Abstract
In the last decade, Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy has emerged as a promising immunotherapeutic approach to fight cancers. This approach consists of genetically engineered immune cells expressing a surface receptor, called CAR, that specifically targets antigens expressed on the surface of tumor cells. In hematological malignancies like leukemias, myeloma, and non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphomas, adoptive CAR-T cell therapy has shown efficacy in treating chemotherapy refractory patients. However, the value of this therapy remains inconclusive in the context of solid tumors and is restrained by several obstacles including limited tumor trafficking and infiltration, the presence of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, as well as adverse events associated with such therapy. Recently, CAR-Natural Killer (CAR-NK) and CAR-macrophages (CAR-M) were introduced as a complement/alternative to CAR-T cell therapy for solid tumors. CAR-NK cells could be a favorable substitute for CAR-T cells since they do not require HLA compatibility and have limited toxicity. Additionally, CAR-NK cells might be generated in large scale from several sources which would suggest them as promising off-the-shelf product. CAR-M immunotherapy with its capabilities of phagocytosis, tumor-antigen presentation, and broad tumor infiltration, is currently being investigated. Here, we discuss the emerging role of CAR-T, CAR-NK, and CAR-M cells in solid tumors. We also highlight the advantages and drawbacks of CAR-NK and CAR-M cells compared to CAR-T cells. Finally, we suggest prospective solutions such as potential combination therapies to enhance the efficacy of CAR-cells immunotherapy.
Keywords: CAR-T, CAR-NK, CAR-M, Cellular immunotherapy, Solid tumors, Combined therapies
Introduction
Cancer presents a paramount health issue with increasing annual incidence and mortality rates [1]. Conventional therapeutic approaches involving surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy have major drawbacks and many patients with metastatic or recurrent disease still face dismal outcomes [2, 3]. In the last decade, various targeted treatments have considerably evolved owing to increasing knowledge in cancer molecular medicine and in immuno-oncology, allowing the development of precision medicine as a more specific and less toxic way to manage cancer [4]. Antitumor immunotherapy provided a major advance in the treatment of cancer by modulating the immune system to enhance its ability to recognize and destroy the malignant cells [5]. A broadly successful antitumor cellular immunotherapy approach consists of engineering immune cells to express cell surface receptor/s capable of recognizing antigens expressed on the surface of tumor cells and destroying them [6]. Subsequently, genetically modified immune cells are redirected through the Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) to the tumor cells [7]. Currently, approved CAR-T cell therapy targets are mostly the B cell maturation antigen (BCMA) for multiple myeloma (MM) [8, 9] and the B cell antigen CD19 for various lymphoid malignancies including B-cell leukemias [10–12] and some types of lymphomas [13, 14]. Indeed, according to published anti-BCMA CAR-T cell clinical trials, complete remission rates of 29 to 60% were reached in a total of 61 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma (r/r MM) [15]. CAR-T cells targeting CD19 led to initial complete remission in up to 85% of patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) [16] and in up to 100% of patients with refractory or relapsed B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (r/r B-ALL) [17]. CAR-T cells targeting large B cell lymphoma are currently approved for second-line therapy after chemotherapy failure [18]. The application of CAR-T cell therapy in hematological malignancies showed promising results that increases the prospect to use this strategy in other types of malignancies.
Currently, there are several ongoing clinical trials utilizing CAR-T cell therapy for solid tumors including glioblastoma [19], lung cancer [20], liver cancer [21], gastric cancer [22], renal cancer [23], prostate cancer [24], osteosarcoma, peritoneal carcinomatosis, pleural cancer, central nervous system tumors and neuroblastoma [25]. This immunotherapeutic approach generated promising clinical outcome. However, it has also shown several radical limitations such as difficulty of the cytotoxic T cells to infiltrate the tumor, insufficiency of T cell recruitment to the tumor site due to abnormal chemokines secreted by solid tumor cells and to the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment [26, 27]. Moreover, other limitations are related to CAR-T cell side effects including the on-target off-tumor toxicities and the cytokine-released syndrome (CRS) which present the two major adverse events that restrain the therapeutic index [28, 29]. In addition, other toxicities induced by CAR-T cells, such as tumor lysate syndrome, neurotoxicity, cytopenia-related adverse events are also common limitations of this therapy [30]. In the interest of overcoming these obstacles, various innovative strategies are currently under investigation. In addition, scientists are seeking alternative immune effector cells that can be engineered with CARs to be used as antitumor cellular immunotherapy. The increasing understanding of the prominent characteristics of NK cells and macrophages, related to the interaction with other cellular components of the tumor microenvironment, expanded the research focus from CAR-T to CAR-NK and CAR-M cellular immunotherapy [31–35].
Here we discuss the current status, the challenges and prospects regarding the clinical applications of CAR-T, CAR-NK, and CAR-M cells in the management of patients with solid tumors. We also highlight the potential advantages of CAR-NK and CAR-M cells over CAR-T cells.
CAR-T cell therapy in solid tumors: applications, challenges and recent advances
In recent years, T cells engineered with CAR demonstrated promising outcomes against B cell leukemia and lymphoma, proving its therapeutic anti-cancer potential [36]. Indeed, two CAR-T cell therapies Tisagenlecleucel and Axicabtagen-ciloleucel, were approved by the European Medical Agency (EMA) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [37–40]. Two additional products have also been approved for these indications: brexucabtagene autoleucel (mantle lymphoma and ALL) and lisocabtagene maraleucel (DBCL, follicular lymphoma, high grade lymphoma). This success is largely due to the choice of the target, the B-cell marker CD19, generating a T cell immune response against the malignant B cells in a MHC-independent manner [41, 42]. Other target antigens: BCMA and CD38 are also found on myeloma cells [37, 38]. Therefore, cellular BCMA-CD38-CAR-T cell therapy is feasible in treating patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma (r/r MM), with high response rate, low recurrence rate and manageable CRS [43]. Importantly, BCMA-CAR-T immunotherapies Ciltacabtagene-autoleucel and Idecabtagene-vicleucel are now available for the treatment of patients with relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma [44]. These significant achievements in the treatment of hematological malignancies advocate CAR-T cell application for the treatment of solid tumors. In recent years, an increasing number of CAR-T cell clinical trials targeting solid tumors have been carried out. In the next subchapter, we report the promising clinical outcomes covering the most common target antigens according to the data provided by ClinicalTrials.gov and the literature.
Promising clinical outcomes of CAR-T cells in solid tumors
CAR-T cell therapy has achieved important breakthroughs in the treatment of some solid tumors. CAR-T cell clinical trials, targeting several antigens expressed in tumors of different organs, are registered on clinicaltrials.gov and summarized in Table 1. The common CAR-T cell targets in solid tumors have been recently reviewed [45, 46]. Promising clinical outcomes of CAR-T cell therapy in solid tumors are reported in this section according to the targeted tumor antigens.
Table 1.
Clinical trials of CAR-T cell therapy in solid tumors (ClinicalTrials.gov)
| CAR-T product | Clinical trial identifier | Targeted antigen | Disease | Cell source | Clinical trial phase | Status | Estimated enrollment (EE)/ Actual enrollment (AE)/ Treated patients (TP) | Study objectives |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSLN-CAR-T cells | NCT05531708 | MSLN | Mesothelin-positive advanced refractory solid tumors | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 20 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of novel mesothelin CAR-T in patients with mesothelin-positive advanced refractory solid tumors. |
| MSLN-CAR-T cells | NCT05373147 | MSLN | Mesothelin-positive solid tumors | Autologous T cells | Early Phase 1 | Recruiting | 21 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and tolerability of autologous MSLN-CAR-T cells secreting PD-1 nanobodies (αPD1-MSLN-CAR T cells) in patients with solid tumors. |
| MSLN CAR-T cells | NCT04489862 | MSLN |
Non-small cell lung cancer Mesothelioma |
Autologous T cells | Early Phase 1 | Recruiting | 10 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and tolerability of autologous MSLN-CAR-T cells secreting PD-1 nanobodies (αPD1-MSLN-CAR T cells) in patients with solid tumors. |
| MSLN CAR-T cells | NCT05141253 | MSLN | MSLN-positive solid tumors | RD133 autologous T cells | Early Phase 1 | Recruiting | 24 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of RD133 MSLN CAR-T cells in subjects with relapsed or refractory MSLN-positive solid tumors. |
| MSLN CAR-T cells | NCT05166070 | MSLN | Solid tumors | RD133 autologous T cells | Early Phase 1 | Recruiting | 24 (EE) | Evaluation of the Safety and efficacy of RD133 in subjects with relapsed or refractory MSLN-Positive solid tumors. |
| MSLN CAR T cells secreting PD-1 nanobodies | NCT04489862 | MSLN | Non-small-cell lung cancer Mesothelioma | Autologous T cells | Early Phase 1 | Recruiting | 10 (EE) | Exploratory study of MSLN-CAR-T Cells secreting PD-1 nanobodies for the treatment of MSLN-positive advanced solid tumors. |
| PD-1 antibody expressing MSLN CAR-T cells | NCT03615313 | MSLN | MSLN-positive advanced recurrent or refractory malignant solid tumors | Autologous T cells |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Unknown |
50 (EE) 1 (TP) |
Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of infusion of autologous T cells engineered to target mesothelin and express PD-1 antibodies in adult patients with advanced recurrent or refractory malignant solid tumors, which were positive expression of mesothelin. |
| MSLN CAR-T cells | NCT02159716 | MSLN |
Metastatic Pancreatic (Ductal) Adenocarcinoma Epithelial ovarian cancer Malignant epithelial pleural mesothelioma |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Completed |
19 (AE) 15 (TP) |
Evaluation of the safety and feasibility of intravenously administered lentiviral transduced CART-meso cells administered with and without cyclophosphamide in a 3 + 3 dose escalation design in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer, serous epithelial ovarian cancer, or pleural mesothelioma. |
| αPD1-MSLN-CAR T Cells | NCT04503980 | MSLN |
Colorectal cancer Ovarian cancer |
Autologous T cells | Early Phase 1 | Unknown | 10 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and tolerability of autologous mesothelin (MSLN)-targeted chimeric antigen receptor (MSLN-CAR) T cells secreting PD-1 nanobodies (αPD-1-MSLN-CAR T cells) in patients with solid tumors. |
| CTLA-4/PD-1 antibodies expressing MSLN CAR-T cells | NCT03182803 | MSLN | Advanced solid tumors | Autologous T cells |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Unknown | 40 (EE) | Assessment of the efficacy and safety of the CTLA-4 and PD-1 antibodies expressing mesothelin-CAR-T (mesoCAR-T) for patients with mesothelin positive, advanced recurrent or refractory malignant solid tumors |
| PD-1 antibody expressing MSLN CAR-T cells | NCT03030001 | MSLN |
Solid tumors Adult advanced cancer |
Autologous T cells |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Unknown | 40 (EE) | Determination of the safety and efficacy of infusion of autologous T cells engineered to express immune checkpoint antibody and chimeric antigen receptor targeting mesothelin in adult patients with mesothelin positive, recurrent, or refractory malignant tumors. |
| MSLN CAR-T cells | NCT03545815 | MSLN | MSLN-positive multiple solid tumors | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Unknown | 10 (EE) | Evaluation of the feasibility and safety of CRISPR-Cas9 mediated PD-1 and TCR gene-knocked out CAR-T cells in patients with mesothelin positive multiple solid tumors. |
| GD2/PSMA bi-specific CAR-T cell | NCT05437315 | GD2/PSMA | GD2 and PPSMA-positive tumors | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Recruiting | 60 (EE) |
Assessment of the feasibility, safety, and efficacy of anti-GD2/PSMA bi-specific CAR-T cell therapy in patients with GD2 and PSMA-positive tumors. Evaluation of the function of the anti-GD2/PSMA bi-specific CAR-T cells and their persistency in patients. |
| GD2 CAR-T cells | NCT02107963 | GD2 |
Sarcoma Osteosarcoma Neuroblastoma Melanoma |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Completed | 15 (AE) | Evaluation of the antitumor effects, persistence, and safety of GD2 CAR-T cells in children and young adults with GD2-positive solid tumors. |
| GD2 CAR-T01 cells | NCT03373097 | GD2 |
Neuroblastoma recurrent GD2-positive solid tumors Osteosarcoma Ewing sarcoma |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Recruiting | 42 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of GD2-CART01, a CAR-T cell treatment targeting GD2 in pediatric or young adult patients with high-risk and/or relapsed/refractory neuroblastoma. |
| GD2 CAR T cells | NCT04196413 | GD2 |
Glioma of spinal cord Glioma of Brainstem |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting |
45 (EE) 4 (TP) |
Evaluating whether GD2-CAR T cells can be successfully made from immune cells collected from children and young adults with H3K27M-mutant diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) or spinal H3K27M-mutant diffuse midline glioma (DMG). H3K27Mmutant testing will occur as part of standard of care prior to enrollment. |
| GD2 CAR T cells | NCT00085930 | GD2 | Neuroblastoma | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Active, not recruiting | 19 (TP) | Study of blood T-cells and EBV specific CTLs Expressing GD-2 Specific Chimeric T cell receptors in patients with neuroblastoma |
| CLDN18.2 CAR-T cells | NCT04467853 | CLDN18.2 | Claudin18.2-positive advanced solid tumors | LCAR-C18S cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 34 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and anti-tumor efficacy profiles of the cell-based LCAR-C18S (hereinafter “LCAR-C18S”) in subjects with claudin18.2-positive advanced solid tumors. |
| CLDN18.2 CAR-T cells | NCT05472857 | CLDN18.2 |
Gastric cancer Pancreatic cancer Advanced ovarian carcinoma Gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 30 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of autologous claudin18.2 CAR-T cell therapy in advanced solid tumors with positive CLDN18.2 expression. |
| CLDN18.2 CAR-T cells | NCT03874897 | CLDN18.2 | Advanced solid Tumor | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting |
123 (EE) 37 (TP) |
Evaluation of the safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics of autologous humanized anti-claudin18.2 CAR-T cells in advanced solid tumor. |
| CLDN18.2 CAR-T cells | NCT04581473 | CLDN18.2 |
Gastric adenocarcinoma Pancreatic cancer Gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma |
CT041 autologous T cells | Phase 1b Phase 2 | Recruiting | 192 (EE) | Evaluation of the efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of CT041 autologous CAR-T cells. Injection in patients with CLDN18.2-positive advanced gastric/ gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma and pancreatic cancer. |
| CLDN18.2 CAR-T cells | NCT05199519 | CLDN18.2 | Solid tumors | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 30 (EE) | Evaluate the safety, tolerance, pharmacokinetics, and preliminary efficacy of IBI345 in patients with CLDN18.2-positive solid tumors. |
| CLDN18.2 CAR-T cells | NCT05620732 | CLDN18.2 |
Advanced pancreatic carcinoma Advanced gastric carcinoma |
Autologous T cells | N/A | Recruiting | 20 (EE) | Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of claudin18.2 CAR-T in advanced pancreatic cancer and gastric carcinoma. |
| CLDN18.2 CAR-T cells | NCT05472857 | CLDN18.2 |
Gastric cancer Pancreatic cancer Advanced ovarian carcinoma Gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 30 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of autologous claudin18.2 CAR-T cell therapy in advanced solid tumors with positive CLDN18.2 expression. |
| CLDN6 CAR-T cells | NCT04503278 | CLDN6 | Solid Tumor | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Recruiting | 96 (EE) | Evaluation of safety and preliminary efficacy of CLDN6 CAR-T With or Without CLDN6 RNA-LPX in patients with CLDN6-positive relapsed or refractory advanced solid tumors. |
| CEA CAR-T cells | NCT05415475 | CEA |
Colorectal cancer Esophageal cancer Stomach cancer Pancreatic cancer Metastatic tumor Recurrent cancer |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 36 (EE) |
Verification of the safety and efficacy of CAR-T cells in the treatment of CEA-positive advanced malignant tumors, and to obtain the recommended dose and infusion scheme of CAR-T cells for the treatment of patients with CEA-positive advanced malignant tumors. Administration method: intravenous infusion or intraperitoneal injection. |
| CEA CAR-T cells | NCT04348643 | CEA |
Solid tumor Lung cancer Colorectal cancer Liver cancer Pancreatic cancer Gastric cancer Breast cancer |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Recruiting | 40 (EE) | Evaluation of the efficacy and safety of CEA-targeted CAR-T cells for patients with relapsed/refractory CEA-positive cancer and to obtain the recommended dose and infusion plan. |
| CEA CAR-T cells | NCT05538195 | CEA |
Gastric cancer Colon cancer Rectal cancer Esophageal cancer Pancreatic cancer |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Recruiting | 60 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of CEA-targeted CAR-T cell in CEA-positive advanced malignant tumors. |
| CEA CAR-T cells | NCT05396300 | CEA |
Colorectal cancer Esophageal cancer Stomach cancer Pancreatic cancer Metastatic tumors Recurrent cancer |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Completed | 60 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and tolerability of CAR-T in patients with CEA-positive advanced malignant solid tumors, and to obtain the maximum tolerated dose of CAR-T and phase II recommended dose. |
| CEA CAR-T cells | NCT02349724 | CEA |
Lung cancer Colorectal cancer Gastric Cancer Breast Cancer Pancreatic Cancer |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Unknown |
75 (EE) 10 (TP) |
Verification of the safety of CEA targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cells and to determine the proper dosage of CAR T cells infused |
| CEA CAR-T cells | NCT02416466 | CEA | Liver metastases | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Completed |
8 (AE) 6 (TP) |
Study of anti-CEA CAR-T cells hepatic artery infusions and yttrium-90 SIR-Spheres in patients with CEA-expressing liver metastases |
| CEA CAR-T cells | NCT02850536 | CEA | Liver metastases | Autologous T cells | Phase 1b | Completed |
5 (AE) 1 (TP) |
Study of anti-CEA CAR-T cell infusions delivered via the hepatic artery or splenic vein using the Sure-fire Infusion System (SIS) for patients with CEA-expressing liver metastases or pancreas cancer. |
| ROR1 CAR-T cells | NCT05274451 | ROR1 |
Triple-negative breast cancer Non-small cell lung cancer Metastatic non-small cell carcinoma of the lung Breast cancer Advanced lung carcinoma Recurrent NSCLC Relapse/recurrence breast cancer |
LYL797 autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 54 (EE) | Assessment of the safety and efficacy of LYL797, ROR1-targeting CAR-T cells, in adults with relapsed and/or refractory solid-tumor malignancies. |
| ROR1 CAR-T cells | NCT02706392 | ROR1 | Advanced ROR1-positive TNBC and NSCLC | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Terminated |
21 (AE) 5 (TP) |
Evaluation of the safety and anti-tumor activity of adoptively transferred autologous ROR1 CAR-T cells in pts. with advanced ROR1+ TNBC and NSCLC. |
| ROR2 CAR-T cells | NCT03960060 | ROR2 | Recurrent or refractory solid tumors | CCT301–59 autologous T cells | Active, not recruiting | 18 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and preliminary therapeutic efficacy of CCT301–59 T cells in adult subjects with relapsed and refractory stage IV metastatic solid tumors (soft tissue sarcoma, gastric cancer, pancreatic cancer, bladder cancer). | |
| NKG2DL CAR-T cells | NCT05382377 | NKG2DL | CRC, advanced NKG2DL-positive solid tumors | KD-025 autologous cell | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 18 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of NKG2D-based CAR-T cell infusion in the treatment of advanced NKG2DL-positive solid tumors. |
| NKG2DL+/CLDN18.2+ CAR-T cells | NCT05583201 | NKG2D/CLDN18.2 | NKG2D/CLDN18.2-positive solid tumor | KD-496 autologous cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 18 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of NKG2D/CLDN18.2-based CAR-T cell infusion in the treatment of advanced NKG2DL+/CLDN18.2+ solid tumors. |
| NKG2DL CAR-T cells | NCT04107142 | NKG2DL |
Colorectal Cancer Triple negative breast cancer Sarcoma Nasopharyngeal carcinoma Prostate cancer Gastric cancer |
Haploidentical / Allogeneic T cells | Phase 1 | Unknown | 10 (EE) | Evaluation of the haploidentical / allogeneic Natural Killer Group 2D Ligand (NKG2DL)-targeting chimeric antigen receptor-grafted Gamma Delta (γδ) T Cells (CTM-N2D) in subjects with relapsed or refractory solid tumour |
| CD70 CAR-T cells | NCT05420545 | CD70 |
Metastatic tumor Advanced solid tumor Renal cell carcinoma Ovarian cancer Cervix cancer |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 36 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and tolerability of CAR-T in patients with CD70-positive advanced/metastatic solid tumors, and to obtain the maximum tolerated dose of CAR-T and phase II recommended dose. |
| CD276 CAR-T cells | NCT04691713 | CD276 | CD276-positive advanced solid tumors | Autologous T cells | N/A | Unknown | 5 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of targeting CD276 auto-chimeric antigen receptor T cells in the treatment of CD276-positive advanced solid tumors. |
| HER2 CAR-T cells | NCT04650451 | HER2 |
HER2-positive gastric cancer HER2-positive breast cancer HER-2 protein overexpression solid tumor |
BPX-603 autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Recruiting | 220 (EE) | Investigation of the safety, tolerability, and clinical activity of HER2-specific dual-switch CAR-T cells, BPX-603, administered with rimiducid to subjects with previously treated, locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors which are HER2 amplified/overexpressed. |
| HER2 CAR-T cells | NCT04511871 | HER2 |
Solid tumor Gastric cancer Breast cancer Ovarian cancer Sarcoma |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 15 (EE) | Assessment of the safety, tolerability, and anti-tumor activity of autologous CAR-T cells (CCT303–406) in patients with relapsed or refractory HER2 Positive solid tumors. |
| HER2 CAR-T cells | NCT03740256 | HER2 | Solid tumors | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 45 (EE) | Study of the effect of binary oncolytic adenovirus in combination with HER2-Specific autologous CAR-T Cells in patients with advanced HER2 Positive solid tumors. |
| HER2 CAR-T cells | NCT00902044 | HER2 | Advanced sarcoma | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Active, not recruiting |
36 (EE) 19 (TP) |
Administration of HER2 CAR-T cells for subjects with advanced sarcoma (HEROS) |
| HER2 CAR-T cells | NCT01109095 | HER2 | Glioblastoma multiforme | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Completed |
16 (AE) 17 (TP) |
Evaluation of the safety and antitumor efficacy of autologous HER2-specific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)–modified virus-specific T cells (VSTs) in patients with progressive glioblastoma |
| HER2 CAR-T cells | NCT01935843 | HER2 | Advanced HER-2-positive solid tumors | Autologous T cells |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Unknown |
10 (EE) 11 (TP) |
Evaluation of the safety, feasibility, and activity of CAR-T cell immunotherapy targeting human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) in patients with advanced biliary tract cancers (BTCs) and pancreatic cancers (PCs) |
| HER2 CAR-T cells | NCT03500991 | HER2 | HER2-positive recurrent/refractory pediatric CNS tumors | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting |
48 (EE) 3 (TP) |
Assessing the feasibility, safety, and tolerability; secondary objectives include assessing CAR-T cell distribution and disease response |
| EGFR-TGFβR-KO CAR-T cells | NCT04976218 | EGFR | EGFR-positive solid tumors | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 30 (EE) | Evaluation of the anti-tumor activities and safety profiles of CAR-EGFR-TGFβR-KO T cell in previously treated advanced EGFR positive solid tumors. CAR-EGFR-TGFβR-KO T cell engineered by knocking out TGF-β receptor II through CRISPR/Cas9. |
