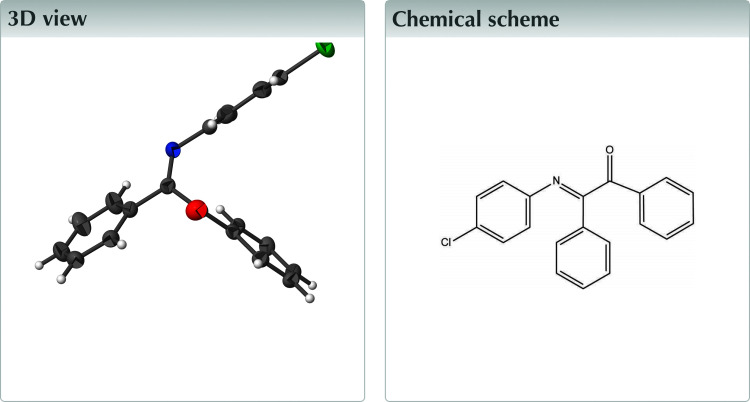
In the title Schiff base, the dihedral angle between the phenyl rings of the benzil unit is 74.14 (5)°.
Keywords: crystal structure, benzil, C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, Hirshfeld surface analysis
Abstract
The title Schiff base, C20H14ClNO, obtained from the reaction of 4-chloro aniline with benzil, has an approximate T shape. The dihedral angle between the phenyl rings of the benzil unit is 74.14 (15)°. The extended structure features C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds.
Structure description
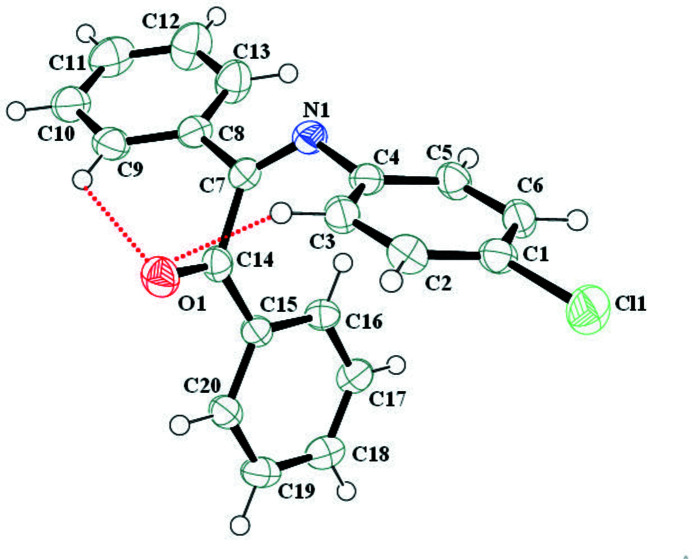
There are only a few reported crystal structures of Schiff bases derived from benzil (Tabbiche et al., 2022 ▸; Bouchama et al., 2007 ▸; Bai et al., 2006 ▸). We recently synthesized the title compound and we now report its crystal structure. The asymmetric unit contains one independent molecule (Fig. 1 ▸). The O and the imine N atoms are trans with respect to the C7—C14 bond. The C1–C6 phenyl ring makes dihedral angles of 20.56 (6) and 74.03 (6)°with the C9–C10 and C15–C16 phenyl ring, respectively, of the benzil unit. The dihedral angle between the phenyl rings of the benzil unit is 74.14 (5)°. The C—N iminium bond length [1.268 (3) Å] is comparable to that observed in (E)-1-[4-({4-[(4-methoxybenzylidene)amino]phenyl}sulfanyl)phenyl]ethan-1-one [1.252 (4) Å; Hebbachi et al., 2015 ▸]. Atom O1 accepts two long and presumably weak intramolecular hydrogen bonds with atoms H3 and H9 (Fig. 1 ▸), which generate S(6) and S(7) rings motifs, respectively: the former is approximately planar.
Figure 1.
The title molecule with the labelling scheme and 50% probability ellipsoids. Dashed lines indicate the intramolecular hydrogen bonds.
