ABSTRACT
Objectives.
To characterize the distribution profile of dengue, chikungunya, and Zika virus infections in Latin America and the Caribbean and to identify possible factors associated with the risk of dissemination and severity of these arboviruses.
Methods.
The protocol of this review was registered on the PROSPERO platform. Searches were carried out in the following databases: Virtual Health Library, MEDLINE/PubMed, and Embase. The search terms were: Zika virus, Zika virus infection, dengue, dengue virus, chikungunya virus, chikungunya fever, epidemiology, observational study, Latin America, and Caribbean region. Studies that addressed the distribution of these arboviruses and the risk factors associated with dengue, Zika virus disease, and chikungunya, published between January 2000 and August 2020 in English, Portuguese, and Spanish, were included.
Results.
Of 95 studies included, 70 identified risk factors, clinical manifestations, and outcomes for arbovirus infections and 25 described complications and/or deaths. The highest frequency of confirmed cases was for dengue. Brazil reported most cases of the three arboviruses in the period analyzed. Environmental and socioeconomic factors facilitated the proliferation and adaptation of vectors, and host-related factors were reported to aggravate dengue. Most deaths were due to chikungunya, Zika virus disease caused most neurological alterations, and dengue resulted in greater morbidity leading to more frequent hospitalization.
Conclusions.
The review provides a broad view of the three arboviruses and the intrinsic aspects of infections, and highlights the factors that influence the spread of these viruses in the populations studied.
Keywords: Arboviruses, arbovirus infections, risk factors, systematic review, Latin America, Caribbean
RESUMEN
Objetivos.
Caracterizar el perfil de distribución de infecciones por dengue, chikungunya y el virus de Zika en América Latina y el Caribe, y determinar posibles factores relacionados con el riesgo de propagación y gravedad de estas arbovirosis.
Métodos.
Se registró el protocolo de esta revisión en la plataforma PROSPERO. Se realizaron búsquedas en las siguientes bases de datos: Virtual Health Library, MEDLINE/PubMed y Embase. Los términos de búsqueda fueron: “zika virus” [virus del Zika], “zika virus infection” [infección por el virus del Zika], “dengue”, “dengue virus” [virus del dengue], “chikungunya virus” [virus del chikunguña], “chikungunya fever” [fiebre de chikunguña], “epidemiology” [epidemiología], “observational study” [estudio observacional], “Latin America” [América Latina] y “Caribbean región” [Caribe]. Se incluyeron estudios que abordaban la distribución de estas arbovirosis y los factores de riesgo asociados con el dengue, la enfermedad por el virus del Zika y el chikunguña, publicados entre enero del 2000 y agosto del 2020 en español, inglés y portugués.
Resultados.
De los 95 estudios incluidos, 70 establecieron factores de riesgo, manifestaciones clínicas y resultados de las infecciones por arbovirus y 25 describieron complicaciones o muertes. La mayor frecuencia de casos confirmados fue del dengue. Brasil notificó la mayoría de los casos de infección por los tres arbovirus en el período analizado. Los factores ambientales y socioeconómicos facilitaron la proliferación y adaptación de los vectores, y se notificó que los factores relacionados con el huésped agravaban el dengue. El chikunguña causó la mayor parte de las muertes, la enfermedad por el virus del Zika causó la mayor parte de las alteraciones neurológicas y el dengue fue responsable de una mayor morbilidad, lo que llevó a una hospitalización más frecuente.
Conclusiones.
Esta revisión ofrece un panorama de las tres arbovirosis y de los aspectos intrínsecos de las infecciones, y pone de relieve los factores que influyen en la propagación de estos virus en las poblaciones estudiadas.
Palabras clave: Arbovirus, infecciones por arbovirus, factores de riesgo, revisión sistemática, América Latina, Región del Caribe
RESUMO
Objetivos.
Descrever a distribuição das arboviroses causadas pelo vírus da dengue, zika e chikungunya na América Latina e no Caribe e identificar possíveis fatores associados ao potencial de disseminação e à gravidade dessas infecções.
Métodos.
O protocolo desta revisão sistemática foi registado na plataforma PROSPERO. Foram realizadas buscas nas bases de dados Biblioteca Virtual em Saúde, MEDLINE/PubMed e Embase. Os termos de busca foram: vírus zika, infecção pelo vírus zika, dengue, vírus da dengue, vírus chikungunya, febre chikungunya, epidemiologia, estudo observacional, América Latina e região do Caribe. Foram selecionados estudos publicados em inglês, português e espanhol, entre janeiro de 2000 e agosto de 2020, que tratavam da distribuição desses arbovírus e de fatores de risco associados à dengue, à infecção pelo vírus zika e à febre chikungunya.
Resultados.
Dos 95 estudos selecionados, 70 descreveram fatores de risco, manifestações clínicas e desfechos das arboviroses e 25 destacaram as complicações e/ou mortes. Houve uma maior taxa de casos confirmados de dengue. O Brasil foi o país onde se registrou a maioria dos casos dessas três arboviroses no período analisado. Fatores ambientais e socioeconômicos facilitaram a proliferação e a adaptação dos vetores dos arbovírus e fatores próprios do hospedeiro são determinantes na gravidade da dengue. As mortes ocorreram principalmente nos casos de febre chikungunya, as manifestações neurológicas foram mais comuns na infecção pelo vírus zika e a dengue resultou em maior morbidade e internação hospitalar.
Conclusões.
Esta revisão sistemática oferece um panorama destas três arboviroses e de suas peculiaridades destacando os fatores que influenciam a disseminação destes arbovírus nas populações estudadas.
Palavras-chave: Arbovirus, infecções por arbovirus, fatores de risco, revisão sistemática, América Latina, Região do Caribe
Dengue, Zika virus disease, and chikungunya are mosquito-borne diseases caused by dengue virus (DENV), Zika virus (ZIKV) and chikungunya virus (CHIKV), respectively, which are relevant to public health in Latin America and the Caribbean (1). Dengue is reported worldwide, especially in tropical and subtropical regions. In the Americas, dengue reappeared in the 1960s and 1970s, with the occurrence of classic dengue epidemics. In the past decade, morbidity and mortality caused by these viruses in the Americas and Caribbean region have increased significantly. In the Americas alone, in 2019, more than 2.7 million cases of dengue were reported, of which 22 127 were severe cases, and 1206 deaths were reported (2, 3).
The first reports of ZIKV infections in the Americas and the Caribbean date back to 2013, but it was in 2014 that some states in north-eastern Brazil reported cases among suspected cases of dengue and measles. In 2015, the virus emerged and spread to other countries in South and Central America, and to 47 countries and territories overall (4, 5).
CHIKV has reached several regions of Europe and Asia and it was reported for the first time in the Americas and the Caribbean in 2013. In 2015, almost 1 million cases were reported, which resulted in 7 126 deaths. Autochthonous transmission has been reported in more than 50 territories (4). However, since 2018, the number of cases of chikungunya has been decreasing (6, 7).
Despite the efforts to contain these diseases, epidemic cycles still occur with an increase in cases of infections, and are related to vector control, viral transmission, and the exposure of people susceptible to infection (8, 9).
