Abstract
Background
Reflective writing (RW) allows physicians to step back, review their thoughts, goals and actions and recognise how their perspectives, motives and emotions impact their conduct. RW also helps physicians consolidate their learning and boosts their professional and personal development. In the absence of a consistent approach and amidst growing threats to RW’s place in medical training, a review of theories of RW in medical education and a review to map regnant practices, programs and assessment methods are proposed.
Methods
A Systematic Evidence-Based Approach guided Systematic Scoping Review (SSR in SEBA) was adopted to guide and structure the two concurrent reviews. Independent searches were carried out on publications featured between 1st January 2000 and 30th June 2022 in PubMed, Embase, PsychINFO, CINAHL, ERIC, ASSIA, Scopus, Google Scholar, OpenGrey, GreyLit and ProQuest. The Split Approach saw the included articles analysed separately using thematic and content analysis. Like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle, the Jigsaw Perspective combined the themes and categories identified from both reviews. The Funnelling Process saw the themes/categories created compared with the tabulated summaries. The final domains which emerged structured the discussion that followed.
Results
A total of 33,076 abstracts were reviewed, 1826 full-text articles were appraised and 199 articles were included and analysed. The domains identified were theories and models, current methods, benefits and shortcomings, and recommendations.
Conclusions
This SSR in SEBA suggests that a structured approach to RW shapes the physician’s belief system, guides their practice and nurtures their professional identity formation. In advancing a theoretical concept of RW, this SSR in SEBA proffers new insight into the process of RW, and the need for longitudinal, personalised feedback and support.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12909-022-03924-4.
Keywords: Reflection, Reflective writing, Medical education, Professional identity formation, Undergraduate medical education, Postgraduate medical education
Introduction
Reflective practice in medicine allows physicians to step back, review their actions and recognise how their thoughts, feelings and emotions affect their decision-making, clinical reasoning and professionalism [1]. This approach builds on Dewey [2], Schon [3, 4], Kolb [5], Boud et al. [6] and Mezirow [7]’s concepts of critical self-examination. It sees new insights drawn from the physician’s experiences and considers how assumptions may integrate into their current values, beliefs and principles (henceforth belief system) [8, 9].
Teo et al. [10] build on this concept of reflective practice. The authors suggest that the physician’s belief system informs and is informed by their self-concepts of identity which are in turn rooted in their self-concepts of personhood - how they conceive what makes them who they are [11]. This posit not only ties reflective practice to the shaping of the physician’s moral and ethical compass but also offers evidence of it's role in their professional identity formation (PIF) [8, 12–23]. With PIF [8, 24] occupying a central role in medical education, these ties underscore the critical importance placed on integrating reflective practice in medical training.
Perhaps the most common form of reflective practice in medical education is reflective writing (RW) [25]. Identified as one of the distinct approaches used to achieve integrated learning, education, curriculum and teaching [26], RW already occupies a central role in guiding and supporting longitudinal professional development [27–29]. Its ability to enhance self-monitoring and self-regulation of decisional paradigms and conduct has earned RW a key role in competency-based medical practice and continuing professional development [30–36].
However, the absence of consistent guiding principles, dissonant practices, variable structuring and inadequate assessments have raised concerns as to RW’s efficacy and place in medical training [25, 37–39]. A Systematic Scoping Review is proposed to map current understanding of RW programs. It is hoped that this SSR will also identify gaps in knowledge and regnant practices, programs and assessment methods to guide the design of RW programs.
Methodology
A Systematic Scoping Review (SSR) is employed to map the employ, structuring and assessment of RW in medical education. An SSR-based review is especially useful in attending to qualitative data that does not lend itself to statistical pooling [40–42] whilst its broad flexible approach allows the identification of patterns, relationships and disagreements [43] across a wide range of study formats and settings [44, 45].
To synthesise a coherent narrative from the multiple accounts of reflective writing, we adopt Krishna’s Systematic Evidence-Based Approach (SEBA) [10, 15, 21, 46–53]. A SEBA-guided Systematic Scoping Review (SSR in SEBA) [13–24, 50, 53–55] facilitates reproducible, accountable and transparent analysis of patterns, relationships and disagreements from multiple angles [56].
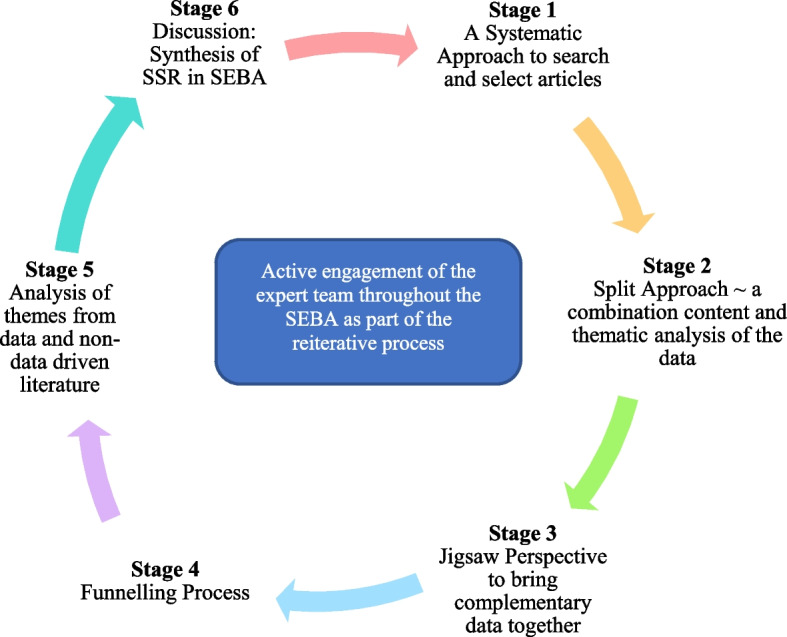
The SEBA process (Fig. 1) comprises the following elements: 1) Systematic Approach, 2) Split Approach, 3) Jigsaw Perspective, 4) Funnelling Process, 5) Analysis of data and non-data driven literature, and 6) Synthesis of SSR in SEBA [10, 15, 21, 46–53, 57–60] . Every stage was overseen by a team of experts that included medical librarians from the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine (YLLSoM) at the National University of Singapore, and local educational experts and clinicians at YLLSoM, Duke-NUS Medical School, Assisi Hospice, Singapore General Hospital, National Cancer Centre Singapore and Palliative Care Institute Liverpool.
Fig. 1.
The SEBA Process
STAGE 1 of SEBA: Systematic Approach
Determining the title and background of the review
Ensuring a systematic approach, the expert team and the research team agreed upon the overall goals of the review. Two separate searches were performed, one to look at the theories of reflection in medical education, and another to review regnant practices, programs, and assessment methods used in reflective writing in medical education. The PICOs is featured in Table 1.
Table 1.
PICOs inclusion and exclusion criteria
| Inclusion criteria | Exclusion criteria | |
|---|---|---|
| Search #1: Theories of reflection in medical education | ||
| Population |
• Healthcare personnel and educators in allied health specialities and medicine • Undergraduate and postgraduate medical students • Physicians |
• Non-healthcare educators and specialities |
| Intervention | • Papers addressing theory building relevant to reflection or reflective practices in education |
• Evaluation of reflective practices without reference to theory relating to reflection or reflective practices in education • Evaluation of reflective practices for purposes other than improving reflective capacity of users • Papers with little detail on implementation or assessment details of reflective writing |
| Comparison Outcome |
• Comparison of various modes of reflective practices and how they differed in terms of theory • Impact of the use of reflective writing within the clinical, medical, research and/or academic settings Papers that discussed reflective writing without the above comparisons were also included |
|
| Study design |
• All study designs including mixed methods research, meta-analyses, systematic reviews, randomised controlled trials, cohort studies, case-control studies, cross-sectional studies, descriptive papers, grey literature, opinions, letters, commentaries and editorials • Articles in English or translated to English • Year of Publication: Jan 2000–Jun 2022 |
• Non-English language articles |
| Search #2: Reflective writing in medical education | ||
| Population |
• Junior doctors, residents, specialists and/or doctors and/or physicians and/or medical students within the clinical, medical, research and/or academic settings • Undergraduate and postgraduate medical students |
• Allied health specialties such as Pharmacy, Dietetics, Chiropractic, Midwifery, Podiatry, Speech Therapy, Occupational and Physiotherapy, Physician Assistants • Non-medical specialties such as Clinical and Translational Science, Alternative and Traditional Medicine, Veterinary, Dentistry |
| Intervention |
• Papers that addressed the incorporation of reflective writing for junior doctors, residents, specialists and/or doctors and/or physicians and/or medical students within the clinical, medical, research and/or academic settings • Papers that addressed assessment of reflective writing |
• Papers with little detail of implementation or assessment of reflective writing in curriculum • Papers that evaluated reflective writing for purposes other than improving reflective capacity of users |
| Comparison Outcome |
Papers that addressed the following comparisons were also included: • Comparison of the various uses of reflective writing in different teaching settings • Evaluation of the effectiveness of reflective writing in comparison to other educational interventions • Papers that discussed reflective writing without the above comparisons were also included Papers that measured the following outcomes were also included: • Impact of the use of reflective writing on junior doctors, residents, specialists and/or doctors and/or physicians and/or medical students within the clinical, medical, research and/or academic settings • Impact of the use of reflective writing on teaching • Impact of the use of reflective writing on assessment • Gaps and improvements to current reflective writing programs |
|
| Study design |
• All study designs including: mixed methods research, meta-analyses, systematic reviews, randomised controlled trials, cohort studies, case-control studies, cross-sectional studies, descriptive papers, grey literature, opinions, letters, commentaries and editorials • Articles in English or translated to English • Year of Publication: Jan 2000–Jun 2022 |
• Non-English language articles |
Identifying the research question
Guided by the Population Concept, Context (PCC) elements of the inclusion criteria and through discussions with the expert team, the research question was determined to be: “How is reflective writing structured, assessed and supported in medical education?” The secondary research question was “How might a reflective writing program in medical education be structured?”
Inclusion criteria
All study designs including grey literature published between 1st January 2000 to 30th June 2022 were included [61, 62]. We also consider data on medical students and physicians from all levels of training (henceforth broadly termed as physicians).
Searching
Ten members of the research team carried out independent searches using seven bibliographic databases (PubMed, Embase, PsychINFO, CINAHL, ERIC, ASSIA, Scopus) and four grey literature databases (Google Scholar, OpenGrey, GreyLit, ProQuest). Variations of the terms “reflective writing”, “physicians and medical students”, and “medical education” were applied.
Extracting and charting
Titles and abstracts were independently reviewed by the research team to identify relevant articles that met the inclusion criteria set out in Table 1. Full-text articles were then filtered and proposed. These lists were discussed at online reviewer meetings and Sandelowski and Barroso [63]’s approach to ‘negotiated consensual validation’ was used to achieve consensus on the final list of articles to be included.
Stage 2 of SEBA: Split Approach
The Split Approach was employed to enhance the trustworthiness of the SSR in SEBA [64, 65]. Data from both searches were analysed by three independent groups of study team members.
The first group used Braun and Clarke [66]’s approach to thematic analysis. Phase 1 consisted of ‘actively’ reading the included articles to find meaning and patterns in the data. The analysis then moved to Phase 2 where codes were constructed. These codes were collated into a codebook and analysed using an iterative step-by-step process. As new codes emerge, previous codes and concepts were incorporated. In Phase 3, codes and subthemes were organised into themes that best represented the dataset. An inductive approach allowed themes to be “defined from the raw data without any predetermined classification” [67]. In Phase 4, these themes were then further refined to best depict the whole dataset. In Phase 5, the research team discussed the results and consensus was reached, giving rise to the final themes.
The second group employed Hsieh and Shannon [68]’s approach to directed content analysis. Categories were drawn from Mann et al. [9]’s article, “Reflection and Reflective Practice in Health Professions Education: A Systematic Review” and Wald and Reis [69]’s article “Beyond the Margins: Reflective Writing and Development of Reflective Capacity in Medical Education”.
The third group created tabulated summaries in keeping with recommendations drawn from Wong et al. [56]’s "RAMESES Publication Standards: Meta-narrative Reviews" and Popay et al. [70]’s “Guidance on the Conduct of Narrative Synthesis in Systematic Reviews”. The tabulated summaries served to ensure that key aspects of included articles were not lost.
Stage 3 of SEBA: Jigsaw Perspective
The Jigsaw Perspective [71, 72] saw the findings of both searches combined. Here, overlaps and similarities between the themes and categories from the two searches were combined to create themes/categories. The themes and subthemes were compared with the categories and subcategories identified, and similarities were verified by comparing the codes contained within them. Individual subthemes and subcategories were combined if they were complementary in nature.
Stage 4 of SEBA: Funnelling Process
The Funnelling Process saw the themes/categories compared with the tabulated summaries to determine the consistency of the domains created, forming the basis of the discussion.
Stage 5: Analysis of data and non-data driven literature
Amidst concerns that data from grey literature which were neither peer-reviewed nor necessarily evidence-based may bias the synthesis of the discussion, the research team separately thematically analysed the included grey literature. These themes were compared with themes from data-driven or research-based peer-reviewed data and were found to be the same and thus unlikely to have influenced the analysis.
Stage 6: Synthesis of SSR in SEBA
The Best Evidence Medical Education (BEME) Collaboration Guide and the Structured approach to the Reporting In healthcare education of Evidence Synthesis (STORIES) were used to guide the discussion.
Results
A total of 33,076 abstracts were reviewed from the two separate searches on theories of reflection in medical education, and on regnant practices, programs and assessments of RW programs in medical education. A total of 1826 full-text articles were appraised from the separate searches, and 199 articles were included and analysed. The PRISMA Flow Chart may be found in Fig. 2a and b. The domains identified when combining the findings of the two separate searches were 1) Theories and Models, 2) Current Methods, 3) Benefits and Shortcomings and 4) Recommendations.
