Abstract
Formation of long-lasting memory lymphocytes is one of the foundational characteristics of adaptive immunity and the basis of many vaccination strategies. Following the rapid expansion and contraction of effector CD8 T cells, the surviving antigen (Ag)-specific cells give rise to the memory CD8 T cells that persist for a long time and are phenotypically and functionally distinct from their naïve counterparts. Significant heterogeneity exists within the memory CD8 T cell pool, as different subsets display distinct tissue localization preferences, cytotoxic ability, and proliferative capacity, but all memory CD8 T cells are equipped to mount an enhanced immune response upon Ag re-encounter. Memory CD8 T cells demonstrate numerical stability under homeostatic conditions, but sepsis causes a significant decline in the number of memory CD8 T cells and diminishes their Ag-dependent and -independent functions. Sepsis also rewires the transcriptional profile of memory CD8 T cells, which profoundly impacts memory CD8 T cell differentiation and, ultimately, the protective capacity of memory CD8 T cells upon subsequent stimulation. This review delves into different aspects of memory CD8 T cell subsets as well as the immediate and long-term impact of sepsis on memory CD8 T cell biology.
Keywords: sepsis, memory, CD8 T cell, composition, differentiation, function, Immunoparalysis
Introduction
Populations of memory CD8 T cells can be maintained for their entire lifetime of the host once formed, and these cells confer protection against intracellular infections and mediate antitumor immunity (1–5). Generation of these cells is an important objective for many vaccination strategies (6–9). Compared to their naïve counterparts, memory CD8 T cells typically exist at a much higher frequency, are localized to different lymphoid and non-lymphoid tissues throughout the body and have a less stringent activation mechanism (10–13). These characteristics allow memory CD8 T cells to quantitively and qualitatively mount a more robust immune response than naïve CD8 T cells, collectively resulting in more effective control of intracellular pathogens (14–16). Significant heterogeneity exists within the memory CD8 T cell pool at epigenetic, transcriptional, and protein expression levels prompting further classification based on their phenotype, localization, and function (17–21). Thanks to their durability and diverse subsets, memory CD8 T cells provide protective responses against reinfections even years after the initial challenge; however, the quantitative and qualitative changes experienced by memory CD8 T cells responses after the onset of a lymphopenic event such as sepsis remain to be fully understood.
Sepsis is defined as an exaggerated immune response to a systemic infection that leads to organ dysfunction (22). The disseminated infection initially triggers the exacerbated generation of an array of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines, collectively regarded as “cytokine storm” (23, 24). Most sepsis patients can now survive the acute phase of sepsis as recent advancements in critical care have alleviated the tissue/organ damage inflicted by the cytokine storm (25). However, transient lymphopenia and long-lasting immune dysfunction (termed ‘immunoparalysis’) follows the cytokine storm, rendering surviving patients more susceptible to secondary infections, viral reactivation, and decreased 5-year survival compared to non-septic patients (26–29).
Sepsis is a challenging health crisis affecting nearly 50 million people annually, with a mortality rate of approximately 20%. It disproportionally affects the elderly; 75% of sepsis-related mortality occurs in individuals above 65 (30–32). On the other hand, as individuals age, they accumulate more memory T cells due to vaccinations and (re)infections which is associated with decreased susceptibility to infections. In fact, memory CD8 T cells constitute more than two-thirds of the CD8 T cell population in adult humans (33–35). Tissue-wide presence of memory T cells and their crucial role in protecting against pathogens call for a detailed analysis of the impact of sepsis on memory T cells. Hence, investigating the short- and long-term effects of sepsis on memory T cells is imperative. In this review, we will first provide an overview of different subsets of memory CD8 T cells and how time and multiple antigen encounters influence their characteristics. We will then discuss the acute and sustained impairments of sepsis on memory CD8 T cells.
Origin of memory CD8 T cells
Different models have been proposed to explain the origin and formation of antigen (Ag)-specific memory CD8 T (TMEM) cells following the rapid expansion/contraction of effector CD8 T cells (36, 37). One model argues for the linear differentiation of naïve CD8 T cells to effector CD8 T cells and then to memory CD8 T cells (38–43). An alternative model proposes memory CD8 T cells are directly derived from naïve CD8 T cells without undergoing the effector phase differentiation (44–46). Elegant human and murine studies have provided compelling evidence to support both models; however, one common theme between the two theories is that there exist two subsets of memory precursor (MP) or terminal effector (TE) CD8 T cells by which the former population gives rise to the memory pool and the latter is programmed to contraction (40, 41, 47). Presence and appropriate number of both subsets at the right time is crucial to clear the pathogen without causing immunopathology and generating a diverse memory pool for recall responses. MP and TE cells have been conventionally parsed out based on CD127 and KLRG1 expression. MP cells are CD127hi and KLRG1lo, whereas TE cells are CD127lo and KLRG1hi (40), although recent work suggests a fraction of KLRG1+ effector cells can contribute to the memory pool (48–50). Nevertheless, the combination of Ag stimulation strength, inflammatory milieu, and tissue microenvironment alters Ag-specific CD8 T cell transcriptional programs, so that either subset is formed shortly after Ag encounter (15, 51–58). MP CD8 T cells express high levels of EOMES (59), FOXO1 (60), BCL-6 (61), ID3 (62), and TCF-1 (63, 64), whereas TE CD8 T cells express high levels of T-bet (40, 65), BLIMP-1 (66), ID2 (62), and Zeb2 (67). Each of these transcription factors (TF) plays a vital role in the formation, differentiation, and fate of effector cells. For example, Ag-specific CD8 T cells lacking EOMES or TCF-1 display diminished ability in differentiating to long-lasting memory CD8 T cells. In contrast, T-bet deficient CD8 T cells do not give rise to TE CD8 T cells (59, 63).
Subsets of CD8 memory T cells
The first category of TMEM cells ( Table 1 ) is circulating memory (TCIRCM) CD8 T cells, which have been classically subdivided into two subsets of CD62Llo CCR7lo effector (TEM) and CD62Lhi CCR7hi central memory (TCM) CD8 T cells ( Table 1 ) (68). TCIRCM CD8 cells can circulate between blood, secondary lymphoid organs, and non-lymphoid organs. However, the expression of lymph node homing receptors CCR7 and CD62L enhance the localization of TCM cells in lymph nodes (LN) and white pulp of spleen, whereas TEM cells are more prevalent in blood, red pulp of spleen, and non-lymphoid tissues (10, 68, 69). Functional studies have indicated both subsets are robust producers of IFN-γ and TNF-α in response to cognate Ag stimulation, but CD62L+ TCM cells have enhanced proliferative potential and IL-2 production. In contrast, TEM cells exhibit more efficient cytotoxicity and effector-like functions. The differential localization and functional abilities of TCM and TEM cells render each subset more effective against different pathogens, determined by the nature of infection elicited by each pathogen. For example, TCM cells are more protective against LCMV-clone 13 and malignancies, while TEM cells clear intracellular bacterium Listeria monocytogenes (LM) infections more efficiently (21, 70–73). Nevertheless, the distinct localization and functional abilities of TEM and TCM cells confer protection against a wide range of pathogens.
Table 1.
Subsets of memory CD8 T cell pool and their characteristics.
| Subset | Phenotype | Location | Function | Transcription Factors (TFs) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TCM | CD62Lhi, CCR7hi, CD127hi CD27hi, CX3CR1lo, KLRG1lo | Circulation, Primarily in LN and SLO | ++ Ag-dependent expansion +/- Cytotoxicity |
Eomes, FOXO1, Bcl6, Id3, TCF1 |
| TEM | CD62Llo, CCR7lo, CD127hi/lo CD27hi/lo, CX3CR1hi/lo KLRG1hi/lo | Circulation, primarily in blood and occasionally NLT | +/- Ag-dependent expansion ++ Cytotoxicity |
T-bet, Blimp1, Zeb2, Id2 |
| TRM | CD69hi depending on NLT: CD103hi CD49ahi, CXCR3hi, CXCR6hi | Primarily NLTs, also found in draining LN | + Proliferation ++ Sense and alarm function |
Hobit, Blimp1, Runx3 |
+/- means a great fraction of the cells in the subset is endowed with the function while a noticeable population within the subset is not.
In addition to TCIRCM, tissue-resident memory (TRM) CD8 T cells are non-lymphoid tissue-restricted TMEM cells that patrol tissues for pathogen invasion ( Table 1 ) (74–76). These cells are typically situated in barrier sites and act as first responders upon Ag re-encounter with their sensing and alarm function; they mediate protection through cytotoxicity and/or secreting cytokines to recruit other immune cells to the site of pathogen invasion (75, 77–80). Although Hobit+ MP cells in non-lymphoid tissues (NLTs) are thought to be the major population contributing to the TRM pool (76, 81, 82), it is not yet clear whether the potentiation of the effector cells to TRM fate is induced either in the circulation prior to NLT recruitment or once located into NLT (83). TRM cell fate requires downregulation of T-bet, EOMES, and TCF-1 to enable responsiveness to TGF-β, which signals for expression CD103, a critical tissue retention factor important in the generation of TRM in epithelial tissue (58, 84, 85). Additionally, HOBIT/Blimp1 and Runx3 play a critical role in TRM formation and differentiation (82, 86–88). ‘IV exclusion’ (89) and expression of tissue residence markers such as CD69 and CD103 are the most widely-used markers to distinguish TRM cells from other TMEM cells (76, 90). However, technically-challenging parabiosis experiments remain the gold-standard method to determine tissue residency (74, 91). Due to their strategic localization, which allows for early defense against pathogens, many studies have explored vaccination strategies that generate long-lasting TRM cells to improve the efficacy of immunizations (92–98).