| Anti-CTLA-4/PD-1 expressing EGFR-CAR-T | NCT03182816 | EGFR | EGFR-positive advanced solid tumors | Autologous T cells |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Unknown |
40 (EE) 9 (TP) |
Assessment of the efficacy and safety of the CTLA-4 and PD-1 antibodies expressing EGFR-CAR-T for patients with EGFR positive advanced recurrent or refractory malignant solid tumors |
| EGFR CAR-T cells | NCT01869166 | EGFR | EGFR-positive advanced solid tumors | Autologous T cells |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Unknown |
60 (EE) 14 (TP) |
Evaluation of the safety, feasibility of the chimeric antigen receptor T cells transduced with the anti-EGFR and their in vivo survival duration. |
| EGFRvIII CAR-T cells | NCT02209376 | EGFRvIII | Residual or reccurent EGFRvIII- positive Glioma | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Terminated |
11 (EE) 10 (TP) |
Evaluation of the safety and feasibility of CART-EGFRvIII (autologous T cells transduced with a lentiviral vector to express a chimeric antigen receptor specific for EGFRvIII) in the treatment of patients with EGFRvIII+ glioblastoma who have had their first recurrence as determined by standard imaging or have residual disease after initial resection. |
| PD-1 antibody expressing EGFR CAR-T Cells | NCT02873390 | EGFR | EGFR-positive advanced solid tumors | Autologous T cells |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Unknown | 20 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of cell therapy using herinCAR-PD1 cells to treat advanced cancer. |
| PD-1 antibodies expressing EGFR CAR-T Cells | NCT02862028 | EGFR | EGFR-positive advanced solid tumors (Lung, Liver and Stomach) |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Unknown | 20 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of cell therapy using herinCAR-PD1 cells to treat relapsed or refractory cancer | |
| VEGFR1/PD-L1 CAR-T cells | NCT05477927 | VEGFR1 and PD-L1 |
Malignant peritoneal effusion Malignant ascites Serous cavity metastatises |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 58 (EE) | Dose-escalation and expansion study of specific dual-targeting VEGFR1 and PD-L1 CAR-T in cancer patients with pleural or peritoneal metastases. |
| EGFR/B7-H3 CAR-T cells | NCT05341492 | EGFR and B7-H3 |
Advanced lung cancer Advanced triple-negative breast cancer |
Autologous T cells | Early Phase 1 | Recruiting | 30 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of EGFR/B7H3 CAR-T in patients with EGFR/ B7-H3-positive advanced solid tumors (Lung and Triple-negative Breast Cancer). |
| B7-H3 CAR-T cells | NCT04897321 | B7-H3 |
Pediatric solid tumor Sarcoma |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 32 (EE) |
Evaluation of the use of autologous T cells genetically engineered to express B7-H3-CARs for patients ≤21 years old, with relapsed/refractory B7-H3-positive solid tumors. Evaluation of the safety and maximum tolerated dose of B7-H3-CAR-T cells. Finding the highest dose of B7-H3-CAR T cells that are safe to give to patients with B7-H3-positive solid tumors. |
| B7-H3 CAR-T cells | NCT04483778 | B7-H3 | Recurrent/Refractory solid tumors in children and young adults | Allogeneic T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 68 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety, feasibility, and efficacy of administering T cell products derived from the research participant’s blood that have been genetically modified to express a B7-H3-specific receptor CAR that will target and kill solid tumors that express B7-H3. |
| B7-H3 CAR-T cells | NCT05190185 | B7-H3 | Malignant melanoma lung cancer, or colorectal cancer | TAA06 autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 18 (EE) |
Evaluation of the safety and tolerability of TAA06 CAR-T cells targeting B7-H3 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Evaluation of the distribution, proliferation, and persistence of B7-H3-targeted CAR T cells and their efficacy. |
| CD276 CAR-T | NCT04691713 | CD276 | Solid tumors | Autologous T cells | N/A | Recruiting | 5 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of targeting CD276 auto-CAR-T cells in the treatment of CD276-positive advanced solid tumors. |
| CTLA-4 and PD-1 antibodies expressing MUC1-CAR-T Cells | NCT03179007 | MUC1 | MUC1-positive advanced recurrent or refractory malignant solid tumors. | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Unknown | 40 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of infusion of autologous T cells engineered to express immune checkpoint antibodies (CTLA-4 and PD-1) and chimeric antigen receptor targeting MUC1 in adult patients with MUC1 positive, advanced recurrent or refractory malignant solid tumors. |
| PD-1 -Knockout MUC1 CAR-T cells | NCT03706326 | MUC1 | Advanced esophageal cancer | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Unknown | 20 (EE) | Assessment of the safety and efficacy of the immunotherapies using anti-MUC1 CAR T cells and /or PD-1 knockout engineered T cells in the treatment of patients with advanced esophageal cancer. |
| MUC1 CAR T Cells | NCT02587689 | MUC1 |
Hepatocellular carcinoma Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Pancreatic Carcinoma Triple-negative invasive breast carcinoma |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Unknown | 20 (EE) | Determination of whether autologous T cells bearing chimeric antigen receptor that can specifically recognize (Mucin 1) MUC1 is safe and effective for patients with relapsed or refractory solid tumor. |
| MUC1 CAR T Cells | NCT02617134 | MUC1 |
Malignant glioma of brain Colorectal carcinoma Gastric Carcinoma |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Unknown | 20 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of CAR-T cell immunotherapy in patients with MUC1 positive relapsed or refractory solid tumors. |
| P-MUC1C-ALLO1 CAR-T cells | NCT05239143 | MUC1C |
Breast cancer Ovarian cancer Non-small cell lung cancer Colorectal cancer Pancreatic cancer Renal cell carcinoma Nasopharyngeal cancer Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma Gastric cancer |
Allogeneic T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting |
100 (EE) 3 (TP) |
Determination of the recommended phase 2 dose of P-MUC1C-ALLO1 an allogeneic CAR-T cell therapy designed to target cancer cells expressing Mucin1 cell surface-associated C-Terminal (MUC1-C) antigen. |
| TnMUC1 CAR-T cells | NCT04025216 | TnMUC1 | Advanced TnMUC1-positive solid tumors | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Active, not recruiting | 112 (EE) | Identification of the dose and regimen of CART-TnMUC1 cells that can be safely administered intravenously following the lymphodepletion (LD) regimen to patients with (1) advanced TnMUC1+ solid tumors (triple negative breast cancer, epithelial ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, and non-small cell lung cancer) and (2) advanced TnMUC1+ multiple myeloma |
| Lewis Y CAR-T cells | NCT03851146 | Lewis Y | Advanced cancer | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Completed | 20 (EE) | Investigation of the safety, tolerability, and immunological effects of T Lymphocytes transduced with an anti-Lewis Y (LeY) CAR gene (LeY-CAR-T) in patients with LeY antigen expressing advanced solid tumors. |
| OX40 CAR-T cells | NCT04952272 | OX40 |
Lung cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma Solid tumor |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 50 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and clinical effects of intratumor injecting CpG-ODN and in situ release of tumor antigen by interventional ablation or drug-eluting beads to treat advanced solid tumors. With or without infusion of CAR-T cells secreting scFv against OX40. |
| EpCAM CAR-T cells | NCT02915445 | EpCAM |
Malignant neoplasm of nasopharynx TNM staging distant metastasis Breast cancer Recurrent gastric cancer with metastasis |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 30 (EE) | Determination of the safety of CAR-T cells recognizing EpCAM. |
| TM4SF1- and EpCAM- CAR-T cells | NCT04151186 |
TM4SF1/ EpCAM |
EpCAM-positive Recurrent/Refractory solid tumors | Autologous T cells | N/A | Unknown | 72 (EE) | Evaluation of the Safety and efficacy of CAR-T-cell therapy for the TM4SF1- and EpCAM-positive Recurrent/Refractory solid tumors |
| NKG2DL CAR-T cells | NCT05382377 | NKG2DL | Solid tumors | KD-025 autologous T cells | Early Phase 1 | Recruiting | 30 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of KD-025 CAR-T Therapy in advanced NKG2DL-positive solid tumors. |
| PSCA CAR-T cells | NCT02744287 | PSCA |
Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate cancer Metastatic prostate cancer |
BPX-601 autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Recruiting | 151 (EE) | Evaluation of the feasibility, safety, and activity of PSCA-Specific CAR Engineered T Cells (BPX-601) in subjects with previously treated advanced solid tumors. |
| GUCY2C CAR-T cells | NCT05287165 | GUCY2C |
Advanced solid tumors Digestive system neoplasms Pancreatic cancer Resectable colorectal (colon or rectal) cancer |
IM96 autologous T cells | Early Phase 1 | Recruiting | 19 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of IM96 CAR-T Cells therapy in patients with advanced digestive system neoplasms. |
| 4SCAR-IgT- cells | NCT03356782 | CD133, GD2, MUC1, CD117 | Sarcoma osteoid Sarcoma Ewing Sarcoma | Autologous T cells | Phase1 Phase 2 | Recruiting | 20 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of 4th generation 4SCAR-IgT cells targeting sarcomas. |
| IL7, CCL19, IL12-expressing Nectin4 CAR-T cells | NCT03932565 | Nectin4 | Nectin4-positive malignant solid tumors | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Unknown | 30 (EE) | Study of the intravenous minimally invasive surgery combined with intratumoral injection of Nectin4/FAP-targeted fourth-generation CAR-T cells (expressing IL7 and CCL19, or IL12) are used to treat Nectin4-positive advanced malignant solid tumors, maximally eliminating residual cancer cells, and preventing recurrence. |
| GPC3 CAR-T cells | NCT02932956 | Glypican 3 | Pediatric solid tumors | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 | Active, not recruiting | 10 (EE) | The purpose of this study is to find the biggest dose of GAP T cells that is safe, to see how long they last in the body, to learn what the side effects are and to see if the GAP T cells will help people with GPC3-positive solid tumors. This study enrolls patients who have GPC3-positive solid tumors |
| CAR-T cells | NCT03356795 | GD2, PSMA, MUC1, MSLN or other markers | Cervical cancer | Autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Unknown | 20 (EE) | Assessment of the feasibility, safety, and efficacy of CAR T cells immunotherapy in patients who have GD2, PSMA, Muc1, Mesothelin or other markers positive cervical cancer. Another goal of the study is to learn more about the persistence and function of CAR T cells in the body. |
| CAR-T cells | NCT04981119 | N/A |
Solid tumor Colorectal cancer Non-small cell lung cancer Pancreatic cancer |
Autologous T cells | N/A | Recruiting | 200 (EE) | Collect information on how often a solid tumor cancer might lose the Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) by next-generation sequencing and perform leukapheresis to collect and store an eligible participant’s own T cells for future use to make CAR-T Cell therapy for their disease treatment. |
| N/A | NCT04082910 | N/A |
Solid tumor Hematological malignancy |
Autologous T cells | Phase 1 Phase 2 | Recruiting | 30 (EE) |
Evaluation of the feasibility and efficacy of metoprolol, a beta-1 adrenergic receptor blocker, in the treatment of cytokine release syndrome (CRS) caused by CAR-T cell infusions. Evaluation of the effects of the treatment on the serum levels of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and other cytokines. |
Clinical outcomes of CAR-T cell therapy targeting HER2
Encouraging outcomes were demonstrated in a phase I/II clinical study (NCT00902044) using human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2)-CAR-T cells in the treatment of 19 patients with HER2-positive sarcomas (16 osteosarcomas, 1 primitive neuroectodermal, 1 Ewing sarcoma, and 1 protofibroblastic small round cell tumor) [39]. In this study, out of 17 evaluable patients, 4 experienced stable disease for 3 to 14 months, 3 of these patients received no additional therapy and had their tumor removed, with 1 showing ≥90% tumor necrosis [47]. The 19 infused patients had a median overall survival of 10.3 months (from 5.1 to 29.1 months). Interestingly, no adverse events were observed after high-dose treatment of CAR-T cell, except for high fever in one patient [39]. Moreover, a phase I study (NCT01109095) of a HER2 specific CAR-T cell treatment of 17 patients with glioblastoma reported a great tolerance to the CAR-T cells administered doses and a median overall survival (OS) of 11.1 months for 8 patients after treatment and 24.5 months after diagnosis. Furthermore, 3 patients were alive with no disease progression at the last follow-up [19]. A phase I clinical trial (NCT01935843) of CAR-T cells targeting the HER2 marker in 11 patients with pancreatic cancers (PCs) and advanced biliary tract cancers (BTCs) observed a median OS of 4.8 months (range, 1.5–8.3 months) with minimal and reversible toxic effects [48]. An additional phase I clinical trial (NCT03500991) conducted in a group of young people and children with refractory or recurrent Central Nervous System (CNS) tumors, including diffuse midline gliomas, demonstrated that iterative local HER2 CAR- T cell administration induced increased secretion of chemokines like C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2 (CCL2) and C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10 (CXCL10) in the cerebrospinal fluid with no CAR-T cell dose-related toxicity [49]. These findings allow the suggestion of developing CXCR/CCR-expressing-CAR-T cells thereby improving their binding with the tumor antigen.
Clinical outcomes of CAR-T cell therapy targeting IL-13Rα2
IL-13Rα2 is highly expressed in glioblastoma (GBM) tumor cells but is rarely expressed in normal brain cells, making it an interesting target for CAR-T cell therapy in glioblastoma cancer [40].. In Brown and colleagues’ study (NCT02208362), multi-dose treatment with IL-13Rα2-CAR-T cells induced a complete tumor regression for nearly 8 months in a patient with disseminated glioblastoma [40]. For the same targeted tumor antigen, another clinical trial (NCT00730613) used anti-IL-13Rα2-CAR-T cells for the treatment of 3 patients with recurrent GBM [50]. The therapy was well tolerated with controlled brain inflammation in all patients with recurrent disease. A short remission was observed in one patient, possibly due to IL-13Rα2 antigen loss on the relapsing tumor [50].
Clinical outcomes of CAR-T cell therapy targeting GD2
In neuroblastoma cells, disialoganglioside (GD2) is highly expressed [51] and might be considered as another interesting target for CAR-T cells in GBM. Recently, Majzner et al. [52], reported the outcomes of a first-in-human phase I clinical trial (NCT04196413) in 4 patients with H3K27M-mutated DIPG or spinal cord DMG-treated with GD2 CAR-T cells. Three out of four patients exhibited clinical and radiographic improvement associated with high levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the plasma and cerebrospinal fluid without on-target/off-tumor “OTOT” toxicity. Furthermore, a phase-I clinical trial (NCT00085930) evaluating GD2 CAR-T cells effect on 11 patients with neuroblastoma, showed complete remission in 3 patients [53]. GD2 was also targeted in a phase-I trial (ACTRN12613000198729) for GD2 positive metastatic melanoma patients treated with CAR-T cell therapy. The data of this study showed upregulated lymphocyte-activation gene 3 (LAG-3) and programmed cell death protein1 (PD-1) expression in administered CAR-T cells [54]. Therefore, combined CAR-T cells with PD-1 immune checkpoint blockade may enhance the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy.
Clinical outcomes of CAR-T cell therapy targeting ROR1
The orphan tyrosine kinase receptor ROR1 is a candidate target for CAR-T cell therapy because it is expressed on the surface of many lymphatic and epithelial malignancies and has a putative role in tumor cell survival [55]. A phase I trial (NCT02706392) examined the efficacy and safety of CAR-T cell targeting the transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor (ROR1) expressed in lung and breast cancers [56]. In this study, 4 out of 5 patients with lung and breast cancer experienced a mixed response with lower tumor burden at some metastatic sites [56].
Clinical outcomes of CAR-T cell therapy targeting EGFR
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) plays an important role in the development and progression of solid tumors and has emerged as an important therapeutic target in different types of cancer such as non-small-cell lung carcinoma, breast, gastroesophageal and colorectal cancers [57]. In addition, many clinical trials have been conducted on CAR-T cells targeting EGFR for the treatment of EGFR-positive solid tumors [45]. A phase-I clinical trial (NCT01869166) of EGFR CAR-T cell therapy in 11 patients with EGFR+ refractory/ relapsed non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) showed that 2 patients achieved partial response and 5 had stable disease for 2 to 8 months without severe toxicity [58]. Moreover, in a phase-I clinical trial, 10 patients with recurrent EGFRvIII+ glioblastoma (GBM) were treated with EGFRvIII engineered CAR-T cells (NCT02209376) [59]. The results of this study showed an anti-tumor effect of CAR-T cells with a median OS of approximately 8 months in all patients [59]. Other antigens that are targeted by CAR-T cells for GBM therapy are ephrin type-A receptor 2 (EphA2) (NCT02575261), and mucin 1 (MUC1) (NCT02839954, NCT02617134). In addition, in a phase I clinical trial (NCT03182816), EGFR was targeted by non-viral piggyBac transposon system-engineered EGFR-CAR T-cell therapy in 9 patients with non-small cell lung cancer. In this study, 1 patient had a sustained response of more than 13 months while 6 had stable disease, and 2 had progressed disease. The median progression-free survival was 7.13 months, with a median overall survival of 15.63 months [60]. This study showed that the non-viral piggyBac transposon system-engineered EGFR-CAR T-cell therapy is feasible and safe in the treatment of EGFR-positive advanced relapsed/refractory NSCLC patients [60].
Clinical outcomes of CAR-T cell therapy targeting CEA
A high level of Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) is known to be associated with poor cancer prognosis [61]. For this reason CEA has been targeted for the treatment of lung [62], breast [63], pancreatic and gastric cancers [64, 65], and it is considered as one of the most promising targets for colorectal cancer (CRC) [66]. A phase-I, escalating-dose trial of CAR-T cell therapy (NCT02349724) targeting CEA expressed in metastatic CRC reported that 7 out of 10 patients presented stable disease for up to 30 weeks and 2 patients experienced tumor reduction with no adverse events [67]. Additionally, Katz et al. [68] tested the effect of intra-arterial anti-CEA CAR-T cells therapy combined with internal radiation therapy in 6 patients with liver metastases. The data of this phase-Ib clinical trial (NCT02416466) demonstrated tolerated response to CAR-T cell therapy with non-observed grade 4 or 5 toxicities, and without instances of severe CRS or neurotoxicity. Additionally, the median survival OS was 8 months [68]. Moreover, anti-CEA CAR-T cell therapy demonstrated a significant beneficial effect in a patient with liver metastases secondary to stage IV pancreatic adenocarcinoma, and who received locally infused CEA CAR-T cells at the site of a solid tumor by Pressure-enabled Drug Delivery (PEDD) [69]. In this clinical trial (NCT02850536), anti-CEA CAR-T cell induced a complete metabolic response within the liver which was durable and sustained for 13 months with no serious adverse events above grade 3, highlighting the importance of combining CAR-T cell therapy with PEDD technology [69].
Clinical outcomes of CAR-T cell therapy targeting MSLN
Several CAR-T cell clinical trials targeting Mesothelin+ (MSLN) ovarian cancer (OC) have been undertaken. In a phase I/II clinical study (NCT03615313), a patient with relapsed epithelial OC was treated with MSLN-CAR-T cells and PD-1 blockade in combination with lapatinib, an angiogenesis inhibitor [70]. Interestingly, the patient achieved partial remission, survived for more than 17 months and experienced minimal side effects like grade-1 hypertension and fatigue [70]. Moreover, CAR-T cells targeting MSLN were administered to patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma, malignant pleural mesothelioma and OC who participated in a phase I clinical trial (NCT02159716) [71]. The study showed that lentiviral-transduced MSLN CAR-T cells expanded well in the peripheral blood, but their persistence was limited despite pre-treatment with cyclophosphamide [71]. Post-treatment stable disease in over 11 patients out of 15, was the best overall response reported in this study [71]. In another study, the intravenous injection of interleukin 7 (IL-7) and Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand-19 (CCL19)-MSLN secreting CAR-T cells (NCT03198546) in a patient with advanced pancreatic cancer induced complete regression of the tumor 240 days post-treatment [72]. No high-grade adverse events were observed [72].
Clinical outcomes of CAR-T cell therapy targeting CD133
CD133 is widely used as a marker to identify CRC stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells [73]. It can also be used to predict tumor progression, patient survival and chemoradiotherapy resistance in CRC [74, 75] and is one of the most well-characterized markers of cancer stem cells (CSCs) in various tumor types, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [76]. In a phase I/II clinical trial (NCT02541370), CD133 CAR-T cells were administered to 21 patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma [77]. This study demonstrated antitumor efficacy with low treatment-related toxicity. Of 21 evaluable patients, 1 had a partial response, 14 had stable disease for 2 to 16.3 months, and 6 had progressed disease after CAR-T cell administration [77]. Only 4 patients developed grade 3 hyperbilirubinemia and 2 patients had grade-3 anemia with no other serious adverse events [77].
Clinical outcomes of CAR-T cell therapy targeting Claudin 18.2
Claudin18.2, a stomach-specific isoform of Claudin-18, is expressed in 70% of primary gastric adenocarcinomas and their metastases [78]. It is considered as a potential target for the treatment of these malignancies. CT041, an anti-CLDN18.2 CAR-T cell product, has received Investigational New Drug (IND) clearance from the United States FDA in patients with CLDN18.2-expressing stomach, pancreatic, and gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma [79]. The IND clearance was supported by a phase-I trial (NCT03874897) which found that a Claudin18.2 CAR-T cell resulted in an overall response rate and disease control rate of 57.1 and 75.0%, respectively, in gastric cancer patients and the 6-month overall survival rate was 81.2%. No serious adverse events were reported [80]. This CAR-T cell therapy study resulted in an overall response rate (ORR) of 33%, a median progression free survival (PFS) of 130 days and a tolerable safety profile with no serious adverse events [80].
Clinical outcomes of CAR-T cell therapy targeting MUC1
Glycoprotein Mucin 1 (MUC1) is a transmembrane protein that belongs to the mucin family. This molecule is associated with metastases and tumor progression, especially in stomach cancer [81]. An open-label dose-escalation phase-I study (NCT05239143) has been recently activated to study the treatment effects of P-MUC1C-ALLO1 in subjects with advanced or metastatic solid tumors [82]. P-MUC1C-ALLO1 is an allogeneic CAR-T cell therapy designed to target cancer cells expressing Mucin 1 cell surface-associated C-terminal antigen. The results of this study showed an early efficacy at the low dose of the CAR-T cells with partial response in one patient (HR+, Her2- Breast cancer). No P-MUC1C-ALLO1 related toxicities were observed [82]. Although CAR-T cell therapy showed encouraging clinical outcomes, a meta-analysis on the efficacy of this innovative approach on solid tumors, showed a comprehensive response rate of only 9% [29]. Indeed, various drawbacks hinder the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy against solid tumors including the lack of tumor-specific antigens (TSAs) and antigen heterogeneity [83]. Moreover, CAR-T cell trafficking and infiltration in the tumor site [84] and the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment are major limitations, significantly impeding the function and persistence of CAR-T cells [85–87]. Due to these challenges, improving the design of CAR-T cell therapy for solid tumors merits special considerations in the future.
Challenges of CAR-T cells and innovative strategies to advance this therapy for solid tumors
Major challenges for CAR-T cell therapy in solid tumors include the identification of truly specific tumor antigens as targets, overcoming tumor antigen escape, improving CAR-T cells trafficking, infiltration and expansion at the tumor site as well as their persistence and functions in a hostile tumor microenvironment. To overcome these challenges and to enhance efficiency of CAR-T cells in solid tumors, various strategies have been developed such as optimizing CAR constructs or identifying innovative therapeutic combination strategies, thereby enhancing specificity, infiltration, and efficacy of CAR-T cell treatment and to modulate the inhibitory conditions (Table 2).
Table 2.