Fig. 2.
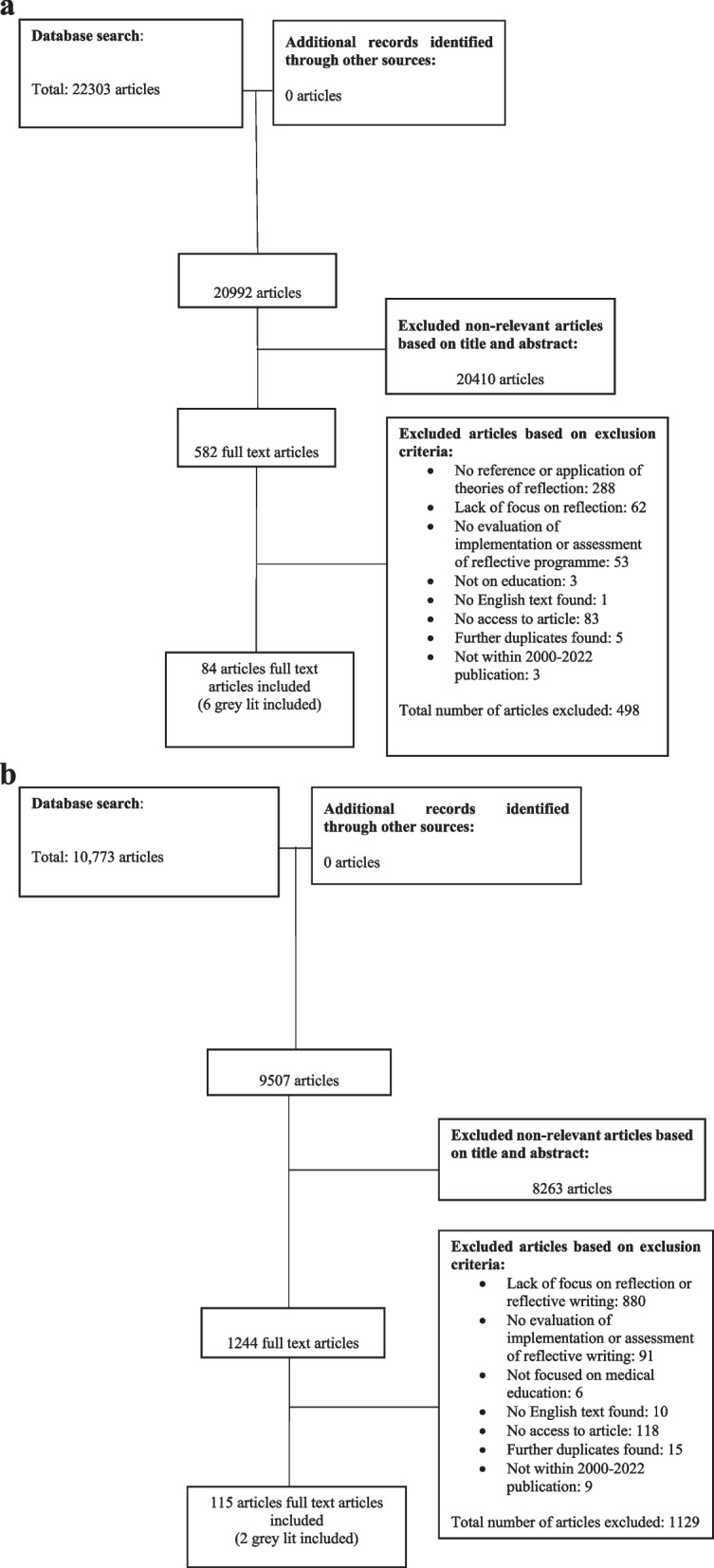
a PRISMA Flow Chart (Search Strat #1: Theories of Reflection in Medical Education). b PRISMA Flow Chart (Search Strat #2: Reflective Writing in Medical Education)
Domain 1: Theories and Models
Many current theories and models surrounding RW in medical education are inspired by Kolb’s Learning Cycle [5] (Table 2). These theories focus on descriptions of areas of reflection; evaluations of experiences and emotions; how events may be related to previous experiences; knowledge critiques of their impact on thinking and practice; integration of learning points; and the physician’s willingness to apply lessons learnt [6, 73–75]. In addition, some of these theories also consider the physician’s self-awareness, ability and willingness to reflect [76], contextual factors related to the area of reflection [4, 77] and the opportunity to reflect effectively within a supportive environment [78, 79]. Ash and Clayton's DEAL Model recommends inclusion of information from all five senses [80–83]. Johns's Model of Structured Reflection [84] advocates giving due consideration to internal and external influences upon the event being evaluated. Rodgers [39] underlines the need for appraisal of the suppositions and assumptions that precipitate and accompany the effects and responses that may have followed the studied event. Griffiths and Tann [75], Mezirow [77], Kim [85], Roskos et al. [86], Burnham et al. [87], Korthagen and Vasalos [78] and Koole et al. [74] build on Dewey [2] and Kolb [5]’s notion of creating and experimenting with a ‘working hypothesis’. These models also propose that the lessons learnt from experimentations should be critiqued as part of a reiterative process within the reflective cycle. Underlining the notion of the reflective cycle and the long-term effects of RW, Pearson and Smith [88] suggest that reflections should be carried out regularly to encourage longitudinal and holistic reflections on all aspects of the physician’s personal and professional life.
Table 2.
Theories and models referred for implementation - iterative stages of reflection
| Author | Process of reflection | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description of event | Deconstructing event | Learning outcomes | Framing | |
| Schon's Reflection-in-Action and Reflection-on-Action [4] | Knowing in action, Reflection-in-action, Reflection-on-action | |||
| Argyris and Schon's Organisational Learning [89] | Single and Double loop learning | |||
| Gibbs' Reflective Cycle [73] |
Description What happened? |
Evaluation What was good and bad about the experience? |
Action Plan If it arose again, what would you do? |
|
|
Feelings What were you thinking and feeling? |
Analysis What else can you make of the situation? |
|||
|
Conclusion What else could you have done? | ||||
| Kolb’s Learning Cycle [5] |
Concrete experience Doing/ having an experience |
Reflective observation Reviewing/ reflecting on experience |
Abstract conceptualisation Concluding/ learning from experience |
|
|
Active experimentation Planning/ trying out what you have learned | ||||
| Kim’s Critical Reflective Inquiry [85] | Description of situation | Reflection and analysis of situation | Critical phase focused on correcting ineffective practice and moving to changed perspectives and actions | |
| Boud's Reflection Model [6] |
Experience Behaviour Ideas Feelings |
Reflective process Returning to experience Attending to feelings Re-evaluating experience |
Outcomes New perspectives Change in behaviour Readiness for application Commitment to action |
|
| Griffiths and Tann's 5 Level Model of Reflection [75] |
Action Rapid reaction (immediate) |
Analysis Review (after the event) |
Planning Retheorize/ reformulate (formal and rigorous appraisal) |
|
|
Observation Repair (momentary) |
Evaluation Research (systematic) |
|||
| Mamede and Schmidt's 5-Factor Model of Reflective Practice [90] |
Reporting What were your feelings and responses to the situation? |
Relating Are there any connections between this event and your past experience and understanding? |
Reconstructing In the future, can you develop some action plans based on this event? |
|
|
Reasoning Can you analyse more about the event? Did you find any significant factors underlying this clinical encounter? |
Reflecting Can you give some feedback on this debriefing? |
|||
| Ryan’s 4Rs of Reflection [91] |
Reporting What happened? |
Relating Have I seen this before? Were the conditions same or different? Do I have the skills or knowledge to deal with this? |
Reconstructing How would I deal with this next time? What might work and why? What might happen if…? Are my ideas supported by theory? |
|
|
Reasoning Factors underlying issue Why they are important Refer to relevant theory Consider different perspectives | ||||
| Beauchamp's Integrative Framework [92] | Examining | Thinking and understanding | Developing and transforming | Concerning a particular object, and in view of achieving a particular goal, or rationale |
| Problem solving | ||||
| Analysing | ||||
| Evaluating and/ or constructing | ||||
| Pearson and Smith's Debriefing [88] |
Log What happened? |
Diary How do you feel? |
Journal What does it all mean? |
|
| Johns' Model of Structured Reflection [84] |
Description of experience Phenomenon Describe the ‘here and now’ experience |
Reflection What was I trying to achieve? Why did I intervene/ react as I did? What were the consequences of my actions? How did I feel about this experience? How did the other person feel? How do I know how the other person felt? |
Learning What other choices did I have What would be the consequences how do i feel now how have i made sense of this experience how has this experience changed my ways of knowing |
|
|
Influencing factors Internal factors External factors Sources of knowledge | ||||
| Koole et al.'s 'Eclectic' Model [74] |
Reviewing the experience Adequate description of an event Identify essential elements and describe own thoughts and feelings |
Critical analyses Searching questions Frames of reference |
Reflective outcome Conclusions Concrete learning goals Plans for future actions |
|
| Dewey’s 5 Phases [2] | Disturbance and uncertainty | Studying conditions of situation and formation of working hypothesis | Testing hypothesis in action | |
| Intellectualisation and definition of problem | Reasoning | |||
| Atkins and Murphy's Model of Reflection [93] | Identify and learning | Analysis | ||
| Awareness of discomfort or action or experience | Evaluate | |||
| Describe the situation | ||||
| Roskos et al.'s Reflection and Learning [86] | Describe an activity | Interpret activity | Critique activity | |
| Evaluate activity | ||||
| Mezirow’s Transformative Learning [77] | Disorienting dilemma | Critical assessment of assumptions | Exploration of new roles, relationships and actions | |
| Self-examination with feelings | Recognition of one’s discontent | Planning a course of action | ||
| Acquiring knowledge and skills for implementing plans | ||||
| Provisional trying of new roles | ||||
| Building competence and self confidence in new roles | ||||
| Reintegration of new perspectives | ||||
| Ash and Clayton's DEAL Model [80–83] |
Describe Factual overview 5 senses |
Examine |
Articulate learning What was learned? How it was learned? Why is it important? How learning can be applied to future practices? |
|
| Korthagen's ALACT Model of Reflection [78] | Acting | Awareness of essential aspects | Creating alternative methods of action | |
| Looking back on action | Trial | |||
| McLeod's 9 Steps of Reflection [79] | Readiness to be open | Recognising personal influences | Responding by making appropriate changes | |
| Recalling situation | Reflecting on experiences from other’s perspectives | Remembering benefits of learning | ||
| Reviewing | ||||
| Relating to relevant reading | ||||
| Re-appraising relevance | ||||
| Bass et al.'s Model of Holistic Reflection [76] | Self awareness |
Reflection Thoughts and feelings |
Learning Synthesis/ action |
|
| Description | Influences | |||
|
Evaluation Analysis/ conclusions | ||||
| Carver and Scheier's Model of Behavioural Self-Regulation [94] | Context of goals wished to pursue | |||
| Grant's Life Coaching [95] | Context of goals wished to pursue | |||
| Burnham's GGRRAAACCEEESSS Model [87] | Gender, geography, race, religion, age, ability, appearance, class, culture, ethnicity, education, employment, sexuality, sexual orientation and spirituality | |||
Regnant theories shape assessments of RW (Table 3). This extends beyond Thorpe [96]’s study which categorises reflective efforts into ‘non-reflectors’, ‘reflectors’, ‘critical reflectors’, and focuses on their process, structure, depth and content. van Manen [97], Plack et al. [98], Rogers et al. [99] and Makarem et al. [100] begin with evaluating the details of the events. Kim’s Critical Reflective Inquiry Model [85] and Bain’s 5Rs Reflective Framework [101] also consider characterisations of emotions involved. Other models appraise the intentions behind actions and thoughts [85], the factors precipitating the event [101] and meaning-making [85]. Other theories consider links with previous experiences [100], the integration of thoughts, justifications and perspectives [99], and the hypothesising of future strategies [98].
Table 3.