Heterogeneity of TCIRCM and TRM cells
With the advent of multi-spectral flow cytometry and single-cell transcriptomics, the heterogeneity of both TEM and TCM populations has become more evident. CD62L- TCIRCM can further be subdivided into two populations of CD127- CD27- or CD127+ CD27+ subsets. The former subset is a descendant of KLRG1+ TE cells and termed long-lived effector cells (LLEC) (49) and/or terminally-differentiated effector memory cells (t-TEM) (50), as they express TE signature genes such as KLRG1 and CX3CR1 as well as some memory-signature genes such as Bcl2 and TCF-1. Compared to TCM and CD127+ TEM cells, t-TEM cells demonstrate the highest expression of granzymes and provide robust protection in LM rechallenge models on a per-cell basis indicating superior cytolytic function, but t-TEM cells show impaired IL-2 production and poor tumor control. Interestingly, once t-TEM cells are parsed out of CD62L- TCIRCM and TEM cells are redefined as CD127+ CD62L- memory CD8 T cells, the functional differences between the redefined TEM and CD62L+ TCM cells are minimized. This suggests the t-TEM cells that make up a significant population of CD62L- TCIRCM cells may drive the differences that have previously been reported with respect to proliferative and cytotoxic abilities of CD62L+ and CD62L- TCIRCM cells.
Recent studies have shed light on the heterogeneity within the TCM population. A small subset of CD62L+ TCF1+ MP cells with restrained effector-phase proliferation and expression of inhibitory receptors have been identified to give rise to a multipotent subset of TCM cells with superior recall responses (99), matching another finding where CD62L+ TCF1hi MP cells form TCM cells with stemness features (100). Additionally, a study by Bresser et al. suggests the replicative history of the TCM pool dictates the transcriptional program and functionality of TCM cells (101). Specifically, TCM that have undergone fewer prior cell divisions demonstrate quiescence and stemness features with more efficient recall responses than the TCM with more cell divisions which exhibit effector-like characteristics. The quiescent cells within the TCM pool share features of self-renewal and multipotency with stem cell-like memory cells (TSCM) that remain poorly defined in murine models (42, 45).
Much of the heterogeneity described to the TRM population is attributed to the distinct tissue microenvironment that TRM cells are exposed to from tissue to tissue (102–104). Differential microenvironmental features lead to the phenotypic and transcriptomic alterations during the generation, differentiation, and maintenance of TRM cells found in different organs, even in the same infectious model (105). This is well-reflected in the distinct TRM markers and tissue-specific retention proteins; for example, despite the uniform expression of CD69 by TRM cells in different tissues, expression of CD103, adhesion molecule CD49a, and chemokine receptors CXCR3 and CXCR6 are variable (103, 104). Notably, the heterogeneity of TRM cells from different tissues is not limited to surface markers. It is also observed in transcriptional makeup and genome accessibility as tissue milieu instructs TRM cells with a transcriptional network required for specific tissue adaptation (76, 105). Recent work also suggests TRM cells within the small intestine could be further subdivided into stem-like Id3hi TRM and effector-like Id3lo TRM cells with differential multipotency and effector function capacity (106). Nevertheless, more studies are needed to fully delineate the heterogeneity within TRM pool.
Evolution of the TMEM pool after multiple antigen encounters
One hallmark of TMEM cells generated via infection and/or vaccination is their ability to maintain their number and function for the life of the individual. The durability of TMEM in an Ag-independent fashion relies on homeostatic signals from IL-7 and IL-15 that promote memory T cell survival (107). Despite their relative numerical stability, the CD8 memory pool undergoes significant transcriptional and phenotypic changes over time. With increasing time, the frequency of TCIRCM cells expressing TCF1, Bcl6, Id3, and EOMES and long-term memory maintenance genes such as CD27, CD127, and CD122 increases while the expression of T-bet, Zeb2, Runx1, and Id2 and effector-like genes such as CX3CR1 and KLRG1 decreases. At an early memory timepoint, TEM cells with high expression of effector-like genes are the dominant subset of TCIRCM; however, superior hemostatic proliferative capacity of TCM cells and/or direct conversion of CD127+ CD62L- TEM cells to TCM cells results in gradual increase in TCM representation over time. This results in late TCIRCM cells to possess greater capacity for IL-2 production, secondary expansion, and higher order memory potential than early TCIRCM cells (5, 21, 36, 108). On the other hand, TRM cells of distinct tissues exhibit differential longevity; lung TRM cells wane over time resulting in loss of protection (109, 110) while skin TRM cells persist for a long time with robust protective function (111). Nevertheless, few studies have examined the impact of time on the phenotype and function of TRM cells.
Following pathogen re-encounter and secondary expansion of primary (1°) TCIRCM cells, secondary (2°) TCIRCM cells are generated which can give rise to higher order TCIRCM cells upon additional Ag encounter. Higher order TCIRCM cells display differential tissue localization, phenotypic, and functional characteristics than 1° TCIRCM cells. With increasing number of Ag stimulations, higher order TMEM cells become more cytolytic with greater ability in trafficking to peripheral tissues, but reduced progression to a TCM phenotype, responsiveness to homeostatic cues, and proliferative capacity (112–116). ‘TEM -like’ features of higher order TMEM cells render this population more protective than 1° TMEM cells against pathogens, such as LM, that primarily infect and localize to peripheral tissues (73, 117). Although the more Ag encounters TMEM cells experience, the more they become phenotypically and functionally like TEM cells, gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) shows no progressive enrichment in TEM-associated genes in 2°, 3°, or 4° TMEM cells (118). Hence, repeated Ag stimulation induces major changes in gene expression patterns of individual cells as opposed to merely changing the TEM : TCM ratio.
Antigenic challenge induces robust cytokine response from 1° TRM cells which recruits immune cells including TRM precursors to the site of infection to generate more TRM population. Data suggested that 1° TRM cells could also proliferate upon reinfection to give rise to 2° TRM cells (119, 120); however, recent findings provided evidence that different subsets of TRM possess different proliferation capacity. Using a fate-mapping system to track CD103-expressing CD8 T cells, von Hoesslin et al. and Fung et al. showed that CD103+ TRM cells have limited proliferation capacity, but CD103- TRM cells undergo robust expansion upon Ag re-encounter, further highlighting the heterogeneity within TRM pool (121, 122). Nonetheless, successive Ag exposures improve the longevity and protective function of TRM pool; for example, 4° influenza-specific TRM cells show enhanced durability and heterosubtypic immunity than 1° TRM cells (123). This is attributed to continuous localization of 4° TEM cells to lungs followed by subsequent conversion to TRM cells. Several studies have reported lymph node TRM cells in the context of skin and lung infections (124, 125) and Ag re-encounter may lead to migration of TRM offspring to the draining lymph node (125). Similarly, repeated Ag exposures result in higher lymph node TRM cells and increased representation of CD103+ CD69+ LN TRM cells, leading to better local protection than 1° TRM cells (126). Overall, repetitive Ag encounter consolidates the TRM memory pool through the formation of higher order TRM cells and/or differentiating pre-existing TCIRCM to TRM cells upon recruiting to the tissue.
Short- and long-term impact of sepsis on the composition of TMEM pool
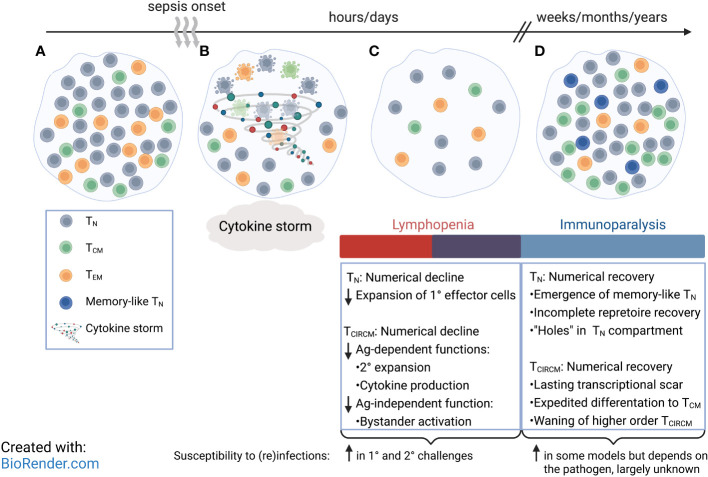
Sepsis significantly reduces the number of lymphocytes (127–130), including CD8 T cells, via apoptosis (131–133). While naive (TN) CD8 T cells are more susceptible to radiation-induced apoptosis and are lost to a greater extent than TCIRCM cells (134), both TN and TCIRCM cells display similar susceptibility to the sepsis-induced numerical decline (135–137). Additionally, further investigation into the subset composition of TCIRCM cells before and after sepsis reveals the numerical decline of TCM is equal to that of CD62L- TEM cells. Hence, sepsis stochastically targets CD8 T cells, and all circulating CD8 T cells are lost in a non-discriminatory fashion regardless of their antigen exposure history ( Figures 1B, C ) (135, 137). Indeed, this interpretation is validated as 1° and 4° TCIRCM cells exhibit similar fold loss following a septic event (138).
