Abstract
On December 7, 2022, China adjusted public health control measures, there have been widespread of SARS-CoV-2 infections in Chinese mainland. As the number of infected people increased, the mutation probability of SARS-CoV-2 is also raised. Therefore, it is of great importance to monitor SARS-CoV-2 variants and its mutations in China. In this current study, 665 SARS-CoV-2 genomes from China deposited in the public database were used to analyze the proportion of different variants; to determine the composition of variants in China across different provinces; and analyze specific mutation frequency, focusing on 12 immune escape residues. The results showed that no new mutations were generated on the 12 immune escape residues. The evolutionary analysis of the BF.7 variant circulating in China showed that there is an independent evolutionary branch with unique mutation sites, officially named BF.7.14 by PANGO. This variant may have been imported from Russia to Inner Mongolia at the end of September 2022 and continued its spread in China. The evolutionary analysis of BA.5.2 variant shows that the variant is composed of two sub-variants, named BA.5.2.48 and BA.5.2.49 by PANGO, respectively. This variant may have been imported from abroad to Beijing at the beginning of September 2022 and formed two sub-variants after domestic transmission. Finally, this study showed that current epidemic variants in China were already circulating in other countries, and there were no additional mutations on immune escape residues that could pose a threat to other countries.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, Immune escape, Evolutionary analysis
1. Introduction
After December 2021, with the emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant, the global epidemic has entered a new stage. Omicron’s lower hospitalization rate and mortality rates compared to other VOC variants led most countries around the world to release control measures in early 2022. With the adjustment of the global prevention and control strategy, the number of infected people increased, undoubtedly resulted in abundant virus circulation in a significant population worldwide, which in turn led to constant viral mutation and variation.1 Up to now, more than 700 omicron variants have been identified,2 but only 20 variants are noted to be associated with global epidemic.3
The main prevalent variants in China are BA.5.2 and BF.7,4 which are the most prevalent around the world from July to October 2022. Compared with BQ.1.1 and XBB.1.5, BA.5.2 and BF.7 have fewer mutations on immune escape residues.5 With the increasing number of infected people in China, the transmission frequency of the virus in the population also increases, and the mutation probability of SARS-CoV-2 will consequently rise. Therefore, it is very important to monitor the evolutionary process of epidemic variants in China.
In this study, we used 665 genomes sequences of SARS-CoV-2 for evolutionary analysis of BA.5.2 and BF.7 variants in China. Analysis of the fraction of prevalent variants in China and different provinces showed the circulating BF.7 variant is a single independent evolutionary branch with three unique non-synonymous mutation (NS7a:H47Y, NSP2:V94L, and Spike:C1243F); which was named BF.7.14 by PANGO. The results implying that the current domestic epidemic BF.7 variant may have originated from the Inner Mongolia around the end of September 2022. The BA.5.2 variant circulating in China is composed of two branches, which are named BA.5.2.48 and BA.5.2.49 by PANGO. The origin of BA.5.2 variant circulating in China can be traced back to the beginning of September 2022 in Beijing. In addition, analysis of 12 immune escape residues, showed no high-frequencies mutations in these residues in the populations of BA.5.2 and BF.7 variants circulating in China.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Data mining
SARS-CoV-2 sequences were retrieved from the Global Initiative on Sharing Avian Influenza Data (GISAID) initiative database.6 Complete genomes with an N-content lower than 0.01 % and high-coverage were selected for subsequent analysis. A Multiple Alignment using Fast Fourier Transform (MAFFT)-generated alignment of high-coverage complete genome sequences was downloaded from the website.