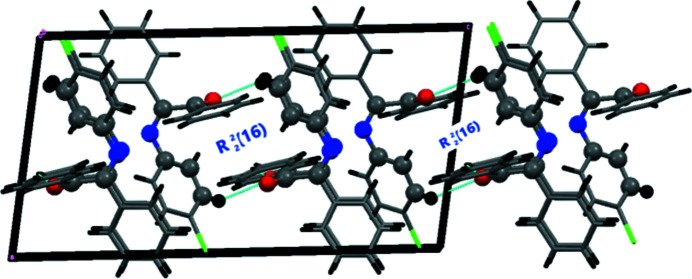
In the crystal, the molecules are aligned head-to-foot along the b-axis direction, forming layers that extend in zigzag parallel to the ac plane. In the extended structure, two weak C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds help to consolidate the packing (Table 1 ▸, Fig. 2 ▸). The C18—H18⋯O1 hydrogen bonds generate a succession of infinite chains [graph set
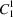 (7)] while C2—H2⋯O1 hydrogen bonds link the chains into layers, which are formed by a succession of
(7)] while C2—H2⋯O1 hydrogen bonds link the chains into layers, which are formed by a succession of
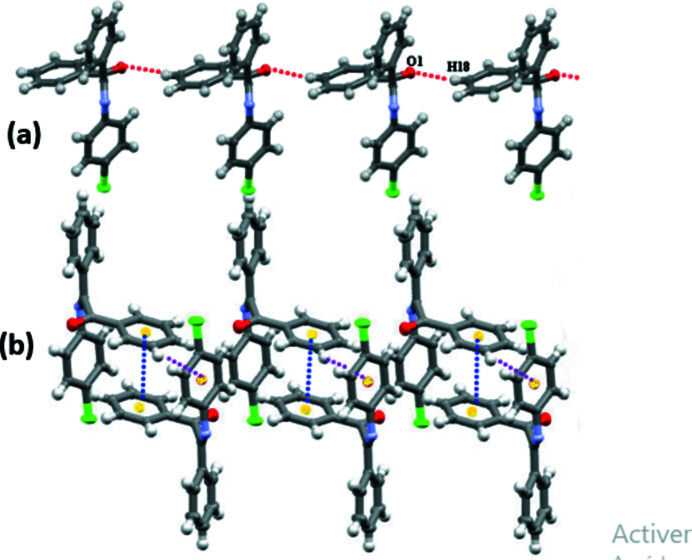
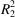 (16) rings, parallel to the bc plane [Fig. 3 ▸(a)]. Together, these hydrogen bonds lead to the formation of a three-dimensional network. Aromatic π–π stacking generates inversion dimers featuring the C15–C20 phenyl rings with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.744 (3) Å [Fig. 3 ▸(b)]. Along the c-axis direction, weak C—H⋯π(ring) interactions occur.
(16) rings, parallel to the bc plane [Fig. 3 ▸(a)]. Together, these hydrogen bonds lead to the formation of a three-dimensional network. Aromatic π–π stacking generates inversion dimers featuring the C15–C20 phenyl rings with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.744 (3) Å [Fig. 3 ▸(b)]. Along the c-axis direction, weak C—H⋯π(ring) interactions occur.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3—H3⋯O1 | 0.93 | 2.67 | 3.247 (3) | 120 |
| C9—H9⋯O1 | 0.93 | 2.64 | 3.231 (3) | 122 |
| C2—H2⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.360 (3) | 139 |
| C19—H19⋯Cg1ii | 0.93 | 2.88 | 3.689 (3) | 146 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
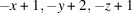 ; (ii)
; (ii)
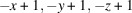 .
.
Figure 2.
Packing arrangement of the title compound viewed along the c-axis direction. C— H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Figure 3.
(a) View of part of the crystal structure, showing the formation of a hydrogen-bonded C18—H18⋯O1 chain and (b) the intermolecular C—H⋯π(ring) and π–π stacking interactions bonds (violet and blue dashed lines, respectively) in the ab plane.
