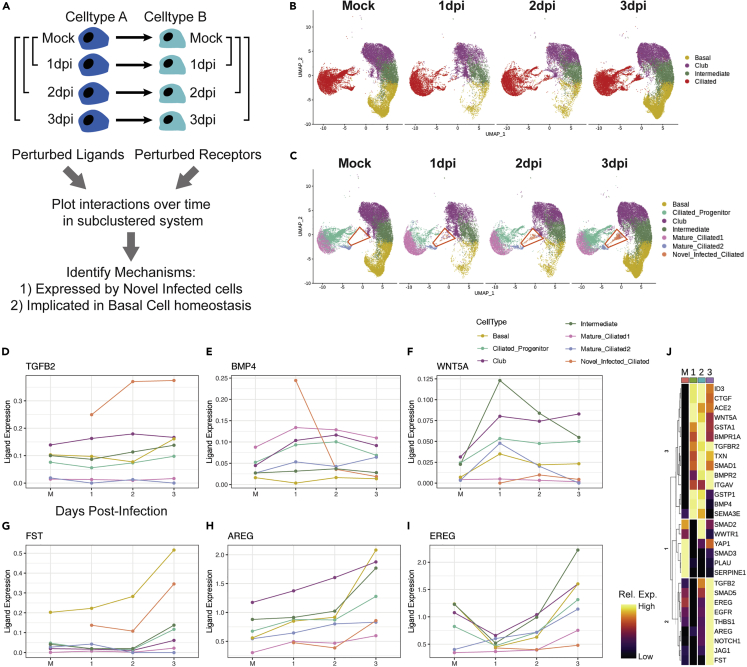
Figure 4.
Analysis of signaling networks during infection
(A) To determine the set of ligands and receptors that were perturbed by infection, paired Wilcoxon rank-sum tests were performed, by bulk cell type, using mock cells as the reference, for each post-infection time point on all genes in the FANTOM5 database.
(B) This routine was performed with the ciliated subtypes grouped as a single cell type.
(C) All ligand-receptor interactions found to be significantly perturbed were then plotted over time, with the ciliated population broken into subtypes; particular focus was given to the novel infected ciliated cell population (red trapezoid), which does not exist in the mock condition and only appears post-infection.
(D–I) Longitudinal line plots of key ligands of interest, split and colored by cell type, over time. Ligand expression was calculated using a standard log-normalization technique (see STAR Methods).
(J) Heatmap of all genes of interest over time; columns represent average expression per cluster, and rows are unity normalized and colored by relative expression (see STAR Methods). See also Figure S1.