Abstract
Background
Vancomycin (VCM) has long been used clinically to fight against Gram-positive bacterial infections. In recent decades, an increased number of kidney injury cases caused by VCM overdose have been reported. In this study, we further investigated the mechanism of VCM-overdose-induced kidney injury.
Methods
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining, RT-qPCR and Western blot assays were used to determine ki67, DDX5, PTGS2, GPX4 and SLC7A11 expressions in the kidney tissues of mice. CCK-8 and flow cytometry assays were used to determine HK2 cell viability and apoptosis. In addition, RT-qPCR and Western blot assays was applied to evaluate the expressions of ACSL4, PTGS2, GPX4, SLC7A11, DDX5 and Ki67 in HK2 cells.
Results
We found that VCM induced ferroptosis in vitro and in vivo. Ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1) is a potent inhibitor of ferroptosis, Fer-1 rescued cell viability and renal function renal morphology in VCM-treated cells and mice, respectively. Further, GPX4, which plays an essential role in reducing lipid hydroperoxides and preventing ferroptosis, was observed to be downregulated by VCM treatment. Interestingly, we found that GPX4-knockdown HK-2 cells exhibited a similar phenotype and gene expression level of ACSL4, PTGS2, DDX5 and Ki67 compared with VCM-treated cells, which suggested that VCM could induce ferroptosis in HK2 cells by down-regulating GPX4.
Conclusion
In conclusion, VCM induced renal injury in the kidney tissues of mice. In addition, VCM induced ferroptosis cell death in HK-2 cells and in the kidney tissues of mice by down-regulating GPX4 and causing the accumulation of peroxides. These data suggested that VCM could induce renal injury in vitro and in vivo via triggering ferroptosis. This study further elucidates the mechanism of VCM-induced renal injury and provides additional references for clinical use of VCM.
Keywords: vancomycin, ferroptosis, glutathione peroxidase 4, reactive oxygen species, kidney injury
Introduction
The kidney is the main excretory organ for many drugs and is easily exposed to toxins. Therefore, kidney injury is closely related to the loss of excretion and detoxification functions. In serious cases, persistent kidney injury can result in irreversible death of kidney cells and nephrons, leading to chronic kidney diseases.1 It has been reported that some drugs, such as cisplatin and vancomycin (VCM), could induce nephrotoxicity, and approximately 30% of patients being treated with VCM will develop acute kidney injury.2,3
VCM, previously known as compound 05865, was found in the 1950s. It was originally isolated from Streptomyces orientalis and has been an effective inhibitor of infections caused by most gram-positive organisms.4 VCM has been more frequently used in the last decade due to the increased infections caused by penicillin-resistant organisms.5 However, VCM overdose can put a heavy burden on the kidney, which may even cause serious kidney injury. A series of cohort and retrospective studies have shown that the incidence of nephrotoxicity is dependent on the dose of VCM.3 In addition, several clinical studies have reported risk factors associated with VCM-induced nephrotoxicity, including the maximal dose of VCM, the loading dose of VCM, the administration method, and the duration of VCM treatment.6 Furthermore, VCM can also promote reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in rat kidney.7 Despite these associations between VCM usage and kidney injury, the mechanism underlying VCM-induced nephrotoxicity remains unclear.
Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent, programmed necrosis caused by the accumulation of intracellular lipid ROS. Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) is a member of the glutathione peroxidase family, which distributed on membrane structures in the cell and has the effect of antagonizing elevated lipid ROS and inhibiting ferroptosis.8 Ferroptosis is an iron-dependent form of programmed cell death. Its main mechanism is that when the intracellular antioxidant system is damaged, ferroptosis is catalyzed by iron divalent or ester oxygenase. Phospholipid molecules containing long chains of unsaturated fatty acids (PUFA-PLS) on the cell membrane system can induce lipid peroxidation, which leads to cell death.9 Accumulation of ROS may cause imbalance of lipid regulation. We speculated that ferroptosis plays a vital role in VCM-induced nephrotoxicity.
Therefore, we aimed to explore how VCM could induce kidney injury in vivo and in vitro via triggering ferroptosis. Meanwhile, we investigated the mechanism by which VCM induces ferroptosis in vivo and in vitro.