The geographic distribution of cases is related to: the presence of susceptible populations; the biological cycle of the vectors in the environment; and the relationships between vectors and viruses and non-viruses (4). Research is necessary to understand the epidemiology of these arboviruses and the many factors that can facilitate their spread, infection, and worsening disease.
This systematic review aimed to identify and evaluate studies on DENV, ZIKV and CHIKV infections in Latin America and the Caribbean to characterize the distribution of cases of these arboviruses and assess the factors associated with the risk of dissemination, severity of infection, and death.
METHODS
Study design
This was a systematic review of studies on the epidemiological and geographical features of dengue, Zika, and chikungunya arboviruses, including their distribution and associated risks. Studies in English, Portuguese, and Spanish were retrieved from Virtual Health Library, MEDLINE/PubMed, and Embase. This study is registered on the PROSPERO platform (identification number CRD42020158290) and is reported in line with the PRISMA guidelines (10).
Search strategy
The following Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) terms were used in the search: “zika virus”, “zika virus infection”, “dengue”, “dengue virus”, “chikungunya virus”, “chikungunya fever”, “epidemiology”, “observational study”, “Latin America”, and “Caribbean region”. Search terms were combined with the Boolean operators, AND and OR.
A gray literature search was done using the online database of the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) and searching for health indicators available by year of interest: total dengue cases (2000–2020), total Zika virus disease cases (2015–2020), and total chikungunya cases (2018–2020) for the Andes, Central America and Mexico, Latin Caribbean, Non-Latin Caribbean, and Southern Cone regions. With regard to complications of these arboviruses, only data on severe dengue and deaths resulting from it (2000–2020) were available (11).
Study selection
The study was performed using Rayyan (web organization tool for systematic reviews) for exclusion of duplicates and then for the initial screening of studies. This procedure was performed by two authors independently.
Cohort, case–control, cross-sectional and ecological studies were included, as were studies on the epidemiological profile (distribution and risk factors) of DENV, ZIKV, and CHIKV infections. Regions other than Latin America and the Caribbean and data that did not cover the period from January 2000 to August 2020 were excluded. Clinical trials, other intervention studies, and studies on other diseases were also excluded.
Assessment of quality and methodological bias
The articles included were analyzed using two design tools for observational study. Case–control, cohort, and cross-sectional studies were evaluated using the tool of the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Ecological studies were evaluated using the tool of the Joanna Briggs Institute. In addition, two authors independently assessed the risk of methodological bias. Any differences were resolved by consensus.
Data extraction and synthesis of results
The data collected were stratified according to: identification of risk factors; clinical manifestations; and outcomes of arbovirus infections and complications related to these.
RESULTS
A total of 5 489 references were obtained. After elimination of duplicates and the initial screening process, 190 studies were included for review of the full text. Of these 190 studies, 95 met the defined criteria, of which 70 identified risk factors and clinical manifestations (see supplementary material, Table S1), and 25 described complications and/or deaths related to arboviruses (Table 1). In addition, PAHO documents on the health indicators of the arboviruses were included in this review. The selection process is outlined in Figure 1.
TABLE 1. Complications and deaths from arbovirus infections, Latin America and the Caribbean.
|
Author, year |
Type of study |
Arbovirus |
Population |
Complications/deaths |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Angelo et al., 2020 |
Ecological |
DENV & ZIKV |
1.9 million individuals |
Inflammatory polyneuropathy |
|
Araújo et al., 2018 |
Case–control |
ZIKV |
91 neonatal cases |
Severe microcephaly, stillbirths with positive serology for ZIKV |
|
Bertolotti et al., 2020 |
Prospective cohort |
CHIKV |
193 cases |
Aggravating role of dehydration during the acute phase of chikungunya |
|
Brasil et al., 2016 |
Cross-sectional |
ZIKV |
364 suspected cases |
One patient with neurological symptoms of peripheral nerve involvement; one abortion |
|
Chang et al., 2018 |
Cohort |
CHIKV |
500 individuals |
Persistent joint pain reported by 123 people 20 months after infection |
|
Couzigou et al., 2018 |
Cohort |
CHIKV |
Population of Martinique (Caribbean) |
Of 509 cases, 200 reported persistent pain after 3 months of infection |
|
De Lima et al., 2020 |
Cross-sectional |
CHIKV |
100 fatal cases of arbovirus infections |
22% of fatal cases had CHIKV and DENV; 39 CHIKV cases had signs of neurological impairment |
|
Einspieler et al., 2019 |
Cohort |
ZIKV |
444 children |
Of 56 children exposed to ZIKV, 46 had congenital microcephaly |
|
Freitas et al., 2019 |
Ecological |
CHIKV |
Jamaica (Caribbean) |
2499 deaths positively related to the high incidence of chikungunya during the period evaluated |
|
Frutuoso et al., 2020 |
Cross-sectional |
CHIKV |
5 850 cases registered with chikungunya and died |
3135 deaths, with 21.4% of cases laboratory confirmed |
|
Godaert et al., 2018 |
Cohort |
CHIKV |
385 patients > 64 years |
35 deaths with seven prognostic factors associated with the outcome: cardiovascular disorders, respiratory infection, sensorimotor deficit, absence of musculoskeletal pain, history of alcoholism, digestive symptoms, and presence of confusion or delirium |
|
Godaert et al., 2019 |
Cohort |
CHIKV |
268 patients positive for CHIKV |
53 deaths, 4.6% of acute clinical cases, 19.0% of atypical cases, 19.2% of severe acute cases, and 23.5% of unclassifiable cases |
|
Gregianini et al., 2017 |
Cross-sectional |
CHIKV & ZIKV |
1 276 suspected cases of arboviruses |
Three conformed cases of congenital Zika syndrome |
|
Hoen et al., 2018 |
Cohort |
ZIKV |
555 fetuses and children |
28 premature or stillborn and 527 live births with congenital Zika syndrome |
|
Kohler et al., 2018 |
Cross-sectional |
CHIKV |
31 individuals |
50–69 years old; women developed disabling arthralgia |
|
Mora-Salamanca et al., 2020 |
Ecological |
CHIKV, DENV & ZIKV |
Population of Colombia |
The highest proportion of DALYs was caused by chronic complications of arboviruses |
|
Oliveira et al., 2020 |
Ecological |
CHIKV, DENV & ZIKV |
12 130 550 DENV; 501 202 CHIKV cases |
52% of dengue cases confirmed; 63% of chikungunya cases confirmed; 24% of the total cases evaluated were ZIKV |
|
Paixão et al., 2015 |
Ecological |
DENV |
4 995 546 cases in Brazil (2001–2011) |
Increase in the case fatality rate from dengue hemorrhagic fever in Brazil, with 3156 deaths recorded |
|
Peters et al., 2018 |
Cohort |
CHIKV |
470 suspected cases |
Arthralgia after 3 months of infection |
|
Pinto et al., 2016 |
Cohort |
DENV |
105 459 reported cases |
1605 cases of severe dengue with 61 deaths recorded |
|
Pinto et al., 2019 |
Cross-sectional |
CHIKV |
Population of Fortaleza |
Hospitalization and 269 deaths |
|
Read et al., 2018 |
Cohort |
ZIKV |
7191 children |
351 confirmed cases; 80 with chronic complications and 69 developing asthma |
|
Santiago et al., 2019 |
Cross-sectional |
DENV & ZIKV |
1070 ZIKV; 312 DENV-2; and 260 DENV-3 |
1.7% of patients with ZIKV hospitalized, 50.6% and 43.8% of DENV-2 and DENV-3 cases, respectively, hospitalized, both for complications |
|
Tomashek et al., 2017 |
Cohort |
CHKIV & DENV |
8996 individuals |
46.7% of DENV cases hospitalized due to symptoms and severe forms of dengue |
|
Vianna et al., 2019 |
Cohort |
ZIKV |
108 children |
26 congenital Zika syndrome diagnoses: 18 microcephaly and 16 epilepsy |
DENV, dengue virus; ZIKV; Zika virus, CHIKV, chikungunya virus; DALY, disability-adjusted life year.