Figure 1.
Compositional and phenotypical changes of circulatory CD8 T cell pool after sepsis. (A) Circulatory CD8 T cell pool consists of naïve CD8 T (TN) cells and memory CD8 T (TCIRCM) cell subsets. (B) Increased levels of circulating pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines mark the initial phase of a septic insult, followed by induction of apoptosis in CD8 TN and TCIRCM in a stochastic manner. (C) Rapid loss of CD8 TN and TCIRCM and other lymphocytes result in transient lymphopenia, accompanied with early signs of immunoparalysis. (D) Number of CD8 TN and TCIRCM return to pre-sepsis values; however, some CD8 TN express memory-like phenotype, and the central memory CD8 T (TCM) cells are enriched over effector memory CD8 T (TEM) cells. Many patients continue to suffer from a long-lasting state of immunoparalysis.
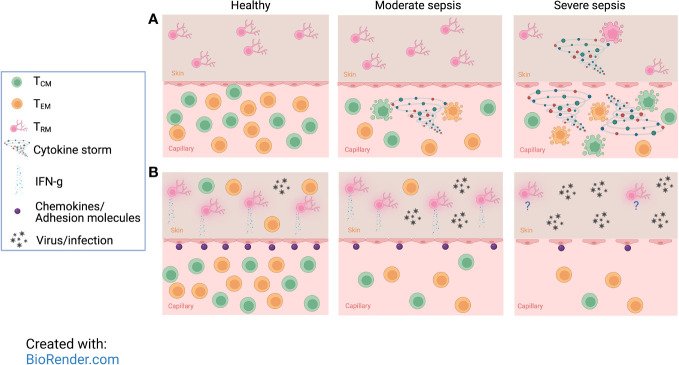
Unlike TCIRCM cells, TRM cell numbers remain unchanged following sepsis-induction that leads to low mortality levels (0-20% - moderate sepsis). Using a vaccinia infection model to generate TCIRCM and TRM with the same Ag specificity, we found the number of ‘IV positive’ TCIRCM cells significantly declined after moderate sepsis, but the number of ‘IV negative’ skin TRM cells were held constant ( Figure 2A , middle) (137, 139). Interestingly, TRM cells within tumors and non-lymphoid organs are also more protected from radiation-induced cell death than circulatory T cells (140). Two explanations were postulated to justify the resistance of TRM cells to sepsis-induced apoptosis. One is that TRM-specific factors may protect this subset from sepsis-mediated apoptosis, as TRM and TCIRCM cells are phenotypically and transcriptionally distinct. Alternatively, the local environment in which TCIRCM and TRM cells reside may predispose one subset to sepsis-induced apoptosis but protect the other. Specifically, TRM cells that reside in NLTs and have limited access to circulation may be more protected from the cytokine storm than the TCIRCM cell typically found in blood and SLO. While the first explanation has yet to be examined, the second one was tested elegantly through varying the severity of sepsis. To do so, the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) method with one or two punctures was implemented to recapitulate moderate or severe sepsis, respectively (141, 142). Moderate CLP-induced sepsis did not inflict enough damage to increase endothelial vascular permeability and leakage of cytokine storm to NLTs; however, severe sepsis led to a disruption of the endothelial barrier exposing the once-shielded NLT to pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines (and other proteins and metabolites). Therefore, severe sepsis not only instigates a more dramatic TCIRCM cell loss compared to moderate sepsis, but it also results in a significant decline in the number of TRM cells ( Figure 1A , right) (142). Overall, these data demonstrate TCIRCM and TRM cells display differential susceptibility to sepsis due to their distinct anatomical localization.
Figure 2.
Severe sepsis imposes more drastic numerical and functional diminishment in memory CD8 T cells than moderate sepsis. (A) Despite rapid loss of CD8 TCIRCM, undamaged endothelial barriers protect tissue-resident memory CD8 T (TRM) cells from moderate sepsis-induced apoptosis. However, severe sepsis not only causes a more drastic decline in number of TCIRCM, but it also overcomes the endothelial barrier and TRM become vulnerable to detrimental effects inflicted by the sepsis-induced cytokine storm resulting in rapid apoptosis of TRM cells. (B) Moderate sepsis does not change the number and per cell function of TRM cells, but it reduces the ability of endothelial cells to upregulate chemokines and adhesion molecules in response to TRM-derived cues which leads to reduced recruitment of effector cells and poor protection against localized rechallenges. With increasing severity of sepsis, the protection against localized reinfections is even more compromised due to reduced number of TCIRCM and TRM. This figure was designed using “The Inflammatory response” template available at BioRender.com.
Sepsis-induced lymphopenia is a transient event, and lymphocyte numbers will eventually return to pre-sepsis levels. However, there is limited information detailing the mechanisms responsible for the numerical restoration and the long-term impact of sepsis on T cell biology. Longitudinal studies using TCR-transgenic CD8 T cells (i.e., P14) adoptively transferred into C57/Bl6 recipients have shown that the number of both TN and TCIRCM cells quickly bounce back to the pre-sepsis baseline state. Lymphopenia-induced proliferation is thought to drive the numerical recovery of TN and TCIRCM cells as IL-7 and IL-15 mediate rapid proliferation of surviving lymphocytes to fill the empty space. Increased frequency of Ki-67+, marker for cell cycling and a non-G0 status, TN and TCIRCM cells in both murine and human septic samples provides evidence for increased proliferation of CD8 T cells after resolution of the acute phase of sepsis (143, 144). Recent murine and clinical studies have exploited the pro-survival features of IL-7 on T cells, as IL-7 treatment alleviates sepsis-indued T cell loss via preventing apoptosis and accelerating numerical recovery of lymphocytes (145–147). This notion has opened new lines of investigation to explore the therapeutic effects of IL-7 and other cytokine complex treatments in ameliorating sepsis-induced immune dysfunction.
Despite apparent numerical recovery of TN cells, the composition and phenotype of the post-sepsis TN pool is altered. Reduced primary effector responses in the post-septic host indicates an incomplete repertoire recovery and a less diverse TN pool. This is indeed the case for naïve Ag-specific CD4 T cells (148), but it remains to be determined if the same thing occurs for CD8 T cells. In addition, some studies suggest post-sepsis TN cells have increased expression of memory-associated markers, such as CD11a, for an unknown period ( Figure 1D ) (143). These observations have prompted more detailed investigation into long-term impact of sepsis on the numerically recovered TMEM compartment.
Transcriptional analysis of TCIRCM cells from sepsis survivors indicates that sepsis causes a long-lasting ‘transcriptional scar’ in TCIRCM cells by inducing transcriptional changes both immediately after onset of sepsis and during the recovery phase. Specifically, TCIRCM cells from CLP hosts show upregulation of pathways that work in concert to aid in cell cycling and increase the proliferation output long after sepsis induction. Additionally, TCIRCM transcripts from sham hosts are more effector-like whereas TCIRCM transcripts from CLP hosts are enriched in sets of genes associated with long-term memory, pointing to potential composition differences between the two groups. Indeed, the post-sepsis environment greatly shapes the phenotype and the composition of TCIRCM pool. Precisely, the numerical recovery of TCIRCM cells is accompanied with increased representation of TCM cells, the memory subset with highest proliferation capacity ( Figure 1D ). Examining the effector and memory-related markers shows the enrichment of CD62L+ KLRG1- CD127+ CX3CR1- TCIRCM cells in the septic host. The enrichment of TCM cells is ascribed to the enhanced capacity of TCM cells to sense lymphopenia-induced homeostatic cues that trigger rapid cell cycling and enrichment of TCM cells in the TCIRCM pool (144). Taken together, despite equal susceptibility of TCIRCM subsets to sepsis, surviving TCIRCM cells with greater homeostatic proliferation potential preferentially repopulate the lymphopenic space leading to long-lasting altered TCIRCM subset composition.