2.2. Mutation analysis
The complete SARS-CoV-2 genome isolate WIV04 (MN996528.1) was used as the reference genome; mutations in all other samples were compared to this reference isolate. In order to make sure the accuracy of mutations, detected mutations were visualized using Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV),7 and the mutations nearby the insertion and deletion region were manually confirmed. The confirmed mutations were converted into a Variant Call Format (VCF) format file using in-house script, then the mutations were annotated with the SnpEff program.8
2.3. Construction of phylogenetic tree with full-length genomic sequences
All genomes were aligned using MAFFT v7.310.9 The aligned sequences were converted to the phylip file format with ClustalW,10 then maximum likelihood (ML) trees were constructed in RaxML v8.2.1211 with the number of bootstrap replicates set to 100. The time-scaled phylogenetic tree was constructed using NextStrain12 and Treetime.13 The phylogenetic trees were visualized with FigTree v1.4.414 and GrapeTree.15
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Global epidemic of SARS-CoV-2 variants in 2022
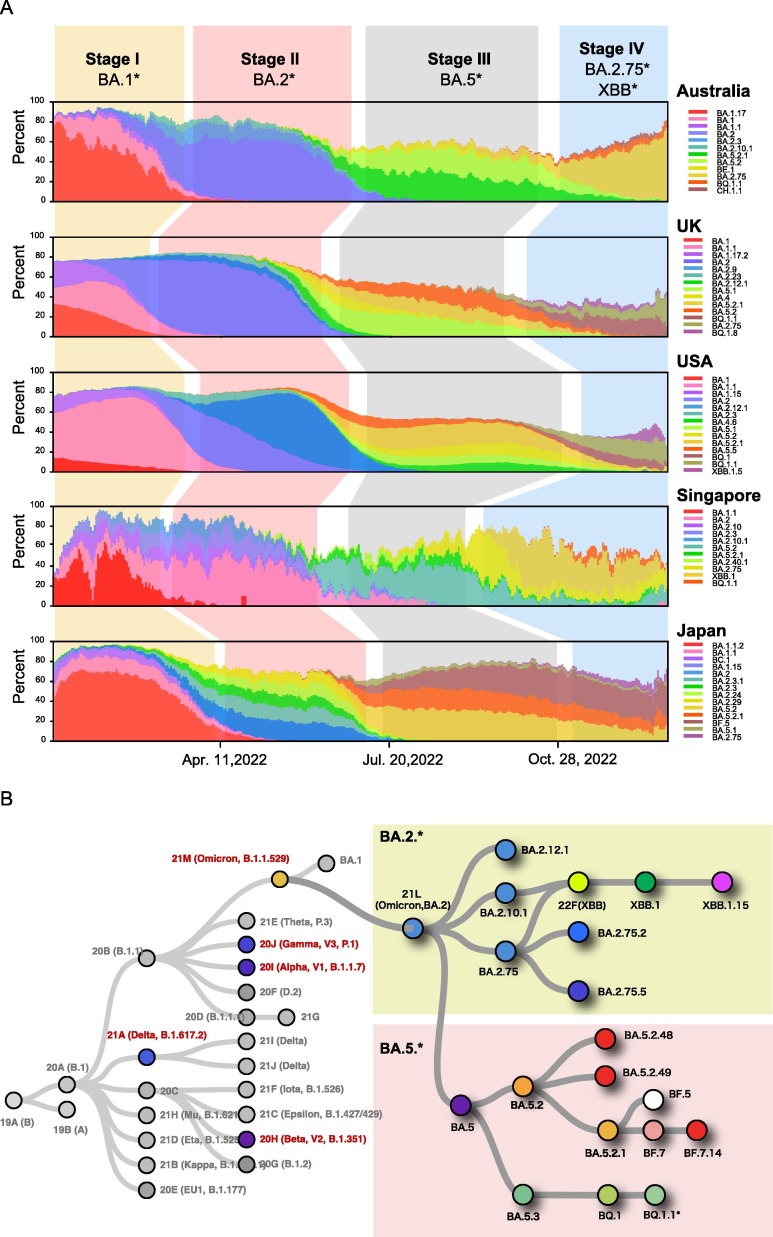
Analysis of the main epidemic variants from different countries at different periods in 2022 showed that the global epidemic of SARS-CoV-2 variants could be divided into four stages (Fig. 1 A). In the first stage, from December 2021 to March 2022, the main epidemic variants over the world are BA. 1 and its sub-variants, include: BA. 1, BA. 1.1, BA. 1.17 and BA.1.15; the second stage, from April 2022 to around July 2022, was dominated by BA.2 and its sub-variants, including BA.2.11, BA.2.10, and BA.2.75; The third stage is from August 2022 to December 2022, and the main epidemic variants are BA.5 and its sub-variants BA.5.2, BA.5.2.1, BF.7, and BQ.1.1; and the fourth stage, from December 2022 until now, when the proportion of BA. 5 and its sub-variants gradually decreased, and BA. 2.75 and XBB and their sub-variants increased rapidly. Because the sub-variants of BA.2.75 and XBB originated from Asia, Singapore and Australia entered the fourth stage earlier than the United Kingdom and the United States.