Source: Prepared by authors from studies retrieved.
FIGURE 1. Flowchart of screening of studies.
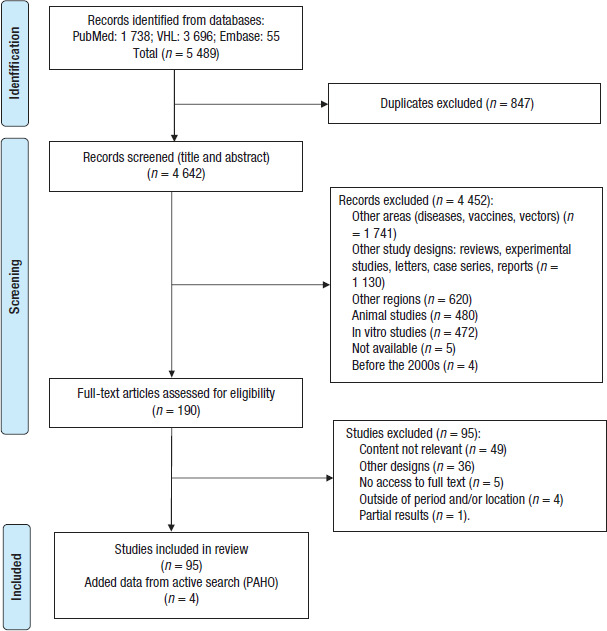
VHL, Virtual Health Library; PAHO, Pan American Health Organization.
Source: Prepared by authors based on the PRISMA flow diagram.
Distribution
In the studies included, the frequency of confirmed cases was highest for DENV (7 942 963 cases), followed by ZIKV (4 385 581 cases), and then CHIKV (136 805 cases). Co-infection among the arboviruses studied was reported in 52 753 cases.
The PAHO literature showed the number of cases of arbovirus infections distributed by the regions of interest: Andes; Central America and Mexico; Latin Caribbean; Non-Latin Caribbean; and Southern Cone (11). For dengue, the epidemic years were 2014, 2015, 2019, and 2022. The Southern Cone region had the highest number of cases of dengue, with incidence rates ranging from 628.19 to 841.97 per 100 000 population. The largest number of severe dengue cases and deaths in this region was concentrated in Brazil. In Central America and Mexico, the highest incidence rates of dengue were 175.69 per 100 000 in 2015 and 388.52 per 100 000 in 2019, with the highest incidence rates of severe dengue in Mexico. Aruba in the Latin Caribbean region had the highest incidence rates of dengue in all the Americas of 1 157 per 100 000 in 2016 and 1 505 per 100 000 in 2017, with no record of severe dengue cases or deaths.
Cases of ZIKV infection have been reported in all regions since its introduction, with the number of cases declining after 2017. The Southern Cone region had the highest cumulative incidence of ZIKV infection.
For chikungunya, registered cases fluctuated in different regions. In 2014 and 2015, the Latin Caribbean region had the highest incidence rates, with the highest rates found in the Dominican Republic (539.62 per 100 000). In 2016, it was the Andes region, with the highest rates found in Colombia (294.81 per 100 000). As of 2017, the highest incidence was in the Southern Cone region, with the highest rates found in Brazil (773.0 per 100 000).
Environmental and socioeconomic factors
Being a tropical and subtropical area was associated with the spread and positivity of ZIKV (12) and CHIKV (13), while the spread of DENV was associated with a semi-arid climate (14). Increase in temperature and dry weather were associated with circulation of the three arboviruses (15). Increased rainfall and population density were associated with ZIKV and CHIKV infection (16) and DENV infection (17). The three arboviruses were found in North and Northeast regions of Brazil with concomitant transmission reported (18). The estimated risk of death from CHIKV was higher in: individuals living in the Northeast region; males; those with little schooling; those of white race; and very young and very old people (19). Specific regions of the cities surveyed, such as urbanized areas and proximity to empty places, contributed to the presence of ZIKV and DENV (20, 21).
Low socioeconomic status was associated with the presence of CHIKV (22) and DENV (23). However, high socioeconomic status was associated with ZIKV in one study (24). Populated areas were cited as a facilitating factor for ZIKV (25). Living in places with a high turnover of people, mainly related to tourism, was an important factor in exposure to the vector and the possibility of infection by ZIKV and DENV (26, 27), and CHIKV (27). A high density of people also influenced the dispersion of ZIKV and CHIKV (28).
Host-associated factors
Age influenced infection by the three viruses. One study reported that younger age facilitated CHIKV and DENV infection (29). Some studies reported other associations, such as the presence and persistence of rheumatic pain and aging for CHIKV (30), and the possibility of death with DENV (29, 31) and CHIKV (32) infections. Being a male child and an elderly man have been associated with DENV and CHIKV infections (33, 34), but other studies have described an increased risk of CHIKV infection in older women (35) and increased risk of ZIKV and DENV infections in children of both sexes (36, 37).
A second infection is a facilitator to trigger DENV severity (36). However, it has been suggested that a previous DENV infection may protect against symptomatic ZIKV infection in a pediatric population (37), which corroborates the findings of a cohort of adults in Brazil, where a reduced risk of infection and fewer symptoms for ZIKV infection were seen in individuals seropositive for DENV (38).
Underlying diseases, such as diabetes mellitus, and hematological, chronic kidney, liver, gastric, and autoimmune diseases, are thought to facilitate complications in cases of dengue (39). Low immunity is also a factor for DENV infection (36). One study associated mixed race with a greater likelihood of developing dengue than other ethnicities (40).
Epidemiological factors
Living in the countryside and working outdoors, such as on a farm with animals, were facilitators of acute DENV infection in adults (41). More than one circulating DENV serotype and the presence of vectors are risk factors for these arboviruses (42). A second epidemic wave may be a facilitating factor for infection, especially for CHIKV, and is associated with more severe cases of the disease (43). CHIKV itself was a factor for increased mortality in the regions studied (44) or for the development of atypical forms of the disease, as no other significant associations were found (45). One study reported an association between education and marital status and DENV infection (39).