Materials and Methods
Animal Model
VCM (400 mg/kg/day) was injected intraperitoneally into C57BL/6J mice for 7 consecutive days to construct a mouse model of kidney injury.10 Erastin (10 mg/kg/day), which is a known ferroptosis inducer that functions by depleting glutathione (GSH), was intraperitoneally injected into the mice following the same scheme to establish a positive group. To test the effects of Fer-1 on mice treated with VCM, VCM (400 mg/kg/day) and Fer-1 (1 mg/kg/day) were intraperitoneally injected into the mice at the same time for 7 consecutive days. In the blank control group, phosphate buffered saline (PBS, pH=7.4) was intraperitoneally injected simultaneously. Kidney tissues were then obtained from mice of different groups for weighing and further analyses. The kidney tissues were subsequently made into slices, which were stained with hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) to observe histopathological changes and with specific antibodies to evaluate protein expression in situ following Bushwillow’s protocol. Protein and RNA were also extracted from the kidney tissues for Western blotting and quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analyses following previously published protocols.11 Animal study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of experimental Animal Management and Ethics Committee, Shanghai Children’s Hospital (NO.SHCH-IACUC-2022-XMSB-34) and performed according to the ARRIVE guidelines and the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS) Staining
The kidney tissues were fixed with 4% buffered paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, and cut into 2-μm-thick sections, which were stained with the PAS Stain Kit (Abcam, USA, Cat. No. ab150680) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions.12
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining
The kidney tissues were fixed with 4% buffered paraformaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, and cut into 2-μm-thick sections for staining with the Ultra Vision Quanto Detection System HRP DAB kit (Thermo Scientific, Fremont, CA, USA) and being probed with primary antibodies of anti-Ki67 (1:200 dilution, 27309-1-AP, Proteintech, China), anti-DEAD-box helicase 5 (DDX5) (1:100 dilution, 10804-1-AP, Proteintech, China), anti-GPX4 (1:100 dilution, 14432-1-AP, Proteintech, China), anti-prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2) antibody (1:200 dilution, ab179800, Abcam, China), in accordance with the manufacturers’ instructions.13
Cell Culturing and VCM Treatment
The HK-2 cell line was obtained from Shanghai Zhong Qiao Xin Zhou Biotechnology (China) and maintained in high-glucose Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator. At 70% confluency, HK-2 cells were treated with different concentrations (2 mM, 4 mM and 6 mM) of VCM for 24 h and harvested for further analyses. Erastin (5 mM) was used to treat the cells to generate a positive group. To test if VCM was responsible for the decline in cell viability, HK-2 cells were treated simultaneously with both Fer-1 (1 mM) and VCM for 24 h and harvested for further analyses.14
Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) Assay
The viability of HK-2 cells with different treatments was detected by CCK-8 (C0038, Beyotime, China). In brief, the harvested cells were seeded into a 96-well plate and incubated with the CCK-8 solution at 37 °C for 2 h. Then the optical absorbance of each well was measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader. and the survival rate of cells was calculated. Cell viability (%) = A (dosing)/B (undosed) ×100%. A (dosing): Absorbance of pores with cells, CCK-8 and drug solution. B (undosed): Absorbance of pores with cells, CCK-8 and drug-free solution. Using cell viability rate as the horizontal axis and logarithm of drug concentration as the horizontal axis to make semi-logarithm plots, calculated by plotting method via GraphPad prism software 9.0.15
Propidium Iodide (PI) Staining
For monolayer HK-2 cells, the cell culture medium was removed, and the cells were washed twice with PBS (pH=7.4). Afterwards, a PI working solution (0.5 mg/mL in PBS) was added into the cells for incubation for 15 minutes at room temperature. Then the cells were observed with a fluorescence microscope (ECLIPSE NI, NIKON, JAPAN) at the excitation wavelength of 488 nm.
Annexin V/PI Staining for Flow Cytometry Analysis
The HK-2 cells were digested with trypsin-EDTA, collected, and washed with PBS twice. Then the cells were incubated in a 400-μL mixture of PI (4 μg/mL) and Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) (4 μg/mL) for 30 minutes in the dark at room temperature. Afterwards, 400 μL PBS was used to gently resuspend the cells. At last, the cells were analyzed by flow cytometry.16
Total Protein Extraction and Western Blotting
HK-2 cells were incubated in a radio immunoprecipitation assay (RIPA) lysis buffer (P0013C, Beyotime, China) containing phenylmethanesulfonylfluoride (PMSF, 1mM) at 4 °C for 10 minutes to extract total protein. The total protein samples were denatured in a boiling water bath for 10 minutes and quantified by the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay following the standard instructions. The concentration of the protein samples was adjusted to 2 mg/mL before performing sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE). The protein samples separated by SDS-PAGE were transferred onto polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membranes. After blocking the membranes with 5% skim milk in phosphate-buffered saline with Tween 20 (PBST) for 1 h, the membranes were incubated in primary antibodies, including the anti-DDX5 antibody (1:1000 dilution, 10804-1-AP, Proteintech, China), anti-GPX4 antibody (1:1000 dilution, 67763-1-Ig, Proteintech, China), anti-acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4) antibody (1:1000 dilution, ab81150, Abcam, USA), anti-Ki67 antibody (1:1000 dilution, 27309-1-AP, Proteintech, China), anti-PTGS2 antibody (1:500 dilution, ab179800, Abcam, USA), anti-solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) antibody (1:1000 dilution, 26864-1-AP, Proteintech, China), and anti-Tubulin antibody (1:8000 dilution, AF0001, Beyotime, China) at 4 °C overnight. After rinsing the membranes three times with PBST (10 minutes each time), the membranes were incubated in the corresponding horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated secondary antibody (1:1000 dilution) for 1 h at room temperature. After rinsing the membranes three times with PBST (10 minutes each time), the protein bands on the membranes were visualized using the Super Signal West Pico kit (Pierce).15
Total RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
Total RNA was extracted with the TRIzol reagent following the standard instructions. The purified RNA was treated with DNase to remove DNA contamination and the first strand of cDNA was synthesized using a cDNA synthesis kit (11123ES60, Yeasen, China). The synthesized cDNA was used as a template for qRT-PCR using the SYBR-Green Real-Time PCR Master Mix (11202ES08, Yeasen, China). GAPDH was utilized as the internal reference gene for normalization of target gene expression. The RT-qPCR primers are listed in Table 1.17
Table 1.