Advantages, limitations, and potential strategies improving CAR-T, CAR-NK and CAR-M therapy
| CAR-T cells | CAR-NK cells | CAR-M cells | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
- Sufficient number of circulating T cells - Previous studies on hematological malignancies facilitating its use on solid tumors |
- Natural ability against non-self-cells - Direct and indirect killing functions due respectively to CAR and ADCC - Self-identification of normal cells by KIR - Reduced risk of CRS, ICANS and GvHD - Can be generated from different sources |
- M1 macrophages feature a pro-inflammatory phenotype - Antitumor activity by phagocytosis, presenting tumor antigen to Th1 cells and production of anti-inflammatory factors - Most abundant population in the TME of many cancer types - Important source of matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) which degrades almost all ECM - Can be generated from different sources |
| Limitations |
- Tumor antigen heterogeneity and tumor antigens loss - Difficulty in infiltrating tumors - Limited survival and persistence in the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment - CRS, OTOT toxicity, neurotoxicity and GvHD |
- Limited tumor infiltration - Limited efficacy in CAR transduction - Limited survival and persistence in the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment |
- Limited efficacy in CAR transduction - CRS toxicity - OTOT toxicity - Need differentiation to M1 phenotype |
| Strategies |
➣ Overcoming tumor antigen heterogeneity and tumor antigen loss: - Bispecific-CAR-T cells - Pooled CAR-T cells - Switch on or off CAR-T cells - AI (radiomics) ➣ Facilitating CAR-T cell tumor infiltration: - Nanobody-based CAR-T cell therapy - Chemokine receptor-expressing CAR-T cells - CAR-T cells local administration: intraperitoneal, intra-tumoral injection, porous microneedle patch - CAR-T cells targeting stromal cell-associated antigens - Matrix-degrading enzymes-secreting CAR-T cells - Molecular torpedo - Modifying CARs design, e.g., Hinge domain, transmembrane domain and co-stimulatory signaling - Alternative non-LV or RV transduction and in vivo delivery of CARs - CAR-T cells combination with ICIs (anti-CTLA-4 or anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies) - PD-1/CTLA-4- antibodies secreting CAR-T cells ➣ Overcoming the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and persistence: - CAR-T cells secreting immunostimulatory factors such as IL12, IL18, and IL15 - CAR-T cells targeting Treg, MDSCs and M2 macrophages - Combining CAR-T cells with chemotherapy ➣ Overcoming CAR-T cells’ CRS toxicity: - IL-1R antagonists-secreting CAR-T - IL-6 blockade - Neutralizing GM administration - CAR construct improvement - Control of CAR activity and survival in vivo |
➣ Improving the trafficking to the tumor site: - CAR-NK expressing chemokine receptors ➣ Improving the transduction efficiency of NK cells: - Retronectin, ectofusin-1 used as transduction enhancer - Baboon envelope pseudotyped lentivirus (BaEV-LV) - Electroporation and transposons for non-viral transduction ➣ Improving CAR-NK cytotoxicity: - Armored CAR-NK with co-stimulatory domains (DAP-10, DAP-12 or 2B4) - Combining CAR-NK with tyrosine kinase inhibitors - Combining CAR-NK with immune checkpoints inhibitors (anti-PD-1 antibodies) ➣ Improving in vivo survival and persistence within the TME: - Engineered CAR-NK to co-express stimulatory cytokine - Designed chimeric co-stimulatory converting receptor (CCCR)-NK for switching the immunosuppressive negative signal to an activating one - Combining CAR-NK cells with chemotherapy and radiotherapy ➣ Improving NK cell generation: - Using different sources of NK cells including NK92 cell line, iPSCs, hESC. |
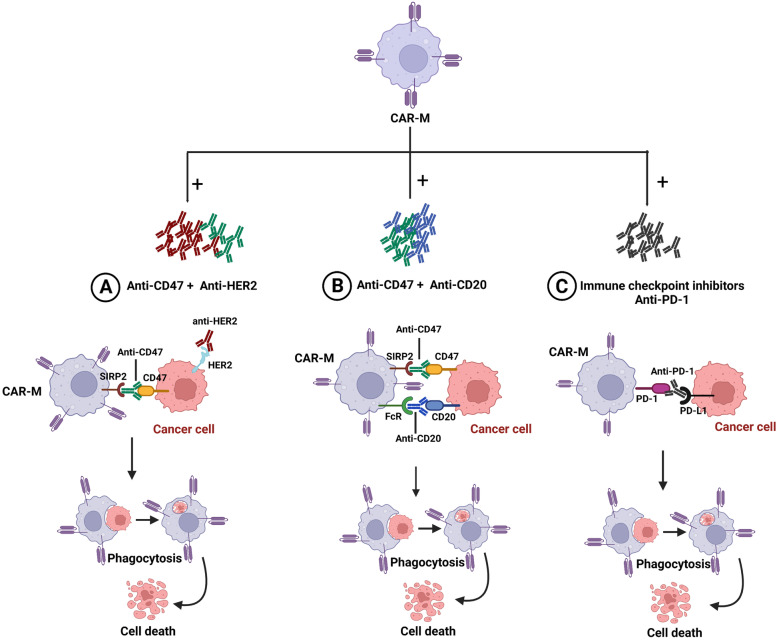
➣ Improving the bioengineering of CAR-M: - Use of modified lentiviral virions containing Vpx - Use of adenovirus 5-fiber 35 vector (Ad5f35) for efficient gene transfer - Mannose-conjugated polyethyleneimine (MPEI) for effective gene delivery ➣ Enhancing the antitumor activity of CAR-M: - M2 to an M1 phenotype polarization - CAR iMAC ➣ Enhancing trafficking and persistence within the immunosuppressive TME: - CAR-CD147 construct - CCL19-expressing CAR-macrophages - Combination therapy with anti-CD47, anti-CD20 and anti-TAA antibodies |
Overcoming tumor antigens heterogeneity, tumor antigens loss and scFv-based CAR-T cell limitations
An important challenge for CAR-T cells’ design and development is to find the appropriate antigen that is uniquely expressed by tumor cells and not by benign tissues. CARs targeting more than one antigen are being tested to overcome antigen loss variants of sub-clonal populations. Pooled CAR-T cell strategies consist of using two or more different CAR-T cells together, each targeting a single antigen. This strategy targets tumor cells in case of antigen loss, decreasing the chances of tumors resistance. Indeed, the combination of EGFR- and CD133-specific CAR-T cells showed improved outcomes in cholangiocarcinoma [88]. Additionally, in a NSCLC model, the combination of prostate stem cell antigen (PSCA)- and MUC1-targeting CAR-T cells synergistically eliminated PSCA+ and MUC1+ cancer cells [89]. A similar approach was applied for lung cancer by pooling EphA2-targeting CAR-T cells against tumor cells and fibroblast activation protein-α (FAPα)-targeting CAR-T cells against FAP+ stromal cells. This strategy was meant to kill cancer cells and simultaneously decrease the immunosuppressive function of FAP+ stromal cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME) [90]. This combinatorial strategy demonstrated significant tumor killing in vitro and extended the survival of mouse xenografts compared to each CAR-T cell therapy alone [90].
Multiplexing CAR strategy can also include dual tumor antigens targeted by bispecific-CAR-T cells (biCAR-T). Interestingly, using a combination therapy targeting IL13Rα2 and HER2 by bispecific CAR-T cells co-expressing IL13Rα2 and HER2 CAR molecules demonstrated significant potential for eliminating solid tumor cells and showed less antigen escape compared with mono-specific or pooled HER2-CAR-T and IL13Rα2-CAR-T cells alone in a glioblastoma model [91]. In breast cancer, biCAR-T cells targeting ErbB2 and MUC1 in vitro, showed efficient antitumor activity [92]. The development of biCAR-T cells with dissociated signaling pathways connected to a costimulatory signal and an activation signal is another promising strategy to improve T cells’ specificity. In this case, T-cell activation signal is physically dissociated from the costimulatory signal in two different CARs. Hence, biCAR-T cells become activated only when they simultaneously encounter two specific tumor cell antigens by tumor cells [84]. Some studies have proposed approaches to switch on or off CAR-T cells. Such strategies provide an accurate control of CAR-T cells activation and inhibition if toxic reactions arise [93]. For instance, using a bifunctional small “switch” molecule, which is composed of folate and fluorescein isothiocyanate (folate-FITC), allowed CAR-T cells to specifically identify tumor cells overexpressing folate receptors [94]. In addition, using suicide genes or antibody-mediated killing would shut-down CAR-T cells activity. Indeed, incorporating the inducible caspase 9 (iCasp9) system into CAR-T cells induced apoptosis leading to a repression of CAR-T cells activity [95]. Interestingly, using CAR-T cells targeting glycosylated antigens that are expressed on cancer cells, is also an interesting approach to overcome the tumor-immune response escape [96]. The success of CAR-T cell cocktails described above confronts related toxicities to be further investigated for fully evaluating clinical safety, particularly regarding OTOT toxicity [86] that may cause damage to healthy cells and organs. The risk of OTOT is enhanced by using more specific multi-antigens targeting CAR-T cells [87]. Therefore, controlling “on-target/off-tumor” (OTOT) toxicity during CAR T-cell therapy is one of the most important current challenges for optimal success of this new treatment strategy.
Structurally, CAR molecule is composed of an ectodomain, transmembrane domain, one or two costimulatory domains, and an activation domain [97]. The ectodomain is the extracellular section of CAR molecule in which a targeting domain can recognize antigens [98]. Single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is the most common targeting domain of CARs. It is responsible of recognizing the cell surface target antigens of interest and it mediates specific cytotoxicity against cells expressing these antigens [99–101]. However, Multiple limitations that can appear as obstacles to the safety and efficacy of CAR-T products are related to their targeting domains such as scFvs [99, 102]. These limitations of scFv-based CAR-T cells including the emergence of anti-idiotypic responses against the CAR targeting domain, and scFv aggregation resulting in pre-mature and antigen-independent CAR-T exhaustion can be overcome using nanobody-based CAR-T cell therapy. In different in vitro preclinical xenograft models, and in clinical studies, VHH-based CAR-T cells exhibited target antigen-dependent cytotoxicity against various types of malignancies [102].
Facilitating CAR-T cells tumor infiltration
Before antigen recognition, CAR-T cells need to successfully access the tumor site. CAR-T cells migration depends on chemokines secreted by tumor cells and chemokine receptors (CCRs) expressed by effector T-cells. Therefore, optimizing CAR-T cell therapy expressing appropriate CCRs that are capable of binding to specific chemokines secreted by tumors would promote their infiltration into the tumor microenvironment. Along this line, it has been shown that T-cells engineered with the chemokine receptor CXCR2, binding to the ligand CXCL1 on melanoma cells, had an effective trafficking effect to the tumor site [103]. Accordingly, in malignant pleural mesothelioma and neuroblastoma, tumor infiltration was improved through CCR2b-expression in mesothelin- and GD2-targeting CAR-T cells, respectively [104]. Several studies demonstrated the involvement of IL-8 (CCL8) as a pro-inflammatory chemokine promoting angiogenesis and tumorigenesis in many cancer types including prostate [105], ovarian [106], breast [107] melanoma [108] and colon [109]. Thus, researchers have generated a CAR-T cell strategy capable of expressing IL-8 receptors (CXCR1 or CXCR2) thereby enhancing their capacity of infiltrating solid tumors, consequently exerting an anti-tumor effect. Data of this research conducted on solid tumors in mouse models showed increased CAR-T cell tumor infiltration and persistence, with significant tumor toxicity [110, 111]. In a preclinical study, CX3CR1-expressing CAR-T cells showed significantly enhanced trafficking of CX3CL1-producing tumor cells accompanied with cancer cell regression [112]. In another preclinical study, Lo et al. have engineered CAR-T cells expressing macrophage colony-stimulating factor- 1 receptor (CSF-1R) binding to CSF1, a monocyte-recruiting chemokine synthetized by tumor cells, thereby enhancing CAR-T cells infiltration [113].
Another strategy which has recently been evaluated is the design of CD39- expressing CAR-T cells with triple shRNA knockdown of mucin domain-3 (TIM-3), lymphocyte-activation gene and PD-1, T-cell immunoglobulin domain-3 (LAG-3) to enhance their infiltration to the tumor site. CD39 is an extracellular ATP hydrolase enzyme expressed by CD8+ T cells; its expression is necessary for CAR-T cells cytotoxicity [114]. This evaluation showed that CD39 + -CAR-T cells had an enhanced antitumor effect in HCC organoids and PDX thereby improving migration to the tumor. Moreover, local application of CAR-T cells, such as intraperitoneal and intra-tumoral injection, would likely increase their accumulation at the tumor site. Local application via the peritoneal and pleural cavities has also been effective in ovarian cancer and malignant pleural mesothelioma [115]. Recently, Hongjun et al. have implemented a transdermal porous microneedle patch allowing the intra-tumoral penetration of CAR-T cells and enhancing their infiltration, as compared to direct intra-tumoral injection in solid tumor [116]. Moreover, local CAR-T cell administration prevented adverse effects associated with on-target, off-tumor responses, and lowered occurrence of Cytokine Release Syndrome (CRS) [117]. However, this approach is thus far limited by its high technical complexity and optimal delivery approaches necessary for patients with solid tumors that are unattainable to local delivery, such as brain and bone tumors [118].
Among the obstacles that circumvent CAR-T cells infiltration to the tumor site is abnormal vascularization which serves as an oxygen and nutrition source for tumors and also as a principal support for the circulation of tumors to other organs [97, 119]. To overcome the poor vascularization, recent studies have been targeting the vascular stroma instead of directly targeting cancer cells using anti-angiogenic molecules which are present in many types of cancers. Examples include vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR-2) in metastatic melanoma and other solid tumors [120, 121], VEGFR-1 in lung cancer [122], αvβ3 integrin in metastatic melanoma [123], αvβ6 integrin in cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) [124], ovarian, breast and pancreatic cancer [125]. An example of this is VEGFR-2-specific CAR-T generated against VEGFR2+ cells in the tumor vasculature [121]. The trial was effective in improving CAR-T cells infiltration and decreasing the growth of several vascularized syngeneic tumors of various sources [121]. A study conducted by Wang et al. showed that VEGFR-1 CAR-T cells can inhibit the resistance to traditional therapies targeting angiogenesis and provide CAR-T cells with tumor-killing ability [122]. Notably, the expression of integrin αvβ3 on activated endothelial cells and neo-vessels, but not on normal tissues, makes it an ideal target against many solid tumors [126]. In preclinical models, Wallstabe et al. demonstrated inhibition of tumor growth using αvβ3+ CAR-T cells [123].. The study also showed that results were improved when αvβ3+ CAR-T cells were combined with anti-avb3 mAbs [123].
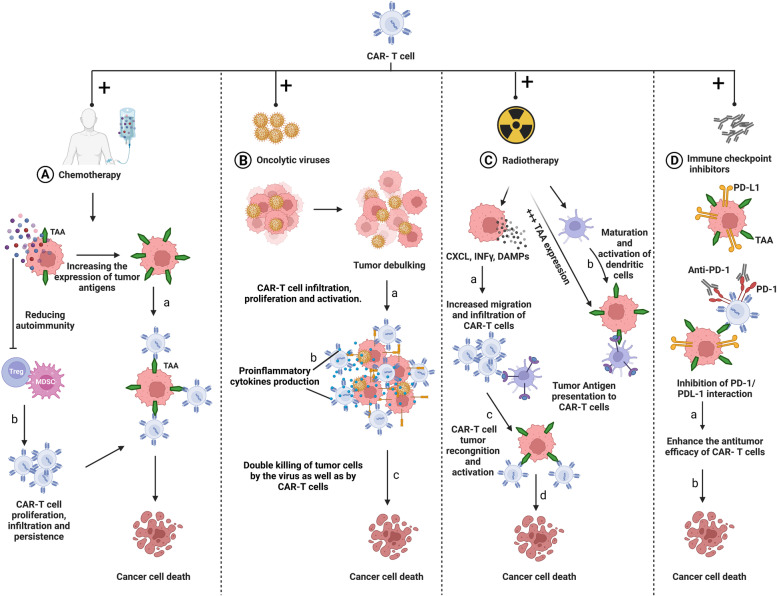
Another potential approach besides recognizing stromal cell-associated antigens, is to enhance migration and infiltration capacity of CAR cells via disrupting physical barriers in solid tumors by designing CAR-T cells secreting matrix-degrading enzymes. Studies have shown that targeting CAR-T cells to fibroblast activation protein (FAP) can remove stromal cells, and engineering CAR-T cells secreting Heparinase enzyme (HPSE) can degrade the tumor matrix thereby overcoming tissue barriers [127–129]. Interestingly, scientists have discovered and are exploring ways to overcome the obstacle that solid tumors shield themselves in a “sugar coat”; sugars (glycans) on the surface of cells that renders themselves resistant to CAR-T cell attack. This has led to designing a molecular “torpedo” that can break the sugar shield thereby clearing a path for CAR-T cells to invade and destroy solid cancers [130]. The improvement of redirecting CAR-T cells to tumor cells is also achieved by modifying the design of CARs, e.g., Hinge domain, transmembrane domain and co-stimulatory signaling [131, 132]. Alternative non-LV or RV transduction and in vivo delivery of CARs [133]. Another strategy to increase CAR-T cell infiltration and counteract the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) is to combine CAR-T cell therapy with other therapies like immune-checkpoint blockade. This combinatorial concept is detailed in subchapter 4 of this review.
Overcoming the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment
Another challenge facing CAR-T cells in solid tumors, is the immunosuppressive TME. Indeed, once they reach the tumor, CAR-T cells must overcome a complex microenvironment structure with altered extracellular matrices (ECM), variable interstitial fluid pressure, hypoxic regions [134], immunosuppressive cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs), myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), and tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) for example [97]. Therefore, targeting immunosuppressive cells in the TME may improve efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy. Overcoming the immunosuppressive TME by developing armored CAR-T cells secreting immunostimulatory cytokines such as IL-12, IL-18, or IL-15, for example, modulates an immunomodulatory microenvironment leading to better CAR-T cell survival and to the recruitment of endogenous immune cells such as stem cells-like T-memory cells and central-memory T cells better fit for in vivo proliferation, survival, and persistence and to the recruitment of NK cells [135, 136]. Indeed, introduction of IL-12-secreting CAR-T cells resulted in increased anti-tumor immune response, especially by reducing CAR-T cell sensitivity to Treg inhibition [137] and also by reducing Tregs levels in the TME [138]. Similarly, IL-18- secreting CAR-T cells induced efficient antitumor immune responses by increasing the level of NK cells and M1 proinflammatory macrophages and by reducing CD103+ suppressive dendritic cells (DCs), and M2 anti-inflammatory macrophages density in the TME [139, 140].
Tregs are a main orchestrator of immune suppression in the TME through production of TGF-β (transforming growth factor-beta), which dampens the efficiency of immune effectors [141]. Therefore, different strategies have been conceived in deleting or inhibiting TGF-β receptor on the surface of CAR-T cells. Among others, CAR-T TGF-β dominant negative receptors (DNRs). In addition, swing receptors with chimeric signaling domains can convert TGF-β signals through engagement of the receptor modified to signal through co-stimulatory domains such as 4-1BB- or IL-12 stimulatory signals. Similarly, cytokine receptors containing the extracellular domain of the IL-4 receptor fused with the endo-domain of the IL-7 receptor turn swing suppressive into activating messages [142, 143]. Another strategy used recently is CRISPR gene editing technology to precisely insert the CAR in the genome of T cells [144]. To enhance CAR-T cells efficacy, CRISPER/Cas9 approach was used to knock out the endogenous TGF-β receptor-II (TGFBR2) gene in CAR-T cells, consequently inhibiting the effect of TGF-ꞵ and thereby reducing Treg cell induction and preventing CAR T cell depletion [145]. CRISPR can also be used to knock out the expression of PD-1 on the surface of CAR-T cells which can enhance their tumor-killing activity against PD-L1-expressing cancer cells, and prevent cancer relapse [146].
MDSCs can suppress the immune T cell response by various mechanisms such as impediment of disintegrin and the metalloproteinase- 17 (ADAM17) responsible for L-selectin-ectodomain cleavage, release of Nitric oxide (NO) and reactive oxygen species (ROS) [147, 148]. Hence, several strategies have been suggested to overcome the suppression of CAR-T cells by MDSCs. One of them is by decreasing the effects of ROS with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) [149]. Several combination therapies which address this obstacle will be described in subchapter 4.
Despite the important role of macrophages in the immune response against foreign pathogens, macrophages polarized towards an M2 phenotype play an anti-inflammatory and pro-tumor cell in the TME. Macrophages facilitate tumor progression and metastasis by promoting tumor cell invasion, angiogenesis, and immunosuppression [150, 151]. Several preclinical studies have targeted M2 macrophages with engineered CAR-T cells which can specifically deplete them. For example, folate receptor beta (FRβ)-specific CAR-T cells cause depletion of FRβ positive M2 cells in colon adenocarcinoma and melanoma [152]. A recent study conducted by Sanchez-Paulete and colleagues on a mouse orthotopic lung tumor model, showed that targeting the macrophage marker (F4/80) with F4-CAR-T cells delayed solid tumor progression, thereby enhancing anti-tumor immunity comparably to PD-1 blockade and prolonged animal survival [153]. The antitumor effect was also demonstrated in mouse models of pancreatic and ovarian cancer [153]. Additionally, repolarizing M2 into the proinflammatory M1 phenotype is a good strategy in order to reduce M2 macrophages and increase the antitumor M1 phenotype in the TME [154, 155].
Overcoming CAR-T cells’ toxicities
The cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is a common life-threatening inflammatory syndrome generated by overactivation of the immune response associated with CAR-T cell therapy. Cytokines, including interferon-γ (IFN-γ), IL-1, IL-6 and -10 have been associated with CAR-T cells-related CRS [156, 157]. To prevent CRS, many strategies have been developed including the administration of Anakinra, an IL-1 receptor (IL-1R) antagonist that demonstrated some effectiveness in treating CRS [158]. CAR-T cells secreting IL-1R antagonist have been constructed and suggested prevention of CRS-related mortality [159]. Also, IL-6 blockade by blocking IL-6R signals can decrease iNOS positive macrophage number and prevent CRS [160]. In addition, neutralizing granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), an important monocyte activator, could be an alternative approach for managing CRS as well as neurotoxicity [161]. An innovative study has shown that the release of cytokines and catecholamines, resulting from the interaction of CAR-T cells with the tumor, can be inhibited by catecholamine blockade with Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) [162].
Multiple other types of toxicity can occur in association with CAR-T cell treatment of solid tumors as well as hematological malignancies including on-target/off-tumor toxicity, neurological toxicity, anaphylaxis and graft versus host disease are also managed with different innovative strategies [163, 164]. Furthermore, the improvement of CARs, including controls of their activity and survival in vivo is considered as control of toxicities [165, 166].
In conclusion, the heterogeneous tumor antigen expression, lack of specific tumor antigen, limited tumor infiltration, and the immunosuppressive TME are the main challenges that impede the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy in solid tumors. Further studies are required to improve CAR-T cell efficacy and toxicity by extending their persistence, facilitating their trafficking, and improving their infiltration to the tumor site. Furthermore, combination therapy with chemotherapy, radiotherapy and/or with other immunotherapies may improve CAR-T cell therapy in the future.
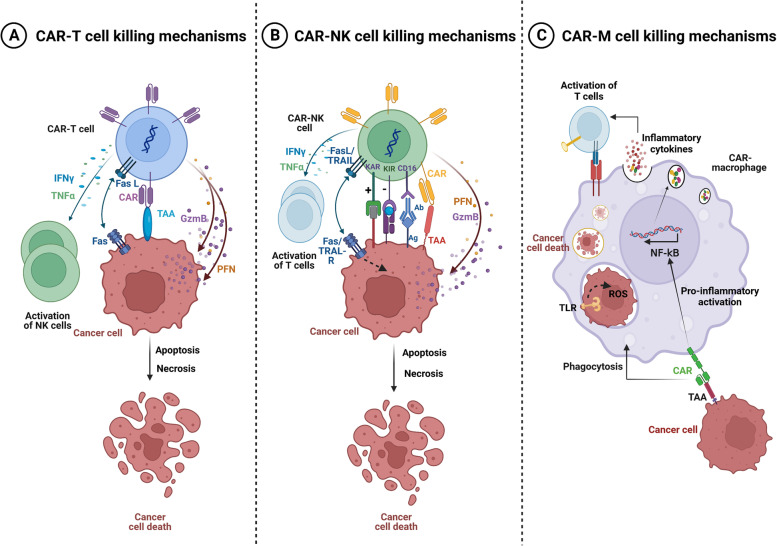
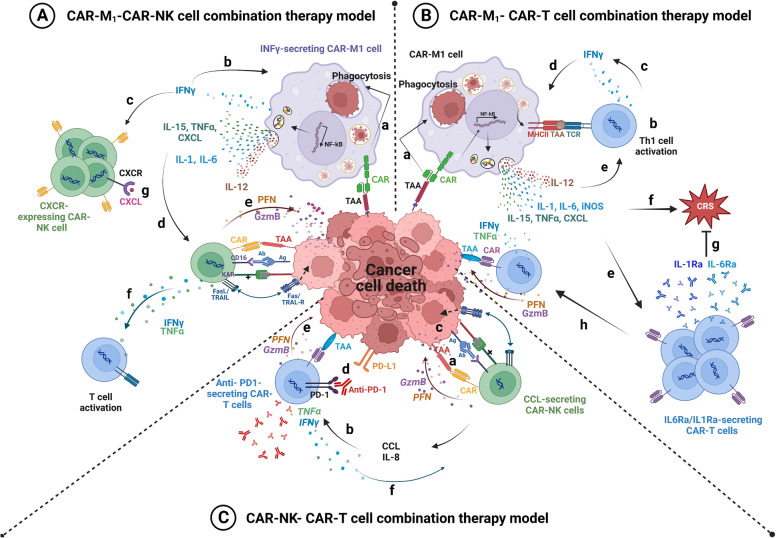
CAR-NK cell therapy in solid tumors: applications, challenges and recent advances
Taking into consideration the shortcomings of CAR-T cells, there is a need to investigate other immune cells for CAR therapy, with increased attention on NK cells due to their immunological properties and their multiple sources [167]. Several advantages make NK cells an attractive alternative to CAR-T cells (Table 2).