Complications
Among the 95 selected studies, 25 described complications and/or deaths related to arboviruses. The main virus associated with complications was CHIKV, followed by ZIKV and DENV (Table 1).
PAHO indicators were searched to quantify possible complications related to arboviruses and cases of and mortality from severe dengue were found. The Andes region recorded the most serious cases of dengue between 2000 and 2010 (104 762 cases), while between 2011 and 2020, the Southern Cone region recorded the most serious cases (30 605 cases). The highest number of deaths from cases of severe dengue was in 2019, with 1 773 deaths recorded across Latin America and the Caribbean.
DISCUSSION
DENV, ZIKV, and CHIKV are arboviruses that affect mainly tropical and subtropical regions, and thousands of people have already been infected, with significant morbidity and mortality (13, 14). In Latin America and the Caribbean, these diseases have spread and produced major epidemics since the introduction of dengue in recent decades and the emergence of ZIKV and CHIKV infections in the past decade (2, 5, 6).
According to PAHO data, the Southern Cone region registered the largest number of cases of the three arboviruses, with Brazil reporting the most cases in all of Latin America and the Caribbean of the three arboviruses in the observed period (11). A recent estimate indicates that the numbers of cases of these arboviruses increased substantially after 2013 in these regions (19).
The geographical distribution of cases is due to several factors and is related to the biological cycle of vectors in the environment and the relationships between vectors and viruses. Climate, and particularly temperature and precipitation, have a significant effect on the distribution and abundance of different mosquito species (1, 46). The increase in global temperature reduces larval development time, promoting an increase in adult vectors, and natural day–night temperature fluctuations also influence vector competence (the ability of a vector to transmit disease). As a result, the extrinsic incubation period is also reduced, favoring the possibility of viral transmission (18).
Factors related to the environment in which an individual lives also affect arboviruses and vectors. The proximity of abandoned and/or empty places, which may accumulate trash, has been reported as favoring the proliferation of mosquitoes (18). The lack of inspection of residences and the presence of objects that can collect water also favor the reproduction of vectors (29) and put at risk not only the residents of the house but the entire population around them.
The combination of objects that can collect water, the increase in rainfall, and the low level of sanitation provide a perfect scenario for the reproduction of the vectors of these arboviruses, with more breeding sites for female mosquitoes to lay their eggs (1). On the other hand, not only is the period of high rainfall a concern but also periods of drought should be considered, as they may require water storage which could serve as potential breeding grounds for vectors (1).
Socioeconomic factors are associated the incidence of arboviruses. A low economic status usually implies inadequate living conditions that can produce favorable environments for vector replication. It is common for poorer populations to live in agglomerations, informal settlements, or slums, with little provision of basic services such as health and sanitation (18, 19). These conditions can contribute to the spread of arboviruses, since Aedes aegypti is a highly anthropophilic species living in close proximity to human dwellings.
Some studies did not find an association between the incidence of arboviruses and standard of living (18). However, populated areas are cited as a risk factor for ZIKV (25), as is the use of public transport for DENV (28). Living in places with a high turnover of people can be a risk factor for exposure to the vector, increasing the possibility of infection by ZIKV (25) and DENV (26).
The epidemiology of these diseases has shown important changes, with a greater number of cases and hospitalizations in recent years and epidemics of greater magnitude. This situation highlights the process of dissemination of transmission and the occurrence of cases among children and elderly people (27, 28), as age is associated with severity of the diseases. Younger individuals may be less able to compensate for capillary leaks and are therefore at greater risk of developing more severe forms of disease, as reported with dengue (19). On the other hand, older individuals may have other diseases as a result of the natural aging process and be more debilitated, which may increase the risk of death from infection with these arboviruses (32).
Another factor related to host characteristics is the development of more severe dengue after a second infection with a different serotype. This may be because an individual who was previously infected by one of the serotypes can produce an immune response such that an antibody-dependent enhancement occurs, which acts as a facilitating mechanism for the entry of the virus into cells. This amplifies the effect of the immune response against the virus, assuming the dependent modulation of the subclasses of immunoglobulin G (IgG) in the increase of the release of cytokines, chemokines, interferons, and nitric oxide. These pro-inflammatory molecules may favor more severe forms of dengue, such as hemorrhagic dengue (47). The increase in the severity of cases raises the mortality rate between 1% and 20%. However, it is speculated that a first DENV infection may provide protection against a symptomatic ZIKV infection (20).
Other host-related conditions, such as underlying diseases, have also been reported: diabetes mellitus, and hematologic, chronic renal, hepatic, gastric, and autoimmune diseases are potential facilitators of DENV infection (31).
As regards ethnicity, there is still no consensus on whether certain ethnic groups are more susceptible to arboviruses than others. In the immune response mediated by the human leukocyte antigen system, for example, some genetic alterations that may be characteristic of the ethnicity of a population may promote more severe infection by some arboviruses (48). However, this variable has low sensitivity because ethnicity is often subjective and self-perceived. Socioeconomic status and education are more strongly associated with infection.
The relationship between sex and arbovirus infection is also unclear. Some studies show that dengue may be more frequent in men than women (20), and others that the disease is more severe in women than men, because of possible hormonal influences on the immune system (48). The higher frequency of cases in women has been attributed to the culture as women seek health services for treatment more than men, often through programs aimed at women's health. In addition, women may have more body areas exposed because of clothing style. However, random surveys have found no difference in arbovirus infection between the sexes (36).
The data obtained by PAHO showed that in the decade 2000–2009, the Andes region recorded the most severe cases of dengue while in the decade 2010–2020, the Southern Cone region had the most severe cases. However, in those 2 decades, although the numbers fluctuated over time, the number of serious cases recorded in the second decade dropped significantly compared with the previous decade. The number of deaths was distributed more evenly among the regions (47).
Among the complications caused by arboviruses, the frequency of death was higher for CHIKV (32) infection than for DENV or ZIKV infections. Most individuals who died were elderly people (32). Chikungunya is often associated with morbidities as a result of the disease, such as respiratory failure, cardiovascular decompensation, meningoencephalitis, seizures, Guillain–Barré syndrome (49), and severe polyarthralgia (29). Severe arthralgia is a characteristic symptom of the chronic phase of chikungunya, which can last for months or years after infection.
Neurological symptoms resulting from CHIKV infection have also been reported, although less frequently. Guillain-Barré syndrome was most associated with chikungunya; despite being a benign syndrome, severe forms can lead to death. Guillain–Barré syndrome is also associated with ZIKV infection and severe forms of dengue (49). Studies suggest that these arboviruses induce a reactive immune response with peripheral nerves, promoting acute polyneuropathy (24).
Conditions caused by ZIKV such as epilepsy, cerebral palsy, neuropathies, and microcephaly were frequently cited. Several studies correlated neurological alterations in fetuses and newborns because of maternal infection with ZIKV (45), giving rise to congenital Zika syndrome. Vertical transmission of the virus has been confirmed as it is known that ZIKV can cross the blood–brain barrier and often exerts cytotoxic effects on neural cells (37).
