Abstract
Previous studies have shown tart cherry (TC) to improve exercise performance in normoxia. The effect of TC on hypoxic exercise performance is unknown. This study investigated the effects of 5 days of tart cherry (TC) or placebo (PL) supplementation on hypoxic exercise performance. Thirteen healthy participants completed an incremental cycle exercise test to exhaustion (TTE) under two conditions: (i) hypoxia (13% O2) with PL and (ii) hypoxia with TC (200 mg anthocyanin per day for 4 days and 100 mg on day 5). Pulmonary gas exchange variables, peripheral arterial oxygen saturation (SpO2), deoxygenated hemoglobin (HHb), and tissue oxygen saturation (StO2) assessed by near-infrared spectroscopy in the vastus lateralis muscle were measured at rest and during exercise. Urinary 8-hydro-2′ deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) excretion was evaluated pre-exercise and 1 and 5 h post-exercise. The TTE after TC (940 ± 84 s, mean ± standard deviation) was longer than after PL (912 ± 63 s, p < 0.05). During submaximal hypoxic exercise, HHb was lower and StO2 and SpO2 were higher after TC than PL. Moreover, a significant interaction (supplements × time) in urinary 8-OHdG excretion was found (p < 0.05), whereby 1 h post-exercise increases in urinary 8-OHdG excretion tended to be attenuated after TC. These findings indicate that short-term dietary TC supplementation improved hypoxic exercise tolerance, perhaps due to lower HHb and higher StO2 in the working muscles during submaximal exercise.
Keywords: antioxidant, blood flow, DNA damage, O2 extraction, oxidative stress, tissue oxygenation, vasodilation
1. Introduction
Improvements in endurance exercise performance, such as time trials under a given distance or time to exhaustion, are important for endurance athletes. It has been reported that tart cherry (TC) might improve endurance exercise performance via the facilitation of oxygen delivery (O2) to exercising muscles [1], perhaps due to possible mechanisms by increasing nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability [2]. A recent meta-analysis summarized that TC supplementation significantly improved exercise performance (standardized mean difference: 0.36; 95% confidential interval: 0.07 to 0.64, p = 0.01) upon pooling previous literature [3]. However, when viewed separately, some studies have shown that dietary TC supplementation extended the time to exhaustion or shortened time trials [1,4]; however, others had contradictory findings [5,6]. One possible explanation for these discrepancies may be related to different study settings (e.g., dosage of supplement, exercise mode, or population features). It should be noted that these studies were conducted only under normoxia [1,4,5,6]. Another distinctive advantage of TC supplementation has been proposed to reduce subset of oxidative stress markers [7,8]. However, whether this property would improve exercise performance seems to be uncertain.
Hypoxic exposure elevates several biomarkers of oxidative stress such as 8-hydro-2′ deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) [9,10,11,12,13] or 2-thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances [14,15,16] as indexes of oxidative damage to DNA or lipids, as well as exercise-induced elevated oxidative stress [17]. In general, increased oxidative stress may be associated with impaired vascular function, resulting in insufficient oxygen delivery (O2) to exercising muscles during exercise with the following mechanisms: (i) reducing the bioavailability of NO [18], (ii) increasing sympathetically mediated vascular tone [19], (iii) enhancing angiotensin II-mediated vasoconstriction [20], and (iv) endothelin-1 activity [18,21].
In this regard, TC could potentially improve hypoxic exercise performance by increasing the O2 to exercising muscles [1] via increasing NO bioavailability [2] and hypoxia-induced vasodilation during exercise [22]. These effects would (presumably) serve to improve O2-to-O2 uptake (O2) matching, thereby increasing muscle and microvascular O2 pressure (PO2) and enhancing blood myocyte O2 flux and mitochondrial control by increasing intracellular PO2 [23,24]. TC supplementation may also improve exercise performance via an antioxidant effect that prolongs the optimal cellular redox state for force production [25].
Accordingly, it was hypothesized that TC supplementation would improve exercise performance under hypoxia, lower oxidative stress, and increase tissue oxygenation in exercising muscles compared to placebo. Tissue oxygenation and deoxygenation kinetics in exercising vastus lateralis muscles were evaluated by near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS).
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Sample Size and Participants
A previous study reported that 7 days of TC supplementation improved time trial performance by ~4.7% (effect size = 0.78) [1]. To estimate the required sample size, one- and two-tailed paired t-tests were performed with an error probability of 0.05 (α), a power (1-β) of > 0.80, and an effect size of 0.78 using G Power 3.1 analysis software [26]. The required sample size of 12 (one-tailed) or 15 (two-tailed) participants was estimated.
Fifteen young, healthy, recreationally active volunteers (11 men and 4 women) were enrolled using a digital and paper flyer in the local community (Kawaguchiko town and Fuji-yoshida city, Yamanashi, Japan) and an adjacent university (Health Science University). Exclusion criteria included pregnancy, stationary bike use, current smoker, any known cardiometabolic disorders, use of medications known to affect cardiovascular responses, and regular engagement in moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (≥120 min/week) [27]. The participants were stratified by sex and randomly assigned to the starting condition. Women were studied during the follicular phase just after menstruation based on their basal body temperature and self-report [27]. After a detailed explanation of the study procedure and the possible risks and benefits of participation in this study, each participant signed an informed consent form. This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Mount Fuji Research Institute in Japan and was performed in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki (No. 202001).
