ABSTRACT
The whole-genome sequences of 15 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) strains from nasopharyngeal swab samples collected in the Republic of Moldova in June 2020 to September 2021 were determined. Little variability was observed in the early stages, when mostly clade 19A was circulating, followed by clade 20B. Later, multiple introductions of SARS-CoV-2 lineages B.1.1., B.1.1.7, and B.1.1.525 were detected. The B.1.1.7 lineage became predominant between December 2020 and June 2021, followed by the Delta variant.
ANNOUNCEMENT
The Republic of Moldova is a small Eastern European country with a population of 3.6 million (1). On 7 March 2020, a 48-year-old woman who returned from Italy represented the first recorded case of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) (family Coronaviridae, genus Betacoronavirus), as confirmed by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) (2). In 1 month, the number of cases increased to 965, with 854 cases being estimated to be due to local transmission and 111 being imported cases (3). To date, there have been 590,811 confirmed coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) cases and 11,858 deaths (4).
This study involves the full genome sequencing of 15 SARS-CoV-2 isolates that were collected between June 2020 (4 samples) and September 2021 (11 samples) at the State University of Medicine and Pharmacy (SUMPh) in the Republic of Moldova, in collaboration with Alfa Diagnostica Laboratory. Nasopharyngeal swab samples were taken from suspected cases that met the guidelines of the Moldovan government (5).
We made an effort to make the sequences publicly available as soon as possible, with an average collection-to-submission time of 68 days. This report aims at framing these data in the context of SARS-CoV-2 molecular evolution in the country and in Europe in general.
Samples were collected in 1,000 μL transport medium (product number C-8885; Vector-Best). The nucleic acid extraction from clinical samples was carried out using a DNA/RNA manual extraction kit (product number C-8896; Vector-Best). For diagnosis, a SARS-CoV-2/SARS-CoV multiplex real-time PCR detection kit (product number R3-P436-23/9EU; DNA-Technology Research & Production) was used with primers targeting the E gene and the N gene. A CFX96 Touch real-time thermal cycler system (Bio-Rad) was used for amplification. Samples with cycle threshold (CT) values of <30 were considered for full genome sequencing. RNA from selected samples was aliquoted, anonymized, and sent at −80°C to the International Centre for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (ICGEB).
Library preparation and sequencing were performed as described previously (6–9). Briefly, a Qubit 2.0 fluorimeter (Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA) and 2100 Bioanalyzer (Agilent Technologies, USA) were used to assess RNA quantities and qualities, respectively. One hundred nanograms of RNA was processed with the Swift Amplicon SARS-CoV-2 research panel (Swift Biosciences, USA). Sequencing was conducted using an Illumina MiSeq sequencer with the standard protocol for paired-end 150-bp reads.
Quality control of raw data was conducted using FastQC v.0.11.9 (https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc). For adapter removal and read trimming, the Primerclip trimming tool and adapter sequences for Swift Biosciences Accel-Amplicon panels were used. Genome assembly was conducted using dedicated Swift dockerized data analysis guidelines (10, 11). All tools were run with default parameters unless otherwise specified. For each sample, the sequencing parameters are listed in Table 1.
TABLE 1.