ZIKV promotes microcephaly in newborns when transmitted vertically to the fetus, especially when maternal infection occurs in the first trimester of pregnancy, as this corresponds to the neurogenic development phase of the embryo (18). However, infections after the first trimester can also affect neural development in children. Some newborns infected by the virus during the second or third trimester of pregnancy but not classified as having microcephaly at birth may have decreased head circumference or other neurological diseases (50). Hospitalizations and deaths from ZIKV infection were little reported in the studies analyzed.
As for dengue, severe forms of the disease can lead to hospitalization and death. Dengue can cause severe organ dysfunction, hepatitis, encephalitis or myocarditis, plasma leakage, or shock (47). When these cases arise, monitoring must be constant, as the risk of death increases substantially.
Dengue remains the most prevalent arbovirus, but some of the early cases of CHIKV and ZIKV infections may have been misclassified as dengue cases. However, no research is available on the scope or magnitude of this potential bias in our study settings.
A limitation of our study is that data from arbovirus notification records in Latin America were superficially analyzed. We focused on analysis of the studies included based on certain criteria. Therefore, some publications on the subject in the region may have been missed.
To conclude, in this review, we established a distribution profile of arboviruses in the studies. The Southern Cone region was responsible for registering the highest number of cases of the three arboviruses, with Brazil as the country with the most reported cases throughout Latin America and the Caribbean. The main environmental and epidemiological factors influencing virus propagation were increases in temperature and rainfall. Socioeconomic and host-related factors, such as underlying diseases, were reported to facilitate the aggravation of dengue. The outcomes reported included deaths, mainly due to CHIKV, neurological changes resulting from ZIKV infection, and hospitalization because of severe DENV infections.
Disclaimer.
The authors hold sole responsibility for the views expressed in the manuscript, which may not necessarily reflect the opinion or policy of the Revista Panamericana de Salud Pública / Pan American Journal of Public Health and/or those of the Pan American Health Organization.
Acknowledgements.
We thank the Postgraduate Program in Assistance and Evaluation in Health of the Federal University of Goias, the Institute of Tropical Pathology and Public Health, researchers and colleagues from the Laboratory of Virology and Cell Culture, and Molecular Biology Laboratory and Technologies Applied to Laboratory Diagnosis for encouraging studies related to arboviruses.
Footnotes
Author contributions.
LLMS, YMFT, and VCRF conceived, designed, and wrote the paper. LLMS, ECA, and SMF collected and analyzed the data. LLMS, ECA, YMFT, and VCRF interpreted the results. All authors reviewed and approved the final version.
Conflicts of interest.
None declared.
Availability of supplementary materials.
Supplementary materials are available from the corresponding author upon request.
REFERENCES
- 1.Leta S, Beyene TJ, De Clercq EM, Amenu K, Kraemer MU, Revie CW. Global risk mapping for major diseases transmitted by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Int J Infect Dis. 2018;67:25–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2017.11.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Leta S, Beyene TJ, De Clercq EM, Amenu K, Kraemer MU, Revie CW. Global risk mapping for major diseases transmitted by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus. Int J Infect Dis. 2018;67:25–35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 2.Torres JR, Orduna TA, Piña-Pozas M, Vázquez-Vega D, Sarti E. Epidemiological Characteristics of Dengue Disease in Latin America and the Caribbean: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J Trop Med. 2017;2017:1–18. doi: 10.1155/2017/8045435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Torres JR, Orduna TA, Piña-Pozas M, Vázquez-Vega D, Sarti E. Epidemiological Characteristics of Dengue Disease in Latin America and the Caribbean: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J Trop Med. 2017;2017:1–18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 3.Organização Pan-Americana de Saúde Dengue nas Américas atinge o maior número de casos já registrado. 2020. [Accessed on 25 Nov 2021]. Available from: https://www.paho.org/pt/noticias/13-11-2019-dengue-nas-americas-atinge-maior-numero-casos-ja-registrado.; Organização Pan-Americana de Saúde, 2020. Dengue nas Américas atinge o maior número de casos já registrado. Available from: https://www.paho.org/pt/noticias/13-11-2019-dengue-nas-americas-atinge-maior-numero-casos-ja-registrado. Accessed on 25 Nov 2021.
- 4.Peña-García VH, McCracken MK, Christofferson RC. Examining the potential for south American arboviruses to spread beyond the New World. Curr Clin Microbiol Rep. 2017;4(4):208–217. doi: 10.1007/s40588-017-0076-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Peña-García VH, McCracken MK, Christofferson RC. Examining the potential for south American arboviruses to spread beyond the New World. Curr Clin Microbiol Rep. 2017;4(4):208–17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.Donalisio MR, Freitas ARR, Zuben APBV. Arboviroses emergentes no Brasil: desafios para a clínica e implicações para a saúde pública. Rev Saude Publica. 2017;51:30. doi: 10.1590/S1518-8787.2017051006889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Donalisio MR, Freitas ARR, Zuben APBV. Arboviroses emergentes no Brasil: desafios para a clínica e implicações para a saúde pública. Rev Saude Publica. 2017;51:30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 6.Figueiredo LTM. Large outbreaks of Chikungunya virus in Brazil reveal uncommon clinical features and fatalities. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2017;50(5):583–584. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0397-2017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Figueiredo LTM. Large outbreaks of Chikungunya virus in Brazil reveal uncommon clinical features and fatalities. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2017;50(5):583–4. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 7.Rico-Mendoza A, Alexandra PR, Chang A, Encinales L, Lynch R. Co-circulation of dengue, chikungunya, and Zika viruses in Colombia from 2008 to 2018. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2019;43:e49. doi: 10.26633/RPSP.2019.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Rico-Mendoza A, Alexandra PR, Chang A, Encinales L, Lynch R. Co-circulation of dengue, chikungunya, and Zika viruses in Colombia from 2008 to 2018. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2019;43:e49. doi:10.26633/RPSP.2019.49 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 8.Teixeira MG, Barreto ML, Guerra Z. Epidemiology and dengue prevention measures. Inf Epidemiol Sus. 1999;8(4):5–33. [Google Scholar]; Teixeira MG, Barreto ML, Guerra Z. Epidemiology and dengue prevention measures. Inf Epidemiol Sus. 1999;8(4):5–33.
- 9.Costa CF, da da Costa CF, dos Passos RA, Lima JBP, Roque RA, de Souza Sampaio V, et al. Transovarial transmission of DENV in Aedes aegypti in the Amazon basin: a local model of xenomonitoring. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10(1):249. doi: 10.1186/s13071-017-2194-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Costa CF da, da Costa CF, dos Passos RA, Lima JBP, Roque RA, de Souza Sampaio V, et al. Transovarial transmission of DENV in Aedes aegypti in the Amazon basin: a local model of xenomonitoring. Parasit Vectors. 2017;10(1):249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 10.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Pan American Health Organization: PLISA Health Information Platform for the Americas . Washington, D.C.: PAHO; 2021. [Accessed on 03 Nov 2021]. Available from: https://www3.paho.org/data/index.php/en/ [Google Scholar]; Pan American Health Organization: PLISA Health Information Platform for the Americas. Washington, D.C.: PAHO; 2021. Available from: https://www3.paho.org/data/index.php/en/. Accessed on 03 Nov 2021.