2.2. Experimental Procedures
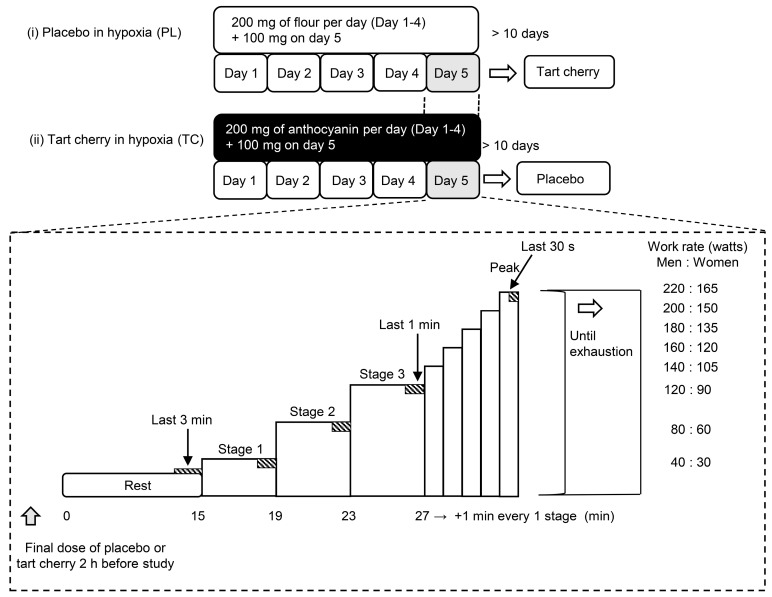
As shown in Figure 1, this study was a randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled crossover design with two experimental conditions including incremental normobaric hypoxic exercise (fraction of inspired oxygen [FiO2] = 0.13, equivalent altitude is approximately 3800 m) (i) with a placebo supplementation (PL) and (ii) with TC supplementation. The participants were requested to abstain from caffeinated beverages for 12 h and strenuous exercise and alcohol for 24 h before each session. The participants visited the laboratory on three occasions, including one familiarization with all measurement techniques (i.e., wearing a mask, hypoxic gas inspiration, and semi-recumbent leg cycling exercise) and two experimental visits. During the second and third visits, the participants were randomized to PL or TC. The order of the trials was counterbalanced. These two trials were performed at the same time (08:30–11:30 h) to avoid the effect of a circadian rhythm with at least a 10-day wash-out period. All studies were performed in an environmental chamber (TBR-4, 5SA2GX, Tabai Espec Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) set at a room temperature of 24 °C and relative humidity of 50%. After a 15-minute semi-recumbent position during the resting period, all participants performed an incremental maximal leg cycling test starting for 4 min at a power output for men and women of 40 W or 30 W, respectively (stage 1), followed by 4 min at 80 W or 60 W (stage 2) and 4 min at 120 W or 90 W (stage 3). Subsequently, the power output increased by 20 W or 10 W per min until exhaustion for men or women, respectively (Figure 1). The participants pedaled at a cadence of 60 rpm as set by a metronome. The criteria for exhaustion were as follows: (1) no increase in O2 despite a further increase in work rate, (2) heart rate (HR) at 90% of the age-predicted maximal value (208 − age × 0.7), (3) a rating of 19 on Borg’s scale of perceived exertion, or (4) can no longer maintain the pedaling rate above 50 rpm despite strong verbal encouragement. The test was terminated when participants met at least one of these 3 criteria and could not maintain the pedaling rate of 50 rpm despite strong verbal encouragement [28].
Figure 1.
Study protocol of the present study. PC; placebo, TC; tart cherry. Rectangles with diagonal lines indicate the cardiorespiratory and near-infrared spectroscopy measurement period.
2.3. Supplementation Protocol
Participants were assigned in a double-blinded and randomized manner to ingest TC (tart cherry 1200 mg capsule containing 100 mg of anthocyanin, Nature’s Life, Orem, UT, USA) or a flour placebo. The TC and PL supplementations were visually indistinguishable as they were ground to powder and encapsulated in a gelatin capsule. Participants were instructed to ingest one capsule at 08:00 h and one capsule at 18:00 h for 4 consecutive days before the main experiment, and one capsule 2 h before exercise on the day of the main experiment. The selected TC dose was based on a recent meta-analysis [3] where daily anthocyanin supplementation ranged from 40 to 270 mg per day. Additionally, participants were provided with a list of foods rich in antioxidants and instructed to avoid the consumption of these foods and maintain their normal dietary intake for the duration of the study.
2.4. Measurements
2.4.1. Cardiorespiratory Variables
Pulmonary ventilation and gas exchange variables were measured using a breath-by-breath metabolic measurement system (AE-310S; Minato Medical Science, Osaka, Japan). The inspired and expired gas volumes were measured using a hot-wire respiratory flow system. Flow signals were electrically integrated for the duration of each breath to calculate minute ventilation. The expired fractions of O2 and CO2 were analyzed using an O2 and CO2 gas analyzer. Standard gases (O2 15.23%, CO2 4.999%, and N2 balance) and room air were used to calibrate the gas analyzer before each test. HR and peripheral arterial oxygen saturation (SpO2) were continuously measured with a wireless heart rate monitor (Polar RC800X; Polar Electro Japan, Tokyo, Japan) and a pulse oximeter (WB-100; Nihon Seimitsu Sokki Co., Ltd., Gunma, Japan).
2.4.2. Tissue Oxygenation Profiles
Local muscle oxygenation profiles at the vastus lateralis muscle (active muscle) were measured using NIRS (BOM-L1TRW; Omegawave, Tokyo, Japan), as previously described [24]. This device uses three laser diodes (780, 810, and 830 nm) and calculates the relative tissue levels of oxygenated and deoxygenated hemoglobin (HbO2 and HHb) according to the modified Beer–Lambert law [29]. Tissue O2 saturation (StO2) was calculated by dividing HbO2 by total Hb (HbO2 plus HHb). NIRS optodes were placed on the lower third of the vastus lateralis muscle (10–12 cm above the knee joint) [30]. The measurement depth of the NIRS signal was approximately half the distance between the two fiber optic bundles placed over the skin, one comprising the light source and detector [31]. With this in mind, we used 40 mm between the probes, which provides a NIRS signal traverse distance of ~20 mm. This would have allowed the appropriate depth to sample from the vastus lateralis muscles, because the sum of adipose tissue and muscle thickness in vastus lateralis muscle was >20 mm [31]. Indeed, the measured adipose tissue and muscle thickness were 5.4 ± 1.1 mm and 20.6 ± 2.6 mm. These numbers indicate that the near-infrared light was transmitted to the desired muscle bed. The probe holder contained one light source probe, and two detectors were placed 20 mm (detector 1) and 40 mm (detector 2) away from the source. The Hb concentrations received by detector 1 were subtracted from those received by detector 2. This procedure allowed us to minimize the influence of skin blood flow [29].