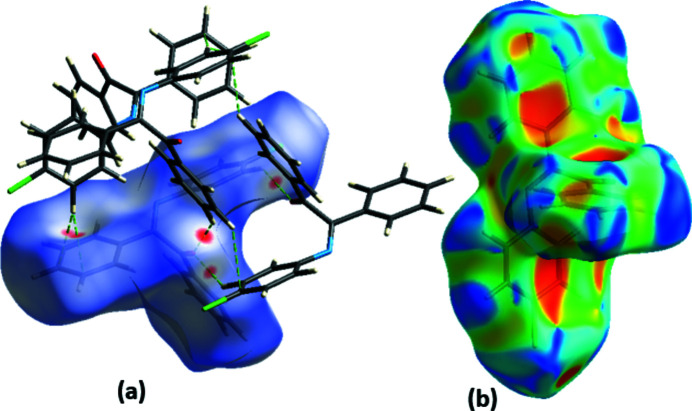
A Hirshfeld surface (HS) analysis was performed and the associated two-dimensional fingerprint (FP) plots (Spackman & Jayatilaka, 2009 ▸) were generated using Crystal Explorer 3.1 (Turner et al., 2017 ▸). Fig. 4 ▸ shows the HS mapped over d norm (–0.11 to 1.54 a.u.) and shape-index. The red spots in Fig. 4 ▸(a) reflect the formation of C—H⋯O, C—H⋯π and π–π stacking interactions. In the shape-index map [Fig. 4 ▸(b)], the adjacent red and blue triangle-like patches represent concave regions that indicate C—H⋯π(ring) and π–π stacking interactions. The two-dimensional FP plots indicate that the most important contributions to the packing, in descending percentage contribution, are from H⋯C (37.7%), H⋯H (34.6%), H⋯Cl (14.0%), H⋯O (6.1%), H⋯N (4.0%) and C⋯C (1.9%) contacts.
Figure 4.
HS mapped over (a) d norm, showing the C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π interactions, and (b) shape-index.
Synthesis and crystallization
To a solution of benzil (2.1 g, 0.01 mmol) and 1 ml of acetic acid in ethanol (20 ml) was added 4-chloro aniline (0.01 mmol) dissolved in ethanol (15 ml). The mixture was stirred for 3 h under reflux. The product was isolated, recrystallized from ethanol solution and then dried in a vacuum to give the title compound (yield 59%; m.p. > 260°C). Yellow single crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation of a ethanol solution. IR ν, cm−1: 1594 (C=N, imine), 1660 (C=O), 3064 (aromatic C—H), 1212 (C—N) and 718 (C—Cl).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C20H14ClNO |
| M r | 320.78 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 293 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 10.0982 (12), 8.2447 (11), 19.365 (3) |
| β (°) | 98.592 (12) |
| V (Å3) | 1594.2 (4) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.24 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.20 × 0.17 × 0.12 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Xcalibur, Atlas, Gemini ultra |
| Absorption correction | Analytical (CrysAlis PRO; Rigaku OD, 2018 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.968, 0.974 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 13558, 4026, 2805 |
| R int | 0.045 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.700 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.062, 0.186, 1.11 |
| No. of reflections | 4026 |
| No. of parameters | 209 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.38, −0.58 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623000652/hb4414sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623000652/hb4414Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623000652/hb4414Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2237868
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| C20H14ClNO | F(000) = 668 |
| Mr = 320.78 | Dx = 1.337 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 10.0982 (12) Å | Cell parameters from 3987 reflections |
| b = 8.2447 (11) Å | θ = 4.3–29.1° |
| c = 19.365 (3) Å | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| β = 98.592 (12)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 1594.2 (4) Å3 | Block, clear pinkish yellow |
| Z = 4 | 0.20 × 0.17 × 0.12 mm |
Data collection
| Xcalibur, Atlas, Gemini ultra diffractometer | 2805 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Detector resolution: 10.4685 pixels mm-1 | Rint = 0.045 |
| ω scans | θmax = 29.9°, θmin = 2.7° |
| Absorption correction: analytical (CrysAlisPro; Rigaku OD, 2018) | h = −13→14 |
| Tmin = 0.968, Tmax = 0.974 | k = −11→11 |
| 13558 measured reflections | l = −23→26 |