Theories and models referred for assessment - vertical levels of reflection
| Author | Depth of reflection | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-reflectors (e.g. habitual reflection, thoughtful action, introspection) | Reflectors (e.g. content reflection, process reflection, content and process reflection) | Critical reflectors (e.g. Premise reflection) | Content of reflection/ criterion | |
| Kember et al.'s Reflective Thinking Scale [102] | Habitual action, Understanding | Reflection | Critical reflection | |
| Hatton and Smith's 4 Levels of Reflective Writing [103] | Description | Descriptive reflection, Dialogic reflection | Critical reflection | |
| Dewey's 5 Phases [2] | Content and process reflection | Premise/ critical reflection | ||
| Moon's Map of Learning [104] | Noticing, Making sense | Making meaning, Working with meaning | Transformative learning | |
| Mezirow's Transformative Learning [7] | Habitual action, Thoughtful action, Understanding | Reflection | Critical reflection | |
| Wald et al.'s REFLECT Rubric [105] |
Habitual action Thoughtful action or introspection |
Reflection | Critical reflection |
Writing spectrum Presence/ sense of writer Description of conflict or disorienting dilemma Attending to emotions Analysis and meaning making |
| Stein's Critical Reflection [106] | No evidence of reflection (Descriptive only, no suggestions for maintaining strengths and improving weaknesses) | Developing reflection (Strengths and weaknesses identified; incorporation of two of following: patient feedback, past experience, evidence for patient-centered interviewing) | Deep reflection |
Skills Feelings Rationale Patient’s reactions Patient feedback Patient-centered interviewing |
| Bain's 5Rs Reflective Framework [101] |
Component 1: Reporting (Micro-reflection) i.e. Describing what happened |
Component 3: Relating (Micro-reflection) i.e. Finding connections between incident and writer’s own experiences and understanding |
Component 5: Reconstructing (Micro-reflection) i.e. Reframing or reconstruction of future practices and own understanding |
|
|
Component 2: Responding (Micro-reflection) i.e. Making observations, expressing feelings or asking questions |
Component 4: Reasoning (Micro-reflection) i.e. Identifying factors underlying incident |
Component 6: Representing (Macro-reflection) i.e. Framing of reflection into local, regional, national and global context |
||
| Morrow's Critical Reflection [107] |
Personal Interpersonal Contextual Critical/ Evaluation – limitations faced, social, ethical problems faced |
|||
| Plack et al.'s Method of Assessing Reflective Journal Writing [108] | No evidence of reflection | Evidence of reflection |
Evidence of critical reflection i.e. exploration of existence of problem, where problems arises from, underlying assumptions; revisits experience to challenge assumptions and modification of biases |
|
| Kims’s Critical Reflective Inquiry Model [85] |
Descriptive Description of practice events, actions, thoughts and feelings |
Reflective Analysis of situation, of intentions |
Critical Critique of practice regarding conflicts, distortion and inconsistencies Engagement in emancipatory change process |
|
| Makaram et al.'s GRE-9 [100] |
What happened? What is special about this event? Feelings when it happened? What was the outcome for the concerned? Understanding of the event |
Congruence of actions and beliefs New thoughts and feelings after reflection |
Reference to old experience and others How this incident will affect future role |
|
| Aukes et al.'s Groningen Reflection Ability Scale [109] |
Self-reflection Empathetic reflection Reflective communication |
|||
| Wang and Liao's Analytic Reflective Writing Scoring Rubric for Healthcare Students and Providers [1] |
Focus and contextualisation Ideas and elaboration Voices and points of view Critical thinking and representation Depth of reflection regarding personal growth Language and style |
|||
| Plack et al.'s Modified Cuppernull Bloom’s Taxonomy [98] |
Level 1: Knowledge and comprehension Description of event |
Level 2: Analysis Deconstruction of experience, examination of alternative explanations |
Level 3: Synthesis and evaluation Conclusions Hypothesize different strategies for future Articulation of learning |
|
| Rogers et al.'s Reflection Rubric [99] |
Beginning i.e. Thoughts conveyed but no to minimal integration of personal thoughts into experience/ justification/ based on one or two perspectives with no to minimal evidence |
Developing i.e. some integration of personal thoughts/ some justification/ two perspectives with some evidence |
Distinguished i.e. strong integration of personal thoughts/ substantial justification/ more than two perspectives with substantial evidence |
Presentation Perspective taking Connection Understanding-cognition Understanding-emotion |
|
Proficient i.e. Moderate integration of personal thoughts/ moderate justification/ two perspectives with moderate evidence | ||||
| Bradley's Model for Evaluating Student Learning [110] | Descriptive | Analytical |
Integrative Impact on global issues |
|
| Lee’s 3 Levels of Reflection [111] |
Recall level (R1) Description |
Rationalisation level (R2) Reasons and rationale Guiding principles |
Reflectivity level (R3) Perspective finding |
|
| van Manen's Tact of Teaching [97] |
Technical rationality Practical action Description of event |
Critical reflection Using personal and other’s experiences to systematically examine phenomenon Reflection on reflection Metacognitive processing |
||
Domain 2: Current methods of structuring RW programs
Current programs focus on supporting the physician throughout the reflective process. Whilst due consideration is given to the physician’s motivations, insight, experiences, capacity and capabilities [25, 96, 112–116], programs also endeavour to ensure appropriate selection and training of physicians intending to participate in RW. Efforts are also made to align expectations, and guide and structure the RW process [37, 116–122]. Physicians are provided with frameworks [76, 79, 105, 123, 124], rubrics [99, 123, 125, 126], examples of the expected quality and form of reflection [96, 115, 116], and how to include emotional and contextual information in their responses [121, 127–129].
Other considerations are enclosed in Table 4 including frequency, modality and the manner in which RW is assessed.
Table 4.
Current methods of structuring RW programs
| Methods of structuring RW programs | Elaboration |
|---|---|
| Structured vs unstructured reflection |
Orientation of user to benefits of reflection and key aspects of reflection [25, 96, 112–116] ° Novices requiring explicit instructions [130] ° Practice sessions for reflective journaling at the beginning of program [114] Prompt questions and suggested frameworks ° To recount and describe event [114, 121, 131, 132] ° To retrospectively analyse own behaviour and rationalise actions [114, 121, 131, 133–137] ° To reflect on emotions and feelings [121, 127–129] ° Action for learning [114, 121, 132–134, 136, 138, 139] ° No frameworks, structure or prompts given to users [120, 140, 141] Suggested events to reflect on ° On self-identified significant clinical encounters [37, 116–122] ° On competency domains [113, 119, 142, 143] ° On hypothetical scenarios [144] Examples of good reflection given to users [96, 115, 116] Benefits of scaffolding ° Frameworks help users to obtain greater breadth and depth in their reflective capacity [76, 79, 105, 123, 124] and can be used as an assessment rubric and guide for self-reflection processes [99, 123, 125, 126], especially for new users [138] ° Simple frameworks allow for RW to be assessed with limited faculty training time or high volume of written reflections to be scored [145] ° Ease of use allows users to peer assess one another [126] Cons of scaffolding ° Prompts could restrict ability of users to engage in reflective writing [146] |
| Frequency of reflection |
Once-off [112, 115, 118, 123, 139, 142, 144, 145, 147–154] Weekly [116, 122, 136, 157–164] Monthly [135] |
| Modality of reflection |
Modality of reflection ° Electronic portfolios ° Written reflective essays/ journals ° Oral narration (i.e. interviews, focused groups discussion) ° Written and verbal adjunct ° Written and video adjunct Comparison of e-journals with hardcopy journals ° Benefits of e-journals: convenience, ease of use, immediacy in terms of feedback, accessibility and visual impact [29, 162, 166] Use of video journals ° Allows for more authentic responses which can later be reviewed, discussed and reflected upon in sessions [167] |
| Group vs individual activity |
Face to face meetings for feedback/ discussion ° One-on-one meetings [30, 119, 128, 143, 148, 150, 167, 168] ° Small group discussions [96, 115, 148, 169–175] Provision of feedback/ sharing of reflections ° Assurance of confidentiality [96, 120, 148, 152, 176, 177] ° Importance of feedback for improvement of experience [30, 96, 173, 178–180] ° Peer to peer feedback allowed for increased sense of camaraderie with classmates [120, 181] ° Peer to peer feedback allowed for enhanced learning [69], increased awareness of personal strengths, while self-reflection enhanced personal weaknesses [173] ° Peer to peer relationships oscillate between support and judgement [149] |
| Formative vs summative assessment |
Formatives Summative No assessment given Dilemmas regarding assessment of RW ° Compulsory assessments encourage users to take assignments seriously and participate [114, 182] ° Assessments allow for developing of reflective skills [183] ° Compulsory assessments result in users writing down what they believe is expected of them instead of their own genuine responses [114, 143, 155, 184] |
Domain 3: Benefits and Shortcomings
The benefits of RW are rarely described in detail and may be divided into personal and professional benefits as summarised in Table 5 for ease of review. From a professional perspective, RW improves learning [96, 112, 119, 147, 157, 170, 179, 185–192], facilitates continuing medical education [119, 128, 173, 174, 193–195], inculcates moral, ethical, professional and social standards and expectations [118, 156, 160], improves patient care [29, 120, 129, 131, 135, 142, 194, 196–199] and nurtures PIF [150, 157, 172, 191, 200].
Table 5.
Benefits of RW programs
| Benefits of RW programs | Elaboration |
|---|---|
| Reflective writing supporting professional formation of physicians |
Physical act of writing ° Daily writing of experiences enhanced observation skills and allowed for review of actions [157, 168, 201, 202] Improvement of self through the sharing of reflections and receiving of feedback [149, 172, 198] ° Personalised feedback for personal growth and sense of self [150, 157, 172, 200] ° Clarification of values through feedback [200, 203] Identity formation through exploration of emotions ° Acknowledgment of personal feelings and impact on clinical decisions [156, 198, 199] ° Development of empathy by reflecting upon own emotions and identifying with patients [154, 172, 204, 205] ° Acknowledgement of own coping mechanisms and vulnerability [154, 160, 206] ° Expression of humanity [156] ° Identification of morals and values, both personal and the patient’s [118, 156, 160] Identity formation through sharing of stories and experiences [137] Improving communication [115, 118, 173] ° Development of ability to relate and hence communicate with others [114] Changes in perspectives, expectations and pre-conceived assumptions [148, 149, 156, 207, 208] Areas for improvement in RW to further professional identity formation ° Reflection framework needed to most effectively improve professional decision-making [37, 191] |
| RW as a tool for learning enhancement |
Becoming active and independent learners [96, 179, 209, 210] ° Understanding the meaning and importance of what they are learning [112, 170, 198, 207] ° Initiation of learning by consolidating past experiences and applying to future practice [174, 211] ° Asking for feedback from mentors [119, 179] ° Facilitates lifelong learning [119, 128, 173, 174, 193–195] Sharing of reflections ° Understanding other perspectives and ideas [118, 149, 153] RW as another avenue for users to engage in learning in addition to more traditional methods in classrooms ° RW assignments lend flexibility to a traditional classroom [119, 212] Integration of existing knowledge with new learning [37, 174, 197] ° By observing and reflecting on experiences to make sense of lived experiences [127, 161, 166, 174, 181, 213] ° Consolidation of learning and making connections between concepts [214, 215] Reaping the rewards of RW for learning enhancement ° Lack of appreciation for the benefits of RW for those who only completed assignments out of obligation [214] ° Too time-consuming to reflect on daily performance [119] ° Difficulty in assessing true learning potential of RW assignments, little evidence in relationship between academic achievement and reflective capacity [144, 184, 207] |
| RW in aiding self-understanding |
Documentation of change and growth [154, 193] Increasing self-awareness [114, 127, 137, 161, 166, 179, 185, 216] ° Greater understanding of their professional role and competencies needed to fulfil responsibilities [131, 150, 174, 205, 217] ° Insights into own strengths, weaknesses and learning needs [112, 119, 150, 152, 170, 218, 219] ° Increased awareness of their own mental health with acknowledgement of fears and vulnerabilities made possible in a safe space [120, 181] ° Questioning of personal beliefs and actions [141, 153, 212, 217, 219–221] ° Making meaning in their lives [129, 166] Acknowledgement and embracing of personal emotions [166] ° Expression and confrontation of emotions they had grappled with and felt they were denied of [114, 129, 156, 172, 200, 208, 209] ° Sense of vulnerability in expression of self [160] ° Recognition of previous sense of emotional detachment [115, 129, 158] ° Emotional stability [200] Stumbling blocks for improving self-awareness ° Unfamiliarity with RW assignments increased discomfort especially with lack of support [37, 157] ° Assessments made users feel inhibited from being genuine with regards to complex situations and feelings [222] |
| RW enhances self-assessment |
Identification of strengths and weaknesses [114, 146, 161, 193, 217] ° Promotes culture of self-monitoring and self-improvement [130, 172, 173, 185, 193, 198] ° Developing critical perspectives of self [193, 223] ° Greater ease with receiving critical feedback from others [198] |
| RW assists with development of clinical behaviour and patient care |
Improved communication skills between healthcare professionals and with patients [29, 131, 142, 194, 196–198] ° Realised importance of interprofessional teamwork [131, 135, 197] ° Improved skill in breaking bad news [129, 199] ° Improved skill in active listening [120] Improved clinical reasoning and decision making [118, 126, 194, 196, 199, 200] ° Reflection on clinical situations or incidents to rationalise behaviour retrospectively [37, 174, 177, 224, 225] ° Reflection in action [226] Development of soft skills ° Development of empathy [38, 127, 158, 185, 197, 200, 205, 219, 227] Patient-centred care [131, 212] ° To be more aware of patient autonomy and respecting each individual’s wishes [118, 129, 131, 228] ° Realised importance of trust in doctor-patient relationship [171, 198, 205] ° Improvement in patient outcomes [195] |
From a personal perspective, RW increases self-awareness [114, 127, 137, 161, 166, 179, 185, 202, 216], self-advancement [9, 131, 134, 150, 168, 174, 195, 205, 217, 229], facilitates understanding of individual strengths, weaknesses and learning needs [112, 119, 150, 152, 170, 218, 219], promotes a culture of self-monitoring, self-improvement [130, 172, 173, 185, 193, 198, 201, 210, 211], developing critical perspectives of self [193, 223] and nurtures resilience and better coping [154, 160, 206]. RW also guides shifts in thinking and perspectives [148, 149, 156, 203, 207, 208] and focuses on a more holistic appreciation of decision-making [37, 118, 126, 174, 177, 194, 196, 199, 200, 224–226] and their ramifications [37, 112, 116, 130, 131, 141, 154, 179, 193, 194, 196, 204, 207, 218, 230].
Table 6 combines current lists of the shortcomings of RW. These limitations may be characterised by individual, structural and assessment styles.
Table 6.