2.4.3. Urine Sample and Analysis
Total urine samples were collected in a light-shielding bottle (500 mL) pre-exercise and 1 and 5 h post-exercise, and immediately stored at −80 °C for further analysis. At each sampling point, urine volume was measured, and the collection time was recorded. We also recorded the time of urination just before exercise. Urinary 8-OHdG, an oxidative derivative of deoxyguanosine implying oxidative damage to DNA [32], was analyzed.
2.5. Data Analysis
At rest, all cardiorespiratory variables and NIRS signals were averaged over the last 3 min immediately before the exercise (resting baseline values). During submaximal exercise for 4 min at each exercise intensity (i.e., 40–80–120 W and 30–60–90 W for men and women, respectively), these physiological values were averaged over the last 1 min at each exercise intensity. At the maximal level, data were averaged over the last 30 s prior to exhaustion. As our NIRS device represents HHb and total Hb signals as arbitrary units, to compare both signals between participants, the changes in HHb and total Hb were quantified as percentages from the resting baseline values. Specifically, resting baseline values in each trial were defined as 100% and were shown as relative changes. Based on a previous study [33], urinary 8-OHdG excretion was calculated and represented per individual body weight per given time, i.e., as the unit of ng·kg−1·h−1.
2.6. Statistical Analyses
All values were represented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Statistical analyses were performed using the commercial software Jamovi ver. 2.2.5. Only participants with complete data for primary outcomes were included in the analyses. A paired t-test was used to compare the time to exhaustion between PL and TC. Two-way (trial × time points) repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to compare all physiological variables. When p values were <0.05, Tukey’s post hoc test was used for further comparisons. Effect sizes were calculated as Cohen’s d, defined as small (0.2), medium (0.5), and large (0.8) for paired t-tests, and as η2, defined as small (0.01), medium (0.06), and large (0.14) effects [34]. A p value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
Two of the fifteen participants claimed severe headache and nausea during hypoxic exercise and had to drop out of the experiments (one participant claimed under PL condition, and the other claimed under TC condition). Thus, 13 participants (10 men and 3 women) aged 21 ± 1 years, with a body mass index of 22.1 ± 2.7 kg·(m2)−1, completed all trials and were used for further analysis.
3.1. Exercise Performance in Normobaric Hypoxia
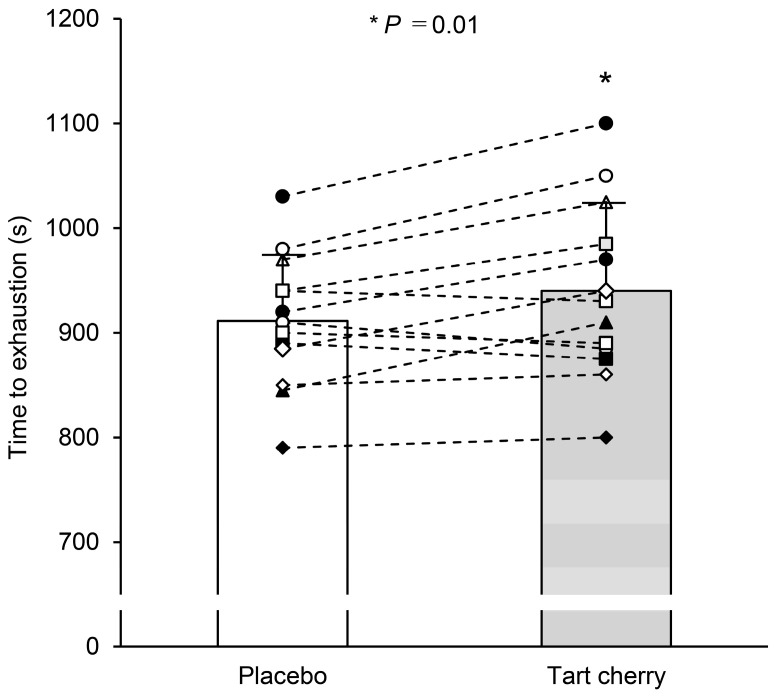
TC supplementation improved the time to exhaustion compared with that of PL (940 ± 84 s with TC vs. 912 ± 63 s with PL, t = 2.87, Cohen’s d = 0.80, p = 0.01) (Figure 2). Specifically, 10 of 13 participants reported improved exercise performance after TC.
Figure 2.
Time to exhaustion during incremental hypoxic exercise after 5 days of placebo and tart cherry supplementation. Different symbols with dotted lines indicate individual data, and the bars indicate supplementation group mean values. Values are the mean ± standard deviation (SD). * p < 0.05 between PL and TC.
3.2. Cardiorespiratory Responses at Rest and During Exercise
A two-way repeated measures ANOVA revealed no interaction effects in any cardiorespiratory variables (O2, carbon dioxide output (CO2), respiratory gas exchange ratio (RER), pulmonary ventilation (E), HR, and SpO2) (all p > 0.05). Further, no condition effects were observed for O2, CO2, RER, E, and HR (all p > 0.05) (Table 1). In contrast, there was a significant condition effect for SpO2 (p = 0.001), where SpO2 was higher after TC than PL. As expected, there were also significant main effects of time for all cardiorespiratory variables (all p < 0.001).
Table 1.
Cardiorespiratory responses at rest, during submaximal exercise (Stages 1, 2, and 3), and at exercise exhaustion (peak) after 5 days of placebo and tart cherry supplementation.
