Abstract
Metabolism is intimately linked to aging. There is a growing number of studies showing that endogenous metabolites may delay aging and improve healthspan. Through the analysis of existing transcriptome data, we discover a link between activation of the transsulfuration pathway and a transcriptional program involved in peroxisome function and biogenesis in long-lived glp-1(e2141ts) mutant Caenorhabditis elegans worms. Subsequently, we show that supplementation with α-ketobutyrate, an intermediate of the transsulfuration pathway, extends lifespan in wild-type worms. Alpha-ketobutyrate augments the production of NAD+ via the lactate dehydrogenase LDH-1, leading to SIR-2.1/SIRT1-mediated enhanced peroxisome function and biogenesis, along with a concomitant increase in the expression of acox-1.2/ACOX1 in the peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation pathway. ACOX-1.2/ACOX1 promotes H2O2 formation, thereby resulting in activation of SKN-1/NRF2. This transcription factor in turn extends the lifespan of worms by driving expression of autophagic and lysosomal genes. Finally, we show that α-ketobutyrate also delays the cellular senescence in fibroblast cells through the SIRT1-ACOX1-H2O2-NRF2 pathway. This finding uncovers a previously unknown role for α-ketobutyrate in organismal lifespan and healthspan by coordinating the NAD+-SIRT1 signaling and peroxisomal function.
Subject terms: Senescence, Autophagy, Peroxisomes
Understanding how metabolites modulate longevity is crucial for reducing aging-related disease. Here, the authors demonstrate that α-ketobutyrate exhibits an anti-aging effect by coordinating NAD + -SIRT1 signaling and peroxisome function.
Introduction
The transsulfuration pathway (TSP) is an evolutionarily conserved pathway that commits methionine to cysteine synthesis in metazoan1–3. There are two key enzymes, cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) and cystathionase (CTH, also called cystathionine γ-lyase, GCL), in this pathway. CBS converts serine and homocysteine into cystathionine, while CTH catalyzes the elimination of cystathionine to form cysteine and α-ketobutyrate (α-KB)1,2. Both CBS and CTH catalyze the production of a gas hydrogen sulfide (H2S) via condensation of cysteine and homocysteine, and desulfhydration of cysteine, respectively2,4. In the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster and the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, overexpression of CBS extends lifespan, which is probably due to increased H2S production4,5. As a product of TSP, H2S can function as a signaling molecule to extend lifespan and improve healthspan4,6,7. Although the underlying mechanism remains unknown, supplementation with NaHS, a compound that can produce H2S, increases the NAD+ levels in mammalian cells8. It has been well-established that elevation of intracellular NAD+ levels by supplementation of NAD+ precursors such as nicotinamide mononucleotide (NAM) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), or activation of the de novo NAD+ synthesis pathway, promotes healthspan and extends lifespan via a mechanism requiring SIRT1/SIR-2.1 across species from worms to mammals9–12. However, the role of α-KB, another product of TSP, in the regulation of longevity remains unknown.
In C. elegans, glp-1 encodes a Notch receptor crucial for the regulation of the germline stem cell pool13. The germline can be removed by blocking germline stem-cell proliferation with the temperature-sensitive (ts) glp-1(e2144ts) mutation14,15. The germ-cell loss extends C. elegans lifespan through activating transcription factors such as DAF-16/FOXO and SKN-1/NRF2 and nuclear hormone receptors such as DAF-12 and NHR-8014–22. Interestingly, the levels of H2S production are also elevated, which is mediated by reactive oxygen species (ROS) derived from mitochondria, in the germline-deficient glp-1(e2141ts) mutants. H2S promotes the nuclear translocation of SKN-1, thereby extending lifespan in the germline-deficient worms15. Besides glp-1(e2141ts) mutants, ROS levels are elevated in respiration mutants, such as clk-1(qm30), isp-1(qm150), and nuo-6(qm200) mutants, which are responsible for longevity extension by increasing the activity of hypoxia-inducible factor HIF-123,24. Meanwhile, lifespan is extended in response to increased levels of ROS through treatment with 2-deoxyglucose or a low dosage of the oxidant paraquat in worms25–27. These data suggest that ROS act as signaling molecules to regulate lifespan.
By analyzing existing transcriptome data of long-lived glp-1(e2141ts) mutants in two independent studies (GSE43864 and GSE63075)20,28, we observed an upregulation of a set of peroxisome-related genes, which are involved in peroxisomal biogenesis, peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation, and amino acid metabolism. These data implicate a role of enhanced peroxisomal function in lifespan extension in germline-deficient worms. As a representative of highly plastic organelles, peroxisomes are capable of modifying their size, abundance, and morphology in response to cellular or environmental cues29. The peroxisome has been implicated in aging and longevity regulation30–33, yet the exact role and mechanism of action of peroxisome in longevity are far from fully elucidated.
In this study, we demonstrated that the levels of α-KB, another product of TSP, were elevated in germline-deficient glp-1(e2141ts) mutants. Supplementation with α-KB promoted peroxisome biogenesis, leading to an increase in H2O2 production, in an NAD+-SIRT1 signal-dependent manner. H2O2, in turn, induced autophagy via SKN-1/NRF2, thereby extending lifespan in the germline-deficient animals. Finally, our data demonstrated that α-KB treatment reduced cellular senescence in mammalian cells. These findings provide novel pharmacological approaches to prevent age-related physiological decline.
Results
Alpha-KB extends the lifespan in worms
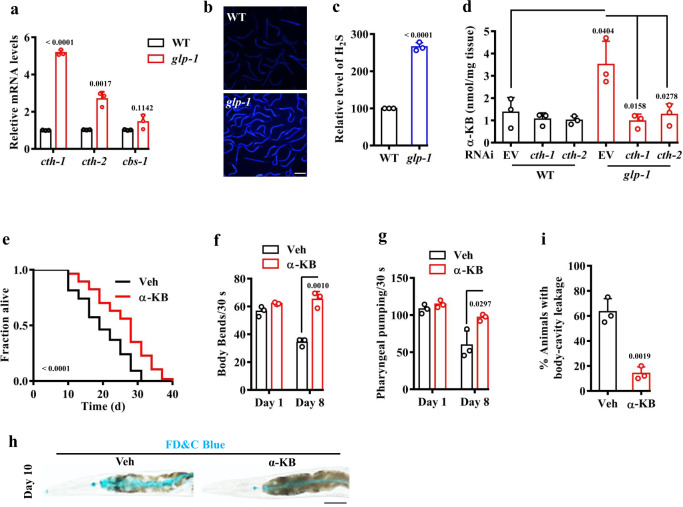
We analyzed the transcriptome data of glp-1(e2141ts) mutants in two independent studies20,28, and identified that there were 3208 overlapped genes upregulated between the two datasets (Supplementary Fig. 1a), including the major genes in TSP, such as cth-1, cth-2, and cbs-1 (Supplementary Fig. 1b). These results implicate that TSP is activated in germline-deficient worms. To assess whether TSP is activated in germline-deficient glp-1(e2141ts) mutants, we first determined the expressions of cbs-1, cth-1, and cth-2, the major genes in TSP4,7. Using qPCR, we found that the expressions of cth-1, and cth-2, but not cbs-1, were markedly upregulated in germline-deficient animals (Fig. 1a). Previously, we developed a fluorescent chemodosimeter for monitoring endogenous H2S in mammalian cells, flies and worms34. Using the fluorescent probe, we found that the relative levels of H2S were significantly increased in germline-deficient animals (Fig. 1b, c), which was consistent with a previous study15. These data suggest that TSP is activated in germline-deficient worms. We then asked whether another product of TSP, α-KB, which is derived from the elimination of cystathionine catalyzed by CTH2,3, was elevated in these animals. Using LC-MS, we found that the levels of α-KB were significantly increased in germline-deficient mutants, compared with those in wild-type (WT) worms (Fig. 1d). RNAi knockdown of either cth-1 or cth-2 reduced the levels of α-KB in germline-deficient worms back to those of WT worms (Fig. 1d).
Fig. 1. Alpha-KB promotes lifespan in worms.
a The mRNA levels of cth-1 and cth-2, but not cbs-1, were upregulated in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants, compared with those in wild-type (WT) worms. These results are means ± SD of three independent experiments. b, c Representative images of H2S formation detected by a fluorescent probe. A similar pattern of H2S formation was observed in three independent experiments. Scale bars: 500 μm. c Quantification of fluorescent intensity in b. The content of H2S was increased in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants, compared with that in WT worms. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 35 worms per experiment). P values (a, c) were calculated using the two-sample t-test. d The levels of α-ketobutyrate (α-KB) were increased in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants, compared with that in WT worms. RNAi knockdown of either cth-1 or cth-2 reduced the contents of α-KB in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants back to those of WT worms. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments. e Supplementation with α-KB (500 μM) extended lifespan in WT worms. Veh vehicle. P value was calculated using a log-rank test. See survival statistics in Supplementary Data 1. f–i Supplementation with α-KB delayed the appearance of the aging markers, including pharyngeal pumping (f), body bending (g), and body-cavity leakages (h, i) in WT worms. Scale bars: 500 μm. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 25 worms per experiment). P values (d, f, g, i) were calculated using a one-way ANOVA followed by a Student–Newman–Keuls test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
A previous study has demonstrated that the knockdown of cth-2 does not affect the lifespan of WT animals35. Likewise, the cth-1(ok3319) mutants do not exhibit an overall significantly shorter maximal lifespan although these animals initially display a much higher death rate36. Consistent with these observations, we found that RNAi knockdown of either cth-1 or cth-2 did not alter the lifespan of WT worms (Supplementary Fig. 2a, b and Supplementary Data 1). However, RNAi knockdown of either cth-1 or cth-2 shortened the lifespan of germline-deficient worms (Supplementary Fig. 2a, b). Although supplementation with α-KB did not further extend the lifespan of germline-deficient worms, it partially restored the lifespan of germline-deficient worms subjected to cth-1 or cth-2 RNAi (Supplementary Fig. 2a, b). In addition, we determined the effect of α-KB supplementation on lifespan in other three longevity pathways: DR (the feeding deficient mutant eat-2), reduced insulin/IGF-1 signaling (the receptor mutant daf-2), reduced mitochondrial respiration (the mitochondrial complex III mutant isp-1). We found that supplementation with α-KB could extend the lifespan of eat-2(ad1116), but not isp-1(qm150) and daf-2(e1370) (Supplementary Fig. 3a–c and Supplementary Data 1).