Shortcomings of RW programs
| Shortcomings of RW programs | Elaboration |
|---|---|
| Problems found in implementation of RW curriculum |
Anxiety with having their private thoughts being shared with others ° Preference for one-on-one sharing with tutors instead [129, 149, 209, 231] ° Censorship of thoughts and reflections when sharing with others [37, 114, 136, 149, 160, 183] ° Process of sharing could feel impersonal if sharing is done virtually [165] May fail to cater to the different learning styles of users [220, 232] ° Query as to the extent that writing may be able to capture elements of the users’ reflective processes [118] ° Other modalities for reflection (e.g. blogging) might have greater appeal to users [120] ° RW too restrictive for more experienced users due to rigidity of suggested frameworks [142, 196] Barriers to user participation ° Lack of time and fatigue [29, 119, 136, 138, 157, 161, 167–169, 176, 181, 193, 196, 226, 232, 233] ° Lack of self-direction and motivation [29, 79, 119, 176, 188, 226, 231] ° Difficulty dealing with negative emotions arising from reflecting on difficult events [114, 168, 176, 193, 230] ° Felt that RW was unnecessary as they were already adept at introspection [227] Objectives were not clearly defined to users and assessors ° Greater clarity of goals of RW needed throughout course for users to understand importance of what they were doing [114, 129, 135, 138, 142, 209, 227] ° Greater emphasis to be placed on role of assessors for them to provide adequate feedback and mentorship for users [50, 138] |
| Factors affecting quality of reflection |
Lack of confidentiality and trust resulting in censorship of genuine thoughts and reflections [37, 114, 136, 149, 169, 183, 196] Lack of support and feedback from mentors [37, 119, 133, 196] Problems relating to writing ° Language competencies affecting expression [167, 229] ° Learning to write in a new voice unlike academic writing [114, 136] Decreased authenticity of reflections to meet expectations of graded curriculum [9, 115, 157, 161, 166, 193, 209, 234] Did not take module seriously due to it being formatively assessed [114, 172, 182, 226] Enforcing of daily reflections caused users to reflect on experiences that were insignificant [119, 235, 236] |
| Problems found with assessment of RW curriculum |
Assessment distracts users from the essence of reflection ° Grading pressures users to write for approval [114, 115, 118, 129, 138, 143, 149, 155, 157, 209, 232, 237, 238] ° Assessment causes censorship of tension of ethical dilemmas or censorship of unconventional opinions [119, 209] Faculty’s confusion with assessment of reflection ° Uncomfortable with idea of reflection due to lack of experience [115, 226] ° Inconsistent definitions of reflections [114, 133, 188, 237] ° Subjective nature of judging the content [237] ° Influence of writing ability [132, 174, 180, 183] ° Lack of confidence in correlating assessment grade with depth of reflection [29, 105, 118, 126, 177, 207] Problems with rubrics ° Unclear rubric categories with overlaps between different levels [145] ° Difficulty maintaining a consistent high inter-rater variability [143, 239] |
| Possible problems with reflection in itself |
Triggering of negative emotions which users are unable to escape ° Questioning what has always been instinctual knowledge or status quo might bring instead a sense of uncertainty which complicates decision-making [207, 240] ° Users might become overly critical of themselves [207, 241] ° Self-doubt [225] Becoming negatively self-isolated ° Personal forms of critical reflection might have the unintended effect of users becoming too focused on themselves instead [207] Could distract learners from spending time on technical skills or knowledge acquisition [207, 225] |
It is suggested that RW does not cater to the different learning styles [220, 232], cultures [190], roles, values, processes and expectations of RW [114, 129, 135, 138, 142, 209, 227, 234], and physicians' differing levels of self-awareness [29, 79, 119, 176, 188, 226, 231, 236], motivations [29, 119, 136, 138, 157, 161, 167–169, 176, 181, 193, 196, 226, 232, 233] and willingness to engage in RW [37, 114, 136, 149, 160, 183]. RW is also limited by poorly prepared physicians and misaligned expectations whilst a lack of privacy and a safe setting may precipitate physician anxiety at having their private thoughts shared [129, 149, 209, 231]. RW is also compromised by a lack of faculty training [143, 145, 239], mentoring support [37, 50, 119, 133, 196] and personalised feedback [50, 114, 136, 167, 229] which may lead to self-censorship [37, 114, 136, 149, 160, 183] and an unwillingness to address negative emotions arising from reflecting on difficult events [114, 168, 176, 193, 230], circumventing the reflective process [118, 142, 165, 196] .
Variations in assessment styles [9, 115, 157, 161, 166, 193, 209], depth [29, 105, 118, 126, 177, 207] and content [37, 114, 136, 149, 169, 183, 196], and pressures to comply with graded assessments [114, 115, 118, 129, 138, 143, 149, 155, 157, 209, 232, 237, 238] also undermine efforts of RW.
Domain 4. Recommendations
In the face of practice variations and challenges, there have been several recommendations on improving practice.
Boosting awareness of RW
Acknowledging the importance of a physician’s motivations, willingness and judgement [37], an RW program must acquaint physicians with information on RW’s role [128], program expectations, the form, frequency and assessments of RW and the support available to them [130, 132, 150, 154, 242] and its benefits to their professional and personal development [96, 227] early in their training programs [115, 220, 242, 243]. Physicians should also be trained on the knowledge and skills required to meet these expectations [1, 37, 135, 151, 160, 215, 244, 245].
A structured program and environment
Recognising that effective RW requires a structured program. Recommendations focus on three aspects of the program design [132]. One is the need for trained faculty [9, 115, 219, 220, 230, 233, 242, 246], accessible communications, protected time for RW and debriefs [125], consistent mentoring support [190] and assessment processes [247]. This will facilitate trusting relationships between physicians and faculty [30, 114, 168, 196, 231, 233]. Two, the need to nurture an open and trusting environment where physicians will be comfortable with sharing their reflections [96, 128], discussing their emotions, plans [127, 248] and receiving feedback [9, 37, 79, 114, 119, 128, 135, 173, 176, 179, 190, 237]. This may be possible in a decentralised classroom setting [163, 190]. Three, RW should be part of the formal curriculum and afforded designated time. RW should be initiated early and longitudinally along the training trajectory [116, 122].
Adjuncts to RW programs
Several approaches have been suggested to support RW programs. These include collaborative reflection, in-person discussion groups to share written reflections [128, 131, 138, 196, 199, 231, 249] and reflective dialogue to exchange feedback [119], use of social media [149, 160, 169, 194, 204, 230], video-recorded observations and interactions for users to review and reflect on later [133]. Others include autobiographical reflective avenues in addition to practice-oriented reflection [137], support groups to help meditate stress or emotions triggered by reflections [249] and mixing of reflective approaches to meet different learning styles [169, 250].
Discussion
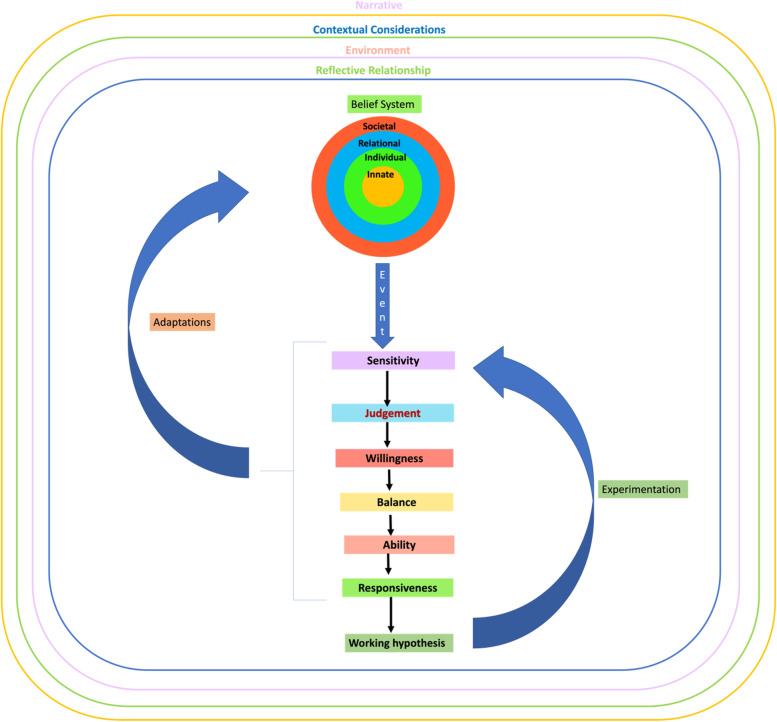
In answering the primary research question, “How is reflective writing structured, assessed and supported in medical education?”, this SSR in SEBA highlights several key insights. To begin, RW involves integrating the insights of an experience or point of reflection (henceforth ‘event’) into the physician’s currently held values, beliefs and principles (henceforth belief system). Recognising that an ‘event’ has occurred and that it needs deeper consideration highlights the physician’s sensitivity. Recognising the presence of an ‘event’ triggers an evaluation as to the urgency in which it needs to be addressed, where it stands amongst other ‘events’ to be addressed and whether the physician has the appropriate skills, support and time to address the ‘event’. This reflects the physician’s judgement. The physician must then determine whether they are willing to proceed and the ramifications involved. These include ethical, medical, clinical, administrative, organisational, sociocultural, legal and professional considerations. This is then followed by contextualising them to their own personal, psychosocial, clinical, professional, research, academic, and situational setting. Weighing these amidst competing ‘events’ underlines the import of the physician’s ability to ‘balance’ considerations. Creating and experimenting on their ‘working hypothesis’ highlights their ‘ability’, whilst how they evaluate the effects of their experimentation and how they adapt their practice underscores their ‘responsiveness’ [2, 5, 74, 75, 77, 78, 85–87, 90].
The concepts of ‘sensitivity’, ‘judgement’, ‘willingness’, ‘balance’, ‘ability’ and ‘responsiveness’ spotlight environmental and physician-related factors. These include the physician’s motivations, knowledge, skills, attitudes, competencies, working style, needs, availabilities, timelines, and their various medical, clinical, administrative, organisational, sociocultural, legal, professional, personal, psychosocial, clinical, research, academic and situational experiences. It also underlines the role played by the physician’s beliefs, moral values, ethical principles, familial mores, cultural norms, attitudes, thoughts, decisional preferences, roles and responsibilities. The environmental-related factors include the influence of the curriculum, the culture, structure, format, assessment and feedback of the RW process and the program it is situated in. Together, the physician and their environmental factors not only frame RW as a sociocultural construct necessitating holistic review but also underscore the need for longitudinal examination of its effects. This need for holistic and longitudinal appraisal of RW is foregrounded by the experimentations surrounding the ‘working hypothesis’ [2, 5, 72, 74, 77, 84–86, 90]. In turn, experimentations and their effects affirm the notion of regular use of RW and reiterate the need for longitudinal reflective relationships that provide guidance, mentoring and feedback [87, 90]. These considerations set the stage for the proffering of a new conceptual model of RW.
To begin, the Krishna Model of Reflective Writing (Fig. 3) builds on the Krishna-Pisupati Model [10] used to describe evaluations of professional identity formation (PIF) [8, 10, 24, 251]. Evidenced in studies of how physicians cope with death and dying patients, moral distress and dignity-centered care [46, 54], the Krishna-Pisupati Model suggests that the physician’s belief system is informed by their self-concepts of personhood and identity. This is effectively characterised by the Ring Theory of Personhood (RToP) [11].
Fig. 3.
Krishna Model of Reflective Writing
The Krishna Model of RW posits that the RToP is able to encapsulate various aspects of the physician’s belief system. The Innate Ring which represents the innermost ring of the four concentric rings depicting the RToP is derived from currently held spiritual, religious, theist, moral and ethical values, beliefs and principles [13, 51, 53, 252]. Encapsulating the Innate Ring is the Individual Ring. The Individual Ring’s belief system is derived from the physician’s thoughts, conduct, biases, narratives, personality, decision-making processes and other facets of conscious function which together inform the physician’s Individual Identity [13, 51, 53, 252]. The Relational Ring is shaped by the values, beliefs and principles governing the physician’s personal and important relationships [13, 51, 53, 252]. The Societal Ring, the outermost ring of the RToP is shaped by regnant societal, religious, professional and legal expectations, values, beliefs and principles which inform their interactions with colleagues and acquaintances [13, 51, 53, 252]. Adoption of the RToP to depict this belief system not only acknowledges the varied aspects and influences that shape the physician’s identity but that the belief system evolves as the physician’s environment, narrative, context and relationships change.
The environmental factors influencing the belief system include the support structures used to facilitate reflections such as appropriate protected time, a consistent format for RW, a structured assessment program, a safe environment, longitudinal support, timely feedback and trained faculty. The Krishna Model of RW also recognises the importance of the relationships which advocate for the physician and proffer the physician with coaching, role modelling, supervision, networking opportunities, teaching, tutoring, career advice, sponsorship and feedback upon the RW process. Of particular importance is the relationship between physician and faculty (henceforth reflective relationship). The reflective relationship facilitates the provision of personalised, appropriate, holistic, and frank communications and support. This allows the reflective relationship to support the physician as they deploy and experiment with their ‘working hypothesis’. As a result, the Krishna Model of RW focuses on the dyadic reflective relationship and acknowledges that there are wider influences beyond this dyad that shape the RW process. This includes the wider curriculum, clinical, organisational, social, professional and legal considerations within specific practice settings and other faculty and program-related factors. Important to note, is that when an ‘event’ triggers ‘sensitivity’, ‘judgement’, ‘willingness’, ‘balance’, ‘ability’ and ‘responsiveness’, the process of creating and experimenting with a ‘working hypothesis' and adapting one's belief system is also shaped by the physician’s narratives, context, environment and relationships.
