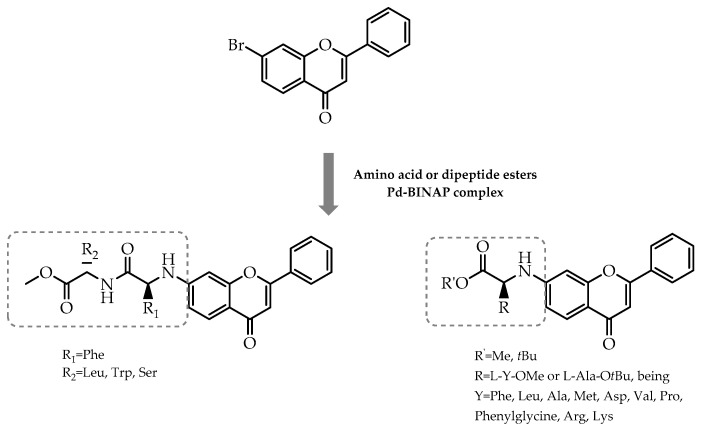
Moreover, the work of Pajtás et al. [104] constituted another contribution to the employment of amino acids and peptide moieties in flavonoids. As reported by them, the insertion of these chiral molecules via the Buchwald–Hartwig amination of bromoflavones in the presence of BINAP and palladium as a catalyst complex averted the racemisation of the resulting products, culminating in the enantiomeric pure forms of flavone derivatives [104] (Figure 32). Furthermore, these compounds were, subsequently, tested in vitro for cytotoxic activity, in which a compound revealed significant cytotoxic activity (95.43% in a concentration of 50 µM) in the U87 glioblastoma cell line [104].
Figure 32.
Schematic representation of flavone-amino acid hybrids synthesis via Buchwald–Hartwig reaction.
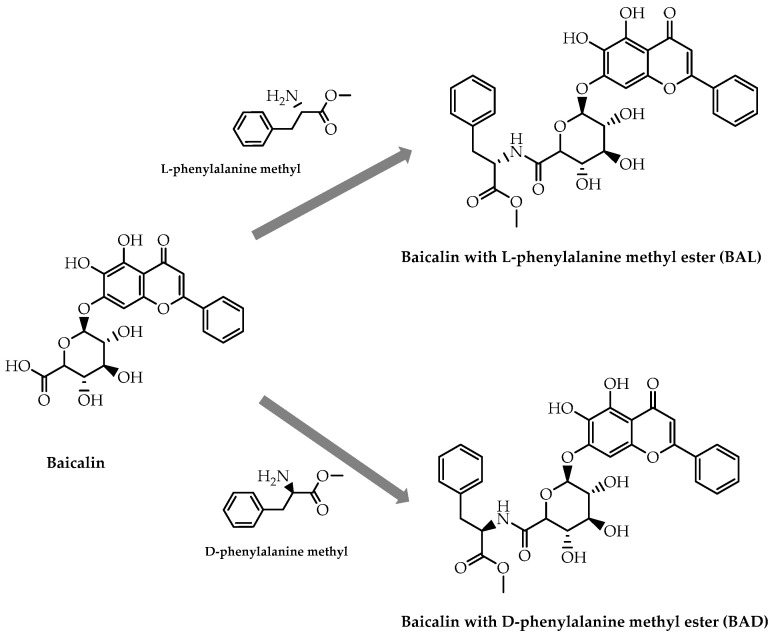
More recently, Hou et al. [105] synthesised enantiomeric forms of baicalin derivatives, combining this natural flavonoid with phenylalanine methyl esters in order to improve antitumor activity (Figure 33). As predicted, the introduction of this chiral amino acid ester increased the inhibitory effect on cancer cell growth, particularly in A549 cells, exhibiting an inhibition rate of 88.95% at 48 h in a concentration of 50 µg/mol for baicalin with L-phenylalanine methyl ester (BAD), and an inhibition rate of 94.13% for baicalin with D-phenylalanine methyl ester (BAL) [105]. Furthermore, immunohistochemistry data showed that these baicalin derivatives suppressed tumor angiogenesis, with BAL being more potent than BAD [105]. These results confirm that the molecular modification of flavonoids with different enantiomeric forms of natural chiral molecules, such as amino acids, could result in bioactive compounds with different potency.
Figure 33.
Schematic representation of the synthesis of baicalin phenylalanine methyl esters derivatives.
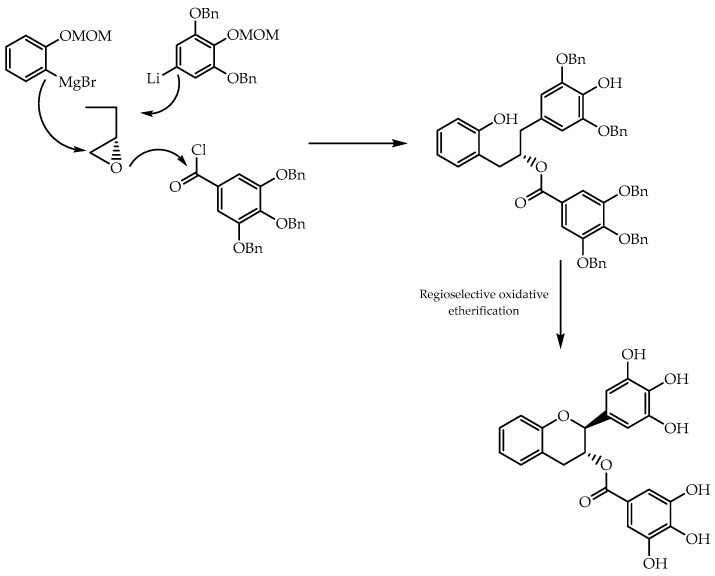
The chiral pool method was also used for other building blocks, namely epichlorohydrin. Shiraishi et al. [106] synthesised enantiomeric forms of trans-flavan-3-ol gallates, using (S) and (R)-epichlorohydrine (Figure 34) as an integrant part of 1,3-diaryl-2-propanols, which are intermediates in this reaction pathway. The final products were, subsequently, obtained by regioselective oxidation etherification with 2,3-dichloro-5,6-dicyano-1,4-benzoquinone, and were screened after for anticancer activity [106]. From the experiments in the U266 cell line (multiple myeloma), it was possible to observe that both enantiomers displayed similar IC50 values, suggesting that chirality might not be a detrimental feature for the antitumor effect of the obtained trans-flavan-3-ol gallates [106].
Figure 34.
Production of trans-flavan-3-ols gallates from epichlorohydrin using chiral pool approach.