Primer Sequences
| Name | Primer Sequences | |
|---|---|---|
| Ki67 | Forward | 5’-AAACCCCACCAAGTAAAACA-3’ |
| Reverse | 5’-CCAAGGCAAGCTCAGGAC-3’ | |
| GPX4 | Forward | 5’-AGTGGATGAAGATCCAACCCAAGG-3’ |
| Reverse | 5’-GGGCCACACACTTGTGGAGCTAGA3’ | |
| PTGS2 | Forward | 5’-TGACCAGAGCAGGCAGATGA-3’ |
| Reverse | 5’-CCAGTAGGCAGGAGAACATATAACA-3’ | |
| SLC7A11 | Forward | 5’-GTCTGGAGAAACAGCCAAGG-3’ |
| Reverse | 5’-CGGAGTTCCTCGAATAGCTG-3’ | |
| ACSL4 | Forward | 5’-GTAATTGGTGGACAGAACATC-3’ |
| Reverse | 5’-TACTCTCCTGCTTGTAACTTC-3’ | |
| GAPDH | Forward | 5’-AAAGAAGCTCAACTACATGG-3’ |
| Reverse | 5’-TGCAAAGAATGCGTCCCAGAG-3’ |
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
The production of the cellular labile iron pool (LIP) was determined through assessing intracellular iron concentration by using an iron assay kit (Abcam, ab83366). In addition, ROS (cat. no. E004), and GSH (cat. no. A006) was determined using commercial ELISA kits (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, China) according to the manufacturers’ instructions.18
siRNA Transfection
The siRNA targeting GPX4, and a non-targeting negative control (NC) siRNA were purchased from General BIOL. The sequence of siRNA NC is: 5’-GACTCACGTGGTAAGGAGCTCAATT-3’. The sequence of GPX4-specific siRNA is: 5’-GGAUGAAAGUCCAGCCCAATT-3’. These siRNAs were transfected into HK-2 cells at 70% confluency by Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen, USA). For the inhibition of ferroptosis, the transfected cells were incubated with Fer-1 (1 mM) for 72 h.19
Statistical Analysis
Each experiment was repeated three times. All data are presented as mean ± standard deviation. Differences among multiple groups were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance and Tukey’s post-hoc test. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Fer-1 Reverses VCM-Induced Renal Injury in Mice
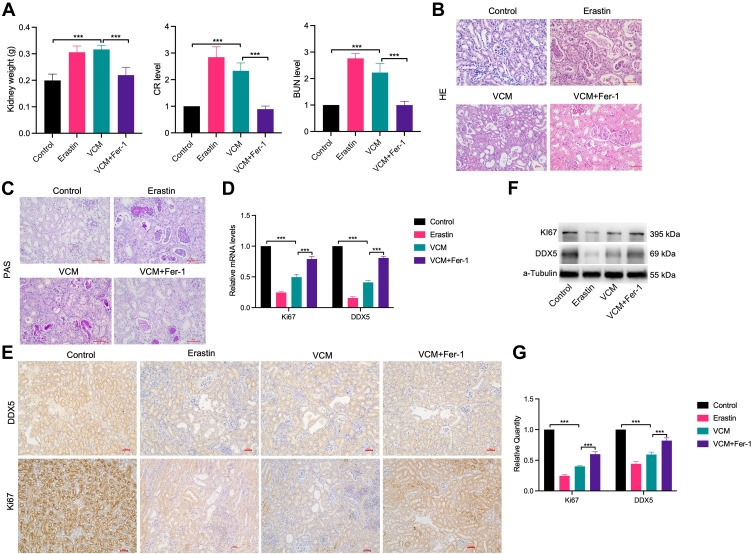
Substantial studies have demonstrated that ferroptosis of renal tubular cells significantly contributes to the process of kidney injury.20 To explore the role of ferroptosis in VCM- induced kidney injury, we constructed a kidney injury model by treating mice with 200 mg/kg VCM. Compared with the mice in the control group, which were injected with normal saline, the kidney tissues of mice treated with VCM were pale and swollen, indicating abnormal kidney morphology. We weighed the kidneys isolated from VCM-treated and erastin-treated mice and found that they were significantly heavier than those from control mice. In addition, Fer-1 treatment significantly reduced the kidney weight in VCM-treated mice (Figure 1A). Additionally, the levels of serum CR and BUN were elevated in VCM-treated mice, while Fer-1 reduced serum CR and BUN levels in VCM-treated mice (Figure 1A). These findings indicated that the abnormal kidney function induced by VCM was reversed by Fer-1 treatment. H&E staining showed that in the VCM-treated group was significantly enlarged and the the nucleus shrinks, dissolves, and disappears. Necrotic renal tubular epithelial cells shed into the lumen, showing fuzzy granular structures, similar to the pathological features of the Erastin-treated group, while Fer-1 reversed the enlarged kidney luminal area induced by VCM treatment (Figure 1B). The results of PAS staining (Figure 1C) showed swollen renal tissue and obvious collagen deposition in the glomerulus of the VCM-treated mice. These pathological changes were reversed by Fer-1. Furthermore, RT-qPCR, immunohistochemistry staining and Western blot assays revealed a decreased level of Ki67 in VCM-treated mice, while Fer-1 rescued the downregulated expression of Ki67 induced by VCM (Figure 1D–G). Taken together, the above results demonstrated that VCM treatment caused renal injury in mice, reduced renal cell viability, and promoted renal cell death. Fer-1 is an inhibitor of ferroptosis, in addition, Fer-1 treatment reversed all the aforementioned effects induced by VCM treatment.
Figure 1.
VCM caused obvious renal injury in C57BL/6J mice, while Fer-1 treatment reversed the harmful effects of VCM. (A) The dissected renal tissue was weighed after injection of VCM. After VCM injection, the weight of renal tissue increased. In addition, serum CR and BUN levels in mice were assessed by ELISA. (B) H&E staining (400×) showed that the mice injected with VCM had significantly enlarged lumen areas in the kidney, which were reversed by Fer-1 treatment. (C) PAS staining showed swollen glomerulus with obvious collagen deposition in the kidney tissues of mice injected with VCM. Expression levels of Ki67 and DDX5 in the kidney tissues of mice measured by (D) qRT-PCR analysis, (E) immunohistochemistry staining (200×), (F) Western blotting analysis and (G) quantification of Western blotting results. The results showed that the mRNA and protein levels of Ki67 and DDX5 decreased in the kidney tissues of mice injected with VCM. Moreover, Fer-1 treatment restored the expression of Ki67 and DDX5 at the mRNA and protein levels. ***P<0.001.