In answering its secondary question, “How might a reflective writing program in medical education be structured?”, the data suggests that an RW program ought to be designed with due focus on the various factors influencing the physician's belief system, their ‘sensitivity’, ‘judgement’, ‘willingness’, ‘balance’, ‘ability’ and ‘responsiveness’, and their creation and experimentation with their ‘working hypothesis’. These will be termed the ‘physician's reactions’. The design of the RW program ought to consider the following factors:
- Belief system
-
i.Narratives
- Recognising that the physician’s notion of ‘sensitivity’, ‘judgement’, ‘willingness’, ‘balance’, ‘ability’ and ‘responsiveness’ is influenced by their experience, skills, knowledge, attitude and motivations, physicians recruited to the RW program should be carefully evaluated
- To align expectations, the physician should be introduced to the benefits and role of RW in their personal and professional development
- The ethos, frequency, goals and format of the reflection and assessment methods should be clearly articulated to the physician [253]
- Training and support must also be personalised
-
ii.Contextual considerations
- Recognising that the physician’s academic, personal, research, administrative, clinical, professional, sociocultural and practice context will change, the structure, approach, assessment and support provided must be flexible and responsive
- The communications platform should be easily accessible and robust to attend to the individual needs of the physician in a timely and appropriate manner
- The program must support diversity [207]
-
iii.Environment
- The reflective relationship is shaped by the culture and structure of the environment in which the program is hosted in
-
iv.Reflective relationship
- The faculty must be trained and provided access to counselling, mindfulness meditation and stress management programs [249]
- The faculty must be responsive to changes and provide appropriate personal, educational and professional support and adaptations to the assessment process when required [207]
- To facilitate the development of effective reflective relationships, a consistent faculty member should work with the physician and build a longitudinal trusting, open and supportive reflective relationship
-
i.
- Physician’s reactions
- The evolving nature of the various structures and influences upon the RW process underscores the need for longitudinal assessment and support
- The physician must be provided with timely, appropriate and personalised training and feedback
- The program’s structure and oversight must also be flexible and responsive
- There must be accessible longitudinal mentoring support
- The format and assessment of RW must account for growing experience and competencies as well as changing motivations and priorities
On assessment
Assessment rubrics should be used to guide the training of faculty, education of physicians and guidance of reflections [37, 116–122]
Assessments ought to take a longitudinal perspective to track the physician's progress [116, 122]
Based on the results from this SSR in SEBA, we forward a guide catering to novice reflective practitioners (Additional file 1).
Limitations
This SSR in SEBA suggests that, amidst the dearth of rigorous quantitative and qualitative studies in RW and in the presence of diverse practices, approaches and settings, conclusions may not be easily drawn. Extrapolations of findings are also hindered by evidence that appraisals of RW remain largely reliant upon single time point self-reported outcomes and satisfaction surveys.
Conclusion
This SSR in SEBA highlights a new model for RW that requires clinical validation. However, whilst still not clinically proven, the model sketches a picture of RW’s role in PIF and the impact of reflective processes on PIF demands further study. As we look forward to engaging in this area of study, we believe further research into the longer-term effects of RW and its potential place in portfolios to guide and assess the development of physicians must be forthcoming.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1. Guide to Reflective Writing.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to dedicate this paper to the late Dr. S Radha Krishna and A/Prof Cynthia Goh whose advice and ideas were integral to the success of this review and Thondy and Maia Olivia whose lives continue to inspire us.
The authors would also like to thank the anonymous reviewers, Dr. Ruaraidh Hill and Dr. Stephen Mason for their helpful comments which greatly enhanced this manuscript.
Abbreviations
- RW
Reflective Writing
- PIF
Professional Identity Formation
- RToP
Ring Theory of Personhood
- BEME
Best Evidence Medical Education
- STORIES
Structured approach to the Reporting In healthcare education of Evidence Synthesis
- PRISMA
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
- SSR
Systematic Scoping Review
- SEBA
Systematic Evidence-Based Approach
- YLLSoM
Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine
- PICOs
Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome, Study Design
- RAMESES
Realist And Meta-narrative Evidence Syntheses - Evolving Standards
Authors’ contributions
All authors were involved in data curation, formal analysis, investigation, preparing the original draft of the manuscript as well as reviewing and editing the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
No funding was received for this review.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analysed during this review are included in this published article and its supplementary files.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
NA
Consent for publication
NA
Competing interests
All authors have no competing interests for this review.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Wang Y-H, Liao H-C. Construction and validation of an analytic reflective writing scoring rubric for healthcare students and providers. 醫學教育. 2020;24(2):53–72. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dewey J. How we think: a restatement of the relation of reflective thinking to the educative process. Am J Psychol. 1933;46:528. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schon DA. The reflective practitioner: how professionals think in action. New York: Basic Books; 1983. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schon DA. Educating the reflective practitioner: towards a new design for teaching and learning in the profession. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass; 1987. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kolb DA. Experiential learning: experience as the source of learning and development. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall; 1984. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Boud D, Keogh R, Walker D. Reflection: turning experience into learning. London: Kogan Page; 1985. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mezirow J. Fostering critical reflection in adulthood: a guide to transformative and emancipatory learning. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass; 1990. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sarraf-Yazdi S, Teo YN, How AEH, Teo YH, Goh S, Kow CS, et al. A scoping review of professional identity formation in undergraduate medical education. J Gen Intern Med. 2021;36(11):3511–3521. doi: 10.1007/s11606-021-07024-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mann K, Gordon J, MacLeod A. Reflection and reflective practice in health professions education: a systematic review. Adv Health Sci Educ. 2009;14(4):595–621. doi: 10.1007/s10459-007-9090-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Teo KJH, Teo MYK, Pisupati A, Ong RSR, Goh CK, Seah CHX, et al. Assessing professional identity formation (PIF) amongst medical students in Oncology and Palliative Medicine postings: a SEBA guided scoping review. BMC Palliat Care. 2022;21(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12904-022-01090-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Radha Krishna LK, Alsuwaigh R. Understanding the fluid nature of personhood - the ring theory of personhood. Bioethics. 2015;29(3):171–181. doi: 10.1111/bioe.12085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ryan M, Ryan M. Theorising a model for teaching and assessing reflective learning in higher education. High Educ Res Dev. 2013;32(2):244–257. doi: 10.1080/07294360.2012.661704. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Huang H, Toh RQE, Chiang CLL, Thenpandiyan AA, Vig PS, Lee RWL, et al. Impact of dying neonates on doctors’ and nurses’ personhood: a systematic scoping review. J Pain Symptom Manag. 2022;63(1):e59–e74. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2021.07.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Vig PS, Lim JY, Lee RW, Huang H, Tan XH, Lim WQ, Lim MB, Lee AS, Chiam M, Lim C, Baral VR. Parental bereavement–impact of death of neonates and children under 12 years on personhood of parents: a systematic scoping review. BMC Palliat Care. 2021;20(1):1–7. doi: 10.1186/s12904-021-00831-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chan NPX, Chia JL, Ho CY, Ngiam LXL, Kuek JTY, Ahmad Kamal NHB, et al. Extending the ring theory of personhood to the care of dying patients in intensive care units. Asian Bioeth Rev. 2022;14(1):71–86. doi: 10.1007/s41649-021-00192-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tay J, Compton S, Phua G, Zhuang Q, Neo S, Lee G, et al. Perceptions of healthcare professionals towards palliative care in internal medicine wards: a cross-sectional survey. BMC Palliat Care. 2021;20(1):101. doi: 10.1186/s12904-021-00787-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Teo YH, Peh TY, Abdurrahman A, Lee ASI, Chiam M, Fong W, et al. A modified Delphi approach to enhance nurturing of professionalism in postgraduate medical education in Singapore. Singap Med J. 2021. 10.11622/smedj.2021224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Chiam M, Ho CY, Quah E, Chua KZY, Ng CWH, Lim EG, et al. Changing self-concept in the time of COVID-19: a close look at physician reflections on social media. Philos Ethics Humanit Med. 2022;17(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s13010-021-00113-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Zhou JX, Goh C, Chiam M, Krishna LKR. Painting and Poetry From a Bereaved Family and the Caring Physician. J Pain Symptom Manage. 2022;S0885-3924(22):00476-6. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 20.Cheong CWS, Quah ELY, Chua KZY, Lim WQ, Toh RQE, Chiang CLL, et al. Post graduate remediation programs in medicine: a scoping review. BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):294. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03278-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Goh S, Wong RSM, Quah ELY, Chua KZY, Lim WQ, Ng ADR, et al. Mentoring in palliative medicine in the time of covid-19: a systematic scoping review. BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):359. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03409-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Venktaramana V, Loh EKY, Wong CJW, Yeo JW, Teo AYT, Chiam CSY, et al. A systematic scoping review of communication skills training in medical schools between 2000 and 2020. Med Teach. 2022;44(9):997-1006. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 23.Chia EW, Huang H, Goh S, Peries MT, Lee CC, Tan LH, Khoo MS, Tay KT, Ong YT, Lim WQ, Tan XH. A systematic scoping review of teaching and evaluating communications in the intensive care unit. Asia Pac Schol. 2021;6(1):3–29. doi: 10.29060/TAPS.2021-6-1/RA2351. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Toh RQE, Koh KK, Lua JK, Wong RSM, Quah ELY, Panda A, et al. The role of mentoring, supervision, coaching, teaching and instruction on professional identity formation: a systematic scoping review. BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):531. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03589-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Charon R, Hermann N. Commentary: a sense of story, or why teach reflective writing? Acad Med. 2012;87(1):5–7. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e31823a59c7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Matinho D, Pietrandrea M, Echeverria C, Helderman R, Masters M, Regan D, et al. A systematic review of integrated learning definitions, frameworks, and practices in recent health professions education literature. Educ Sci. 2022;12(3):165. doi: 10.3390/educsci12030165. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Saltman DC, Tavabie A, Kidd MR. The use of reflective and reasoned portfolios by doctors. J Eval Clin Pract. 2012;18(1):182–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2010.01514.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kinsella EA. Technical rationality in Schön’s reflective practice: dichotomous or non-dualistic epistemological position. Nurs Philos. 2007;8(2):102–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1466-769X.2007.00304.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tsingos C, Bosnic-Anticevich S, Smith L. Reflective practice and its implications for pharmacy education. Am J Pharm Educ. 2014;78(1):18. doi: 10.5688/ajpe78118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Arntfield S, Parlett B, Meston CN, Apramian T, Lingard L. A model of engagement in reflective writing-based portfolios: interactions between points of vulnerability and acts of adaptability. Med Teach. 2016;38(2):196–205. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2015.1009426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Edgar L, et al. ACGME: the milestones guidebook. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 32.Council GM . Tomorrow’s doctors. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Council GM. The reflective practitioner - guidance for doctors and medical students. Available from: https://www.gmc-uk.org/education/standards-guidance-and-curricula/guidance/reflective-practice/the-reflective-practitioner-guidance-for-doctors-and-medical-students. Accessed 3 Aug 2022.
- 34.England RCoSo. Good surgical practice. Available from: https://www.rcseng.ac.uk/standards-and-research/gsp/. Accessed 3 Aug 2022.
- 35.Physicians TRACo . The Royal Australasian College of Physicians basic training curriculum standards: competencies. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Surgeons RACo. RACS competencies. Available from: https://www.surgeons.org/en/Trainees/the-set-program/racs-competencies. Accessed 3 Aug 2022.
- 37.Murdoch-Eaton D, Sandars J. Reflection: moving from a mandatory ritual to meaningful professional development. Arch Dis Child. 2014;99(3):279–283. doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2013-303948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Thompson N, Pascal J. Developing critically reflective practice. Reflective Pract. 2012;13(2):311–325. doi: 10.1080/14623943.2012.657795. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Rodgers C. Defining reflection: another look at John Dewey and reflective thinking. Teach Coll Rec. 2002;104:842–866. doi: 10.1111/1467-9620.00181. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Hinchcliff R, Greenfield D, Moldovan M, Westbrook JI, Pawsey M, Mumford V, et al. Narrative synthesis of health service accreditation literature. BMJ Qual Saf. 2012;21(12):979–991. doi: 10.1136/bmjqs-2012-000852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Boden C, Ascher MT, Eldredge JD. Learning while doing: program evaluation of the medical library association systematic review project. J Med Libr Assoc. 2018;106(3):284. doi: 10.5195/jmla.2018.286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Mays N, Roberts E, Popay J. Synthesising research evidence. Studying the organisation and delivery of health services: research methods. 2001. p. 220. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Davey S, Davey A, Singh J. Metanarrative review: current status and opportunities for public health research. Int J Health Syst Disaster Manag. 2013;1(2):59–63. doi: 10.4103/2347-9019.128111. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Greenhalgh T, Wong G. Training materials for meta-narrative reviews. UK: Global Health Innovation and Policy Unit Centre for Primary Care and Public Health Blizard Institute, Queen Mary University of London; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Osama T, Brindley D, Majeed A, Murray KA, Shah H, Toumazos M, et al. Teaching the relationship between health and climate change: a systematic scoping review protocol. BMJ Open. 2018;8(5):e020330. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2017-020330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Chua KZY, Quah ELY, Lim YX, Goh CK, Lim J, Wan DWJ, et al. A systematic scoping review on patients’ perceptions of dignity. BMC Palliat Care. 2022;21(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12904-022-01004-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Hong DZ, Lim AJS, Tan R, Ong YT, Pisupati A, Chong EJX, et al. A systematic scoping review on portfolios of medical educators. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2021;8:23821205211000356. doi: 10.1177/23821205211000356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tay KT, Ng S, Hee JM, Chia EWY, Vythilingam D, Ong YT, et al. Assessing professionalism in medicine - a scoping review of assessment tools from 1990 to 2018. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2020;7:2382120520955159. doi: 10.1177/2382120520955159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lim C, Zhou JX, Woong NL, Chiam M, Krishna LKR. Addressing the needs of migrant workers in ICUs in Singapore. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2020;7:2382120520977190. doi: 10.1177/2382120520977190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ong YT, Quek CWN, Pisupati A, Loh EKY, Venktaramana V, Chiam M, et al. Mentoring future mentors in undergraduate medical education. PLoS One. 2022;17(9):e0273358. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0273358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Kuek JTY, Ngiam LXL, Kamal NHA, Chia JL, Chan NPX, Abdurrahman ABHM, et al. The impact of caring for dying patients in intensive care units on a physician’s personhood: a systematic scoping review. Philos Ethics Humanit Med. 2020;15(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s13010-020-00096-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Ngiam L, Ong YT, Ng JX, Kuek J, Chia JL, Chan N, Ho CY, Abdurrahman A, Kamal N, Cheong C, Ng CH, Tan XH, Tan L, Chin A, Mason S, Jumat MR, Chiam M, Krishna L. Impact of caring for terminally ill children on physicians: a systematic scoping review. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2021;38(4):396–418. doi: 10.1177/1049909120950301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ho CY, Lim N-A, Ong YT, Lee ASI, Chiam M, Gek GPL, et al. The impact of death and dying on the personhood of senior nurses at the National Cancer Centre Singapore (NCCS): a qualitative study. BMC Palliat Care. 2022;21(1):1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12904-022-00974-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Quah ELY, Chua KZY, Lua JK, Wan DWJ, Chong CS, Lim YX, et al. A systematic review of stakeholder perspectives of dignity and assisted dying. J Pain Symptom Manag. 2022. 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2022.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 55.Quek CWN, Ong RRS, Wong RSM, Chan SWK, Chok AK-L, Shen GS, et al. Systematic scoping review on moral distress among physicians. BMJ Open. 2022;12(9):e064029. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-064029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wong G, Greenhalgh T, Westhorp G, Buckingham J, Pawson R. RAMESES publication standards: meta-narrative reviews. BMC Med. 2013;11(1):20. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Pring R. The ‘false dualism’of educational research. J Philos Educ. 2000;34(2):247–260. doi: 10.1111/1467-9752.00171. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Crotty M. The foundations of social research: meaning and perspective in the research process. Thousand Oaks: SAGE; 1998.