Genomic parameters of SARS-CoV-2 strains from the Republic of Moldova
| Sample no. | Straina | GISAID accession no. | GenBank accession no. | SRA accession no. | Patient location | Sample collection date (day/mo/yr) | GISAID clade | Nextstrain clade | No. of raw reads | Genome size (bp) | Coverage depth (×) | GC content (%) | Pango lineageb | Amino acid substitutions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_MD6/2020 | EPI_ISL_516938 | OP783441 | SRX14472462 | Rabnita, Moldova | 18/6/2020 | GR | 20B | 1,111,830 | 29,900 | 5,570 | 45.20 | B.1.1 (Pango v.3.1.20) | Spike D614G, N G204R, N R203K, NS3 S165F, NSP2 L410F, NSP3 N1785D |
| 2 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_MD7/2020 | EPI_ISL_516936 | OP783440 | SRX14472461 | Straseni, Moldova | 18/6/2020 | GR | 20B | 1,050,968 | 29,886 | 8,149 | 45.00 | B.1.1 (Pango v.3.1.20) | |
| 3 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_MD4/2020 | EPI_ISL_516935 | OP783439 | SRX14472460 | Balti, Moldova | 17/6/2020 | G | 20A | 1,080,708 | 21,179 | 5,312 | 45.50 | B.1 | |
| 4 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_MD1/2020 | EPI_ISL_516934 | OP783438 | SRX14472459 | Chisinau, Moldova | 17/6/2020 | GR | 20B | 932,600 | 29,867 | 7,583 | 45.50 | B.1.1 (Pango v.3.1.20) | |
| 5 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_818767_S16/202 | EPI_ISL_3886568 | OP783436 | SRX13323315 | Cimislia, Moldova | 11/5/2021 | GR | 20I/501Y.V1 | 929,928 | 29,540 | 8,149 | 45.30 | B.1.1.7 (Pango v.3.1.20), Alpha (B.1.1.7-like) (Scorpio) | Spike A570D, spike D614G, spike D1118H, spike P681H, spike S982A, spike T716I, N D3L, N G204R, N R203K, N S235F, NS3 D27Y, NS8 Q27stop, NS8 R52I, NS8 Y73C, NSP3 A890D, NSP3 I1412T, NSP3 T183I, NSP6 G188C, NSP12 P323L, NSP12 V405A |
| 6 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_819913_S18/2021 | EPI_ISL_3903719 | OP783437 | SRX13323314 | Chisinau, Moldova | 12/5/2021 | GR | 20I/501Y.V1 | 513,580 | 29,542 | 8,149 | 45.80 | B.1.1.7 (Pango v.3.1.20), Alpha (B.1.1.7-like) (Scorpio) | Spike A570D, spike D614G, spike D1118H, spike N501Y, spike P681H, spike S982A, spike T716I, spike V445I, N D3L, N G204R, N R203K, N S235F, NS7a P84A, NS8 Q27stop, NS8 R52I, NS8 Y73C, NSP2 R362H, NSP3 A890D, NSP3 D410G, NSP3 I1412T, NSP3 T183I, NSP12 P323L |
| 7 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_809515_S10/2021 | EPI_ISL_3886566 | OP783435 | SRX13323313 | Chisinau, Moldova | 5/5/2021 | GR | 20I/501Y.V1 | 435,738 | 29,540 | 8,149 | 45.90 | B.1.1.7 (Pango v.3.1.20), Alpha (B.1.1.7-like) (Scorpio) | Spike A570D, spike D614G, spike D1118H, spike P681H, spike S982A, spike T716I, N D3L, N G204R, N R203K, N S235F, NS8 Q27stop, NS8 R52I, NS8 Y73C, NSP3 I1412T, NSP3 T183I, NSP5 Y101C, NSP12 P323L, NSP13 T115I |
| 8 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_812387_S15/2021 | EPI_ISL_3886564 | OP783434 | SRX13323312 | Dubasari, Moldova | 7/5/2021 | GR | 20I/501Y.V1 | 551,564 | 29,541 | 8,149 | 46.10 | B.1.1.7 (Pango v.3.1.20), Alpha (B.1.1.7-like) (Scorpio) | Spike A570D, spike D614G, spike D1118H, spike N501Y, spike P681H, spike S982A, spike T716I, N D3L, N G204R, N R203K, N S235F, NS8 Q27stop, NS8 R52I, NS8 Y73C, NSP3 A890D, NSP3 I1412T, NSP3 T183I, NSP12 P323L |