2.8. Other Synthetic Methologies
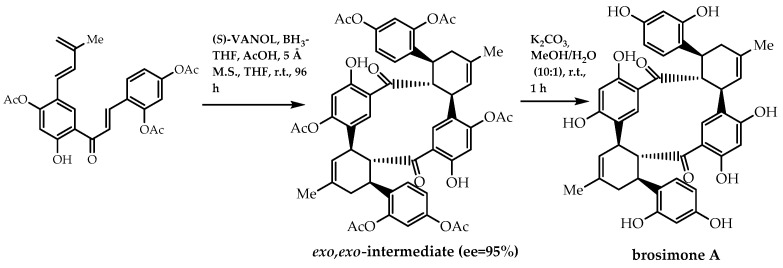
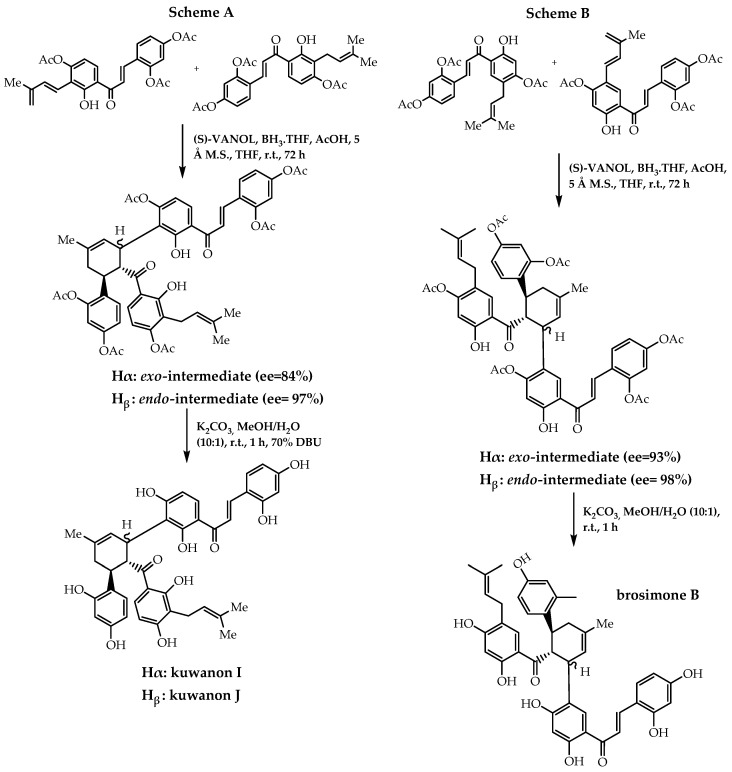
There are also reports of other synthetic processes with the goal of obtaining enantiomeric pure forms of flavonoids, namely the Diels–Alder reaction. As promising anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and antiviral agents, prenylflavonoids have been arousing interest from researchers. In 2014, Han et al. [107] reported a stereoselective biomimetic total synthesis of (-)-brosimone A (Figure 35), (-)-kuwanon I (scheme A, Figure 36), (+)-kuwanon J (scheme A, Figure 36), and (-)-brosimone B (scheme B, Figure 36). In order to establish the stereogenic centres of these Diels–Alder natural products, they resorted to an asymmetric Diels–Alder cycloaddition of a 2′-hydroxychalcone derivative, using a chiral boron-VANOL complex as the catalyst. Lately, they have employed this methodology to obtain chalconoids (-)-nicolaioidesin C and (-)-panduratine A, with 96% and 87% of enantiomeric excess, respectively [108].
Figure 35.
Synthesis of (-)-brosimone A.
Figure 36.
Synthesis of (−)-kuwanon I, (+)-kuwanon J, and (−)-brosimone B. Scheme A: Stereoselective biomimetic total synthesis of (−)-kuwanon I and (+)-kuwanon J; Scheme B: Stereoselective biomimetic total synthesis of (−)-brosimone B.
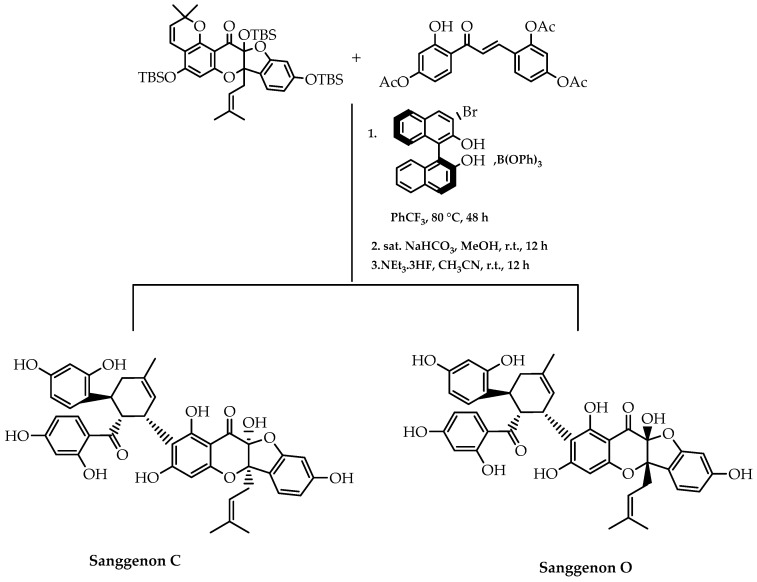
Another method to synthesise Diels–Alder natural products was demonstrated by Qi et al. [109]. They embarked on a strategic stereodivergent reaction of a racemic mixture (RRM) to obtain (+)-sanggenon C and (-)-sanggenon O, involving an asymmetric [4+2] cycloaddition catalysed by a boron-BINOL complex (Figure 37). Using this reaction process, these flavonoid derivatives were obtained with an enantiomeric excess of 98% and 93%, respectively [109].
Figure 37.
Stereoselective synthesis of sanggenon C and O via [4+2] cycloaddition based on stereodivergent RRM.