- 59.Ford K. Taking a narrative turn: possibilities, challenges and potential outcomes. OnCUE J. 2012;6(1):23-36.
- 60.Schick-Makaroff K, MacDonald M, Plummer M, Burgess J, Neander W. What synthesis methodology should I use? A review and analysis of approaches to research synthesis. AIMS Public Health. 2016;3:172–215. doi: 10.3934/publichealth.2016.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Peters M, Godfrey C, McInerney P, Soares C, Khalil H, Parker D. The Joanna Briggs Institute reviewers’ manual 2015: methodology for JBI scoping reviews2015 April 29. 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Peters MD, Godfrey CM, Khalil H, McInerney P, Parker D, Soares CB. Guidance for conducting systematic scoping reviews. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2015;13(3):141–146. doi: 10.1097/XEB.0000000000000050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Sandelowski M, Barroso J. Handbook for synthesizing qualitative research. New York: Springer; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 64.Chua WJ, Cheong CWS, Lee FQH, Koh EYH, Toh YP, Mason S, et al. Structuring mentoring in medicine and surgery. A systematic scoping review of mentoring programs between 2000 and 2019. J Contin Educ Health Prof. 2020;40(3):158–168. doi: 10.1097/CEH.0000000000000308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ng YX, Koh ZYK, Yap HW, Tay KT, Tan XH, Ong YT, et al. Assessing mentoring: a scoping review of mentoring assessment tools in internal medicine between 1990 and 2019. PLoS One. 2020;15(5):e0232511. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77–101. doi: 10.1191/1478088706qp063oa. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Cassol H, Pétré B, Degrange S, Martial C, Charland-Verville V, Lallier F, et al. Qualitative thematic analysis of the phenomenology of near-death experiences. PLoS One. 2018;13(2):e0193001. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0193001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hsieh H-F, Shannon SE. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual Health Res. 2005;15(9):1277–1288. doi: 10.1177/1049732305276687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Wald H, Reis S. Beyond the margins: fostering reflective capacity through reflective writing in medical education. J Gen Int Med. 2010;25:746–749. doi: 10.1007/s11606-010-1347-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Popay J, Roberts H, Sowden A, Petticrew M, Arai L, Rodgers M, et al. Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in systematic reviews. A product from the ESRC methods programme version. 2006. p. b92. [Google Scholar]
- 71.France EF, Wells M, Lang H, Williams B. Why, when and how to update a meta-ethnography qualitative synthesis. Syst Rev. 2016;5:44. doi: 10.1186/s13643-016-0218-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Noblit GW, Hare RD, Hare RD. Meta-ethnography: synthesizing qualitative studies. Newbury Park: Sage Publications; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Gibbs G. Learning by doing: a guide to teaching and learning methods. Thousand Oaks: FEU; 1988.
- 74.Koole S, Dornan T, Aper L, Scherpbier A, Valcke M, Cohen-Schotanus J, et al. Factors confounding the assessment of reflection: a critical review. BMC Med Educ. 2011;11(1):104. doi: 10.1186/1472-6920-11-104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Day C. Reflection: A Necessary but Not Sufficient Condition for Professional Development. British Educational Research Journal. 1993;19(1):83–93.
- 76.Sweet L, Bass J, Sidebotham M, Fenwick J, Graham K. Developing reflective capacities in midwifery students: enhancing learning through reflective writing. Women Birth. 2019;32(2):119–126. doi: 10.1016/j.wombi.2018.06.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Mezirow J. Understanding transformation theory. Adult Educ Q. 1994;44(4):222–232. doi: 10.1177/074171369404400403. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Korthagen F, Vasalos A. Levels in reflection: core reflection as a means to enhance professional growth. Teach Teach. 2005;11(1):47–71. doi: 10.1080/1354060042000337093. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 79.McLeod N. Reflecting on reflection: improving teachers’ readiness to facilitate participatory learning with young children. Prof Dev Educ. 2015;41(2):254–272. [Google Scholar]
- 80.Ash SL, Clayton PH. The articulated learning: an approach to guided reflection and assessment. Innov High Educ. 2004;29(2):137–154. doi: 10.1023/B:IHIE.0000048795.84634.4a. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ash S, Clayton P. Generating, deepening, and documenting learning: the power of critical reflection in applied learning. J Appl Learn High Educ. 2009;1:25–48. [Google Scholar]
- 82.Lay K, McGuire L. Teaching students to deconstruct life experience with addictions: a structured reflection exercise. J Teach Addict. 2008;7(2):145–163. doi: 10.1080/15332700802269227. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Lay K, McGuire L. Building a lens for critical reflection and reflexivity in social work education. Soc Work Educ. 2010;29(5):539–550. doi: 10.1080/02615470903159125. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Johns C. Nuances of reflection. J Clin Nurs. 1994;3(2):71–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.1994.tb00364.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kim HS. Critical reflective inquiry for knowledge development in nursing practice. J Adv Nurs. 1999;29(5):1205–1212. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2648.1999.01005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Roskos K, Vukelich C, Risko V. Reflection and learning to teach reading: a critical review of literacy and general teacher education studies. J Lit Res. 2001;33:595–635. doi: 10.1080/10862960109548127. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Burnham J. Developments in Social GGRRAAACCEEESSS: visible-invisible, voiced-unvoiced. In I. Krause (Ed.), Cultural Reflexivity. London: Karnac.
- 88.Pearson M, Smith D. In: Debriefing in experience-based learning, reflection: turning experience into learning. Boud D, Keogh R, Walker D, editors. London: Kogan Page; 1985. [Google Scholar]
- 89.Argyris C, Schön DA. Organizational learning: A theory of action perspective, Reading, Mass: Addison Wesley. 1978.
- 90.Mamede S, Schmidt HG. The structure of reflective practice in medicine. Med Educ. 2004;38(12):1302–1308. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2929.2004.01917.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Ryan M. Improving reflective writing in higher education: a social semiotic perspective. Teach High Educ. 2011;16(1):99–111. doi: 10.1080/13562517.2010.507311. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Beauchamp C. Understanding reflection in teaching: a framework for analyzing the literature. 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 93.Atkins S, Murphy K. Reflection: a review of the literature. J Adv Nurs. 1993;18(8):1188–1192. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2648.1993.18081188.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Carver CS, Scheier MF. On the self-regulation of behavior. New York: Cambridge University Press; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Grant A. The impact of life coaching on goal attainment, metacognition and mental health. Soc Behav Personal Int J. 2003;31:253–263. doi: 10.2224/sbp.2003.31.3.253. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Thorpe K. Reflective learning journals: from concept to practice. Reflective Pract. 2004;5(3):327–343. doi: 10.1080/1462394042000270655. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 97.van Manen M. The tact of teaching: the meaning of pedagogical thoughtfulness. NY: SUNY Press; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Plack MM, Driscoll M, Marquez M, Cuppernull L, Maring J, Greenberg L. Assessing reflective writing on a pediatric clerkship by using a modified Bloom’s taxonomy. Ambul Pediatr. 2007;7(4):285–291. doi: 10.1016/j.ambp.2007.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Rogers J, Peecksen S, Douglas M, Simmons M. Validation of a reflection rubric for higher education. Reflective Pract. 2019;20(6):761–776. doi: 10.1080/14623943.2019.1676712. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Makarem NN, Saab BR, Maalouf G, Musharafieh U, Naji F, Rahme D, et al. Grading reflective essays: the reliability of a newly developed tool- GRE-9. BMC Med Educ. 2020;20(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02213-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Bain J, Ballantyne R, Mills C, Lester N. Reflecting on practice: student teachers’ perspectives. 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 102.Kember D, Leung DYP, Jones A, Loke AY, McKay J, Sinclair K, et al. Development of a questionnaire to measure the level of reflective thinking. Assess Eval High Educ. 2000;25(4):381–395. doi: 10.1080/713611442. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Hatton N, Smith D. Reflection in teacher education: towards definition and implementation. Teach Teach Educ. 1995;11(1):33–49. doi: 10.1016/0742-051X(94)00012-U. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Moon JA. Reflection in learning and professional development: theory and practice. 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 105.Wald HS, Borkan JM, Taylor JS, Anthony D, Reis SP. Fostering and evaluating reflective capacity in medical education: developing the REFLECT rubric for assessing reflective writing. Acad Med. 2012;87(1):41–50. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e31823b55fa. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Stein D. Teaching critical reflection. Myths and realities no. 7. Undefined. 2000. pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- 107.Morrow E. Teaching critical reflection. Teach High Educ. 2011;16:211–223. doi: 10.1080/13562517.2010.515022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Plack MM, Driscoll M, Blissett S, McKenna R, Plack TP. A method for assessing reflective journal writing. J Allied Health. 2005;34(4):199–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Aukes LC, Geertsma J, Cohen-Schotanus J, Zwierstra RP, Slaets JP. The development of a scale to measure personal reflection in medical practice and education. Med Teach. 2007;29(2–3):177–182. doi: 10.1080/01421590701299272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Bradley J. Connecting cognition and action: evaluation of student performance in service learning courses. 1995. A model for evaluating student learning in academically based service; pp. 13–26. [Google Scholar]
- 111.Lee H-J. Understanding and assessing preservice teachers’ reflective thinking. Teach Teach Educ. 2005;21(6):699–715. doi: 10.1016/j.tate.2005.05.007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Kanthan R, Senger JL. An appraisal of students’ awareness of “self-reflection” in a first-year pathology course of undergraduate medical/dental education. BMC Med Educ. 2011;11:67. doi: 10.1186/1472-6920-11-67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Kassab SE, Bidmos M, Nomikos M, Daher-Nashif S, Kane T, Sarangi S, et al. Construct validity of an instrument for assessment of reflective writing-based portfolios of medical students. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2020;11:397–404. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S256338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Pavlovich K. The development of reflective practice through student journals. High Educ Res Dev. 2007;26(3):281–295. doi: 10.1080/07294360701494302. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Sukhato K, Sumrithe S, Wongrathanandha C, Hathirat S, Leelapattana W, Dellow A. To be or not to be a facilitator of reflective learning for medical students? A case study of medical teachers’ perceptions of introducing a reflective writing exercise to an undergraduate curriculum. BMC Med Educ. 2016;16:102. doi: 10.1186/s12909-016-0624-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Tuncer H, Özkan Y. A case study on assessing reflectivity levels of pre-service language teachers through journals. Novitas-ROYAL Res Youth Lang. 2018;12(2):173–186. [Google Scholar]
- 117.Albanese MA. Crafting the reflective lifelong learner: why, what and how. Med Educ. 2006;40(4):288–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2929.2006.02470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Ament Giuliani Franco C, Franco RS, Cecilio-Fernandes D, Severo M, Ferreira MA, de Carvalho-Filho MA. Added value of assessing medical students’ reflective writings in communication skills training: a longitudinal study in four academic centres. BMJ Open. 2020;10(11):e038898. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-038898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Embo MP, Driessen E, Valcke M, Van Der Vleuten CP. Scaffolding reflective learning in clinical practice: a comparison of two types of reflective activities. Med Teach. 2014;36(7):602–607. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2014.899686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Kasman DL. “Doctor, are you listening?” A writing and reflection workshop. Fam Med. 2004;36(8):549–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Locher M, Koenig R, Meier J. Narrative matters in medical contexts across disciplines. Amsterdam: John Benjamins; 2015. A genre analysis of reflective writing texts by English medical students; pp. 141–164. [Google Scholar]
- 122.Miller Juve AK, Kirsch JR. Does participation in written guided reflective practice exercises affect readiness for self-directed learning in a sample of US anesthesiology residents? J Educ Perioper Med. 2019;21(2):E622. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Krueger RB, Sweetman MM, Martin M, Cappaert TA. Self-reflection as a support to evidence-based practice: a grounded theory exploration. Occup Ther Health Care. 2020;34(4):320–350. doi: 10.1080/07380577.2020.1815929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Wegner C, Remmert K, Ohlberger S. Evaluation of a wiki for lesson reflection in the project “Kolumbus-Kids” at Bielefeld University. Electron J Sci Educ. 2017;21(4):1–40. [Google Scholar]