Advantages related to CAR-NK cell generation and manufacturing
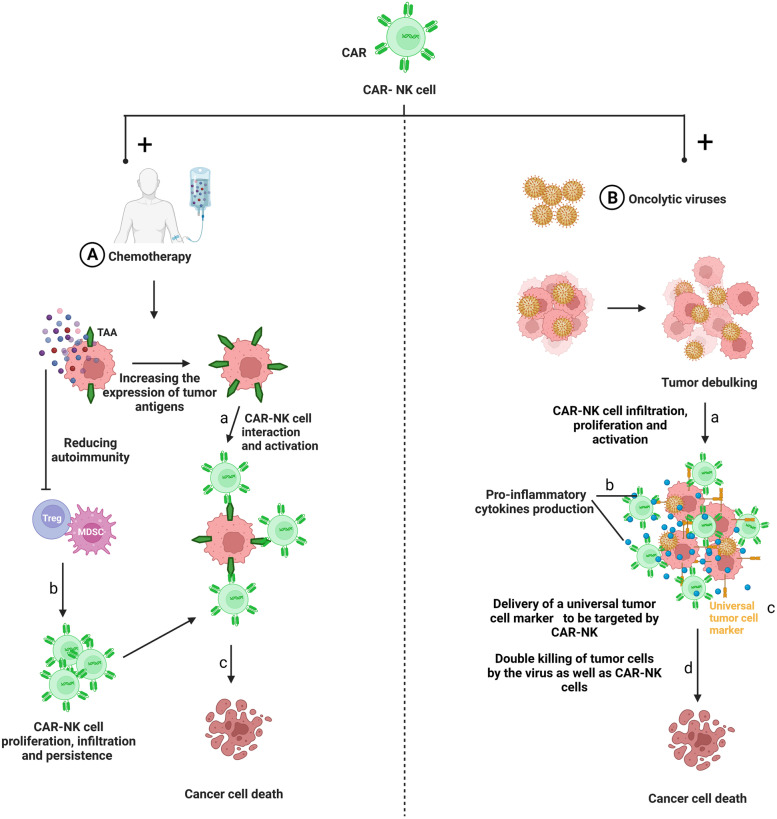
For cancer immunotherapy, patient-derived NK cells function is usually hampered by curative treatments [168]. In fact, during tumor progression, the TME components can reduce NK cell capacity for proliferation, as well as ability of degranulation or cytokines secretion (such as TNF-α and IFN-γ) or expression of activating receptors [169]. Therefore, allogeneic NK cells are usually the first choice for cellular immunotherapy. Furthermore, while T cells are isolated from peripheral blood, either from the patient (autologous) or from a healthy donor (allogeneic), several sources have been used to generate allogeneic CAR-NK cells including peripheral blood (PB) from healthy donors, umbilical cord blood (UCB), induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) or commercially available NK cell lines (NK92) [170]. Hence, “off-the-shelf” CAR-NK cells can be manufactured and infused to patients on-demand [171]. In addition, at least in theory, this type of production could reduce manufacturing costs and overcome the limited availability of autologous products in some malignancies, particularly in heavily pre-treated patients [172].
At least 90% of peripheral blood NK cells (PB-NK) are CD56dimCD16bright, representing a mature population with high cytotoxic potential [173, 174]. However, relatively few cells can be isolated from PB donors (around 10%) [175]. On the contrary, a high number of NK cells can be generated from umbilical cord blood (UCB) [176]. In addition, human-Embryonic Stem Cells (hESCs) and induced-Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)-derived NK can be generated in high quantity for immunotherapy use [177–179]. Consequently, the NK-92 cell line, isolated from a non-Hodgkin lymphoma patient, may be a potential source for limitless CAR-NK cells with high anti-tumor activity and direct cytotoxicity [180]. However, as NK92 cell lines are cytogenetically abnormal, they require irradiation prior to infusion with patients [181]. All these sources allow large-scale CAR-NK cell production to support multi-dose therapeutic infusion and on-demand cell product availability.
Clinical application of CAR-NK cell therapy in solid tumors
NK cells possess advantageous characteristics, including non-MHC-restricted recognition, ability to infiltrate tumor tissues, cytolytic ability, minimal side effects (e.g., CRS, Graft versus host disease (GvHD) and Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS). Therefore, CAR-NK cells can be considered an encouraging therapeutic option for the treatment of solid tumors. To date, only a few clinical studies evaluated NK92, PB-NK and UCB-NK based CAR-NK cell products with increasing interest in some commonly tumor targeted antigens such as Roundabout homolog 1 (ROBO1), NK cells activating receptor (NKG2D), MSLN, HER2 and MUC1 are registered in ClinicalTrials.gov and summarized in Table 3.
Table 3.
Clinical trials of CAR-NK cell therapy in solid tumors (ClinicalTrials.gov)
| CAR-NK Product | Clinical trial identifier | Targeted antigen | Disease | Cell source | Clinical trial phase | Status | Estimated enrollment (EE)/ Treated patients (TP) | Study objectives |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROBO1 CAR-NK cells | NCT03940820 | ROBO1 | Solid tumor | Human primary NK cells |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Unknown | 20 | Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness ROBO1 CAR-NK cells to treat solid tumors. |
| MUC1 CAR-NK cells | NCT02839954 | MUC1 | MUC1 positive relapsed or refractory solid tumor | Human primary NK cells |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Unknown |
10 (EE) 8 (TP) |
Evaluation of the safety and effectiveness of CAR-pNK cell immunotherapy in patients with MUC1 positive relapsed or refractory solid tumor. |
| BiCAR-NK cells ROBO1 CAR-NK cells | NCT03941457 | ROBO1 | Pancreatic cancer | NK92 cell line |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Unknown | 9 (EE) | Evaluation of the effect of ROBO1-specific BiCAR-NK cells on patients with pancreatic cancer. |
| Claudin6 CAR-NK cells | NCT05410717 | Claudin6 |
Stage IV ovarian cancer Testis cancer Refractory endometrial cancer |
Human primary NK cells |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Recruiting | 40 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and preliminary efficacy of CLDN6-CAR-NK in patients with CLDN6-positive advanced solid tumors. |
| NKG2D-CAR-NK92 cells | NCT05528341 | NKG2D | Relapsed/refractory solid tumors | NK92 cell line | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 20 (EE) | Clinical investigation of NKG2D-CAR-NK92 cells in the treatment of relapsed/refractory solid tumors. |
| NKG2DL CAR-NK cells | NCT03415100 | NKG2D | Metastatic solid tumors | Autologous or allogeneic NK cells | Phase 1 | Unknown |
30 (EE) 3 (TP) |
Study of NKG2D-Ligand CAR-NK cells in patients with metastatic solid tumors. |
| 5 T4 CAR-NK | NCT05194709 | Advanced solid tumors | N/A | Early Phase 1 | Recruiting | 40 (EE) | Study of Anti-5 T4 oncofetal trophoblast glycoprotein (5 T4) conjugated antibody redirecting CAR-NK cells in advanced solid tumors. | |
| 5 T4 CAR-NK Cells | NCT05137275 | 5 T4 | Locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors | N/A | Early Phase 1 | Recruiting | 56 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety, tolerability, and efficacy of Anti-5 T4 CAR-raNK cell therapy in locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors. |
| Mesothelin CAR NK Cells | NCT03692637 | Mesothelin | Epithelial ovarian cancer | Human primary NK cells | Early Phase 1 | Unknown | 30 (EE) | Investigation of the safety and efficacy of anti-Mesothelin CAR-NK cells with epithelial ovarian cancer. |
| PSMA CAR NK Cell | NCT03692663 | PSMA | Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer | Human primary NK cells | Early Phase 1 | Recruiting | 9 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety, tolerability, and preliminary efficacy of TABP EIC in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. |
| HER2-CAR-NK | NCT03383978 | HER2 | Glioblastoma | NK92 cell line | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 42 (EE) | Study of intracranial injection of NK-92/5.28.z cells in combination with intravenous ezabenlimab in patients with recurrent HER2-positive glioblastoma. |
| CCCR-NK92 | NCT03656705 | Non-small cell lung carcinoma | NK-92 cell line | Phase 1 | Enrolling by invitation | 5 (EE) | Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of CCCR-modified NK92 infusions in previously treated advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). | |
| MUC1 CAR-pNK cells | NCT02839954 | MUC1 |
Hepatocellular carcinoma Non-small cell lung cancer Pancreatic carcinoma Triple-negative invasive breast carcinoma Malignant glioma of the brain Colorectal carcinoma Gastric carcinoma |
NK92 cell line |
Phase 1 Phase 2 |
Unknown | 10 (EE) | Evaluate the safety and efficacy of CAR-pNK cell immunotherapy in patients with MUC1 positive relapsed or refractory solid tumor. |
| MICA/B CAR-NK cells | NCT05395052 | MICA/B |
Non-Small cell lung cancer Colorectal cancer Breast cancer Ovarian cancer Pancreatic cancer Head and neck cancer Gastroesophageal cancer |
Allogeneic natural killer | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 322 (EE) | Study of FT536 as monotherapy and in combination with monoclonal antibodies in subjects with advanced solid tumors. |
Human primary NK cells have been tested in numerous clinical trials producing CAR-NK against specific tumor antigens, including ROBO1 for targeting several solid tumors (NCT03940820), PSMA for prostate cancer (NCT03692663), MSLN for epithelial ovarian cancer (NCT03692637) and Claudin6-for ovarian, testis cancer and refractory endometrial cancer (NCT05410717). Various clinical trials investigating CAR-NK92 cell therapy: HER2 CAR-NK targeted Glioblastoma (NCT03383978), and chimeric costimulatory converting receptor (CCCR) CAR-NK against non-small cell lung cancer (NCT03656705). MUC-1 specific CAR-NK cells are conceived for multiple relapsed or refractory solid tumors treatment (NCT02839954). In this study, of the 8 evaluable patients, seven achieved stable disease without serious adverse events [7]. Another study was performed to evaluate the clinical potential of a combination therapy using anti-ROBO1-specific biCAR-NK-92 in a patient with pancreatic cancer (NCT03941457). Another phase-I clinical trial (NCT05528341) investigated the effect of NKG2D CAR-NK92 cells for the treatment of relapsed/refractory solid tumors. Currently, a phase-I clinical trial (NCT03415100) was conducted recruiting patients with metastatic solid tumors to evaluate the safety of allogeneic or autologous NKG2DL-targeting CAR-NK cells transfected by mRNA electroporation [182]. Two early phase-I clinical trials (NCT05137275 and NCT05194709) targeting the 5 T4 oncofetal antigen in locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors by CAR-NK cells are currently recruiting patients.
On January 2022 the FDA allowed an investigational application for FT536 (by Fate Therapeutics) (NCT05395052), a CAR-NK cell therapy designed to treat patients with advanced solid tumors. FT536 is an allogeneic, multiplexed-engineered induced pluripotent stem cell-derived NK cell therapy genetically modified to targets the alpha-3 domain of the MHC class-I-related proteins-A (MICA) and -B (MICB). In addition, Benjamin H. et al. have recently described iPSC-NK cells as a promising alternative to T- cells for cellular therapy [183]. The promising conclusion was based on their proven safety profile, ability to be used as an allogeneic treatment and to be produced in large numbers to make an “off-the-shelf” therapy for the treatment of solid malignancies [183].
Advantages related to mechanisms of CAR-NK cell recognition and killing of cancer cells
Human NK cells are innate cytotoxic immune cells that have been characterized by their “natural” ability to exert immune response to non-self-cells [184, 185]. NK cells use similar mechanisms to cytotoxic T-lymphocytes (CTLs) to kill cancer cells, but their target recognition mechanism is different [186, 187]. In fact, NK cells recognize malignant cells via multiple signals arising from different cell surface receptors, including activating and inhibitory killer cell Immunoglobulin-like receptors (KARs and KIRs) [188]. NK cells’ KIRs allows them to identify “self” [188], with this self-identification they can inhibit the cytotoxic activity against normal cells and prevent NK cell-derived “on-target, off-tumor” toxicity [189–191]. Moreover, while CAR-T cells only kill cells that have specific target antigens [192], CAR-NK cells exhibit intrinsic cytolytic activity, thus they would kill even cancer cells that do not express the target antigen [186] (Fig. 1A and B). In fact, CAR-NK cells still exert NK natural cytotoxic activity against tumor cells by the release of granzyme and perforin, for example, and can be activated via CAR-independent mechanisms, like natural cytotoxicity receptors (NCRs); NKp46, NKp44, and NKp30, NKG2D, co-stimulatory receptor; DNAX accessory molecule (DNAM-1), and specific activating KIRs (KIR2DS1, KIR2DS4 and KIR2DL4) [193, 194] which induce caspase-mediated apoptosis of targeted cancer cells. Moreover, NK cells can eradicate tumor cells by CD16-mediated Antibody-Dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC) [195]. Thus, CAR-NK cells would be able to efficiently eliminate tumors via both CAR-dependent and NK cells receptor-dependent mechanisms (Fig. 1B).
Fig. 1.
Killing mechanisms of CAR-T, CAR-NK, and CAR-M cells. A Tumor killing mechanisms of CAR-T cells. Activated CAR-T cells can specifically recognize the tumor associated antigen (TAA). Cytotoxic activity of Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T cells is mediated by perforin (PFN) and granzyme (GzmB) granules secretion, and by activation of death receptor pathways such as Fas/Fas-L leading to cancer cells apoptosis and necrosis. Activated CAR-T cells also secrete Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα) which can promote Natural Killer (NK) cell anti-tumor cytotoxic activity. B Tumor killing mechanisms of CAR-NK cells. The activity of CAR-NK cells is regulated by the signal of activating (KAR) and inhibitory receptors (KIR) expressed on NK cells. Activated CAR-NK cells secrete the cytotoxic proteins perforin and granzyme B which synergize to induce cancer cell necrosis and apoptosis. NK cells also express the death ligands FasL and TRAIL which will bind to Fas and TRAIL-R on cancer cells and induce apoptosis. Moreover, CAR-NK cells trigger ADCC through the CD16 Fc receptor which recognize antibody-opsonized cancer cells. In addition, CAR-NK cells secrete IFN-γ and TNFα which promote their activation and stimulate other T-lymphocytes leading to increased anti-tumor immune response. NK: cell-Natural killer cells; IFN-γ: Interferon-gamma; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha; TRAIL-R: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand, KIR: Killer Inhibitory Receptors, KAR: Killer Activation Receptor, ADCC: Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, (PFN) perforin and (GzmB) granzyme. C Tumor killing mechanisms of CAR-M. The binding of a specific tumor associated antigen (TAA) with CAR receptor on the surface of CAR-M generates activation signals that mediate tumor phagocytosis, activation of transcription factors such as NF-kB and subsequent release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, which in turn can activate T cell-mediated immunity against the tumor
CAR-NK cells can recognize and kill tumor cells that don’t express MHC molecules [196] while reducing the risk of life-threatening GvHD and enabling allogeneic CAR-NK cell transplantations. Interestingly, unlike CAR-T cells, CAR-NK cells do not seem to cause severe toxicities such as CRS and ICANS [31]. This is partly due to a differential cytokine secretion profile, for example, activated NK cells usually produce IFN-γ and GM-CSF [197] whereas CAR-T cells predominantly produce IL-1, IL-6, Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) or Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1), all which are associated with CRS and severe neurotoxicity [198]. Consequently, CAR-NK cells could be safer for clinical applications, compared to CAR-T cell products and toxicity.
Limitations associated with CAR-NK cells and strategies to increase their effectiveness
Similar to CAR-T cells, CAR-NK cells face various obstacles in solid tumors such as migration to tumor site, persistence into the immunosuppressive TME and transduction [199]. Preclinical research is currently ongoing to optimize CAR-NK product in order to enhance their efficacy (see Table 2).
Generation of NK cell-specific CAR constructs to improve cytotoxic anti-tumor effects
In order to increase CAR-NK cells anti-tumor efficacy, several studies proposed to enrich CARs with certain domains associated with NK cell signaling such as NK-specific 2B4 and DNAX-activation proteins-10 or − 12 (DAP-10 or DAP-12) as co-stimulatory domains. This specific-NK cells construct showed greater cytotoxic effect and increased IFN-γ secretion compared to CAR-T cells constructs [200]. Armored CAR-NK with NKG2D receptor and costimulatory receptor 2B4 showed an increased cytotoxic effect in a xenograft ovarian mouse model expressing MSLN [201]. The result of this study was that MSLN-specific NKG2D.2B4.CD3ζ.CAR-NK cells induced higher tumor eradication and greater survival rate compared to the MSLN-specific CAR-T cells [201]. Furthermore, PSCA-specific CAR-NK cells equipped with DAP12, exerted higher anti-tumor activity compared to CD3ζ- CAR-NK cells in PSCA-positive tumor xenografts in immunodeficient mice [202].
NK cells specific CAR construct to improve in vivo survival and persistence within the TME
Another important challenge in CAR-NK generation is to extend their persistence in the peripheral blood and tissue. To achieve this goal, NK cells CAR construct can be armored with stimulatory cytokine-transgenes secreting for example IL-21, IL-15, IL-7 and IL-2 which promote NK cell proliferation and survival [203]. In order to preserve NK cells in vivo expansion after infusion, several feeders have been used such as autologous PBMCs, EBV-transformed lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCLs), and several NK cell-sensitive cell lines including K562 or 721.22 1[204, 205]. To overcome the immunosuppressive TME, chimeric co-stimulatory converting receptor (CCCR)-NK cells inhibited lung cancer growth in xenograft mouse models by switching the immunosuppressive negative PD-1 signal to an activating one [206].
Genetically engineered NK cells to improve trafficking to the tumor site
Müller and colleagues have shown that NK cells genetically engineered with EGFRvIII-specific CAR and a chemokine receptor CXCR4 have increased ability to infiltrate into the tumor site which can improve immunotherapy of solid tumors [207]. Another study investigated the transfection of NK cells with chemokine receptor CXCR1-mRNA construct and a CAR-mRNA construct against tumor-associated NKG2D ligands. The CXCR1-engineered NK cells showed enhanced in vitro migration toward tumor supernatants and increased in vivo infiltration into human tumors in subcutaneous and intraperitoneal xenograft models [208]. One of the major factors in the regulation of lymphocyte chemotaxis is CXCR3 expressed on activated NK cells inducing their migration toward chemokine ligands; CXCL9, − 10 and − 11. Therefore, CXCR3 receptor construct added to NK activating signaling domains may enhance the chemotaxis of NK cells to chemokine-secreting tumors and consequently improve their migration to the tumor site [209]. The engineering of NK- with CD19-CAR plus CXCR4 demonstrated in a pre-clinical model, the implementation of the migration of NK cells to bone marrow [210]. These findings suggest that the tumor infiltration can be improved in CAR-NK cell therapy and better clinical outcome can be expected.
New viral transduction enhancers for treatment of NK-cell-mediated CAR therapy
NK cells products are considered “hard-to-engineer” in comparison with T cells. To ameliorate NK cells transduction efficiency, lentiviral transductions have been significantly improved by incorporating new transduction enhancers which would help viral entry such as polybrene, (a cationic polymer frequently used to mediate viral entry into cell membranes) [211]. Retronectin has been described as a truncated version of fibronectin, which can colocalize cell’s surface with the virus [212] and vectofusin-1, a short cationic peptide which can considerably enhance the NK-cells viral transduction [213]. All of them may help CAR-NK engineering using viral transduction.
Electroporation and transposons for non-viral transduction of NK-cell mediated CAR therapy
Electroporation is a non-viral method to genetically engineer NK cells which promises 80 to 90% efficiency for mRNA-based plasmids but low efficiency for DNA electroporation [182, 214]. To introduce CAR constructs into the genomes of NK cells and ensure prolonged transgene expression, DNA transposons are most commonly used. These systems are composed of sleeping beauty (SB) subsets and the PiggyBac (PB) [201]. For instance, the generation of transposon-engineered CAR-NK cells, was found to be effective to achieve stable expression without viral integration in addition to other advantages including capacity for large gene fragment transduction, increased biosafety, low immunogenicity and worthful cost-effectiveness [215].
CAR-M cell therapy in solid tumors: applications, challenges and recent advances
Currently, continuous investigational studies are trying to identify the ideal CAR cell type for targeting solid tumors. Macrophages have recently emerged as competitive candidates for the treatment of solid tumors due to their phagocytosis functional properties, antigen presentation and natural infiltration into the tumor microenvironment [34, 35] (Table 2).
Advantages related to various sources of human CAR-macrophages production
Similar to CAR-NK, CAR-M can be generated from different sources including peripheral blood, iPSCs and the human leukemia monocytic cell line THP-1 (Table 4). PBMC derived M1 macrophages are characterized by their important production of proinflammatory factors such as IL-8, IL-6 and TNF-α [216], and a prominent expression of inflammatory surface markers such as natriuretic peptide receptor (NPR), CD14 and CD68 [217].. iPSCs can be induced into CAR-expressing macrophages (CAR-iMacs) exerting innate immune functions, such as repolarization of M2 phenotype into pro-inflammatory M1 in an antigen-dependent way, secretion of immune-related cytokines, as well as phagocytosis and antitumor capacity [218]. In addition, THP-1 cells can generate M1 macrophage after being stimulated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and IFN-γ and are easy to culture and to differentiate into macrophages [219–222].
Table 4.
Comparison of CAR T, NK, and macrophages in solid tumors treatment
| Criteria | CAR-T | CAR-NK | CAR-M |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cell sources |
- PB (autologous/ allogeneic) - Rarely from iPSC and UCB |
- UCB - BM - hESCs - IPSCs - NK92 cell line - PB |
- UCB - BM - hESCs - IPSCs - HPSCs - THP1 cell line - PB |
| Availability |
- Autologous - MHC-matched allogeneic CAR-T cells - Unlikely “Off-the-shelf” product |
- Autologous - Off-the-shelf CAR-NK product |
- Autologous - Off-the-shelf CAR-M product |
| In vivo safety and persistence |
- Long-term persistence, - On-target/off-tumor toxicity - GVHD, CRS and Neurotoxicity |
- Limited lifespan - Reduced on-target/off-tumor toxicity - GVHD, no CRS nor Neurotoxicity. |
- Limited time in circulation - Less On-target/off-tumor toxicity - No GVHD - CRS and Neurotoxicity |
| FDA-regulated CAR-cell products |
- P-MUC1C-ALLO1 CAR-T cells (NCT05239143) - GD2 CAR T cells (NCT04196413) - GD2 CAR T cells (NCT00085930) - ROR1 CAR-T cells (LYL797) (NCT05274451) - ROR1 CAR-T cells (NCT02706392) - HER2 CAR-T cells (NCT03740256) - B7-H3 CAR-T cells (NCT04897321) - B7-H3 CAR-T cells (NCT04483778) - PSCA CAR-T cells (BPX-601) (NCT02744287) - PSCA CAR-T cells (NCT02744287) |
- MICA/B CAR-NK cells (FT536) (NCT05395052) | - HER2 CAR-Macrophage (CT-0508) (NCT04660929) |
Taken together, unlike CAR-T cells, CAR-M can be generated using several reliable sources. As an additional advantage, CAR-M bear a low risk of GvHD. Therefore, CAR-M approach might be an attractive allogeneic cell immunotherapy for solid tumors (Table 4).