Considering both CTH-1 and CTH-2 are H2S-producing enzymes1,2, we tested the combined effects of α-KB and H2S. Like α-KB, supplementation with NaHS (300 μM) also partially restored the lifespan of glp-1(e2141ts) mutants subjected to either cth-1 or cth-2 RNAi (Supplementary Fig. 2a, b). However, supplementation with both α-KB and NaHS did fully restore the lifespan of glp-1(e2141ts) mutants subjected to either cth-1 or cth-2 RNAi (Supplementary Fig. 2a, b). These results indicate that the upregulation of either cth-1 or cth-2 contributes to lifespan extension in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants via both α-KB and H2S.
Next, we investigated the effect of α-KB in WT worms and found that supplementation with α-KB significantly extended the lifespan of WT worms (Fig. 1e and Supplementary Data 1). Moreover, we determined the effect of α-KB on several age-associated markers, pharyngeal-pumping rate, body bending, lipofuscin autofluorescence37,38, the integrity of intestinal barrier, and aggregation of polyglutamine::YFP (Poly-Q35::YFP)39. As expected, the reduction in both pharyngeal-pumping rate (Fig. 1f) and body bending (Fig. 1g) in 8-day-old worms was significantly inhibited after α-KB treatment. We detected the integrity of the intestinal barrier using food dye FD&C Blue No. 1, and found that the body-cavity leakage in 10-day-old worms treated with α-KB than that in age-matched worms with vehicle (Fig. 1h, i). In contrast, supplementation with α-KB did not affect the number of Poly-Q35::YFP aggregates in body wall muscle cells of 8-day-old worms (Supplementary Fig. 4a, b). Taken together, these results suggest that α-KB treatment delays the aging process in worms.
Lifespan extension involves NAD+ production in a SIR-2.1-dependent fashion
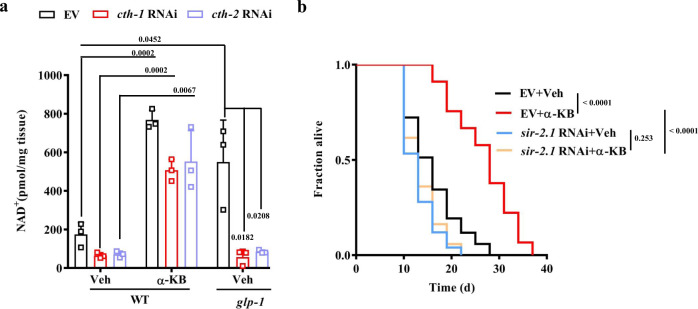
Increased oxidized nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) levels improve lifespan and healthspan across species, including worms10,11,40–42. Alpha-KB is readily reduced via lactate dehydrogenase or other intracellular dehydrogenases to generate NAD+43,44. Indeed, using LC-MS, we found that supplementation with α-KB increased the NAD+ levels in WT worms (Fig. 2a). Knockdown of either cth-1 or cth-2 by RNAi reduced the levels of NAD+ in WT worms, which were restored by supplementation with α-KB. Furthermore, an increase in the NAD+ levels was observed in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants (Fig. 2a). Knockdown of either cth-1 or cth-2 by RNAi reduced the levels of NAD+ in germline-deficient worms back to those of WT worms (Fig. 2a).
Fig. 2. Lifespan extension by α-KB depends on the NAD+-SIR-2.1 pathway.
a The contents of NAD+ were increased in α-ketobutyrate (α-KB, 500 μM) -treated wild-type (WT) worms or glp-1(e2141ts) mutants. Knockdown of either cth-1 or cth-2 by RNAi reduced the levels of NAD+ in germline-deficient worms back to those of WT worms. Veh vehicle. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments. P value was calculated using a one-way ANOVA followed by a Student–Newman–Keuls test. b RNAi knockdown of sir-2.1 inhibited lifespan extension by α-KB (500 μM) in WT worms. P values were calculated using a log-rank test. See survival statistics in Supplementary Data 1. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
The beneficial effects of NAD+ on lifespan extension depend on SIR-2.1 (the C. elegans ortholog of SIRT1), a member of the sirtuin family of NAD+-dependent deacylases10,11,41,42. We then asked whether SIR-2.1 was involved in α-KB-mediated lifespan extension. RNAi knockdown of sir-2.1 completely blocked lifespan extension by α-KB treatment (Fig. 2b and Supplementary Data 1) but only partially reduced lifespan extension by the glp-1(e2141ts) mutation (Supplementary Fig. 5 and Supplementary Data 1). Thus, SIR-2.1 is specifically required for α-KB-mediated lifespan extension. By contrast, SIR-2.1 is not specific to longevity in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants. Taken together, these results suggest that α-KB extends the lifespan by increasing NAD+ levels and its effect depends on the concomitant activity of SIR-2.1.
Alpha-KB stimulates peroxisome biogenesis and function
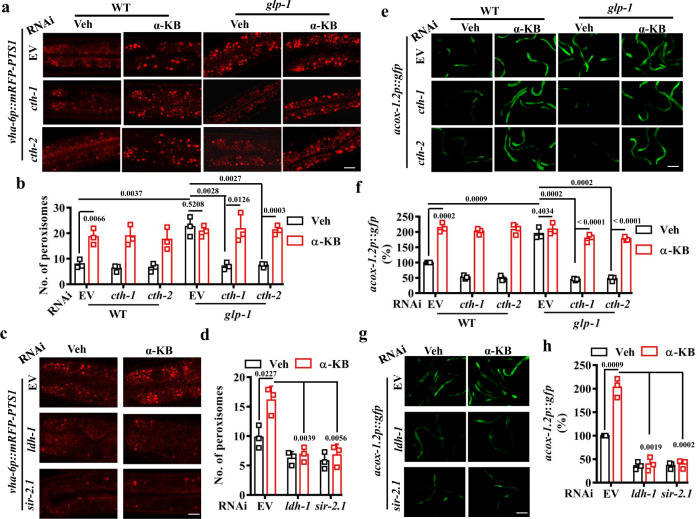
As mentioned above, we compared with the expression profiles of glp-1(e2141ts) mutants from two previous transcriptomic studies20,28 (Supplementary Fig. 1a). Among the overlapping genes from those two studies, both KEGG pathway and Gene Ontology enrichment analyses revealed that one of the top five overrepresented categories was “peroxisome” (Supplementary Fig. 1c). The “peroxisome” genes included peroxins (PEXs) required for peroxisomal protein import and proliferation (e.g., prx-1, -2, -3, -5, -11, -12, and -19)45, and peroxisomal genes required for fatty acid beta-oxidation (e.g., acox-1.1, -1.2, -1.3,- 1.4, -1.5, -1.6, -3, acs-2, -5, -13, -16, -17, and dhs-28) (Supplementary Fig. 1d). These results suggest that germline removal probably enhances peroxisome biogenesis. To monitor whether peroxisome number and size were altered, we used a C. elegans peroxisome reporter in which mRFP was linked to a peroxisome-targeting sequence (PTS1) under control by an intestinal promoter (vha-6p::mRFP-PTS1)31. Confocal images were taken from the Int1 and Int2 cells (the first two anterior rings of the intestine) (Supplementary Fig. 6a). We found that germline-deficient animals displayed an increase in the abundance of mRFP puncta over WT animals (Fig. 3a, b). Meanwhile, the size of peroxisomes also increased in germline-deficient animals (Supplementary Fig. 6b). It should be noted that the punctate pattern was not observed in non-fluorescent strains (Supplementary Fig. 6a). RNAi knockdown of either cth-1 or cth-2 reduced the number and size of peroxisomes in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants back to those of WT worms (Fig. 3a, b and Supplementary Fig. 6b). Although supplementation with α-KB did not influence the number and size of peroxisomes in germline-deficient animals, it significantly restored the number and size of peroxisomes in these animals subjected to cth-1 or cth-2 RNAi (Fig. 3a, b and Supplementary Fig. 6b). Meanwhile, the number and size of peroxisomes were considerably increased in WT worms treated with α-KB (Fig. 3c, d and Supplementary Fig. 6c).
Fig. 3. Alpha-KB promotes peroxisome function and biogenesis via the NAD+-SIR-2.1 pathway.
a Representative images of peroxisomes in glp-1(e2141ts) mutant worms expressing vha-6p::mRFP-PTS1. Scale bars: 2.5 μm. Veh vehicle. b The number of peroxisomes was increased in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants. RNAi knockdown of either cth-1 or cth-2 inhibited this increase, which was rescued by supplementation with α-ketobutyrate (α-KB, 500 μM). Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 25 worms per experiment). c Representative images of peroxisomes in transgenic worms expressing vha-6p::mRFP-PTS1 after treatment with α-KB. d Supplementation with α-KB (500 μM) increased the number of peroxisomes in worms, which was inhibited by RNAi knockdown of either ldh-1 or sir-2.1. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 25 worms per experiment). e Representative images of acox-1.2p::gfp in glp-1(e2141ts) worms. Scale bars: 150 μm. f Expression of acox-1.2p::gfp was upregulated in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants. RNAi knockdown of either cth-1 or cth-2 inhibited this increase, which was rescued by supplementation with α-KB (500 μM). Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 35 worms per experiment). g Representative images of acox-1.2p::gfp in worms after treatment with α-KB. h Supplementation with α-KB (500 μM) increased the expression of acox-1.2p::gfp in WT worms, which was inhibited by RNAi knockdown of either ldh-1 or sir-2.1. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 35 worms per experiment). P values throughout were calculated using a one-way ANOVA followed by a Student–Newman–Keuls test. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
Although PTS1-labeled marker proteins, such as mRFP-PTS1 or GFP-SKL, have been used to determine the number and size of peroxisomes31,46, they actually represent peroxisomal import function31. We thus determined the number and size of peroxisomes using transgenic worms expressing pmp-2p::pmp-2::mCherry. PMP-2, the C. elegans homolog of mammalian PMP70, is a peroxisomal membrane protein46. We observed that both the number and size of peroxisomes were increased in both glp-1(e2141ts) mutants and α-KB-treated worms expressing pmp-2p::pmp-2::mCherry (Supplementary Fig. 7a–f). As PEX11 in yeast and mammals is involved in peroxisomal division and proliferation, we also determined the effect of α-KB on the number and size of peroxisomes by measuring the expression of prx-11p::prx-11::gfp, the C. elegans homolog of PEX11. We found that both the number and size of peroxisomes were increased in α-KB-treated worms expressing prx-11p::prx-11::gfp (Supplementary Fig. 8a–c). These results suggest that elevated α-KB levels via upregulation of cth-1 and cth-2 in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants or supplementation with α-KB in WT worms increase the number and size of peroxisomes.