| Placebo | Tart Cherry | Two-Way Repeated Measures ANOVA Results | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Suppl. | Time | Interaction | ||||
| O2 (mL·min−1) | ||||||
| Rest | 271 ± 29 | 269 ± 32 | F | 1.27 | 327.17 | 1.95 |
| Stage 1 | 785 ± 110 | 752 ± 104 | p | 0.28 | <0.001 | 0.12 |
| Stage 2 | 1175 ± 161 | 1153 ± 127 | η2 | 0.000 | 0.918 | 0.000 |
| Stage 3 | 1577 ± 151 | 1558 ± 167 | ||||
| Peak | 2058 ± 340 | 2080 ± 376 | ||||
| CO2 (mL·min−1) | ||||||
| Rest | 261 ± 33 | 261 ± 34 | F | 0.432 | 204.22 | 1.516 |
| Stage 1 | 801 ± 126 | 757 ± 119 | p | 0.52 | <0.001 | 0.21 |
| Stage 2 | 1291 ± 194 | 1256 ± 161 | η2 | 0.000 | 0.891 | 0.002 |
| Stage 3 | 1813 ± 216 | 1691 ± 494 | ||||
| Peak | 2547 ± 426 | 2651 ± 525 | ||||
| E (L·min−1) | ||||||
| Rest | 11.0 ± 1.8 | 11.3 ± 1.3 | F | 0.471 | 474.06 | 1.907 |
| Stage 1 | 28.2 ± 3.5 | 27.2 ± 3.4 | p | 0.51 | <0.001 | 0.13 |
| Stage 2 | 44.6 ± 5.1 | 43.9 ± 4.6 | η2 | 0.000 | 0.958 | 0.000 |
| Stage 3 | 65.8 ± 7.2 | 67.0 ± 6.8 | ||||
| Peak | 107.9 ± 14.2 | 111.5 ± 13.2 | ||||
| RER | ||||||
| Rest | 0.96 ± 0.05 | 0.97 ± 0.05 | F | 0.693 | 121.83 | 1.662 |
| Stage 1 | 1.02 ± 0.06 | 1.01 ± 0.08 | p | 0.42 | <0.001 | 0.17 |
| Stage 2 | 1.10 ± 0.07 | 1.09 ± 0.06 | η2 | 0.001 | 0.699 | 0.005 |
| Stage 3 | 1.15 ± 0.11 | 1.17 ± 0.07 | ||||
| Peak | 1.24 ± 0.06 | 1.27 ± 0.07 | ||||
| HR (bpm) | ||||||
| Rest | 80 ± 8 | 79 ± 8 | F | 0.426 | 608.78 | 0.686 |
| Stage 1 | 114 ± 9 | 112 ± 9 | p | 0.53 | <0.001 | 0.61 |
| Stage 2 | 135 ± 10 | 134 ± 11 | η2 | 0.000 | 0.926 | 0.000 |
| Stage 3 | 156 ± 11 | 155 ± 9 | ||||
| Peak | 175 ± 11 | 176 ± 11 | ||||
| SpO2 (%) | ||||||
| Rest | 86.6 ± 1.8 | 87.1 ± 1.9 | F | 18.53 | 40.10 | 1.75 |
| Stage 1 | 82.5 ± 3.1 | 83.3 ± 3.3 | p | 0.001 | <0.001 | 0.15 |
| Stage 2 | 80.8 ± 3.0 | 81.6 ± 3.9 | η2 | 0.009 | 0.482 | 0.002 |
| Stage 3 | 78.2 ± 3.8 | 79.9 ± 4.6 | ||||
| Peak | 75.8 ± 5.0 | 76.8 ± 5.7 | ||||
Values are mean ± standard deviation. ANOVA, analysis of variance; Suppl., supplementation; O2, pulmonary oxygen uptake; CO2, carbon dioxide output; E, pulmonary ventilation; RER, respiratory gas exchange ratio; HR, heart rate; bpm, beats per minute; SpO2, peripheral arterial oxygen saturation.
3.3. Muscle Oxygenation Profiles during Exercise
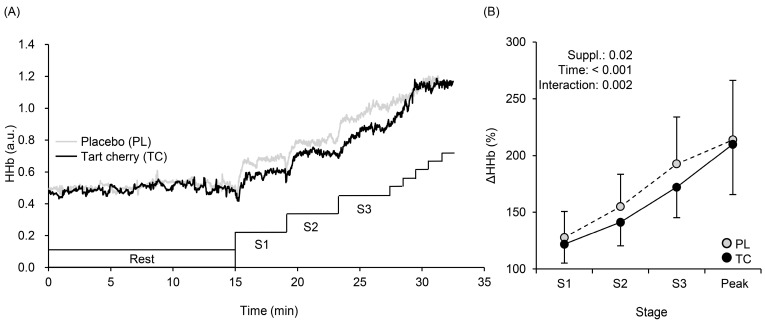
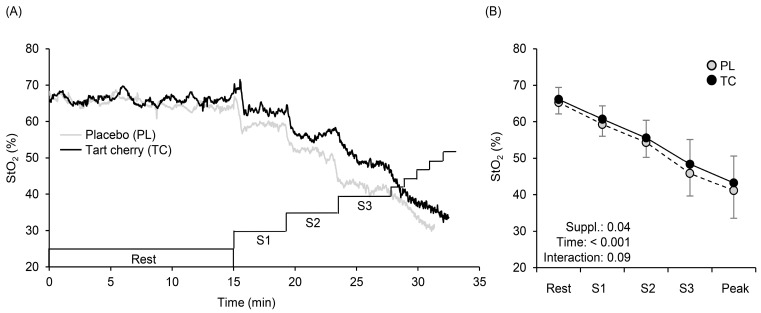
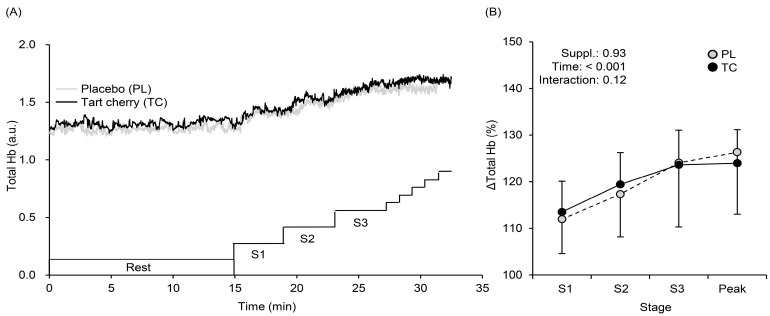
Figure 3 shows a typical example (panel A) and the averaged values of % changes (panel B) in the HHb. During exercise, HHb values at Stages 1 (40 or 30 W for men or women), 2 (80 or 60 W), and 3 (120 or 90 W) were lower with TC than PL (Figure 3A). A typical example (panel A) and averaged values of % changed (panel B) in StO2 are shown in Figure 4. During exercise, StO2 values at Stages 1, 2, and 3 were higher with TC than PL (Figure 4A,B). Total Hb gradually increased (F = 39.01, η2 = 0.228, p < 0.001) during exercise with no condition (F = 0.008, η2 = 0.000, p = 0.93) and interaction effects (F = 2.06, η2 = 0.007, p = 0.12) (Figure 5).
