Summary
Alternative polyadenylation (APA) gives rise to transcripts with distinct 3′ untranslated regions (3′ UTRs), thereby affecting the fate of mRNAs. APA is strongly associated with cell proliferation and differentiation status, and thus likely plays a critical role in the embryo development. However, the pattern of APA in mammalian early embryos is still unknown. Here, we analyzed the 3′ UTR lengths in human and mouse pre-implantation embryos using available single cell RNA-seq datasets and explored the underlying mechanism driving the changes. Although human and mouse early embryos displayed distinct patterns of 3′ UTR changing, RNA metabolism pathways were involved in both species. The 3′ UTR lengths are likely determined by the abundance of the cleavage factor I complex (CFIm) components NUDT21 and CPSF6 in the nucleus. Importantly, depletion of either component resulted in early embryo development arrest and 3′ UTR shortening. Collectively, these data highlight an essential role for APA in the development of mammalian early embryos.
Keywords: pre-implantation embryo development, alternative polyadenylation, 3′UTR length, APAtrap, CFIm, NUDT21, CPSF6, CPSF7
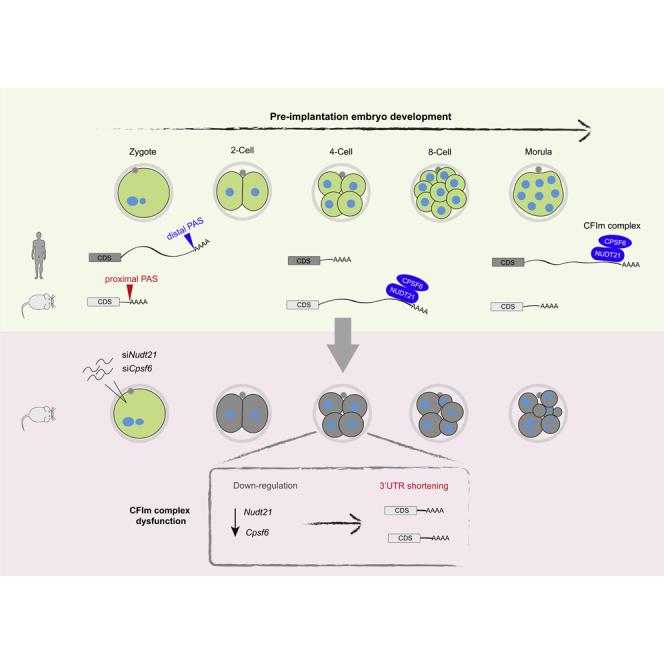
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
Distinct patterns of 3′ UTR dynamics in mouse and human early embryos
-
•
The CFIm components NUDT21 and CPSF6 are required for early embryo development
-
•
Disruption of the CFIm complex causes 3′ UTR shortening in mouse early embryos
In this article, Li and colleagues found extensive 3′ UTR length changes in human and mouse pre-implantation embryos. Downregulation of Nudt21 or Cpsf6, a key component of the CFIm complex, caused developmental arrest of mouse early embryos and overall shortening of 3′ UTRs. Their findings uncover an indispensable role of alternative polyadenylation in the development of pre-implantation embryos.
Introduction
In eukaryotic cells, the 3' end of pre-mRNAs undergoes cleavage and polyadenylation (hereafter referred to as polyadenylation), generating mature mRNAs with a poly(A) tail (Tian and Manley, 2017). The length of the poly(A) tail is critical for the nuclear export, stability, and translational efficiency of mature transcripts, as its shortening triggers degradation of the mRNAs (Weill et al., 2012). In addition to the poly(A) tail, the 3' untranslated region (3′ UTR) of a mature transcript often contains binding sites for miRNAs and RNA-binding proteins, as well as motifs for other post-transcriptional modifications, such as N6-methyladenosine (m6A) (Mayr, 2019). Thus, in coordination with each other, these two features enable spatial and temporal regulation of gene expression.
Polyadenylation is largely mediated by a multi-complex machinery (Shi et al., 2009). Works from yeast and mammalian cells have unraveled the composition of this machinery, including the complexes of cleavage and polyadenylation specificity factor (CPSF), cleavage stimulation factor (CstF), cleavage factor I (CFIm), and cleavage factor II (CFIIm), as well as other individual proteins (Shi et al., 2009). These complexes are recruited to the 3′ end of an mRNA precursor by cis elements flanking the polyadenylation site (PAS) (Zhu et al., 2018). Genome-wide sequencing studies have found that, in mammalian cells, at least 70% of protein-coding genes contain more than one PAS (Derti et al., 2012). The usage of different PASs generates transcripts with 3′ UTRs of various lengths (Tosi et al., 1981), a phenomenon often referred to as alternative polyadenylation (APA) (Rosenfeld et al., 1984).
To date, bulk sequencing studies have unraveled tissue- and context-specific patterns of APA (Zhang et al., 2005; Derti et al., 2012; Morris et al., 2012). For instance, proliferating cells, such as germ cells in the testis (Li et al., 2016b), favor the proximal PASs to have short 3′ UTRs (Sandberg et al., 2008), whereas differentiated cells like neurons exhibit long 3′ UTRs (MacDonald, 2019). Using available single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) datasets of mouse embryonic day (E)9.5–13.5 embryos, a recent study revealed global lengthening of 3′ UTRs during embryogenesis, except in cells of the hematopoietic lineages (Agarwal et al., 2021). However, the APA pattern in pre-implantation embryos is still unknown. With the availability of scRNA-seq data, here we analyzed the APA patterns during early embryo development and shed light on the underlying mechanism that dictates it.
Results
Identification of PASs in human and mouse early embryos
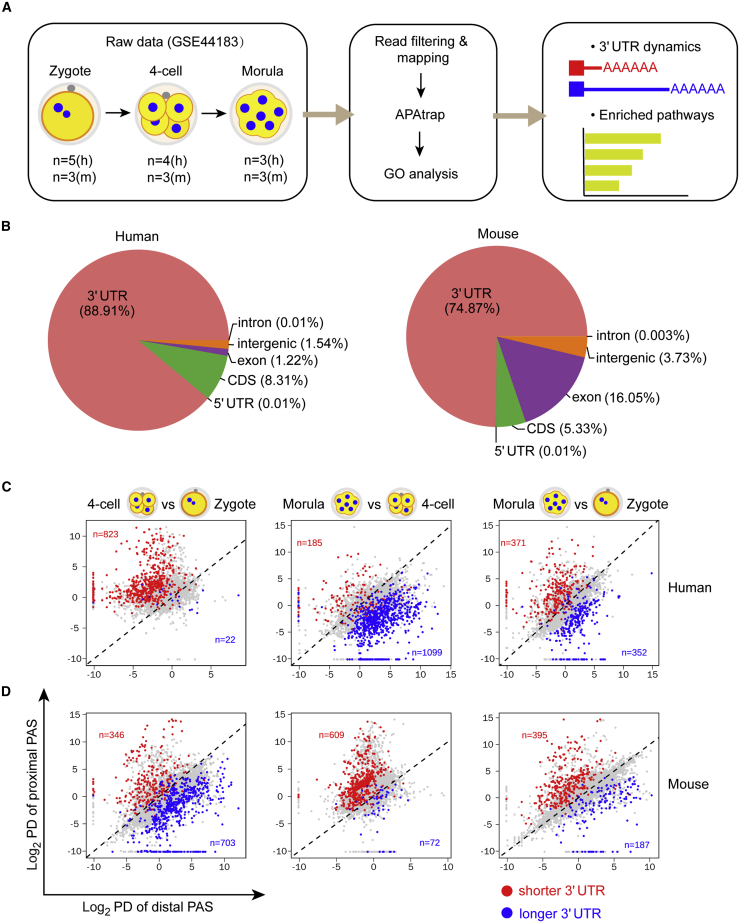
A large number of studies have utilized pre-implantation embryos for single-cell sequencing; the datasets are publicly available. To map the PASs in both human and mouse early embryos, we selected the scRNA-seq dataset GEO: GSE44183, which was generated with the same protocol applied to both human and mouse embryo cells, thus devoid of the variation caused by different methodologies (Xue et al., 2013). We retrieved the original sequencing data of zygotes, four-cell, and morula embryos for APA analysis, containing 21 samples in total (Figure 1A). Low-quality or adaptor-containing reads were filtered out before mapping. Filtered reads were mapped to the reference genomes. After removal of duplicate reads, each sample possessed 4.2 to 18.3 million reads suitable for further analysis.
Figure 1.