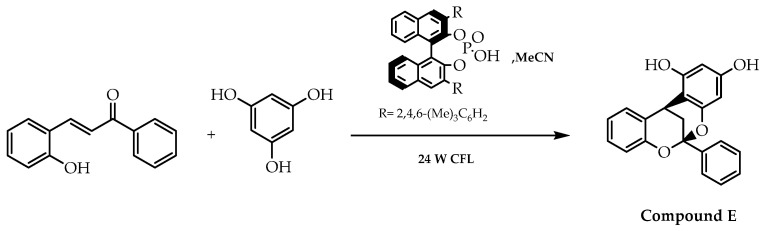
As prior demonstrated, enantioselective biomimetic reactions enable synthesising chiral flavonoids with diverse biological activities. Taking into consideration the anticancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial potential of hybrid flavonoids, Gao et al. [110] developed a methodology based on the asymmetric coupling of 2-hydroxychalcone using an appropriate Brønsted acid as the catalyst, an adequate nucleophile, and a visible light as the reaction promotor [110]. Subsequently, this photochemical bio-inspired reaction was applied to obtain enantiomeric forms of hybrid flavonoids with indole, cyclohexa-1,3-dione, or phloroglucinol, highlighting the formation of the 2-hydroxychalcone phloroglucinol hybrid (compound E, Figure 38) as a result of the counter-anion-directed enantioselective addition of 2-hydroxychalcone and phloroglucinol with an enantiomeric excess of 70% [110].
Figure 38.
Bio-inspired stereoselective synthesis of phloroglucinol–flavonoid hybrid.
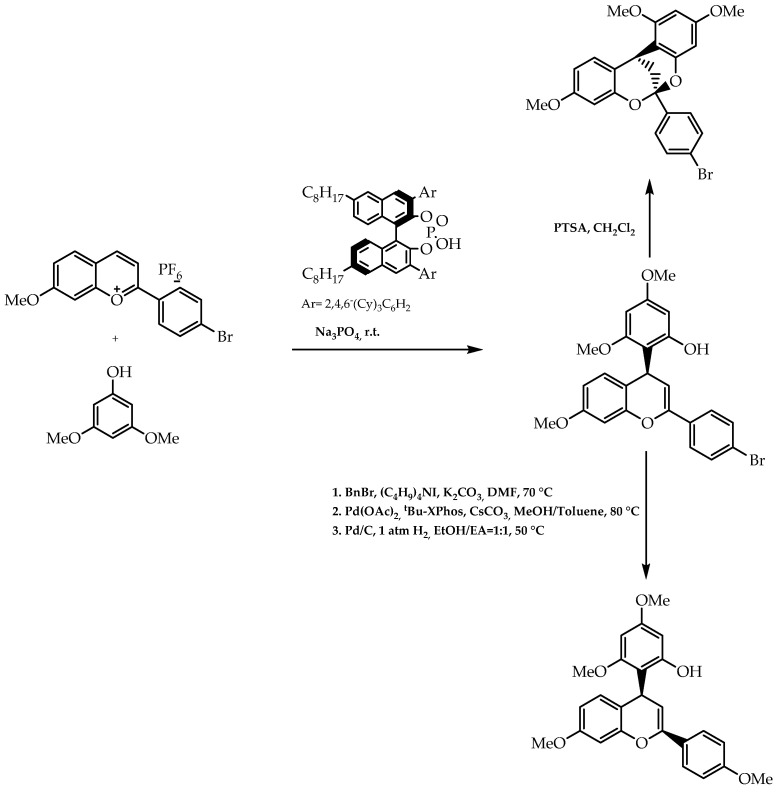
Another example of the implementation of a biomimetic reactional approach is the synthetic methodology developed by Yang et al. [111]. This approach was based on the application of a chiral anion phase in order to promote the addition of nucleophilic phenols to benzopyrylium salts (Figure 39), synthesising 2,4-diarylbenzopyran and 2,8-dioxabicyclo [3.3.1]nonane with enantiomeric excesses of 91% and 94%, respectively [111]. These scaffolds have crucial importance from a synthetic point of view due to the fact that they integrate flavonoid-related compounds [111]; therefore, a reaction pathway was unfolded to access natural products with a diversified array of biological activities.
Figure 39.
Stereoselective synthesis of scaffolds integrated in flavonoid-related compounds by chiral anion phase-transfer.
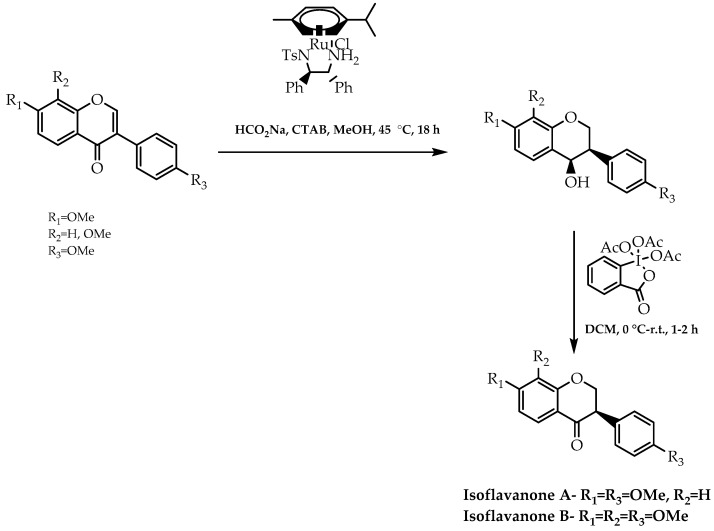
More recently, in this thematic field of stereoselective synthesis, and inspired by Metz et al. [112,113] and their previous works [114], Gaspar et al. [115] were able to enlarge the scope of ATH-DKR to obtain cis-3-phenylchroman-4-ols and, subsequently, use them as intermediates for the synthesis of chiral isoflavanones, which possess crucial biological activities [116]. With the aim of accomplishing their goal, they applied a Noyori–Ikariya ruthenium complex as the catalyst and sodium formate as the hydrogen source to the reaction (first reaction step, Figure 40), culminating in the formation of (R,R)-cis-alcohols in a range between 92% and 99% of the enantiomeric ratio [115]. Thereafter, they used a Dess–Martin periodinane (DMP) oxidation to synthesise two chiral natural isoflavanones (second reaction step, Figure 40), maintaining the enantiomeric ratios previously acquired [115].
Figure 40.
Enantioselective synthesis of isoflavanones via asymmetric ATH-DKR and DMP oxidation.
3. Conclusions
Flavonoids are natural polyphenolic compounds mainly found in plants and associated with a wide range of biological activities, including antiviral, antimicrobial, antitumor, and antioxidant activities. They can be also employed in the cosmetic, food, textile, and metallurgic fields.