GPX4 Was Downregulated in Mice Injected with VCM
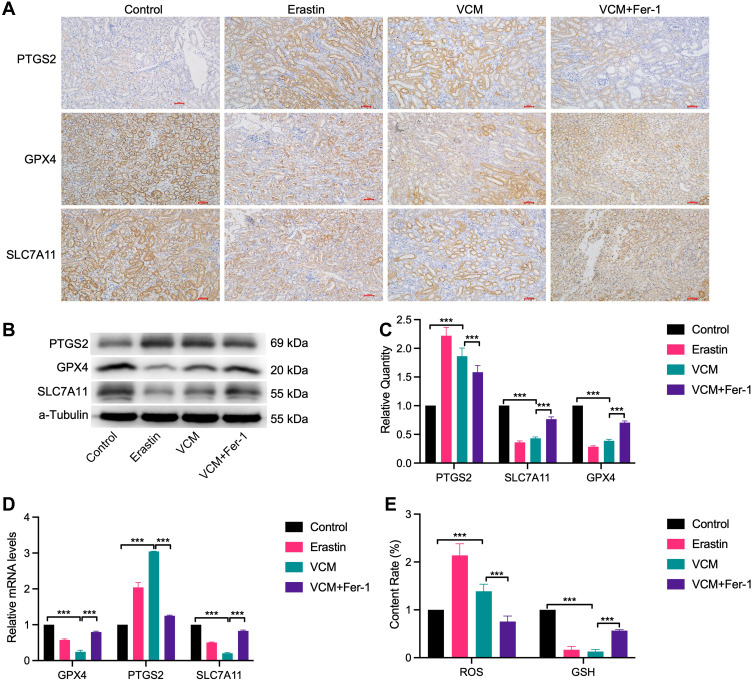
To further explore whether VCM induces ferroptosis in renal cells, we determined the expression levels of ferroptosis-related genes in VCM-treated mice. As expected, the expressions of GPX4 and SLC7A11 were down-regulated at both the mRNA and protein levels in VCM-treated mice, while the mRNA and protein levels of PTGS2 were up-regulated (Figure 2A–D). In addition, Fer-1 up-regulated GPX4 and SLC7A11 levels and down-regulated PTGS2 level in VCM-treated mice (Figure 2A–D). Next, we obtained the serum of experimental mice and determined the contents of ROS and GSH, which are indicators for ferroptosis. In the serum of mice treated with VCM, ROS content was up-regulated, while GSH content was down-regulated; Fer-1 restored the serum levels of ROS and GSH (Figure 2E). Overall, VCM treatment induced a ferroptosis-like phenotype in mouse kidneys.
Figure 2.
VCM caused renal injury via inducing ferroptosis cell death in animals. (A) IHC staining showed that GPX4 and SLC7A11 were downregulated and PTGS2 was upregulated in the kidney tissues of VCM-treated mice. In addition, Fer-1 restored the expressions of GPX4 and SLC7A11 and reduced the expression of PTGS2 in mice injected with VCM. Expression levels of PTGS2, GPX4 and SLC7A11 in the kidney tissues of mice measured by (B) Western blotting analysis and (C) quantification of Western blotting results, (D) qRT-PCR analysis. The results indicated that VCM increased the expression of PTGS2 and decreased the expression of GPX4 and SLC7A11 at the mRNA and protein levels in the kidney tissues of mice. In addition, Fer-1 treatment restored the expression of GPX4 and SLC7A11 and decreased the expression of PTGS2 at the mRNA and protein levels in the kidney tissues of VCM-treated mice. (E) ELISA results revealed the accumulation of ROS and the reduction of GSH content in the serum of VCM-treated mice. Fer-1 treatment reversed the effects of VCM on serum ROS and GSH contents. ***P<0.001.
VCM Induced HK-2 Cell Death
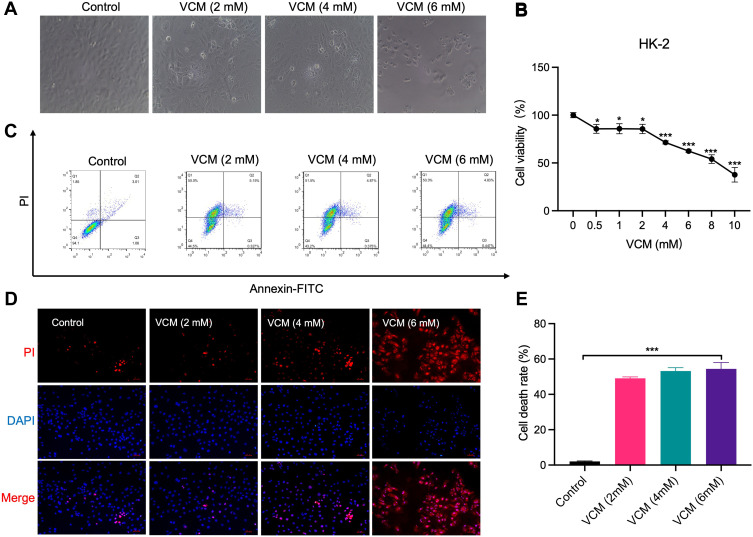
HK-2 is a normal human kidney proximal tubular cell line. We attempted to investigate the effects of VCM on the kidney in vitro by treating HK-2 cells with different concentrations of VCM and monitoring the cells’ morphology and viability. Under a bright-field microscope, the VCM-treated HK-2 cells appeared more coarse and shorter (Figure 3A). The number of cells in the VCM-treated group was significantly lower compared with the control group (Figure 3A). The cell viability was examined by CCK-8 assay. As expected, VCM reduced the viability of HK-2 cells to different degrees (Figure 3B). 2, 4, and 6 mM VCM induced about 15%, 29% and 38% growth inhibition in HK2 cells, suggesting that VCM obviously reduced the viability of HK-2 cells (Figure 3B). We selected different concentrations (2 mM, 4 mM and 6 mM) of VCM for further analyses. We further determined the viability of HK-2 cells by PI staining. As shown in Figure 3D, the number of PI-positive cells was significantly higher in the VCM-treated group compared with the control group and that number increased dose-dependently with VCM. To further examine whether the decreased cell number in the VCM-treated group was a result of apoptosis, we carried out flow cytometry analyses. Compared with the control group, the ratio of apoptotic HK-2 cells was not significantly increased by VCM treatment. Instead, the proportion of dead cells increased in the VCM-treated group (Figure 3C and E), which was consistent with the findings of CCK-8 assay and PI staining. These results demonstrated that VCM induced non-apoptotic HK-2 cell death.
