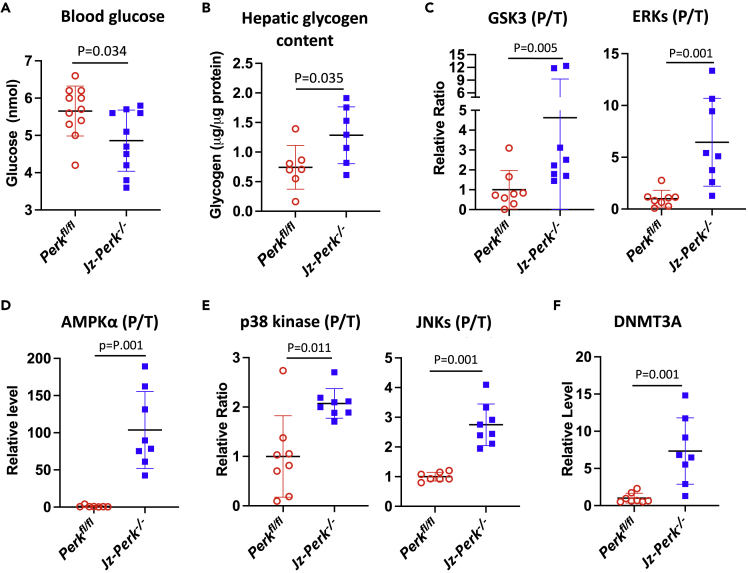
Figure 5.
Jz-specific ER stress alters maternal blood glucose and induces hepatic metabolic dysfunction and cellular stress, and potentially facilitates epigenetic change
(A) Maternal blood glucose concentration was measured by Glucometer at E18.5. Data are presented as mean ± SD, Jz-Perk−/− = 10; Perkfl/fl = 11. Unpaired t-test.
(B) Glycogen content in maternal liver measured at E18.5 Data are presented as mean ± SD, Jz-Perk−/−; Perkfl/fl both n = 7. Unpaired t-test.
(C–E) Western blot analysis of maternal liver for kinases or proteins involved in hepatic insulin and metabolic signaling and cellular stress pathways. (C) GSK3s and ERKs; (D) AMPKα; (E) p38 kinase and JNKs.
(F) Western blot analysis of DNA methyltransferase 3 alpha (DNMT3A) in maternal liver. (C–F) Data are presented as median with 95% Cl, n = 8. Mann-Whitney U test.