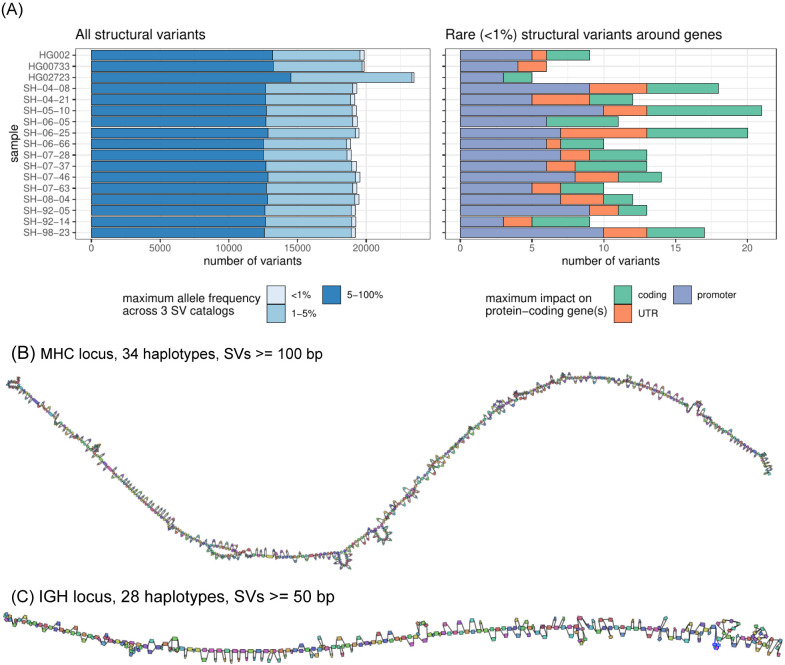
Figure 6. Structural variant landscape summary.
(A) The number of structural variants across samples. In the left panel, structural variants were annotated with three SV catalogs (the gnomAD-SV database, a long-read-based SV catalog, and the HPRC v1.0 SV catalog). SVs are matched if they have at least 10% genomic overlap. SVs close to centromeres, telomeres, or within segmental duplications were removed. The colors highlight the maximum frequency across these catalogs, the lighter blue showing “rare” SVs (with an allele frequency below 1%) in the catalogs, or unmatched. SVs may be unmatched, either because they are novel or due to the difficulties in the database comparison. The right panel shows the number of rare structural variants in protein-coding genes, grouped by their impact on the gene structure. (B) MHC pangenome built from 28 brain and 6 cell line haplotypes, containing 640 nodes, SVs over 100bp are shown. (C) IGH pangenome built from 28 brain haplotypes containing 268 nodes. In contrast, cell lines are typically derived from B-cell lymphocytes and contain extensive somatic rearrangements in this locus.