- 125.Too WK. Facilitating the development of pre-service teachers as reflective learners: a Malaysian experience. Lang Learn J. 2013;41(2):161–174. doi: 10.1080/09571736.2013.790131. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Tsingos C, Bosnic-Anticevich S, Lonie JM, Smith L. A model for assessing reflective practices in pharmacy education. Am J Pharm Educ. 2015;79(8):124. doi: 10.5688/ajpe798124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Eriksen M. Facilitating authentic becoming. J Manag Educ. 2012;36(5):698–736. doi: 10.1177/1052562911423883. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Henderson E, Berlin A, Freeman G, Fuller J. Twelve tips for promoting significant event analysis to enhance reflection in undergraduate medical students. 2002. pp. 121–124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Rosenbaum ME, Lobas J, Ferguson K. Using reflection activities to enhance teaching about end-of-life care. J Palliat Med. 2005;8(6):1186–1195. doi: 10.1089/jpm.2005.8.1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Bernard AW, Gorgas D, Greenberger S, Jacques A, Khandelwal S. The use of reflection in emergency medicine education. Acad Emerg Med. 2012;19(8):978–982. doi: 10.1111/j.1553-2712.2012.01407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Nagano H, Obara H, Takayama Y. A brief home-based palliative care learning experience for medical students and resident doctors in Okinawa, Japan. PLoS One. 2019;14(6):e0218780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0218780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Zhu X. Student teachers’ reflection during practicum: plenty on action, few in action. Reflective Pract. 2011;12(6):763–775. doi: 10.1080/14623943.2011.601097. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Jamil FM, Hamre BK. Teacher reflection in the context of an online professional development course: applying principles of cognitive science to promote teacher learning. Action Teach Educ. 2018;40(2):220–236. doi: 10.1080/01626620.2018.1424051. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Larsen DP, London DA, Emke AR. Using reflection to influence practice: student perceptions of daily reflection in clinical education. Perspect Med Educ. 2016;5(5):285–291. doi: 10.1007/s40037-016-0293-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Naeger DM, Hua EW, Ahearn B, Webb EM. Reflective writing: a potential tool to improve interprofessional teamwork with radiologists. Acad Radiol. 2015;22(10):1221–1225. doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2015.07.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Raut AV, Gupta SS. Reflection and peer feedback for augmenting emotional intelligence among undergraduate students: a quasi-experimental study from a rural medical college in central India. Educ Health (Abingdon) 2019;32(1):3–10. doi: 10.4103/efh.EfH_31_17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Spector-Mersel G. Life story reflection in social work education: a practical model. J Soc Work Educ. 2017;53(2):286–299. doi: 10.1080/10437797.2016.1243498. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Martin M. Reflection in teacher education: how can it be supported? Educ Action Res. 2005;13(4):525–542. doi: 10.1080/09650790500200343. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Thomas PA, Goldberg H. Tracking reflective practice-based learning by medical students during an ambulatory clerkship. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22(11):1583–1586. doi: 10.1007/s11606-007-0315-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Kitchen M. Junior doctors’ guide to portfolio learning and building. Clin Teach. 2012;9(5):308–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-498X.2012.00544.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Shoffner M. Informal reflection in pre-service teacher education. Reflective Pract. 2008;9(2):123–134. doi: 10.1080/14623940802005392. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Adams CL, Nestel D, Wolf P. Reflection: a critical proficiency essential to the effective development of a high competence in communication. J Vet Med Educ. 2006;33(1):58–64. doi: 10.3138/jvme.33.1.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Moniz T, Arntfield S, Miller K, Lingard L, Watling C, Regehr G. Considerations in the use of reflective writing for student assessment: issues of reliability and validity. Med Educ. 2015;49(9):901-8. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 144.Ottenberg AL, Pasalic D, Bui GT, Pawlina W. An analysis of reflective writing early in the medical curriculum: the relationship between reflective capacity and academic achievement. Med Teach. 2016;38(7):724–729. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2015.1112890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Miller-Kuhlmann R, O'Sullivan PS, Aronson L. Essential steps in developing best practices to assess reflective skill: A comparison of two rubrics. Med Teach. 2016;38(1):75-81. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 146.Khanna R, Singh RK, Singhal R. Reflective learning for behavioral guidance in pediatric dentistry. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2020;38(3):293–303. doi: 10.4103/JISPPD.JISPPD_33_20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Abdullah M. Promoting reflective thinking skills by using web 2.0 application. Online Submission. 2015:1–15.
- 148.Ballon BC, Skinner W. “Attitude is a little thing that makes a big difference”: reflection techniques for addiction psychiatry training. Acad Psychiatry. 2008;32(3):218–224. doi: 10.1176/appi.ap.32.3.218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Brown A, Jauregui J, Ilgen JS, Riddell J, Schaad D, Strote J, et al. Does the medium matter? Evaluating the depth of reflective writing by medical students on social media compared to the traditional private essay using the REFLECT rubric. West J Emerg Med. 2020;21(1):18–25. doi: 10.5811/westjem.2019.11.44263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Chuang LL, Liu HW, Lin YC, Wang YW, Chu SY. Using structured narrative to help a medical student reflect on an unexpected clinical situation. Tzu Chi Med J. 2013;25(1):68–70. doi: 10.1016/j.tcmj.2012.05.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Goldman JDG, Grimbeek P. Pre-service primary school teachers’ self-reflective competencies in their own teaching. Eur J Psychol Educ. 2015;30(2):189–207. doi: 10.1007/s10212-014-0231-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Liu GZ, Jawitz OK, Zheng D, Gusberg RJ, Kim AW. Reflective writing for medical students on the surgical clerkship: oxymoron or antidote? J Surg Educ. 2016;73(2):296–304. doi: 10.1016/j.jsurg.2015.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Sellheim D, Weddle M. Using a collaborative course reflection process to enhance faculty and curriculum development. Coll Teach. 2015;63(2):52–61. doi: 10.1080/87567555.2015.1005039. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Shiozawa T, Glauben M, Banzhaf M, Griewatz J, Hirt B, Zipfel S, et al. An insight into professional identity formation: qualitative analyses of two reflection interventions during the dissection course. Anat Sci Educ. 2020;13(3):320–332. doi: 10.1002/ase.1917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Shaughnessy AF, Allen L, Duggan A. Attention without intention: explicit processing and implicit goal-setting in family medicine residents’ written reflections. Educ Prim Care. 2017;28(3):150–156. doi: 10.1080/14739879.2016.1278562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Vicini A, Shaughnessy AF, Duggan AP. Cultivating the inner life of a physician through written reflection. Ann Fam Med. 2017;15(4):379–381. doi: 10.1370/afm.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Bruno A, Dell'Aversana G. Reflective practice for psychology students: the use of reflective journal feedback in higher education. Psychol Learn Teach. 2017;16(2):248–260. doi: 10.1177/1475725716686288. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 158.DasGupta S, Charon R. Personal illness narratives: using reflective writing to teach empathy. Acad Med. 2004;79(4):351–356. doi: 10.1097/00001888-200404000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Etscheidt S, Curran CM, Sawyer CM. Promoting reflection in teacher preparation programs: a multilevel model. Teach Educ Spec Educ. 2012;35(1):7–26. doi: 10.1177/0888406411420887. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Eutsler L, Curcio R. Private blog reflections connecting course content with field experiences: preservice teachers grapple with teacher identity. Reflective Pract. 2019;20(2):250–265. doi: 10.1080/14623943.2019.1586663. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Freeman M. Reflective logs: an aid to clinical teaching and learning. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2001;36(Suppl):411–416. doi: 10.3109/13682820109177921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Wetmore AO, Boyd LD, Bowen DM, Pattillo RE. Reflective blogs in clinical education to promote critical thinking in dental hygiene students. J Dent Educ. 2010;74(12):1337–1350. doi: 10.1002/j.0022-0337.2010.74.12.tb05009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Young MR. Reflection fosters deep learning: the ‘reflection page & relevant to you’ intervention. J Instr Pedagog. 2018;20:1–17. [Google Scholar]
- 164.Zoellner BP, Chant RH, Lee K. Do we do Dewey? Using a dispositional framework to examine reflection within internship professional development plans. Teach Educ. 2017;52(3):203–221. doi: 10.1080/08878730.2017.1316623. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Peterkin A, Roberts M, Kavanagh L, Havey T. Narrative means to professional ends: new strategies for teaching CanMEDS roles in Canadian medical schools. Can Fam Physician. 2012;58(10):e563–e569. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Pavlovich K, Collins E, Jones G. Developing students’ skills in reflective practice: design and assessment. J Manag Educ. 2009;33(1):37–58. doi: 10.1177/1052562907307640. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Janson C, Filibert S. Discursive digital reflection: a method for enhancing supervision and training. References. 2018;2:200–212. [Google Scholar]
- 168.Glassburn S, McGuire LE, Lay K. Reflection as self-care: models for facilitative supervision. Reflective Pract. 2019;20(6):692–704. doi: 10.1080/14623943.2019.1674271. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Fischer MA, Haley HL, Saarinen CL, Chretien KC. Comparison of blogged and written reflections in two medicine clerkships. Med Educ. 2011;45(2):166–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2923.2010.03814.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Grant A, Kinnersley P, Metcalf E, Pill R, Houston H. Students’ views of reflective learning techniques: an efficacy study at a UK medical school. Med Educ. 2006;40(4):379–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2929.2006.02415.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Hargreaves K. Reflection in medical education. J Univ Teach Learn Pract. 2016;13(2):1–21. [Google Scholar]
- 172.Wald HS, Reis SP, Monroe AD, Borkan JM. ‘The loss of my elderly patient:’ interactive reflective writing to support medical students’ rites of passage. Med Teach. 2010;32(4):e178–e184. doi: 10.3109/01421591003657477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Hulsman RL, Harmsen AB, Fabriek M. Reflective teaching of medical communication skills with DiViDU: assessing the level of student reflection on recorded consultations with simulated patients. Patient Educ Couns. 2009;74(2):142–149. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2008.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Karnieli-Miller O, Palombo M, Meitar D. See, reflect, learn more: qualitative analysis of breaking bad news reflective narratives. Med Educ. 2018;52(5):497–512. doi: 10.1111/medu.13582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Stephens MB, Reamy BV, Anderson D, Olsen C, Hemmer PA, Durning SJ, et al. Writing, self-reflection, and medical school performance: the human context of health care. Mil Med. 2012;177(9 Suppl):26–30. doi: 10.7205/MILMED-D-12-00235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Biggerstaff MA. Social work ethics online: reflective learning. J Technol Hum Serv. 2005;23(3–4):245–257. doi: 10.1300/J017v23n03_06. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Campbell BH, Treat R, Johnson B, Derse AR. Creating reflective space for reflective and “unreflective” medical students: exploring seminal moments in a large-group writing session. Acad Med. 2020;95(6):882–887. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000003241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Coulehan J, Granek IA. Commentary: “I hope I’ll continue to grow”: rubrics and reflective writing in medical education. Acad Med. 2012;87(1):8–10. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e31823a98ba. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.McGuire L, Lay K, Peters J. Pedagogy of reflective writing in professional education. J Scholarsh Teach Learn. 2009;9(1):93–107. [Google Scholar]
- 180.Nurulhuda MH, Siti Norazlina J, Harmy MY, Norwati D, Hassan Basri M. Enhancing reflective writing through e-learning in undergraduate medical education. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 181.Herrick-Reynolds K, Sewanan LR, Zheng DJ, Wang P, Encandela J, Shahu A, et al. A novel near-peer reflective writing workshop. Clin Teach. 2019;16(4):339–344. doi: 10.1111/tct.13057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Devi V, Abraham RR, Kamath U. Teaching and assessing reflecting skills among undergraduate medical students experiencing research. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017;11(1):Jc01–Jjc5. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/20186.9142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Vivekananda-Schmidt P, Marshall M, Stark P, McKendree J, Sandars J, Smithson S. Lessons from medical students’ perceptions of learning reflective skills: a multi-institutional study. Med Teach. 2011;33(10):846–850. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2011.577120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Grierson L, Winemaker S, Taniguchi A, Howard M, Marshall D, Zazulak J. The reliability characteristics of the REFLECT rubric for assessing reflective capacity through expressive writing assignments: a replication study. Perspect Med Educ. 2020;9(5):281–285. doi: 10.1007/s40037-020-00611-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Charon R, Hermann N, Devlin MJ. Close reading and creative writing in clinical education: teaching attention, representation, and affiliation. Acad Med. 2016;91(3):345–350. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000000827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Coward M. Does the use of reflective models restrict critical thinking and therefore learning in nurse education? What have we done? Nurse Educ Today. 2011;31(8):883–886. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2011.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Dyke M. The role of the “other” in reflection, knowledge formation and action in a late modernity. Int J Lifelong Educ. 2006;25(2):105–123. doi: 10.1080/02601370500510728. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Nguyen QD, Fernandez N, Karsenti T, Charlin B. What is reflection? A conceptual analysis of major definitions and a proposal of a five-component model. Med Educ. 2014;48(12):1176–1189. doi: 10.1111/medu.12583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Shaw R. A model of the transformative journey into reflexivity: an exploration into students’ experiences of critical reflection. Reflective Pract. 2013;14(3):319–335. doi: 10.1080/14623943.2013.767229. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Xiao Q, Zhu P, Hsu MK, Zhuang W, Peltier J. Reflective learning in a Chinese MBA Programme: scale assessment and future recommendations. J Furth High Educ. 2016;40(1):1–22. doi: 10.1080/0309877X.2013.869563. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Yakov G, Riskin A, Flugelman AA. Mechanisms involved in the formation of professional identity by medical students. Med Teach. 2021;43(4):428–438. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2020.1854706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Tan XH, Foo MA, Lim SLH, Lim MBXY, Chin AMC, Zhou J, et al. Teaching and assessing communication skills in the postgraduate medical setting: a systematic scoping review. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):483. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02892-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Baldwin K, Lucas B. Promoting reflective practice skills for postgraduate GPs: do journals aid journeys? Educ Prim Care. 2012;23(3):213–216. doi: 10.1080/14739879.2012.11923899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Chretien KC, Chheda SG, Torre D, Papp KK. Reflective writing in the internal medicine clerkship: a national survey of clerkship directors in internal medicine. Teach Learn Med. 2012;24(1):42–48. doi: 10.1080/10401334.2012.641486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.McGlinn EP, Chung KC. A pause for reflection: incorporating reflection into surgical training. Ann Plast Surg. 2014;73(2):117–120. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000000295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Bjerkvik LK, Hilli Y. Reflective writing in undergraduate clinical nursing education: a literature review. Nurse Educ Pract. 2019;35:32–41. doi: 10.1016/j.nepr.2018.