Figure 7.
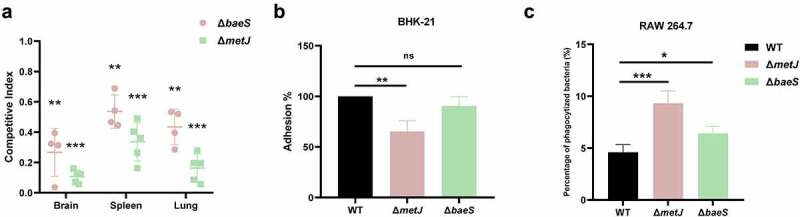
Two regulatory genes are critical fitness factors. (a) competitive infection assay. 200 μL of cell suspension containing a total of 6 × 105 CFU of cells of WT and each indicated strain with a ratio of 1:1 was used to intraperitoneally inject mice with five mice in each group. At 12 hpi, mice were euthanized, and brain, spleen, and lung tissues were taken, homogenized, diluted, and plated on LB agar plates with and without appropriate antibiotics, respectively, to distinguish the mutant and the wild-type cells. The bacteria were enumerated and the competition index (CI) was calculated. The student’s t test (two-tail, unpaired) was used to calculate the statistical difference between the mean CI value and 1. ** indicates p <0.01, and *** indicates p <0.001. (b) cell adhesion assay. the bacterial cells at the mid-log phase were used to infect BHK-21 cells with a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10:1 in a six-well plate followed by incubation at 37°C for 1 h. The mixture was washed with sterile PBS and then sterile water was added to the mixture which was incubated at 4°C for 1 h for cell lysis. The lysate was serially diluted and applied to LB agar plates for bacterial counting. (c) macrophage phagocytosis assay. the bacterial cells were mixed with RAW 264.7 cells with a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 10:1 followed by incubation at 37°C for 1 h. The cells were then washed twice with sterile PBS, and incubated with PBS containing chloramphenicol (final concentration 50 μg/ml). The macrophage cells were then lysed with sterile water and the lysate was serially diluted and applied to LB agar plates for bacterial counting. The student’s t test (two-tail, unpaired) was used to calculate the statistical difference between the two groups. ns indicates no significant difference, * indicates p <0.05, ** indicates p <0.01, ** indicates p <0.001.