Figure 3.
VCM induced HK-2 cell death. (A) Morphological changes of HK-2 cells caused by low concentrations of VCM (2–6 mM). (B) CCK-8 assays revealed decreased viability of HK-2 cells caused by different concentrations of VCM. (C) Flow cytometry analysis revealed VCM-induced HK-2 cell death. (D) Fluorescence microscopy showed more PI-positive cells after treatment with different concentrations of VCM. Bar graph, 50 μm. (E) Statistical analysis of the flow cytometry results. *P<0.05, *** P<0.001.
Figure 4.
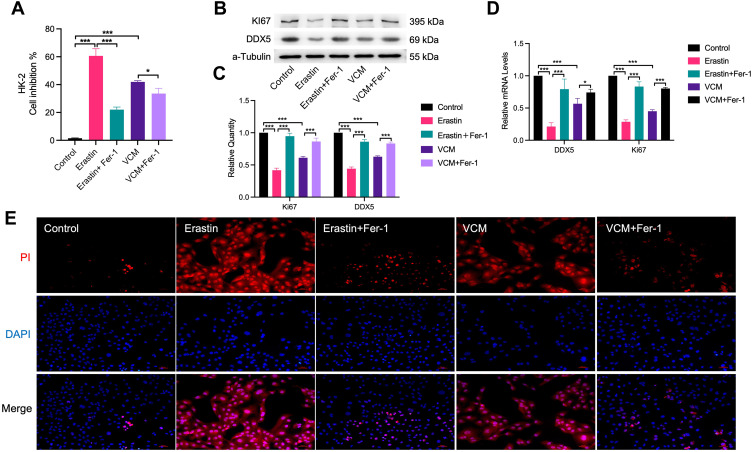
Fer-1 restored the viability of HK-2 cells. The (A) cell viability, (B) Ki67 and DDX5 protein levels, and (C) Ki67 and DDX5 mRNA levels measured by CCK-8, Western blotting analysis and qRT-PCR analysis, respectively, of VCM-treated HK-2 cells were restored by Fer-1 co-treatment. (D) Quantification of Western blotting results. (E) Fluorescence microscopy showed less PI-positive cells in the Fer-1 co-treatment groups. *P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
Figure 6.
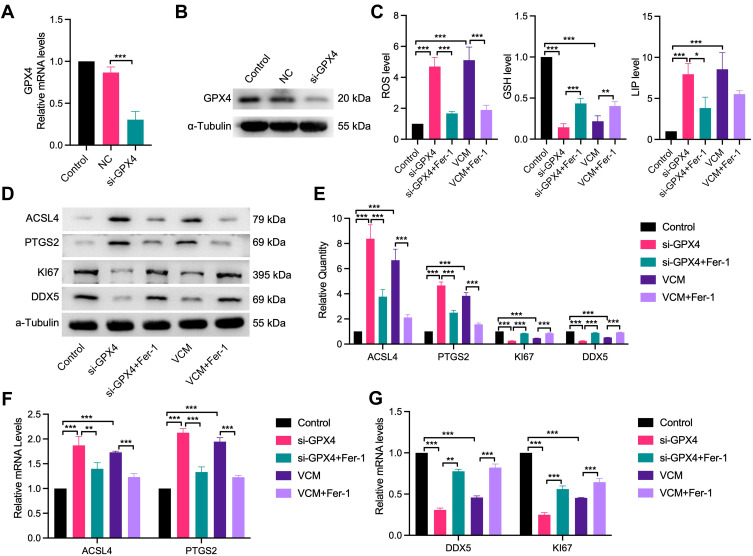
VCM induced ferroptosis in HK-2 cells through downregulation of GPX4. HK-2 cells were transfected with siRNA NC or GPX4 siRNA (si-GPX4) for 24 h. (A) qRT-PCR and (B) Western blotting results confirming the knockdown efficiency of the GPX4-specific siRNA. (C) ELISA results revealing the contents of ROS, GSH and LIP in HK-2 cells. We observed that the contents of ROS and LIP increased, while that of GSH decreased in GPX4-KD HK-2 cells. Furthermore, Fer-1 co-treatment inhibited the accumulation of LIP and ROS and restored the content of GSH partly in GPX4-KD HK-2 cells. Expression levels of ACSL4, PTGS2, Ki67 and DDX5 in HK-2 cells measured by (D) Western blotting analysis, (E) quantification of Western blotting results and (F) qRT-PCR analysis. (G) qRT-PCR analysis of DDX5 and Ki67 at the mRNA level. The results revealed that GPX4 knockdown in HK-2 cells increased the expression of ACSL4 and PTGS2 and decreased the expression of DDX5 and Ki67 at the mRNA and protein levels. In addition, Fer-1 decreased the expression of ACSL4 and PTGS2 and restored the expression of DDX5 and Ki67 at the mRNA and protein levels in GPX4-KD HK-2 cells. These results were consistent with those observed in VCM-treated HK-2 cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
Fer-1 Restored the Viability of VCM-Treated HK-2 Cells
We speculated that Fer-1 could rescue the viability of VCM-treated HK-2 cells. To test this hypothesis, we treated HK-2 cells with VCM and Fer-1 at the same time and determined the cell viability. Excitingly, we found that Fer-1 indeed successfully rescued the viability of HK-2 cells treated with VCM and Erastin (Figure 4A). These results implied that ferroptosis might play an important role in renal injury induced by VCM. Furthermore, the mRNA and protein levels of Ki67, a marker of cell proliferation, and DDX5 (Involved in gene expression regulation and ATP-dependent RNA helicase activity, participates in proliferation-related regulation) were up-regulated after Fer-1 treatment in VCM-treated HK-2 cells (Figure 4B–D). At the same time, the ratio of PI-positive cells was reduced after Fer-1 treatment compared with cells treated with VCM only (Figure 4E).