The landscape of alternative polyadenylation in human and mouse early embryos
(A) Schematic of analysis of 3′ UTR dynamics during early embryo development using a publicly available RNA-seq dataset. n indicates the number of samples.
(B) Distribution of PASs in human and mouse transcriptomes, analyzed by APAtrap. PASs detected at the zygote, four-cell, and morula stages are pooled together.
(C and D) Percentage difference (PD) of proximal and distal PAS in human and mouse early embryos. Genes with a significantly changed 3′ UTR between the two indicated embryonic stages are colored in blue or red (PD ≥ 0.5 as cutoff). The total number of genes in each category is indicated. Significance was determined by Benjamini-Hochberg method (adjusted p value < 0.05). Note that a value of 0.0009 is added to those PD values of 0 to shift the data points slightly away from the axes. See also Figure S1.
Several bioinformatics tools have been developed to identify and/or measure the usage of PASs based on RNA-seq data (Gruber and Zavolan, 2019). Among those, APAtrap is able to not only capture novel PASs but also quantify the usage of proximal or distal sites with high efficiency and flexibility (Ye et al., 2018). We therefore employed it for our analysis (Figure 1A). The APAtrap-detected PASs with fewer than 10 reads were discarded. The remaining sites were mapped to the corresponding genomes and were pooled together to obtain the overall distribution. As expected, the majority of the PASs are located within the 3′ UTRs, 88.9% for the human and 74.9% for the mouse (Figure 1B). For the following analysis, we focused on APA events in 3′ UTRs that use proximal or distal PASs to produce distinct transcripts.
APA is dynamic during human and mouse early embryo development
We next assessed the APA dynamics at a single gene level during early embryogenesis. As APAtrap could capture multiple proximal PASs for one gene with the respective usage frequencies, we selected the most frequent one as the representative and plotted it for three pre-implantation stages. Overall, APA occurred more frequently at the proximal PASs than the distal ones in both human and mouse early embryos (Figure S1A).
To pinpoint the genes that exhibited 3′ UTR length switching, we quantified 3′ UTR length changing between two pre-implantation stages using APAtrap. The number of genes exhibiting significant 3′ UTR switching ranged from 22 to 1,099 in the human (Figure 1C) and from 72 to 703 in the mouse (Figure 1D). For instance, 3′ UTR shortening was detected in 823 genes, whereas the lengthening was in 22 genes, during the progression from the zygote to four-cell stage of human embryos (Figure 1C). Unexpectedly, this trend was reversed at the morula stage, when genes with 3′ UTR lengthening significantly outnumbered those with 3′ UTR shortening (1,099 versus 185; Figure 1C). In the mouse, in contrast, 3′ UTR lengthening was present in 703 genes at the four-cell stage, whereas the shortening was in 609 genes at the morula (Figure 1D).
A previous study has suggested that conserved PASs reduce the diversity of 3′ end processing, thus facilitating a consistent APA pattern across species (Wang et al., 2018). To address whether the distinct patterns of 3′ UTR switching in the human and the mouse were attributed to non-conserved distal PASs, we identified 3,569 conserved distal PASs, accounting for 18% of the total distal PASs from both species. Plotting the usage of the conserved distal PASs at the zygote, four-cell, and morula stages in both species revealed the same trends as the overall usage of distal PASs in the respective species (Figure S1B), suggesting that conserved and non-conserved distal PASs are recognized similarly during the developmental window from zygote to morula, and that the distinct patterns of 3′ UTR switching are not caused by non-conserved distal PASs.
Collectively, these results unravel a dynamic switch of 3′ UTR lengths during early embryo development, the pattern of which depends on the species as well as the developmental stage.
APA modulates multiple pathways in human and mouse early embryos
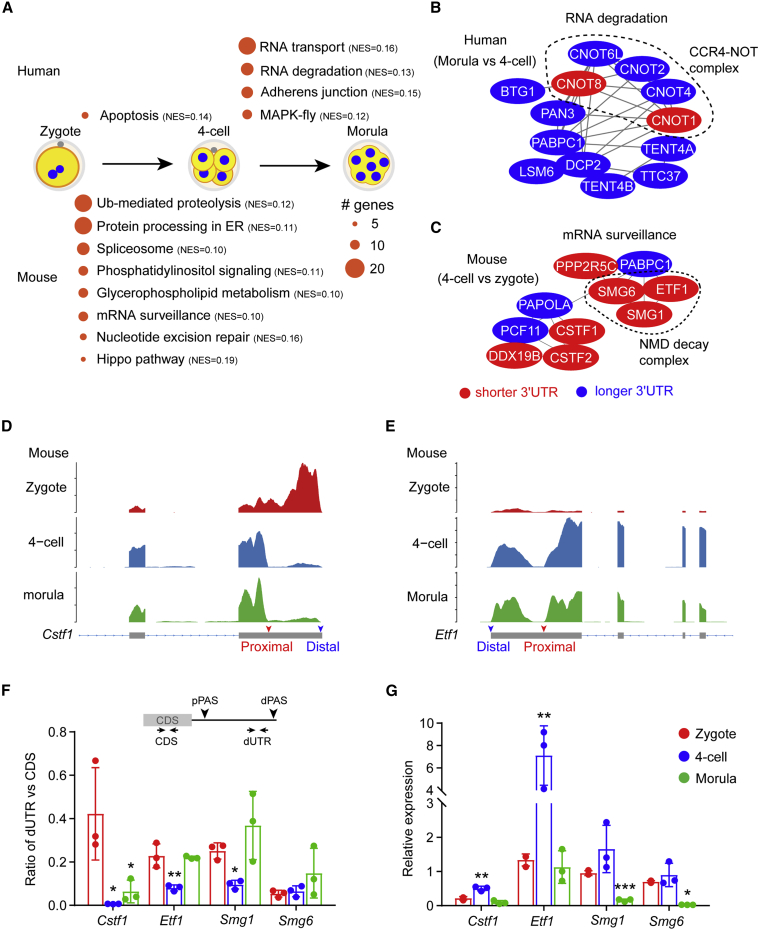
The change of 3′ UTR lengths via APA may have a profound impact on mRNA stability, translation, and localization (Mayr, 2019), thereby modulating the activity of affected pathways. Given that a large number of genes per stage exhibited 3′ UTR length switching during the pre-implantation development of both human and mouse embryos, we performed a gene set enrichment analysis to identify pathways affected by APA. In the human, genes involved in apoptosis were highly enriched when zygotes developed into four-cell embryos (Figure 2A); from the four-cell stage to the morula, the most enriched pathways included RNA transport, RNA degradation, adherens junction, and MAPK pathway (Figure 2A). In contrast, during the progression from zygotes to four-cell embryos in the mouse, the highly enriched pathways were ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis, protein processing in ER, spliceosome, phosphatidylinositol signaling, glycerophospholipid metabolism, mRNA surveillance, nucleotide excision repair, and Hippo pathway (Figure 2A). Notably, apart from RNA processing pathways (RNA transport and RNA degradation in the human, mRNA surveillance in the mouse), other pathways were not shared by human and mouse embryos (Figure 2A), suggesting a species-specific consequence of APA in early embryo development.
Figure 2.
Enriched pathways modulated by alternative polyadenylation in early embryos
(A) KEGG pathways in which genes with a significant 3′ UTR change are enriched. Only pathways with an adjusted p value < 0.05 are shown. Normalized enrichment score (NES) for each pathway is also shown.
(B and C) Network analysis of proteins associated with RNA degradation or mRNA surveillance. Nodes in blue or red indicate corresponding genes with a lengthened or shortened 3′ UTR.
(D and E) Read distribution of Cstf1 and Etf1 showing change of the 3′ UTR in mouse early embryos. Arrowheads mark the proximal or distal PAS in the terminal exon, curated by PolyASite 2.0 database.
(F and G) Quantification of 3′ UTR change and relative expression of candidate genes in mouse early embryos by qPCR. The locations of the primer pairs for quantifying the distal PAS usage are illustrated. Data are represented as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (vs. zygotes).
A previous transcriptomic profiling study has unveiled a conserved role of RNA processing in the development of both human and mouse embryos (Xue et al., 2013). In agreement with this, we identified two APA-modulated pathways related to RNA processing: RNA degradation at the morula stage in the human and mRNA surveillance at the four-cell stage in the mouse (Figure 2A). Network analysis revealed that the CCR4-NOT complex was at the core of the RNA degradation pathway enriched in human embryos (Figure 2B), including CNOT6L, CNOT8, CNOT1, CNOT2, and CNOT4. Among these, CNOT8 and CNOT1 displayed a shortened 3′ UTR at the morula, in contrast to the other three (Figure 2B). In addition to the CCR4-NOT complex, PAN3, the subunit of the PAN2-PAN3 complex, was also present in this pathway (Figure 2B). These two complexes catalyze the deadenylation of mRNAs to initiate degradation (Wahle and Winkler, 2013), suggesting that APA is probably involved in the regulation of mRNA turnover. In support of this notion, a recent transcriptome-wide mRNA poly(A) profiling study revealed a dynamic change of poly(A) tail lengths during human oocyte-to-embryo transition (Liu et al., 2021b).
