The imidazolidine ring is slightly ruffled while the attached phenyl rings are rotated well out of its mean plane. In the crystal, N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds form inversion dimers, which are connected into layers parallel to (101) by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The layers are connected into a three-dimensional network by additional C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π(ring) interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure, imidazolidenedione, hydrogen bond, C—H⋯π(ring) interaction
Abstract
The imidazolidine ring in the title molecule, C17H15BrN2O2, is slightly ruffled [r.m.s. deviation = 0.0192 Å], while the attached phenyl rings at the C atom at the position between the amine and carbonyl centres are rotated well out of its mean plane [dihedral angles with the imidazolidine ring = 63.60 (8) and 76.4 (1)°]. In the crystal, a three-dimensional network features N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds together with C—H⋯π(ring) interactions.
Structure description
Phenytoine (5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione) is a drug widely prescribed as an anticonvulsant agent and for the treatment of many other diseases, including HIV (Weichet, 1974 ▸; Havera & Strycker, 1976 ▸; Khodair et al., 1997 ▸; Thenmozhiyal et al., 2004 ▸). Given the wide range of therapeutic applications for such compounds, and in a continuation of our work in this area (Ramli et al., 2017a ▸,b ▸; Akrad et al., 2017 ▸; Guerrab et al., 2019 ▸, 2020a ▸,b ▸, 2022a ▸,b ▸), the title compound (Fig. 1 ▸) was prepared and its crystal structure determined.
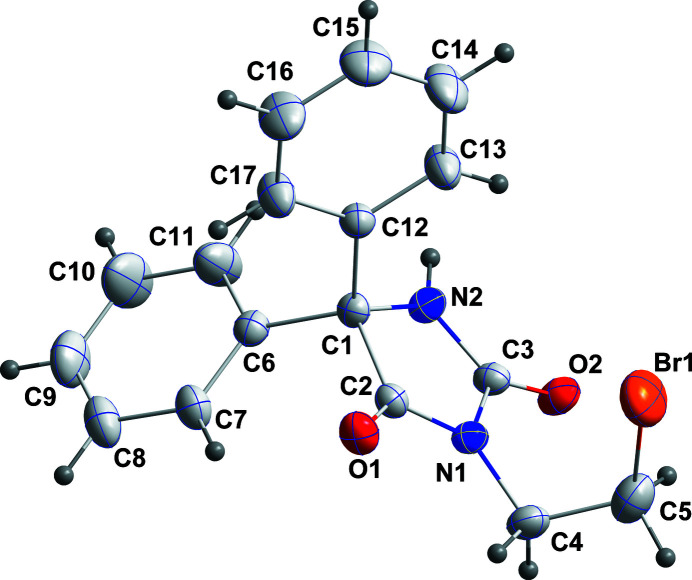
Figure 1.
The title molecule showing the atom-labelling scheme and 30% probability ellipsoids.
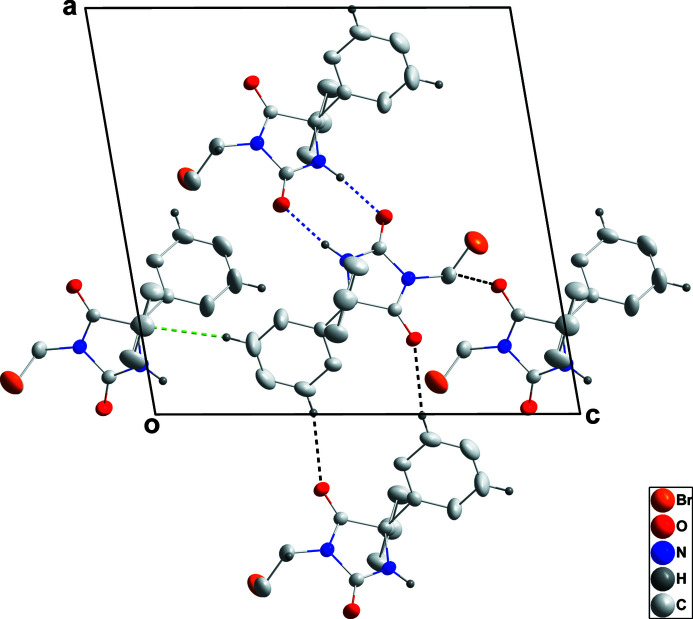
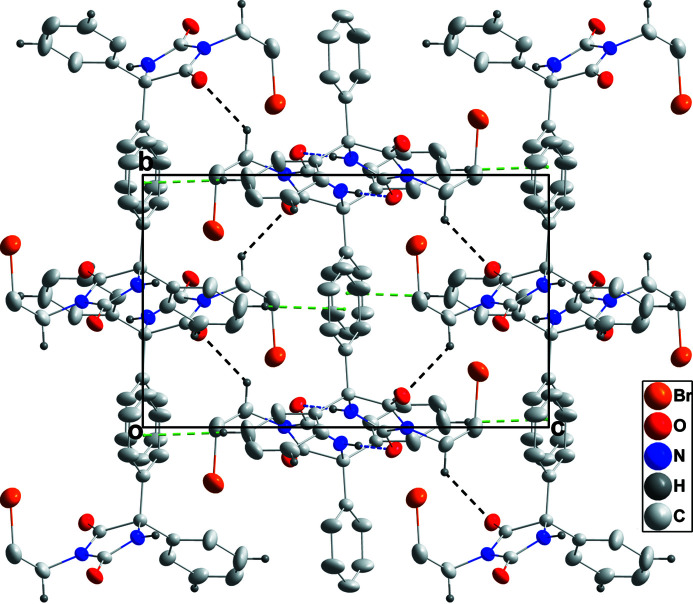
The C1/C2/N1/C3/N2 ring is planar to within 0.0254 (13) Å (r.m.s. deviation of the fitted atoms = 0.0192 Å) with the atoms alternately disposed above and below the mean plane. The C6–C11 and C12–C17 phenyl rings are inclined at 63.60 (8) and 76.4 (1)°, respectively, to the the above plane. In the crystal, inversion dimers are formed by N2—H2⋯O2 hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸) and are connected into layers parallel to (101) by C4—H4A⋯O1 hydrogen bonds (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 2 ▸). These layers are joined into a three-dimensional network by C8—H8⋯O1 hydrogen bonds and C10—H10⋯Cg(C12–C17) interactions (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 3 ▸).