| 9 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_819835_S17/2021 | EPI_ISL_3886562 | OP783433 | SRX13323311 | Causeni, Moldova | 12/5/2021 | GR | 688,252 | 29,541 | 8,149 | 46.40 | B.1.1.523 (Pango v.3.1.20) | Spike D614G, spike D839V, spike E780A, spike F306L, spike N211K, spike T1027I, M I82T, N D22Y, N G204R, N G212C, N R203K, NSP2 N269D, NSP3 F1496L, NSP3 M84V, NSP3 R1297I, NSP4 T114I, NSP5 V303I, NSP6 V84F, NSP10 T111I, NSP12 P323L, NSP12 S229N, NSP13 L455M, NSP13 P77L, NSP15 V338A | |
| 10 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_797186_S3/2021 | EPI_ISL_3886560 | OP783432 | SRX13323323 | Chisinau, Moldova | 24/4/2021 | GR | 20I/501Y.V1 | 608,708 | 29,541 | 8,149 | 45 | B.1.1.7 (Pango v.3.1.20), Alpha (B.1.1.7-like) (Scorpio) | Spike A570D, spike D614G, spike D1118H, spike P681H, spike S982A, spike T716I, N D3L, N G204R, N R203K, N S235F, NS3 I232V, NS8 Q27stop, NS8 R52I, NS8 Y73C, NSP3 A338T, NSP3 A890D, NSP3 I1412T, NSP3 T183I, NSP12 P323L |
| 11 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_823299_S20/2021 | EPI_ISL_3886557 | OP783431 | SRX13323320 | Stefan Voda, Moldova | 14/5/2021 | GR | 20I/501Y.V1 | 817,382 | 29,541 | 8,149 | 45.50 | B.1.1.7 (Pango v.3.1.20), Alpha (B.1.1.7-like) (Scorpio) | Spike A570D, spike D614G, spike D1118H, spike G1219C, spike P681H, spike S982A, spike T716I, N D3L, N G204R, N R203K, N S235F, NS8 Q27stop, NS8 R52I, NS8 Y73C, NSP3 A890D, NSP3 I1412T, NSP3 T183I, NSP6 A51V, NSP12 P323L |
| 12 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_810217_S12/2021 | EPI_ISL_3886556 | OP783430 | SRX13323319 | Chisinau, Moldova | 5/5/2021 | GR | 20I/501Y.V1 | 518,006 | 29,534 | 8,149 | 46 | B.1.1.7 (Pango v.3.1.20), Alpha (B.1.1.7-like) (Scorpio) | Spike A570D, spike D614G, spike D1118H, spike H69del, spike P681H, spike S982A, spike T716I, spike V70del, N D3L, N G204R, N R203K, N S235F, NS8 Q27stop, NS8 R52I, NS8 Y73C, NSP3 A890D, NSP3 I1412T, NSP3 T183I, NSP9 T19I, NSP12 P323L |
| 13 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_797065_S2/2021 | EPI_ISL_3886554 | OP783429 | SRX13323318 | Chisinau, Moldova | 24/4/2021 | GR | 20I/501Y.V1 | 553,028 | 29,540 | 8,149 | 45.60 | B.1.1.7 (Pango v.3.1.20), Alpha (B.1.1.7-like) (Scorpio) | Spike A570D, spike D614G, spike D1118H, spike P681H, spike S982A, spike T716I, N D3L, N G204R, N R203K, N S235F, NS3 T271I, NS7b F9S, NS8 Q27stop, NS8 R52I, NS8 Y73C, NSP3 I1412T, NSP3 T183I, NSP12 P323L |
| 14 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_798119_S4/2021 | EPI_ISL_3886552 | OP783428 | SRX13323310 | Chisinau, Moldova | 26/4/2021 | GR | 20I/501Y.V1 | 995,082 | 29,689 | 8,149 | 44.80 | B.1.1.7 (Pango v.3.1.20), Alpha (B.1.1.7-like) (Scorpio) | Spike A570D, spike D614G, spike D1118H, spike P631S, spike P681H, spike S982A, spike T716I, spike W152R, N D3L, N G204R, N R203K, N S235F, NS8 Q27stop, NS8 R52I, NS8 Y73C, NSP3 A890D, NSP3 I1412T, NSP3 S1717L, NSP3 T183I, NSP12 P323L, NSP14 K165R, NSP16 P236L |
| 15 | hCoV-19/Moldova/ICGEB_796301_S1/2021 | EPI_ISL_3886549 | OP783427 | SRX13323309 | Hincesti, Moldova | 24/4/2021 | GR | 20I/501Y.V1 | 621,908 | 29,541 | 8,149 | 45.80 | B.1.1.7 (Pango v.3.1.20), Alpha (B.1.1.7-like) (Scorpio) | Spike A570D, spike D614G, spike D1118H, spike P681H, spike S982A, spike T716I, N D3L, N G204R, N R203K, N S235F, NS7a P34S, NS8 Q27stop, NS8 R52I, NS8 Y73C, NSP2 L550F, NSP2 S203G, NSP3 A890D, NSP3 I1412T, NSP3 T183I, NSP3 V473F, NSP6 L37F, NSP8 T187I, NSP12 P323L, NSP16 D179G |
For the amino acid substitutions, the original/reference strain (hCoV-19/Wuhan/WH01/2019 (EPI_ISL_402125)) was used for comparison.
Pango v.3.1.20 is dated 28 February 2022.