Figure 3.
The typical time course changes in muscle deoxygenation (HHb) profiles at rest and during exercise (A). Changes in mean HHb with SD obtained at rest, at each stage (S1, S2, S3), and at exercise exhaustion (Peak) after 5 days of tart cherry (TC) and placebo (PL) supplementation (B). Suppl., supplementation; S1–S3, Stages 1–3.
Figure 4.
The typical time course changes of tissue oxygen saturation (StO2) profiles at rest and during exercise (A). Changes in mean StO2 with SD obtained at rest, at each stage (S1, S2, S3), and at exercise exhaustion (Peak) after 5 days of tart cherry (TC) and placebo (PL) supplementation (B).
Figure 5.
The typical time course changes in total hemoglobin (total Hb) profiles at rest and during exercise (A). Changes in mean total Hb with SD obtained at rest, at each stage (S1, S2, S3), and at exercise exhaustion (Peak) after 5 days of tart cherry (TC) and placebo (PL) supplementation (B).
3.4. Oxidative Stress Marker in Urine
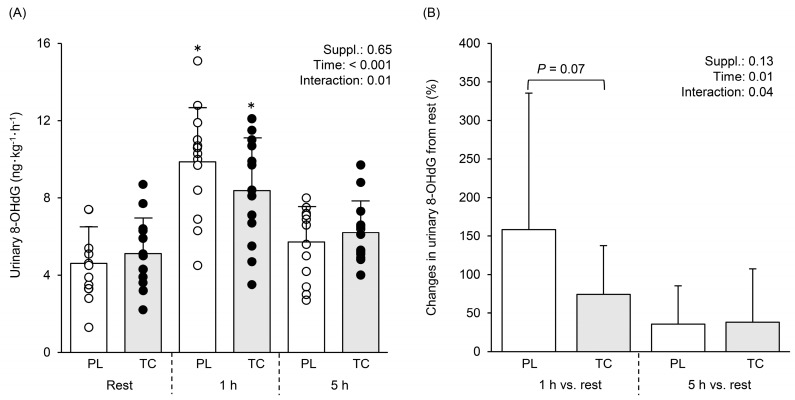
Figure 6A shows comparisons in urinary 8-OHdG excretion at rest and 1 and 5 h post-exercise after TC and PL. Significant time (F = 30.06, η2 = 0.413, p < 0.001) and interaction (F = 5.375, η2 = 0.028, p = 0.01) effects with no condition effect (F = 0.218, η2 = 0.001, p = 0.65) were found. Tukey post hoc tests revealed that 1 h post-exercise 8-OHdG was increased from rest after PL and TC (Figure 6A, p < 0.05), with the increase tending to be greater after PL than TC (Figure 6B, p = 0.07).
Figure 6.
Comparisons in urinary 8-hydroxy-2deoxy guanosine (8-OHdG) excretion at rest and 1 h and 5 h post-exercise after 5 days placebo and tart cherry supplementation (A). Relative changes (%) from rest (B). White and black circles indicate individual data for PL and TC. Bar graphs indicate mean values with SD. * indicates significant difference between rest and 1 h within the same conditions.
4. Discussion
This is the first study to investigate the effects of dietary TC supplementation on exercise performance under hypoxia. The primary findings of the present study were three-fold; compared with PL condition, five days of dietary TC supplementation (i) extended time to exhaustion during an incremental exercise test, (ii) lowered HHb and increased StO2 in the vastus lateralis muscle, and increased SpO2 during hypoxic exercise, and (iii) attenuated urinary 8-OHdG excretion 1 h post-exercise, which suggests reduced oxidative stress.
4.1. Exercise Performance in Normobaric Hypoxia
Previous studies have shown that TC supplementation improves exercise performance in normoxia [1,4]. The current study extends these findings by showing for the first time that TC supplementation can also improve exercise performance in a hypoxic environment. Comparing the effect sizes of this (d = 0.80) and a previous study (d = 0.78) [1] highlights that the improvement in exercise performance after TC supplementation is similar irrespective of different inspired oxygen concentrations.
4.2. Systemic Arterial and Local Muscle O2 Saturation
In the present study, TC supplementation decreased HHb and increased StO2 during incremental exercise (Figure 3 and Figure 4) in hypoxia, which provides one explanation for the improved exercise performance after TC supplementation. Lower HHb suggests enhancements in O2-to-O2 matching, resulting in lower fractional O2 extraction during incremental exercise to meet muscle demands, especially in the vastus lateralis muscle [35,36], perhaps due to greater venous O2 content and higher arterial O2 content (SpO2 as an index of arterial O2 content) was observed with TC (Table 1).
Muscle StO2 is calculated by dividing HbO2 by total Hb (HbO2 plus HHb). In the present study, total Hb gradually increased with no differences between the conditions (Figure 5), which was associated with no differences in microvascular Hb volume [37,38,39]. Therefore, higher StO2 with TC might be caused either by higher HbO2 and/or lower HHb. Although HbO2 may be affected by cutaneous blood flow [40], and thus, we cannot completely exclude HbO2 effects on cutaneous circulation. However, lower HHb found after TC supplementation (Figure 3) indicates sufficient O2 and TC-induced vasodilation in the vastus lateralis (exercising) muscle, which may consequently have led to higher StO2 and SpO2, and more efficient metabolism during exercise. This explanation has been suggested in a previous study [41] using similar vasodilatory supplements.
There are several possible explanations for these findings. It has been suggested that TC supplementation induces vasodilation via NO bioavailability [2]. Previous studies reported that antioxidant supplementation with similar supplements as used in the present study augmented endothelium-dependent vasodilation [42,43,44] through NO-dependent mechanisms [43]. However, this study was conducted using a local muscle exercise (handgrip) for older adults [43]. Therefore, further investigation is warranted to confirm this underlying mechanism in exercise involving large muscle groups as in the present study.