Using qPCR, we determined the expression of the peroxisome-related genes, such as prx-2, prx-19, acox-1.2, acox-3, acs-2, and acs-5. Of these genes, the expressions of these peroxisome-related genes were significantly upregulated in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants, compared with those in WT worms (Supplementary Fig. 9a). Knockdown of cth-1 or cth-2 by RNAi reduced the expressions of these genes in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants back to those of WT worms. Utilizing transgenic worms expressing acox-1.2p::gfp, we found that the expression of acox-1.2p::gfp was substantially upregulated in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants (Fig. 3e, f). RNAi knockdown of cth-1 or cth-2 reduced the expression of acox-1.2p::gfp in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants back to those of WT worms. This increase in the expression of acox-1.2p::gfp was inhibited after the knockdown of cth-1 and cth-2 by RNAi. Although supplementation with α-KB did not influence the expression of acox-1.2p::gfp in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants, it markedly restored its expression in these animals subjected to cth-1 or cth-2 RNAi (Fig. 3e, f). Finally, we found that α-KB treatment significantly upregulated the expression of acox-1.2p::gfp and ctl-2, encoding a peroxisomal catalase, in WT worms (Fig. 3g, h and Supplementary Fig. 9b). Taken together, these results suggest that peroxisome biogenesis and function are promoted by α-KB.
We asked the question of whether α-KB promoted peroxisome biogenesis by the production of NAD+. As α-KB can produce NAD+ via the lactate dehydrogenase43,44, we blocked the production of NAD+ by silencing ldh-1, which encoded the C. elegans lactate dehydrogenase. We found that knockdown of ldh-1 by RNAi significantly inhibited the increase in the number and the size of peroxisomes (Fig. 3c, d and Supplementary Fig. 6c), and inhibited the expression of acox-1.2p::gfp in α-KB-treated WT worms (Fig. 3g, h). Next, knockdown of sir-2.1 by RNAi suppressed the increase in either the number and size of peroxisomes (Fig. 3c, d and Supplementary Fig. 6c) or the expression of acox-1.2p::gfp in WT worms treated with α-KB (Fig. 3g, h). In addition, we tested the roles of NAD+ precursors, such as NAM, NMN, and nicotinamide riboside (NR)12. We found that supplementation with NAM, NMN, and NR considerably promoted the number and size of peroxisomes (Supplementary Figs. 10a–c, 11a–c), and upregulated the expression of acox-1.2p::gfp in WT worms (Supplementary Fig. 10d, e). Taken together, these results indicate that α-KB promotes peroxisome biogenesis and function by NAD+ and sir-2.1.
A previous study has demonstrated that AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and caloric restriction promote longevity via remodeling mitochondrial and peroxisomal networks in worms31, raising the possibility that α-KB may function in mitochondria-peroxisome coordination. However, we found that α-KB did not delay the reduction in mitochondrial content with age (Supplementary Fig. 12a). Furthermore, RNAi knockdown of aak-2, which encodes catalytic subunits of AMPK, did not affect the lifespan of α-KB-treated WT animals (Supplementary Fig. 12b and Supplementary Data 1). More importantly, supplementation with α-KB did not affect the levels of phosphorylated AMPK(Thr172) in both worms and senescent IMR90 cells, a human lung fibroblast strain (Supplementary Fig. 12c, d). By contrast, the levels of phosphorylated AMPK(Thr172) were markedly higher in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants than those in WT worms (Supplementary Fig. 12c). Thus, lifespan extension by α-KB is not linked to maintenance of the mitochondrial networks mediated by AMPK.
Peroxisome function and H2O2 production are required for α-KB-mediated lifespan extension
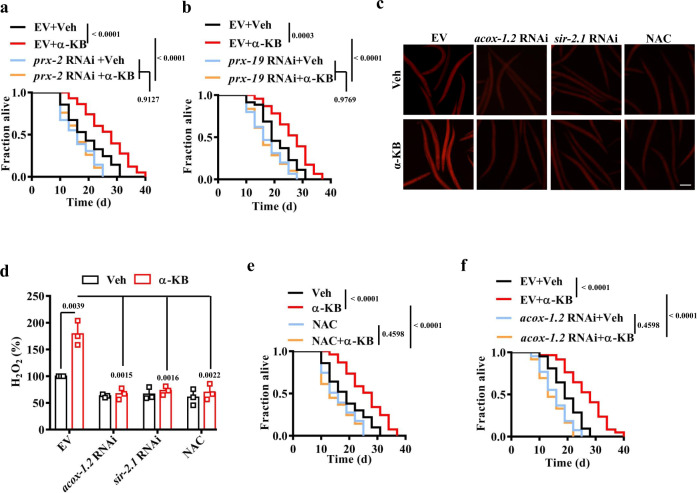
To determine whether the peroxisomal function is required for longevity, we silenced the peroxisomal genes, prx-2 (the C. elegans homolog of mammalian peroxisome biogenesis factor 2; PEX2) and prx-19 (the C. elegans homolog of mammalian peroxisome biogenesis factor 19; PEX19), which are involved in the peroxisomal import proteins47. In WT worms treated with α-KB or vehicle, RNAi knockdown of either prx-2 or prx-19 severely reduced the number of peroxisomes (Supplementary Fig. 13a, b). These results indicate that mRFP fails to import into peroxisomes. Moreover, the knockdown of prx-2 and prx-19 by RNAi reduced the lifespan of α-KB-treated WT worms back to that of WT worms treated with vehicle (Fig. 4a, b and Supplementary Data 1). Thus, peroxisome function is required for lifespan extension mediated by α-KB.
Fig. 4. Peroxisome function and H2O2 production are involved in α-KB-mediated lifespan extension.
a, b RNAi knockdown of prx-2 (a) and prx-19 (b) inhibited the lifespan extension of wild-type (WT) worms by treatment of α-ketobutyrate (α-KB, 500 μM). Veh vehicle. P values (a, b) were calculated using a log-rank test. c Representative images of H2O2 formation detected by fluorescence dye DCHP. Scale bars: 150 μm. d Quantification of fluorescence intensity. The levels of H2O2 were increased in WT worms treated with α-KB. RNAi knockdown of either acox-1.2 or sir-2.1 inhibited the levels of H2O2 in α-KB-treated WT worms. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 35 worms per experiment). P values were calculated using a one-way ANOVA followed by a Student–Newman–Keuls test. e Supplementation with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) (5 mM) shortened the lifespan of WT worms treated with α-KB (500 μM). f Knockdown of acox-1.2 by RNAi suppressed the lifespan of WT worms treated with α-KB (500 μM). P values (e, f) were calculated using a log-rank test. See survival statistics in Supplementary Data 1. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
ROS are involved in life extension induced by germ-cell loss6. One of the products in the first step of peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation is H2O2, which is produced by acyl-CoA oxidases (ACOXs)48. We thus asked whether H2O2 production was increased when peroxisome biogenesis is enhanced. Using a fluorescence dye DCHP49, we found that the levels of H2O2 were increased in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants (Supplementary Fig. 14a, b). To determine which ACOX is involved in H2O2 formation, we screened the upregulated acox genes, including acox-1.1, -1.2, -1.3, -1.4, -1.5, -1.6, and -3, by RNAi. Of these seven genes, RNAi knockdown of acox-1.2, rather than the other six acox genes, significantly reduced the levels of H2O2 in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants (Supplementary Fig. 14c), suggesting that ACOX-1.2 is required for H2O2 production. Furthermore, supplementation with α-KB significantly promoted the production of H2O2 (Fig. 4c, d). We found that RNAi knockdown of acox-1.2 not only inhibited H2O2 formation in WT worms, but also reduced the levels of H2O2 in WT α-KB-treated worms (Fig. 4c, d). Similar results were obtained by knockdown of sir-2.1 by RNAi (Fig. 4c, d). These results suggest that H2O2 formation is induced by α-KB via ACOX-1.2.
To test whether the induction of H2O2 formation is involved in lifespan extension, an antioxidant N-acetylcysteine (NAC) was pre-treated with worms. H2O2 formation was markedly attenuated by NAC in α-KB-treated WT worms (Fig. 4c, d). Furthermore, supplementation with α-KB failed to extend the lifespan of either NAC- or acox-1.2 RNAi-treated worms (Fig. 4e, f and Supplementary Data 1). Consistent with a previous observation15, NAC treatment shortened the lifespan of glp-1(e2141ts) mutants (Supplementary Fig. 15 and Supplementary Data 1). Although the knockdown of acox-1.2 by RNAi also suppressed the lifespan of glp-1(e2141ts) mutants, it did not further reduce the lifespan of NAC-treated glp-1(e2141ts) mutants (Supplementary Fig. 15, Supplementary Data 1). Taken together, these results suggest that H2O2 production from peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation is crucial in α-KB-mediated lifespan extension.
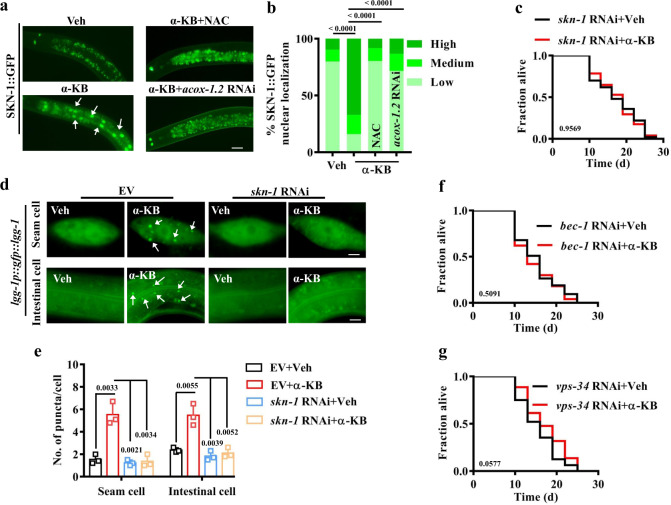
SKN-1 is involved in α-KB-induced lifespan extension
How might H2O2 from peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation extend lifespan? The oxidative stress-response transcription factors DAF-16 and SKN-1, which are involved in lifespan extension in germline-defective worms20,50, are potential candidates to serve as a downstream signal of H2O2. To test this hypothesis, we first determined whether α-KB activated SKN-1 and DAF-16. Utilizing transgenic worms expressing skn-1p::skn-1::gfp and daf-16p::daf-16::gfp, we observed that α-KB supplementation promoted the nuclear translocation of SKN-1, but not DAF-16 (Fig. 5a, b and Supplementary Fig. 16a, b). Furthermore, the expression of gst-4p::gfp, a SKN-1 target gene, was upregulated by α-KB supplementation (Supplementary Fig. 17a, b). Next, NAC treatment inhibited the nuclear translocation of SKN-1 in WT worms treated with α-KB (Fig. 5a, b). Furthermore, the knockdown of acox-1.2 by RNAi also significantly suppressed the nuclear translocation of SKN-1 in worms treated with α-KB (Fig. 5b). These results suggest that H2O2 from peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation activates SKN-1.