| 4026 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.062 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0695P)2 + 1.2547P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.186 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.11 | Δρmax = 0.38 e Å−3 |
| 4026 reflections | Δρmin = −0.58 e Å−3 |
| 209 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL-2018/3 (Sheldrick 2015b), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0115 (19) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. H-atom treatment: Fixed Uiso At 1.2 times of: All C(H) groups 2.a Aromatic/amide H refined with riding coordinates: C2(H2), C3(H3), C5(H5), C6(H6), C9(H9), C10(H10), C11(H11), C12(H12), C13(H13), C16(H16), C17(H17), C18(H18), C19(H19), C20(H20) |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.8370 (2) | 0.8256 (3) | 0.40271 (13) | 0.0317 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.7484 (3) | 0.9348 (3) | 0.42442 (13) | 0.0329 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.773837 | 0.997474 | 0.464122 | 0.040* | |
| C3 | 0.6214 (3) | 0.9505 (3) | 0.38673 (13) | 0.0318 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.561128 | 1.023849 | 0.401135 | 0.038* | |
| C4 | 0.5837 (2) | 0.8566 (3) | 0.32725 (12) | 0.0291 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.6759 (2) | 0.7494 (3) | 0.30579 (13) | 0.0335 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.652069 | 0.688099 | 0.265528 | 0.040* | |
| C6 | 0.8023 (2) | 0.7329 (3) | 0.34361 (13) | 0.0330 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.863287 | 0.660176 | 0.329374 | 0.040* | |
| C7 | 0.3486 (2) | 0.8532 (3) | 0.30665 (13) | 0.0289 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.2203 (2) | 0.8607 (3) | 0.25828 (13) | 0.0322 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.1038 (3) | 0.9201 (4) | 0.27901 (15) | 0.0402 (6) | |
| H9 | 0.104682 | 0.955946 | 0.324621 | 0.048* | |
| C10 | −0.0139 (3) | 0.9263 (4) | 0.23202 (17) | 0.0480 (8) | |
| H10 | −0.091026 | 0.969215 | 0.245795 | 0.058* | |
| C11 | −0.0170 (3) | 0.8691 (4) | 0.16500 (17) | 0.0521 (8) | |
| H11 | −0.096307 | 0.872138 | 0.133672 | 0.062* | |
| C12 | 0.0979 (3) | 0.8075 (4) | 0.14449 (18) | 0.0547 (8) | |
| H12 | 0.095682 | 0.767683 | 0.099394 | 0.066* | |
| C13 | 0.2163 (3) | 0.8044 (4) | 0.19061 (15) | 0.0458 (7) | |
| H13 | 0.293727 | 0.764354 | 0.176137 | 0.055* | |
| C14 | 0.3371 (2) | 0.8150 (3) | 0.38222 (12) | 0.0292 (5) | |
| C15 | 0.3471 (2) | 0.6436 (3) | 0.40449 (12) | 0.0268 (5) | |
| C16 | 0.3846 (2) | 0.5223 (3) | 0.36134 (12) | 0.0306 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.403267 | 0.548117 | 0.317048 | 0.037* | |
| C17 | 0.3940 (3) | 0.3635 (3) | 0.38435 (14) | 0.0359 (6) | |
| H17 | 0.420029 | 0.282786 | 0.355635 | 0.043* | |
| C18 | 0.3652 (3) | 0.3243 (3) | 0.44943 (14) | 0.0377 (6) | |
| H18 | 0.370854 | 0.216977 | 0.464414 | 0.045* | |
| C19 | 0.3277 (3) | 0.4438 (3) | 0.49268 (14) | 0.0363 (6) | |
| H19 | 0.308420 | 0.416916 | 0.536746 | 0.044* | |
| C20 | 0.3191 (2) | 0.6030 (3) | 0.47047 (12) | 0.0311 (5) | |
| H20 | 0.294378 | 0.683342 | 0.499741 | 0.037* | |
| Cl1 | 0.99595 (7) | 0.80122 (10) | 0.45011 (4) | 0.0468 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.4585 (2) | 0.8715 (3) | 0.28342 (10) | 0.0312 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.31698 (19) | 0.9261 (2) | 0.42112 (10) | 0.0386 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0287 (12) | 0.0394 (13) | 0.0268 (12) | −0.0027 (10) | 0.0034 (9) | 0.0037 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0341 (13) | 0.0343 (13) | 0.0306 (12) | −0.0052 (11) | 0.0054 (10) | −0.0028 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0315 (12) | 0.0310 (12) | 0.0339 (13) | 0.0012 (10) | 0.0081 (10) | −0.0001 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0277 (12) | 0.0333 (12) | 0.0261 (11) | −0.0009 (10) | 0.0036 (9) | 0.0052 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0303 (12) | 0.0443 (14) | 0.0262 (12) | 0.0002 (11) | 0.0047 (10) | −0.0041 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0273 (12) | 0.0423 (14) | 0.0299 (12) | 0.0022 (11) | 0.0063 (10) | −0.0026 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0305 (12) | 0.0253 (11) | 0.0310 (12) | 0.0026 (10) | 0.0051 (10) | 0.0018 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0312 (12) | 0.0317 (12) | 0.0329 (13) | −0.0005 (10) | 0.0019 (10) | 0.0048 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0323 (13) | 0.0520 (16) | 0.0369 (14) | 0.0013 (12) | 0.0077 (11) | 0.0126 (12) |
| C10 | 0.0293 (13) | 0.0615 (19) | 0.0535 (18) | 0.0031 (13) | 0.0069 (13) | 0.0206 (15) |
| C11 | 0.0379 (16) | 0.0588 (19) | 0.0537 (19) | −0.0061 (14) | −0.0123 (14) | 0.0087 (15) |
| C12 | 0.0476 (18) | 0.064 (2) | 0.0466 (18) | 0.0059 (15) | −0.0120 (14) | −0.0122 (15) |
| C13 | 0.0417 (16) | 0.0536 (17) | 0.0396 (16) | 0.0099 (13) | −0.0026 (12) | −0.0083 (13) |
| C14 | 0.0240 (11) | 0.0337 (12) | 0.0298 (12) | 0.0020 (10) | 0.0040 (9) | −0.0024 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0231 (11) | 0.0344 (12) | 0.0222 (11) | −0.0005 (9) | 0.0007 (8) | −0.0010 (9) |
| C16 | 0.0338 (13) | 0.0320 (12) | 0.0253 (11) | −0.0010 (10) | 0.0022 (9) | 0.0002 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0425 (15) | 0.0315 (12) | 0.0318 (13) | 0.0036 (11) | −0.0007 (11) | −0.0031 (10) |
| C18 | 0.0384 (14) | 0.0354 (13) | 0.0372 (14) | −0.0040 (11) | −0.0010 (11) | 0.0063 (11) |
| C19 | 0.0353 (13) | 0.0434 (15) | 0.0296 (13) | −0.0062 (11) | 0.0036 (10) | 0.0081 (10) |
| C20 | 0.0302 (12) | 0.0364 (13) | 0.0274 (12) | −0.0008 (10) | 0.0060 (10) | −0.0010 (9) |
| Cl1 | 0.0312 (4) | 0.0681 (5) | 0.0381 (4) | 0.0023 (3) | −0.0047 (3) | −0.0040 (3) |
| N1 | 0.0274 (10) | 0.0365 (11) | 0.0290 (10) | 0.0012 (9) | 0.0022 (8) | 0.0043 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0460 (11) | 0.0336 (9) | 0.0378 (10) | 0.0018 (8) | 0.0115 (8) | −0.0051 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C6 | 1.377 (4) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.379 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.378 (5) |
| C1—Cl1 | 1.737 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.384 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.382 (4) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.393 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C14—O1 | 1.222 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.392 (4) | C14—C15 | 1.477 (3) |
| C4—N1 | 1.419 (3) | C15—C20 | 1.390 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.380 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.391 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C16—C17 | 1.382 (4) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C7—N1 | 1.268 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.374 (4) |
| C7—C8 | 1.482 (3) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C14 | 1.518 (3) | C18—C19 | 1.382 (4) |
| C8—C13 | 1.385 (4) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.388 (4) | C19—C20 | 1.380 (4) |
| C9—C10 | 1.385 (4) | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C10—C11 | 1.377 (5) | ||
| C6—C1—C2 | 121.3 (2) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C6—C1—Cl1 | 118.4 (2) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| C2—C1—Cl1 | 120.3 (2) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.3 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.5 (2) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.2 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.8 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.2 | C12—C13—C8 | 120.4 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.1 (2) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.8 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.0 | C8—C13—H13 | 119.8 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.0 | O1—C14—C15 | 123.2 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.2 (2) | O1—C14—C7 | 118.9 (2) |