Some possibilities can be included. Blockade of NO synthase increased muscle O2 extraction during handgrip exercise under hypoxia (SpO2 ∼85%) [45] and a-vO2 difference during knee extension exercise under normoxia [46], reflecting increases in HHb. Additionally, blockade of NO synthase during knee extension exercise under normoxia decreased venous oxygen saturation [47], which may lead to lower StO2. Taken together, TC supplementation, which is known to have antioxidant-induced vasodilation effects [43], altered systemic and local oxygen saturation during hypoxic exercise. In another respect, dietary nitrate (NO3) supplementation reduced HHb and increased StO2, which potentially caused vasodilation via the NO3−–nitrite (NO2−)–NO pathway [48] and improved hypoxic exercise performance [29,49]. These results are in line with our findings and support our hypothesis (Figure 2).
4.3. Effects of Tart Cherry Supplementation on Oxidative Stress
The present study identified an attenuated increase in the oxidative stress marker urinary 8-OHdG excretion. Indeed, 1 h post-exercise, the increase from rest in urinary 8-OHdG was halved after TC compared to PL (160% PL vs. and 75% TC Figure 6). These findings agree with previous studies that have also reported that TC supplementation attenuated an increase in lipid peroxide as an oxidative stress marker [5,7] and increased total antioxidant status [5]. Although the oxidative stress markers were different between our study and previous studies [5,7], our findings might be supported by these studies [5,7]. The underlying mechanisms that account for the present results may be related to NO bioavailability. Recent studies demonstrated that black soybean, which includes rich polyphenols with antioxidant effects, improved vascular stiffness, increased urinary NO2 and NO3 levels, and decreased urinary 8-OHdG in healthy adults [50,51]. Moreover, it has been suggested that anthocyanins activate Nrf-2, which increases expressions of detoxifying enzymes and antioxidant enzymes, resulting in the elimination of reactive oxygen species and oxidant-induced injury cells [52,53]. Our study design cannot clarify these possible mechanisms, and hence, future studies are needed.
4.4. Methodological Considerations and Potential Implications
Several limitations should be considered when interpreting our findings. First, blood flow or vascular conductance as indexes of vasodilation in the working muscles were not evaluated. However, it may be difficult to precisely and continuously measure blood flow in the working muscle during leg cycling (e.g., at the femoral artery). Further, our exercise mode (leg cycling) may be more practically relevant than a local exercise, such as a handgrip or knee extension exercise, which has been conducted with the measurement of blood flow in previous studies [43,54]. Second, the present study did not conduct a normoxic exercise with or without TC supplementation as a control condition. However, our main aim was to investigate the effects of dietary TC supplementation on hypoxic exercise performance and not to compare normoxic and hypoxic exercise with TC. Third, rather than assessing a broad range of oxidative stress markers, only one oxidative stress marker, urinary 8-OHdG excretion was evaluated. Nonetheless, the urinary excretion of 8-OHdG has been recognized as a stable biomarker of DNA oxidative damage and reflects overall systemic oxidative stress level [55]. Fourth, to date, studies examining of TC supplementation effects on exercise have used a variety of supplements produced using different production methods [3], and hence, it is difficult to draw direct comparisons between these studies and determine a consensus for an appropriate dose for sports performance. However, our results demonstrate that whole-body exercise tolerance in hypoxia is improved with 5 days of TC supplementation in healthy young men and women. As a practical implication, examples include mountain stages in cycling (up to 2800 m in the Tour de France) and mountain running events (e.g., Mount Fuji, up to 3776 m in Japan, or Pikes Peak, up to 4300 m in Colorado, USA). Thus, our findings can potentially be applied to these elite sports.
5. Conclusions
Short-term dietary TC supplementation improved hypoxic exercise performance. The improved exercise performance may be explained by decreases in HHb levels and increases in StO2 levels in the working (vastus lateralis) muscles during exercise. Moreover, TC supplementation may attenuate oxidative stress, as indicated by attenuated urinary 8-OHdG excretion rates 1 h post-exercise.
Acknowledgments
We thank all participants for taking the time and effort to participate in the experiment. We also thank Misato Watanabe for her technical assistance in performing the study procedures.
Author Contributions
M.H., Y.F., K.K. and S.J.O. conceived the concept and design of this study; M.H. performed the experiments; M.H., Y.F., K.K. and S.J.O. analyzed the data; M.H., Y.F., K.K. and S.J.O. interpreted the results; M.H. wrote the original draft, including the table and figures; Y.F., K.K. and S.J.O. critically revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Mount Fuji Research Institute in Japan and was performed in accordance with the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki (No. 202001).
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants after a detailed explanation of the purpose of the study, procedures, possible risks, and benefits of participation.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding Statement
This study was partly supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (no. 18K11012 to M.H.).