Clinical applications of CAR-macrophages for the treatment of solid tumors
To date, a few clinical trials of CAR-M are conducted and registered on clinicaltrials.gov (Table 5) and only one clinical trial of CAR-M has received the FDA approval. The first Phase I clinical trial (NCT04660929) CT-0508, a drug candidate from CARISMA Therapeutics, engineered with chimeric adenoviral vector Ad5f35 to target HER2 in solid tumors. In this study conducted by Klichinsky et al., the use of adenoviral infection induced macrophages differentiation into a pro-inflammatory M1 phenotype [223]. A phase-I clinical trial (NCT05007379) using HER2 CAR-M, is designed against organoids from breast cancer patients at different clinical stages. Another phase I clinical trial (NCT04405778) targeted Glypican 3 (GPC3), a protein expressed by some solid tumors but not expressed by normal cells, making it an ideal target for solid tumors. In this study, TAK-102, a GPC3 CAR-M, was tested in GPC3 positive solid tumors patients. Additionally, TAK-103, a MSLN specific CAR-M was also clinically tested (NCT05164666) in patients with MSLN-expressing advanced or metastatic solid tumors.
Table 5.
Clinical trials of CAR-Macrophages cell therapy in solid tumors (ClinicalTrials.gov)
| CAR-M Product | Clinical trial identifier | Targeted antigen | Disease | Cell source | Clinical trial phase | Status | Estimated enrollment (EE) | Study objectives |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HER2 CAR- macrophages | NCT04660929 | HER2 | HER2 overexpressing solid tumors |
Autologous macrophages (CT-0508) |
Phase 1 | Recruiting | 48 | Study of anti-HER2 CAR- macrophages in subjects with HER2 overexpressing solid tumors. |
| HER2 CAR-macrophages | NCT05007379 | HER2 | Breast cancer | N/A | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 100 | Collection of tumor samples to develop patients’ derived organoids to test the antitumor activity of newly developed CAR-macrophages. |
| Glypican 3 (GPC3) CAR-macrophages | NCT04405778 | GPC3 | Solid tumors | N/A | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 18 | Study of TAK-102 in adult patients with GPC3-expressing previously treated solid tumors. |
| Mesothelin CAR-macrophages | NCT05164666 | Mesothelin | Advanced or metastatic solid tumors | Autologous white blood cells | Phase 1 | Recruiting | 21 | Study of TAK-103 in adult patients with mesothelin-expressing advanced or metastatic solid tumors. |
Advantages related to the biological properties of macrophages
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) often undergo activation into M1 (classical-activated macrophages) or M2 (alternative-activated macrophages) phenotype [224]. In terms of solid tumor therapies, M1 macrophages are involved in killing tumor cells by phagocytosis, reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/iNOS) release following the activation of Toll-Like Receptors (TLRs) [225] (Fig. 1C). In addition, M1 macrophages can release the pro-inflammatory IL-12 which initiates NK cells killing activity and stimulates both Th1 and tumor-specific CD8+ cytotoxic T cells responses [216, 217]. Furthermore, M1 macrophages can act as tumor antigen presenting cells inducing adaptive antitumor immune response [226]. Therefore, they are considered as anti-tumor or “good” macrophages [227] while M2 are considered as pro-tumor or “bad” macrophages [228]. For this reason, converting M2 TAMs into M1 macrophages is a promising immunotherapeutic approach for solid tumors [114]. Interestingly, CAR-M possess unique advantages over CAR-T and CAR-NK cells with regards to two major obstacles observed in solid tumors: ability to migrate and infiltrate into the immunosuppressive TME. In fact, in contrast to T cells poor infiltration, macrophages represent the predominant population of immune cells in the TME (reaching 50%) of various types of cancer such as melanoma, renal, and colorectal cancer [229]. In contrary to lymphocyte-based therapies, macrophages are able to remodel the extracellular matrix (ECM) [230]. Moreover, macrophages are an important source of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) which degrade almost all ECM [33]. Taken together, CAR-M uses unique macrophage properties, especially phagocytosis which gives them a particular value over CAR-T and CAR-NK cell therapies. Consequently, CAR-M would have a significant potential in driving anti-tumor immunity in solid tumors.
Limitations associated with CAR-M cells and strategies to optimize their use in solid tumor therapy
Several limitations are related to CAR-M bioengineering, storage, expansion, persistence at the TME, and toxicity (see Table 2).
Strategies to overcome the limitations in CAR-M bioengineering
Recent advances in gene transfection into effector cells have promoted diverse viral and non-viral engineering methods to overcome this challenge. Indeed, it has been shown that modified lentiviral virions containing Vpx; an accessory protein can efficiently deliver transgenes to myeloid cells [231]. In fact, Vpx, can mediate degradation of SAM domain and HD domain-containing protein 1 (SAMHD1); a myeloid-specific HIV-1 restriction factor that inhibits lentiviral transduction [232]. A supplementary option for macrophage transduction is the use of the chimeric Adenovirus 5-fiber 35 vector (Ad5f35) which can mediate efficient gene transfer into human macrophages [233]. In various studies, Ad5f35 showed a robust transduction of primary human macrophages [223, 234]. In addition, Ad5f35 infected macrophages activate the inflammasome and participate in maintaining the M1 phenotype generated by proinflammatory priming signals [235]. Additionally, transposon systems, mRNA transfection and bacterial plasmid DNA, have also been used as non-viral strategies for macrophages bioengineering [236–238]. Moreover, using polymer nanocarriers (mannose-conjugated polyethyleneimine (MPEI)), Kang and colleagues, were able to transfer the genes encoding CAR and IFN-γ into macrophages to enhance their anti-tumor potential [226].
Strategies to enhance the antitumor activity of CAR-M
In response to external stimuli, macrophages differentiate into antitumor proinflammatory M1. This concept prompted the first-in-human clinical trial conducted by Klichinsky et al. who demonstrated that anti-HER2 CAR-M efficiently induced phagocytosis of the HER2+ ovarian SKOV3 tumor cells, pro-inflammatory cytokines secretion, macrophages polarization from M2 to M1 phenotype and were capable of cross-presenting the New York Esophageal Squamous cell carcinoma 1 (NY-ESO-1) antigen to T cells, following NY-ESO-1+ SKOV3 tumor cells phagocytosis [223]. Moreover, Zhang et al., showed that CAR (MSLN)-iMacs can switch to the inflammatory M1 subtype and promote phagocytosis and immune activation when incubated in-vitro with MSLN-expressing ovarian (OVCAR3) and pancreatic (ASPC1), cancer cells [218]. This study also reported that CAR transgene expression was up to 85% in CAR-iMac cells [218].
Strategies to enhance trafficking and persistence of CAR-M within the immunosuppressive TME
Zhang’s CAR macrophages (CAR-147) consisting of scFv conjugated to a hinge region and CD147 transmembrane and intracellular domain to target HER2+ tumor cells effectively activated the expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) such as MMP9, MMP10 and MMP12 [239–241]. Interestingly, this special CAR-CD147 construct can destroy the tumor’s extracellular matrix without affecting the phagocytic activity and inflammatory cytokines and ROS production [239, 240]. In addition, it was found that this CAR construct reduced the tumor growth and increased the T cell infiltration [239, 240]. Moreover, Niu et al. designed CAR-M to express CCR7 nature ligand, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 19 (CCL19), in an attempt to target CCR7-expressing immunosuppressive cells [242]. The use of this CAR construct induced the of CD3+ T cells into tumors, increased pro-inflammatory cytokines production, suppressed tumor growth, decreased metastasis, and prolonged survival [242].
Overcoming CAR-M toxicity
Other hurdles faced by the CAR-M therapeutic approach are the potential to induce CRS and off target toxicity. Indeed, macrophages represent the principal source of the cytokine storms which can lead to CRS [243]. Additionally, since macrophages are distributed throughout the body, particularly in the liver [244] the use of CAR-M can lead to off target toxicity and limit efficacy. Therefore, further investigations are needed to optimize CAR-M production and ensure their safety.
Potential combination therapies to enhance CAR-cell functions
Many studies demonstrated that CAR-cell monotherapy has limited efficacy for treating solid tumors [245–247]. Therefore, innovative combinations have been tested to synergize CAR-cell therapy.
Combination with chemotherapy
When administered at low doses, chemotherapy plays an immunomodulatory role; it promotes dendritic cells activation and tumor antigen presentation to CAR-T cells, inhibits suppressive immune cells leading to increased persistence of CAR-T cells and sensitizes tumor cells to CAR-T cell activity by promoting granzyme B penetration into tumor cells [246, 248, 249] (Fig. 2A). Recently, Safarzadeh Kozani P et al. have reviewed in detail the positive effects of combining chemotherapy with CAR-T cell therapy [97]. This combination therapy can address the issue of CAR-T cells tumor trafficking to the TME resulting in more pronounced tumoricidal responses and increasing the rate of tumor rejection resulting higher survival rates [250]. Such positive effects have been attributed to the oxaliplatin-induced secretion of T cell-attractive chemokines by tumor associated macrophages resulting in improved CAR-T cell infiltration, remodeling of the tumor microenvironment, and increased tumor sensitivity to anti-PD-L1 [251].
Fig. 2.
Possible combination therapies for CAR-T cells. A Combination of CAR-T cells with chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is known to increase the expression of tumor associated antigen (TAA) on cancer cells. This effect will help in (a) enhancing CAR-T cells interaction with cancer cells. Moreover, by downregulating regulatory T cells (Treg) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), chemotherapy (b) promotes CAR-T cells proliferation, infiltration and extend their persistence in the TME. These mechanisms strongly support the use of CAR-T cells with chemotherapy for a more potent anti-tumor effect. B Combination of CAR-T cells with oncolytic viruses: Oncolytic viruses promote tumor debulking which (a) enhance CAR-T cells infiltration, proliferation, and activation (b) induce proinflammatory cytokines production, and (c) increase tumor cell death through a double mechanism: direct effect of the virus and enhanced CAR-T cells activity. C Combination of CAR-T cells with radiotherapy: Radiotherapy induces chemokines (CXCLs), interferon-gamma (INF-γ), damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) release by tumor cells leading to (a) increased migration and infiltration of CAR-T cells. Radiotherapy also upregulates TAA expression on tumor cells allowing (b) maturation and activation of dendritic cells associated with better TAA presentation to T cells followed by (c) enhanced CAR-T cells tumor recognition and activation and leading to (d) increased cancer cells death. D Combination of CAR-T cells with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs): ICIs targeting PD1/PDL-1 interaction unleash CAR-T cells inhibition by this repressive pathway. This effect will (a) enhance CAR-T cells cytotoxic activity and consequently (b) promote cancer cell death
Importantly, it was demonstrated that sequential combination therapy with cisplatin followed by CD133-CAR-NK and CD44-CAR-NK92 cells led to the strongest killing effect on ovarian cancer stem cell lines compared to control NK cells [252, 253] (Fig. 3A).
Fig. 3.
Possible combination therapies for CAR-NK cells. A Combination of CAR-NK cells with chemotherapy: The upregulation of tumor associated antigen (TAA) on cancer cells (a) enhances CAR-NK cells interaction with cancer cells and promotes their cytotoxic activity. Moreover, by decreasing Treg and MDSCs, chemotherapy (b) promotes CAR-NK cells proliferation, infiltration and prolongates their survival in the TME. Therefore, combination of CAR-NK cells with chemotherapy would (c) enhance tumor cell death. B Combination of CAR-NK cells with oncolytic viruses: The tumor debulking induced by oncolytic viruses (a) enhances CAR-NK cells infiltration, proliferation, and activation and (b) proinflammatory cytokines production. Chemotherapy can (c) deliver a universal tumor cell marker to be targeted by CAR-NK cells. Combination of CAR-NK cells with oncolytic viruses will (d) induce double killing of tumor cells by the virus and the CAR-NK cells
Combination with radiotherapy
Radiotherapy can directly kill cancer cells by apoptosis and necrosis, which induces dendritic cells maturation and activation and promotes tumor antigens’ presentation [254]. Following radiation, damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPS) and INF-γ are released leading to an increased migration and infiltration of CAR-T cells into the tumor [255] (Fig. 2C). Combining CAR-T cell therapy with radiotherapy exerts a synergistic antitumor efficacy [97, 256].
Combination with oncolytic viruses
Another combination strategy is the combination of CAR-T cells with an oncolytic virus [257, 258] (Fig. 2B). This combination overcomes major challenges that limits the efficacy of CAR-T cell therapy alone [259–261]. First, the virus can break through the tumor cells a difficult mission for CAR-T cell monotherapy. Second, the oncolytic virus can induce tumor debulking by destroying the molecular shield used by some solid tumors to escape the immune system attack. This effect may enhance CAR-T cells infiltration into the tumor site. Third, the oncolytic virus reverts the immunosuppressive TME to proinflammatory environment leading to increased proliferation and survival of CAR-T cells [259–261] (mechanisms illustrated in Fig. 3B). Several studies have demonstrated that this approach help increase the anti-tumor efficacy against solid tumors [262, 263].
Combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors
It has been widely shown that PD-1 blocking antibodies, called immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), would reinvigorate the CTL anti-tumor functions [264] (Fig. 2D). Combining CARs with ICIs demonstrated encouraging results. Interestingly, PD-1 blocking antibodies secreted by CAR-T cells themselves can competitively bind to PD-1 and enhances CAR-T cells proliferation and cytotoxicity [265–268].
A recent study showed that combining anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody with anti-PSMA CAR-NK-92 cells, enhances the antitumor efficacy against castration-resistant prostate cancer [269]. Furthermore, F Strassheimer et al. have demonstrated that combining CAR-NK cells with anti-PD-1 antibody enhances the cytotoxic T lymphocytes infiltration in the tumor site leading to a primed immune response and high tumoricidal activity against advanced-stage glioblastoma [270]. ICIs also improved macrophage phagocytic capabilities in vivo [271]. Combination therapy of CAR-M with PD-1 ICI, leads to synergistic tumor control and significantly increases overall survival in a syngeneic CT26 model [272]. In addition, antibodies blocking the interaction between CD47; overexpressed on many types of tumor cells and signal regulatory protein α (SIRPα) expressed in myeloid cells or the inhibitory Fc receptor FcγRIIB have been shown to enhance phagocytosis of macrophages [273] (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
Possible combination therapies for CAR-M. CAR-M activation requires cancer cell recognition and interaction. Immune cell inhibitory mechanisms such as CD47/SIRPα or FcR/CD20 can limit CAR-M activity. CAR-M therapy demonstrated enhanced phagocytosis when combined with anti-CD47 and anti-HER2 (Trastuzumab) (A), with anti-CD47 and anti-CD20 (Rituximab) (B), as well as with anti-PD-1 (C). HER2; human epidermal growth factor receptor 2; PD-1; programmed cell death protein, SIRPα; signal regulatory protein α
Combination with local tumor’ immunomodulating therapies
Local ablative therapies such as microwave (MWA) can destroy tumors causing hyperthermic damages in cancer cells and induces the release of immunomodulatory factors, such as danger signals, tumor antigens and cytokines responsible for stimulating an antitumor immune response [274]. A recent study demonstrated that combining MWA with CAR-T cells targeting a receptor tyrosine kinase (AXL) (AXL-CAR T cells) in NSCLC patient-derived xenografts, enhances the infiltration, activation, persistence, and tumor killing [275]. Photothermal ablation of the tumor combined with chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan-4 (CSPG4)-specific CAR T cells, demonstrated superior antitumor activity on melanoma WM115 cell line [276].
Conclusion and perspectives
Recently, the clinical development of CAR-T cell therapy against solid tumors has tremendously evolved. However, some challenges facing CAR-T cell therapy in solid tumors are related to the tumor microenvironment such as: the lack of tumor-specific antigen, low efficiency of CAR-T cell trafficking, migration into tumor sites, and the presence of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment. Other major challenges are directly related to CAR-T cells including “on-target, off-tumor” toxicity, CRS, neurotoxicity and GvHD. These last limitations can be overcome using CAR-NK cell therapy which has been also preclinically well studied and translated to the clinical use. In fact, cytokines released by NK cells represent a diminished risk of CRS and neurotoxicity. Moreover, CAR-NK cells can be generated from different sources with reduced risk for alloreactivity and they can attack tumors through both CAR-dependent and CAR-independent manners which is considered as unique advantage of NK cells. However, some other challenges associated with CAR-T cells are also observed with CAR-NK cells including accessing the tumor tissue and resisting its immunosuppressive microenvironment. Advantages of CAR-NK therapy especially the reduced toxicities and their ability to produce a ready to use “off-the-shelf” product, make them a potential alternative to CAR-T cell therapy (Table 4).
As mentioned earlier in the previous parts of this review, blocking the PD1/PD-L1 axis by different strategies including PD1-blocking antibodies secreting CAR-T cells, lead to a better antitumor killing by CAR-T cells. In addition, CAR-NK cells secreting chemokines can recruit T cells. Considering these observations, we suggest combining PD1-blocking antibodies secreting CAR-T cells with CCL-CAR-NK cells could also be interesting to enhance CAR-T cell antigen recognition, interaction, and cytotoxicity against solid tumors (Fig. 5C).
Fig. 5.
Combined CAR cells therapies would improve their efficacy. A CAR-M1/CAR-NK cell combination therapy model. (a) CAR-M1 genetically modified to secrete INF-γ recognize the TAA through the CAR and phagocyte the tumor. (b) The continuous secretion of INF-γ by these CAR-M maintains them in M1 phenotype and (c) induces the recruitment of CAR-NK cells genetically modified to express CXCR. Additionally, CAR-M1 secrete IL-1, IL-12 and IL-15 which (d) induce the upregulation of CAR-NK KAR), CXCR, FASL and CD16. The upregulation of activated CAR-NK cells (e) enhanced cytotoxicity against tumor cells. Additionally, activated CAR-NK cells secrete IFN-γ and TNFα which (f) stimulate endogenous cytotoxic T cells. Moreover, (g) CXCR-expressing CAR-NK cells have a higher potential to migrate and infiltrate the CXCL secreting TME. B CAR-M1/CAR-T cell combination therapy model. (a) CAR-M1 recognize TAA with CAR and phagocyte the tumor. TAA presentation by CAR-M1 induces (b) the activation of Th1 immune responses. The interaction between CAR-M1-MHC-TAA and Th1 induces (c) IFN-γ production by Th1. (d) IFN-γ maintains CAR-M in M1 phenotype. (e) Activated CAR-M1 cells produces pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, ROS and TNF-α involved in the activation of Th1 and the recruitment of CAR-T cells into the tumor site. (f) CAR-M1 are also able to produce NO which contributes with IL-1 and IL-6 to the generation of CRS. (g) IL-1Ra-expressing-genetically modified CAR-T cells inhibit the CRC mediated by IL-1 and IL-6. (h) Recruited CAR-T cells recognize TAA and induce tumor cytotoxicity. C CAR-NK/CAR-T cell combination therapy model. (a) CAR-NK cells recognize TAA by CAR and ligands expressed on tumor cells. (b) CCL-secreting CAR-NK cells recruit CAR-T cells by releasing IL-8, CCL3, and CCL5. CAR-NK expressing chemokines are better recruited to cancer cells and (c) kill them directly by apoptosis. (d) CAR-T cells secrete PD-1 blocking antibodies and inhibits this interaction with PDL-1. (e) CAR-T cells induce cancer cells killing by releasing granzyme and perforin. (f) CAR-T cell recruit CAR-NK
CAR-M cell mediated therapy addresses key challenges faced by current CAR-T-cell therapy by engaging both the innate and adaptive immune systems thereby launching a multipronged attack against tumors. Recent findings have highlighted the importance in the interaction of modified or non-modified macrophages with T- or NK-cells in tumor regression [277]. Considering these advantages, we suggest combining CAR-M with CAR-NK cells or CAR-T cells to enhance their antitumor efficacy (Fig. 5A and B).
Importantly, the 3 models would provide the benefit of targeting different tumor antigens at the same time by each of these CAR-cell therapies. In addition, a particular advantage associated with the models in Fig. 5A and C is represented by the possibility of using allogeneic CAR-cells from different sources.
Researchers are currently looking to improve the efficacy of CAR-cell therapy by using various strategies including the Artificial Intelligence (AI) which could serve to counter many hurdles associated with CAR-cell therapy [278, 279]. In fact, radiomics, a quantitative approach to medical imaging may be useful for predicting novel cancer-associated antigens, new molecules in immune cells as well as analyzing safety and efficacy of CAR-cells [278, 279]. At the larger scale, AI can be used in automated CAR-T cell manufacturing which allows shorter production and delivery times to positively increase the number of patient treatments [280].
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the Medical Research Center at Hamad Medical Corporation for supporting this work under the approved project IRGC-04-SI-17-137. Open Access funding provided by the Qatar National library.
Abbreviations
- CAR-T cells
Chimeric antigen receptor T cells
- CAR-NK cells
Chimeric antigen receptor natural killer cells
- CAR-M cells
Chimeric antigen receptor macrophages cells
- CD
Clusters of differentiation
- CRS
Cytokine released syndrome
- BCMA
B cell maturation antigen
- HER2
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2
- BTCs
Biliary tract cancers
- PCs
Pancreatic cancers
- OS
Overall survival
- CNS
Central nervous system
- CCL2
C-C motif chemokine ligand 2
- CXCL
C-X-C motif chemokine ligand
- CXCR
C-X-C chemokine receptor
- CCR
Chimeric costimulatory receptor
- IL-13Rα2
Interleukin-13 receptor subunit Alpha2
- GBM
Glioblastoma
- GD2
Disialoganglioside
- DIPG
Diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma
- DMG
Diffuse midline glioma
- LAG-3
Lymphocyte activation gene 3
- PD-1
Programmed cell death protein 1
- ROR1
Receptor tyrosine kinase like orphan receptor1
- ORR
Overall response rate
- PFS
Progression free survival
- EGFR
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- NSCLC
Non-small cell lung cancer
- CEA
Carcinoembryonic antigen
- CRC
Colorectal cancer
- CRS
Cytokine release syndrome
- PEDD
Pressure enabled drug delivery
- MSLN
Mesothelin
- OC
Ovarian cancer
- IL
Interleukin
- TSAs
Tumor specific antigens
- TAAs
Tumor- associated antigens
- PSCA
Prostate stem cell antigen
- MUC1
Mucin 1
- EphA2
Ephrin type-A receptor 2
- FAP
Fibroblast activation protein
- biCAR-T
Bispecific-CAR-T
- iCasp9
Incorporating the inducible Caspase 9
- OTOT
On-target/off-tumor
- CX3CR1
CX3C motif chemokine receptor 1
- CX3CL1
C-X3-C motif chemokine ligand 1
- CSF-1R
Colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor
- VEGFR
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor
- HPSE
Heparinase enzyme
- TME
Tumor microenvironment
- ECM
Extracellular matrices
- MDSCs
Myeloid derived suppressor cells
- TAMs
Tumor associated macrophages
- TGF
Transforming growth factor
- DNRs
Dominant negative receptors
- NO
Nitric oxide
- ROS
Reactive oxygen species
- ATRA
All-trans retinoic acid
- TLR
Toll like receptor
- FRβ
Folate receptor beta
- ANP
Atrial natriuretic peptide
- CTLs
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes
- ICANS
Immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome
- TNF
Tumor necrosis factor
- MCP
Monocyte chemoattractant protein
- NCRs
Natural cytotoxicity receptors
- ADCC
Antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity
- MHC
Major histocompatibility complex
- GvHD
Graft versus host disease
- APCs
Antigen presenting cells
- PBMCs
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- UCB
Umbilical cord blood
- PB-NK
Peripheral blood NK cells
- hESC
Human embryonic stem cells
- iPSC
Induced pluripotent stem cells
- ROBO1
Roundabout homolog 1
- PSMA
Prostate specific membrane antigen
- CCCR
co-stimulating conversion receptors
- mRNA
Messenger RNA
- FDA
Food and drug administration
- mbIL-15
Membrane-bound interleukin − 15
- LCLs
Lymphoblastoid cell lines
- SDF-1α
Stromal cell-derived factor-1α
- BaEV-LV
Baboon envelope pseudotyped lentivirus
- CSF1
Colony stimulating factor 1
- VEGF
Vascular endothelial growth factor
- NPR
Natriuretic peptide receptor
- LPS
Lipopolysaccharide
- SAMHD1
SAM domain and HD domain-containing protein 1
- HPSCs
Hematopoietic stem cells
- NY-ESO-1
New York ESOophageal squamous cell carcinoma 1
- MMP
Matrix metalloproteinases
- DAMPS
Damage associated molecular patterns
- EpCAM
Epithelial cell adhesion molecule
- PD-L1
Programmed death-ligand 1
- ICIs
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
- CTL
Cytotoxic T lymphocytes
- GEMs
Genetically engineered macrophages
Authors’ contributions
K.M.M. collected relevant literature, conceptualized, and wrote the manuscript, designed figures and prepared tables. S.D. and M.M collected relevant literature, made a substantial contribution to the concept of the article and drafted manuscript. V.P. prepared figures and abbreviations. C.M., F.M., M.S. and H.C. provided intellectual and scientific input. S.D., M.M., K.M.M, V.P., C.M., F.M., M.S., H.C., S.U., MA., and S.M. made significant revisions to the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Open Access funding provided by the Qatar National Library. This work was supported by the Medical Research Center (MRC) at Hamad Medical Corporation as part of the approved funded project (IRGC-04-SI-17-137).