1° TCIRCM cells are not the only TMEM cells affected by sepsis. Our lab has recently demonstrated that higher order TCIRCM cells are equally susceptible to the sepsis-induced death as 1° TCIRCM cells. This is particularly important as the human population, especially the elderly with the highest susceptibility to sepsis complications, is seeded with a diverse pool of TMEM cells and different Ag exposure histories. Additionally, we speculated the diminished baseline proliferative capacity of higher order TCIRCM cells vs. 1° TCIRCM cells leads to preferential numerical recovery of 1° TCIRCM cells and dilution of higher order TCIRCM cells post-sepsis. Examining Ki-67 expression and BrdU incorporation of 1° and 4° TCIRCM cells revealed that unlike in 1° TCIRCM cells, sepsis did not invoke vigorous proliferation in 4° TCIRCM cells. Subsequently, the frequency of 4° TCIRCM cells progressively decreased while 1° TCIRCM increased resulting in a less diverse TCIRCM pool. Despite triggering rapid proliferation of 1° TCIRCM cells, administration of IL-7 did not boost the numerical restoration of 4° TCIRCM cells which further capitalizes the accumulation of 1° TCIRCM cells after sepsis (138). Overall, the post-sepsis environment favors the repopulation of TCIRCM cells with high proliferative capacity, leading to altered subset composition and reduced heterogeneity within the TCIRCM pool.
Short- and long-term impact of sepsis on the function of TMEM pool
Increased susceptibility of sepsis survivors to previously-encountered pathogens and viral reactivation insinuates compromised protection conferred by TMEM. The impact of sepsis on the protective capacity of TMEM can be dissected at different levels because the ‘per cell’ functional fitness (such as cytolytic capacity and cytokine secretion) of TMEM cells is key in mediating pathogen clearance, in addition to their number, tissue localization, and ability to communicate with other cells being crucial for mounting a protective immune response. Thus, we will next discuss the immediate effect of sepsis on functional capacity of different subsets of the TMEM pool and finish with a description of the long-term impact of sepsis on TMEM -mediated immunity.
Lymphopenia is not the only immunological catastrophe that a septic host experiences shortly after the onset of sepsis. Sepsis impairs the Ag-dependent functions of TCIRCM on a per cell basis. Particularly, sepsis diminishes the IFN-γ production in response to cognate Ag resulting in decreased Ag sensitivity and functional avidity of TCIRCM cells. In response to the cognate antigen, the compromised cytokine production and proliferative capacity of TCIRCM render septic hosts more susceptible to homologous reinfections. Nevertheless, TMEM cells do not mediate protection only in presence of their cognate Ag. When TMEM are ‘bathed’ in a highly inflammatory environment, they are activated to produce more cytokines and cytotoxic granules such as granzyme B. This ‘bystander activation’ of TMEM is Ag-independent, but inflammation-dependent (149–152). Interestingly, sepsis also impairs the Ag-independent functions of TMEM. In response to a heterologous infection, upregulation of activation markers and granzyme B was compromised in TCIRCM of CLP hosts (135). Together, these results suggest sepsis impairs the Ag-dependent and -independent functions of TCIRCM through influencing T-cell intrinsic and extrinsic factors.
Due to their localization to NLTs and being shielded from the damages of moderate cytokine storm, TRM maintain their numbers, and their ‘sensing and alarm’ function as measured by IFN-γ production in response to Ag stimulation ( Figure 2B , middle). Surprisingly, despite the intact number and function of TRM in the post-septic host, the protective capacity of TRM is diminished after moderate sepsis. In vaccina virus (VacV)-immune mice that underwent either CLP or sham surgeries, CLP hosts showed sustained high viral load and inability to clear VacV after re-challenge (139). Interestingly, this finding is contrary to other data suggesting TRM confer better protection than TCIRCM against VacV reinfections (74). This difference raises the question as to how sepsis diminishes the protective capacity of TRM despite their unchanged numbers and function. Subsequent investigation revealed that sepsis decreases the ability of vascular endothelium to express chemokines and adhesion molecules in response to TRM inflammatory cues ( Figure 2B , middle), resulting in the inefficient recruitment of effector cells to the site of pathogen invasion and ultimately poor pathogen control (139). In severe sepsis, the numerical decline of TRM further exacerbates the diminished protection in localized reinfections ( Figure 2B , right) (142). Collectively, these results suggest sepsis diminishes TRM recall responses through disrupting their ability to recruit effector cells.
How tissue-specific factors contribute to the resistance of TRM cells to moderate sepsis-induced cell death and functional impairment remains elusive. Blockade of TGF-β has been shown to render tumor TRM cells more susceptible to radiation-induced numerical decline (140); hence, the potential role of TGF-β signaling in maintaining TRM number and function after moderate sepsis should be explored. Additionally, the impact of sepsis on TRM cells within NLTs other than skin and SLO TRM cells in draining LN should be further investigated. While the data from our laboratory suggest that skin TRM cells that are anatomically separated from circulation are numerically and functionally protected from moderate sepsis, the crosstalk of SLO TRM cells with circulatory factors and the increased exposure of liver TRM cells to blood may increase the sensitivity of SLO and liver TRM cells to sepsis-mediated numerical loss and dysfunction. On the other hand, one could also argue for presence of shared TRM-specific factors that protect TRM cells found in different tissues from moderate sepsis regardless of their localization.
Our discussion so far has focused on describing the functional impairments with the CD8 T cell compartment that ensue after septic insult. While they shed light on factors contributing to the increased susceptibility of septic hosts early after the insult, a noticeable percentage of sepsis survivors suffer from long-lasting immunoparalysis. Our studies on the TCIRCM pool long after sepsis suggest the impairment in cytokine production after restimulation is resolved. In fact, a higher frequency of TCIRCM from CLP hosts produce IL-2 in response to Ag stimulation when examined 30 days post-sepsis. Increased IL-2 production aligns with the enrichment of TCM in the TCIRCM pool at a late time post sepsis, as these cells have better IL-2 production than TEM. However, the preferential skewing of TCIRCM pool by cells with the greatest proliferative capacity (i.e., 1° TCM) results in the reduced prevalence of TCIRCM cells with greatest cytotoxic function (TEM and higher order TCIRCM cells) (138, 144). Enrichment of TCM negatively impacted the ability of CLP hosts to clear pathogens in a LM rechallenge model (144). Additionally, recent studies have identified TEM as the population seeding TRM pools (109). TCM overrepresentation may affect the maintenance of the TRM pool by decreasing the supply of TEM. Overall, a memory pool with a diverse (but balanced) subset of cells is needed for the host to mount the most robust immune response possible. Enrichment of a subset of TMEM at the expense of other subsets may substantially affect the overall fitness of TMEM pool as each subset possesses a specialized role and function.
Conclusion
Sepsis research has shifted focus to characterizing the factors leading to the long-lasting state of immunoparalysis that emerges following the resolution of acute phase of sepsis. Since sepsis survivors show increased susceptibility to secondary and recurring infections, these studies demand an in-depth analysis of the impact of sepsis on memory lymphocytes – the body’s most potent weapon in fighting against reinfections. Circulating memory CD8 T cells undergo substantial numerical attrition and functional impairment shortly after a septic insult deriving the host susceptible to heterologous and homologous reinfections. Additionally, tissue-resident memory CD8 T cells also display a diminished ability in recruiting effector cells in response to localized re-infections. Despite the apparent numerical recovery and per cell function, circulatory memory CD8 T cells demonstrate long-lasting changes in their transcriptional and epigenetic programs after sepsis resolution, with the most proliferative subset being overrepresented over time. Therefore, sepsis ultimately leads to altered subset composition and reduced heterogeneity in memory CD8 T cells in the circulation. Further investigation is required to delineate the long-term sepsis-induced changes in function and maintenance of tissue-resident memory CD8 T cells.
Author contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
Acknowledgments
We apologize to those colleagues whose work we could not cite owing to space limitations.