VCM Promoted the Accumulation of LIP and ROS
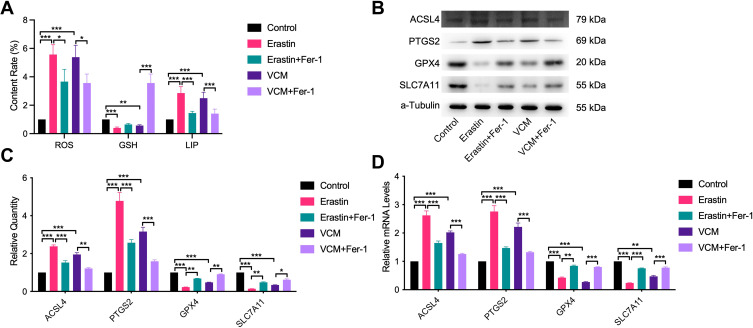
Lipid peroxidation by itself is sufficient to induce ferroptosis.21 There are many reasons for an increase in LIP, which is an important ferroptosis feature. The imbalance of LIP in vivo usually causes the accumulation of ROS. We have shown that Fer-1 can successfully rescue the viability of VCM-treated HK-2 cells. Based on this finding, we hypothesized that the cytotoxicity of VCM was closely associated with ferroptosis. To test this hypothesis, we first determined the contents of LIP and ROS in VCM-treated HK-2 cells by ELISA. The results indicated that both LIP and ROS were increased in VCM-treated HK-2 cells (Figure 5A). In contrast, the contents of LIP and ROS decreased after the addition of Fer-1 in VCM-treated HK-2 cells (Figure 5A).
Figure 5.
VCM promoted the accumulation of LIP and ROS and regulated the expression of ferroptosis-related proteins ACSL4, PTGS2, GPX4 and SLC7A11 in HK-2 cells. (A) ELISA results revealing the contents of ROS, GSH and LIP in HK-2 cells. We found that the contents of ROS and LIP increased, while that of GSH decreased in VCM-treated HK-2 cells. Furthermore, Fer-1 co-treatment inhibited the accumulation of LIP and ROS and restored the content of GSH partly in VCM-treated HK-2 cells. Expression levels of ACSL4, PTGS2, GPX4 and SLC7A11 in HK-2 cells measured by (B) qRT-PCR analysis, (C) Western blotting analysis and (D) quantification of Western blotting results. The findings exhibited that VCM induced the expression of ACSL4 and PTGS2 while reduced the expression of GPX and SLC7A11 at the mRNA and protein levels in HK-2 cells. In addition, Fer-1 co-treatment decreased the expression of ACSL4 and PTGS2 and restored the expression of GPX and SLC7A11 at the mRNA and protein levels in VCM-treated HK-2 cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
GSH is one of the most significant reducing agents for hydrogen peroxide detoxification.22 As shown in Figure 5A, the intracellular concentration of GSH was reduced after VCM treatment, suggesting that the content of GSH in cells decreased in VCM-treated HK-2 cells, while Fer-1 restored the concentration of GSH in VCM-treated HK-2 cells. It has been previously reported that GPX4, ACSL4, PTGS2, and SLC7A11 are proteins correlated with ferroptosis. We therefore evaluated their expression at the mRNA and protein levels. We noticed that ACSL4 and PTGS2 were up-regulated, while GPX4 and SLC7A11 were down-regulated after VCM treatment (Figure 5B–D). These observations were similar to those obtained from Erastin-treated HK-2 cells. Thus, these results confirmed that VCM-induced cell death was closely associated with ferroptosis.
VCM Induced Ferroptosis in HK-2 Cells Through Downregulation of GPX4
GPX4 is a well-known GSH peroxidase in mammals. It is the only enzyme capable of converting lipid hydroperoxyl derivatives (L-OOH) to lipid hydroxy derivatives (L-OH).23 To explore the effect of VCM on ferroptosis in HK-2 cells, as displayed in Figure 5A and C, we found that the levels of GSH and GPX4 reduced simultaneously in VCM-treated HK-2 cells. We therefore tested whether the ferroptosis of VCM-treated HK-2 cells were induced by the reduction of GPX4 expression. We knocked down GPX4 in HK-2 cells using a GPX4-specific siRNA and validated the knockdown effects with qRT-PCR and Western blotting analyses (Figure 6A and B). We observed downregulation of Ki67 and DDX5 and upregulation of ACSL4 and PTGS2 at the mRNA and protein levels in GPX4-knockdown (GPX4-KD) HK-2 cells (Figure 6D–G). As a result, the proliferation of GPX4-KD HK-2 cells was decreased. These results were consistent with those observed in VCM-treated HK-2 cells. At the same time, we observed the accumulation of LIP and ROS and the reduction of GSH concentration by ELISA (Figure 6C) in GPX4-KD HK-2 cells, which, again, resembled the findings in VCM-treated HK-2 cells. More importantly, Fer-1 co-treatment successfully reversed the adverse effects of GPX4 knockdown on HK-2 cells by enhancing Ki67 and DDX5 expression, decreasing ACSL4 and PTGS2 expression, reducing LIP and ROS contents, and increasing intracellular GSH concentration (Figure 6C), again resembling the observations in VCM-treated HK-2 cells. Taken together, these findings suggested that VCM induced ferroptosis in HK-2 cells through downregulation of GPX4.