Fig. 5. SKN-1-mediated autophagy is crucial for α-KB-induced lifespan extension.
a Representative images of SKN-1::GFP translocation. Veh vehicle. Scale bars: 20 μm. b Quantification of SKN-1 nuclear accumulation. Supplementation with α-ketobutyrate (α-KB, 500 μM) promoted nuclear translocation of SKN-1::GFP in the intestine of worms, which was inhibited by treatment of N-acetylcysteine (NAC, 5 mM) or knockdown of acox-1.2 by RNAi. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 35 worms per experiment). P values were calculated using the Friedman test (with Dunn’s test for multiple comparisons). c Knockdown of skn-1 by RNAi suppressed the lifespan of wild-type (WT) worms treated with α-KB (500 μM). P value was calculated using a log-rank test. d Representative images of autophagosomes (GFP::LGG-1 puncta) in the seam cells and intestinal cells of worms treated with α-KB (500 μM). Scale bars: 5 μm. e The numbers of GFP::LGG-1 puncta were counted. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments (n = 35 worms per experiment). P values were calculated using a one-way ANOVA followed by a Student–Newman–Keuls test. f, g Knockdown of either bec-1 (f) or vps-34 (g) by RNAi significantly reduced the lifespan of WT worms treated with α-KB (500 μM). P values were calculated using a log-rank test. See survival statistics in Supplementary Data 1. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
SKN-1 is needed for longevity in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants20. Likewise, the knockdown of skn-1 by RNAi also inhibited the lifespan extension in WT worms supplemented with α-KB (Fig. 5c and Supplementary Data 1). As induction of autophagy is required for longevity in glp-1(e2141ts) mutants51,52, we hypothesized that the activation of SKN-1 by α-KB might promote autophagy in worms. We thus determined autophagy levels by using transgenic worms carrying GFP::LGG-1. During autophagic processes, LGG-1/ATG8 is sequestered at the membrane of autophagosomes and condenses into puncta, which is a reliable indicator of autophagy53,54. The numbers of GFP::LGG-1-positive puncta in both the seam cells and the intestine in WT worms treated with α-KB were significantly higher than those in WT worms treated with vehicle (Fig. 5d, e). Knockdown of skn-1 by RNAi substantially reduced the abundance of GFP::LGG-1 puncta in both the seam cells and the intestine in WT worms treated with α-KB (Fig. 5d, e). The accumulation of LGG-1 puncta may result from either induction of autophagy or a block in autophagy at a late step. To distinguish between these possibilities, we monitored both autophagosomes and autolysosomes using transgenic worms expressing lgg-1p::mCherry::GFP::lgg-1. In these worms, autophagosomes are positive for both GFP and mCherry, whereas autolysosomes are only positive for mCherry as the low pH quenched GFP in autolysosomes51 (Supplementary Fig. 18a, b). We observed mCherry single-positive autolysosome puncta and mCherry/GFP double-positive autophagosome puncta in seam cells and the intestine of control worms. Supplementation with α-KB significantly increased the numbers of both autophagosome and autolysosome puncta in worms subjected to empty vector, but not skn-1 RNAi. These results indicate that α-KB promotes autophagic flux via SKN-1.
Next, we asked whether SKN-1 modulates autophagy transcriptionally. Using qPCR, we determined the expressions of autophagy-related genes, including those involved in autophagosome formation and autophagic flux, such as atg-2, atg-11, lgg-2, vps-34, sqst-1/SQSTM1/p62, and unc-51/ULK1/ATG1; lysosome-autophagosome fusion, such as lmp-1/LAMP-1 and lmp-2/LAMP-1 genes with lysosomal functions, such as subunits of vacuolar ATPases (vha-10 and vha-14), cathepsins (Y16B4A.2, asp-3/cathepsin D, asp-4 /cathepsin D, and tag-196/cathepsin F), and hlh-30/TFEB. We found that most of these genes were upregulated in WT worms treated with α-KB (Supplementary Fig. 18c). Knockdown of skn-1 by RNAi substantially reduced the transcription of most of these genes. These data suggest that the change in the expression of these autophagy- and lysosome-related genes is transcriptionally regulated by SKN-1.
To test whether autophagy is required for SKN-1-mediated lifespan extension, two autophagy-related genes bec-1 and vps-34 were silenced by RNAi. Both BEC-1 (the C. elegans homolog of ATG6/VPS30/beclin1) and VPS-34 (the C. elegans homolog of the yeast phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase Vps34p) are key regulators of autophagy initiation and progression55,56. We found that supplementation with α-KB failed to extend the lifespan of worms subjected to either bec-1 or vps-34 RNAi (Fig. 5f, g and Supplementary Data 1). These results indicate that SKN-1 is required for α-KB-induced lifespan extension by activating autophagy. As autophagy plays a crucial role in clearing damaged organelles, such as mitochondria, peroxisomes, and endoplasmic reticulum57, these results also raised the possibility that the induction of autophagy by SKN-1, which is activated by H2O2 derived from the peroxisome, could, in turn, degrades the peroxisome itself. To test this hypothesis, we determined the number of peroxisomes in worms treated with α-KB with increasing incubation time. However, we found that the number of peroxisomes was elevated at 24, 36, and 48 h after the addition of α-KB (Supplementary Fig. 19a, b). Furthermore, RNAi knockdown of skn-1 did not affect the increase in the number of peroxisomes in worms after the addition of α-KB.
Alpha-KB delays senescence in mammalian cells
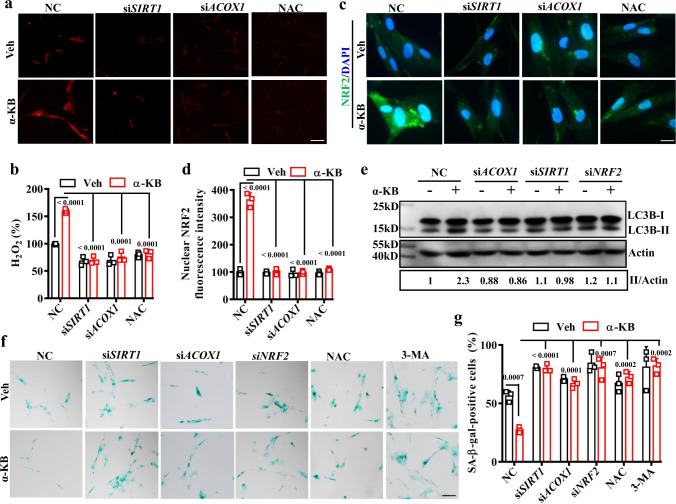
Since supplementation with α-KB extends lifespan in worms, we next asked whether such an intervention is beneficial for controlling cellular aging. For this, we tested the effect of α-KB on cell senescence using senescent IMR90 cells at population doubling (PD) 50. We found that treatment with α-KB led to a significant increase in H2O2 formation (Fig. 6a, b). However, knockdown of either SIRT1 or ACOX1 by RNAi or pre-treatment with NAC abrogated these effects of α-KB.
Fig. 6. Alpha-KB delays senescence in mammalian cells.
a Representative images of H2O2 formation detected by fluorescence dye DCHP in IMR90 cells. Scale bars: 15 μm. b Quantification of Fluorescence intensity. The H2O2 levels were increased in cells treated with α-ketobutyrate (α-KB, 500 μM) for 12 h, which was inhibited by RNAi knockdown of SIRT1 or ACOX1, or pre-treatment with N-acetylcysteine (NAC, 5 mM). Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments. P values were calculated using a one-way ANOVA followed by a Student–Newman–Keuls test. c Representative images of immunofluorescence staining with anti-NRF2 antibodies. Scale bars: 5 μm. d Quantification of fluorescence intensity of NRF2 in the nucleus. Supplementation with α-KB (500 μM) induced nuclear accumulation of NRF2 in IMR90 cells, which was blocked by RNAi knockdown of SIRT1 or ACOX1, or pre-treatment with NAC (5 mM). Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments. e Supplementation with α-KB (500 μM) increased the protein levels of LC3B-II in worms, which was blocked by RNAi knockdown of SIRT1, or ACOX1, or pre-treatment with NAC (5 mM). The blot shown here is typical of three independent experiments. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments. P = 0.008, α-KB versus vehicle (veh); P = 0.0065, ACOX1 RNAi + α-KB versus α-KB; P = 0.0057, SIRT1 RNAi + α-KB versus α-KB; P = 0.0112, NRF2 RNAi + α-KB versus α-KB. f Representative images of senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) staining. Scale bars: 15 μm. g Quantification of SA-β-gal activity. Supplementation with α-KB (500 μM) reduced the SA-β-gal activity. Knockdown of SIRT1, ACOX1, or NRF2 by RNAi, and pre-incubation of 3-MA (10 mM) abrogated the inhibitory effect of α-KB on SA-β-gal activity in cells treated with α-KB. Data were presented as mean values ± SEM of three independent experiments. P values throughout were calculated using a one-way ANOVA followed by a Student–Newman–Keuls test. Veh vehicle, NC negative control. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
Next, we tested the effect of α-KB on nuclear location of NRF2, a feature that concurs with its activation58. Immunofluorescence analysis with anti-total NRF2 antibodies revealed that NRF2 exhibited a dual nuclear and cytoplasmic distribution in IMR90 cells under basal conditions (Fig. 6c, d). Treatment of α-KB promoted NRF2 translocation to the nucleus, which was inhibited by si-SIRT1, si-ACOX1, or NAC. We observed that phosphorylated NRF2 was exclusively located in the nucleus when detected using anti-phospho-NRF2(Ser40) antibodies (Supplementary Fig. 20a, b). Treatment of α-KB significantly increased the phosphorylated NRF2 levels in the nucleus, which was inhibited by si-SIRT1, si-ACOX1, or NAC. These results suggest that α-KB activates NRF2 mediated by the SIRT1-ACOX1 pathway.