Recent analyses on the poly(A) have shown that, in early embryos, the non-A residues within the poly(A) tail are incorporated between de- and re-adenylation, which are used as a marker for distinguishing zygotic mRNAs from maternal ones (Liu et al., 2021a, 2021b). For instance, G residues, added by TENT4A/B, stabilize zygotic mRNAs, whereas U residues promote fast degradation of maternal mRNAs (Liu et al., 2021a). Interestingly, the 3′ UTRs of TENT4A/B (also known as PAPD7/5) transcripts, were extended at the morula stage, compared with the four-cell stage (Figure 2B), suggesting that the activity of TENT4A/B is coupled with the deadenylation complexes in human early embryos.
In mouse embryos, genes clustered in the mRNA surveillance pathway can be further divided into two main functional groups: non-sense mediated mRNA decay (NMD) and polyadenylation (Figure 2C). The former includes Smg1, Smg6, and Etf1, the products of which form the NMD complex (Chang et al., 2007), whereas the latter consists of Cstf1, Cstf2, Pcf11, Pabpc1, and Papola (Figure 2C). The 3′ UTRs of the NMD complex transcripts were shortened at the four-cell stage, compared with the zygote stage (Figure 2C). A similar switch was also observed for Cstf1, Cstf2, Ppp2r5c, and Ddx19b (Figure 2C). The connection between the NMD and the polyadenylation groups was Pabpc1 (poly(A) binding protein cytoplasmic 1) and Papola (poly (A) polymerase alpha), which, on the contrary, exhibited 3′ UTR extension at the four-cell stage.
Next, we performed quantitative PCR (qPCR) to validate the 3′ UTR change in genes involved in mRNA surveillance. For example, both Cstf1 and Etf1 have two PASs of high usage within the terminal exon (Figures 2D and 2E), which are annotated in the database PolyASite 2.0 (Herrmann et al., 2020). We designed two pairs of primers for each gene, one pair adjacent to the distal PAS for quantification of the level of the long 3′ UTR (referred to as dUTR), whereas the other in the CDS region for quantification of the total mRNA level (Figure 2F). The ratio of the normalized expression obtained from two pairs of primers correlates with the frequency of the distal PAS usage. Consistent with the results obtained with APAtrap, Cstf1, Etf1, and Smg1 showed a decreased usage of the distal PASs in mouse four-cell embryos (Figure 2F). At the morula, in contrast to Cstf1, the 3′ UTR of which remained shortened, Etf1 and Smg1 had an extended 3′ UTR (Figure 2F), similar to the situation at the zygote stage. Overall but not strictly, we observed a negative correlation between the distal PAS usage and the mRNA levels (Figures 2F and 2G).
Together, these results suggest a widespread APA in pathways critical for early embryo development.
Pathways regulated by 3′ UTR extension in pre-implantation embryos
As mentioned above, the mRNA levels appeared to negatively correlate with the distal PAS usage. Moreover, a 3′ UTR often harbors miRNA binding sites and cis-acting elements, such as a cytoplasmic polyadenylation element (CPE) and a Pumilio-binding element (Grimson et al., 2007; Piqué et al., 2008; Dai et al., 2019). Thus, 3′ UTR lengthening may bring in such elements and profoundly impact the behavior of an mRNA, such as the stability and translational efficiency.
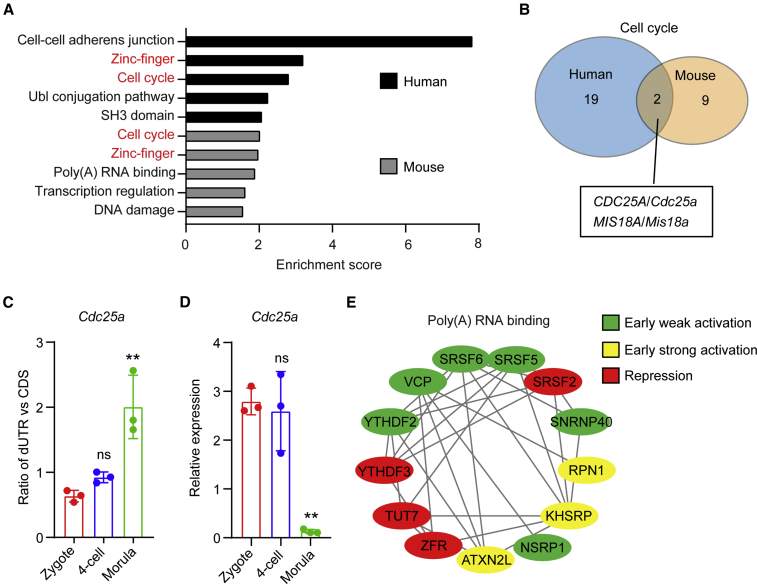
We next performed an enrichment analysis of the genes with an extended 3′ UTR to pinpoint the pathways. Figure 3A shows the top five pathways enriched in human morulae and mouse four-cell embryos, respectively. Two clusters, zinc-finger and cell cycle, were identified in both human and mouse embryos. Among the cell cycle genes, only CDC25A/Cdc25a and MIS18A/Mis18a were shared by human and mouse embryos (Figure 3B). The former triggers cell cycle progression through de-phosphorylation of CDK1 (Lindqvist et al., 2005), whereas the latter is localized at the centromere (Nardi et al., 2016). qPCR revealed a slightly elevated usage of the distal PAS in Cdc25a at the four-cell stage in the mouse, followed by a drastic increase of the usage at the morula stage (Figure 3C). Again, the extension of the 3′ UTR correlated with downregulation of Cdc25a mRNA (Figure 3D).
Figure 3.
Pathways regulated by 3′ UTR lengthening in early embryos
(A) Gene set enrichment analysis of transcripts with a lengthened 3′ UTR.
(B) Venn diagram of overlapping genes related to cell cycle regulation in human and mouse early embryos.
(C and D) Quantification of 3′ UTR changes and relative expression of Cdc25a in mouse early embryos by qPCR. Data are represented as mean ± SD. ∗∗p < 0.01; ns, no significance; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (vs. zygotes).
(E) Network analysis of proteins involved in poly(A) RNA binding. The combinatorial codes for translational control present in extended 3′ UTRs of corresponding genes were analyzed by CPE-mediated translational control web server and classified as early weak or strong activation or repression. See also Table S2.
The other three pathways were differentially enriched in the mouse and the human. Notably, genes encoding cell-cell adherens junction proteins, including E-cadherin, β-catenin, TJP1, PAK2, and anillin (Table S2), were highly enriched in human morulae (Figure 3A). On the other hand, the cluster of poly(A) RNA binding, including m6A readers (Ythdf2 and Ythdf3) and alternative splicing factors (Srsf2, Srsf5, and Srsf6), appeared specific to the mouse (Figures 3A and 3E). To assess a potential impact of 3′ UTR extension on translation, we used the CPE-mediated translational control web server to identify the combinatorial code (Piqué et al., 2008), revealing that either early activating or repressive elements can be present within the extended 3′ UTRs (Figure 3E).
Collectively, these results suggest a multifaceted role of 3′ UTR extension in regulating mRNA behavior during early embryo development.