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Maysaloun Merhi, Email: mmerhi@hamad.qa.
Said Dermime, Email: sdermime@hamad.qa.
References
- 1.World Health Organization (WHO) Cancer [https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer].
- 2.GlobalSurg C. National Institute for Health Research Global Health Research Unit on Global S: Global variation in postoperative mortality and complications after cancer surgery: a multicentre, prospective cohort study in 82 countries. Lancet. 2021;397:387–397. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00001-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Albano D, Benenati M, Bruno A, Bruno F, Calandri M, Caruso D, Cozzi D, De Robertis R, Gentili F, Grazzini I, et al. Imaging side effects and complications of chemotherapy and radiation therapy: a pictorial review from head to toe. Insights Imaging. 2021;12:76. doi: 10.1186/s13244-021-01017-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Orzetti S, Tommasi F, Bertola A, Bortolin G, Caccin E, Cecco S, Ferrarin E, Giacomin E, Baldo P. Genetic Therapy and Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oncology: Safety, Pharmacovigilance, and Perspectives for Research and Clinical Practice. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23:3012. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Papaioannou NE, Beniata OV, Vitsos P, Tsitsilonis O, Samara P. Harnessing the immune system to improve cancer therapy. Ann Transl Med. 2016;4:261. doi: 10.21037/atm.2016.04.01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Poorebrahim M, Abazari MF, Sadeghi S, Mahmoudi R, Kheirollahi A, Askari H, Wickstrom SL, Poortahmasebi V, Lundqvist A, Kiessling R, Cid-Arregui A. Genetically modified immune cells targeting tumor antigens. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;214:107603. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wang X, Yang X, Yuan X, Wang W, Wang Y. Chimeric antigen receptor-engineered NK cells: new weapons of cancer immunotherapy with great potential. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2022;11:85. doi: 10.1186/s40164-022-00341-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Munshi NC, Anderson LD, Jr, Shah N, Madduri D, Berdeja J, Lonial S, Raje N, Lin Y, Siegel D, Oriol A, et al. Idecabtagene Vicleucel in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:705–716. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2024850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wang T, He T, Ma L, Yang Y, Feng R, Ding Y, Shan Y, Bu B, Qi F, Wu F, et al. Clinical Outcomes of BCMA CAR-T Cells in a Multiple Myeloma Patient With Central Nervous System Invasion. Front Oncol. 2022;12:854448. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.854448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.O'Leary MC, Lu X, Huang Y, Lin X, Mahmood I, Przepiorka D, Gavin D, Lee S, Liu K, George B, et al. FDA Approval Summary: Tisagenlecleucel for Treatment of Patients with Relapsed or Refractory B-cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2019;25:1142–1146. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rosenbaum L. Tragedy, Perseverance, and Chance - The Story of CAR-T Therapy. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1313–1315. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1711886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Maude SL, Laetsch TW, Buechner J, Rives S, Boyer M, Bittencourt H, Bader P, Verneris MR, Stefanski HE, Myers GD, et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. New England J Med. 2018;378:439–448. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1709866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Abramson JS, Palomba ML, Gordon LI, Lunning MA, Wang M, Arnason J, Mehta A, Purev E, Maloney DG, Andreadis C, et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel for patients with relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): a multicentre seamless design study. Lancet. 2020;396:839–852. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31366-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Viardot A, Wais V, Sala E, Koerper S. Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy as a treatment option for patients with B-cell lymphomas: perspectives on the therapeutic potential of Axicabtagene ciloleucel. Cancer Manag Res. 2019;11:2393–2404. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S163225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Que Y, Xu M, Xu Y, Almeida VDF, Zhu L, Wang Z, Wang Y, Liu X, Jiang L, Wang D, et al. Anti-BCMA CAR-T Cell Therapy in Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma Patients With Extramedullary Disease: A Single Center Analysis of Two Clinical Trials. Front Immunol. 2021;12:755866. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.755866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pasquini MC, Hu ZH, Curran K, Laetsch T, Locke F, Rouce R, Pulsipher MA, Phillips CL, Keating A, Frigault MJ, et al. Real-world evidence of tisagenlecleucel for pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020;4:5414–5424. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2020003092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pan J, Zuo S, Deng B, Xu X, Li C, Zheng Q, Ling Z, Song W, Xu J, Duan J, et al. Sequential CD19–22 CAR T therapy induces sustained remission in children with r/r B-ALL. Blood. 2020;135:387–391. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019003293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shargian L, Raanani P, Yeshurun M, Gafter-Gvili A, Gurion R. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy is superior to standard of care as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Haematol. 2022;198:838–846. doi: 10.1111/bjh.18335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ahmed N, Brawley V, Hegde M, Bielamowicz K, Kalra M, Landi D, Robertson C, Gray TL, Diouf O, Wakefield A, et al. HER2-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor–Modified Virus-Specific T Cells for Progressive Glioblastoma: A Phase 1 Dose-Escalation Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3:1094. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.0184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hu Z, Zheng X, Jiao D, Zhou Y, Sun R, Wang B, Tian Z, Wei H. LunX-CAR T Cells as a Targeted Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020;17:361–370. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2020.04.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Batra SA, Rathi P, Guo L, Courtney AN, Fleurence J, Balzeau J, Shaik RS, Nguyen TP, Wu M-F, Bulsara S, et al. Glypican-3–Specific CAR T Cells Coexpressing IL15 and IL21 Have Superior Expansion and Antitumor Activity against Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Res. 2020;8:309–320. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jiang H, Shi Z, Wang P, Wang C, Yang L, Du G, Zhang H, Shi B, Jia J, Li Q, et al. Claudin18.2-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor Engineered T Cells for the Treatment of Gastric Cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2019;111:409–418. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djy134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li H, Ding J, Lu M, Liu H, Miao Y, Li L, Wang G, Zheng J, Pei D, Zhang Q. CAIX-specific CAR-T Cells and Sunitinib Show Synergistic Effects Against Metastatic Renal Cancer Models. J Immunother. 2020;43:16–28. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gorchakov AA, Kulemzin SV, Kochneva GV, Taranin AV. Challenges and Prospects of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell Therapy for Metastatic Prostate Cancer. European Urol. 2020;77:299–308. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2019.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Safarzadeh Kozani P, Safarzadeh Kozani P, Ahmadi Najafabadi M, Yousefi F, Mirarefin SMJ, Rahbarizadeh F. Recent Advances in Solid Tumor CAR-T Cell Therapy: Driving Tumor Cells From Hero to Zero? Front Immunol. 2022;13:795164. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.795164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Liu Z, Zhou Z, Dang Q, Xu H, Lv J, Li H, Han X. Immunosuppression in tumor immune microenvironment and its optimization from CAR-T cell therapy. Theranostics. 2022;12:6273–6290. doi: 10.7150/thno.76854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Liu G, Rui W, Zhao X, Lin X. Enhancing CAR-T cell efficacy in solid tumors by targeting the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol Immunol. 2021;18:1085–1095. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00655-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang E, Cesano A, Butterfield LH, Marincola F. Improving the therapeutic index in adoptive cell therapy: key factors that impact efficacy. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8(2):e001619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Hou B, Tang Y, Li W, Zeng Q, Chang D. Efficiency of CAR-T Therapy for Treatment of Solid Tumor in Clinical Trials: A Meta-Analysis. Disease Markers. 2019;2019:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2019/3425291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Miao L, Zhang Z, Ren Z, Li Y. Reactions Related to CAR-T Cell Therapy. Front Immunol. 2021;12:663201. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.663201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Liu E, Marin D, Banerjee P, Macapinlac HA, Thompson P, Basar R, Nassif Kerbauy L, Overman B, Thall P, Kaplan M, et al. Use of CAR-Transduced Natural Killer Cells in CD19-Positive Lymphoid Tumors. New England J Med. 2020;382:545–553. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Basar R, Daher M, Rezvani K. Next-generation cell therapies: the emerging role of CAR-NK cells. Hematology. 2020;2020:570–578. doi: 10.1182/hematology.2020002547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cassetta L, Kitamura T. Macrophage targeting: opening new possibilities for cancer immunotherapy. Immunology. 2018;155:285–293. doi: 10.1111/imm.12976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dolgin E. Cancer-eating immune cells kitted out with CARs. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38:509–511. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0520-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Guerriero JL. Macrophages: The Road Less Traveled, Changing Anticancer Therapy. Trends in Mol Med. 2018;24:472–489. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2018.03.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Halim L, Maher J. CAR T-cell immunotherapy of B-cell malignancy: the story so far. Ther Adv Vaccines Immunother. 2020;8:2515135520927164. doi: 10.1177/2515135520927164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Fischer JW, Bhattarai N. CAR-T Cell Therapy: Mechanism, Management, and Mitigation of Inflammatory Toxicities. Front Immunol. 2021;12:693016. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.693016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Vucinic V, Quaiser A, Lückemeier P, Fricke S, Platzbecker U, Koehl U. Production and Application of CAR T Cells: Current and Future Role of Europe. Front Med. 2021;8:713401. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.713401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ahmed N, Brawley VS, Hegde M, Robertson C, Ghazi A, Gerken C, Liu E, Dakhova O, Ashoori A, Corder A, et al. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) -Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells for the Immunotherapy of HER2-Positive Sarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:1688–1696. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.0225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Brown CE, Alizadeh D, Starr R, Weng L, Wagner JR, Naranjo A, Ostberg JR, Blanchard MS, Kilpatrick J, Simpson J, et al. Regression of Glioblastoma after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. New England J Med. 2016;375:2561–2569. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1610497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Maude SL, Frey N, Shaw PA, Aplenc R, Barrett DM, Bunin NJ, Chew A, Gonzalez VE, Zheng Z, Lacey SF, et al. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Sustained Remissions in Leukemia. New England J Med. 2014;371:1507–1517. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1407222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Neelapu SS, Locke FL, Bartlett NL, Lekakis LJ, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, Braunschweig I, Oluwole OO, Siddiqi T, Lin Y, et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:2531–2544. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1707447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Tang Y, Yin H, Zhao X, Jin D, Liang Y, Xiong T, Li L, Tang W, Zhang J, Liu M, et al. High efficacy and safety of CD38 and BCMA bispecific CAR-T in relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41:2. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02214-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sadowski K, Olejarz W, Basak G. Modern advances in CARs therapy and creating a new approach to future treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(23):15006. doi: 10.3390/ijms232315006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Qu C, Zhang H, Cao H, Tang L, Mo H, Liu F, Zhang L, Yi Z, Long L, Yan L, et al. Tumor buster - where will the CAR-T cell therapy ‘missile’ go? Mol Cancer. 2022;21:201. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01669-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Patel U, Abernathy J, Savani BN, Oluwole O, Sengsayadeth S, Dholaria B. CAR T cell therapy in solid tumors: A review of current clinical trials. EJHaem. 2022;3:24–31. doi: 10.1002/jha2.356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ahmed N, Brawley VS, Hegde M, Robertson C, Ghazi A, Gerken C, Liu E, Dakhova O, Ashoori A, Corder A, et al. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2) –Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor–Modified T Cells for the Immunotherapy of HER2-Positive Sarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:1688–1696. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2014.58.0225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Feng K, Liu Y, Guo Y, Qiu J, Wu Z, Dai H, Yang Q, Wang Y, Han W. Phase I study of chimeric antigen receptor modified T cells in treating HER2-positive advanced biliary tract cancers and pancreatic cancers. Protein Cell. 2018;9:838–847. doi: 10.1007/s13238-017-0440-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Vitanza NA, Johnson AJ, Wilson AL, Brown C, Yokoyama JK, Kunkele A, Chang CA, Rawlings-Rhea S, Huang W, Seidel K, et al. Locoregional infusion of HER2-specific CAR T cells in children and young adults with recurrent or refractory CNS tumors: an interim analysis. Nat Med. 2021;27:1544–1552. doi: 10.1038/s41591-021-01404-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Brown CE, Badie B, Barish ME, Weng L, Ostberg JR, Chang WC, Naranjo A, Starr R, Wagner J, Wright C, et al. Bioactivity and Safety of IL13Ralpha2-Redirected Chimeric Antigen Receptor CD8+ T Cells in Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21:4062–4072. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Doronin II, Vishnyakova PA, Kholodenko IV, Ponomarev ED, Ryazantsev DY, Molotkovskaya IM, Kholodenko RV. Ganglioside GD2 in reception and transduction of cell death signal in tumor cells. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:295. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Majzner RG, Ramakrishna S, Yeom KW, Patel S, Chinnasamy H, Schultz LM, Richards RM, Jiang L, Barsan V, Mancusi R, et al. GD2-CAR T cell therapy for H3K27M-mutated diffuse midline gliomas. Nature. 2022;603:934–941. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-04489-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Louis CU, Savoldo B, Dotti G, Pule M, Yvon E, Myers GD, Rossig C, Russell HV, Diouf O, Liu E, et al. Antitumor activity and long-term fate of chimeric antigen receptor–positive T cells in patients with neuroblastoma. Blood. 2011;118:6050–6056. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-05-354449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Gargett T, Yu W, Dotti G, Yvon ES, Christo SN, Hayball JD, Lewis ID, Brenner MK, Brown MP. GD2-specific CAR T Cells Undergo Potent Activation and Deletion Following Antigen Encounter but can be Protected From Activation-induced Cell Death by PD-1 Blockade. Mol Ther. 2016;24:1135–1149. doi: 10.1038/mt.2016.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Berger C, Sommermeyer D, Hudecek M, Berger M, Balakrishnan A, Paszkiewicz PJ, Kosasih PL, Rader C, Riddell SR. Safety of targeting ROR1 in primates with chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells. Cancer Immunol Res. 2015;3:206–216. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-14-0163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Specht JM, Lee S, Turtle C, Berger C, Veatch J, Gooley T, Mullane E, Chaney C, Riddell S, Maloney DG. Phase I study of immunotherapy for advanced ROR1+ malignancies with autologous ROR1-specific chimeric antigen receptor-modified (CAR)-T cells. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2018;36:TPS79. [Google Scholar]
- 57.Friedlaender A, Subbiah V, Russo A, Banna GL, Malapelle U, Rolfo C, Addeo A. EGFR and HER2 exon 20 insertions in solid tumours: from biology to treatment. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2022;19:51–69. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00558-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Feng K, Guo Y, Dai H, Wang Y, Li X, Jia H, Han W. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for the immunotherapy of patients with EGFR-expressing advanced relapsed/refractory non-small cell lung cancer. Sci China Life Sci. 2016;59:468–479. doi: 10.1007/s11427-016-5023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.O'Rourke DM, Nasrallah MP, Desai A, Melenhorst JJ, Mansfield K, Morrissette JJD, Martinez-Lage M, Brem S, Maloney E, Shen A, et al. A single dose of peripherally infused EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9:eaaa0984. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa0984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Ding Y, Fang Y, Wang P, Chu W, Jin Z, Yang X, Wang J, Lou J, Qian Q. Phase I clinical trial of EGFR-specific CAR-T cells generated by the piggyBac transposon system in advanced relapsed/refractory non-small cell lung cancer patients. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021;147:3725–3734. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03613-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Wu Y, Jiang M, Qin Y, Lin F, Lai M. Single and combined use of neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, platelet-lymphocyte ratio and carcinoembryonic antigen in diagnosing gastric cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 2018;481:20–24. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2018.02.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Taheri N, Khoshsafar H, Ghanei M, Ghazvini A, Bagheri H. Dual-template rectangular nanotube molecularly imprinted polypyrrole for label-free impedimetric sensing of AFP and CEA as lung cancer biomarkers. Talanta. 2022;239:123146. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.123146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Correa TS, Bocca AL, Figueiredo F, Lima ECO, Almeida Santos MFM, Lacava ZGM, et al. Anti-CEA tagged iron nanoparticles for targeting triple-negative breast cancer. Biomed Mater. 2021;16(3). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 64.Yang L, Wang Y, Wang H. Use of immunotherapy in the treatment of gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;18:5681–5690. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Zhang Q, Zhang Z, Peng M, Fu S, Xue Z, Zhang R. CAR-T cell therapy in gastrointestinal tumors and hepatic carcinoma: From bench to bedside. Oncoimmunology. 2016;5:e1251539. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2016.1251539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Lazaro-Gorines R, Ruiz-de-la-Herran J, Navarro R, Sanz L, Alvarez-Vallina L, Martinez-Del-Pozo A, Gavilanes JG, Lacadena J. A novel Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA)-Targeted Trimeric Immunotoxin shows significantly enhanced Antitumor Activity in Human Colorectal Cancer Xenografts. Sci Rep. 2019;9:11680. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-48285-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Zhang C, Wang Z, Yang Z, Wang M, Li S, Li Y, Zhang R, Xiong Z, Wei Z, Shen J, et al. Phase I Escalating-Dose Trial of CAR-T Therapy Targeting CEA(+) Metastatic Colorectal Cancers. Mol Ther. 2017;25:1248–1258. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.03.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Katz SC, Hardaway J, Prince E, Guha P, Cunetta M, Moody A, Wang LJ, Armenio V, Espat NJ, Junghans RP. HITM-SIR: phase Ib trial of intraarterial chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy and selective internal radiation therapy for CEA(+) liver metastases. Cancer Gene Ther. 2020;27:341–355. doi: 10.1038/s41417-019-0104-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Katz SC, Moody AE, Guha P, Hardaway JC, Prince E, LaPorte J, Stancu M, Slansky JE, Jordan KR, Schulick RD, et al. HITM-SURE: Hepatic immunotherapy for metastases phase Ib anti-CEA CAR-T study utilizing pressure enabled drug delivery. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e001097. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Fang J, Ding N, Guo X, Sun Y, Zhang Z, Xie B, Li Z, Wang H, Mao W, Lin Z, et al. alphaPD-1-mesoCAR-T cells partially inhibit the growth of advanced/refractory ovarian cancer in a patient along with daily apatinib. J Immunother Cancer. 2021;9:e001162. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Haas AR, Tanyi JL, O'Hara MH, Gladney WL, Lacey SF, Torigian DA, Soulen MC, Tian L, McGarvey M, Nelson AM, et al. Phase I Study of Lentiviral-Transduced Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells Recognizing Mesothelin in Advanced Solid Cancers. Mol Ther. 2019;27:1919–1929. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.07.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Pang N, Shi J, Qin L, Chen A, Tang Y, Yang H, Huang Y, Wu Q, Li X, He B, et al. IL-7 and CCL19-secreting CAR-T cell therapy for tumors with positive glypican-3 or mesothelin. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:118. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01128-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Czeczko LEA, Ribas C, Czeczko NG, Skare TL, Yamakawa CK, Gionedis G, Vasconcelos C, Bremer FP, Castoldi DF, Gasser M, Waaga-Gasser AM. Are Stem Cell Marker Expression and Cd133 Analysis Relevant to Differentiate Colorectal Cancer? Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2021;33:e1568. doi: 10.1590/0102-672020200004e1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Ren F, Sheng WQ, Du X. CD133: a cancer stem cells marker, is used in colorectal cancers. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19:2603–2611. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i17.2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414:105–111. doi: 10.1038/35102167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Liu F, Qian Y. The role of CD133 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2021;22:291–300. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2021.1916381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Dai H, Tong C, Shi D, Chen M, Guo Y, Chen D, Han X, Wang H, Wang Y, Shen P. Efficacy and biomarker analysis of CD133-directed CAR T cells in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-arm, open-label, phase II trial. Oncoimmunology. 2020;9:1846926. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2020.1846926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Lyons TG, Ku GY. Systemic therapy for esophagogastric cancer: targeted therapies. Chin Clin Oncol. 2017;6:48. doi: 10.21037/cco.2017.07.02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.CARsgen Therapeutics Receives IND Clearance from the US FDA for CT041 CLDN18.2-CAR-T Cells [https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/carsgen-therapeutics-receives-ind-clearance-from-the-us-fda-for-ct041-cldn18-2-car-t-cells-301060555.html].
- 80.Zhan X, Wang B, Li Z, Li J, Wang H, Chen L, Jiang H, Wu M, Xiao J, Peng X, et al. Phase I trial of Claudin 18.2-specific chimeric antigen receptor T cells for advanced gastric and pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2019;37:2509. [Google Scholar]
- 81.Bebnowska D, Grywalska E, Niedzwiedzka-Rystwej P, Sosnowska-Pasiarska B, Smok-Kalwat J, Pasiarski M, Gozdz S, Rolinski J, Polkowski W. CAR-T Cell Therapy-An Overview of Targets in Gastric Cancer. J Clin Med. 2020;9:1894. doi: 10.3390/jcm9061894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Oh DY, Henry JT, Baranda J, Dumbrava EE, Cohen E, Eskew JD, et al. Poseida therapeutics: development of an allogeneic CAR-T targeting MUC1-C (MUC1, cell surface associated, C-terminal) for epithelial derived tumors - Form 8-K. 2022.