Furthermore, we determined the effect of α-KB on autophagic activity by detecting LC3B-II levels. Upon the induction of autophagy, MAP1LC3B/LC3B (microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3b) is cleaved at the carboxyl terminus and conjugated to phosphatidylethanolamine. The conversion of cytosolic LC3B (LC3B-I) to phagophore-associated LC3B-II is a marker for autophagy. We observed a dramatic increase in the protein levels of LC3B-II in IMR90 cells treated with α-KB (Fig. 6e). However, knockdown of SIRT1, ACOX1, or NRF2 by dsRNA significantly suppressed autophagy induced by α-KB. Finally, we determined the effect of α-KB on β-galactosidase activity, a well-established marker of cellular senescence59. The addition of α-KB reduced the β-galactosidase activity (Fig. 6f, g). Pre-treatment of NAC or RNAi knockdown of SIRT1, ACOX1, or NRF2 significantly abrogated the inhibitory effect of α-KB on β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) activity in IMR90 cells treated with α-KB. Likewise, pre-incubation of 3-methyladenine (3-MA)_ increased β-galactosidase activity and also abrogated the effect of α-KB (Fig. 6f, g). Together, these results suggest that α-KB also provides beneficial effects in mammalian cells by inducing autophagy through the SIRT1-ACOX1-H2O2- NRF2 pathway.
Discussion
Increased TSP activity promotes lifespan extension in both flies and worms4,5. As an intermediate in TSP, H2S functions to mediate longevity in yeast, worms, and fruit fly, and protect against hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury1,4,6,15,60,61. The central finding in this study is that supplementation with exogenous α-KB, another intermediate in TSP, extends C. elegans lifespan and delays senescence in fibroblast cells. This longevity effect is likely mediated by the augmentation of NAD+ via LDH-1. This increase in substrate allows for SIR-2.1/SIRT1-dependent increases in peroxisome function and biogenesis, thus leading to upregulation of acox-1.2/ACOX1, a key gene in the peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation pathway. ACOX-1.2/ACOX1 enhances the production of H2O2, which subsequently activates SKN-1/NRF2. This transcription factor induces autophagy by driving the expression of autophagic and lysosomal genes, which in turn promotes longevity (Fig. 7). Our findings demonstrate a novel mechanism for extending lifespan that is mediated by an endogenous metabolite.
Fig. 7. Schematic model for α-KB-mediated longevity.
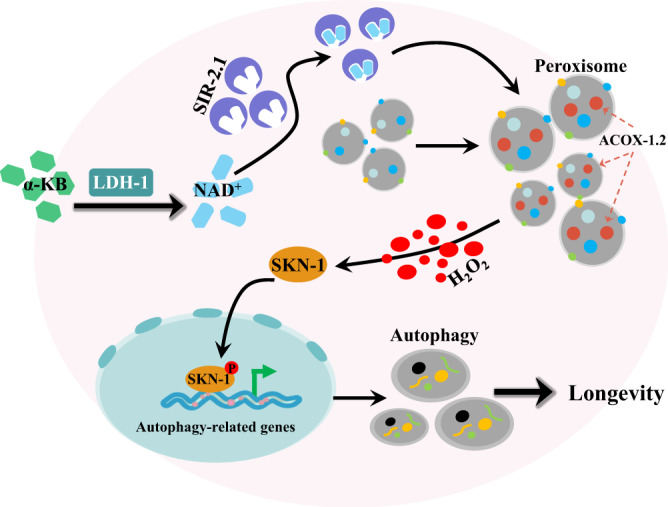
Supplementation with exogenous α-ketobutyrate (α-KB) increases the NAD+ contents via LDH-1. The NAD+-SIR-2.1/SIRT1 signaling enhances peroxisome function and biogenesis, thus leading to the upregulation of acox-1.2/ACOX1, a key gene in the peroxisomal fatty acid β-oxidation pathway. ACOX-1.2/ACOX1 promotes the production of H2O2, which in turn activates SKN-1/NRF2. This transcription factor induces autophagy by regulating the expressions of autophagic and lysosomal genes at a transcription level. Increased autophagic activity promotes longevity and delays cellular senescence.
By mining two transcriptomic datasets20,28, we show that there are ~50 peroxisomal genes upregulated in the long-lived germline-deficient worms. In contrast, a proteome analysis shows that the abundance of ~30 peroxisomal proteins is reduced, and protein import into the peroxisome is compromised in old worms30. These omics data implicate an association between peroxisome and aging. However, until now, the exact role of peroxisome in aging and longevity remains largely unknown. While knockdown of peroxisomal genes pex1/prx-1 and pex13/prx-13 promotes lifespan in flies32, deletion of pex5/prx-5 significantly shortens chronological lifespan in yeast33. In long-lived double null drp-1;fzo-1 mutant worms, the size of peroxisomes is significantly increased31. Inhibition of peroxisomal function by silencing pex5/prx-5 almost blocks lifespan extension by a double mutation in drp-1;fzo-1. In this study, supplementation with α-KB remarkably increases the abundance and size of peroxisomes, which is required for lifespan extension by α-KB. Thus, our findings support the idea that enhanced peroxisome function may represent a common signature associated with longevity.
During aging, the intracellular NAD+ levels are reduced in a variety of tissues in mammals62–64. The increase in intracellular NAD+ levels by supplementation of NAD+ precursors such as NAM and NMN, or activation of the de novo NAD+ synthesis pathway, improves lifespan and healthspan, and prevents age-associated metabolic dysfunction via a mechanism requiring SIRT1/SIR-2.1 in species ranging from mammals to worms9–11,41. Our data show that the long-lived glp-1(e2141ts) animals have higher NAD+ levels, which are attributed to increased endogenous α-KB by CTH-1 and CTH-2. Furthermore, supplementation with exogenous α-KB increases the production of NAD+, thus extending the lifespan in WT worms in a SIRT1/SIR-2.1-dependent manner. These results suggest that α-KB exhibits its beneficial effect on delaying senescence, at least in part, via the production of NAD+. The NAD+-SIRT1 pathway promotes longevity and prevents age-related physiological decline by inducing the mitochondrial unfolded protein response in worms and mammalian cells41. Moreover, NAD+ augmentation significantly extends lifespan and improves healthspan by promoting mitophagy via SIRT1/SIRT2.1 in worm and mouse models of Ataxia Telangiectasia9, a rare autosomal recessive disease, and in worm and fly models of Werner syndrome65, a human premature aging disease. In this study, our data demonstrate that supplementation with α-KB remarkably increases peroxisome function and biogenesis in WT worms in a SIRT2.1-dependent manner. Likewise, the NAD+ precursors, including NAM, NMN, and NR, also induces an increase in peroxisome function and biogenesis in worms. Thus, our study identifies enhanced peroxisome function as a downstream mechanism underlying NAD+-SIR-2.1-mediated longevity.
Although mitochondria are the main organelle responsible for ROS produced within cells, the peroxisome also generates ROS. In germline-deficient worms, the production of ROS is significantly elevated15. Besides these two sources of ROS (the mitochondrial ROS and DHE-reactive ROS produced by KRI-1)15, we show that H2O2 produced from the peroxisomal β-oxidation mediated by α-KB is another source of ROS in the germline-deficient worms. Accumulating evidence suggests that ROS may function as important modulators to promote lifespan in worms15,23–26,66,67. Interestingly, younger cells or worms are capable of generating more ROS than older individuals in response to environmental stresses68. Such redox-stress-response capacity is pivotal to maintain cellular redox and protein homeostasis. In the present study, α-KB-mediated H2O2 extends the lifespan in worms and delays cellular senescence by activating the ROS-sensitive transcription factor SKN-1/NRF2. SKN-1/NRF2 plays an important role in promoting longevity and delaying senescence in worms and mammals58,69,70; however, it is not known whether SKN-1 exhibits its effect on longevity by modulating autophagy. We show that SKN-1 activates autophagy by initiating a transcriptional program that coordinates the different steps of the autophagic pathway, thereby extending the lifespan in worms. As NRF2 has been proven to positively modulate autophagy in mammalian cells71, it is concluded that, like HLH-30/TFEB52, SKN-1/NRF2 is probably another master regulator of autophagy across species.
In conclusion, our findings present new insights into the mechanism underlying endogenous metabolite-mediated longevity. Besides α-KB, other endogenous metabolites, such as oxaloacetate72, ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids73, and α-ketoglutarate74, can also delay aging and extend lifespan, suggesting that the key to longevity is hidden in our body. The endogenous metabolites provide new approaches for the prevention and treatment of aging and aging-related diseases.
Methods
Nematode strains
Multiple mutants and transgenic strains used in this study included glp-1(e2141ts), Strains BC14661 (sEx14661 [rCes acox-1.2::GFP + pCeh361]), CL2166 (dvIs19 [(pAF15)gst-4p::GFP::NLS]), eat-2(ad1116), daf-2(e1370), isp-1(qm150), and AM140 (rmls132[unc-54p::Q35::YFP]) were kindly provided by the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (CGC; http://www.cbs.umn.edu/CGC), funded by NIH Office of Research Infrastructure Programs (P40 OD010440). The nematode strains VS10 (hjIs37 [vha-6p::mRFP-PTS1 + Cbr-unc-119(+)]), DA2123 (adIs2122 [lgg-1p::GFP::lgg-1 + rol-6(su1006)]), (hqIs181[sdhl-1p::mtLs-gfp]), MAH215 (sqIs11[lgg-1p::mCherry::GFP:: lgg-1]), pmp-2p::pmp-2::mCherry, and prx-11p::prx-11::gfp were kindly provided by Drs. Bin Liang (Yunnan University), Bin Qi (Yunnan University), Meng-Qiu Dong (National Institute of Biological Sciences, Beijing), Hong Zhang (Institute of Biophysics, Chinese Academy of Science), and Huanhu Zhu (ShanghaiTech University), respectively. Mutants were backcrossed three times into the N2 strain used in the laboratory. All strains were grown on nematode growth media (NGM) plates with E. coli OP50 at 20 °C75.
Cell culture
The human lung fibroblast IMR90 cells were a gift from Dr. Xudong Zhao (Sichuan University West China Medical School) and obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC; CCL-186). The cells were grown in MEM with 1% sodium pyruvate, 1% penicillin-streptomycin, and 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, A3161001C) in a humidified, 5% CO2:95% air incubator at 37 °C. When attained 50 PD, IMR90 cells were treated with 500 μM of α-KB (MACKLIN, C10962521), 5 mM NAC (MACKLIN, N800425), or 10 mM 3-Methyladenine (MACKLIN, 5142-23-4). ddH2O or DMSO was used as a control.