Fig. 1.
A) Distribution of different SARS-CoV-2 variants during 2022. Different colors represent different variants. The variants alternate dominance over time forming a four stage epidemic. B) Phylogeny tree shows the current major variants, BA.2.* and BA.5.*, and other variants that previously originated from the original SARS-CoV-2 virus.
The global epidemic SARS-CoV-2 variants included two major branches, BA.2 and BA.5 branch (Fig. 1B). The increasing number pre-immune individuals, either vaccinated or previously infected people, makes immune evasion the main selection pressure and driver of SARS-CoV-2 evolution.16 Therefore, the history of previous infection in a country or region will affect the viral transmission and evolution in this same country or region. For countries with BA.2 previous infection history, the proportion of BA5 variant cases will rise rapidly in the future (such as India and Singapore at this stage); meanwhile, countries with a history of previous infection with BA.5 variant, the proportion of BA2 variant cases will rise rapidly in the future (such as Australia, the United Kingdom and the United States at this stage). Due to the genetic diversity between the two branches, BA.2 branch and BA.5 branch, is large, and cross immune protection is poor, which helps one escape virus-neutralizing antibodies elicited by the other. Finally, with the continuous evolution of SARS-CoV-2, the genetic differences of SARS-CoV-2 between BA.2 and BA.5 branches will further increase, and the ability of cross-immune protection decrease. In the future, we believe the two branch variants will become alternating epidemics.
3.2. Proportion of circulating variants in China
A total of 665 high quality genome sequence of SARS-CoV-2 published by Shanghai Jiaotong University and China Center for Disease Control and Prevention were used to analyze the proportion of circulating variants in China and different provinces (Fig. 2 ).4 Nationwide, the proportion of BA.5.2 variant was 47.8 %, BA.5.2.48 was 36.3 %, BA.5.49 was 9.8 %, and BF.7 was 45.3 %, while other variants accounted for only 6.9 %. Focusing on different provinces, the proportion of BF.7 variants in Inner Mongolia, Beijing and Anhui was higher (accounting for 100 %, 75.4 %, and 70.0 %, respectively). In contrast, the proportion of BA.5.2 variants was higher in Guangzhou, Chongqing, Hunan, Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Gansu and Sichuan. It is noteworthy that only the BF.7 variant was detected in Inner Mongolia. Many other variants have been detected in coastal provinces such as Shanghai, Jiangsu and Guangzhou. These variants were introduced from aboard and have not spread widely locally. BA. 5.2 variant circulating in China includes two sub-variants, BA.5.248 and BA.5.249, with BA.5.2.48 being most prevalent in the majority of the provinces, while BA.5.2.49 was most prevalent in Sichuan, Shanghai, Fujian, Tianjin.
Fig. 2.
Distribution of SARS-CoV-2 variants in the major provinces of China.
3.3. Mutation frequency
To monitor the mutation of BA.5.2 and BF.7 circulating in China, we analyzed the mutation frequency of BA.5.2 and BF.7, focusing on the 12 immune escape related residues (Fig. 3 ). The results showed that BF.7 has 59 high-frequency non-synonymous mutations, of which, 56 were characteristic of this variant. The remaining three high-frequency mutations, NS7a:H47Y, NSP2:V94L, and Spike:C1243F mutations were unique to the prevalent variant in China. This variant has been officially named BF.7.14 by PANGO. The mutation frequency analysis of BA.5.2 branch showed that there were 57 high-frequency mutations, of which, 55 were characteristic mutations of BA.5.2 variant; one high-frequency mutation (ORF1b: T1050N) was unique for BA.5.2 variant circulating in China. This variant is named BA.5.2.48 by PANGO. The other high-frequency mutation, Spike:T883I, was characteristic in a sub-branch of BA.5.2 circulating in China, which is named BA.5.2.49 by PANGO.