The expression and localization of CFIm components in mouse early embryos
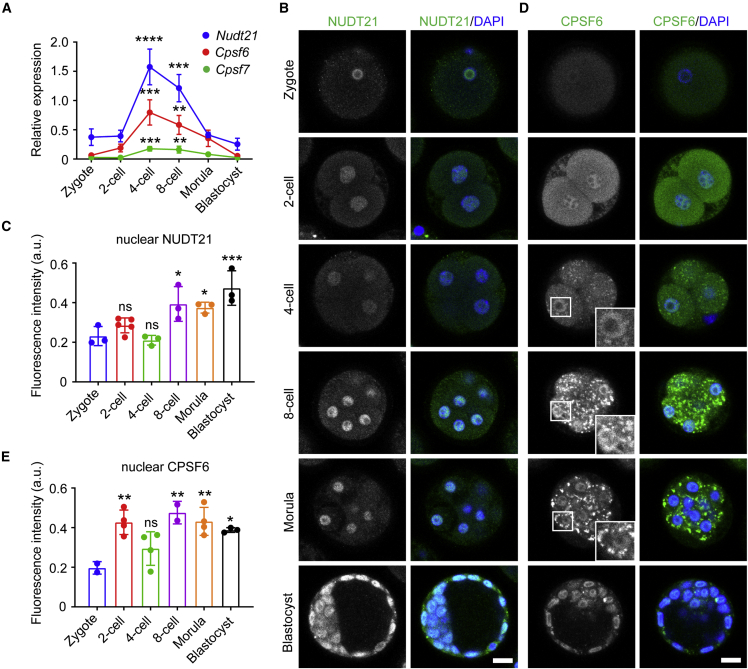
It has been well established that the length of a 3′ UTR is determined by the large polyadenylation machinery consisting of ∼20 core proteins (Shi et al., 2009). Among the four complexes, the CFIm complex plays a pivotal role in promoting the usage of the distal PAS in various contexts (Martin et al., 2012; Masamha et al., 2014; Brumbaugh et al., 2018; Marini et al., 2021; Ghosh et al., 2022). Albeit not essential for polyadenylation, revealed by reconstitution of pre-mRNA cleavage in vitro (Schmidt et al., 2022), the CFIm complex enhances the selection of the distal PAS by binding to the UGUA motif upstream of AAUAAA (Zhu et al., 2018). We inferred that the switching of 3′ UTR lengths in early embryos could be attributed to the changed abundance of CFIm components (NUDT21, CPSF6, and CPSF7). To measure their expression, we isolated mouse zygotes for in vitro culture and harvested the embryos at different stages for qPCR, revealing that the mRNA level of CFIm components peaked at the four-cell stage, concomitant with the lengthening of 3′ UTRs (Figure 1D), and then decreased gradually until the blastocyst (Figure 4A).
Figure 4.
Expression and localization of CFIm components in mouse early embryos
(A) Relative expression of CFIm components in mouse early embryos quantified by qPCR.
(B−E) Immunostaining of NUDT21 and CPSF6 in mouse early embryos. Nuclear NUDT21 (C) and CPSF6 (E) intensities in mouse early embryos were quantified. Each dot represents the mean intensity of each embryo.
Data are represented as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; ns, no significance; one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (vs. zygotes). Scale bar, 20 μm. See also Figures S2 and S3.
We next examined their localization by immunostaining. siRNA knockdown followed by immunoblotting validated the specificity of the antibodies and also the effectiveness of the siRNAs (Figures S2A–S2C). Immunofluorescence showed that all three components were localized within the nucleus in HeLa cells (Figures S2D–S2F). We then applied these antibodies to mouse early embryos. As expected, NUDT21 was localized in the nucleus of blastomeres throughout pre-implantation (Figure 4B). Nuclear NUDT21 significantly increased at the eight-cell stage, and reached the highest level at the blastocyst (Figure 4C).
Unlike NUDT21, CPSF6 displayed a varying distribution, which was detected not only in the nucleus but also in the cytoplasm (Figure 4D). Nuclear CPSF6 became more detectable at the two-cell stage and remained throughout pre-implantation (Figure 4D). Notably, granules of CPSF6 were observed in the cytoplasm at the four-cell stage, peaked at the eight-cell stage, then declined at the morula, and finally disappeared at the blastocyst (Figure 4D). Such granules might be specific to early embryo development because they were absent in HeLa cells (Figure S2E). Quantification showed that the fluorescence intensity of nuclear CPSF6 rose from the zygote to the two-cell stage (Figure 4E), likely due to an increased mRNA level (Figure 4A). The fall of nuclear CPSF6 at the four-cell stage might result from the retention of CPSF6 in the cytoplasmic granules. At the eight-cell stage, in contrast to a further deceased level of Cpsf6 mRNA, nuclear CPSF6 increased to a similar level to that of the two-cell stage (Figure 4E). In contrast to the nuclear localization in HeLa cells (Figure S2F), CPSF7 was exclusively localized in the cytoplasm of blastomeres in pre-implanted embryos (Figure S3). Collectively, these results demonstrate a differential localization of CFIm components in mouse early embryos.
The distribution of CFIm components in human early embryos
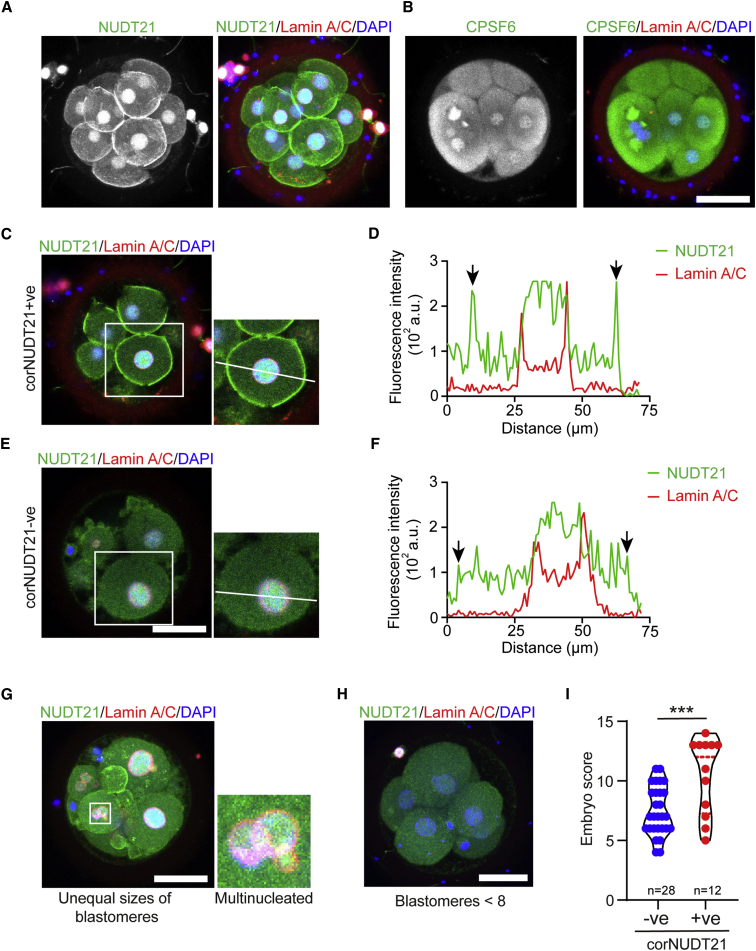
We next examined the localization of NUDT21 and CPSF6 in human early embryos, which were generated by in vitro fertilization (IVF) at a fertility clinic, cultured for 3 or 6 days (D3, D6), but unsuitable for embryo transfer or freezing because of low quality. Consistent with the localization in mouse embryos, NUDT21 was found in the nucleus in a D3 embryo that consisted of 14 blastomeres (Figure 5A). Notably, strong staining at the cell cortex was also observed (Figure 5A and Video S1), which was confirmed by co-staining with phalloidin that marks the cortical actin filament (Figure S4A). The cortical localization of NUDT21 was not seen in any human blastocysts we stained (n = 3; Figure S4B), nor in mouse embryos, suggesting that it might be specific to pre-compaction human embryos.
Figure 5.
Cortex-localized NUDT21 positively correlates with the score of human D3 embryos
(A and B) Immunostaining of NUDT21 and CPSF6 in human D3 embryos. Lamin A/C marks the nuclear membrane. Shown are maximum projection images of Z-stack.
(C−F) Examples of embryos with or without cortex-localized NUDT21 (corNUDT21+ve/−ve) in blastomeres. NUDT21 was mainly detected in the nucleus in corNUDT21−ve blastomeres. Note that the image in (C) was from the same embryo as in (A). Profiling of NUDT21 fluorescence intensity across a blastomere in (C) and (E), respectively. Arrows indicate the signals at the cortical region.
(G) An example of human D3 embryos with multinucleated blastomeres and blastomeres of unequal sizes.
(H) An example of D3 embryos with fewer than eight blastomeres.
(I) Quality scores of corNUDT21+ve (n = 12) and corNUDT21−ve (n = 28) embryos based on the morphology criteria. ∗∗∗p < 0.001, two-tailed Student’s t test. Scale bar, 50 μm (B, E, G, H). See also Figures S4 and S5.
CPSF6 displayed a diffuse signal within the cytoplasm in D3 human embryos, besides nuclear localization (Figure 5B). In contrast to the mouse, CPSF6 granules were absent in D3 human embryos (Figure 5B). In blastocysts, strong signals of NUDT21 and CPSF6 were detected in the nucleus (Figures S4B and S4C). In addition, discontinuous CPSF6 puncta were detected along the cell-cell junctions (Figure S4C).