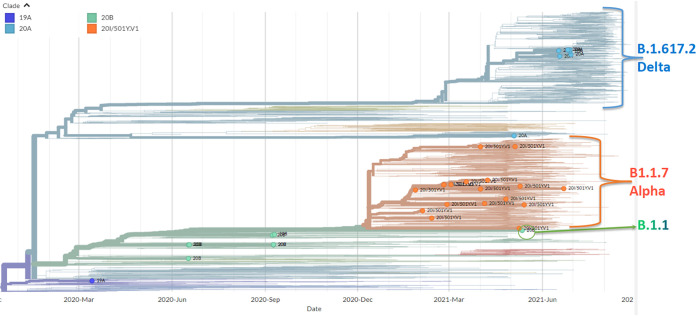
Phylogenetic analyses were performed through the Nextstrain bioinformatics platform (12). A Moldova-focused country-level subsampling strategy was used in the context of the Nextregions/Europe data set (updated to 1 September 2021); the reference strain hCoV-19/Wuhan/WH01/2019 (GISAID accession number EPI_ISL_402125) was used as the original root. From this analysis, 4 clades were identified, i.e., 19A, 20A, 20B, and 20I/501Y.V1 (Table 1 and Fig. 1). Although limited in numbers, the present study enriches the collection of sequences from Moldova and provides a framework for enhanced molecular epidemiology in the country.
FIG 1.
Phylogenetic tree, in rectangular view, for European SARS-CoV-2 strains, including the 15 strains collected in the Republic of Moldova.
The study was reviewed and approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Nicolae Testemitanu SUMPh (protocol number 3/24.01.22). All samples were coded, and the information obtained from the study participants was kept confidential. Sample selection followed WHO recommendations for countries with limited resources (13).
Data availability.
The metadata and the coding-complete genome sequences of all 15 samples were submitted to the GISAID (www.gisaid.org) database and can be found under GISAID accession number EPI_SET_221017uv (https://doi.org/10.55876/gis8.221017uv). Sequences are also available in the NCBI database under BioSample accession numbers SAMN26687402, SAMN26687401, SAMN26687400, SAMN26687399, SAMN23672914, SAMN23672913, SAMN23672912, SAMN23672911, SAMN23672910, SAMN23672909, SAMN23672906, SAMN23672905, SAMN23672904, SAMN23672901, and SAMN23672900. The raw reads were deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database under SRA accession numbers SRX14472462, SRX14472461, SRX14472460, SRX14472459, SRX13323315, SRX13323314, SRX13323313, SRX13323312, SRX13323311, SRX13323323, SRX13323320, SRX13323319, SRX13323318, SRX13323310, and SRX13323309 and BioProject accession number PRJNA786454. Genome sequences were deposited in the NCBI GenBank database under accession numbers OP783427 to OP783441 (Table 1).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We gratefully acknowledge the support of the Autonomous Region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, Regional Law 19/2000 (Strengthening epidemiological surveillance capacity to address COVID-19 and other epidemics [CUP D87D20000020009]), the ICGEB COVID-19 Resource Program (https://www.icgeb.org/covid19-resources), the Fast-Track Sequencing Program from the AREA Science Park (Trieste, Italy), and the FOCEM (MERCOSUR Structural Convergence Fund) (COF 03/11).
We thank all of those who have contributed sequences in real time to the GISAID database (https://www.gisaid.org) and Nextstrain (https://nextstrain.org).
Footnotes
[This article was published on 12 December 2022 with an error in Fig. 1. The figure was corrected in the current version, posted on 20 December 2022.]
Contributor Information
Mariana Ulinici, Email: mariana.ulinici@usmf.md.
Simon Roux, DOE Joint Genome Institute.
REFERENCES
- 1.Landgeist. 2022. Emigration in Europe. https://landgeist.com/2022/08/23/emigration-in-europe/?fbclid=IwAR27CfqYOAroK9lhCQnXlCEanlVzkdn9ovhmqVV91nSxI0gNSczbb6bD0m8. Accessed 25 August 2022.
- 2.Ministerul Sănătății al Republicii Moldova. 7 March 2020. MSMPS confirmă primul caz de Coronavirus de tip nou în Republica Moldova [MSMPS confirms first new-type coronavirus case in the Republic of Moldova. (In Romanian). https://msmps.gov.md/comunicare/comunicate/in-republica-moldova-a-fost-confirmat-primul-caz-de-coronavirus-se-iau-masuri-pentru-limitarea-raspandirii-virusului/. Accessed 25 February 2022.