Fig. 3.
The mutations frequency of BF.5.* and BF.7.* variants. The blue points indicate that the mutation is a common mutation of the variant, and the red points indicate a unique mutation. NSP13:T127N is a unique mutation for BA.5.2.48, Spike:T883I is a unique mutation for BA.2.5.49, and NS7a:H47Y, NSP2:V94L, and Spike:C1243F are tree unique mutations for BF.7 variants. The bottom of the figure shows the mutation frequency on the 12 immune escape residues of the Spike protein region from variants BA.5.2 and BF.7.
Previous studies showed that omicron had some important immune escape sites, including R346, K356, K444, V445, G446, N450, L452, N460, F486, F490, R493, and S494.5 Most mutations on these residues are key to evade neutralizing antibody, as revealed by deep mutational scanning (DMS).17, 18, 19, 20, 21 To determine the mutation frequency in the immune escape residues on variants prevalent in China, we next analyzed mutations on these 12 immune escape residues in BF.7 and BA.5.2 variant from October 2022 to January 2023 (Fig. 3). The results showed that for BA. 5.2 circulating in China, there is no high-frequency mutation on 12 immune escape residues except for two common residues (L452 and F486). For BF.7 circulating in China, there are also no high-frequency mutation on these 12 immune escape residues, except for three common residues (R346, L452 and F486). We speculate two reasons for SARS-CoV-2 variants in circulation in China have not evolved a new immune escape residue: (1) the domestic epidemic is still in the process of the first round of infection, the immune barrier has not been fully established, and the immune escape selection pressure has not yet formed; (2) The neutralizing antibody level of the recently infected population in China is too high that does not allow for breakthrough infection and emergence of variant escape mutants. However, with once immune barrier establishes and the antibody levels wane, immune escape variants will emerge in China. Thus, continuous monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 evolution is crucial. BA.5.2 and BF.7 are now prevalent in China and contain only 2 and 3 immune evasion-related mutations, respectively. However, the major international variants show 6–8 immune evasion related mutations. For example, BQ.1.1 contains 6 immune evasion-related mutations, and XBB.1.5 contains 7 immune evasion-related mutations. In addition, we also analyzed the mutation frequencies of seven amino acid residues M177, L270, P272, L452, Y453, R765, and D1118, which substitutions affect recognition of T cell epitopes.22 The results showed that there is no high-frequency mutation on 7 residues with cellular immunity except for a common residues (L452). Therefore, at this stage, the prevalence of BA.5.2 and BF.7 in China will not pose a higher threat to other countries than the already circulating strains.
3.4. Evolutionary analysis of variant BF.7 in China
To determine the origin of the domestic epidemic BF.7 variant, we extracted 1,434 genome sequence of the BF.7 variant from all countries in the GISAID database from September 2022 to date and constructed the evolutionary tree. The results showed that BF.7 variant in China is an independent evolutionary branch (Fig. 4 A). The closest branch to the BF.7 variant is a strain from Russia in October 2022. In order to determine the evolutionary relationship of BF.7 across different provinces in China, we conducted a separate evolutionary analysis for the domestic circulation BF.7 sequences. The results showed that BF.7 isolated from Inner Mongolia at the end of September 2022 was closer to the ancestor node (Fig. 4B), implying that the current domestic epidemic BF.7 variant may have originated from the Inner Mongolia around the end of September 2022. Based on the above information, we speculated that BF.7 variant circulating in China was imported from Russia to Inner Mongolia and then to Beijing, Hebei and other provinces, establishing a local transmission chain.
Fig. 4.
Evolutionary analysis based on SARS CoV-2 variant BF.7. A) Phylogenetic tree based on 1,434 genome sequence of the BF.7 variant from all countries. The red dot represents the genome collected from China, and the black dot represents the sample collected from other countries. B) Phylogenetic tree based on genomes containing BF.7 genomes collected from different provinces in China (showed in different colored blocks). The collection date ranged from September 2022 to January 2023.