- 12.Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Haque U, Ball JD, García-Loaiza CJ, Galindo-Marquez ML, Sabogal-Roman JA, et al. Spatial distribution of Zika virus infection in Northeastern Colombia. Infez Med. 2017;25(3):241–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Haque U, Ball JD, García-Loaiza CJ, Galindo-Marquez ML, Sabogal-Roman JA. et al. Spatial distribution of Zika virus infection in Northeastern Colombia. Infez Med. 2017;25(3):241–246. [PubMed]
- 13.Gregianini TS, Ranieri T, Favreto C, Nunes ZMA, Tumioto Giannini GL, Sanberg ND, et al. Emerging arboviruses in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil: Chikungunya and Zika outbreaks, 2014–2016. Rev Med Virol. 2017;27(6):e1943. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Gregianini TS, Ranieri T, Favreto C, Nunes ZMA, Tumioto Giannini GL, Sanberg ND et al.. Emerging arboviruses in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil: Chikungunya and Zika outbreaks, 2014–2016. Rev Med Virol. 2017;27(6):e1943 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 14.Rodrigues NCP, Lino VTS, Daumas RP, Andrade MKDN, O'Dwyer G, Monteiro DL, et al. Temporal and spatial evolution of dengue incidence in Brazil, 2001–2012. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0165945. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0165945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Rodrigues NCP, Lino VTS, Daumas RP, Andrade MKDN, O'Dwyer G, Monteiro DL, et al. Temporal and spatial evolution of dengue incidence in Brazil, 2001–2012. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0165945 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Robert MA, Tinunin DT, Benitez EM, Ludueña-Almeida FF, Romero M, Stewart-Ibarra AM, Estallo EL. Arbovirus emergence in the temperate city of Córdoba, Argentina, 2009–2018. Sci Data. 2019;6(1):1–6. doi: 10.1038/s41597-019-0295-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Robert MA, Tinunin DT, Benitez EM, Ludueña-Almeida FF, Romero M, Stewart-Ibarra AM, Estallo EL. Arbovirus emergence in the temperate city of Córdoba, Argentina, 2009–2018. Sci Data. 2019;6(1):1–6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Fuller TL, Calvet G, Genaro Estevam C, Rafael Angelo J, Abiodun GJ, Halai UA, et al. Behavioral, climatic, and environmental risk factors for Zika and Chikungunya virus infections in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2015–16. PloS One. 2017;12(11):e0188002. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0188002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Fuller TL, Calvet G, Genaro Estevam C, Rafael Angelo J, Abiodun GJ, Halai UA. et al. Behavioral, climatic, and environmental risk factors for Zika and Chikungunya virus infections in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2015–16. PloS One. 2017;12(11):e0188002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 17.Sippy R, Herrera D, Gaus D, Gangnon RE, Patz JA, Osorio JE. Seasonal patterns of dengue fever in rural Ecuador: 2009–2016. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019;13(5):e0007360. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Sippy R, Herrera D, Gaus D, Gangnon RE, Patz JA, Osorio JE. Seasonal patterns of dengue fever in rural Ecuador: 2009–2016. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019;13(5):e0007360 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Silva MM, Tauro LB, Kikuti M, Anjos RO, Santos VC, Gonçalves TS, et al. Concomitant transmission of dengue, chikungunya, and Zika viruses in Brazil: clinical and epidemiological findings from surveillance for acute febrile illness. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;69(8):1353–1359. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Silva MM, Tauro LB, Kikuti M, Anjos RO, Santos VC, Gonçalves TS et al. Concomitant transmission of dengue, chikungunya, and Zika viruses in Brazil: clinical and epidemiological findings from surveillance for acute febrile illness. Clin Infect Dis. 2019;69(8):1353–1359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 19.Frutuoso LCV, Freitas ARR, Cavalcanti LPDG, Duarte EC. Estimated rate and leading causes of death among individuals with chikungunya in 2016 and 2017 in Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2020;53 doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0580-2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Frutuoso LCV, Freitas ARR, Cavalcanti LPDG, Duarte EC. Estimated rate and leading causes of death among individuals with chikungunya in 2016 and 2017 in Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2020;53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 20.Lozier MJ, Burke RM, Lopez J, Acevedo V, Amador M, Read JS, et al. Differences in prevalence of symptomatic Zika virus infection, by age and sex-Puerto Rico, 2016. J Infect Dis. 2018;217(11):1678–1689. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Lozier MJ, Burke RM, Lopez J, Acevedo V, Amador M, Read JS et al. Differences in prevalence of symptomatic Zika virus infection, by age and sex-Puerto Rico, 2016. J Infect Dis. 2018;217(11):1678–1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 21.Kenneson A, Beltrán-Ayala E, Borbor-Cordova MJ, Polhemus ME, Ryan SJ, Endy TP, Stewart-Ibarra AM. Social-ecological factors and preventive actions decrease the risk of dengue infection at the household-level: Results from a prospective dengue surveillance study in Machala, Ecuador. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11(12):e0006150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Kenneson A, Beltrán-Ayala E, Borbor-Cordova MJ, Polhemus ME, Ryan SJ, Endy TP, Stewart-Ibarra AM. Social-ecological factors and preventive actions decrease the risk of dengue infection at the household-level: Results from a prospective dengue surveillance study in Machala, Ecuador. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;11(12):e0006150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 22.Oviedo-Pastrana M, Méndez N, Mattar S, Arrieta G, Gomezcaceres L. Lessons learned from emerging Chikungunya virus in two populations of social vulnerability of the Colombian tropics: epidemiological analysis. Arch Public Health. 2018;76(1):1–10. doi: 10.1186/s13690-018-0284-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Oviedo-Pastrana M, Méndez N, Mattar S, Arrieta G, Gomezcaceres L. Lessons learned from emerging Chikungunya virus in two populations of social vulnerability of the Colombian tropics: epidemiological analysis. Arch Public Health. 2018;76(1):1-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Farinelli EC, Baquero OS, Stephan C, Chiaravaloti-Neto F. Low socioeconomic condition and the risk of dengue fever: a direct relationship. Tropical Act. 2018;180:47–57. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Farinelli EC, Baquero OS, Stephan C, Chiaravaloti-Neto F. Low socioeconomic condition and the risk of dengue fever: a direct relationship. Tropical Act. 2018;180:47–57. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 24.McHale TC, Romero-Vivas CM, Fronterre C, Arango-Padilla P, Waterlow NR, Nix CD, et al. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity in the distribution of chikungunya and Zika virus case incidences during their 2014 to 2016 epidemics in Barranquilla, Colombia. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(10):1759. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16101759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; McHale TC, Romero-Vivas CM, Fronterre C, Arango-Padilla P, Waterlow NR, Nix CD, et al. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity in the distribution of chikungunya and Zika virus case incidences during their 2014 to 2016 epidemics in Barranquilla, Colombia. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(10):1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 25.Sharp TM, Quandelacy TM, Adams LE, Aponte JT, Lozier MJ, Ryff K, et al. Epidemiologic and spatiotemporal trends of Zika Virus disease during the 2016 epidemic in Puerto Rico. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020;14(9):e0008532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Sharp TM, Quandelacy TM, Adams LE, Aponte JT, Lozier MJ, Ryff K. et al. Epidemiologic and spatiotemporal trends of Zika Virus disease during the 2016 epidemic in Puerto Rico. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020;14(9):e0008532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 26.Gregianini TS, Tumioto-Giannini GL, Favreto C, Plentz LC, Ikuta N, da Veiga ABG. Dengue in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil: 2014 to 2016. Rev Med Virol. 2018;28(1):e1960. doi: 10.1002/rmv.1960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Gregianini TS, Tumioto-Giannini GL, Favreto C, Plentz LC, Ikuta N, da Veiga ABG. Dengue in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil: 2014 to 2016. Rev Med Virol. 2018;28(1):e1960. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 27.Kazazian L, Neto ASL, Sousa GS, do Nascimento OJ, Castro MC. Spatiotemporal transmission dynamics of co-circulating dengue, Zika, and chikungunya viruses in Fortaleza, Brazil: 2011–2017. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020;14(10):e0008760. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Kazazian L, Neto ASL, Sousa GS, do Nascimento OJ, Castro MC. Spatiotemporal transmission dynamics of co-circulating dengue, Zika, and chikungunya viruses in Fortaleza, Brazil: 2011–2017. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020;14(10):e0008760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 28.Santana LS, Braga JU. Spatial diffusion of Zika fever epidemics in the Municipality of Salvador-Bahia, Brazil, in 2015-2016: does Zika fever have the same spread pattern as Dengue and Chikungunya fever epidemics? Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2020;53:e20190563. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0563-2019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Santana LS, Braga JU. Spatial diffusion of Zika fever epidemics in the Municipality of Salvador-Bahia, Brazil, in 2015-2016: does Zika fever have the same spread pattern as Dengue and Chikungunya fever epidemics? Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2020;53:e20190563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Stewart-Ibarra AM, Ryan SJ, Kenneson A, King CA, Abbott M, Barbachano-Guerrero A, et al. The burden of dengue fever and chikungunya in southern coastal Ecuador: epidemiology, clinical presentation, and phylogenetics from the first two years of a prospective study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;98(5):1444–1459. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.17-0762. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Stewart-Ibarra AM, Ryan SJ, Kenneson A, King CA, Abbott M, Barbachano-Guerrero A, et al. The burden of dengue fever and chikungunya in southern coastal Ecuador: epidemiology, clinical presentation, and phylogenetics from the first two years of a prospective study. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2018;98(5):1444–1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 30.Murillo-Zamora E, Mendoza-Cano O, Trujillo-Hernández B, Alberto Sánchez-Piña R, Guzmán-Esquivel J. Persistent arthralgia and related risks factors in laboratory-confirmed cases of Chikungunya virus infection in Mexico. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2017;41:e72. doi: 10.26633/RPSP.2017.72. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Murillo-Zamora E, Mendoza-Cano O, Trujillo-Hernández B, Alberto Sánchez-Piña R, Guzmán-Esquivel J. Persistent arthralgia and related risks factors in laboratory-confirmed cases of Chikungunya virus infection in Mexico. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2017;41:e72. doi:10.26633/RPSP.2017.72 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 31.Pinto RC, de Castro DB, de Albuquerque BC, Sampaio VS, Passos RA, da Costa CF, et al. Mortality Predictors in Patients with severe dengue in the state of Amazonas, Brazil. Plos One. 2016;11(8):e0161884. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Pinto RC, de Castro DB, de Albuquerque BC, Sampaio VS, Passos RA, da Costa CF, et al. Mortality Predictors in Patients with severe dengue in the state of Amazonas, Brazil. Plos One. 2016;11(8):e0161884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 32.Freitas ARR, Donalisio MR, Alarcón-Elbal PM. Excess mortality and causes associated with chikungunya, Puerto Rico, 2014–2015. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018;24(12):2352. doi: 10.3201/eid2412.170639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Freitas ARR, Donalisio MR, Alarcón-Elbal PM. Excess mortality and causes associated with chikungunya, Puerto Rico, 2014–2015. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018;24(12):2352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 33.Castanha PMS, Montarroyos UR, Silveira SMM, Albuquerque GDM, Mello MJG, Lopes KGS, et al. Incidence and risk factors for dengue virus (DENV) infection in the first 2 years of life in a Brazilian prospective birth cohort. Epidemiol Infect. 2017;145(14):2971–2979. doi: 10.1017/S095026881700214X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Castanha PMS, Montarroyos UR, Silveira SMM, Albuquerque GDM, Mello MJG, Lopes KGS, et al. Incidence and risk factors for dengue virus (DENV) infection in the first 2 years of life in a Brazilian prospective birth cohort. Epidemiol Infect. 2017;145(14):2971–2979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Martínez-Bello DA, López-Quílez A, Prieto AT. Joint Estimation of Relative Risk for Dengue and Zika Infections, Colombia, 2015–2016. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019;25(6):1118. doi: 10.3201/eid2506.180392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Martínez-Bello DA, López-Quílez A, Prieto AT. Joint Estimation of Relative Risk for Dengue and Zika Infections, Colombia, 2015–2016. Emerg Infect Dis. 2019;25(6):1118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 35.Dourado CARO, Quirino EMB, Pinho CM, Silva MASD, Souza SRGD, Andrade MS. Clinical and epidemiological aspects of the elderly with Chikungunya fever. Rev Rene. 2019;20:e41184. [Google Scholar]; Dourado CARO, Quirino EMB, Pinho CM, Silva MASD, Souza SRGD, Andrade MS. Clinical and epidemiological aspects of the elderly with Chikungunya fever, 2019. Rev Rene. 20:e41184.