- 3.Ministerul Sănătății al Republicii Moldova. 7 April 2020. Situația epidemiologică prin infecția COVID-19, 7 aprilie [Epidemiological situation due to COVID-19 infection, April 7]. (In Romanian). https://msmps.gov.md/comunicare/comunicate/situatia-epidemiologica-prin-infectia-covid-19-7-aprilie. Accessed 25 February 2022.
- 4.World Health Organization. https://covid19.who.int/region/euro/country/md. Accessed 6 October 2022.
- 5.Ministerul Sănătății al Republicii Moldova. 30 March 2020. Protocol clinic național provizoriu, infecția cu coronavirus de tip nou (COVID-19) [Interim national clinical protocol, novel coronavirus infection (COVID-19)]. (In Romanian). https://msmps.gov.md/sites/default/files/pcn_provizoriu_-_infectia_cu_coronavirus_de_tip_nou_covid-19_aprobat_prin_ordinul_msmps_nr.336_din_30.03.2020_ro.pdf.
- 6.Bitew M, Hailu G, Gebregziabher Tsegay Y, Tuki K, Asmamaw K, Tesfaye K, Dadi H, Orsini E, Dal Monego S, Licastro D, Marcello A. 2022. SARS-CoV-2 genome sequence obtained from Ethiopia. Microbiol Resour Announc 11:e01182-21. doi: 10.1128/mra.01182-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Paulino-Ramirez R, Riego E, Vallejo-Degaudenzi A, Calderon VV, Tapia L, León P, Licastro D, Dal Monego S, Rajasekharan S, Orsini E, Marcello A. 2021. Whole-genome sequences of SARS-CoV-2 isolates from the Dominican Republic. Microbiol Resour Announc 10:e00952-21. doi: 10.1128/MRA.00952-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Al-Rashedi NAM, Licastro D, Rajasekharan S, Dal Monego S, Marcello A, Munahi MG, Odda BS, Alabdali YAJ, ALObaidi LAH, Jasim A, Abdulzahra IA, Kadhim K, Awad A, Bachay M. 2021. Genome sequencing of a novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 isolate from Iraq. Microbiol Resour Announc 10:e01316-20. doi: 10.1128/MRA.01316-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Licastro D, Rajasekharan S, Dal Monego S, Segat L, D’Agaro P, Marcello A. 2020. Isolation and full-length genome characterization of SARS-CoV-2 from COVID-19 cases in northern Italy. J Virol 94:e00543-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00543-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Corman VM, Landt O, Kaiser M, Molenkamp R, Meijer A, Chu DKW, Bleicker T, Brünink S, Schneider J, Schmidt ML, Mulders DG, Haagmans BL, van der Veer B, van den Brink S, Wijsman L, Goderski G, Romette JL, Ellis J, Zambon M, Peiris M, Goossens H, Reusken C, Koopmans MP, Drosten C. 2020. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill 25:2000045. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Li D, Liu CM, Luo R, Sadakane K, Lam TW. 2015. MEGAHIT: an ultra-fast single-node solution for large and complex metagenomics assembly via succinct de Bruijn graph. Bioinformatics 31:1674–1676. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hadfield J, Megill C, Bell SM, Huddleston J, Potter B, Callender C, Sagulenko P, Bedford T, Neher RA. 2018. Nextstrain: real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics 34:4121–4123. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.World Health Organization. 2021. Genomic sequencing of SARS-CoV-2: a guide to implementation for maximum impact on public health. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240018440. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The metadata and the coding-complete genome sequences of all 15 samples were submitted to the GISAID (www.gisaid.org) database and can be found under GISAID accession number EPI_SET_221017uv (https://doi.org/10.55876/gis8.221017uv). Sequences are also available in the NCBI database under BioSample accession numbers SAMN26687402, SAMN26687401, SAMN26687400, SAMN26687399, SAMN23672914, SAMN23672913, SAMN23672912, SAMN23672911, SAMN23672910, SAMN23672909, SAMN23672906, SAMN23672905, SAMN23672904, SAMN23672901, and SAMN23672900. The raw reads were deposited in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database under SRA accession numbers SRX14472462, SRX14472461, SRX14472460, SRX14472459, SRX13323315, SRX13323314, SRX13323313, SRX13323312, SRX13323311, SRX13323323, SRX13323320, SRX13323319, SRX13323318, SRX13323310, and SRX13323309 and BioProject accession number PRJNA786454. Genome sequences were deposited in the NCBI GenBank database under accession numbers OP783427 to OP783441 (Table 1).