Cell cortex-localized NUDT21 positively correlates with the quality of human early embryos
We observed that some human D3 embryos only displayed nucleus-localized NUDT21 (Figure S4D). Such embryos often contained multinucleated blastomeres (see also later Figure 5G). This prompted us to determine whether the cortical localization of NUDT21 was correlated with embryo quality. Embryos that displayed a spike of NUDT21 signal at the cortex were categorized as cortical NUDT21 positive (corNUDT21+ve; Figures 5C and 5D), whereas those without such a signal were categorized as corNUDT21−ve (Figures 5E and 5F). We examined 40 D3 embryos in total, among which 12 were corNUDT21+ve. Multinucleated blastomeres or blastomeres of unequal sizes were commonly seen in corNUDT21−ve embryos (Figure 5G). The embryos were scored on the basis of blastomere volumes, cleavage synchrony, multinucleation and fragmentation (De Placido et al., 2002). The human D3 embryos with fewer than eight blastomeres were defined as no division (Figure 5H). Overall, the corNUDT21−ve embryos received lower scores (Figure 5I), suggesting that cortex-localized NUDT21 positively correlates with the quality of human early embryos.
The key players that drive embryo compaction are the actomyosin skeleton and the cell adhesion protein E-cadherin (Shahbazi, 2020). We next tested whether NUDT21 interacts with any compaction driver. We transfected a plasmid expressing YFP-NUDT21 into HEK-293 cells and performed immunoprecipitation of YFP. CPSF6, a known interaction partner of NUDT21, was detected by both immunoblotting and mass spectrometry from the immunoprecipitation (Figures S5A and S5B). Mass spectrometry additionally identified CPSF7, hnRNPA3, and RPS7 as high-confidence partners of NUDT21 (Figure S5C), none of which is known to interact with any compaction driver. Thus, at this point we are unable to delineate a mechanism by which NUDT21 is recruited to the cortex.
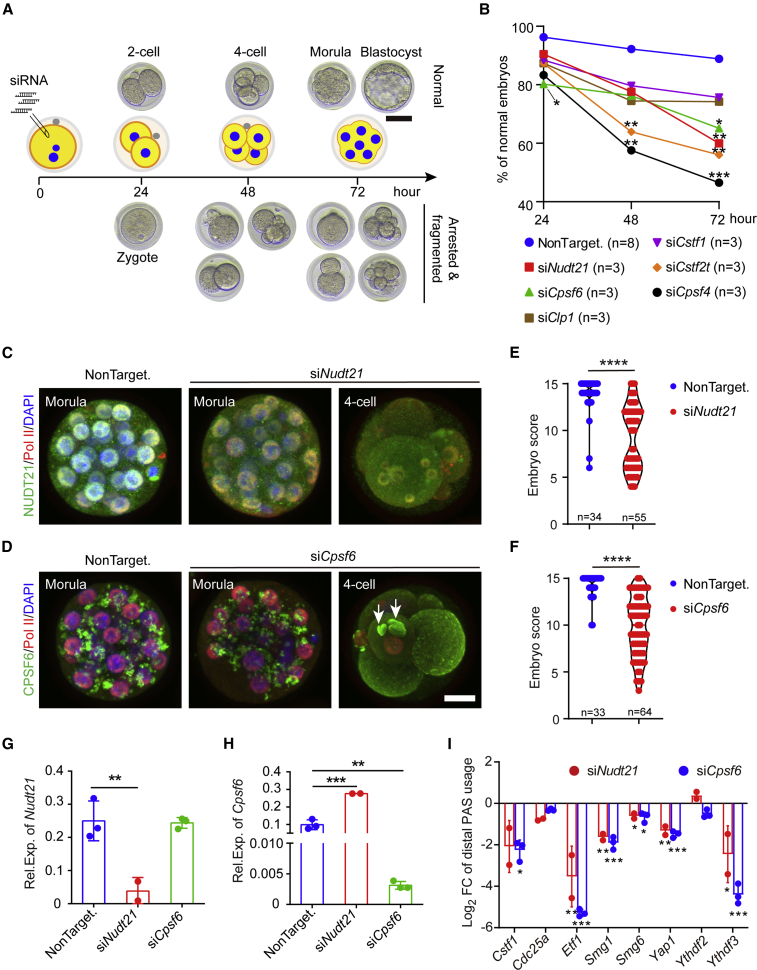
The CFIm complex is required for the normal development of mouse early embryos
To explore the functional significance of APA in early embryo development, we knocked down CFIm components by microinjecting the siRNAs into mouse zygotes. Besides NUDT21 and CPSF6, we also depleted several key players for polyadenylation, including CPSF4 of the CPSF complex, CSTF1 of the CstF complex, CLP1 of the CFIIm complex, and CSTF2T. After microinjection, the zygotes were cultured in vitro and imaged at select time points. Two-cell embryos at 24 h, four-cell embryos at 48 h, and morulae and blastocysts at 72 h were classified as normal embryos, whereas arrested and fragmented embryos were classified as abnormal ones (Figure 6A). At 24 h, only knockdown of Cpsf6 significantly decreased the percentage of two-cell embryos (Figure 6B). At 48 h, knockdown of Cpsf4 or Cstf2t severely impaired the development of early embryos: only 57.6% or 63.9% of the respective embryos reached the four-cell stage (Figure 6B). A large number of the embryos were arrested at an earlier stage or fragmented in these two groups (Figures S6A–S6C). At 72 h, knockdown of Nudt21 or Cpsf6 also dramatically deceased the percentage of normal embryos (60.0% for siNudt21, 65.1% for siCpsf6, 88.9% for NonTargeting control; Figure 6B); in the siCpsf6 group, an increased number of the embryos were arrested at the four-cell stage, while most abnormal embryos in the siNudt21 group were zygotes or fragmented (Figures S6A and S6D). Given that both CPSF4 and CSTF2T are required for the cleavage and polyadenylation (Yao et al., 2013; Chan et al., 2014; Schmidt et al., 2022), it is not surprising that downregulation of either impeded early embryo development. Although the CFIm complex is not essential for polyadenylation (Schmidt et al., 2022), our results indicate that its disruption is also detrimental to early embryos.
Figure 6.
CFIm components are essential for mouse early embryo development
(A) Schematic of evaluation of mouse embryo development after siRNA microinjection using bright-field images.
(B) Percentages of normal embryos at different time points after siRNA microinjection. Data are presented as mean. n indicates the number of independent experiments.
(C and D) Immunostaining of NUDT21 or CPSF6 in mouse embryos 72 h after microinjection. RNA polymerase II (Pol II) marks the nucleus. Shown are maximum projection images of Z-stack.
(E and F) Quality scores of embryos collected at 72 h after siRNA microinjection. n indicates the number of evaluated embryos. ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001, two-tailed Student’s t test with Welch’s correction.
(G and H) Quantification of Nudt21 and Cpsf6 expression in the morulae after siRNA knockdown by qPCR.
(I) Quantification of distal PAS usage of candidate genes in the morulae by qPCR.
Data are represented as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (vs. NonTargeting siRNA). Scale bar, 50 μm (A), 20 μm (D). See also Figure S6.
We collected the 72-h embryos for immunostaining. Albeit still detectable in the nucleus or cytoplasm, the intensity of NUDT21 or CPSF6 was weaker after siRNA treatment (Figures 6C and 6D), suggesting an effective yet incomplete knockdown. In the arrested four-cell embryos, blastomeres with a fragmented nucleus or without a nucleus were frequently observed (Figures 6C and 6D). Of note, large granules of CPSF6 were commonly seen in the arrested four-cell embryos (14 out of 25; Figure 6D). As anticipated, siNudt21 or siCpsf6 significantly reduced the embryo scores (Figures 6E and 6F).
We further performed qPCR to quantify the mRNA levels of Nudt21 and Cpsf6, as well as the distal PAS usage in the select target genes, in the morulae. As expected, injection of the respective siRNA resulted in a dramatic reduction of Nudt21 or Cpsf6 mRNA level (Figures 6G and 6H), which in turn led to decreased usage of the distal PAS for most of the tested genes, including Ythdf3, Yap1, Smg6, Smg1, and Etf1 (Figure 6I).
Taken together, these results underscore the importance of the CFIm complex in the development of mammalian early embryos, probably through promoting 3′ UTR extension.