Discussion
VCM has long been used clinically to fight against Gram-positive bacterial infections. With the emergence of drug-resistant micro-organisms, a higher dose of VCM has been adopted, resulting in severe kidney injury. It has been reported that VCM could induce ROS accumulation in the kidney of rats, and that the aberrant accumulation of ROS induced ferroptosis in many types of cells and tissues, including kidney tissues.24–27
To explore the influence of VCM administration on mice, a mouse model of VCM-induced renal injury was constructed. By H&E staining and PAS staining of mouse kidneys, as expected, the mice injected with VCM showed enlarged kidney luminal regions compared with the mice in control group; however, that change was restored by a ferroptosis inhibitor Fer-1. Moreover, Fer-1 obviously reduced serum CR and BUN levels in VCM-treated mice. Xie et al showed that Fer‑1 could alleviate oxalate‑induced renal injury through suppressing ferroptosis.28 These data indicated that VCM treatment could result in mouse kidney injury by inducing ferroptosis in vivo.
In the present study, we also demonstrated that VCM treatment induced HK2 cell death and LIP and ROS accumulation in HK-2 cells, while the effects of VCM treatment were reversed when the cells were co-treated with Fer-1. These results confirmed that VCM caused renal cell death through inducing ferroptosis. To further verify this conclusion, we examined the expression levels of ferroptosis-related proteins in vitro and in vivo before and after VCM treatment. We found that the expression level of PTGS2 was up-regulated, but GPX4 and SLC7A11 expressions were repressed in the kidney tissues of mice or HK2 cells upon VCM treatment. Surprisingly, inhibiting ferroptosis by Fer-1 enhanced GPX4 and SLC7A11 levels, but reduced PTGS2 level in VCM-treated mice or VCM-treated HK2 cells. These results verified that inhibiting ferroptosis could attenuate VCM-induced kidney injury in vitro and in vivo.
Iron-dependent lipid peroxidation is a hallmark of ferroptosis.29 As an essential enzyme responsible for reducing lipid peroxides, GPX4 depletion is lethal in mice.30 In our experiments, we detected a decrease in GPX4 expression in VCM-treated HK-2 cells. We further speculated whether VCM-induced ferroptosis was caused by the downregulation of GPX4. Thus, we tested this hypothesis by knocking down GPX4 with a specific siRNA in HK-2 cells. Knockdown of GPX4 elevated LIP and ROS level and increased ACSL4 and PTGS2 expressions in HK-2 cells, suggesting that downregulation of GPX4 could induce ferroptosis in HK-2 cells. However, these changes were reversed by Fer-1 treatment. In addition, it has been shown that downregulation of GPX4 could aggravate ischemia reperfusion-induced renal injury in mice.31 These results indicated that VCM could induce ferroptosis in HK-2 cells through down-regulating GPX4, which in turn promote renal injury.
ACSL4 is a member of the acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family which catalyzes fatty acids to produce acyl-CoA. Interestingly, ACSL4 also plays an essential role in induction of ferroptosis.32 ACSL4 facilitates the accumulation of LIP during Erastin-induced ferroptosis.18 In addition, knockdown of ACSL4 increases the resistance to ferroptosis.33 Therefore, ACSL4 has been regarded as a biomarker of ferroptosis. In our study, ACSL4 was up-regulated during VCM treatment, suggesting that VCM could induce ferroptosis in vitro and in vivo via upregulating ACSL4.
SLC7A11 facilitates cystine uptake and glutamate release to promote glutathione synthesis and maintain the redox balance.34 Inhibition of SLC7A11 is accompanied by the accumulation of ROS, which in turn promote tissue injury.35,36 In this study, we found that VCM inhibited the expression of SLC7A11 both in HK-2 cells and in the kidney tissues of mice. These findings indicated that VCM induce ferroptosis in vitro and in vivo via downregulating SLC7A11.
In this study, 400 mg/kg VCM was used to establish a mouse model with kidney injury.37 According to the body surface area normalization method, the dose of 60 kg adult was about 32 mg/kg/d because the dose of mice was 400 mg/kg/d. Hodiamont et al found that 25 mg/kg VCM could not increase the risk of acute kidney injury.38 However, whether 32 mg/kg VCM could lead to kidney injury in human remains unknown, which need to be further investigated.
Conclusion
Our results indicated that VCM induced renal injury in the kidney tissues of mice. In addition, VCM significantly induced ferroptosis in HK-2 cells and in the kidney tissues of mice by down-regulating GPX4. These data suggested that VCM could induce renal injury in vitro and in vivo via triggering ferroptosis. These findings may provide an important molecular mechanism of VCM-induced renal injury.
Acknowledgments
The authors appreciate the support of Dr. Huajun Sun from Shanghai Children’s Hospital.
Funding Statement
The present research was supported by the Shanghai Science and Technology Commission Grant Project (No. 21DZ2300700), Shanghai “Medical Rising Star” Youth Development Program “Excellent Young Medical Talents” (No. SHWSRS (2021)_099), and Shanghai Talent Development Fund (No. 2020110), Innovative research team of high-level local universities in Shanghai (SHSMU-ZDCX20212200).
Abbreviations
VCM, vancomycin; ROS, reactive oxygen species; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; Fer-1, ferrostatin-1; GSH, glutathione; PAS, Periodic acid-Schiff; DDX5, DEAD-box helicase 5; PTGS2, prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2; ACSL4, acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4; SLC7A11, solute carrier family 7 member 11; LIP, labile iron pool.
Disclosure
The authors declare no competing interest in this work.