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Olex AL, DiazGranados D, McInnes BT, Goldberg S. Local topic mining for reflective medical writing. AMIA Summits Transl Sci Proc. 2020;2020:459. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Winkel AF, Yingling S, Jones AA, Nicholson J. Reflection as a learning tool in graduate medical education: a systematic review. J Grad Med Educ. 2017;9(4):430–439. doi: 10.4300/JGME-D-16-00500.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Carr S, Carmody D. Experiential learning in women’s health: medical student reflections. Med Educ. 2006;40(8):768–774. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2929.2006.02536.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Shapiro J, Kasman D, Shafer A. Words and wards: a model of reflective writing and its uses in medical education. J Med Humanit. 2006;27(4):231–244. doi: 10.1007/s10912-006-9020-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Dreyer A, Mlambo M, Mapukata-Sondzaba N. Medical students using the technique of 55-word stories to reflect on a 6-week rotation during the integrated primary care block. Afr J Health Prof Educ. 2021;13(2):135–139. doi: 10.7196/AJHPE.2021.v13i2.1332. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Malau-Aduli BS, Jones K, Smith AM, Sen Gupta T, Hays RB. Understanding medical students’ transformative experiences of early preclinical international rural placement over a 20-year period. BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):652. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03707-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Liao K-C, Peng C-H, Snell L, Wang X, Huang C-D, Saroyan A. Understanding the lived experiences of medical learners in a narrative medicine course: a phenomenological study. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02741-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Bracken RC, Major A, Paul A, Ostherr K. Reflective writing about near-peer blogs: a novel method for introducing the medical humanities in premedical education. J Med Humanit. 2021;42(4):535–569. doi: 10.1007/s10912-021-09693-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Kind T, Everett VR, Ottolini M. Learning to connect: students’ reflections on doctor-patient interactions. Patient Educ Couns. 2009;75(2):149–154. doi: 10.1016/j.pec.2008.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Piumatti G, Guttormsen S, Zurbuchen B, Abbiati M, Gerbase MW, Baroffio A. Trajectories of learning approaches during a full medical curriculum: impact on clinical learning outcomes. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):370. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02809-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Smith E. Teaching critical reflection. Teach High Educ. 2011;16(2):211–223. doi: 10.1080/13562517.2010.515022. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Talarico S, Zubairi M, Daneman D, Punnett A, Martimianakis MAT. Fostering transformative learning in a social pediatrics research summer studentship. Acad Med. 2019;94(5):692–696. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000002597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Cox E. Adult learners learning from experience: using a reflective practice model to support work-based learning. Reflective Pract. 2005;6(4):459–472. doi: 10.1080/14623940500300517. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Yaylaci S, Ulman YI, Vatansever K, Senyurek G, Turkmen S, Aldinc H, et al. Integrating patient management, reflective practice, and ethical decision-making in an emergency medicine intern boot camp. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):536. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02970-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Williams E, Jarrell JA, Rubenstein J. A week in the life: pediatric palliative care through the eyes of a medical student. Children (Basel) 2021;8(11):971. doi: 10.3390/children8110971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Dhaliwal U, Singh S, Singh N. Reflective student narratives: honing professionalism and empathy. Indian J Med Ethics. 2018;3(1):9–15. doi: 10.20529/IJME.2017.069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Janssen F, de Hullu E, Tigelaar D. Using a domain-specific model to improve student teachers’ reflections on positive teaching experiences. Action Teach Educ. 2009;31(2):86–98. doi: 10.1080/01626620.2009.10463520. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Curtis P, Gorolay S, Curtis A, Harris M. What do general practitioners think of written reflection? A focus group study. Educ Prim Care. 2016;27(4):292–298. doi: 10.1080/14739879.2016.1185747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Dalsgaard C. Reflective mediation: toward a sociocultural conception of situated reflection. Frontline Learn Res. 2020;8(1):1–13. doi: 10.14786/flr.v8i1.447. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Sheikh F, Gathecha E, Arbaje AI, Christmas C. Internal medicine residents’ views about care transitions: results of an educational intervention. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2021;8:2382120520988590. doi: 10.1177/2382120520988590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Tashiro J, Shimpuku Y, Naruse K, Maftuhah, Matsutani M. Concept analysis of reflection in nursing professional development. Jpn. J Nurs Sci. 2013;10(2):170–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-7924.2012.00222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Vettraino E, Linds W, Downie H. Embodied reflexivity: discerning ethical practice through the six-part story method. Reflective Pract. 2019;20(2):218–233. doi: 10.1080/14623943.2019.1575197. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Standal Ø, Rugseth G. Practicum in adapted physical activity: a Dewey-inspired action research project. Adapt Phys Act Q. 2014;31(3):219–239. doi: 10.1123/apaq.2013-0105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Ekebergh M. Lifeworld-based reflection and learning: a contribution to the reflective practice in nursing and nursing education. Reflective Pract. 2007;8(3):331–343. doi: 10.1080/14623940701424835. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Farrell TSC. Reflecting on reflective practice: (re)visiting Dewey and Schon. TESOL J. 2012;3(1):7–16. doi: 10.1002/tesj.10. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Curtis P, Taylor G, Riley R, Pelly T, Harris M. Written reflection in assessment and appraisal: GP and GP trainee views. Educ Prim Care. 2017;28(3):141–149. doi: 10.1080/14739879.2016.1277168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Cunningham H, Taylor DS, Desai UA, Ender KL, Glickstein J, Krishnan US, et al. Reading the self: medical students’ experience of reflecting on their writing over time. Acad Med. 2021;96(8):1168–1174. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000003814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Asselin ME. Reflective narrative: a tool for learning through practice. J Nurses Staff Dev. 2011;27(1):2–6. doi: 10.1097/NND.0b013e3181b1ba1a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Smith J. Sailing through social LA GRRAACCEESS: tool for deconstructing and facilitating reflective and reflexive practice. Reflective Pract. 2016;17(5):570–582. doi: 10.1080/14623943.2016.1184634. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Hudson JN, Rienits H, Corrin L, Olmos M. An innovative OSCE clinical log station: a quantitative study of its influence on Log use by medical students. BMC Med Educ. 2012;12:111. doi: 10.1186/1472-6920-12-111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Song P, Stewart R. Reflective writing in medical education. Med Teach. 2012;34(11):955–956. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2012.716552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Jackson P. Understanding the experience of experience: a practical model of reflective practice for Coaching. International Journal of Evidence Based Coaching and Mentoring. 2004;2(1):57–67.
- 229.Meilijson S, Katzenberger I. A clinical education program for speech-language pathologists applying reflective practice, evidence-based practice and case-based learning. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2017;66(4–5):158–163. doi: 10.1159/000366275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Shaughnessy AF, Duggan AP. Family medicine residents’ reactions to introducing a reflective exercise into training. Educ Health (Abingdon) 2013;26(3):141–146. doi: 10.4103/1357-6283.125987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Boudreau JD, Liben S, Fuks A. A faculty development workshop in narrative-based reflective writing. Perspect Med Educ. 2012;1(3):143–154. doi: 10.1007/s40037-012-0021-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Rees CE, Shepherd M, Chamberlain S. The utility of reflective portfolios as a method of assessing first year medical students’ personal and professional development. Reflective Pract. 2005;6(1):3–14. doi: 10.1080/1462394042000326770. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Glod SA, Richard D, Gordon P, Fecile ML, Kees-Folts D, Kreher M, et al. A curriculum for clerkship students to foster professionalism through reflective practice and identity formation. MedEdPORTAL. 2016;12:10416. doi: 10.15766/mep_2374-8265.10416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Pieters J, Verstegen DML, Dolmans DHJM, Warmenhoven FC, van den Beuken-van Everdingen MHJ. Design and evaluation of a learning assignment in the undergraduate medical curricula on the four dimensions of care: a mixed method study. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02681-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 235.Driessen EW, van Tartwijk J, Overeem K, Vermunt JD, van der Vleuten CP. Conditions for successful reflective use of portfolios in undergraduate medical education. Med Educ. 2005;39(12):1230–1235. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2929.2005.02337.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Prosser M, Stephenson T, Mathur J, Enayati H, Kadie A, Abdi MM, et al. Reflective practice and transcultural psychiatry peer e-learning between Somaliland and the UK: a qualitative evaluation. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02465-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Hayton A, Kang I, Wong R, Loo LK. Teaching medical students to reflect more deeply. Teach Learn Med. 2015;27(4):410–416. doi: 10.1080/10401334.2015.1077124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Roberts P. Reflection: a renewed and practical focus for an existing problem in teacher education. Aust J Teach Educ. 2016;41(7):19–35. doi: 10.14221/ajte.2016v41n7.2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Soemantri D, Mustika R, Greviana N. Inter-rater reliability of reflective-writing assessment in an undergraduate professionalism course in medical education. Educ Med J. 2022;14(1).
- 240.Reynolds M. Reflective practice: origins and interpretations, Action Learning: Research and Practice. 2011;8(1):5–13.
- 241.Warner R, Picard M. What do Master’s students’ structured reflections say about the learning processes involved in commencing a research project? J Univ Teach Learn Pract. 2020;17(1):7. [Google Scholar]
- 242.Collin S, Karsenti T, Komis V. Reflective practice in initial teacher training: critiques and perspectives. Reflective Pract. 2013;14(1):104–117. doi: 10.1080/14623943.2012.732935. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Rajhans V, Eichler R, Sztrigler Cohen O, Gordon-Shaag A. A novel method of enhancing students’ involvement in reflective writing. Clin Teach. 2021;18(2):174–179. doi: 10.1111/tct.13303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Goodyear HM, Bindal T, Wall D. How useful are structured electronic portfolio templates to encourage reflective practice? Med Teach. 2013;35(1):71–73. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2012.732246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 245.Tawanwongsri W, Phenwan T. Reflective and feedback performances on Thai medical students’ patient history-taking skills. BMC Med Educ. 2019;19(1):141. doi: 10.1186/s12909-019-1585-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Mohammadi E, Mirzazadeh A, Shahsavari H, Sohrabpour AA. Clinical teachers’ perceptions of role modeling: a qualitative study. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02648-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Hastami Y, Claramita M, Suryadi E. Reflective writing skills of undergraduate medical students. eJournal Kedokteran Indonesia. 2018;6(2):97-104.
- 248.Swan Sein A, Rashid H, Meka J, Amiel J, Pluta W. Twelve tips for embedding assessment for and as learning practices in a programmatic assessment system. Med Teach. 2021;43(3):300–306. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2020.1789081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Sternlieb JL. A guide to introducing and integrating reflective practices in medical education. Int J Psychiatry Med. 2015;49(1):95–105. doi: 10.2190/PM.49.1.g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Sieben JM, Heeneman S, Verheggen MM, Driessen EW. Can concept mapping support the quality of reflections made by undergraduate medical students? A mixed method study. Med Teach. 2021;43(4):388–396. doi: 10.1080/0142159X.2020.1834081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Tan R, Qi Ting JJ, Zhihao Hong D, Sing Lim AJ, Ong YT, Pisupati A, et al. Medical student portfolios: a systematic scoping review. J Med Educ Curric Dev. 2022;9:23821205221076022. doi: 10.1177/23821205221076022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Ong RSR, Wong RSM, Chee RCH, Quek CWN, Burla N, Loh CYL, et al. A systematic scoping review moral distress amongst medical students. BMC Med Educ. 2022;22(1):466. doi: 10.1186/s12909-022-03515-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Schaepkens SPC, Veen M, de la Croix A. Is reflection like soap? a critical narrative umbrella review of approaches to reflection in medical education research. Adv Health Sci Educ Theory Pract. 2022;27(2):537–51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 254.Merlo G, Ryu H, Harris TB, Coverdale J. MPRO: a professionalism curriculum to enhance the professional identity formation of university premedical students. Med Educ Online. 2021;26(1):1886224. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2021.1886224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Whipp JL. Scaffolding critical reflection in online discussions: helping prospective teachers think deeply about field experiences in urban schools. J Teach Educ. 2003;54(4):321–333. doi: 10.1177/0022487103255010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Artioli G, Deiana L, De Vincenzo F, Raucci M, Amaducci G, Bassi MC, et al. Health professionals and students’ experiences of reflective writing in learning: a qualitative meta-synthesis. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):394. doi: 10.1186/s12909-021-02831-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.Sagin A, Ellman MS, Shariff RR, Jones CA, Tindall K, Siropaides CH. A multicenter qualitative analysis of medical student narratives after a palliative care elective. Am J Hosp Palliat Care. 2021;38(9):1126–1134. doi: 10.1177/1049909120971565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Park KH, Kam BS, Yune SJ, Lee SY, Im SJ. Changes in self-reflective thinking level in writing and educational needs of medical students: a longitudinal study. PLoS One. 2022;17(1):e0262250. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Rozental L, Meitar D, Karnieli-Miller O. Medical students’ experiences and needs from written reflective journal feedback. Med Educ. 2021;55(4):505–517. doi: 10.1111/medu.14406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1. Guide to Reflective Writing.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analysed during this review are included in this published article and its supplementary files.