| C5—C4—N1 | 116.9 (2) | C15—C14—C7 | 117.9 (2) |
| C3—C4—N1 | 123.7 (2) | C20—C15—C16 | 119.3 (2) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.7 (2) | C20—C15—C14 | 119.0 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.6 | C16—C15—C14 | 121.7 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.6 | C17—C16—C15 | 119.9 (2) |
| C1—C6—C5 | 119.1 (2) | C17—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| C1—C6—H6 | 120.4 | C15—C16—H16 | 120.0 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.4 | C18—C17—C16 | 120.3 (2) |
| N1—C7—C8 | 120.0 (2) | C18—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| N1—C7—C14 | 124.3 (2) | C16—C17—H17 | 119.8 |
| C8—C7—C14 | 115.6 (2) | C17—C18—C19 | 120.2 (2) |
| C13—C8—C9 | 119.1 (2) | C17—C18—H18 | 119.9 |
| C13—C8—C7 | 118.9 (2) | C19—C18—H18 | 119.9 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 122.0 (2) | C20—C19—C18 | 120.0 (2) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 120.3 (3) | C20—C19—H19 | 120.0 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.9 | C18—C19—H19 | 120.0 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.9 | C19—C20—C15 | 120.2 (2) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.2 (3) | C19—C20—H20 | 119.9 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 119.9 | C15—C20—H20 | 119.9 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 119.9 | C7—N1—C4 | 121.8 (2) |
| C10—C11—C12 | 119.8 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg1 is the centroid of the C1–C6 ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C3—H3···O1 | 0.93 | 2.67 | 3.247 (3) | 120 |
| C9—H9···O1 | 0.93 | 2.64 | 3.231 (3) | 122 |
| C2—H2···O1i | 0.93 | 2.60 | 3.360 (3) | 139 |
| C19—H19···Cg1ii | 0.93 | 2.88 | 3.689 (3) | 146 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Funding Statement
The authors acknowledge the Algerian Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research, the Algerian Directorate for Scientific Research and Technological Development and Setif 1 University for financial support.
References
- Bai, Y., Liu, J., Dang, D.-B. & Duan, C.-Y. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, m1805–m1807.
- Bouchama, A., Bendaâs, A., Bouacida, S., Yahiaoui, M., Benard-Rocherulle, P. & Djedouani, A. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o1990–o1992.
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst. 42, 339–341.
- Hebbachi, R., Djedouani, A., Kadri, S., Mousser, H. & Mousser, A. (2015). Acta Cryst. E71, o109–o110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Rigaku OD (2018). CrysAlis PRO. Rigaku Oxford Diffraction, Yarnton, England.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spackman, M. A. & Jayatilaka, D. (2009). CrystEngComm, 11, 19–32.
- Tabbiche, A., Bouchama, A., Chafai, N., Zaidi, F., Chiter, C., Yahiaoui, M. & Abiza, A. (2022). J. Mol. Struct. 1261, 132865–132879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). CrystalExplorer17.5. The University of Western Australia.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623000652/hb4414sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623000652/hb4414Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623000652/hb4414Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2237868
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report