RNA interference for worms
RNAi bacterial strains containing targeting genes were obtained from the Ahringer RNAi library76. Briefly, E. coli strain HT115(DE3) expressing dsRNA corresponding to each worm gene was grown overnight in LB broth containing 100 μg/ml ampicillin at 37 °C, then spread onto NGM plates containing 100 μg/ml ampicillin and 5 mM isopropyl 1-thio-β-d-galactopyranoside (IPTG). The RNAi-expressing bacteria were then grown overnight at 25 °C. Synchronized L1 larvae were placed on the seeded RNAi plates at 20 °C until animals reached maturity. Young adult worms were used for further experiments.
RNA interference for cells
All chemically synthesized siRNAs were obtained from Gene-Pharma Corporation. To silence the expression of SIRT1, ACOX1, or NRF2 by RNAi, IMR90 cells were transfected at 50% confluence with 100 nM of siRNAs in Opti-MEM medium using Lipofectamine 2000 transfection agent (Thermo Fisher, 11668019). Gene silencing efficiency was confirmed by quantitative real-time PCR 72 h post-transfection. The following siRNAs were used (sequence of the sense strand): SIRT1, 5′-GGGAAAUGUAUUGGCAGUGUU-3′ (F), 5′-CACUGCCAAUACAUUUCCCUU-3′ (R); ACOX1, 5′-UCAUCUAAGAGACCUAGGCTT-3′ (F), 5′-GCCUAGGUCUCUUAGAUGATT-3′ (R); NRF2, 5′-UCAUCUAAGAGACCUAGGCTT-3′ (F), 5′-GCCUAGGUCUCUUAGAUGATT-3′ (R); negative control 5′-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3′ (F), 5′-ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT-3′ (R).
DAVID enrichment analysis
We annotated two published transcriptomic datasets (GSE43864 and GSE63075)20,28 based on the Wormbase database, of version WS236 (www.wormbase.org). We searched for enrichment of KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) pathway gene sets and GO terms using the 3208 upregulated genes overlapped between these two transcriptomic datasets. Identify enriched GO terms and KEGG pathway of the overlapped genes of the expression profiles from these two datasets by Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery (DAVID) version 6.7 (https://david.ncifcrf.gov/home.j sp)77. GO term or KEGG pathway with an adjusted p value <0.01 was defined as significantly changed.
Drug treatment
NGM agar plates seeded with E. coil OP50 were supplemented with 200 and 500 μM of α-KB, or 200 and 500 μM of NAM (MERCK, 98-92-0), or 200 and 500 μM of NMN (MedChemExpress (MCE), HY-F0004), or 200 and 500 μM of NR (MedChemExpress(MCE), HY-123033A), or 5 mM NAC. ddH2O or DMSO was used as a control.
Lifespan analysis
Synchronized populations of young adult worms were grown on NGM agar plates seeded with E. coli OP50 and tested drugs at 20 °C to score lifespan37. To test the effect of drugs on lifespan, the E. coli OP50-seeded NGM agar plates were supplemented with these drugs. The first day of adulthood of animals was recorded as day 1. Worms were transferred to new plates every day during their reproductive period. After reproduction ceases, worms were transferred every three days. The number of worms was counted every day. Worms that did not move when gently prodded and lacking pharyngeal pumping were marked as dead. Three plates of 50–60 worms per plate were tested per assay and all experiments were performed three times independently. Life spans for each assay are provided in Supplementary Data 1.
Age-related phenotypic marker assays in worms
On the first day of adulthood, animals were placed on NGM agar plates containing E. coli OP50 until day 8 of adulthood and the following age-related phenotypes were scored. (1) Pharyngeal pumping was determined by counting the number of contractions in the terminal bulb of the pharynx in 30-s intervals. (2) Body bending was measured by counting the number of body bends in 30 s intervals. 20–30 worms were examined per assay in three independent experiments.
Detection of H2S in worms
The endogenous H2S levels in germline-deficient animals were determined using a lysosome-targeted fluorescent chemodosimeter according to the previously described method34. Briefly, worms were incubated in Petri dishes filled with M9 buffer containing the fluorescent chemodosimeter (10 μM) at 20 °C for 3 h. The worms then were washed three times with M9 buffer and mounted in M9 onto microscope slides. The slides were viewed using a Zeiss Axioskop 2 Plus fluorescence microscope. The brighter the blue coloration, the stronger the fluorescence signal intensity. At least 30 worms were examined per assay in three independent experiments.
Measurement of α-KB by LC/MS
The levels of α-KB in adult worms were determined by LC/MS. Briefly, after ~5 ml of packed worms were (Scanvac-Collsafe 110-4, LaboGene, Lynge, Denmark) for 48 h. The worm samples were then mixed with 2 ml of lysis buffer RIPA (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Haimen, China), and gently ultrasonicated for 20 min. The mixture was centrifuged at 16,600×g for 30 min at 4 °C, and the supernatant was collected and then extracted with ethyl acetate. After the final centrifugation, the supernatant was collected, and analyzed by the Thermo Scientific Dionex Ultimate 3000 UHPLC system equipped with a Thermo high-resolution Q Exactive focus mass spectrometer (Thermo, Bremen, Germany). Samples were separated on a ZORBAX SB-C18 (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm particles; Agilent Technologies) with gradient elution. Ten microliters of samples were injected into the column using an autosampler. The mobile phase consisted of solvent A (water) containing 0.1% formic acid and solvent B (methanol), The flow rate of the mobile phase was 1 ml/min. The gradient program was as follows: 0–2 min (5% B), 2–8 min (5–15% B), 8–12 min (15–98% B), 12–16 min (98% B), 16–20 min (5% B). The instrument settings were as follows: capillary temperature of 320 °C, sheath gas flow rate of 35 (arbitrary units), an auxiliary gas flow rate of 15 (arb), spray voltage of −2.5 kV, full MS resolution of 70,000. Data were analyzed by using Thermo Scientific Xcaliber 4.4 software.
Intestinal barrier function assay in worms
Intestinal barrier function was determined according to the method described previously78. Briefly, young adult worms were grown on standard NGM plates in the presence or absence of α-KB (500 μM) at 20 °C for 10 days. After being removed from the NGM plates, these worms were suspended in an M9 liquid medium containing E. coli OP50 (OD = ∼0.6), 5% food dye FD&C Blue No. 1 (Bis[4-(N-ethyl-N-3-sulfophenylmethyl) aminophenyl]-2-sulfophenylmethylium disodium salt) (AccuStandard, New Haven, CT), and further incubated for 6 h. After washing with M9 buffer four times, the worms were mounted in M9 onto microscope slides. The slides were viewed using a Zeiss Axioskop 2 Plus fluorescence microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany) to measure the leakage of the dyes in the body cavity. The rate of body-cavity leakage was calculated as a percentage by dividing the number of worms with dye leakage by the number of total worms. Five independent experiments were carried out. In each experiment, at least 20 of worms were calculated.
NAD+ measurements by LC/MS
NAD+ in worms was extracted by the method described previously11. Briefly, after ~1 ml of packed worms were freeze-dried in a freeze dryer (Scanvac-Collsafe 110-4, LaboGene, Lynge, Denmark) for 24 h. The worm samples then were extracted with 10% perchloric acid and neutralized in 3 M K2CO3 on ice. After centrifuged at 16,600 × g for 30 min at 4 °C to remove the insoluble residue, the supernatant was filtered, and analyzed by Thermo Scientific Dionex Ultimate 3000 UHPLC system equipped with a Thermo high-resolution Q Exactive focus mass spectrometer (Thermo, Bremen, Germany). Samples were separated on a ZORBAX SB-C18 (4.6 mm × 250 mm, 5 μm particles; Agilent Technologies) with gradient elution. Ten microliters of samples were injected into the column using an autosampler. The mobile phase consisted of solvent A (water) containing 0.1% formic acid and solvent B (methanol). The flow rate of the mobile phase was 1 ml/min. The method to measure NAD+ content is as follows: The gradient program was as follows: 0–2 min (2% B), 2–8 min (2–15% B), and 8–12 min (15–98% B), 12–16 min (98% B), 16–20 min (2% B). The instrument settings were as follows: capillary temperature of 350 °C, sheath gas flow rate of 35 (arbitrary units), an auxiliary gas flow rate of 15 (arb), spray voltage of 3.5 kV, full MS resolution of 70,000. The column temperature was set to 40 °C. Data were analyzed by using Thermo Scientific Xcaliber 4.4 software.
Detection of H2O2 in worms
The H2O2 levels in worms were determined using a fluorescence dye, DCHP, according to the previously described method49. Briefly, worms were incubated in Petri dishes filled with M9 buffer containing DCHP (10 μM) at 20 °C for 5 h. Then, worms were washed with M9 buffer three times and mounted in M9 onto microscope slides. The slides were viewed using a Zeiss Axioskop 2 Plus fluorescence microscope. At least 30 worms were examined per assay in three independent experiments.
Quantitative RT-PCR
Total RNA was extracted from worms with TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). Random-primed cDNAs were generated by reverse transcription of the total RNA samples with SuperScript II (Invitrogen). Quantitative real-time PCR analysis was performed using SYBR Premix (Takara, Dalian, China) on a Roche LightCycler 480 System (Roche Applied Science, Penzberg, Germany). The relative amount of each mRNA to act-1 mRNA (an internal control) was calculated using the method described previously79. The primers used for qPCR assays are listed in Supplementary Data 2, respectively.
Western blotting
Worms or cells were collected and lysed on ice for 30 min in lysis buffer RIPA (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology, Haimen, China). The supernatant was obtained from cell lysates by centrifugation at 16,600 × g for 20 min at 4 °C and used for Western blot analysis. The proteins of lysates (50 μg per well) were separated on a 10% sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel and then transferred to polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. The primary antibodies were anti-LC3B mAb (#3868, 1:3000 dilution, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA), anti-Phospho-AMPKα(Thr172) mAb (#2535, 1:1000 dilution, Cell Signaling Technology), anti-β-Actin mAb (#sc-8432, 1:4000 dilution, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA), and anti-AMPKα antibodies (#2532 S, 1:1000 dilution, Cell Signaling Technology). The secondary antibodies used were HRP-conjugated anti-mouse (#7074 s, 1:3000 dilution, Cell Signaling Technology) or anti-rabbit IgG (#7076p2, 1:3000 dilution, Cell Signaling Technology). An imaging system (Amersham Imager 600) was used for the documentation of the Western blot results.