3.5. Evolutionary analysis of variant BA.5.2 in China
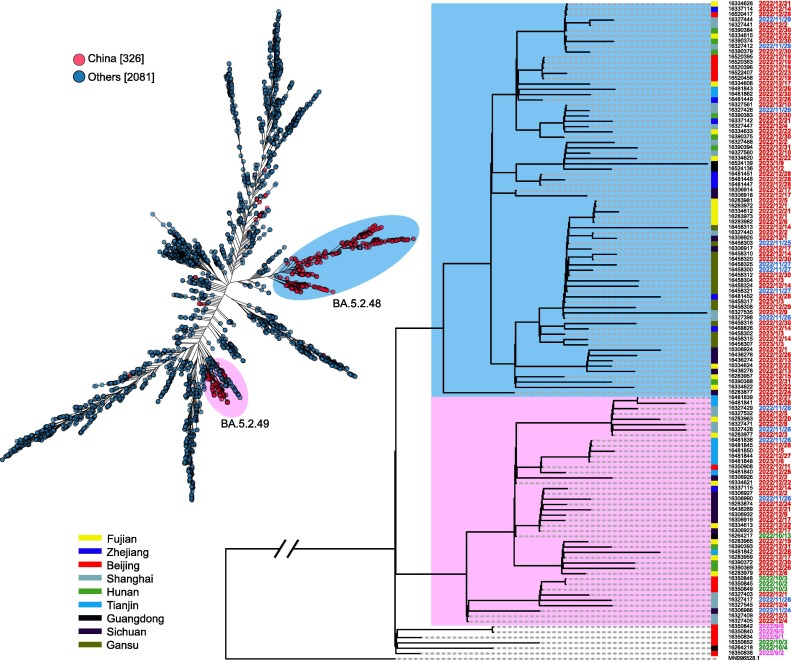
To determine the origin of the BA.5.2 variant in China, we extracted 2,407 genome sequence of the BA.5.2 variant in all countries since September 2022 in the GISAID database and constructed the evolutionary tree. The BA.5.2 variant circulating in China formed two branches. These two branches are closely related to the BA.5.2 variants in circulation in Germany and Spain in October 2022, which may have been imported cases (Fig. 5 A). To determine the evolutionary relationship of BA.5.2 variants across different provinces in China, we reconstructed the evolution tree of BA.5.2 domestic samples. The results showed that the domestic BA.5.2 samples can be divided into two large branches, corresponding to BA. 5.2.48 and BA.5.249 (Fig. 5B). The earliest collection date of BA.5.2.48 and BA.5.249 variant was traced back to the beginning of September 2022, collected in Beijing. This result indicates that the variant of BA.5.2 may have entered Beijing through imported cases as early as September 2022, and has been hidden for 3 months. This is also the main reason why the epidemic in Beijing developed faster than other provinces in December 2022.
Fig. 5.
Evolutionary analysis based on SARS CoV-2 variant BA.5.2. A) Phylogenetic tree based on 2,407 genome sequence of the BA.5.2 variant from all countries. The red dot represents the genome collected from China, and the black dot represents the sample collected from other countries. B) Phylogenetic tree based on genomes containing BA.5.2 genomes collected from different provinces in China (showed in different colored blocks). The collection date ranged from September 2022 to January 2023.
4. Conclusion
By analyzing the main variants of different countries during different periods in 2022, the global epidemic spread was divided into four stages; Furthermore, currently circulation variants, BA.2 and BA.5 branches, might prevail and alternate in the future to cause seasonal epidemics. By analyzing the genome sequences of 665 SARS-CoV-2 from China in the public database, we identified the unique mutations of the prevalent SARS-CoV-2 variants in China. Through mutation analysis of the 12 immune escape residues, we determined that new immune escape variants have not emerged in China so far. Furthermore, We speculate that the BF.7 in China may have been imported from Russia to Inner Mongolia, and that the variant circulation of BA.5.2 in China may have been imported in Beijing at the beginning of September 2022. In summary, this study monitored and analyzed the SARS-CoV-2 variants and mutations most prevalent in China, identified their characteristic mutations, and speculated on their possible evolutionary origin. This work provides a basis for surveillance and traceability of SARS-CoV-2 variants prevalent in China.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Yamin Sun: Writing – original draft, Visualization. Min Wang: Writing – original draft, Visualization. Wenchao Lin: Writing – original draft. Wei Dong: Software, Data curation. Jianguo Xu: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from consultancy project (2022-JB-06) by the Chinese Academy of Engineering (CAE).