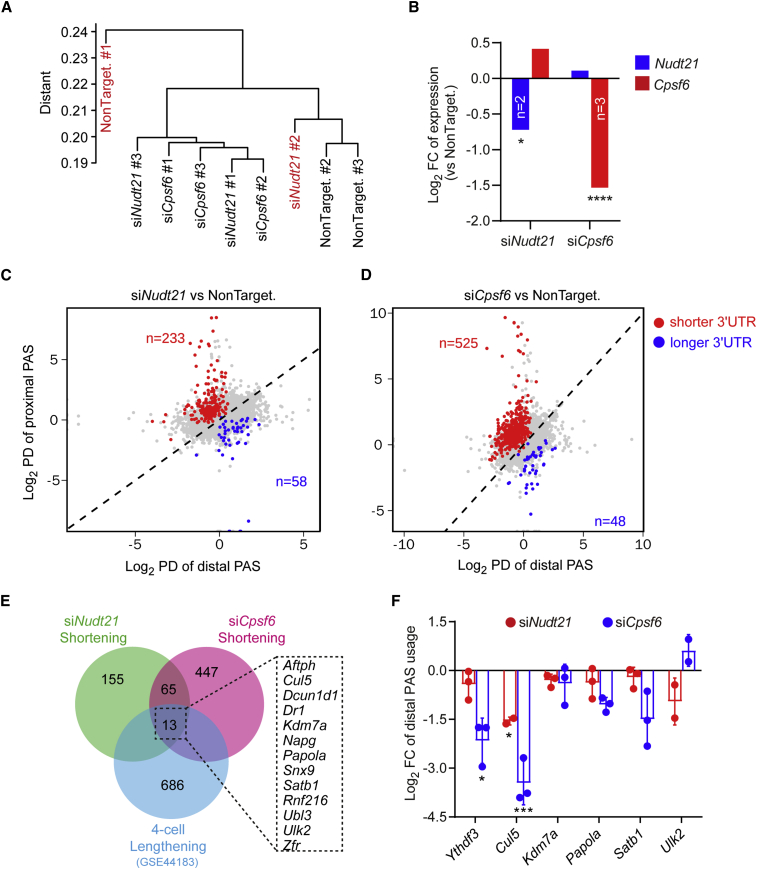
Downregulation of CFIm components results in an overall 3′ UTR shortening in mouse four-cell embryos
To assess whether knockdown of Nudt21 or Cpsf6 would cause a global 3′ UTR shortening, we harvested the mouse four-cell embryos at 48 h after microinjection of the siRNA and performed Smart-seq2. Clustering of the sequenced samples identified two outliners (Figure 7A), which were excluded from subsequent analysis. Analysis by DESeq2 confirmed the knockdown of Nudt21 or Cpsf6 (Figure 7B). We then employed APAtrap to analyze the usage of PASs. Knockdown of Nudt21 or Cpsf6 resulted in a shortened 3′ UTR in 233 or 525 genes and an extended 3′ UTR in 58 or 48 genes, respectively (Figures 7C and 7D). Therefore, knockdown of either Nudt21 or Cpsf6 led to an overall increased usage of the proximal PAS.
Figure 7.
Disruption of the CFIm complex results in 3′ UTR shortening in mouse four-cell embryos
(A) Clustering of four-cell embryos that have been sequenced after siRNA microinjection. The samples in red are regarded as outliners.
(B) Fold change of Nudt21 and Cpsf6 level in four-cell embryos quantified by Smart-seq2. Differential expression was calculated by DESeq2. ∗ adjusted p value < 0.05, ∗∗∗∗ adjusted p value < 0.0001.
(C and D) Percentage difference of proximal or distal PAS usage in four-cell embryos after Nudt21 or Cpsf6 knockdown, analyzed by APAtrap.
(E) Venn diagram of genes with a shortened 3′ UTR after Nudt21 or Cpsf6 knockdown and genes with a lengthened 3′ UTR at four-cell stage.
(F) Quantification of distal PAS usage of candidate genes in mouse four-cell embryos after Nudt21 or Cpsf6 knockdown by qPCR. Data are represented as mean ± SD. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparison test (vs. NonTargeting siRNA).
Analysis of the genes with a shortened 3′ UTR upon the knockdown and those with an extended 3′ UTR at the four-cell stage under the normal development identified 13 shared genes (Figure 7E). We selected five for qPCR validation; we also included Ythdf3, which showed a strong reduction of the distal PAS usage in the 72-h embryos upon Nudt21 or Cpsf6 knockdown. As expected, either knockdown reduced the distal PAS usage for the majority of the tested genes, although not all reached statistical significance (Figure 7F). Notably, the distal PAS usage of Ythdf3 and Cul5 seems to be more sensitive to CFIm perturbation (Figure 7F). Like Ythdf3, the 3′ UTR of Cul5 also contains repressive CPE elements (Piqué et al., 2008); thus, their 3′ UTR shortening might enhance the translation.
Discussion
Our study uncovers the dynamics of 3′ UTR lengths in human and mouse early embryos. Although the APA patterns appear strikingly different between the two species, it can be explained by the different expression profiles of CFIm components. Multiple studies have suggested that the enhancer-dependent APA activity of the CFIm complex is mediated by NUDT21 and CPSF6 (Kim et al., 2010; Martin et al., 2012; Zhu et al., 2018). The surged level of these two components enhances the usage of the distal PAS (Masamha et al., 2014), whereas depletion of either one results in polyadenylation at the proximal PAS (Martin et al., 2012; Zhu et al., 2018; Ghosh et al., 2022), highlighting a key role of the CFIm complex in PAS selection. By using microarray to detect APA in mouse embryos, a previous study found that progressive lengthening of 3′ UTRs started at E1.5 (Ji et al., 2009). Here we unravel that the extension of 3′ UTR is probably driven by the CFIm complex in early embryos, the components of which appear to be upregulated after zygotic genome activation.
Then how was the PAS usage shifted from the distal to the proximal ones, for instance, in mouse morulae? It is well known that the proximal PAS is commonly used in male germ cells (Li et al., 2016b), where both NUDT21 and CPSF6 are highly expressed (Sartini et al., 2008; Li et al., 2016a), suggesting a mechanism overriding the action of the CFIm complex. Based on our results, one plausible explanation is the reduced level of effective CPSF6 protein from the eight-cell stage by downregulation of Cpsf6 mRNA together with cytoplasmic sequestration of the protein into the granules. Another possible explanation is via upregulation of factors that promote the proximal PAS usage, such as CPSF1, CSTF2, CSTF3, and PCF11 (Mohanan et al., 2021). Among these, CPSF1 merits further investigation (Van Etten et al., 2017), as its expression was significantly elevated in mouse morulae (Figure S1C).
Besides the expression levels of CFIm components, the temporal distribution may also determine the activity of the complex, thereby modulating PAS selection. The cytoplasmic localization of CPSF7 in mouse early embryos suggests that CPSF7 is unlikely to complex with NUDT21 in the nucleus of blastomeres. Presumably, the formation of cytoplasmic CPSF6 granules from the four-cell to the morula stage reduces the availability of CPSF6 for the CFIm complex. Lastly, the cortical localization of NUDT21 in human embryos may markedly reduce the activity of the CFIm complex, or shift the subcellular location for APA, or represent a function independent of APA. The mechanisms by which CFIm components are retained in the cytoplasm remain elusive. For the case of NUDT21, given its ability to bind the UGUA motif in 3′ UTR (Zhu et al., 2018), it might be co-transported with cortex-bound, locally translated mRNAs. It is also possible that certain RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) recruit NUDT21 to the cortex, which remain to be identified.
It is commonly thought that the dynamic change of 3′ UTRs orchestrates gene expression, due to miRNA binding sites in this region. However, this view has been challenged by a number of studies. For example, in proliferating T cells, 3′ UTR lengths did not exhibit a strong correlation with protein output (Gruber et al., 2014). If this is also true for early embryos, then what is the role of 3′ UTR lengthening? It seems that the multifaceted features of 3′ UTRs serve the needs of embryo development (Shahbazi, 2020). It should be noted that we observed a negative correlation between the mRNA levels and 3′ UTR extension in most of the qPCR-measured genes, suggesting a repressive effect of long 3′ UTRs on the mRNA levels, although the exact mechanism is unclear. Moreover, long 3′ UTRs can mediate mRNA localization via binding to RBPs (Mayr, 2017), which in turn facilitates transportation and local translation of the mRNAs (Terenzio et al., 2018; Parker et al., 2020). This phenomenon has been commonly seen in neurons (Miura et al., 2013). Perhaps, 3′ UTR-dependent mRNA localization also applies to human early embryos, as the transcripts encoding adherens junction proteins contain a long 3′ UTR, which may promote compaction. Finally, 3′ UTRs can regulate translation via miRNA-independent mechanisms. Using low-input Ribo-seq, a recent study has found that a CPE proximal to the polyadenylation signal in a 3′ UTR activates translation in early embryos (Xiong et al., 2022), providing an insight into how translation is connected with polyadenylation. These findings hint that APA can regulate translation through PAS selection.