References
- 1.Kellum JA, Romagnani P, Ashuntantang G, et al. Acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021;7(1):52. doi: 10.1038/s41572-021-00284-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fang CY, Lou DY, Zhou LQ, et al. Natural products: potential treatments for cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2021;42(12):1951–1969. doi: 10.1038/s41401-021-00620-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Filippone EJ, Kraft WK, Farber JL. The Nephrotoxicity of Vancomycin. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2017;102(3):459–469. doi: 10.1002/cpt.726 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Griffith RS. Vancomycin use--an historical review. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1984;14(Suppl D):1–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Matzke GR, Zhanel GG, Guay DR. Clinical pharmacokinetics of vancomycin. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1986;11(4):257–282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mergenhagen KA, Borton AR. Vancomycin nephrotoxicity: a review. J Pharm Pract. 2014;27(6):545–553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Oktem F, Arslan MK, Ozguner F, et al. In vivo evidences suggesting the role of oxidative stress in pathogenesis of vancomycin-induced nephrotoxicity: protection by erdosteine. Toxicology. 2005;215(3):227–233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Gong Y, Wang N, Liu N, Dong H. Lipid peroxidation and GPX4 inhibition are common causes for myofibroblast differentiation and ferroptosis. DNA Cell Biol. 2019;38(7):725–733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060–1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.He J, Xu W, Zheng X, et al. Vitamin C reduces vancomycin-related nephrotoxicity through the inhibition of oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation in mice. Ann Transl Med. 2021;9(16):1319. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-3294 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hawkins SFC, Guest PC. Multiplex analyses using real-time quantitative PCR. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1546:125–133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bai C, Zhu Y, Dong Q, Zhang Y. Chronic intermittent hypoxia induces the pyroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):7528–7540. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2047394 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Song JX, An JR, Chen Q, et al. Liraglutide attenuates hepatic iron levels and ferroptosis in db/db mice. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):8334–8348. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2051858 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hao J, Zhou Y, Yu W, Li H, He D. Silencing of LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 confers an inhibitory effect on renal fibrosis through repressing miR-124-3p activity. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):10399–10411. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2056816 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wang J, Lv P. Chrysophanol inhibits the osteoglycin/mTOR and activates NF2 signaling pathways to reduce viability and proliferation of malignant meningioma cells. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):755–762. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1885864 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hao J, Zhang W, Huang Z. Bupivacaine modulates the apoptosis and ferroptosis in bladder cancer via phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/AKT pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):6794–6806. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2036909 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ding G, An J, Li L. MicroRNA-103a-3p enhances sepsis-induced acute kidney injury via targeting CXCL12. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):10288–10298. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2062195 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sun L, Wang H, Xu D, et al. Lapatinib induces mitochondrial dysfunction to enhance oxidative stress and ferroptosis in doxorubicin-induced cardiomyocytes via inhibition of PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Bioengineered. 2022;13(1):48–60. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2004980 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Huang J, Chen G, Wang J, Liu S, Su J. Platycodin D regulates high glucose-induced ferroptosis of HK-2 cells through glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4). Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):6627–6637. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2045834 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Osada Y, Nakagawa S, Ishibe K, et al. Antibiotic-induced microbiome depletion alters renal glucose metabolism and exacerbates renal injury after ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021;321(4):F455–F465. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00111.2021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hu Z, Zhang H, Yang SK, et al. Emerging role of ferroptosis in acute kidney injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:8010614. doi: 10.1155/2019/8010614 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wan C, Li S, Wen L, et al. Damage of oxidative stress on mitochondria during microspores development in Honglian CMS line of rice. Plant Cell Rep. 2007;26(3):373–382. doi: 10.1007/s00299-006-0234-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Brigelius-Flohé R, Maiorino M. Glutathione peroxidases. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-General Subjects. 2013;1830(5):3289–3303. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.11.020 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Basit F, Van Oppen LM, Schöckel L, et al. Mitochondrial complex I inhibition triggers a mitophagy-dependent ROS increase leading to necroptosis and ferroptosis in melanoma cells. Cell Death & Disease. 2017;8(3):e2716–e2716. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.133 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Cao JY, Dixon SJ. Mechanisms of ferroptosis. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences. 2016;73(11):2195–2209. doi: 10.1007/s00018-016-2194-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Ma S, Henson E, Chen Y, Gibson S. Ferroptosis is induced following siramesine and lapatinib treatment of breast cancer cells. Cell Death & Disease. 2016;7(7):e2307–e2307. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.208 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Park E, Chung SW. ROS-mediated autophagy increases intracellular iron levels and ferroptosis by ferritin and transferrin receptor regulation. Cell Death & Disease. 2019;10(11):1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2064-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Xie J, Ye Z, Li L, et al. Ferrostatin‑1 alleviates oxalate‑induced renal tubular epithelial cell injury, fibrosis and calcium oxalate stone formation by inhibiting ferroptosis. Mol Med Rep. 2022;26:2. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2022.12772 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Doll S, Conrad M. Iron and ferroptosis: a still ill‐defined liaison. IUBMB Life. 2017;69(6):423–434. doi: 10.1002/iub.1616 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156(1–2):317–331. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhang J, Bi J, Ren Y, et al. Involvement of GPX4 in irisin’s protection against ischemia reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(2):931–945. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29903 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nature Chemical Biology. 2017;13(1):91–98. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2239 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yuan H, Li X, Zhang X, Kang R, Tang D. Identification of ACSL4 as a biomarker and contributor of ferroptosis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2016;478(3):1338–1343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Xu X, Zhang X, Wei C, et al. Targeting SLC7A11 specifically suppresses the progression of colorectal cancer stem cells via inducing ferroptosis. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 2020;152:105450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sun L, Dong H, Zhang W, et al. Lipid peroxidation, GSH depletion, and SLC7A11 inhibition are common causes of EMT and ferroptosis in A549 cells, but different in specific mechanisms. DNA and Cell Biology. 2021;40(2):172–183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jiang H, Wang C, Zhang A, et al. ATF4 protects against sorafenib-induced cardiotoxicity by suppressing ferroptosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2022;153:113280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Zou Y, Zhang M, Zeng D, et al. Periplaneta americana extracts accelerate liver regeneration via a complex network of pathways. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hodiamont CJ, Juffermans NP, Berends SE, et al. Impact of a vancomycin loading dose on the achievement of target vancomycin exposure in the first 24 h and on the accompanying risk of nephrotoxicity in critically ill patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2021;76(11):2941–2949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]