Owing to their biological relevance, flavonoids have been arousing interest and, as a result, synthetic methodologies have been employed in order to obtain these natural compounds, namely the following: Algar–Flynn–Oyamada, Allan–Robinson, Baker–Venkataraman, Claisen–Schmidt, Karl von Auwers, Kostanecki, Mentzer Pyrone, Suzuki–Miyaura, deoxybenzoin route, reductive cleavage of isoxazoles, intramolecular ketene cycloaddition followed by decarboxylation, rearrangement and cyclisation of chalcone epoxides, rearrangement of flavanones, Wacker–Cook tandem conversion of α-methylene deoxybenzoins, Cu(I)-mediated cyclisation of 3-(2-bromophenyl)-3-oxopropanol, Pechmann reaction, Perkin reaction, Wittig reaction of benzophenones, metal-catalysed cross-coupling reactions, and direct arylation of arylboronic acids to coumarins through palladium-catalysed oxidative Heck coupling.
Regarding stereoselective synthesis, many strategies were explored such as chalcone epoxidation, Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation, the Mitsunobu reaction, and the cycloaddition of 1,4-benzoquinones with 2H-chromenes via Ti-TADDOLate catalysis. Chiral auxiliaries were also applied in the synthesis of flavonoids enantiomers, highlighting imidazolidinone in the α-benzylation reaction of phenyl acetic acid derivatives and (S,S)-(+)-pseudoephedrine in an asymmetric aldol reaction. Moreover, organocatalytic processes were used with the aim of attaining enantiomeric pure forms of these natural compounds, enhancing the employment of thiourea and alkaloid moieties in the intramolecular conjugate addition of α-substituted chalcones and deracemization of homoisoflavones, respectively. Furthermore, organometallic complexes were also used with the aim of synthesising chiral flavonoids, namely palladium-pyridinooxazoline/carboline and rhodium in the reaction of the addition of chromones to arylboronic acids. Biocatalysis is an environmentally sustainable tool to proceed with the synthesis of enantiomeric forms of these polyphenolic compounds, highlighting the production of chiral flavanones and cis/trans-flavan-4-ols by yeast strains, (R)-dihydroisoflavone synthesis by daidzein reductase from Eggerthella sp. YY7918, Diels–Alderase application, the stereoselective reduction in flavanones by marine-derived fungi to obtain chiral flavan-4-ols, and the development of chiral NAD(P)H models such as CYNAMs. The chiral pool was also reported as a synthetic route to acquire flavonoid derivatives, mainly by the employment of amino acids and epichlorohydrin. Although the employment of the methodologies mentioned above enabled the obtaining of the enantiomeric pure forms of flavonoids with high enantiomeric excess, the development of novel approaches in order to encompass the synthesis of other flavonoids classes is still required. Henceforward, the study of the biological properties of the chiral flavonoids obtained by the methods mentioned above is of crucial importance from a scientific perspective, and to further explore their pharmacological potential as well as to perform enantioselectivity studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation: H.C. and M.E.T.; Data collection and analysis: A.M.P. and M.E.T.; Writing—original draft preparation: A.M.P.; Writing—reviewing and editing: A.M.P., H.C. and M.E.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding Statement
This research was supported by national funds through the FCT-Foundation for Science and Technology within the scope of UIDB/04423/2020 and UIDP/04423/2020 (Natural Products and Medicinal Chemistry Research Group-CIIMAR), and ERDF, as a result of the projects PTDC/CTA-AMB/6686/2020, and PTDC/CTAAMB/0853/2021. In addition, it was supported by CESPU under the Project Flav4Tumor-GI2-CESPU-2022.
Footnotes
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
References
- 1.Dias M.C., Pinto D., Silva A.M.S. Plant flavonoids: Chemical characteristics and biological activity. Molecules. 2021;26:5377. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rodríguez De Luna S.L., Ramírez-Garza R.E., Serna Saldívar S.O. Environmentally friendly methods for flavonoid extraction from plant material: Impact of their operating conditions on yield and antioxidant properties. Sci. World J. 2020;2020:6792069. doi: 10.1155/2020/6792069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Martins B.T., Correia da Silva M., Pinto M., Cidade H., Kijjoa A. Marine natural flavonoids: Chemistry and biological activities. Nat. Prod. Res. 2019;33:3260–3272. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2018.1470514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Liu W., Feng Y., Yu S., Fan Z., Li X., Li J., Yin H. The flavonoid biosynthesis network in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021;22:12824. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhang M., Chen X., Zhang Y., Zhao X., Zhao J., Wang X. The potential of functionalized dressing releasing flavonoids facilitates scar-free healing. Front. Med. 2022;9:978120. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.978120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Boniface P.K., Ferreira E.I. Flavonoids as efficient scaffolds: Recent trends for malaria, leishmaniasis, Chagas disease, and dengue. Phytother. Res. 2019;33:2473–2517. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rakha A., Umar N., Rabail R., Butt M.S., Kieliszek M., Hassoun A., Aadil R.M. Anti-inflammatory and anti-allergic potential of dietary flavonoids: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022;156:113945. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.113945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shamsudin N.F., Ahmed Q.U., Mahmood S., Shah S.A.A., Sarian M.N., Khattak M.M.A.K., Khatib A., Sabere A.S.M., Yusoff Y.M., Latip J. Flavonoids as antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory agents: A review on structural activity relationship-based studies and meta-analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:12605. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Xing N., Meng X., Wang S. Isobavachalcone: A comprehensive review of its plant sources, pharmacokinetics, toxicity, pharmacological activities and related molecular mechanisms. Phytother. Res. 2022;36:3120–3142. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kashyap P., Thakur M., Singh N., Shikha D., Kumar S., Baniwal P., Yadav Y.S., Sharma M., Sridhar K., Inbaraj B.S. In silico evaluation of natural flavonoids as a potential inhibitor of coronavirus disease. Molecules. 2022;27:6374. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Huang W., Wang Y., Tian W., Cui X., Tu P., Li J., Shi S., Liu X. Biosynthesis investigations of terpenoid, alkaloid, and flavonoid antimicrobial agents derived from medicinal plants. Antibiotics. 2022;11:1380. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11101380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dhaliwal J.S., Moshawih S., Goh K.W., Loy M.J., Hossain M.S., Hermansyah A., Kotra V., Kifli N., Goh H.P., Dhaliwal S.K.S., et al. Pharmacotherapeutics applications and chemistry of chalcone derivatives. Molecules. 2022;27:7062. doi: 10.3390/molecules27207062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Luo Y., Jian Y., Liu Y., Jiang S., Muhammad D., Wang W. Flavanols from nature: A phytochemistry and biological activity review. Molecules. 