Our study suggests that the activity of RNA decay complexes is likely modulated by APA during maternal-to-zygotic transition, a critical stage when maternal mRNAs are cleared by the deadenylase complexes (Sha et al., 2020b). A recent study has shown that the key components of these complexes, such as CNOT7, CNOT6L, and PAN2, are markedly downregulated in human eight-cell embryos (Sha et al., 2020a), suggesting a decreased demand for the deadenylase complexes upon elimination of maternal mRNAs. It is possible that 3′ UTR extension can impose additional repression on the RNA degradation pathway. Quantification of the 3′ UTR lengths of NMD components by APAtrap and qPCR indeed revealed a dynamic change throughout early embryo development.
Most importantly, our study highlights an indispensable role for CFIm-mediated APA in the development of mouse early embryos. This could be attributed to an important role of long 3′ UTRs per se or prevention of mis-polyadenylation at early cryptic PASs. Investigation of the function of APA in pathways essential for early embryo development is the next step toward a better understanding of the regulatory network for embryogenesis. Altogether, our findings complement current knowledge of the APA landscape in mammalian embryo development.
Experimental procedures
Resource availability
Corresponding author
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the corresponding author, H.L. (lihuaibiao@hust.edu.cn).
Materials availability
All unique/stable reagents generated in this study are available from the lead contact without restriction.
Ethics statement
Study using human embryos was approved and overseen by the ethical committee of Wuhan Tongji Reproductive Medicine Hospital (approval number: 2020–005). The embryos were obtained from donor couples with informed consent.
All animal experiments were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology (approval number: 2434) and performed in compliance with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Human embryo collection
Human zygotes were generated by IVF and cultured in K-SICM medium (Cook Medical) covered with mineral oil (Sigma-Aldrich, cat. #M8410) at 37°C with 5% CO2 in a humidified incubator for 3 days (D3). The embryos were then transferred to K-SIBM medium (Cook Medical) and cultured for another 3 days (D6). Embryos at D3 and D6 were assessed by clinicians of Wuhan Tongji Reproductive Medicine Hospital. Embryos unsuitable for transfer or freezing were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA) at room temperature for 30 min before immunostaining.
Mouse embryo collection
To obtain mouse pre-implanted embryos, 8-week-old female ICR mice were intraperitoneally injected with pregnant mare serum gonadotrophin, then with human chorionic gonadotrophin 48 h later, and mated with adult male mice. The next day, female mice with a vaginal plug were separated from male mice. Embryos were collected from the oviduct or uterus of pregnant mice at the respective time points as follows: zygotes (day 1), two-cell embryos (day 2), four-cell embryos (day 2), eight-cell embryos (day 2.5), morulae (day 3), and blastocysts (day 3.5). Embryos were fixed with 4% PFA at room temperature for 15 min before immunostaining.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad). Results are presented as mean ± SD, unless otherwise indicated. Student’s t test or single-factor analysis of variance (one-way ANOVA) was used for significance test.
Author contributions
Conceptualization, H.L. and Y.Cui; investigation, N.L., Y.Cai, and H.L.; formal analysis, N.L., Y.Cai, and J.Z.; resources, M.Z., L.Zhou, and L.Zhang; writing – original draft, N.L., Y. Cai, H.L., and Y.Cui; writing – reviewing and editing, H.L., Y.Cui, and W.X.; funding acquisition, H.L. and L.Zhang; supervision, H.L., Y.Cui, and W.X.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Independent Innovation Research Fund of HUST (5003519003), the joint program of Wuhan National High Magnetic Field Center (WHMFC202105), and the Postgraduate Student Innovation Grants of HUST (2021yjsCXCY100). We thank the reviewers for their constructive comments on the manuscript.
Conflict of interests
J.Z. is a founder and shareholder of Wuhan Jianwen Biological Technology. The company did not provide any funding and was not involved in this study.
Published: December 22, 2022
Footnotes
Supplemental information can be found online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.11.016.
Contributor Information
Wenpei Xiang, Email: wpxiang2010@gmail.com.
Yan Cui, Email: yancui.research@gmail.com.
Huaibiao Li, Email: lihuaibiao@hust.edu.cn.
Supplemental information
Data and code availability
The accession number of the mass spectrometry proteomics data reported in this paper is ProteomeXchange: PXD031134. The accession number of the RNA-seq data reported in this paper is GSA: CRA007735. No novel codes were generated in this study.
References
- Agarwal V., Lopez-Darwin S., Kelley D.R., Shendure J. The landscape of alternative polyadenylation in single cells of the developing mouse embryo. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:5101. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25388-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumbaugh J., Di Stefano B., Wang X., Borkent M., Forouzmand E., Clowers K.J., Ji F., Schwarz B.A., Kalocsay M., Elledge S.J., et al. Nudt21 controls cell fate by connecting alternative polyadenylation to chromatin signaling. Cell. 2018;172:629–631. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.12.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S.L., Huppertz I., Yao C., Weng L., Moresco J.J., Yates J.R., 3rd, Ule J., Manley J.L., Shi Y. CPSF30 and Wdr33 directly bind to AAUAAA in mammalian mRNA 3' processing. Genes Dev. 2014;28:2370–2380. doi: 10.1101/gad.250993.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y.F., Imam J.S., Wilkinson M.F. The nonsense-mediated decay RNA surveillance pathway. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007;76:51–74. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.76.050106.093909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai X.X., Jiang J.C., Sha Q.Q., Jiang Y., Ou X.H., Fan H.Y. A combinatorial code for mRNA 3'-UTR-mediated translational control in the mouse oocyte. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:328–340. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Placido G., Wilding M., Strina I., Alviggi E., Alviggi C., Mollo A., Varicchio M.T., Tolino A., Schiattarella C., Dale B. High outcome predictability after IVF using a combined score for zygote and embryo morphology and growth rate. Hum. Reprod. 2002;17:2402–2409. doi: 10.1093/humrep/17.9.2402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derti A., Garrett-Engele P., Macisaac K.D., Stevens R.C., Sriram S., Chen R., Rohl C.A., Johnson J.M., Babak T. A quantitative atlas of polyadenylation in five mammals. Genome Res. 2012;22:1173–1183. doi: 10.1101/gr.132563.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Ataman M., Bak M., Börsch A., Schmidt A., Buczak K., Martin G., Dimitriades B., Herrmann C.J., Kanitz A., Zavolan M. CFIm-mediated alternative polyadenylation remodels cellular signaling and miRNA biogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50:3096–3114. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimson A., Farh K.K.H., Johnston W.K., Garrett-Engele P., Lim L.P., Bartel D.P. MicroRNA targeting specificity in mammals: determinants beyond seed pairing. Mol. Cell. 2007;27:91–105. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber A.J., Zavolan M. Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019;20:599–614. doi: 10.1038/s41576-019-0145-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruber A.R., Martin G., Müller P., Schmidt A., Gruber A.J., Gumienny R., Mittal N., Jayachandran R., Pieters J., Keller W., et al. Global 3' UTR shortening has a limited effect on protein abundance in proliferating T cells. Nat. Commun. 2014;5:5465. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann C.J., Schmidt R., Kanitz A., Artimo P., Gruber A.J., Zavolan M. PolyASite 2.0: a consolidated atlas of polyadenylation sites from 3' end sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz918. D174-d179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji Z., Lee J.Y., Pan Z., Jiang B., Tian B. Progressive lengthening of 3' untranslated regions of mRNAs by alternative polyadenylation during mouse embryonic development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009;106:7028–7033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900028106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S., Yamamoto J., Chen Y., Aida M., Wada T., Handa H., Yamaguchi Y. Evidence that cleavage factor Im is a heterotetrameric protein complex controlling alternative polyadenylation. Gene Cell. 2010;15:1003–1013. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2443.2010.01436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Frappart L., Moll J., Winkler A., Kroll T., Hamann J., Kufferath I., Groth M., Taudien S., Schütte M., et al. Impaired planar germ cell division in the testis, caused by dissociation of RHAMM from the spindle, results in Hypofertility and seminoma. Cancer Res. 2016;76:6382–6395. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-16-0179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li W., Park J.Y., Zheng D., Hoque M., Yehia G., Tian B. Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation in spermatogenesis connects chromatin regulation with post-transcriptional control. BMC Biol. 2016;14:6. doi: 10.1186/s12915-016-0229-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindqvist A., Källström H., Lundgren A., Barsoum E., Rosenthal C.K. Cdc25B cooperates with Cdc25A to induce mitosis but has a unique role in activating cyclin B1-Cdk1 at the centrosome. J. Cell Biol. 2005;171:35–45. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200503066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Nie H., Wang L.-Y., Wu S., Li W., Zhou Q., Wang J., Lu F. Abundant non-A residues in the poly(A) tail orchestrate the mouse oocyte-to-embryo transition. bioRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.08.29.458077. Preprint at. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Wu K., Shao F., Nie H., Zhang J., Li C., Hou Z., Wang J., Zhou B., Zhao H., Lu F. Dynamics of poly(A) tail length and non-A residues during the human oocyte-to-embryo transition. bioRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.08.29.458075. Preprint at. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald C.C. Vol. 10. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA; 2019. p. e1526. (Tissue-specific Mechanisms of Alternative Polyadenylation: Testis, Brain, and beyond (2018 Update)). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marini F., Scherzinger D., Danckwardt S. TREND-DB-a transcriptome-wide atlas of the dynamic landscape of alternative polyadenylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49 doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa722. D243-d253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G., Gruber A.R., Keller W., Zavolan M. Genome-wide analysis of pre-mRNA 3' end processing reveals a decisive role of human cleavage factor I in the regulation of 3' UTR length. Cell Rep. 2012;1:753–763. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masamha C.P., Xia Z., Yang J., Albrecht T.R., Li M., Shyu A.B., Li W., Wagner E.J. CFIm25 links alternative polyadenylation to glioblastoma tumour suppression. Nature. 2014;510:412–416. doi: 10.1038/nature13261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayr C. Regulation by 3'-untranslated regions. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2017;51:171–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev-genet-120116-024704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayr C. What are 3' UTRs doing? Cold Spring Harbor Perspect. Biol. 2019;11:a034728. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a034728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura P., Shenker S., Andreu-Agullo C., Westholm J.O., Lai E.C. Widespread and extensive lengthening of 3' UTRs in the mammalian brain. Genome Res. 2013;23:812–825. doi: 10.1101/gr.146886.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanan N.K., Shaji F., Koshre G.R., Laishram R.S. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA; 2021. Alternative Polyadenylation: An Enigma of Transcript Length Variation in Health and Disease; p. e1692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A.R., Bos A., Diosdado B., Rooijers K., Elkon R., Bolijn A.S., Carvalho B., Meijer G.A., Agami R. Alternative cleavage and polyadenylation during colorectal cancer development. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012;18:5256–5266. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-12-0543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardi I.K., Zasadzińska E., Stellfox M.E., Knippler C.M., Foltz D.R. Licensing of centromeric chromatin assembly through the Mis18α-Mis18β Heterotetramer. Mol. Cell. 2016;61:774–787. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.02.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker D.M., Winkenbach L.P., Boyson S., Saxton M.N., Daidone C., Al-Mazaydeh Z.A., Nishimura M.T., Mueller F., Osborne Nishimura E. mRNA localization is linked to translation regulation in the Caenorhabditis elegans germ lineage. Development. 2020;147 doi: 10.1242/dev.186817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piqué M., López J.M., Foissac S., Guigó R., Méndez R. A combinatorial code for CPE-mediated translational control. Cell. 2008;132:434–448. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M.G., Amara S.G., Evans R.M. Alternative RNA processing events as a critical developmental regulatory strategy in neuroendocrine gene expression. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 1984;49:27–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg R., Neilson J.R., Sarma A., Sharp P.A., Burge C.B. Proliferating cells express mRNAs with shortened 3' untranslated regions and fewer microRNA target sites. Science. 2008;320:1643–1647. doi: 10.1126/science.1155390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartini B.L., Wang H., Wang W., Millette C.F., Kilpatrick D.L. Pre-messenger RNA cleavage factor I (CFIm): potential role in alternative polyadenylation during spermatogenesis. Biol. Reprod. 2008;78:472–482. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.107.064774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Kluge F., Sandmeir F., Kühn U., Schäfer P., Tüting C., Ihling C., Conti E., Wahle E. Reconstitution of 3' end processing of mammalian pre-mRNA reveals a central role of RBBP6. Genes Dev. 2022;36:195–209. doi: 10.1101/gad.349217.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha Q.Q., Zheng W., Wu Y.W., Li S., Guo L., Zhang S., Lin G., Ou X.H., Fan H.Y. Dynamics and clinical relevance of maternal mRNA clearance during the oocyte-to-embryo transition in humans. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:4917. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18680-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sha Q.Q., Zhu Y.Z., Li S., Jiang Y., Chen L., Sun X.H., Shen L., Ou X.H., Fan H.Y. Characterization of zygotic genome activation-dependent maternal mRNA clearance in mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48:879–894. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahbazi M.N. Mechanisms of human embryo development: from cell fate to tissue shape and back. Development. 2020;147 doi: 10.1242/dev.190629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y., Di Giammartino D.C., Taylor D., Sarkeshik A., Rice W.J., Yates J.R., 3rd, Frank J., Manley J.L. Molecular architecture of the human pre-mRNA 3' processing complex. Mol. Cell. 2009;33:365–376. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2008.12.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenzio M., Koley S., Samra N., Rishal I., Zhao Q., Sahoo P.K., Urisman A., Marvaldi L., Oses-Prieto J.A., Forester C., et al. Locally translated mTOR controls axonal local translation in nerve injury. Science. 2018;359:1416–1421. doi: 10.1126/science.aan1053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian B., Manley J.L. Alternative polyadenylation of mRNA precursors. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017;18:18–30. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Young R.A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. Multiple polyadenylation sites in a mouse alpha-amylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981;9:2313–2323. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Etten J.L., Nyquist M., Li Y., Yang R., Ho Y., Johnson R., Ondigi O., Voytas D.F., Henzler C., Dehm S.M. Targeting a single alternative polyadenylation site coordinately blocks expression of androgen receptor mRNA splice variants in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2017;77:5228–5235. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.Can-17-0320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahle E., Winkler G.S. RNA decay machines: deadenylation by the Ccr4-not and Pan2-Pan3 complexes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013;1829:561–570. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2013.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang R., Zheng D., Yehia G., Tian B. A compendium of conserved cleavage and polyadenylation events in mammalian genes. Genome Res. 2018;28:1427–1441. doi: 10.1101/gr.237826.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weill L., Belloc E., Bava F.A., Méndez R. Translational control by changes in poly(A) tail length: recycling mRNAs. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2012;19:577–585. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Z., Xu K., Lin Z., Kong F., Wang Q., Quan Y., Sha Q.Q., Li F., Zou Z., Liu L., et al. Ultrasensitive Ribo-seq reveals translational landscapes during mammalian oocyte-to-embryo transition and pre-implantation development. Nat. Cell Biol. 2022;24:968–980. doi: 10.1038/s41556-022-00928-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue Z., Huang K., Cai C., Cai L., Jiang C.Y., Feng Y., Liu Z., Zeng Q., Cheng L., Sun Y.E., et al. Genetic programs in human and mouse early embryos revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing. Nature. 2013;500:593–597. doi: 10.1038/nature12364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao C., Choi E.A., Weng L., Xie X., Wan J., Xing Y., Moresco J.J., Tu P.G., Yates J.R., 3rd, Shi Y. Overlapping and distinct functions of CstF64 and CstF64τ in mammalian mRNA 3' processing. RNA. 2013;19:1781–1790. doi: 10.1261/rna.042317.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye C., Long Y., Ji G., Li Q.Q., Wu X. APAtrap: identification and quantification of alternative polyadenylation sites from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics. 2018;34:1841–1849. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H., Lee J.Y., Tian B. Biased alternative polyadenylation in human tissues. Genome Biol. 2005;6:R100. doi: 10.1186/gb-2005-6-12-r100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Y., Wang X., Forouzmand E., Jeong J., Qiao F., Sowd G.A., Engelman A.N., Xie X., Hertel K.J., Shi Y. Molecular mechanisms for CFIm-mediated regulation of mRNA alternative polyadenylation. Mol. Cell. 2018;69:62–74.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.11.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The accession number of the mass spectrometry proteomics data reported in this paper is ProteomeXchange: PXD031134. The accession number of the RNA-seq data reported in this paper is GSA: CRA007735. No novel codes were generated in this study.