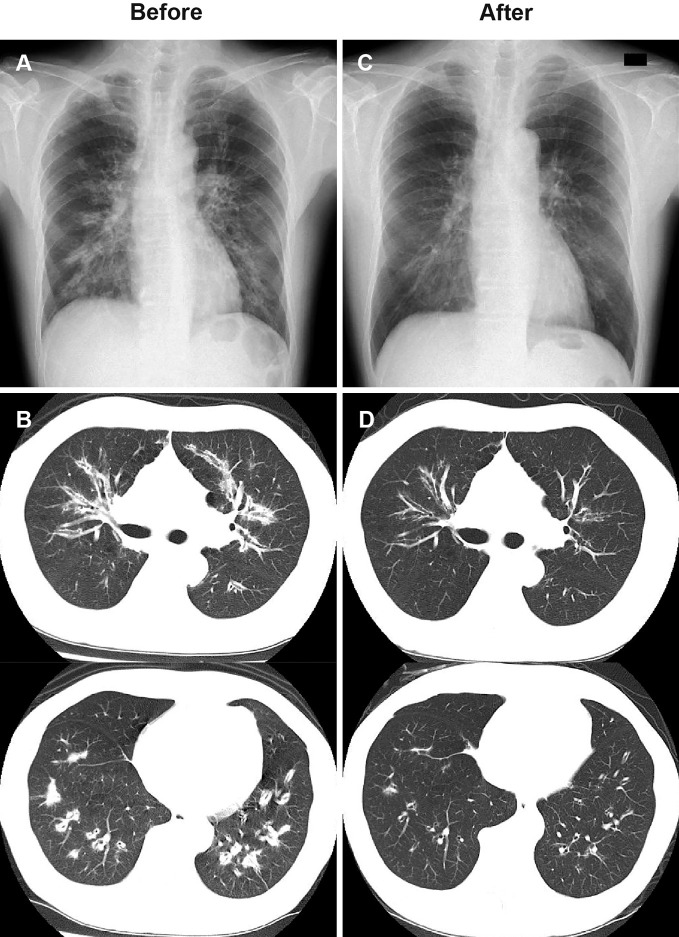
A 54-year-old man presented to our hospital with a 1-week history of numbness in the left lower limb. He had received a diagnosis of asthma. Laboratory studies showed eosinophilia (2,319/μL) and positive myeloperoxidase-anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (114.2 U/mL). Electroneurography showed a pattern of mononeuritis multiplex. Chest radiograph and computed tomography showed diffuse bronchial wall thickening (Picture A, B). The diagnosis of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA) was made according to the American college of rheumatology classification criteria. Intravenous cyclophosphamide, glucocorticoid, and mepolizumab were initiated. Repeat chest imaging performed 19 days after the initial treatment showed a marked reduction in bronchial wall thickening (Picture C, D). He also reported resolution of numbness. EGPA is a heterogeneous disease showing a variety of pulmonary manifestations based on ‘vasculitic’ and ‘eosinophilic’ pathogenesis (1). Given that bronchial wall thickening in the absence of definite lung parenchymal abnormalities is a common feature in eosinophilic asthma (2), such imaging may be a useful clinical marker for applying anti-eosinophil therapy, including mepolizumab, in EGPA. In our case, we used combination therapy to decrease organ damage and achieve rapid glucocorticoid tapering.
Picture.
Written consent was obtained from the patient. The Institutional Research Ethics Board does not require board review for a single case report when the patient's privacy is protected
Author's disclosure of potential Conflicts of Interest (COI).
Tatsuya Atsumi: Honoraria, Sanofi, Astellas, AbbVie, Bristol Myers Squibb, NipponBoehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead Sciences and Eli Lilly.
References
- 1. Trivioli G, Terrier B, Vaglio A. Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis: understanding the disease and its management. Rheumatology (Oxford) 59: iii84-iii94, 2020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Lin X, Lin Y, Lai Z, et al. Retrospective comparison of high-resolution computed tomography of eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis with severe asthma. Ann Transl Med 9: 983, 2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]