2022;27:719. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Gupta D., Guliani E. Flavonoids: Molecular mechanism behind natural chemoprotective behavior-a mini review. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2022;12:5983–5995. doi: 10.33263/BRIAC125.59835995. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pereira D., Pinto M., Correia-da-Silva M., Cidade H. Recent advances in bioactive flavonoid hybrids linked by 1,2,3-triazole ring obtained by click chemistry. Molecules. 2022;27:230. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Moreira J., Almeida J., Saraiva L., Cidade H., Pinto M. Chalcones as promising antitumor agents by targeting the p53 pathway: An overview and new insights in drug-likeness. Molecules. 2021;26:3737. doi: 10.3390/molecules26123737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Khan J., Deb P.K., Priya S., Medina K.D., Devi R., Walode S.G., Rudrapal M. Dietary flavonoids: Cardioprotective potential with antioxidant effects and their pharmacokinetic, toxicological and therapeutic concerns. Molecules. 2021;26:4021. doi: 10.3390/molecules26134021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gervasi T., Calderaro A., Barreca D., Tellone E., Trombetta D., Ficarra S., Smeriglio A., Mandalari G., Gattuso G. Biotechnological applications and health-promoting properties of flavonols: An updated view. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23:1710. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Addi M., Elbouzidi A., Abid M., Tungmunnithum D., Elamrani A., Hano C. An overview of bioactive flavonoids from citrus fruits. Appl. Sci. 2022;12:29. doi: 10.3390/app12010029. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sithuba T., Masia N.D., Moema J., Murulana L.C., Masuku G., Bahadur I., Kabanda M.M. Corrosion inhibitory potential of selected flavonoid derivatives: Electrochemical, molecular Zn surface interactions and quantum chemical approaches. Results Eng. 2022;16:100694. doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2022.100694. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sharma A., Singh Tuli H., Sharma A.K. Chemistry and Synthetic Overview of Flavonoids. In: Singh Tuli H., editor. Current Aspects of Flavonoids: Their Role in Cancer Treatment. Springer; Singapore: 2019. pp. 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Baker W., Chadderton J., Harborne J.B., Ollis W.D. A new synthesis of isoflavones. Part I. J. Chem. Soc. (Resumed) 1953;381:1852–1860. doi: 10.1039/jr9530001852. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Harborne J.B. The flavonoids: Advances in research since 1986. J. Chem. Educ. 1995;72:A73. doi: 10.1021/ed072pA73.11. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dixon R.A., Ferreira D. Genistein. Phytochemistry. 2002;60:205–211. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(02)00116-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Granados-Covarrubias E.H., Maldonado L.A. A Wacker–Cook synthesis of isoflavones: Formononetine. Tetrahedron Lett. 2009;50:1542–1545. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.01.041. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Li Q.-L., Liu Q.-L., Ge Z.-Y., Zhu Y.-M. A novel synthesis of isoflavones via copper(I)-catalyzed intramolecular cyclization reaction. Helv. Chim. Acta. 2011;94:1304–1309. doi: 10.1002/hlca.201000400. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Garazd M.M., Garazd Y.L., Khilya V.P. Neoflavones. 2. Methods for synthesizing and modifying 4-arylcoumarins. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2005;41:245–271. doi: 10.1007/s10600-005-0126-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Li Y., Qi Z., Wang H., Fu X., Duan C. Palladium-catalyzed oxidative Heck coupling reaction for direct synthesis of 4-arylcoumarins using coumarins and arylboronic acids. J. Org. Chem. 2012;77:2053–2057. doi: 10.1021/jo202577m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sharma A., Sharma P., Singh Tuli H., Sharma A.K. eLS. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2018. Phytochemical and Pharmacological Properties of Flavonols; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Suma A.T., Wahyuningsih T. Efficient synthesis of chloro chalcones under ultrasound irradiation, their anticancer activities and molecular docking studies. Rasayan J. Chem. 2019;12:502–510. doi: 10.31788/RJC.2019.1225020. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kristanti A., Suwito H., Aminah N.S., Haq K., Hardiyanti H.D., Anggraeni H., Faiza N., Anto R., Muharromah S. Synthesis of some chalcone derivatives, in vitro and in silico toxicity evaluation. Rasayan J. Chem. 2020;13:654–662. doi: 10.31788/RJC.2020.1315534. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bianco A., Cavarischia C., Farina A., Guiso M., Marra C. A new synthesis of flavonoids via Heck reaction. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003;44:9107–9109. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2003.10.060. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ekanayake U.G.M., Weerathunga H., Weerasinghe J., Waclawik E.R., Sun Z., MacLeod J.M., O’Mullane A.P., Ostrikov K. Sustainable Claisen-Schmidt chalcone synthesis catalysed by plasma-recovered MgO nanosheets from seawater. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2022;32:e00394. doi: 10.1016/j.susmat.2022.e00394. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Taichiro O. A new general method for the synthesis of the derivates of flavonol. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1935;10:182–186. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.10.182. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Nhu D., Hawkins B.C., Burns C.J. Phase transfer catalysis extends the scope of the Algar–Flynn–Oyamada synthesis of 3-hydroxyflavones. Aust. J. Chem. 2015;68:1102–1107. doi: 10.1071/CH14620. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Brennan C.M., Hunt I., Jarvis T.C., Johnson C.D., McDonnell P.D. Stereoelectronic effects in ring closure reactions: The 2′-hydroxychalcone—Flavanone equilibrium, and related systems. Can. J. Chem. 1990;68:1780–1785. doi: 10.1139/v90-277. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tanaka K., Sugino T. Efficient conversion of 2′-hydroxychalcones into flavanones and flavanols in a water suspension medium. Green Chem. 2001;3:133–134. doi: 10.1039/b101826b. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Goud B.S., Panneerselvam K., Zacharias D.E., Desirajua G.R. Intramolecular Michael-type addition in the solid state. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2. 1995:325–330. doi: 10.1039/p29950000325. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sanicanin Z., Tabakovic I. Electrochemical transformations of 2′-hydroxychalcones into flavanoids. Tetrahedron Lett. 1986;27:407–408. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)84031-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Maki Y., Shimada K., Sako M., Hirota K. Photo-oxidative cyclisation of 2′-hydroxychalcones leading to flavones induced by heterocycle n-oxides: High efficiency of pybimido[54-g]pteridine n-oxide for the photochemical dehydrogenation. Tetrahedron. 1988;44:3187–3194. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)85950-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kumar D., Patel G., Kumar A.K., Roy R. Ionic liquid catalyzed expeditious synthesis of 2-aryl-2,3-dihydroquinolin-4(1H)-ones and 2-aryl-2,3-dihydro-4H-chromen-4-ones under microwave irradiation. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2009;46:791–795. doi: 10.1002/jhet.123. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Jiang H., Zheng X., Yin Z., Xie J. An efficient catalytic synthesis of flavanones under green conditions. J. Chem. Res. 2011;35:220–221. doi: 10.3184/174751911X13014075196818. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Son S.H., Cho Y.Y., Yoo H.-S., Lee S.J., Kim Y.M., Jang H.J., Kim D.H., Shin J.-W., Kim N.-J. Divergent synthesis of flavones and flavanones from 2′-hydroxydihydrochalcones via palladium(ii)-catalyzed oxidative cyclization. RSC Adv. 2021;11:14000–14006. doi: 10.1039/D1RA01672E. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Cabrera M., Simoens M., Falchi G., Lavaggi M.L., Piro O.E., Castellano E.E., Vidal A., Azqueta A., Monge A., de Ceráin A.L., et al. Synthetic chalcones, flavanones, and flavones as antitumoral agents: Biological evaluation and structure–activity relationships. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2007;15:3356–3367. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2007.03.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Kulkarni P.S., Kondhare D.D., Varala R., Zubaidha P.K. Cyclization of 2′-hydroxychalcones to flavones using ammonium iodide as an iodine source: An eco-friendly approach. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2013;78:909–916. doi: 10.2298/JSC120901119K. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Gula´csi K., Litkeia G.R., Antus S.N., Gunda T.S.E. A short and facile synthetic route to prenylated flavones. Cyclodehydrogenation of prenylated 2′-hydroxychalcones by a hypervalent iodine reagent. Tetrahedron. 1998;54:13867–13876. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(98)00853-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lamba M., Makrandi J.K. Sodium selenite-dimethylsulfoxide: A highly efficient reagent for dehydrogenation. J. Chem. Res. 2008;2008:225–226. doi: 10.3184/030823408X313591. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ahmed N., Ali H., van Lier J.E. Silica gel supported InBr3 and InCl3: New catalysts for the facile and rapid oxidation of 2′-hydroxychalcones and flavanones to their corresponding flavones under solvent free conditions. Tetrahedron Lett. 2005;46:253–256. doi: 10.1016/j.tetlet.2004.11.062. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Du Z., Ng H., Zhang K., Zeng H., Wang J. Ionic liquid mediated Cu-catalyzed cascade oxa-Michael-oxidation: Efficient synthesis of flavones under mild reaction conditions. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2011;9:6930–6933. doi: 10.1039/c1ob06209c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Yukio H., Toshinori O., Noboru T. The direct preparation of flavones from 2′-hydroxychalcones using disulfides. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1986;59:2351–2352. doi: 10.1246/bcsj.59.2351. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Zambare A.S., Sangshetti J.N., Kokare N.D., Shinde D.B. Development of mild and efficient method for synthesis of substituted flavones using oxalic acid catalyst. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2009;20:171–174. doi: 10.1016/j.cclet.2008.10.042. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wang Z. Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2010. Allan-Robinson Condensation; pp. 64–67. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Horie T., Kawamura Y., Tsukayama M., Yoshikazi S. Studies of the selective O-alkylation and dealkylation of flavonoids. XII.: A new, convenient method for synthesizing 3, 5-dihydroxy-6, 7-dimethoxyflavones from 3, 5, 6, 7-tetramethoxyflavones. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1989;37:1216–1220. doi: 10.1248/cpb.37.1216. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Li J.J. Name Reactions: A Collection of Detailed Mechanisms and Synthetic Applications. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2009. Baker-Venkataraman rearrangement; pp. 14–15. [Google Scholar]
- 55.Limberakis C. Other Six-Membered Heterocycles. In: Li J.J., editor. Name Reactions in Heterocyclic Chemistry. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2004. pp. 521–533. [Google Scholar]
- 56.DeMeyer N.H.A., Mishra L., Pandey H.-K., Pieters L.A.C., Vanden Berghe D.A., Vlietinick A.J. 4′-Hydroxy-3-methoxyflavones with potent antipicornavirus activity. J. Med. Chem. 1991;34:736–746. doi: 10.1021/jm00106a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wang Z. Mentzer pyrone synthesis. In: Wang Z., editor. Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2010. pp. 1901–1904. [Google Scholar]
- 58.Seijas J.A., Vázquez-Tato M.P., Carballido-Reboredo R. Solvent-free synthesis of functionalized flavones under microwave irradiation. J. Org. Chem. 2005;70:2855–2858. doi: 10.1021/jo048685z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Pereira D., Gonçalves C., Martins B.T., Palmeira A., Vasconcelos V., Pinto M., Almeida J.R., Correia-da-Silva M., Cidade H. Flavonoid glycosides with a triazole moiety for marine antifouling applications: Synthesis and biological activity evaluation. Mar. Drugs. 2021;19:5. doi: 10.3390/md19010005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kshatriya R., Jejurkar V.P., Saha S. In memory of Prof. Venkataraman: Recent advances in the synthetic methodologies of flavones. Tetrahedron. 2018;74:811–833. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2017.12.052. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Roy A., Khan A., Ahmad I., Alghamdi S., Rajab B.S., Babalghith A.O., Alshahrani M.Y., Islam S., Islam M.R. Flavonoids a bioactive compound from medicinal plants and its therapeutic applications. Biomed Res. Int. 2022;2022:5445291. doi: 10.1155/2022/5445291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Selepe M.A., Van Heerden F.R. Application of the Suzuki-Miyaura reaction in the synthesis of flavonoids. Molecules. 2013;18:4739–4765. doi: 10.3390/molecules18044739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Miyaura N., Yamada K., Suzuki A. A new stereospecific cross-coupling by the palladium-catalyzed reaction of 1-alkenylboranes with 1-alkenyl or 1-alkynyl halides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1979;20:3437–3440. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)95429-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Hurtová M., Biedermann D., Osifová Z., Cvačka J., Valentová K., Křen V. Preparation of synthetic and natural derivatives of flavonoids using Suzuki-Miyaura cross-coupling reaction. Molecules. 2022;27:967. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Liu Z.-Q. What about the progress in the synthesis of flavonoid from 2020? Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022;243:114671. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Pinto C., Cidade H., Pinto M., Tiritan M.E. Chiral flavonoids as antitumor agents. Pharmaceuticals. 2021;14:1267. doi: 10.3390/ph14121267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Marais J.P., Ferreira D., Slade D. Stereoselective synthesis of monomeric flavonoids. Phytochemistry. 2005;66:2145–2176. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2005.03.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Li F.