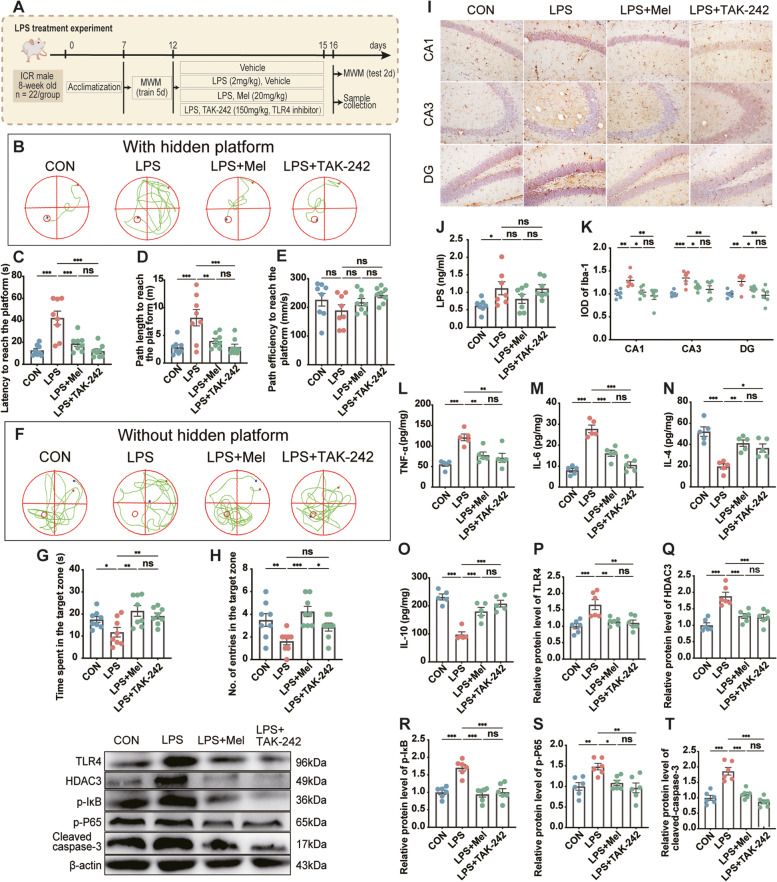
Fig. 8.
Melatonin ameliorates LPS-induced neuroinflammation and memory impairment in mice. A Schematic illustration of experimental design. B Track plot of spatial memory test (with hidden platform). C Latency to reach the platform (n = 8). D Path length to reach the platform (n = 8). E Path efficiency to reach the platform (n = 8). F Track plot of spatial memory test (without hidden platform). G Time spent in the target zone (n = 8). H Number of entries into the target zone (n = 8). I Images of the immunohistochemical microglia in the different experimental groups. The immunohistochemical results were processed using ImageJ. Bar = 50 μm. J The levels of LPS in the hippocampus (n = 7). K IOD of Iba1-positive cells in the hippocampal cornu ammonis (CA)1, CA3, and dentate gyrus (DG) regions (n = 6). L–O The levels of cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, IL-4, and IL-10) in the hippocampus (n = 5). P–T Relative protein levels of TLR4, HDAC3, p-IκB, p-P65, and cleaved caspase-3 in the hippocampus (n = 6). CON: control group, LPS: lipopolysaccharides (2 mg/kg) group, LPS + Mel: LPS + melatonin (20 mg/kg) group, LPS + TAK-242: LPS + TAK-242 (TLR4 inhibitor, 150 mg/kg) group. The data represent the mean ± SEM, p < 0.05 was set as the threshold for significance by one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc comparisons using Tukey’s test for multiple groups’ comparisons, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001