- 83.Junttila MR, de Sauvage FJ. Influence of tumour micro-environment heterogeneity on therapeutic response. Nature. 2013;501:346–354. doi: 10.1038/nature12626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Lanitis E, Poussin M, Klattenhoff AW, Song D, Sandaltzopoulos R, June CH, Powell DJ. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells with Dissociated Signaling Domains Exhibit Focused Antitumor Activity with Reduced Potential for Toxicity <i>In Vivo</i>. Cancer Immunol Res. 2013;1:43–53. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-13-0008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Newick K, O'Brien S, Moon E, Albelda SM. CAR T Cell Therapy for Solid Tumors. Ann Rev Med. 2017;68:139–152. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-062315-120245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Sun S, Hao H, Yang G, Zhang Y, Fu Y. Immunotherapy with CAR-Modified T Cells: Toxicities and Overcoming Strategies. J Immunol Res. 2018;2018:2386187. doi: 10.1155/2018/2386187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Morgan RA, Yang JC, Kitano M, Dudley ME, Laurencot CM, Rosenberg SA. Case Report of a Serious Adverse Event Following the Administration of T Cells Transduced With a Chimeric Antigen Receptor Recognizing ERBB2. Mol Ther. 2010;18:843–851. doi: 10.1038/mt.2010.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Feng K-c, Guo Y-l, Liu Y, Dai HR, Wang Y, Lv HY, Huang JH, Yang QM, Han WD. Cocktail treatment with EGFR-specific and CD133-specific chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in a patient with advanced cholangiocarcinoma. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:4. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0378-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Wei X, Lai Y, Li J, Qin L, Xu Y, Zhao R, Li B, Lin S, Wang S, Wu Q, et al. PSCA and MUC1 in non-small-cell lung cancer as targets of chimeric antigen receptor T cells. OncoImmunology. 2017;6:e1284722. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2017.1284722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Kakarla S, Chow KKH, Mata M, Shaffer DR, Song X-T, Wu M-F, Liu H, Wang LL, Rowley DR, Pfizenmaier K, Gottschalk S. Antitumor Effects of Chimeric Receptor Engineered Human T Cells Directed to Tumor Stroma. Mol Ther. 2013;21:1611–1620. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Hegde M, Corder A, Chow KKH, Mukherjee M, Ashoori A, Kew Y, Zhang YJ, Baskin DS, Merchant FA, Brawley VS, et al. Combinational Targeting Offsets Antigen Escape and Enhances Effector Functions of Adoptively Transferred T Cells in Glioblastoma. Mol Ther. 2013;21:2087–2101. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Wilkie S, van Schalkwyk MC, Hobbs S, Davies DM, van der Stegen SJ, Pereira AC, Burbridge SE, Box C, Eccles SA, Maher J. Dual targeting of ErbB2 and MUC1 in breast cancer using chimeric antigen receptors engineered to provide complementary signaling. J Clin Immunol. 2012;32:1059–1070. doi: 10.1007/s10875-012-9689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Wu C-Y, Roybal KT, Puchner EM, Onuffer J, Lim WA. Remote control of therapeutic T cells through a small molecule–gated chimeric receptor. Science. 2015;350:aab4077. doi: 10.1126/science.aab4077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Kim MS, Ma JS, Yun H, Cao Y, Kim JY, Chi V, Wang D, Woods A, Sherwood L, Caballero D, et al. Redirection of genetically engineered CAR-T cells using bifunctional small molecules. J Am Chem Soc. 2015;137:2832–2835. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b00106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Gargett T, Brown MP. The inducible caspase-9 suicide gene system as a “safety switch” to limit on-target, off-tumor toxicities of chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Front Pharmacol. 2014;5:235. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Meril S, Harush O, Reboh Y, Matikhina T, Barliya T, Cohen CJ. Targeting glycosylated antigens on cancer cells using siglec-7/9-based CAR T-cells. Mol Carcinog. 2020;59:713–723. doi: 10.1002/mc.23213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Safarzadeh Kozani P, Safarzadeh Kozani P, Rahbarizadeh F. Addressing the obstacles of CAR T cell migration in solid tumors: wishing a heavy traffic. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2022;42:1079–1098. doi: 10.1080/07388551.2021.1988509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Strohl WR, Naso M. Bispecific T-Cell Redirection versus Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T Cells as Approaches to Kill Cancer Cells. Antibodies (Basel) 2019;8:41. doi: 10.3390/antib8030041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.June CH, O'Connor RS, Kawalekar OU, Ghassemi S, Milone MC. CAR T cell immunotherapy for human cancer. Science. 2018;359:1361–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.aar6711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Gorovits B, Koren E. Immunogenicity of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapeutics. BioDrugs. 2019;33:275–284. doi: 10.1007/s40259-019-00354-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Long AH, Haso WM, Shern JF, Wanhainen KM, Murgai M, Ingaramo M, Smith JP, Walker AJ, Kohler ME, Venkateshwara VR, et al. 4-1BB costimulation ameliorates T cell exhaustion induced by tonic signaling of chimeric antigen receptors. Nat Med. 2015;21:581–590. doi: 10.1038/nm.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Safarzadeh Kozani P, Naseri A, Mirarefin SMJ, Salem F, Nikbakht M, Evazi Bakhshi S, Safarzadeh Kozani P. Nanobody-based CAR-T cells for cancer immunotherapy. Biomark Res. 2022;10:24. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00371-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Kershaw MH, Wang G, Westwood JA, Pachynski RK, Tiffany HL, Marincola FM, Wang E, Young HA, Murphy PM, Hwu P. Redirecting migration of T cells to chemokine secreted from tumors by genetic modification with CXCR2. Hum Gene Ther. 2002;13:1971–1980. doi: 10.1089/10430340260355374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Craddock JA, Lu A, Bear A, Pule M, Brenner MK, Rooney CM, Foster AE. Enhanced tumor trafficking of GD2 chimeric antigen receptor T cells by expression of the chemokine receptor CCR2b. J Immunother. 2010;33:780–788. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181ee6675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Maynard JP, Ertunc O, Kulac I, Baena-Del Valle JA, De Marzo AM, Sfanos KS. IL8 Expression Is Associated with Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness and Androgen Receptor Loss in Primary and Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Mol Cancer Res. 2020;18:153–165. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-19-0595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Wang Y, Xu RC, Zhang XL, Niu XL, Qu Y, Li LZ, Meng XY. Interleukin-8 secretion by ovarian cancer cells increases anchorage-independent growth, proliferation, angiogenic potential, adhesion and invasion. Cytokine. 2012;59:145–155. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.04.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Todorovic-Rakovic N, Milovanovic J. Interleukin-8 in breast cancer progression. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013;33:563–570. doi: 10.1089/jir.2013.0023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Tobin RP, Jordan KR, Kapoor P, Spongberg E, Davis D, Vorwald VM, Couts KL, Gao D, Smith DE, Borgers JSW, et al. IL-6 and IL-8 Are Linked With Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cell Accumulation and Correlate With Poor Clinical Outcomes in Melanoma Patients. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1223. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Najdaghi S, Razi S, Rezaei N. An overview of the role of interleukin-8 in colorectal cancer. Cytokine. 2020;135:155205. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Jin L, Tao H, Karachi A, Long Y, Hou AY, Na M, Dyson KA, Grippin AJ, Deleyrolle LP, Zhang W, et al. CXCR1- or CXCR2-modified CAR T cells co-opt IL-8 for maximal antitumor efficacy in solid tumors. Nat Commun. 2019;10:4016. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11869-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Liu G, Rui W, Zheng H, Huang D, Yu F, Zhang Y, Dong J, Zhao X, Lin X. CXCR2-modified CAR-T cells have enhanced trafficking ability that improves treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Immunol. 2020;50:712–724. doi: 10.1002/eji.201948457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Siddiqui I, Erreni M, van Brakel M, Debets R, Allavena P. Enhanced recruitment of genetically modified CX3CR1-positive human T cells into Fractalkine/CX3CL1 expressing tumors: importance of the chemokine gradient. J Immunother Cancer. 2016;4:21. doi: 10.1186/s40425-016-0125-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Lo AS, Taylor JR, Farzaneh F, Kemeny DM, Dibb NJ, Maher J. Harnessing the tumour-derived cytokine, CSF-1, to co-stimulate T-cell growth and activation. Mol Immunol. 2008;45:1276–1287. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2007.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Chen Y, Song Y, Du W, Gong L, Chang H, Zou Z. Tumor-associated macrophages: an accomplice in solid tumor progression. J Biomed Sci. 2019;26:78. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0568-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Thadi A, Khalili M, Morano W, Richard S, Katz S, Bowne W. Early Investigations and Recent Advances in Intraperitoneal Immunotherapy for Peritoneal Metastasis. Vaccines. 2018;6:54. doi: 10.3390/vaccines6030054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Li H, Wang Z, Ogunnaike EA, Wu Q, Chen G, Hu Q, Ci T, Chen Z, Wang J, Wen D, et al. Scattered seeding of CAR T cells in solid tumors augments anticancer efficacy. Natl Sci Rev. 2022;9:nwab172. doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwab172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Thadi A, Khalili M, Morano WF, Richard SD, Katz SC, Bowne WB. Early Investigations and Recent Advances in Intraperitoneal Immunotherapy for Peritoneal Metastasis. Vaccines (Basel) 2018;6:54. doi: 10.3390/vaccines6030054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Chua CYX, Ho J, Demaria S, Ferrari M, Grattoni A. Emerging technologies for local cancer treatment. Adv Ther (Weinh) 2020;3:2000027. doi: 10.1002/adtp.202000027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Saman H, Raza SS, Uddin S, Rasul K. Inducing Angiogenesis, a Key Step in Cancer Vascularization, and Treatment Approaches. Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:1172. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Chinnasamy D, Tran E, Yu Z, Morgan RA, Restifo NP, Rosenberg SA. Simultaneous targeting of tumor antigens and the tumor vasculature using T lymphocyte transfer synergize to induce regression of established tumors in mice. Cancer Res. 2013;73:3371–3380. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Chinnasamy D, Yu Z, Theoret MR, Zhao Y, Shrimali RK, Morgan RA, Feldman SA, Restifo NP, Rosenberg SA. Gene therapy using genetically modified lymphocytes targeting VEGFR-2 inhibits the growth of vascularized syngenic tumors in mice. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:3953–3968. doi: 10.1172/JCI43490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Wang W, Ma Y, Li J, Shi HS, Wang LQ, Guo FC, Zhang J, Li D, Mo BH, Wen F, et al. Specificity redirection by CAR with human VEGFR-1 affinity endows T lymphocytes with tumor-killing ability and anti-angiogenic potency. Gene Ther. 2013;20:970–978. doi: 10.1038/gt.2013.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Wallstabe L, Mades A, Frenz S, Einsele H, Rader C, Hudecek M. CAR T cells targeting alpha(v)beta(3) integrin are effective against advanced cancer in preclinical models. Adv Cell Gene Ther. 2018;1:e11. doi: 10.1002/acg2.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Phanthaphol N, Somboonpatarakun C, Suwanchiwasiri K, Chieochansin T, Sujjitjoon J, Wongkham S, Maher J, Junking M, Yenchitsomanus PT. Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells Targeting Integrin alphavbeta6 Expressed on Cholangiocarcinoma Cells. Front Oncol. 2021;11:657868. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.657868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Whilding LM, Vallath S, Maher J. The integrin alphavbeta6: a novel target for CAR T-cell immunotherapy? Biochem Soc Trans. 2016;44:349–355. doi: 10.1042/BST20150249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Liu Z, Wang F, Chen X. Integrin alpha(v)beta(3)-Targeted Cancer Therapy. Drug Dev Res. 2008;69:329–339. doi: 10.1002/ddr.20265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Mondino A, Vella G, Icardi L. Targeting the tumor and its associated stroma: One and one can make three in adoptive T cell therapy of solid tumors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2017;36:57–65. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2017.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Wang L-CS, Lo A, Scholler J, Sun J, Majumdar RS, Kapoor V, Antzis M, Cotner CE, Johnson LA, Durham AC, et al. Targeting fibroblast activation protein in tumor stroma with chimeric antigen receptor T cells can inhibit tumor growth and augment host immunity without severe toxicity. Cancer Immunol Res. 2014;2:154–166. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-13-0027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Caruana I, Savoldo B, Hoyos V, Weber G, Liu H, Kim ES, Ittmann MM, Marchetti D, Dotti G. Heparanase promotes tumor infiltration and antitumor activity of CAR-redirected T lymphocytes. Nat Med. 2015;21:524–529. doi: 10.1038/nm.3833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Greco B, Malacarne V, De Girardi F, Scotti GM, Manfredi F, Angelino E, Sirini C, Camisa B, Falcone L, Moresco MA, et al. Disrupting N-glycan expression on tumor cells boosts chimeric antigen receptor T cell efficacy against solid malignancies. Sci Transl Med. 2022;14:eabg3072. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abg3072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Fujiwara K, Tsunei A, Kusabuka H, Ogaki E, Tachibana M, Okada N. Hinge and transmembrane domains of chimeric antigen receptor regulate receptor expression and signaling threshold. Cells. 2020;9(5):1182. doi: 10.3390/cells9051182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Stock S, Benmebarek MR, Kluever AK, Darowski D, Jost C, Stubenrauch KG, et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells engineered to recognize the P329G-mutated Fc part of effector silenced tumor antigen-targeting human IgG1 antibodies enable modular targeting of solid tumors. J Immunother Cancer. 2022;15(1):47–62. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2022-005054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Chong ZX, Yeap SK, Ho WY. Transfection types, methods and strategies: a technical review. PeerJ. 2021;9:e11165. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Tredan O, Galmarini CM, Patel K, Tannock IF. Drug resistance and the solid tumor microenvironment. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99:1441–1454. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djm135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Zimmermann K, Kuehle J, Dragon AC, Galla M, Kloth C, Rudek LS, Sandalcioglu IE, Neyazi B, Moritz T, Meyer J, et al. Design and Characterization of an “All-in-One” Lentiviral Vector System Combining Constitutive Anti-GD2 CAR Expression and Inducible Cytokines. Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:375. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Huang Y, Li D, Qin DY, Gou HF, Wei W, Wang YS, Wei YQ, Wang W. Interleukin-armed chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for cancer immunotherapy. Gene Ther. 2018;25:192–197. doi: 10.1038/gt.2017.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Pegram HJ, Lee JC, Hayman EG, Imperato GH, Tedder TF, Sadelain M, Brentjens RJ. Tumor-targeted T cells modified to secrete IL-12 eradicate systemic tumors without need for prior conditioning. Blood. 2012;119:4133–4141. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-12-400044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Koneru M, Purdon TJ, Spriggs D, Koneru S, Brentjens RJ. IL-12 secreting tumor-targeted chimeric antigen receptor T cells eradicate ovarian tumors in vivo. Oncoimmunology. 2015;4:e994446. doi: 10.4161/2162402X.2014.994446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Chmielewski M, Abken H. CAR T Cells Releasing IL-18 Convert to T-Bet(high) FoxO1(low) Effectors that Exhibit Augmented Activity against Advanced Solid Tumors. Cell Rep. 2017;21:3205–3219. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.11.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Perna SK, Pagliara D, Mahendravada A, Liu H, Brenner MK, Savoldo B, Dotti G. Interleukin-7 mediates selective expansion of tumor-redirected cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) without enhancement of regulatory T-cell inhibition. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:131–139. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Laine A, Labiad O, Hernandez-Vargas H, This S, Sanlaville A, Leon S, Dalle S, Sheppard D, Travis MA, Paidassi H, Marie JC. Regulatory T cells promote cancer immune-escape through integrin alphavbeta8-mediated TGF-beta activation. Nat Commun. 2021;12:6228. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26352-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Sukumaran S, Watanabe N, Bajgain P, Raja K, Mohammed S, Fisher WE, Brenner MK, Leen AM, Vera JF. Enhancing the Potency and Specificity of Engineered T Cells for Cancer Treatment. Cancer Discov. 2018;8:972–987. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Hou AJ, Chang ZL, Lorenzini MH, Zah E, Chen YY. TGF-beta-responsive CAR-T cells promote anti-tumor immune function. Bioeng Transl Med. 2018;3:75–86. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Razeghian E, Nasution MKM, Rahman HS, Gardanova ZR, Abdelbasset WK, Aravindhan S, Bokov DO, Suksatan W, Nakhaei P, Shariatzadeh S, et al. A deep insight into CRISPR/Cas9 application in CAR-T cell-based tumor immunotherapies. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12:428. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02510-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Tang N, Cheng C, Zhang X, Qiao M, Li N, Mu W, et al. TGF-beta inhibition via CRISPR promotes the long-term efficacy of CAR T cells against solid tumors. JCI Insight. 2020;5(4):e133977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 146.Hu W, Zi Z, Jin Y, Li G, Shao K, Cai Q, Ma X, Wei F. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated PD-1 disruption enhances human mesothelin-targeted CAR T cell effector functions. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2019;68:365–377. doi: 10.1007/s00262-018-2281-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Yang Y, Li C, Liu T, Dai X, Bazhin AV. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in Tumors: From Mechanisms to Antigen Specificity and Microenvironmental Regulation. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1371. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Ohl K, Tenbrock K. Reactive Oxygen Species as Regulators of MDSC-Mediated Immune Suppression. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2499. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Long AH, Highfill SL, Cui Y, Smith JP, Walker AJ, Ramakrishna S, El-Etriby R, Galli S, Tsokos MG, Orentas RJ, Mackall CL. Reduction of MDSCs with All-trans Retinoic Acid Improves CAR Therapy Efficacy for Sarcomas. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016;4:869–880. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Jayasingam SD, Citartan M, Thang TH, Mat Zin AA, Ang KC, Ch'ng ES. Evaluating the Polarization of Tumor-Associated Macrophages Into M1 and M2 Phenotypes in Human Cancer Tissue: Technicalities and Challenges in Routine Clinical Practice. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1512. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Vitale I, Manic G, Coussens LM, Kroemer G, Galluzzi L. Macrophages and Metabolism in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cell Metab. 2019;30:36–50. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2019.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Rodriguez-Garcia A, Lynn RC, Poussin M, Eiva MA, Shaw LC, O'Connor RS, Minutolo NG, Casado-Medrano V, Lopez G, Matsuyama T, Powell DJ., Jr CAR-T cell-mediated depletion of immunosuppressive tumor-associated macrophages promotes endogenous antitumor immunity and augments adoptive immunotherapy. Nat Commun. 2021;12:877. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-20893-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Sanchez-Paulete AR, Mateus-Tique J, Mollaoglu G, Nielsen SR, Marks A, Lakshmi A, Khan JA, Wilk CM, Pia L, Baccarini A, et al. Targeting Macrophages with CAR T Cells Delays Solid Tumor Progression and Enhances Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Immunol Res. 2022;10:1354–1369. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-21-1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Jung K, Heishi T, Incio J, Huang Y, Beech EY, Pinter M, Ho WW, Kawaguchi K, Rahbari NN, Chung E, et al. Targeting CXCR4-dependent immunosuppressive Ly6C(low) monocytes improves antiangiogenic therapy in colorectal cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114:10455–10460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1710754114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Richards DM, Sefrin JP, Gieffers C, Hill O, Merz C. Concepts for agonistic targeting of CD40 in immuno-oncology. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2020;16:377–387. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1653744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Matthys P, Dillen C, Proost P, Heremans H, Van Damme J, Billiau A. Modification of the anti-CD3-induced cytokine release syndrome by anti-interferon-gamma or anti-interleukin-6 antibody treatment: protective effects and biphasic changes in blood cytokine levels. Eur J Immunol. 1993;23:2209–2216. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Tanaka T, Narazaki M, Kishimoto T. Immunotherapeutic implications of IL-6 blockade for cytokine storm. Immunotherapy. 2016;8:959–970. doi: 10.2217/imt-2016-0020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Dinarello CA, Simon A, van der Meer JWM. Treating inflammation by blocking interleukin-1 in a broad spectrum of diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2012;11:633–652. doi: 10.1038/nrd3800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Jatiani SS, Aleman A, Madduri D, Chari A, Cho HJ, Richard S, Richter J, Brody J, Jagannath S, Parekh S. Myeloma CAR-T CRS Management With IL-1R Antagonist Anakinra. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020;20:632–636. doi: 10.1016/j.clml.2020.04.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Giavridis T, van der Stegen SJC, Eyquem J, Hamieh M, Piersigilli A, Sadelain M. CAR T cell-induced cytokine release syndrome is mediated by macrophages and abated by IL-1 blockade. Nat Med. 2018;24:731–738. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0041-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Sterner RM, Sakemura R, Cox MJ, Yang N, Khadka RH, Forsman CL, Hansen MJ, Jin F, Ayasoufi K, Hefazi M, et al. GM-CSF inhibition reduces cytokine release syndrome and neuroinflammation but enhances CAR-T cell function in xenografts. Blood. 2019;133:697–709. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-10-881722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Staedtke V, Bai R-Y, Kim K, Darvas M, Davila ML, Riggins GJ, Rothman PB, Papadopoulos N, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, Zhou S. Disruption of a self-amplifying catecholamine loop reduces cytokine release syndrome. Nature. 2018;564:273–277. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0774-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Bonifant CL, Jackson HJ, Brentjens RJ, Curran KJ. Toxicity and management in CAR T-cell therapy. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2016;3:16011. doi: 10.1038/mto.2016.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Safarzadeh Kozani P, Safarzadeh Kozani P, Rahbarizadeh F, Khoshtinat Nikkhoi S. Strategies for Dodging the Obstacles in CAR T Cell Therapy. Front Oncol. 2021;11:627549. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.627549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Miao L, Zhang Y, Huang L. mRNA vaccine for cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. 2021;20:41. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01335-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Tristan-Manzano M, Justicia-Lirio P, Maldonado-Perez N, Cortijo-Gutierrez M, Benabdellah K, Martin F. Externally-Controlled Systems for Immunotherapy: From Bench to Bedside. Front Immunol. 2020;11:2044. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Shimasaki N, Jain A, Campana D. NK cells for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020;19:200–218. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Tai LH, Zhang J, Auer RC. Preventing surgery-induced NK cell dysfunction and cancer metastases with influenza vaccination. Oncoimmunology. 2013;2:e26618. doi: 10.4161/onci.26618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Zhang W, Zhao Z, Li F. Natural killer cell dysfunction in cancer and new strategies to utilize NK cell potential for cancer immunotherapy. Mol Immunol. 2022;144:58–70. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2022.02.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Fang F, Xie S, Chen M, Li Y, Yue J, Ma J, Shu X, He Y, Xiao W, Tian Z. Advances in NK cell production. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022;19:460–481. doi: 10.1038/s41423-021-00808-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Lupo KB, Matosevic S. Natural Killer Cells as Allogeneic Effectors in Adoptive Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancers. 2019;11:769. doi: 10.3390/cancers11060769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Albinger N, Hartmann J, Ullrich E. Current status and perspective of CAR-T and CAR-NK cell therapy trials in Germany. Gene Therapy. 2021;28:513–527. doi: 10.1038/s41434-021-00246-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Poli A, Michel T, Thérésine M, Andrès E, Hentges F, Zimmer J. CD56 <sup>bright</sup> natural killer (NK) cells: an important NK cell subset. Immunology. 2009;126:458–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.03027.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Del Zotto G, Antonini F, Pesce S, Moretta F, Moretta L, Marcenaro E. Comprehensive Phenotyping of Human PB NK Cells by Flow Cytometry. Cytometry A. 2020;97:891–899. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.24001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Yang Y, Badeti S, Tseng HC, Ma MT, Liu T, Jiang JG, Liu C, Liu D. Superior Expansion and Cytotoxicity of Human Primary NK and CAR-NK Cells from Various Sources via Enriched Metabolic Pathways. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2020;18:428–445. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2020.06.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Sarvaria A, Jawdat D, Madrigal JA, Saudemont A. Umbilical Cord Blood Natural Killer Cells, Their Characteristics, and Potential Clinical Applications. Front Immunol. 2017;8:329. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Knorr DA, Ni Z, Hermanson D, Hexum MK, Bendzick L, Cooper LJN, Lee DA, Kaufman DS. Clinical-Scale Derivation of Natural Killer Cells From Human Pluripotent Stem Cells for Cancer Therapy. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2:274–283. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2012-0084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Ni Z, Knorr DA, Clouser CL, Hexum MK, Southern P, Mansky LM, Park I-H, Kaufman DS. Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Produce Natural Killer Cells That Mediate Anti-HIV-1 Activity by Utilizing Diverse Cellular Mechanisms. J Virol. 2011;85:43–50. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01774-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Woll PS, Grzywacz B, Tian X, Marcus RK, Knorr DA, Verneris MR, Kaufman DS. Human embryonic stem cells differentiate into a homogeneous population of natural killer cells with potent in vivo antitumor activity. Blood. 2009;113:6094–6101. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-06-165225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Wang WN, Zhou GY, Zhang WL. NK-92 cell, another ideal carrier for chimeric antigen receptor. Immunotherapy. 2017;9:753–765. doi: 10.2217/imt-2017-0022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Schönfeld K, Sahm C, Zhang C, Naundorf S, Brendel C, Odendahl M, Nowakowska P, Bönig H, Köhl U, Kloess S, et al. Selective Inhibition of Tumor Growth by Clonal NK Cells Expressing an ErbB2/HER2-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor. Mol Ther. 2015;23:330–338. doi: 10.1038/mt.2014.