The quantification of peroxisome numbers and size
To determine the function and biogenesis of peroxisomes, we used the transgenic worms expressing vha-6p::mRFP-PTS131, pmp-2p::pmp-2::mCherry, and prx-11p::prx-11:gfp46. Briefly, worms were collected and transferred in an Eppendorf tube filled with M9 buffer containing 4% formaldehyde at 20 °C for 5 min. After washing with M9 buffer three times, the worms were mounted in M9 onto microscope slides. The mRFP-PTS1, PMP-2::mCherry, and PRX-11::GFP fluorescence signals were acquired by Leica TCS SP8 STED confocal microscope (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) at 63x magnification. Confocal images were taken from the Int1 and Int2 cells (the first two anterior ring of the intestine). The diameters of peroxisomes were 0.1–1.2 μm80, as a standard for quantifying the number and size of peroxisomes. At least 20 worms were examined per assay in three independent experiments.
Scoring of SKN-1 and DAF-16 nuclear accumulation
Young adult worms expressing skn-1p::skn-1::gfp or daf-16p::daf-16::gfp were grown on NGM agar plates containing E. coil OP50. After being treated with 500 μM α-KB for 24 h, the worms were immediately mounted in M9 onto microscope slides. The slides were viewed using a Zeiss Axioskop 2 Plus fluorescence microscope. The status of DAF-16::GFP localization was categorized as cytosolic localization or nuclear localization when localization was observed throughout the body from head to tail81. When nuclear localization was visible, but not completely throughout the body, the status of DAF-16::GFP localization was characterized as intermediate localization. At least 30 worms were examined per assay in three independent experiments. SKN-1::GFP accumulation in intestinal nuclei was scored as previously described82. “High” indicates that a strong SKN-1::GFP signal was present in all nuclei, “medium” indicates that nuclear SKN-1::GFP was detected in both anterior and poster intestinal nuclei, and “low” indicates that nuclear SKN-1::GFP was barely detectable in either anterior or posterior intestinal nuclei.
Autophagy analysis
Young adult worms expressing GFP::LGG-1 were grown on NGM agar plates containing E. coil OP50 in the presence or absence of 500 μM α-KB. After 24 h of growth, the worms were immediately mounted in M9 onto microscope slides. The slides were viewed using a Zeiss Axioskop 2 Plus fluorescence microscope. GFP::LGG-1 positive puncta were counted in the seam cells or the intestine. At least 30 worms were examined per assay in three independent experiments.
Microscopy
The transgenic worms carrying acox-1.2p::gfp or gst-4p::gfp were treated with 500 μM α-KB for 12 and 24 h. The worms were mounted in M9 onto microscope slides for detecting fluorescent signals. The slides were viewed using a Zeiss Axioskop 2 Plus fluorescence microscope. At least 30 worms were examined per assay in three independent experiments. The fluorescence intensity was analyzed using ImageJ2×V2.1.4.8 (NIH).
Immunofluorescence
Cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) for 10 min at room temperature. After washed with PBS three times and were treated with PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100 for 15 min, the cells were permeabilized, and blocked with PBST containing 5% fetal bovine serum for 90 min at room temperature. Then the cells were immunostained with anti-NRF2 mAb (#2F6C6, 1:500 dilution, Cusabio Technology Llc, Huston, TX) or anti-Phospho-NRF2(Ser40) antibodies (PA5-67520, 1:500 dilution, Thermo Fisher Scientific) overnight at 4 °C. After washed three times with 0.1% Tween-20 in PBS (PBST), these cells were incubated with Alexa Fluor 405 anti-mouse IgG (H + L) (A-55057, 1:200 dilution, Thermo Fisher Scientific) or Alexa Fluor 488 anti-Rabbit IgG (H + L) (A-21206, 1:200 dilution, Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 1 h. Then, the slides were washed three times with PBST and stained with 1 μg/ml of 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) for 30 min to detect nuclei. Images were acquired using a Zeiss Axioskop 2 plus fluorescence microscope (Carl Zeiss, Jena, Germany).
Senescence-associated β-galactosidase staining
Senescence-associated SA-β-gal staining was performed according to the method described previously83. Briefly, IMR90 cells were fixed in 2% formaldehyde and 0.2% glutaraldehyde at room temperature for 10 min, and stained in freshly prepared staining solution (all reagents were from Cell Senescence β-galactosidase Staining Kit, Beyotime, Haimen) at 37 °C overnight. Images were taken and the percentages of SA-β-gal-positive cells were counted and determined using Image J. Each group had three biological replicates.
Statistical analysis
All statistical tests were two-sided, and values of P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. Differences in survival rates were analyzed using the log-rank test. Differences in gene expression, mRNA and protein levels, the contents of metabolites and H2O2, the percentages of SA-β-gal-positive cells, the numbers of GFP::LGG-1 positive puncta, and fluorescence intensity were assessed by performing one-way ANOVA followed by the Student–Newman–Keuls test or the Student’s t-test. Differences in the distribution of SKN-1 were analyzed using the Friedman test (with Dunn’s test for multiple comparisons) or the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. To test for significant overlap between different gene lists, Fisher’s exact test was used. Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 7 (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA).
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Supplementary information
Description of Additional Supplementary Files
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr. Jianping Xu (McMaster University, Canada) for his critical reading of this manuscript. We thank the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center, Drs. B Liang, B Qi, MQ Dong, H Zhang, and H Zhu for nematode strains, and Dr. X Zhao for IMR90 cells. Some nematode strains were kindly provided by the Caenorhabditis Genetics Centre, which is funded by the NIH Office of Research Infrastructure Programs (P40 OD010440). This work was supported by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32170759 to C.-G.Z.), the Major Science and Technology Project in Yunnan Province of China (202001BB050001 to C.-G.Z.), and the independent research fund of Yunnan Characteristic Plant Extraction Laboratory (2022YKZY006 to C.-G.Z.).
Source data
Author contributions
C.-G.Z., N.W., and Y.-C.M. designed the experiments and analyzed the data. N.W., Y.-C.M, X.-Q.G., P.-J.Z., Y.-J.J, Q.Z., and J.-H.D performed the experiments. C.-G.Z., N.W., and Y.-C.M. interpreted the data. C.-G.Z. and Y.-C.M. wrote the manuscript.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Konstantinos Palikaras and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Data availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials. Lifespan data were collected in Supplementary Data 1. The primers used for qRT-PCR are listed in Supplementary Data 2. The transcriptome data that support the findings of this study are available in a publicly accessible repository from the GEO under accession GSE43864 and GSE63075. Source data are provided with this paper.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Nan Wu, Yi-Cheng Ma, Xin-Qian Gong, Pei-Ji Zhao.
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41467-023-35899-1.
References
- 1.Hine C, Mitchell JR. Calorie restriction and methionine restriction in control of endogenous hydrogen sulfide production by the transsulfuration pathway. Exp. Gerontol. 2015;68:26–32. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2014.12.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hine C, Zhu Y, Hollenberg AN, Mitchell JR. Dietary and endocrine regulation of endogenous hydrogen sulfide production: implications for longevity. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018;28:1483–1502. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kabil O, Vitvitsky V, Xie P, Banerjee R. The quantitative significance of the transsulfuration enzymes for H2S production in murine tissues. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011;15:363–372. doi: 10.1089/ars.2010.3781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hine C, et al. Endogenous hydrogen sulfide production is essential for dietary restriction benefits. Cell. 2015;160:132–144. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.11.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kabil H, Kabil O, Banerjee R, Harshman LG, Pletcher SD. Increased transsulfuration mediates longevity and dietary restriction in Drosophila. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:16831–16836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102008108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Miller DL, Roth MB. Hydrogen sulfide increases thermotolerance and lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:20618–20622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0710191104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Qabazard B, et al. Hydrogen sulfide is an endogenous regulator of aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014;20:2621–2630. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Das A, et al. Impairment of an endothelial NAD(+)-H2S signaling network is a reversible cause of vascular aging. Cell. 2018;173:74–89.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fang EF, et al. NAD(+) replenishment improves lifespan and healthspan in ataxia telangiectasia models via mitophagy and DNA repair. Cell Metab. 2016;24:566–581. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.09.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hashimoto T, Horikawa M, Nomura T, Sakamoto K. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide extends the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans mediated by sir-2.1 and daf-16. Biogerontology. 2010;11:31–43. doi: 10.1007/s10522-009-9225-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Katsyuba E, et al. De novo NAD(+) synthesis enhances mitochondrial function and improves health. Nature. 2018;563:354–359. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0645-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mouchiroud L, et al. The NAD+/sirtuin pathway modulates longevity through activation of mitochondrial UPR and FOXO signaling. Cell. 2013;154:430–441. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kimble J, Crittenden SL. Controls of germline stem cells, entry into meiosis, and the sperm/oocyte decision in Caenorhabditis elegans. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007;23:405–433. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Arantes-Oliveira N, Apfeld J, Dillin A, Kenyon C. Regulation of life-span by germ-line stem cells in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2002;295:502–505. doi: 10.1126/science.1065768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wei Y, Kenyon C. Roles for ROS and hydrogen sulfide in the longevity response to germline loss in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2016;113:E2832–E2841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1524727113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Goudeau J, et al. Fatty acid desaturation links germ cell loss to longevity through NHR-80/HNF4 in C. elegans. PLoS Biol. 2011;9:e1000599. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hsin H, Kenyon C. Signals from the reproductive system regulate the lifespan of C. elegans. Nature. 1999;399:362–366. doi: 10.1038/20694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lapierre LR, Gelino S, Meléndez A, Hansen M. Autophagy and lipid metabolism coordinately modulate life span in germline-less C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 2011;21:1507–1514. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2011.07.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shen Y, Wollam J, Magner D, Karalay O, Antebi A. A steroid receptor-microRNA switch regulates life span in response to signals from the gonad. Science. 2012;338:1472–1476. doi: 10.1126/science.1228967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Steinbaugh, M. J. et al. Lipid-mediated regulation of SKN-1/Nrf in response to germ cell absence. Elife4, e07836 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 21.Yamawaki, T. M. et al. The somatic reproductive tissues of C. elegans promote longevity through steroid hormone signaling. PLoS Biol. 8, e1000468 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 22.Wang MC, O’Rourke EJ, Ruvkun G. Fat metabolism links germline stem cells and longevity in C. elegans. Science. 2008;322:957–960. doi: 10.1126/science.1162011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lee SJ, Hwang AB, Kenyon C. Inhibition of respiration extends C. elegans life span via reactive oxygen species that increase HIF-1 activity. Curr. Biol. 2010;20:2131–2136. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2010.10.057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Yang W, Hekimi S. A mitochondrial superoxide signal triggers increased longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS Biol. 2010;8:e1000556. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Schulz TJ, et al. Glucose restriction extends Caenorhabditis elegans life span by inducing mitochondrial respiration and increasing oxidative stress. Cell Metab. 2007;6:280–293. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yee C, Yang W, Hekimi S. The intrinsic apoptosis pathway mediates the pro-longevity response to mitochondrial ROS in C. elegans. Cell. 2014;157:897–909. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.02.055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hwang AB, et al. Feedback regulation via AMPK and HIF-1 mediates ROS-dependent longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:E4458–E4467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1411199111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Gracida X, Eckmann CR. Fertility and germline stem cell maintenance under different diets requires nhr-114/HNF4 in C. elegans. Curr. Biol. 2013;23:607–613. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.02.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lodhi IJ, Semenkovich CF. Peroxisomes: a nexus for lipid metabolism and cellular signaling. Cell Metab. 2014;19:380–392. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.01.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Narayan V, et al. Deep proteome analysis identifies age-related processes in C. elegans. Cell Syst. 2016;3:144–159. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2016.06.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Weir HJ, et al. Dietary restriction and AMPK increase lifespan via mitochondrial network and peroxisome remodeling. Cell Metab. 2017;26:884–896.e885. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2017.09.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zhou B, et al. Midlife gene expressions identify modulators of aging through dietary interventions. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2012;109:E1201–E1209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1119304109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lefevre SD, van Roermund CW, Wanders RJ, Veenhuis M, van der Klei IJ. The significance of peroxisome function in chronological aging of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Aging cell. 2013;12:784–793. doi: 10.1111/acel.12113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zou XJ, et al. A lysosome-targeted fluorescent chemodosimeter for monitoring endogenous and exogenous hydrogen sulfide by in vivo imaging. Chem. Commun. 2014;50:13833–13836. doi: 10.1039/C4CC05539J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Qabazard B, et al. Hydrogen sulfide is an endogenous regulator of aging in Caenorhabditis elegans. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014;20:2621–2630. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zivanovic J, et al. Selective persulfide detection reveals evolutionarily conserved antiaging effects of S-sulfhydration. Cell Metab. 2019;30:1152–1170.e1113. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.10.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chen, Y. L. et al. Adiponectin receptor PAQR-2 signaling senses low temperature to promote C. elegans longevity by regulating autophagy. Nat. Commun.10, 2602 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 38.Garigan D, et al. Genetic analysis of tissue aging in Caenorhabditis elegans: a role for heat-shock factor and bacterial proliferation. Genetics. 2002;161:1101–1112. doi: 10.1093/genetics/161.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Roux AE, Langhans K, Huynh W, Kenyon C. Reversible age-related phenotypes induced during larval quiescence in C. elegans. Cell Metab. 2016;23:1113–1126. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lin SJ, Defossez PA, Guarente L. Requirement of NAD and SIR2 for life-span extension by calorie restriction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science. 2000;289:2126–2128. doi: 10.1126/science.289.5487.2126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mouchiroud L, et al. The NAD(+)/sirtuin pathway modulates longevity through activation of mitochondrial UPR and FOXO signaling. Cell. 2013;154:430–441. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.06.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Schmeisser K, et al. Role of sirtuins in lifespan regulation is linked to methylation of nicotinamide. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013;9:693–700. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.1352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.von Morze C, et al. Hyperpolarized [(13)C]ketobutyrate, a molecular analog of pyruvate with modified specificity for LDH isoforms. Magn. Reson. Med. 2016;75:1894–1900. doi: 10.1002/mrm.25716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sullivan LB, et al. Supporting aspartate biosynthesis is an essential function of respiration in proliferating cells. Cell. 2015;162:552–563. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Thieringer H, Moellers B, Dodt G, Kunau WH, Driscoll M. Modeling human peroxisome biogenesis disorders in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Cell Sci. 2003;116:1797–1804. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Li N, et al. A sphingolipid-mTORC1 nutrient-sensing pathway regulates animal development by an intestinal peroxisome relocation-based gut-brain crosstalk. Cell Rep. 2022;40:111140. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Petriv OI, Pilgrim DB, Rachubinski RA, Titorenko VI. RNA interference of peroxisome-related genes in C. elegans: a new model for human peroxisomal disorders. Physiol. Genomics. 2002;10:79–91. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00044.2002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Poirier Y, Antonenkov VD, Glumoff T, Hiltunen JK. Peroxisomal beta-oxidation–a metabolic pathway with multiple functions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2006;1763:1413–1426. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2006.08.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.He Y, et al. A near-infrared fluorescent probe for detection of exogenous and endogenous hydrogen peroxide in vivo. Dyes Pigments. 2019;168:160–165. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2019.04.055. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Berman JR, Kenyon C. Germ-cell loss extends C. elegans life span through regulation of DAF-16 by kri-1 and lipophilic-hormone signaling. Cell. 2006;124:1055–1068. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chang, J. T., Kumsta, C., Hellman, A. B., Adams, L. M. & Hansen, M. Spatiotemporal regulation of autophagy during Caenorhabditis elegans aging. Elife6, e18459 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 52.Lapierre LR, et al. The TFEB orthologue HLH-30 regulates autophagy and modulates longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Commun. 2013;4:2267. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Meléndez A, et al. Autophagy genes are essential for dauer development and life-span extension in C. elegans. Science. 2003;301:1387–1391. doi: 10.1126/science.1087782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Zhang H, et al. Guidelines for monitoring autophagy in Caenorhabditis elegans. Autophagy. 2015;11:9–27.. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2014.1003478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Ruck A, et al. The Atg6/Vps30/Beclin 1 ortholog BEC-1 mediates endocytic retrograde transport in addition to autophagy in C. elegans. Autophagy. 2011;7:386–400. doi: 10.4161/auto.7.4.14391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Russell RC, et al. ULK1 induces autophagy by phosphorylating Beclin-1 and activating VPS34 lipid kinase. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013;15:741–750. doi: 10.1038/ncb2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Glick D, Barth S, Macleod KF. Autophagy: cellular and molecular mechanisms. J. Pathol. 2010;221:3–12. doi: 10.1002/path.2697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Kapeta S, Chondrogianni N, Gonos ES. Nuclear erythroid factor 2-mediated proteasome activation delays senescence in human fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:8171–8184. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.031575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Dimri GP, et al. A biomarker that identifies senescent human cells in culture and in aging skin in vivo. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 1995;92:9363–9367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.20.9363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kabil O, Banerjee R. Enzymology of H2S biogenesis, decay and signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014;20:770–782. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lee HJ, et al. Prostaglandin signals from adult germ stem cells delay somatic aging of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nat. Metab. 2019;1:790–810. doi: 10.1038/s42255-019-0097-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bai P, et al. PARP-1 inhibition increases mitochondrial metabolism through SIRT1 activation. Cell Metab. 2011;13:461–468. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.03.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Das A, et al. Impairment of an endothelial NAD(+)-H(2)S signaling network is a reversible cause of vascular aging. Cell. 2018;173:74–89.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.02.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Mouchiroud L, Houtkooper RH, Auwerx J. NAD+ metabolism: a therapeutic target for age-related metabolic disease. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013;48:397–408. doi: 10.3109/10409238.2013.789479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Fang EF, et al. NAD(+) augmentation restores mitophagy and limits accelerated aging in Werner syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:5284. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13172-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Hwang PM, Cai F, Pineda-Sanabria SE, Corson DC, Sykes BD. The cardiac-specific N-terminal region of troponin I positions the regulatory domain of troponin C. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA. 2014;111:14412–14417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1410775111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Schieber M, Chandel NS. TOR signaling couples oxygen sensing to lifespan in C. elegans. Cell Rep. 2014;9:9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.08.075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Meng J, et al. The decay of redox-stress response capacity is a substantive characteristic of aging: revising the redox theory of aging. Redox Biol. 2017;11:365–374. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Bishop NA, Guarente L. Two neurons mediate diet-restriction-induced longevity in C. elegans. Nature. 2007;447:545–549. doi: 10.1038/nature05904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Tullet JMA, et al. The SKN-1/Nrf2 transcription factor can protect against oxidative stress and increase lifespan in C. elegans by distinct mechanisms. Aging cell. 2017;16:1191–1194. doi: 10.1111/acel.12627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pajares M, et al. Transcription factor NFE2L2/NRF2 is a regulator of macroautophagy genes. Autophagy. 2016;12:1902–1916. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2016.1208889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Williams DS, Cash A, Hamadani L, Diemer T. Oxaloacetate supplementation increases lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans through an AMPK/FOXO-dependent pathway. Aging Cell. 2009;8:765–768. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2009.00527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.O’Rourke EJ, Kuballa P, Xavier R, Ruvkun G. ω-6 Polyunsaturated fatty acids extend life span through the activation of autophagy. Genes Dev. 2013;27:429–440. doi: 10.1101/gad.205294.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Chin RM, et al. The metabolite α-ketoglutarate extends lifespan by inhibiting ATP synthase and TOR. Nature. 2014;510:397–401. doi: 10.1038/nature13264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Brenner S. The genetics of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1974;77:71–94. doi: 10.1093/genetics/77.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Kamath RS, Ahringer J. Genome-wide RNAi screening in Caenorhabditis elegans. Methods. 2003;30:313–321. doi: 10.1016/S1046-2023(03)00050-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Dennis G, Jr., et al. DAVID: database for annotation, visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol. 2003;4:P3. doi: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-5-p3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ma YC, et al. YAP in epithelium senses gut barrier loss to deploy defenses against pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 2020;16:e1008766. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Pfaffl MW. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001;29:e45. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.9.e45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Nazarko TY, Farré JC, Subramani S. Peroxisome size provides insights into the function of autophagy-related proteins. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2009;20:3828–3839. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-03-0221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Zou CG, Tu Q, Niu J, Ji XL, Zhang KQ. The DAF-16/FOXO transcription factor functions as a regulator of epidermal innate immunity. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003660. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Inoue H, et al. The C. elegans p38 MAPK pathway regulates nuclear localization of the transcription factor SKN-1 in oxidative stress response. Genes Dev. 2005;19:2278–2283. doi: 10.1101/gad.1324805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Zou Z, et al. A single-cell transcriptomic atlas of human skin aging. Dev. Cell. 2021;56:383–397.e388. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Description of Additional Supplementary Files
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials. Lifespan data were collected in Supplementary Data 1. The primers used for qRT-PCR are listed in Supplementary Data 2. The transcriptome data that support the findings of this study are available in a publicly accessible repository from the GEO under accession GSE43864 and GSE63075. Source data are provided with this paper.