References
- 1.Berkhout B., Herrera-Carrillo E. SARS-CoV-2 evolution: On the Sudden Appearance of the Omicron Variant. J Virol. 2022;96 doi: 10.1128/jvi.00090-22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Rambaut A., Holmes E.C., O’Toole Á., et al. A dynamic nomenclature proposal for SARS-CoV-2 lineages to assist genomic epidemiology. Nature Microbiol. 2020;5:1403–1407. doi: 10.1038/s41564-020-0770-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Islam S, Islam T, Islam MR. New Coronavirus Variants are Creating More Challenges to Global Healthcare System: A Brief Report on the Current Knowledge. Clin Pathol. 2022;15:2632010X221075584. 10.1177/2632010x221075584. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Gang Lu Y.L., Jiang M., Tan Y., et al. Primary assessment of the diversity of Omicron sublineages and the epidemiologic features of autumn/winter 2022 COVID-19 wave in Chinese mainland. Front Med. 2022 doi: 10.1007/s11684-022-0981-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cao Y., Jian F., Wang J., et al. Imprinted SARS-CoV-2 humoral immunity induces convergent Omicron RBD evolution. Nature. 2022 doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05644-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Elbe S., Buckland-Merrett G. Data, disease and diplomacy: GISAID's innovative contribution to global health. Global Chall. 2017;1:33–46. doi: 10.1002/gch2.1018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Robinson J.T., Thorvaldsdóttir H., Winckler W., et al. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol. 2011;29:24–26. doi: 10.1038/nbt.1754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cingolani P., Platts A., Wang L.L., et al. A program for annotating and predicting the effects of single nucleotide polymorphisms. SnpEff Fly. 2012;6:80–92. doi: 10.4161/fly.19695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Katoh K., Standley D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30:772–780. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Thompson J.D., Higgins D.G., Gibson T.J. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994;22:4673–4680. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Stamatakis A. RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:2688–2690. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btl446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hadfield J., Megill C., Bell S.M., et al. Nextstrain: real-time tracking of pathogen evolution. Bioinformatics. 2018;34:4121–4123. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sagulenko P., Puller V., Neher R.A. TreeTime: Maximum-likelihood phylodynamic analysis. Virus Evolut. 2018;4 doi: 10.1093/ve/vex042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.FigTree. http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/.
- 15.Zhou Z., Alikhan N.-F., Sergeant M.J., et al. GrapeTree: visualization of core genomic relationships among 100,000 bacterial pathogens. Genome Res. 2018;28:1395–1404. doi: 10.1101/gr.232397.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Konishi T. Mutations in SARS-CoV-2 are on the increase against the acquired immunity. PLoS One. 2022;17:e0271305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0271305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cao Y., Yisimayi A., Jian F., et al. BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by Omicron infection. Nature. 2022;608:593–602. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04980-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cao Y., Wang J., Jian F., et al. Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies. Nature. 2022;602:657–663. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04385-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Greaney A.J., Loes A.N., Crawford K.H.D., et al. Comprehensive mapping of mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain that affect recognition by polyclonal human plasma antibodies. Cell Host Microbe. 2021;29:463–476.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2021.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Greaney A.J., Starr T.N., Gilchuk P., et al. Complete mapping of mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain that escape antibody recognition. Cell Host Microbe. 2021;29:44–57.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.11.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Greaney A.J., Starr T.N., Barnes C.O., et al. Mapping mutations to the SARS-CoV-2 RBD that escape binding by different classes of antibodies. Nat Commun. 2021;12:4196. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24435-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.de Silva T.I., et al. Te impact of viral mutations on recognition by SARS-CoV-2 specifc T-cells. iScience. 2021;24:103353. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.103353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]