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Xiao L, Cen D, Gan H, Sun Y, Huang N, Xiong H, Jin Q, Su L, Liu X, Wang K, et al. Adoptive Transfer of NKG2D CAR mRNA-Engineered Natural Killer Cells in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Mol Ther. 2019;27:1114–1125. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2019.03.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Goldenson BH, Hor P, Kaufman DS. iPSC-Derived Natural Killer Cell Therapies - Expansion and Targeting. Front Immunol. 2022;13:841107. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.841107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Chiossone L, Dumas PY, Vienne M, Vivier E. Natural killer cells and other innate lymphoid cells in cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 2018;18:671–688. doi: 10.1038/s41577-018-0061-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Kiessling R, Klein E, Pross H, Wigzell H. “Natural” killer cells in the mouse. II. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Characteristics of the killer cell. Eur J Immunol. 1975;5:117–121. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Khawar MB, Sun H. CAR-NK Cells: From Natural Basis to Design for Kill. Front Immunol. 2021;12:707542. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.707542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Rosenberg J, Huang J. CD8(+) T Cells and NK Cells: Parallel and Complementary Soldiers of Immunotherapy. Curr Opin Chem Eng. 2018;19:9–20. doi: 10.1016/j.coche.2017.11.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Pende D, Falco M, Vitale M, Cantoni C, Vitale C, Munari E, Bertaina A, Moretta F, Del Zotto G, Pietra G, et al. Killer Ig-Like Receptors (KIRs): Their Role in NK Cell Modulation and Developments Leading to Their Clinical Exploitation. Front Immunol. 2019;10:1179. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Bryceson YT, March ME, Barber DF, Ljunggren H-G, Long EO. Cytolytic granule polarization and degranulation controlled by different receptors in resting NK cells. J Exper Med. 2005;202:1001–1012. doi: 10.1084/jem.20051143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Gunesch JT, Angelo LS, Mahapatra S, Deering RP, Kowalko JE, Sleiman P, Tobias JW, Monaco-Shawver L, Orange JS, Mace EM. Genome-wide analyses and functional profiling of human NK cell lines. Mol Immunol. 2019;115:64–75. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.07.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Angelo LS, Banerjee PP, Monaco-Shawver L, Rosen JB, Makedonas G, Forbes LR, Mace EM, Orange JS. Practical NK cell phenotyping and variability in healthy adults. Immunol Res. 2015;62:341–356. doi: 10.1007/s12026-015-8664-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Benmebarek MR, Karches CH, Cadilha BL, Lesch S, Endres S, Kobold S. Killing Mechanisms of Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:1283. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Sun C, Sun H, Zhang C, Tian Z. NK cell receptor imbalance and NK cell dysfunction in HBV infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Mol Immunol. 2015;12:292–302. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2014.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Sun C, Sun HY, Xiao WH, Zhang C, Tian ZG. Natural killer cell dysfunction in hepatocellular carcinoma and NK cell-based immunotherapy. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2015;36:1191–1199. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Wu J, Mishra HK, Walcheck B. Role of ADAM17 as a regulatory checkpoint of CD16A in NK cells and as a potential target for cancer immunotherapy. J Leukocyte Biol. 2019;105:1297–1303. doi: 10.1002/JLB.2MR1218-501R. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Zhang C, Liu Y. Targeting NK Cell Checkpoint Receptors or Molecules for Cancer Immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1295. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Klingemann H. Are natural killer cells superior CAR drivers? OncoImmunology. 2014;3:e28147. doi: 10.4161/onci.28147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Hunter BD, Jacobson CA. CAR T-Cell Associated Neurotoxicity: Mechanisms, Clinicopathologic Correlates, and Future Directions. J Natl Cancer Institute. 2019;111:646–654. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djz017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Rodriguez-Garcia A, Palazon A, Noguera-Ortega E, Powell DJ, Guedan S. CAR-T Cells Hit the Tumor Microenvironment: Strategies to Overcome Tumor Escape. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1109. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Wrona E, Borowiec M, Potemski P. CAR-NK Cells in the Treatment of Solid Tumors. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22:5899. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 201.Li Y, Hermanson DL, Moriarity BS, Kaufman DS. Human iPSC-Derived Natural Killer Cells Engineered with Chimeric Antigen Receptors Enhance Anti-tumor Activity. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;23:181–192.e185. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2018.06.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 202.Töpfer K, Cartellieri M, Michen S, Wiedemuth R, Müller N, Lindemann D, Bachmann M, Füssel M, Schackert G, Temme A. DAP12-Based Activating Chimeric Antigen Receptor for NK Cell Tumor Immunotherapy. J Immunol. 2015;194:3201–3212. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1400330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 203.Meazza R, Azzarone B, Orengo AM, Ferrini S. Role of Common-Gamma Chain Cytokines in NK Cell Development and Function: Perspectives for Immunotherapy. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:1–16. doi: 10.1155/2011/861920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 204.Lapteva N, Szmania SM, van Rhee F, Rooney CM. Clinical grade purification and expansion of natural killer cells. Crit Rev Oncogenesis. 2014;19:121–132. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.2014010931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 205.Liu E, Ang SOT, Kerbauy L, Basar R, Kaur I, Kaplan M, Li L, Tong Y, Daher M, Ensley EL, et al. GMP-Compliant Universal Antigen Presenting Cells (uAPC) Promote the Metabolic Fitness and Antitumor Activity of Armored Cord Blood CAR-NK Cells. Front Immunol. 2021;12:626098. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.626098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 206.Lu C, Guo C, Chen H, Zhang H, Zhi L, Lv T, Li M, Niu Z, Lu P, Zhu W. A novel chimeric PD1-NKG2D-41BB receptor enhances antitumor activity of NK92 cells against human lung cancer H1299 cells by triggering pyroptosis. Mol Immunol. 2020;122:200–206. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 207.Müller N, Michen S, Tietze S, Töpfer K, Schulte A, Lamszus K, Schmitz M, Schackert G, Pastan I, Temme A. Engineering NK Cells Modified With an EGFRvIII-specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor to Overexpress CXCR4 Improves Immunotherapy of CXCL12/SDF-1α-secreting Glioblastoma. J Immunother. 2015;38:197–210. doi: 10.1097/CJI.0000000000000082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 208.Ng YY, Tay JCK, Wang S. CXCR1 Expression to Improve Anti-Cancer Efficacy of Intravenously Injected CAR-NK Cells in Mice with Peritoneal Xenografts. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2020;16:75–85. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2019.12.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 209.Wennerberg E, Kremer V, Childs R, Lundqvist A. CXCL10-induced migration of adoptively transferred human natural killer cells toward solid tumors causes regression of tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2015;64:225–235. doi: 10.1007/s00262-014-1629-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 210.Jamali A, Hadjati J, Madjd Z, Mirzaei HR, Thalheimer FB, Agarwal S, Bonig H, Ullrich E, Hartmann J. Highly Efficient Generation of Transgenically Augmented CAR NK Cells Overexpressing CXCR4. Front Immunol. 2028;2020:11. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.02028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 211.Davis HE, Morgan JR, Yarmush ML. Polybrene increases retrovirus gene transfer efficiency by enhancing receptor-independent virus adsorption on target cell membranes. Biophys Chem. 2002;97:159–172. doi: 10.1016/s0301-4622(02)00057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 212.Hanenberg H, Xiao XL, Dilloo D, Hashino K, Kato I, Williams DA. Colocalization of retrovirus and target cells on specific fibronectin fragments increases genetic transduction of mammalian cells. Nat Med. 1996;2:876–882. doi: 10.1038/nm0896-876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 213.Fenard D, Ingrao D, Seye A, Buisset J, Genries S, Martin S, Kichler A, Galy A. Vectofusin-1, a new viral entry enhancer, strongly promotes lentiviral transduction of human hematopoietic stem cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2013;2:e90. doi: 10.1038/mtna.2013.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 214.Carlsten M, Childs RW. Genetic Manipulation of NK Cells for Cancer Immunotherapy: Techniques and Clinical Implications. Front Immunol. 2015;6:266. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 215.Tsai HC, Pietrobon V, Peng M, Wang S, Zhao L, Marincola FM, Cai Q. Current strategies employed in the manipulation of gene expression for clinical purposes. J Transl Med. 2022;20:535. doi: 10.1186/s12967-022-03747-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 216.Schildberger A, Rossmanith E, Eichhorn T, Strassl K, Weber V. Monocytes, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and THP-1 cells exhibit different cytokine expression patterns following stimulation with lipopolysaccharide. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:697972. doi: 10.1155/2013/697972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 217.Bruckmeier M, Kuehnl A, Culmes M, Pelisek J, Eckstein H-H. Impact of oxLDL and LPS on C-type natriuretic peptide system is different between THP-1 cells and human peripheral blood monocytic cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;30:199–209. doi: 10.1159/000339044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 218.Zhang L, Tian L, Dai X, Yu H, Wang J, Lei A, Zhu M, Xu J, Zhao W, Zhu Y, et al. Pluripotent stem cell-derived CAR-macrophage cells with antigen-dependent anti-cancer cell functions. J Hematol Oncol. 2020;13:153. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00983-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 219.Mangan DF, Wahl SM. Differential regulation of human monocyte programmed cell death (apoptosis) by chemotactic factors and pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md: 1950) 1991;147:3408–3412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 220.Mangan DF, Welch GR, Wahl SM. Lipopolysaccharide, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and IL-1 beta prevent programmed cell death (apoptosis) in human peripheral blood monocytes. J Immunol (Baltimore, Md: 1950) 1991;146:1541–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 221.Cousins RJ, Blanchard RK, Popp MP, Liu L, Cao J, Moore JB, Green CL. A global view of the selectivity of zinc deprivation and excess on genes expressed in human THP-1 mononuclear cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:6952–6957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0732111100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 222.Rogers PD, Thornton J, Barker KS, McDaniel DO, Sacks GS, Swiatlo E, McDaniel LS. Pneumolysin-dependent and -independent gene expression identified by cDNA microarray analysis of THP-1 human mononuclear cells stimulated by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immunity. 2003;71:2087–2094. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.4.2087-2094.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 223.Klichinsky M, Ruella M, Shestova O, Lu XM, Best A, Zeeman M, Schmierer M, Gabrusiewicz K, Anderson NR, Petty NE, et al. Human chimeric antigen receptor macrophages for cancer immunotherapy. Nat Biotechnol. 2020;38:947–953. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0462-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 224.Zhou J, Tang Z, Gao S, Li C, Feng Y, Zhou X. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: Recent Insights and Therapies. Front Oncol. 2020;10:188. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 225.Pan Y, Yu Y, Wang X, Zhang T. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Tumor Immunity. Front Immunol. 2020;11:583084. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.583084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 226.Kang M, Lee SH, Kwon M, Byun J, Kim D, Kim C, Koo S, Kwon SP, Moon S, Jung M, et al. Nanocomplex-Mediated In Vivo Programming to Chimeric Antigen Receptor-M1 Macrophages for Cancer Therapy. Adv Mater (Deerfield Beach, Fla) 2021;33:e2103258. doi: 10.1002/adma.202103258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 227.Jeannin P, Paolini L, Adam C, Delneste Y. The roles of CSFs on the functional polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. FEBS J. 2018;285:680–699. doi: 10.1111/febs.14343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 228.Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S, Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili S-A, Mardani F, Seifi B, Mohammadi A, Afshari JT, Sahebkar A. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:6425–6440. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 229.van Ravenswaay Claasen HH, Kluin PM, Fleuren GJ. Tumor infiltrating cells in human cancer. On the possible role of CD16+ macrophages in antitumor cytotoxicity. Lab Invest. 1992;67:166–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 230.Yang L, Zhang Y. Tumor-associated macrophages: from basic research to clinical application. J Hematol Oncol. 2017;10:58. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0430-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 231.Bobadilla S, Sunseri N, Landau NR. Efficient transduction of myeloid cells by an HIV-1-derived lentiviral vector that packages the Vpx accessory protein. Gene Ther. 2013;20:514–520. doi: 10.1038/gt.2012.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 232.Laguette N, Sobhian B, Casartelli N, Ringeard M, Chable-Bessia C, Ségéral E, Yatim A, Emiliani S, Schwartz O, Benkirane M. SAMHD1 is the dendritic- and myeloid-cell-specific HIV-1 restriction factor counteracted by Vpx. Nature. 2011;474:654–657. doi: 10.1038/nature10117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 233.Nilsson M, Ljungberg J, Richter J, Kiefer T, Magnusson M, Lieber A, Widegren B, Karlsson S, Fan X. Development of an adenoviral vector system with adenovirus serotype 35 tropism; efficient transient gene transfer into primary malignant hematopoietic cells. J Gene Med. 2004;6:631–641. doi: 10.1002/jgm.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 234.Gabitova L, Menchel B, Gabbasov R, Pierini S, Best A, Ross K, Ohtani Y, Blumenthal D, Abramson S, Condamine T, Klichinsky M. Abstract 1530: Anti-HER2 CAR monocytes demonstrate targeted anti-tumor activity and enable a single day cell manufacturing process. Cancer Res. 2021;81:1530. [Google Scholar]
- 235.Lam E, Stein S, Falck-Pedersen E. Adenovirus Detection by the cGAS/STING/TBK1 DNA Sensing Cascade. J Virol. 2014;88:974–981. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02702-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 236.Wang X, Wang G, Wang N, Liu J, Cai Y, Ren M, Li Z. A simple and efficient method for the generation of a porcine alveolar macrophage cell line for high-efficiency Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus 2 infection. J Virol Methods. 2019;274:113727. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2019.113727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 237.Moradian H, Roch T, Lendlein A, Gossen M. mRNA Transfection-Induced Activation of Primary Human Monocytes and Macrophages: Dependence on Carrier System and Nucleotide Modification. Sci Rep. 2020;10:4181. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60506-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 238.Cha EB, Shin KK, Seo J, Oh D-B. Antibody-secreting macrophages generated using CpG-free plasmid eliminate tumor cells through antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis. BMB Reports. 2020;53:442–447. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2020.53.8.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 239.Toole BP. Emmprin (CD147), a cell surface regulator of matrix metalloproteinase production and function. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2003;54:371–389. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(03)54015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 240.Zhang Y, Kurupati R, Liu L, Zhou XY, Zhang G, Hudaihed A, Filisio F, Giles-Davis W, Xu X, Karakousis GC, et al. Enhancing CD8+ T Cell Fatty Acid Catabolism within a Metabolically Challenging Tumor Microenvironment Increases the Efficacy of Melanoma Immunotherapy. Cancer Cell. 2017;32:377–391.e379. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 241.Zhang W, Liu L, Su H, Liu Q, Shen J, Dai H, Zheng W, Lu Y, Zhang W, Bei Y, Shen P. Chimeric antigen receptor macrophage therapy for breast tumours mediated by targeting the tumour extracellular matrix. Br J Cancer. 2019;121:837–845. doi: 10.1038/s41416-019-0578-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 242.Niu Z, Chen G, Chang W, Sun P, Luo Z, Zhang H, Zhi L, Guo C, Chen H, Yin M, Zhu W. Chimeric antigen receptor-modified macrophages trigger systemic anti-tumour immunity. J Pathol. 2021;253:247–257. doi: 10.1002/path.5585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 243.Hao Z, Li R, Meng L, Han Z, Hong Z. Macrophage, the potential key mediator in CAR-T related CRS. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2020;9:15. doi: 10.1186/s40164-020-00171-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 244.Trouplin V, Boucherit N, Gorvel L, Conti F, Mottola G, Ghigo E. Bone marrow-derived macrophage production. J Vis Exp. 2013;81:e50966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 245.Lin YJ, Mashouf LA, Lim M. CAR T Cell Therapy in Primary Brain Tumors: Current Investigations and the Future. Front Immunol. 2022;13:817296. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.817296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 246.Xu J, Wang Y, Shi J, Liu J, Li Q, Chen L. Combination therapy: A feasibility strategy for CAR-T cell therapy in the treatment of solid tumors. Oncol Lett. 2018;16:2063–2070. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 247.Zhang L, Meng Y, Feng X, Han Z. CAR-NK cells for cancer immunotherapy: from bench to bedside. Biomark Res. 2022;10:12. doi: 10.1186/s40364-022-00364-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 248.Heylmann D, Bauer M, Becker H, van Gool S, Bacher N, Steinbrink K, Kaina B. Human CD4+CD25+ Regulatory T Cells Are Sensitive to Low Dose Cyclophosphamide: Implications for the Immune Response. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e83384. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 249.Parente-Pereira AC, Whilding LM, Brewig N, van der Stegen SJ, Davies DM, Wilkie S, van Schalkwyk MC, Ghaem-Maghami S, Maher J. Synergistic Chemoimmunotherapy of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer Using ErbB-Retargeted T Cells Combined with Carboplatin. J Immunol. 2013;191:2437–2445. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 250.Gao Q, Wang S, Chen X, Cheng S, Zhang Z, Li F, Huang L, Yang Y, Zhou B, Yue D, et al. Cancer-cell-secreted CXCL11 promoted CD8(+) T cells infiltration through docetaxel-induced-release of HMGB1 in NSCLC. J Immunother Cancer. 2019;7:42. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0511-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 251.Srivastava S, Furlan SN, Jaeger-Ruckstuhl CA, Sarvothama M, Berger C, Smythe KS, Garrison SM, Specht JM, Lee SM, Amezquita RA, et al. Immunogenic Chemotherapy Enhances Recruitment of CAR-T Cells to Lung Tumors and Improves Antitumor Efficacy when Combined with Checkpoint Blockade. Cancer Cell. 2021;39:193–208. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.11.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 252.Klapdor R, Wang S, Hacker U, Buning H, Morgan M, Dork T, Hillemanns P, Schambach A. Improved Killing of Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells by Combining a Novel Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Based Immunotherapy and Chemotherapy. Hum Gene Ther. 2017;28:886–896. doi: 10.1089/hum.2017.168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 253.Klapdor R, Wang S, Morgan MA, Zimmermann K, Hachenberg J, Büning H, Dörk T, Hillemanns P, Schambach A. NK Cell-Mediated Eradication of Ovarian Cancer Cells with a Novel Chimeric Antigen Receptor Directed against CD44. Biomedicines. 2021;9:1339. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 254.Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Tesniere A, Obeid M, Ortiz C, Criollo A, Mignot G, Maiuri MC, Ullrich E, Saulnier P, et al. Toll-like receptor 4-dependent contribution of the immune system to anticancer chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Nat Med. 2007;13:1050–1059. doi: 10.1038/nm1622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 255.Lugade AA, Sorensen EW, Gerber SA, Moran JP, Frelinger JG, Lord EM. Radiation-induced IFN-gamma production within the tumor microenvironment influences antitumor immunity. J Immunol. 2008;180:3132–3139. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.5.3132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 256.Weiss T, Weller M, Guckenberger M, Sentman CL, Roth P. NKG2D-Based CAR T Cells and Radiotherapy Exert Synergistic Efficacy in Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2018;78:1031–1043. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 257.Nishio N, Diaconu I, Liu H, Cerullo V, Caruana I, Hoyos V, Bouchier-Hayes L, Savoldo B, Dotti G. Armed oncolytic virus enhances immune functions of chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells in solid tumors. Cancer Res. 2014;74:5195–5205. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 258.Wing A, Fajardo CA, Posey AD, Jr, Shaw C, Da T, Young RM, Alemany R, June CH, Guedan S. Improving CART-Cell Therapy of Solid Tumors with Oncolytic Virus-Driven Production of a Bispecific T-cell Engager. Cancer Immunol Res. 2018;6:605–616. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-17-0314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 259.Guedan S, Alemany R. CAR-T Cells and Oncolytic Viruses: Joining Forces to Overcome the Solid Tumor Challenge. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2460. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 260.Evgin L, Kottke T, Tonne J, Thompson J, Huff AL, van Vloten J, Moore M, Michael J, Driscoll C, Pulido J, et al. Oncolytic virus-mediated expansion of dual-specific CAR T cells improves efficacy against solid tumors in mice. Sci Transl Med. 2022;14:eabn2231. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abn2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 261.Kohlhapp FJ, Kaufman HL. Molecular Pathways: Mechanism of Action for Talimogene Laherparepvec, a New Oncolytic Virus Immunotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22:1048–1054. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 262.Wang X, Wei G, Karki KB, Chan W, Viskovska M, Williams A, Chang N, Jiang H. Abstract 6225: Developing a novel combination therapy using engineered chimeric antigen receptor natural killer cells targeting avsialidase with avsialidase-armed oncolytic vaccinia virus in solid tumor models. Cancer Res. 2022;82:6225. [Google Scholar]
- 263.Ma R, Lu T, Li Z, Teng KY, Mansour AG, Yu M, Tian L, Xu B, Ma S, Zhang J, et al. An Oncolytic Virus Expressing IL15/IL15Ralpha Combined with Off-the-Shelf EGFR-CAR NK Cells Targets Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2021;81:3635–3648. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 264.Tumeh PC, Harview CL, Yearley JH, Shintaku IP, Taylor EJM, Robert L, Chmielowski B, Spasic M, Henry G, Ciobanu V, et al. PD-1 blockade induces responses by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Nature. 2014;515:568–571. doi: 10.1038/nature13954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 265.Rupp LJ, Schumann K, Roybal KT, Gate RE, Ye CJ, Lim WA, Marson A. CRISPR/Cas9-mediated PD-1 disruption enhances anti-tumor efficacy of human chimeric antigen receptor T cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7:737. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00462-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 266.Cherkassky L, Morello A, Villena-Vargas J, Feng Y, Dimitrov DS, Jones DR, Sadelain M, Adusumilli PS. Human CAR T cells with cell-intrinsic PD-1 checkpoint blockade resist tumor-mediated inhibition. J Clin Invest. 2016;126:3130–3144. doi: 10.1172/JCI83092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 267.Yoon DH, Osborn MJ, Tolar J, Kim CJ. Incorporation of Immune Checkpoint Blockade into Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells (CAR-Ts): Combination or Built-In CAR-T. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:340. doi: 10.3390/ijms19020340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 268.Rafiq S, Yeku OO, Jackson HJ, Purdon TJ, van Leeuwen DG, Drakes DJ, Song M, Miele MM, Li Z, Wang P, et al. Targeted delivery of a PD-1-blocking scFv by CAR-T cells enhances anti-tumor efficacy in vivo. Nat Biotechnol. 2018;36:847–856. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 269.Wang F, Wu L, Yin L, Shi H, Gu Y, Xing N. Combined treatment with anti-PSMA CAR NK-92 cell and anti-PD-L1 monoclonal antibody enhances the antitumour efficacy against castration-resistant prostate cancer. Clin Transl Med. 2022;12:e901. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 270.Strassheimer F, Strecker M, Alekseeva T, Macas J, Demes M, Mildenberger I, Tonn T, Wild P, Sevenich L, Reiss Y, et al. P06.12 Combination therapy of CAR-NK-cells and anti-PD-1 antibody results in high efficacy against advanced-stage glioblastoma in a syngeneic mouse model and induces protective anti-tumor immunity <em>in vivo</em>. J ImmunoTher Cancer. 2020;8:A46–A47. [Google Scholar]
- 271.Gordon SR, Maute RL, Dulken BW, Hutter G, George BM, McCracken MN, Gupta R, Tsai JM, Sinha R, Corey D, et al. PD-1 expression by tumour-associated macrophages inhibits phagocytosis and tumour immunity. Nature. 2017;545:495–499. doi: 10.1038/nature22396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 272.Pierini S, Gabbasov R, Gabitova L, Ohtani Y, Shestova O, Gill S, Abramson S, Condamine T, Klichinsky M. Abstract 63: Chimeric antigen receptor macrophages (CAR-M) induce anti-tumor immunity and synergize with T cell checkpoint inhibitors in pre-clinical solid tumor models. Cancer Res. 2021;81:63. [Google Scholar]
- 273.Weiskopf K, Weissman IL. Macrophages are critical effectors of antibody therapies for cancer. MAbs. 2015;7:303–310. doi: 10.1080/19420862.2015.1011450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 274.Chu KF, Dupuy DE. Thermal ablation of tumours: biological mechanisms and advances in therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014;14:199–208. doi: 10.1038/nrc3672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 275.Cao B, Liu M, Wang L, Zhu K, Cai M, Chen X, Feng Y, Yang S, Fu S, Zhi C, et al. Remodelling of tumour microenvironment by microwave ablation potentiates immunotherapy of AXL-specific CAR T cells against non-small cell lung cancer. Nat Commun. 2022;13:6203. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33968-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 276.Chen Q, Hu Q, Dukhovlinova E, Chen G, Ahn S, Wang C, Ogunnaike EA, Ligler FS, Dotti G, Gu Z. Photothermal Therapy Promotes Tumor Infiltration and Antitumor Activity of CAR T Cells. Adv Mater. 2019;31:e1900192. doi: 10.1002/adma.201900192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 277.Nalio Ramos R, Missolo-Koussou Y, Gerber-Ferder Y, Bromley CP, Bugatti M, Núñez NG, Tosello Boari J, Richer W, Menger L, Denizeau J, et al. Tissue-resident FOLR2+ macrophages associate with CD8+ T cell infiltration in human breast cancer. Cell. 2022;185:1189–1207.e1125. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.02.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 278.Lidia Gil MG. Artificial intelligence and chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. Acta Haematol Pol. 2022;53:176–179. [Google Scholar]
- 279.Naghizadeh A, Tsao WC, Hyun Cho J, Xu H, Mohamed M, Li D, Xiong W, Metaxas D, Ramos CA, Liu D. In vitro machine learning-based CAR T immunological synapse quality measurements correlate with patient clinical outcomes. PLOS Comput Biol. 2022;18:e1009883. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 280.Hort S, Herbst L, Bäckel N, Erkens F, Niessing B, Frye M, König N, Papantoniou I, Hudecek M, Jacobs JJL, Schmitt RH. Toward Rapid, Widely Available Autologous CAR-T Cell Therapy - Artificial Intelligence and Automation Enabling the Smart Manufacturing Hospital. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022;9:913287. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.913287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.