-F., Sun Q., Wang D., Liu S., Lin B., Liu C.-T., Li L.-Z., Huang X.-X., Song S.-J. Chiral separation of cytotoxic flavan derivatives from Daphne giraldii. J. Nat. Prod. 2016;79:2236–2242. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Sun Q., Yao G.-D., Song X.-Y., Qi X.-L., Xi Y.-F., Li L.-Z., Huang X.-X., Song S.-J. Autophagy antagonizes apoptosis induced by flavan enantiomers from Daphne giraldii in hepatic carcinoma cells in vitro. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017;133:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.03.072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Yao G.-D., Sun Q., Song X.-Y., Huang X.-X., Song S.-J. Flavan enantiomers from Daphne giraldii selectively induce apoptotic cell death in p53-null hepatocarcinoma cells in vitro. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018;289:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.04.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Xu L., Huang T., Huang C., Wu C., Jia A., Hu X. Chiral separation, absolute configuration, and bioactivity of two pairs of flavonoid enantiomers from Morus nigra. Phytochemistry. 2019;163:33–37. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2019.03.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Hofmann J., Fayez S., Scheiner M., Hoffmann M., Oerter S., Appelt-Menzel A., Maher P., Maurice T., Bringmann G., Decker M. Sterubin: Enantioresolution and configurational stability, enantiomeric purity in nature, and neuroprotective activity in vitro and in vivo. Chem. Eur. J. 2020;26:7299–7308. doi: 10.1002/chem.202001264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Marais J.P.J., Deavours B., Dixon R.A., Ferreira D. The Stereochemistry of Flavonoids. In: Grotewold E., editor. The Science of Flavonoids. Springer; New York, NY, USA: 2006. pp. 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- 74.Helder R., Hummelen J.C., Laane R.W.P.M., Wiering J.S., Wynberg H. Catalytic asymmetric induction in oxidation reactions. The synthesis of optically active epoxides. Tetrahedron Lett. 1976;17:1831–1834. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)93796-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Juliá S., Guixer J., Masana J., Rocas J., Colonna S., Annuziata R., Molinari H. Synthetic enzymes. Part 2. Catalytic asymmetric epoxidation by means of polyamino-acids in a triphase system. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1982;1:1317–1324. doi: 10.1039/P19820001317. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bentley P.A., Bergeron S., Cappi M.W., Hibbs D.E., Hursthouse M.B., Nugent T.C., Pulido R., Roberts S.M., Wu L.E. Asymmetric epoxidation of enones employing polymeric α-amino acids in non-aqueous media. Chem. Commun. 1997;8:739–740. doi: 10.1039/a700550d. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Nel R.J.J., van Rensburg H., van Heerden P.S., Coetzee J., Ferreira D. Stereoselective synthesis of flavonoids. Part 7. Poly-oxygenated β-hydroxydihydrochalcone derivatives. Tetrahedron. 1999;55:9727–9736. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(99)00554-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Jew S.-S., Kim H.-A., Bae S.-Y., Kim J.-H., Park H.-G. Enantioselective synthetic method for 3-hydroxyflavanones: An approach to (2R,3R)-3′,4′-O-dimethyltaxifolin. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000;41:7925–7928. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)01382-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 79.van Rensburg H.S., van Heerden P., Ferreira D. Enantioselective synthesis of flavonoids. Part 3.1trans- and cis-Flavan-3-ol methyl ether acetates. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1. 1997;1997:3415–3422. doi: 10.1039/a703316h. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Panzella L., Napolitano A. Condensed tannins, a viable solution to meet the need for sustainable and effective multifunctionality in food packaging: Structure, sources, and properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022;70:751–758. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Wan S.B., Chan T.H. Enantioselective synthesis of afzelechin and epiafzelechin. Tetrahedron. 2004;60:8207–8211. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2004.06.113. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Pinard E., Gaudry M., Hénot F., Thellend A. Asymmetric total synthesis of (+)-pisatin, a phytoalexin from garden peas (Pisum sativum L.) Tetrahedron Lett. 1998;39:2739–2742. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(98)00299-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Engler T.A., Letavic M.A., Iyengar R., LaTessa K.O., Reddy J.P. Asymmetric reactions of 2-methoxy-1,4-benzoquinones with styrenyl systems: enantioselective syntheses of 8-aryl-3-methoxybicyclo[4.2.0]oct-3-en-2,5-diones, 7-aryl-3-hydroxybicyclo[3.2.1]oct-3-en-2,8-diones, 2-aryl-6-methoxy-2,3-dihydrobenzofuran-5-ols, and pterocarpans. J. Org. Chem. 1999;64:2391–2405. doi: 10.1021/jo982164s. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Chinnabattigalla S., Dakoju R.K., Gedu S. Recent advances on the synthesis of flavans, isoflavans, and neoflavans. J. Heterocycl. Chem. 2021;58:415–441. doi: 10.1002/jhet.4176. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Versteeg M., Bezuidenhoudt B.C.B., Ferreira D., Swart K.J. The first enantioselective synthesis of isoflavonoids: (R)- and (S)-isoflavans. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995:1317–1318. doi: 10.1039/c39950001317. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Xu D., Hu J., Chen L., Chen L., Su J., Yang J., Deng S., Zhang H., Xie W. Asymmetric synthesis of ent-fissistigmatin C. Org. Lett. 2021;23:93–96. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c03766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Vicario J.L., Badía D., Domínguez E., Rodríguez M., Carrillo L. The first stereocontrolled synthesis of isoflavanones. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000;41:8297–8300. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)01464-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Biddle M.M., Lin M., Scheidt K.A. Catalytic enantioselective synthesis of flavanones and chromanones. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007;129:3830–3831. doi: 10.1021/ja070394v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Poisson T., Gembus V., Dalla V., Oudeyer S., Levacher V. Organocatalyzed enantioselective protonation of silyl enol ethers: Scope, limitations and application to the preparation of enantioenriched homoisoflavones. J. Org. Chem. 2010;75:7704–7716. doi: 10.1021/jo101585t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Lestini E., Blackman L.D., Zammit C.M., Chen T., Williams R.J., Inam M., Couturaud B., O’Reilly R.K. Palladium-polymer nanoreactors for the aqueous asymmetric synthesis of therapeutic flavonoids. Polym. Chem. 2018;9:820–823. doi: 10.1039/C7PY02050C. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Holder J.C., Marziale A.N., Gatti M., Mao B., Stoltz B.M. Palladium-catalyzed asymmetric conjugate addition of arylboronic acids to heterocyclic acceptors. Chemistry. 2013;19:74–77. doi: 10.1002/chem.201203643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Timmerman J.C., Sims N.J., Wood J.L. Total synthesis of caesalpinnone A and caesalpinflavan B: Evolution of a concise strategy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019;141:10082–10090. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b04472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Iwasaki K., Wan K.K., Oppedisano A., Crossley S.W.M., Shenvi R.A. Simple, chemoselective hydrogenation with thermodynamic stereocontrol. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014;136:1300–1303. doi: 10.1021/ja412342g. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Yang J., Lai J., Kong W., Li S. Asymmetric synthesis of sakuranetin-relevant flavanones for the identification of new chiral antifungal leads. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022;70:3409–3419. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.1c07557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.He Q., So C.M., Bian Z., Hayashi T., Wang J. Rhodium/chiral diene-catalyzed asymmetric 1,4-addition of arylboronic acids to chromones: A highly enantioselective pathway for accessing chiral flavanones. Chem. Asian J. 2015;10:540–543. doi: 10.1002/asia.201403290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Chubatsu Nunes H.H., Nguyen T.-D., Dang T.-T.T. Chemoenzymatic synthesis of natural products using plant biocatalysts. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2022;35:100627. doi: 10.1016/j.cogsc.2022.100627. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Janeczko T., Dymarska M., Siepka M., Gniłka R., Leśniak A., Popłoński J., Kostrzewa-Susłow E. Enantioselective reduction of flavanone and oxidation of cis- and trans-flavan-4-ol by selected yeast cultures. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2014;109:47–52. doi: 10.1016/j.molcatb.2014.08.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Kawada Y., Goshima T., Sawamura R., Yokoyama S.-I., Yanase E., Niwa T., Ebihara A., Inagaki M., Yamaguchi K., Kuwata K., et al. Daidzein reductase of Eggerthella sp. YY7918, its octameric subunit structure containing FMN/FAD/4Fe-4S, and its enantioselective production of R-dihydroisoflavones. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2018;126:301–309. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2018.03.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Liu X., Yang J., Gao L., Zhang L., Lei X. Chemoenzymatic total syntheses of artonin I with an intermolecular Diels–Alderase. Biotechnol. J. 2020;15:2000119. doi: 10.1002/biot.202000119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.de Matos I.L., Birolli W.G., Santos D.D.A., Nitschke M., Porto A.L.M. Stereoselective reduction of flavanones by marine-derived fungi. Mol. Catal. 2021;513:111734. doi: 10.1016/j.mcat.2021.111734. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Zhu Z.-H., Ding Y.-X., Wu B., Zhou Y.-G. Design and synthesis of chiral and regenerable [2.2]paracyclophane-based NAD(P)H models and application in biomimetic reduction of flavonoids. Chem. Sci. 2020;11:10220–10224. doi: 10.1039/D0SC04188B. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Song X., Liu Y., Ma J., He J., Zheng X., Lei X., Jiang G., Zhang L. Synthesis of novel amino acid derivatives containing chrysin as anti-tumor agents against human gastric carcinoma MGC-803 cells. Med. Chem. Res. 2015;24:1789–1798. doi: 10.1007/s00044-014-1267-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Parveen S., Tabassum S., Arjmand F. Human topoisomerase I mediated cytotoxicity profile of l-valine-quercetin diorganotin(IV) antitumor drug entities. J. Organomet. Chem. 2016;823:23–33. doi: 10.1016/j.jorganchem.2016.09.015. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Pajtás D., Kónya K., Kiss-Szikszai A., Džubák P., Pethő Z., Varga Z., Panyi G., Patonay T. Optimization of the synthesis of flavone–amino acid and flavone–dipeptide hybrids via Buchwald–Hartwig reaction. J. Org. Chem. 2017;82:4578–4587. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.7b00124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Hou Y., Pi C., Feng X., Wang Y., Fu S., Zhang X., Zhao L., Wei Y. Antitumor activity in vivo and vitro of new chiral derivatives of baicalin and induced apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics. 2020;19:67–78. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.08.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Shiraishi N., Kumazoe M., Fuse S., Tachibana H., Tanaka H. The synthesis of trans-flavan-3-ol gallates by regioselective oxidative etherification and their cytotoxicity mediated by 67 LR. Chemistry. 2016;22:13050–13053. doi: 10.1002/chem.201602817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Han J., Li X., Guan Y., Zhao W., Wulff W.D., Lei X. Enantioselective biomimetic total syntheses of kuwanons I and J and brosimones A and B. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014;53:9257–9261. doi: 10.1002/anie.201404499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Li X., Han J., Jones A.X., Lei X. Chiral boron complex-promoted asymmetric Diels–Alder cycloaddition and its application in natural product synthesis. J. Org. Chem. 2016;81:458–468. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.5b02248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Qi C., Xiong Y., Eschenbrenner-Lux V., Cong H., Porco J.A., Jr. Asymmetric syntheses of the flavonoid Diels-Alder natural products sanggenons C and O. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016;138:798–801. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b12778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Gao Y.-Q., Hou Y., Zhu L., Chen G., Xu D., Zhang S.-Y., He Y., Xie W. A bio-inspired synthesis of hybrid flavonoids from 2-hydroxychalcone driven by visible light. RSC Adv. 2019;9:29005–29009. doi: 10.1039/C9RA07198A. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Yang Z., He Y., Toste F.D. Biomimetic approach to the catalytic enantioselective synthesis of flavonoids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016;138:9775–9778. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b05939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Qin T., Metz P. Enantioselective synthesis of isoflavanones by catalytic dynamic kinetic resolution. Org. Lett. 2017;19:2981–2984. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b01218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Ciesielski P., Metz P. Asymmetric one-pot transformation of isoflavones to pterocarpans and its application in phytoalexin synthesis. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:3091. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16933-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Caleffi G.S., Brum J.D.O.C., Costa A.T., Domingos J.L.O., Costa P.R.R. Asymmetric transfer hydrogenation of arylidene-substituted chromanones and tetralones catalyzed by Noyori–Ikariya Ru(II) complexes: One-pot reduction of C=C and C=O bonds. J. Org. Chem. 2021;86:4849–4858. doi: 10.1021/acs.joc.0c02981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Gaspar F.V., Caleffi G.S., Costa-Júnior P.C.T., Costa P.R.R. Enantioselective synthesis of isoflavanones and pterocarpans through a RuII-catalyzed ATH-DKR of isoflavones. ChemCatChem. 2021;13:5097–5108. doi: 10.1002/cctc.202101252. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Al-Maharik N. Isolation of naturally occurring novel isoflavonoids: An update. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019;36:1156–1195. doi: 10.1039/C8NP00069G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.