Footnotes
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
References
- 1.Morgan P.T., Barton M.J., Bowtell J.L. Montmorency cherry supplementation improves 15-km cycling time-trial performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019;119:675–684. doi: 10.1007/s00421-018-04058-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Keane K.M., George T.W., Constantinou C.L., Brown M.A., Clifford T., Howatson G. Effects of Montmorency tart cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) consumption on vascular function in men with early hypertension. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016;103:1531–1539. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.115.123869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gao R., Chilibeck P.D. Effect of Tart Cherry Concentrate on Endurance Exercise Performance: A Meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2020;39:657–664. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2020.1713246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Levers K., Dalton R., Galvan E., O’Connor A., Goodenough C., Simbo S., Mertens-Talcott S.U., Rasmussen C., Greenwood M., Riechman S., et al. Effects of powdered Montmorency tart cherry supplementation on acute endurance exercise performance in aerobically trained individuals. J. Int. Soc. Sport. Nutr. 2016;13:22. doi: 10.1186/s12970-016-0133-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Howatson G., McHugh M.P., Hill J.A., Brouner J., Jewell A.P., van Someren K.A., Shave R.E., Howatson S.A. Influence of tart cherry juice on indices of recovery following marathon running. Scand J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2010;20:843–852. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2009.01005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Davis G.R., Bellar D. Montmorency cherry supplement does not affect aerobic exercise performance in healthy men. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2020;90:403–410. doi: 10.1024/0300-9831/a000575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bell P.G., Walshe I.H., Davison G.W., Stevenson E., Howatson G. Montmorency cherries reduce the oxidative stress and inflammatory responses to repeated days high-intensity stochastic cycling. Nutrients. 2014;6:829–843. doi: 10.3390/nu6020829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ortega D.R., López A.M., Amaya H.M., de la Rosa F.J.B. Tart cherry and pomegranate supplementations enhance recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage: A systematic review. Biol. Sport. 2021;38:97–111. doi: 10.5114/biolsport.2020.97069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chao W.H., Askew E.W., Roberts D.E., Wood S.M., Perkins J.B. Oxidative stress in humans during work at moderate altitude. J. Nutr. 1999;129:2009–2012. doi: 10.1093/jn/129.11.2009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lundby C., Pilegaard H., van Hall G., Sander M., Calbet J., Loft S., Moller P. Oxidative DNA damage and repair in skeletal muscle of humans exposed to high-altitude hypoxia. Toxicology. 2003;192:229–236. doi: 10.1016/s0300-483x(03)00328-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Moller P., Loft S., Lundby C., Olsen N.V. Acute hypoxia and hypoxic exercise induce DNA strand breaks and oxidative DNA damage in humans. FASEB J. 2001;15:1181–1186. doi: 10.1096/fj.00-0703com. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pfeiffer J.M., Askew E.W., Roberts D.E., Wood S.M., Benson J.E., Johnson S.C., Freedman M.S. Effect of antioxidant supplementation on urine and blood markers of oxidative stress during extended moderate-altitude training. Wilderness Environ. Med. 1999;10:66–74. doi: 10.1580/1080-6032(1999)010[0066:EOASOU]2.3.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Schmidt M.C., Askew E.W., Roberts D.E., Prior R.L., Ensign W.Y., Jr., Hesslink R.E., Jr. Oxidative stress in humans training in a cold, moderate altitude environment and their response to a phytochemical antioxidant supplement. Wilderness Environ. Med. 2002;13:94–105. doi: 10.1580/1080-6032(2002)013[0094:OSIHTI]2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bailey D.M., Davies B., Young I.S. Intermittent hypoxic training: Implications for lipid peroxidation induced by acute normoxic exercise in active men. Clin. Sci. 2001;101:465–475. doi: 10.1042/CS20010065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Magalhaes J., Ascensao A., Viscor G., Soares J., Oliveira J., Marques F., Duarte J. Oxidative stress in humans during and after 4 hours of hypoxia at a simulated altitude of 5500 m. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2004;75:16–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pialoux V., Mounier R., Ponsot E., Rock E., Mazur A., Dufour S., Richard R., Richalet J.P., Coudert J., Fellmann N. Effects of exercise and training in hypoxia on antioxidant/pro-oxidant balance. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006;60:1345–1354. doi: 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ji L.L. Antioxidants and oxidative stress in exercise. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1999;222:283–292. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1373.1999.d01-145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Taddei S., Virdis A., Ghiadoni L., Salvetti G., Bernini G., Magagna A., Salvetti A. Age-related reduction of NO availability and oxidative stress in humans. Hypertension. 2001;38:274–279. doi: 10.1161/01.HYP.38.2.274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Thomas G.D., Zhang W., Victor R.G. Impaired modulation of sympathetic vasoconstriction in contracting skeletal muscle of rats with chronic myocardial infarctions: Role of oxidative stress. Circ. Res. 2001;88:816–823. doi: 10.1161/hh0801.089341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.de Groot A.A., van Zwieten P.A., Peters S.L. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in angiotensin II-induced vasoconstriction. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2004;43:154–159. doi: 10.1097/00005344-200401000-00023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Van Guilder G.P., Westby C.M., Greiner J.J., Stauffer B.L., DeSouza C.A. Endothelin-1 vasoconstrictor tone increases with age in healthy men but can be reduced by regular aerobic exercise. Hypertension. 2007;50:403–409. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.088294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Joyner M.J., Casey D.P. Muscle blood flow, hypoxia, and hypoperfusion. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014;116:852–857. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00620.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Fukuoka Y., Poole D.C., Barstow T.J., Kondo N., Nishiwaki M., Okushima D., Koga S. Reduction of VO2 slow component by priming exercise: Novel mechanistic insights from time-resolved near-infrared spectroscopy. Physiol. Rep. 2015;3:e12432. doi: 10.14814/phy2.12432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.McDonough P., Behnke B.J., Padilla D.J., Musch T.I., Poole D.C. Control of microvascular oxygen pressures in rat muscles comprised of different fibre types. J. Physiol. 2005;563:903–913. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.079533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Keane K.M., Bailey S.J., Vanhatalo A., Jones A.M., Howatson G. Effects of montmorency tart cherry (L. Prunus Cerasus) consumption on nitric oxide biomarkers and exercise performance. Scand J. Med. Sci. Sport. 2018;28:1746–1756. doi: 10.1111/sms.13088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Faul F., Erdfelder E., Buchner A., Lang A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods. 2009;41:1149–1160. doi: 10.3758/BRM.41.4.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Horiuchi M., Stoner L. Macrovascular and microvascular responses to prolonged sitting with and without bodyweight exercise interruptions: A randomized cross-over trial. Vasc. Med. 2022;27:127–135. doi: 10.1177/1358863X211053381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dobashi S., Horiuchi M., Endo J., Kiuchi M., Koyama K. Cognitive Function and Cerebral Oxygenation During Prolonged Exercise Under Hypoxia in Healthy Young Males. High Alt. Med. Biol. 2016;17:214–221. doi: 10.1089/ham.2016.0036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Horiuchi M., Endo J., Dobashi S., Handa Y., Kiuchi M., Koyama K. Muscle oxygenation profiles between active and inactive muscles with nitrate supplementation under hypoxic exercise. Physiol. Rep. 2017;5:e13475. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Koga S., Poole D.C., Ferreira L.F., Whipp B.J., Kondo N., Saitoh T., Ohmae E., Barstow T.J. Spatial heterogeneity of quadriceps muscle deoxygenation kinetics during cycle exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007;103:2049–2056. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00627.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Patterson M.S., Chance B., Wilson B.C. Time resolved reflectance and transmittance for the non-invasive measurement of tissue optical properties. Appl. Opt. 1989;28:2331–2336. doi: 10.1364/AO.28.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schalcher T.R., Borges R.S., Coleman M.D., Batista Junior J., Salgado C.G., Vieira J.L., Romao P.R., Oliveira F.R., Monteiro M.C. Clinical oxidative stress during leprosy multidrug therapy: Impact of dapsone oxidation. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e85712. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Morillas-Ruiz J., Zafrilla P., Almar M., Cuevas M.J., Lopez F.J., Abellan P., Villegas J.A., Gonzalez-Gallego J. The effects of an antioxidant-supplemented beverage on exercise-induced oxidative stress: Results from a placebo-controlled double-blind study in cyclists. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005;95:543–549. doi: 10.1007/s00421-005-0017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lakens D. Calculating and reporting effect sizes to facilitate cumulative science: A practical primer for t-tests and ANOVAs. Front. Psychol. 2013;4:863. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2013.00863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Alharbi A.A.D., Ebine N., Nakae S., Hojo T., Fukuoka Y. Application of Molecular Hydrogen as an Antioxidant in Responses to Ventilatory and Ergogenic Adjustments during Incremental Exercise in Humans. Nutrients. 2021;13:459. doi: 10.3390/nu13020459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ferreira L.F., Koga S., Barstow T.J. Dynamics of noninvasively estimated microvascular O2 extraction during ramp exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007;103:1999–2004. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01414.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Burnley M., Doust J.H., Ball D., Jones A.M. Effects of prior heavy exercise on VO(2) kinetics during heavy exercise are related to changes in muscle activity. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002;93:167–174. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01217.2001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.DeLorey D.S., Kowalchuk J.M., Heenan A.P., Dumanoir G.R., Paterson D.H. Prior exercise speeds pulmonary O2 uptake kinetics by increases in both local muscle O2 availability and O2 utilization. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007;103:771–778. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01061.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jones A.M., Fulford J., Wilkerson D.P. Influence of prior exercise on muscle [phosphorylcreatine] and deoxygenation kinetics during high-intensity exercise in men. Exp. Physiol. 2008;93:468–478. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.2007.041897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Koga S., Poole D.C., Kondo N., Oue A., Ohmae E., Barstow T.J. Effects of increased skin blood flow on muscle oxygenation/deoxygenation: Comparison of time-resolved and continuous-wave near-infrared spectroscopy signals. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015;115:335–343. doi: 10.1007/s00421-014-3019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Vanhatalo A., Fulford J., Bailey S.J., Blackwell J.R., Winyard P.G., Jones A.M. Dietary nitrate reduces muscle metabolic perturbation and improves exercise tolerance in hypoxia. J. Physiol. 2011;589:5517–5528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.216341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Donato A.J., Uberoi A., Bailey D.M., Wray D.W., Richardson R.S. Exercise-induced brachial artery vasodilation: Effects of antioxidants and exercise training in elderly men. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010;298:H671–H678. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00761.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Trinity J.D., Wray D.W., Witman M.A., Layec G., Barrett-O’Keefe Z., Ives S.J., Conklin J.D., Reese V., Zhao J., Richardson R.S. Ascorbic acid improves brachial artery vasodilation during progressive handgrip exercise in the elderly through a nitric oxide-mediated mechanism. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016;310:H765–H774. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00817.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wray D.W., Nishiyama S.K., Harris R.A., Zhao J., McDaniel J., Fjeldstad A.S., Witman M.A., Ives S.J., Barrett-O’Keefe Z., Richardson R.S. Acute reversal of endothelial dysfunction in the elderly after antioxidant consumption. Hypertension. 2012;59:818–824. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.189456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Crecelius A.R., Kirby B.S., Voyles W.F., Dinenno F.A. Augmented skeletal muscle hyperaemia during hypoxic exercise in humans is blunted by combined inhibition of nitric oxide and vasodilating prostaglandins. J. Physiol. 2011;589:3671–3683. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2011.209486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Mortensen S.P., Gonzalez-Alonso J., Damsgaard R., Saltin B., Hellsten Y. Inhibition of nitric oxide and prostaglandins, but not endothelial-derived hyperpolarizing factors, reduces blood flow and aerobic energy turnover in the exercising human leg. J. Physiol. 2007;581:853–861. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2006.127423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Boushel R., Langberg H., Gemmer C., Olesen J., Crameri R., Scheede C., Sander M., Kjaer M. Combined inhibition of nitric oxide and prostaglandins reduces human skeletal muscle blood flow during exercise. J. Physiol. 2002;543:691–698. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2002.021477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Lundberg J.O., Weitzberg E. NO-synthase independent NO generation in mammals. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010;396:39–45. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.02.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Masschelein E., Thienen R.V., Wang X., Schepdael A.V., Thomis M., Hespel P. Dietary nitrate improves muscle but not cerebral oxygenation status during exercise in hypoxia. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012;113:736–745. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01253.2011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Yamashita Y., Wang L., Nakamura A., Nanba F., Saito S., Toda T., Nakagawa J., Ashida H. Black soybean improves the vascular function through an increase in nitric oxide and a decrease in oxidative stress in healthy women. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2020;688:108408. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Yamashita Y., Nakamura A., Nanba F., Saito S., Toda T., Nakagawa J., Ashida H. Black Soybean Improves Vascular Function and Blood Pressure: A Randomized, Placebo Controlled, Crossover Trial in Humans. Nutrients. 2020;12:2755. doi: 10.3390/nu12092755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Owuor E.D., Kong A.N.T. Antioxidants and oxidants regulated signal transduction pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002;64:765–770. doi: 10.1016/S0006-2952(02)01137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Shih P.H., Yeh C.T., Yen G.C. Anthocyanins induce the activation of phase II enzymes through the antioxidant response element pathway against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007;55:9427–9435. doi: 10.1021/jf071933i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Rossman M.J., Trinity J.D., Garten R.S., Ives S.J., Conklin J.D., Barrett-O’Keefe Z., Witman M.A., Bledsoe A.D., Morgan D.E., Runnels S., et al. Oral antioxidants improve leg blood flow during exercise in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015;309:H977–H985. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00184.2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Loft S., Fischer-Nielsen A., Jeding I.B., Vistisen K., Poulsen H.E. 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine as a urinary biomarker of oxidative DNA damage. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. 1993;40:391–404. doi: 10.1080/15287399309531806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.