Funding Statement
Supported by NIH Grants GM134880, AI114543 (V.P.B.), R35GM140881 (T.S.G.). The Holden Comprehensive Cancer Center at The University of Iowa and its National Cancer Institute Award P30CA086862 (V.P.B) and a Department of Veterans Affairs Merit Review Award I01BX001324 (T.S.G.). T.S.G. is the recipient of a Research Career Scientist award (IK6BX006192) from the Department of Veterans Affairs. V.P.B. is a University of Iowa Distinguished Scholar.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
- 1. Adamo S, Michler J, Zurbuchen Y, Cervia C, Taeschler P, Raeber ME, et al. Signature of long-lived memory Cd8(+) T cells in acute sars-Cov-2 infection. Nature (2022) 602(7895):148–55. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04280-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Pamer EG. Immune responses to listeria monocytogenes. Nat Rev Immunol (2004) 4(10):812–23. doi: 10.1038/nri1461 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Schmidt ME, Varga SM. The Cd8 T cell response to respiratory virus infections. Front Immunol (2018) 9:678. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00678 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Sahin U, Derhovanessian E, Miller M, Kloke BP, Simon P, Lower M, et al. Personalized rna mutanome vaccines mobilize poly-specific therapeutic immunity against cancer. Nature (2017) 547(7662):222–6. doi: 10.1038/nature23003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Martin MD, Kim MT, Shan Q, Sompallae R, Xue HH, Harty JT, et al. Phenotypic and functional alterations in circulating memory Cd8 T cells with time after primary infection. PloS Pathog (2015) 11(10):e1005219. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Guerrera G, Picozza M, D'Orso S, Placido R, Pirronello M, Verdiani A, et al. Bnt162b2 vaccination induces durable sars-Cov-2-Specific T cells with a stem cell memory phenotype. Sci Immunol (2021) 6(66):eabl5344. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abl5344 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Epstein JE, Tewari K, Lyke KE, Sim BKL, Billingsley PF, Laurens MB, et al. Live attenuated malaria vaccine designed to protect through hepatic Cd8(+) T cell immunity. Science (2011) 334(6055):475–80. doi: 10.1126/science.1211548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Drake CG, Lipson EJ, Brahmer JR. Breathing new life into immunotherapy: Review of melanoma, lung and kidney cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol (2014) 11(1):24–37. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Schmidt NW, Podyminogin RL, Butler NS, Badovinac VP, Tucker BJ, Bahjat KS, et al. Memory Cd8 T cell responses exceeding a Large but definable threshold provide long-term immunity to malaria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2008) 105(37):14017–22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0805452105 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Jung YW, Rutishauser RL, Joshi NS, Haberman AM, Kaech SM. Differential localization of effector and memory Cd8 T cell subsets in lymphoid organs during acute viral infection. J Immunol (2010) 185(9):5315–25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1001948 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Homann D, Teyton L, Oldstone MB. Differential regulation of antiviral T-cell immunity results in stable Cd8+ but declining Cd4+ T-cell memory. Nat Med (2001) 7(8):913–9. doi: 10.1038/90950 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Cho BK, Wang C, Sugawa S, Eisen HN, Chen J. Functional differences between memory and naive Cd8 T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (1999) 96(6):2976–81. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.6.2976 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Veiga-Fernandes H, Walter U, Bourgeois C, McLean A, Rocha B. Response of naive and memory Cd8+ T cells to antigen stimulation in vivo. Nat Immunol (2000) 1(1):47–53. doi: 10.1038/76907 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Badovinac VP, Harty JT. Programming, demarcating, and manipulating Cd8+ T-cell memory. Immunol Rev (2006) 211(1):67–80. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00384.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Harty JT, Badovinac VP. Shaping and reshaping Cd8+ T-cell memory. Nat Rev Immunol (2008) 8(2):107–19. doi: 10.1038/nri2251 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Butz EA, Bevan MJ. Massive expansion of antigen-specific Cd8+ T cells during an acute virus infection. Immunity (1998) 8(2):167–75. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80469-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Weng NP, Araki Y, Subedi K. The molecular basis of the memory T cell response: Differential gene expression and its epigenetic regulation. Nat Rev Immunol (2012) 12(4):306–15. doi: 10.1038/nri3173 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Chen Y, Zander R, Khatun A, Schauder DM, Cui W. Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of effector and memory Cd8 T cell differentiation. Front Immunol (2018) 9:2826. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02826 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Hu G, Chen J. A genome-wide regulatory network identifies key transcription factors for memory Cd8(+) T-cell development. Nat Commun (2013) 4(1):2830. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3830 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Crompton JG, Narayanan M, Cuddapah S, Roychoudhuri R, Ji Y, Yang WJ, et al. Lineage relationship of Cd8(+) T cell subsets is revealed by progressive changes in the epigenetic landscape. Cell Mol Immunol (2016) 13(4):502–13. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2015.32 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Martin MD, Badovinac VP. Defining memory Cd8 T cell. Front Immunol (2018) 9:2692. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02692 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA (2016) 315(8):801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Tamayo E, Fernandez A, Almansa R, Carrasco E, Heredia M, Lajo C, et al. Pro- and anti-inflammatory responses are regulated simultaneously from the first moments of septic shock. Eur Cytokine Netw (2011) 22(2):82–7. doi: 10.1684/ecn.2011.0281 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Rittirsch D, Flierl MA, Ward PA. Harmful molecular mechanisms in sepsis. Nat Rev Immunol (2008) 8(10):776–87. doi: 10.1038/nri2402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Gaieski DF, Edwards JM, Kallan MJ, Carr BG. Benchmarking the incidence and mortality of severe sepsis in the united states. Crit Care Med (2013) 41(5):1167–74. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827c09f8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Venet F, Davin F, Guignant C, Larue A, Cazalis MA, Darbon R, et al. Early assessment of leukocyte alterations at diagnosis of septic shock. Shock (2010) 34(4):358–63. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181dc0977 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Drewry AM, Samra N, Skrupky LP, Fuller BM, Compton SM, Hotchkiss RS. Persistent lymphopenia after diagnosis of sepsis predicts mortality. Shock (2014) 42(5):383–91. doi: 10.1097/shk.0000000000000234 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Donnelly JP, Hohmann SF, Wang HE. Unplanned readmissions after hospitalization for severe sepsis at academic medical center-affiliated hospitals. Crit Care Med (2015) 43(9):1916–27. doi: 10.1097/Ccm.0000000000001147 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Walton AH, Muenzer JT, Rasche D, Boomer JS, Sato B, Brownstein BH, et al. Reactivation of multiple viruses in patients with sepsis. PloS One (2014) 9(2):e98819. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098819 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, et al. Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990-2017: Analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet (2020) 395(10219):200–11. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Thompson K, Venkatesh B, Finfer S. Sepsis and septic shock: Current approaches to management. Intern Med J (2019) 49(2):160–70. doi: 10.1111/imj.14199 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Martin GS, Mannino DM, Moss M. The effect of age on the development and outcome of adult sepsis. Crit Care Med (2006) 34(1):15–21. doi: 10.1097/01.ccm.0000194535.82812.ba [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Sathaliyawala T, Kubota M, Yudanin N, Turner D, Camp P, Thome JJ, et al. Distribution and compartmentalization of human circulating and tissue-resident memory T cell subsets. Immunity (2013) 38(1):187–97. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.09.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Christensen KL, Holman RC, Steiner CA, Sejvar JJ, Stoll BJ, Schonberger LB. Infectious disease hospitalizations in the united states. Clin Infect Dis (2009) 49(7):1025–35. doi: 10.1086/605562 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Farber DL, Yudanin NA, Restifo NP. Human memory T cells: Generation, compartmentalization and homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol (2014) 14(1):24–35. doi: 10.1038/nri3567 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Kaech SM, Cui W. Transcriptional control of effector and memory Cd8+ T cell differentiation. Nat Rev Immunol (2012) 12(11):749–61. doi: 10.1038/nri3307 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Ahmed R, Bevan MJ, Reiner SL, Fearon DT. The precursors of memory: Models and controversies. Nat Rev Immunol (2009) 9(9):662–8. doi: 10.1038/nri2619 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Opferman JT, Ober BT, Ashton-Rickardt PG. Linear differentiation of cytotoxic effectors into memory T lymphocytes. Science (1999) 283(5408):1745–8. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5408.1745 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Jacob J, Baltimore D. Modelling T-cell memory by genetic marking of memory T cells in vivo. Nature (1999) 399(6736):593–7. doi: 10.1038/21208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Joshi NS, Cui W, Chandele A, Lee HK, Urso DR, Hagman J, et al. Inflammation directs memory precursor and short-lived effector Cd8+ T cell fates Via the graded expression of T-bet transcription factor. Immunity (2007) 27(2):281–95. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.07.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Kaech SM, Tan JT, Wherry EJ, Konieczny BT, Surh CD, Ahmed R. Selective expression of the interleukin 7 receptor identifies effector Cd8 T cells that give rise to long-lived memory cells. Nat Immunol (2003) 4(12):1191–8. doi: 10.1038/ni1009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Akondy RS, Fitch M, Edupuganti S, Yang S, Kissick HT, Li KW, et al. Origin and differentiation of human memory Cd8 T cells after vaccination. Nature (2017) 552(7685):362–+. doi: 10.1038/nature24633 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Youngblood B, Hale JS, Kissick HT, Ahn E, Xu XJ, Wieland A, et al. Effector Cd8 T cells dedifferentiate into long-lived memory cells. Nature (2017) 552(7685):404–409. doi: 10.1038/nature25144 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Restifo NP, Gattinoni L. Lineage relationship of effector and memory T cells. Curr Opin Immunol (2013) 25(5):556–63. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2013.09.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Gattinoni L, Lugli E, Ji Y, Pos Z, Paulos CM, Quigley MF, et al. A human memory T cell subset with stem cell-like properties. Nat Med (2011) 17(10):1290–7. doi: 10.1038/nm.2446 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Fuertes Marraco SA, Soneson C, Cagnon L, Gannon PO, Allard M, Abed Maillard S, et al. Long-lasting stem cell-like memory Cd8+ T cells with a naive-like profile upon yellow fever vaccination. Sci Transl Med (2015) 7(282):282ra48. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aaa3700 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Sarkar S, Kalia V, Haining WN, Konieczny BT, Subramaniam S, Ahmed R. Functional and genomic profiling of effector Cd8 T cell subsets with distinct memory fates. J Exp Med (2008) 205(3):625–40. doi: 10.1084/jem.20071641 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Herndler-Brandstetter D, Ishigame H, Shinnakasu R, Plajer V, Stecher C, Zhao J, et al. Klrg1(+) effector Cd8(+) T cells lose Klrg1, differentiate into all memory T cell lineages, and convey enhanced protective immunity. Immunity (2018) 48(4):716–29 e8. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.03.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Renkema KR, Huggins MA, Borges da Silva H, Knutson TP, Henzler CM, Hamilton SE. Klrg1(+) memory Cd8 T cells combine properties of short-lived effectors and long-lived memory. J Immunol (2020) 205(4):1059–69. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1901512 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Milner JJ, Nguyen H, Omilusik K, Reina-Campos M, Tsai M, Toma C, et al. Delineation of a molecularly distinct terminally differentiated memory Cd8 T cell population. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2020) 117(41):25667–78. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008571117 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Badovinac VP, Haring JS, Harty JT. Initial T cell receptor transgenic cell precursor frequency dictates critical aspects of the Cd8(+) T cell response to infection. Immunity (2007) 26(6):827–41. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.04.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Marzo AL, Klonowski KD, Le Bon A, Borrow P, Tough DF, Lefrancois L. Initial T cell frequency dictates memory Cd8(+) T cell lineage commitment. Nat Immunol (2005) 6(8):793–9. doi: 10.1038/ni1227 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Sarkar S, Teichgraber V, Kalia V, Polley A, Masopust D, Harrington LE, et al. Strength of stimulus and clonal competition impact the rate of memory Cd8 T cell differentiation. J Immunol (2007) 179(10):6704–14. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.10.6704 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Badovinac VP, Messingham KA, Jabbari A, Haring JS, Harty JT. Accelerated Cd8+ T-cell memory and prime-boost response after dendritic-cell vaccination. Nat Med (2005) 11(7):748–56. doi: 10.1038/nm1257 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Kaech SM, Wherry EJ. Heterogeneity and cell-fate decisions in effector and memory Cd8+ T cell differentiation during viral infection. Immunity (2007) 27(3):393–405. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2007.08.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Pham NL, Pewe LL, Fleenor CJ, Langlois RA, Legge KL, Badovinac VP, et al. Exploiting cross-priming to generate protective Cd8 T-cell immunity rapidly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2010) 107(27):12198–203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004661107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Skon CN, Lee JY, Anderson KG, Masopust D, Hogquist KA, Jameson SC. Transcriptional downregulation of S1pr1 is required for the establishment of resident memory Cd8+ T cells. Nat Immunol (2013) 14(12):1285–93. doi: 10.1038/ni.2745 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Mackay LK, Wynne-Jones E, Freestone D, Pellicci DG, Mielke LA, Newman DM, et al. T-Box transcription factors combine with the cytokines tgf-beta and il-15 to control tissue-resident memory T cell fate. Immunity (2015) 43(6):1101–11. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2015.11.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Banerjee A, Gordon SM, Intlekofer AM, Paley MA, Mooney EC, Lindsten T, et al. Cutting edge: The transcription factor eomesodermin enables Cd8+ T cells to compete for the memory cell niche. J Immunol (2010) 185(9):4988–92. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002042 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Kim MV, Ouyang W, Liao W, Zhang MQ, Li MO. The transcription factor Foxo1 controls central-memory Cd8+ T cell responses to infection. Immunity (2013) 39(2):286–97. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.07.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Cui WG, Liu Y, Weinstein JS, Craft J, Kaech SM. An interleukin-21-Interleukin-10-Stat3 pathway is critical for functional maturation of memory Cd8(+) T cells. Immunity (2011) 35(5):792–805. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.09.017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Yang CY, Best JA, Knell J, Yang E, Sheridan AD, Jesionek AK, et al. The transcriptional regulators Id2 and Id3 control the formation of distinct memory Cd8+ T cell subsets. Nat Immunol (2011) 12(12):1221–9. doi: 10.1038/ni.2158 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Zhou X, Yu S, Zhao DM, Harty JT, Badovinac VP, Xue HH. Differentiation and persistence of memory Cd8(+) T cells depend on T cell factor 1. Immunity (2010) 33(2):229–40. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.08.002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64. Jeannet G, Boudousquie C, Gardiol N, Kang J, Huelsken J, Held W. Essential role of the wnt pathway effector tcf-1 for the establishment of functional Cd8 T cell memory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2010) 107(21):9777–82. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914127107 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Intlekofer AM, Takemoto N, Wherry EJ, Longworth SA, Northrup JT, Palanivel VR, et al. Effector and memory Cd8+ T cell fate coupled by T-bet and eomesodermin. Nat Immunol (2005) 6(12):1236–44. doi: 10.1038/ni1268 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Rutishauser RL, Martins GA, Kalachikov S, Chandele A, Parish IA, Meffre E, et al. Transcriptional repressor blimp-1 promotes Cd8(+) T cell terminal differentiation and represses the acquisition of central memory T cell properties. Immunity (2009) 31(2):296–308. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2009.05.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67. Omilusik KD, Best JA, Yu B, Goossens S, Weidemann A, Nguyen JV, et al. Transcriptional repressor Zeb2 promotes terminal differentiation of Cd8+ effector and memory T cell populations during infection. J Exp Med (2015) 212(12):2027–39. doi: 10.1084/jem.20150194 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Sallusto F, Lenig D, Forster R, Lipp M, Lanzavecchia A. Two subsets of memory T lymphocytes with distinct homing potentials and effector functions. Nature (1999) 401(6754):708–12. doi: 10.1038/44385 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Masopust D, Vezys V, Marzo AL, Lefrancois L. Preferential localization of effector memory cells in nonlymphoid tissue. Science (2001) 291(5512):2413–7. doi: 10.1126/science.1058867 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70. Wherry EJ, Teichgraber V, Becker TC, Masopust D, Kaech SM, Antia R, et al. Lineage relationship and protective immunity of memory Cd8 T cell subsets. Nat Immunol (2003) 4(3):225–34. doi: 10.1038/ni889 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71. Bachmann MF, Wolint P, Schwarz K, Jager P, Oxenius A. Functional properties and lineage relationship of Cd8+ T cell subsets identified by expression of il-7 receptor alpha and Cd62l. J Immunol (2005) 175(7):4686–96. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.7.4686 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72. Huster KM, Koffler M, Stemberger C, Schiemann M, Wagner H, Busch DH. Unidirectional development of Cd8+ central memory T cells into protective listeria-specific effector memory T cells. Eur J Immunol (2006) 36(6):1453–64. doi: 10.1002/eji.200635874 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73. Nolz JC, Harty JT. Protective capacity of memory Cd8(+) T cells is dictated by antigen exposure history and nature of the infection. Immunity (2011) 34(5):781–93. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.03.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74. Jiang X, Clark RA, Liu L, Wagers AJ, Fuhlbrigge RC, Kupper TS. Skin infection generates non-migratory memory Cd8+ T(Rm) cells providing global skin immunity. Nature (2012) 483(7388):227–31. doi: 10.1038/nature10851 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75. Schenkel JM, Fraser KA, Vezys V, Masopust D. Sensing and alarm function of resident memory Cd8(+) T cells. Nat Immunol (2013) 14(5):509–13. doi: 10.1038/ni.2568 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76. Mackay LK, Rahimpour A, Ma JZ, Collins N, Stock AT, Hafon ML, et al. The developmental pathway for Cd103(+)Cd8+ tissue-resident memory T cells of skin. Nat Immunol (2013) 14(12):1294–301. doi: 10.1038/ni.2744 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77. Ariotti S, Hogenbirk MA, Dijkgraaf FE, Visser LL, Hoekstra ME, Song JY, et al. T Cell memory. skin-resident memory Cd8(+) T cells trigger a state of tissue-wide pathogen alert. Science (2014) 346(6205):101–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1254803 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78. Schenkel JM, Fraser KA, Beura LK, Pauken KE, Vezys V, Masopust D. Resident memory Cd8 T cells trigger protective innate and adaptive immune responses. Science (2014) 346(6205):98–101. doi: 10.1126/science.1254536 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79. Cheuk S, Schlums H, Gallais Serezal I, Martini E, Chiang SC, Marquardt N, et al. Cd49a expression defines tissue-resident Cd8(+) T cells poised for cytotoxic function in human skin. Immunity (2017) 46(2):287–300. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.01.