- 36.Lovera D, Martínez-Cuellar C, Galeano F, Amarilla S, Vazquez C, Arbo A. Clinical manifestations of primary and secondary dengue in Paraguay and its relation to virus serotype. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2019;13(12):1127–1134. doi: 10.3855/jidc.11584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Lovera D, Martínez-Cuellar C, Galeano F, Amarilla S, Vazquez C, Arbo A. Clinical manifestations of primary and secondary dengue in Paraguay and its relation to virus serotype. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2019;13(12):1127–1134. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 37.Gordon A, Gresh L, Ojeda S, Katzelnick LC, Sanches N, Mercado JC, et al. Prior dengue virus infection and risk of Zika: a pediatric cohort in Nicaragua. PloS Med. 2019;16(1):e1002726. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Gordon A, Gresh L, Ojeda S, Katzelnick LC, Sanches N, Mercado JC, et al. Prior dengue virus infection and risk of Zika: a pediatric cohort in Nicaragua. PloS Med. 2019;16(1):e1002726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 38.Rodriguez-Barraquer I, Costa F, Nascimento EJ, Nery N, Castanha PM, Sacramento GA, et al. Impact of preexisting dengue immunity on Zika virus emergence in a dengue endemic region. Science. 2019;363(6427):607–610. doi: 10.1126/science.aav6618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Rodriguez-Barraquer I., Costa F, Nascimento EJ, Nery N, Castanha PM, Sacramento GA, et al. Impact of preexisting dengue immunity on Zika virus emergence in a dengue endemic region. Science. 2019;363(6427):607–610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 39.Viana L. RDC, Pimenta CJL, Araújo EMNFD, Teófilo TJS, Costa TFD, Costa KNDFM. Reemerging arboviruses: clinical-epidemiological profile of hospitalized elderly patients. Rev Esc Enferm USP. 2018;52:e03403. doi: 10.1590/S1980-220X2017052103403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Viana L. RDC, Pimenta CJL, Araújo EMNFD, Teófilo TJS, Costa TFD, Costa KNDFM. Reemerging arboviruses: clinical-epidemiological profile of hospitalized elderly patients. Rev Esc Enferm USP. 2018;52:e03403. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 40.Nascimento IDS, Pastor AF, Lopes TRR, Farias PCS, Gonçales JP, do Carmo RF, et al. Retrospective cross-sectional observational study on the epidemiological profile of dengue cases in Pernambuco state, Brazil, between 2015 and 2017. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09047-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Nascimento IDS, Pastor AF, Lopes TRR, Farias PCS, Gonçales JP, do Carmo RF, et al. Retrospective cross-sectional observational study on the epidemiological profile of dengue cases in Pernambuco state, Brazil, between 2015 and 2017. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 41.Reller ME, de Silva AM, Miles JJ, Jadi RS, Broadwater A, Walker K, et al. Unsuspected dengue as a cause of acute febrile illness in children and adults in Western Nicaragua. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;10(10):e0005026. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Reller ME, de Silva AM, Miles JJ, Jadi RS, Broadwater A, Walker K, et al. Unsuspected dengue as a cause of acute febrile illness in children and adults in Western Nicaragua. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2017;10(10):e0005026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 42.Guerra-Gomes IC, Gois BM, Peixoto RF, Oliveira CA, Maciel BLL, Sarmento MIF, et al. Molecular and clinical epidemiological surveillance of dengue virus in Paraíba, Northeast Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2017;50(1):19–26. doi: 10.1590/0037-8682-0419-2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Guerra-Gomes IC, Gois BM, Peixoto RF, Oliveira CA, Maciel BLL, Sarmento MIF et al. Molecular and clinical epidemiological surveillance of dengue virus in Paraíba, Northeast Brazil. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2017;50(1):19–26. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Gordon A, Gresh L, Ojeda S, Chowell G, Gonzalez K, Sanchez N, et al. Differences in transmission and disease severity between 2 successive waves of chikungunya. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;67(11):1760–1767. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciy356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Gordon A, Gresh L, Ojeda S, Chowell G, Gonzalez K, Sanchez N, et al. Differences in transmission and disease severity between 2 successive waves of chikungunya. Clin Infect Dis. 2018;67(11):1760–1767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 44.Freitas ARR, Alarcon-Elbal PM, Donalisio MR. Excess mortality in Guadeloupe and Martinique, islands of the French West Indies, during the chikungunya epidemic of 2014. Epidemiol Infect. 2018;146(16):2059–2065. doi: 10.1017/S0950268818002315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Freitas ARR, Alarcon-Elbal PM, Donalisio MR. Excess mortality in Guadeloupe and Martinique, islands of the French West Indies, during the chikungunya epidemic of 2014. Epidemiol Infect. 2018;146(16):2059–2065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 45.Bonifay T, Prince C, Neyra C, Demar M, Rousset D, Kallel H, et al. Atypical and severe manifestations of chikungunya virus infection in French Guyana: a hospital-based study. PLoS One. 2018;13(12):e0207406. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Bonifay T, Prince C, Neyra C, Demar M, Rousset D, Kallel H, et al. Atypical and severe manifestations of chikungunya virus infection in French Guyana: a hospital-based study. PLoS One. 2018;13(12):e0207406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 46.Carrillo-Hernández MY, Ruiz-Saenz J, Villamizar LJ, Gómez-Rangel SY, Martínez Gutierrez M. Co-circulation and simultaneous co-infection of dengue, chikungunya, and zika viruses in patients with febrile syndrome at the Colombian-Venezuelan border. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):1–12. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-2976-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Carrillo-Hernández MY, Ruiz-Saenz J, Villamizar LJ, Gómez-Rangel SY, Martínez Gutierrez M. Co-circulation and simultaneous co-infection of dengue, chikungunya, and zika viruses in patients with febrile syndrome at the Colombian-Venezuelan border. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18(1):1–12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 47.Guzman MG, Alvarez M, Halstead SB. Secondary infection as a risk factor for dengue hemorrhagic fever/dengue shock syndrome: an historical perspective and role of antibody-dependent enhancement of infection. Arch Virol. 2013;158(7):1445–1459. doi: 10.1007/s00705-013-1645-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Guzman MG, Alvarez M, Halstead SB. Secondary infection as a risk factor for dengue hemorrhagic fever/dengue shock syndrome: an historical perspective and role of antibody-dependent enhancement of infection. Arch Virol. 2013;158(7):1445–1459. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 48.Sierra B, Alegre R, Pérez AB, García G, Sturn-Ramirez K, Obasanjo O, et al. HLA-A,-B,-C, and-DRB1 allele frequencies in Cuban individuals with antecedents of dengue 2 disease: advantages of the Cuban population for HLA studies of dengue virus infection. Hum Immunol. 2007;68(6):531–540. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2007.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Sierra B, Alegre R, Pérez AB, García G, Sturn-Ramirez K, Obasanjo O, et al HLA-A,-B,-C, and-DRB1 allele frequencies in Cuban individuals with antecedents of dengue 2 disease: advantages of the Cuban population for HLA studies of dengue virus infection. Hum Immunol. 2007;68(6):531–540. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 49.de Sousa Lima ME, Bachur TPR, Aragão GF. Guillain-Barre syndrome and its correlation with dengue, Zika and chikungunya viruses infection based on a literature review of reported cases in Brazil. Acta Trop. 2019;197:105064. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2019.105064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; de Sousa Lima ME, Bachur TPR, Aragão GF. Guillain-Barre syndrome and its correlation with dengue, Zika and chikungunya viruses infection based on a literature review of reported cases in Brazil. Acta Trop. 2019;197:105064. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 50.de Araújo TVB, de Alencar Ximenes RA, de Barros Miranda-Filho D, Souza WV, Montarroyos UR, de Melo APL, et al. Association between microcephaly, Zika virus infection, and other risk factors in Brazil: final report of a case-control study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(3):328–336. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30727-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; de Araújo TVB, de Alencar Ximenes RA, de Barros Miranda-Filho D, Souza WV, Montarroyos UR, de Melo APL, et al. Association between microcephaly, Zika virus infection, and other risk factors in Brazil: final report of a case-control study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18(3):328–336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Supplementary materials are available from the corresponding author upon request.