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80. Mueller SN, Mackay LK. Tissue-resident memory T cells: Local specialists in immune defence. Nat Rev Immunol (2016) 16(2):79–89. doi: 10.1038/nri.2015.3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81. Sheridan BS, Pham QM, Lee YT, Cauley LS, Puddington L, Lefrancois L. Oral infection drives a distinct population of intestinal resident memory Cd8(+) T cells with enhanced protective function. Immunity (2014) 40(5):747–57. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.03.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82. Parga-Vidal L, Behr FM, Kragten NAM, Nota B, Wesselink TH, Kavazovic I, et al. Hobit identifies tissue-resident memory T cell precursors that are regulated by eomes. Sci Immunol (2021) 6(62). doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abg3533 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83. Kok L, Masopust D, Schumacher TN. The precursors of Cd8(+) tissue resident memory T cells: From lymphoid organs to infected tissues. Nat Rev Immunol (2022) 22(5):283–93. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00590-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84. Zhang N, Bevan MJ. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling controls the formation and maintenance of gut-resident memory T cells by regulating migration and retention. Immunity (2013) 39(4):687–96. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2013.08.019 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85. Wu J, Madi A, Mieg A, Hotz-Wagenblatt A, Weisshaar N, Ma S, et al. T Cell factor 1 suppresses Cd103+ lung tissue-resident memory T cell development. Cell Rep (2020) 31(1):107484. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.03.048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86. Mackay LK, Minnich M, Kragten NA, Liao Y, Nota B, Seillet C, et al. Hobit and Blimp1 instruct a universal transcriptional program of tissue residency in lymphocytes. Science (2016) 352(6284):459–63. doi: 10.1126/science.aad2035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87. Milner JJ, Toma C, Yu B, Zhang K, Omilusik K, Phan AT, et al. Runx3 programs Cd8(+) T cell residency in non-lymphoid tissues and tumours. Nature (2017) 552(7684):253–7. doi: 10.1038/nature24993 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88. Fonseca R, Burn TN, Gandolfo LC, Devi S, Park SL, Obers A, et al. Runx3 drives a Cd8+ T cell tissue residency program that is absent in Cd4+ T cells. Nat Immunol (2022) 23(8):1236–45. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01273-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89. Anderson KG, Mayer-Barber K, Sung H, Beura L, James BR, Taylor JJ, et al. Intravascular staining for discrimination of vascular and tissue leukocytes. Nat Protoc (2014) 9(1):209–22. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90. Mackay LK, Braun A, Macleod BL, Collins N, Tebartz C, Bedoui S, et al. Cutting edge: Cd69 interference with sphingosine-1-Phosphate receptor function regulates peripheral T cell retention. J Immunol (2015) 194(5):2059–63. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402256 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91. Steinert EM, Schenkel JM, Fraser KA, Beura LK, Manlove LS, Igyarto BZ, et al. Quantifying memory Cd8 T cells reveals regionalization of immunosurveillance. Cell (2015) 161(4):737–49. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92. Zacharias ZR, Ross KA, Hornick EE, Goodman JT, Narasimhan B, Waldschmidt TJ, et al. Polyanhydride nanovaccine induces robust pulmonary b and T cell immunity and confers protection against homologous and heterologous influenza a virus infections. Front Immunol (2018) 9:1953. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01953 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93. Stephens LM, Ross KA, Waldstein KA, Legge KL, McLellan JS, Narasimhan B, et al. Prefusion f-based polyanhydride nanovaccine induces both humoral and cell-mediated immunity resulting in long-lasting protection against respiratory syncytial virus. J Immunol (2021) 206(9):2122–34. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94. Galvez-Cancino F, Lopez E, Menares E, Diaz X, Flores C, Caceres P, et al. Vaccination-induced skin-resident memory Cd8(+) T cells mediate strong protection against cutaneous melanoma. Oncoimmunology (2018) 7(7):e1442163. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2018.1442163 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95. Knight FC, Gilchuk P, Kumar A, Becker KW, Sevimli S, Jacobson ME, et al. Mucosal immunization with a ph-responsive nanoparticle vaccine induces protective Cd8(+) lung-resident memory T cells. ACS Nano (2019) 13(10):10939–60. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b00326 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96. Nizard M, Roussel H, Diniz MO, Karaki S, Tran T, Voron T, et al. Induction of resident memory T cells enhances the efficacy of cancer vaccine. Nat Commun (2017) 8:15221. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15221 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97. Morabito KM, Ruckwardt TR, Redwood AJ, Moin SM, Price DA, Graham BS. Intranasal administration of rsv antigen-expressing mcmv elicits robust tissue-resident effector and effector memory Cd8+ T cells in the lung. Mucosal Immunol (2017) 10(2):545–54. doi: 10.1038/mi.2016.48 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98. Morabito KM, Ruckwardt TJ, Bar-Haim E, Nair D, Moin SM, Redwood AJ, et al. Memory inflation drives tissue-resident memory Cd8(+) T cell maintenance in the lung after intranasal vaccination with murine cytomegalovirus. Front Immunol (2018) 9:1861. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01861 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99. Johnnidis JB, Muroyama Y, Ngiow SF, Chen ZY, Manne S, Cai ZY, et al. Inhibitory signaling sustains a distinct early memory Cd8(+) T cell precursor that is resistant to DNA damage. Sci Immunol (2021) 6(55). doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abe3702 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100. Pais Ferreira D, Silva JG, Wyss T, Fuertes Marraco SA, Scarpellino L, Charmoy M, et al. Central memory Cd8(+) T cells derive from stem-like Tcf7(Hi) effector cells in the absence of cytotoxic differentiation. Immunity (2020) 53(5):985–1000 e11. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.09.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101. Bresser K, Kok L, Swain AC, King LA, Jacobs L, Weber TS, et al. Replicative history marks transcriptional and functional disparity in the Cd8(+) T cell memory pool. Nat Immunol (2022) 23(5):791–801. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01171-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102. Christo SN, Evrard M, Park SL, Gandolfo LC, Burn TN, Fonseca R, et al. Discrete tissue microenvironments instruct diversity in resident memory T cell function and plasticity. Nat Immunol (2021) 22(9):1140–51. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-01004-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103. Yang K, Kallies A. Tissue-specific differentiation of Cd8(+) resident memory T cells. Trends Immunol (2021) 42(10):876–90. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.08.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104. Konjar S, Ficht X, Iannacone M, Veldhoen M. Heterogeneity of tissue resident memory T cells. Immunol Lett (2022) 245:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2022.02.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105. Crowl JT, Heeg M, Ferry A, Milner JJ, Omilusik KD, Toma C, et al. Tissue-resident memory Cd8(+) T cells possess unique transcriptional, epigenetic and functional adaptations to different tissue environments. Nat Immunol (2022) 23(7):1121–31. doi: 10.1038/s41590-022-01229-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106. Milner JJ, Toma C, He Z, Kurd NS, Nguyen QP, McDonald B, et al. Heterogenous populations of tissue-resident Cd8(+) T cells are generated in response to infection and malignancy. Immunity (2020) 52(5):808–24 e7. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.04.007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107. Jameson SC. Maintaining the norm: T-cell homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol (2002) 2(8):547–56. doi: 10.1038/nri853 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108. Eberlein J, Davenport B, Nguyen T, Victorino F, Haist K, Jhun K, et al. Aging promotes acquisition of naive-like Cd8+ memory T cell traits and enhanced functionalities. J Clin Invest (2016) 126(10):3942–60. doi: 10.1172/JCI88546 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109. Slütter B, Van Braeckel-Budimir N, Abboud G, Varga SM, Salek-Ardakani S, Harty JT. Dynamics of influenza-induced lung-resident memory T cells underlie waning heterosubtypic immunity. Sci Immunol (2017) 2(7):eaag2031. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aag2031 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110. Wu T, Hu Y, Lee YT, Bouchard KR, Benechet A, Khanna K, et al. Lung-resident memory Cd8 T cells (Trm) are indispensable for optimal cross-protection against pulmonary virus infection. J Leukoc Biol (2014) 95(2):215–24. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0313180 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111. Mackay LK, Stock AT, Ma JZ, Jones CM, Kent SJ, Mueller SN, et al. Long-lived epithelial immunity by tissue-resident memory T (Trm) cells in the absence of persisting local antigen presentation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. (2012) 109(18):7037–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1202288109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112. Masopust D, Ha SJ, Vezys V, Ahmed R. Stimulation history dictates memory Cd8 T cell phenotype: Implications for prime-boost vaccination. J Immunol (2006) 177(2):831–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.2.831 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113. Vezys V, Yates A, Casey KA, Lanier G, Ahmed R, Antia R, et al. Memory Cd8 T-cell compartment grows in size with immunological experience. Nature (2009) 457(7226):196–9. doi: 10.1038/nature07486 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114. Martin MD, Shan Q, Xue HH, Badovinac VP. Time and antigen-stimulation history influence memory Cd8 T cell bystander responses. Front Immunol (2017) 8:634. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00634 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115. Rai D, Martin MD, Badovinac VP. The longevity of memory Cd8 T cell responses after repetitive antigen stimulations. J Immunol (2014) 192(12):5652–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1301063 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116. Martin MD, Badovinac VP. Influence of time and number of antigen encounters on memory Cd8 T cell development. Immunol Res (2014) 59(1-3):35–44. doi: 10.1007/s12026-014-8522-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117. Jabbari A, Harty JT. Secondary memory Cd8+ T cells are more protective but slower to acquire a central-memory phenotype. J Exp Med (2006) 203(4):919–32. doi: 10.1084/jem.20052237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118. Wirth TC, Xue HH, Rai D, Sabel JT, Bair T, Harty JT, et al. Repetitive antigen stimulation induces stepwise transcriptome diversification but preserves a core signature of memory Cd8(+) T cell differentiation. Immunity (2010) 33(1):128–40. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.06.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119. Park SL, Zaid A, Hor JL, Christo SN, Prier JE, Davies B, et al. Local proliferation maintains a stable pool of tissue-resident memory T cells after antiviral recall responses. Nat Immunol (2018) 19(2):183–91. doi: 10.1038/s41590-017-0027-5 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120. Beura LK, Mitchell JS, Thompson EA, Schenkel JM, Mohammed J, Wijeyesinghe S, et al. Intravital mucosal imaging of Cd8(+) resident memory T cells shows tissue-autonomous recall responses that amplify secondary memory. Nat Immunol (2018) 19(2):173–82. doi: 10.1038/s41590-017-0029-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121. von Hoesslin M, Kuhlmann M, de Almeida GP, Kanev K, Wurmser C, Gerullis A-K, et al. Secondary infections rejuvenate the intestinal Cd103(+) tissue-resident memory T cell pool. Sci Immunol (2022) 7(77):eabp9553. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abp9553 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122. Fung HY, Teryek M, Lemenze AD, Bergsbaken T. Cd103 fate mapping reveals that intestinal Cd103- tissue-resident memory T cells are the primary responders to secondary infection. Sci Immunol (2022) 7(77):eabl9925. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abl9925 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123. Van Braeckel-Budimir N, Varga SM, Badovinac VP, Harty JT. Repeated antigen exposure extends the durability of influenza-specific lung-resident memory Cd8(+) T cells and heterosubtypic immunity. Cell Rep (2018) 24(13):3374–82 e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.08.073 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124. Beura LK, Wijeyesinghe S, Thompson EA, Macchietto MG, Rosato PC, Pierson MJ, et al. T Cells in nonlymphoid tissues give rise to lymph-Node-Resident memory T cells. Immunity (2018) 48(2):327–38 e5. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.01.015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125. Stolley JM, Johnston TS, Soerens AG, Beura LK, Rosato PC, Joag V, et al. Retrograde migration supplies resident memory T cells to lung-draining ln after influenza infection. J Exp Med (2020) 217(8). doi: 10.1084/jem.20192197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126. Anthony SM, Van Braeckel-Budimir N, Moioffer SJ, van de Wall S, Shan Q, Vijay R, et al. Protective function and durability of mouse lymph node-resident memory Cd8(+) T cells. Elife (2021) 10. doi: 10.7554/eLife.68662 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127. Muenzer JT, Davis CG, Chang K, Schmidt RE, Dunne WM, Coopersmith CM, et al. Characterization and modulation of the immunosuppressive phase of sepsis. Infection Immun (2010) 78(4):1582–92. doi: 10.1128/IAI.01213-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128. Hotchkiss RS, Tinsley KW, Swanson PE, Schmieg RE, Jr., Hui JJ, Chang KC, et al. Sepsis-induced apoptosis causes progressive profound depletion of b and Cd4+ T lymphocytes in humans. J Immunol (2001) 166(11):6952–63. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.11.6952 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129. Taylor MD, Fernandes TD, Kelly AP, Abraham MN, Deutschman CS. Cd4 and Cd8 T cell memory interactions alter innate immunity and organ injury in the clp sepsis model. Front Immunol (2020) 11:563402. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.563402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130. Hoser GA, Skirecki T, Zlotorowicz M, Zielinska-Borkowska U, Kawiak J. Absolute counts of peripheral blood leukocyte subpopulations in intraabdominal sepsis and pneumonia-derived sepsis: A pilot study. Folia Histochem Cytobiol (2012) 50(3):420–6. doi: 10.5603/19751 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131. Hotchkiss RS, Nicholson DW. Apoptosis and caspases regulate death and inflammation in sepsis. Nat Rev Immunol (2006) 6(11):813–22. doi: 10.1038/nri1943 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132. Hotchkiss RS, Coopersmith CM, Karl IE. Prevention of lymphocyte apoptosis–a potential treatment of sepsis? Clin Infect Dis (2005) 41 Suppl 7:S465–9. doi: 10.1086/431998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133. Sun Y, Anyalebechi JC, Sun H, Yumoto T, Xue M, Liu D, et al. Anti-tigit differentially affects sepsis survival in immunologically experienced versus previously naive hosts. JCI Insight (2021) 6(5). doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.141245 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134. Grayson JM, Harrington LE, Lanier JG, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R. Differential sensitivity of naive and memory Cd8+ T cells to apoptosis in vivo. J Immunol (2002) 169(7):3760–70. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.7.3760 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135. Duong S, Condotta SA, Rai D, Martin MD, Griffith TS, Badovinac VP. Polymicrobial sepsis alters antigen-dependent and -independent memory Cd8 T cell functions. J Immunol (2014) 192(8):3618–25. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1303460 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136. Serbanescu MA, Ramonell KM, Hadley A, Margoles LM, Mittal R, Lyons JD, et al. Attrition of memory Cd8 T cells during sepsis requires lfa-1. J Leukocyte Biol (2016) 100(5):1167–80. doi: 10.1189/jlb.4A1215-563RR [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137. Jensen IJ, Sjaastad FV, Griffith TS, Badovinac VP. Sepsis-induced T cell immunoparalysis: The ins and outs of impaired T cell immunity. J Immunol (2018) 200(5):1543–53. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1701618 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138. Moioffer SJ, Berton RR, McGonagill PW, Jensen IJ, Griffith TS, Badovinac VP. Inefficient recovery of repeatedly stimulated memory Cd8 T cells after polymicrobial sepsis induction leads to changes in memory Cd8 T cell pool composition. J Immunol (2023) 210(2):168–179. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200676 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139. Danahy DB, Anthony SM, Jensen IJ, Hartwig SM, Shan Q, Xue HH, et al. Polymicrobial sepsis impairs bystander recruitment of effector cells to infected skin despite optimal sensing and alarming function of skin resident memory Cd8 T cells. PloS Pathog (2017) 13(9):e1006569. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006569 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140. Arina A, Beckett M, Fernandez C, Zheng W, Pitroda S, Chmura SJ, et al. Tumor-reprogrammed resident T cells resist radiation to control tumors. Nat Commun (2019) 10(1):3959. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11906-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141. Sjaastad FV, Jensen IJ, Berton RR, Badovinac VP, Griffith TS. Inducing experimental polymicrobial sepsis by cecal ligation and puncture. Curr Protoc Immunol (2020) 131(1):e110. doi: 10.1002/cpim.110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142. Moioffer SJ, Danahy DB, van de Wall S, Jensen IJ, Sjaastad FV, Anthony SM, et al. Severity of sepsis determines the degree of impairment observed in circulatory and tissue-resident memory Cd8 T cell populations. J Immunol (2021) 207(7):1871–81. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2001142 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143. Condotta SA, Rai D, James BR, Griffith TS, Badovinac VP. Sustained and incomplete recovery of naive Cd8+ T cell precursors after sepsis contributes to impaired Cd8+ T cell responses to infection. J Immunol (2013) 190(5):1991–2000. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1202379 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144. Jensen IJ, Li X, McGonagill PW, Shan Q, Fosdick MG, Tremblay MM, et al. Sepsis leads to lasting changes in phenotype and function of memory Cd8 T cells. Elife (2021) 10. doi: 10.7554/eLife.70989 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145. Unsinger J, Burnham CA, McDonough J, Morre M, Prakash PS, Caldwell CC, et al. Interleukin-7 ameliorates immune dysfunction and improves survival in a 2-hit model of fungal sepsis. J Infect Dis (2012) 206(4):606–16. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis383 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146. Unsinger J, McGlynn M, Kasten KR, Hoekzema AS, Watanabe E, Muenzer JT, et al. Il-7 promotes T cell viability, trafficking, and functionality and improves survival in sepsis. J Immunol (2010) 184(7):3768–79. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0903151 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147. Francois B, Jeannet R, Daix T, Walton AH, Shotwell MS, Unsinger J, et al. Interleukin-7 restores lymphocytes in septic shock: The iris-7 randomized clinical trial. JCI Insight (2018) 3(5). doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.98960 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148. Cabrera-Perez J, Condotta SA, James BR, Kashem SW, Brincks EL, Rai D, et al. Alterations in antigen-specific naive Cd4 T cell precursors after sepsis impairs their responsiveness to pathogen challenge. J Immunol (2015) 194(4):1609–20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401711 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149. Berg RE, Cordes CJ, Forman J. Contribution of Cd8+ T cells to innate immunity: Ifn-Γ secretion induced by il-12 and il-18. Eur J Immunol (2002) 32(10):2807–16. doi: [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150. Berg RE, Crossley E, Murray S, Forman J. Memory Cd8+ T cells provide innate immune protection against listeria monocytogenes in the absence of cognate antigen. J Exp Med (2003) 198(10):1583–93. doi: 10.1084/jem.20031051 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151. Freeman BE, Hammarlund E, Raué H-P, Slifka MK. Regulation of innate Cd8(+) T-cell activation mediated by cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci (2012) 109(25):9971–6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1203543109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152. Martin MD, Jensen IJ, Ishizuka AS, Lefebvre M, Shan Q, Xue HH, et al. Bystander responses impact accurate detection of murine and human antigen-specific Cd8 T cells. J Clin Invest (2019) 129(9):3894–908. doi: 10.1172/JCI124443 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]