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg3 is the centroid of the C12–C17 benzene ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2—H2⋯O2i | 0.89 | 1.98 | 2.862 (3) | 174 |
| C4—H4A⋯O1ii | 0.97 | 2.49 | 3.175 (3) | 128 |
| C8—H8⋯O1iii | 0.93 | 2.56 | 3.387 (3) | 148 |
| C10—H10⋯Cg3iv | 0.93 | 2.85 | 3.771 (5) | 173 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
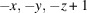 ; (iv)
; (iv)
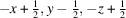 .
.
Figure 2.
Detail of the intermolecular interactions viewed along the b-axis direction. N—H⋯O and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are shown, respectively, by blue and black dashed lines, while the C—H⋯π(ring) interactions are shown by green dashed lines.
Figure 3.
Packing viewed along the a-axis direction with intermolecular interactions depicted as in Fig. 2 ▸.
Synthesis and crystallization
To a solution of 5,5-diphenylimidazolidine-2,4-dione (500 mg, 1.98 mmol), one equivalent of 1,2-dibromoethane (171.58 ml, 1.98 mmol), in absolute dimethylformamide (DMF, 15 ml), was added and the resulting solution heated under reflux for 3 h in the presence of 1.2 equivalents of K2CO3 (331.20 mg, 2.37 mmol). The reaction mixture was filtered while hot, and the solvent evaporated under reduced pressure. The residue obtained was dried and recrystallized from an ethanol solution to yield colourless blocks (Guerrab et al., 2018 ▸).
Refinement
Crystal and refinement details are presented in Table 2 ▸.
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C17H15BrN2O2 |
| M r | 359.22 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/n |
| Temperature (K) | 298 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 13.7083 (5), 8.6500 (3), 14.1183 (5) |
| β (°) | 99.724 (1) |
| V (Å3) | 1650.05 (10) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 2.50 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.42 × 0.32 × 0.25 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker SMART APEX CCD |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.46, 0.58 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 30580, 4284, 3056 |
| R int | 0.028 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.678 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.052, 0.170, 1.06 |
| No. of reflections | 4284 |
| No. of parameters | 199 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.82, −0.67 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623000603/tk4088sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623000603/tk4088Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623000603/tk4088Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2235944
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
Author contributions are as follows. Conceptualization, YR; methodology, WG and AA; investigation, WG, AEMAA; writing (original draft), JMT and YR; writing (review and editing of the manuscript), YR; formal analysis, AA and YR; supervision, YR; crystal-structure determination and validation, JTM.
full crystallographic data
Crystal data
| C17H15BrN2O2 | F(000) = 728 |
| Mr = 359.22 | Dx = 1.446 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 13.7083 (5) Å | Cell parameters from 9961 reflections |
| b = 8.6500 (3) Å | θ = 2.3–27.3° |
| c = 14.1183 (5) Å | µ = 2.50 mm−1 |
| β = 99.724 (1)° | T = 298 K |
| V = 1650.05 (10) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.42 × 0.32 × 0.25 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 4284 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3056 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.028 |
| Detector resolution: 8.3333 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 28.8°, θmin = 1.9° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −18→17 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.46, Tmax = 0.58 | l = −19→19 |
| 30580 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.052 | Hydrogen site location: mixed |
| wR(F2) = 0.170 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.06 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0893P)2 + 0.7858P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4284 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 199 parameters | Δρmax = 0.82 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.67 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The diffraction data were obtained from 3 sets of 400 frames, each of width 0.5° in ω, colllected at φ = 0.00, 90.00 and 180.00° and 2 sets of 800 frames, each of width 0.45° in φ, collected at ω = –30.00 and 210.00°. The scan time was 15 sec/frame. |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. H-atoms attached to carbon were placed in calculated positions (C—H = 0.93 - 0.97 Å) while that attached to nitrogen was placed in a location derived from a difference map and its coordinates adjusted to give N—H = 0.89 %A. All were included as riding contributions with isotropic displacement parameters 1.2 - 1.5 times those of the attached atoms. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.42103 (4) | 0.22083 (6) | 0.82606 (3) | 0.0970 (2) | |
| O1 | 0.18452 (12) | 0.1239 (2) | 0.63926 (13) | 0.0510 (4) | |
| O2 | 0.48438 (13) | −0.0886 (2) | 0.61836 (13) | 0.0529 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.33335 (14) | −0.0021 (2) | 0.65056 (13) | 0.0403 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.37878 (14) | 0.0634 (2) | 0.51316 (14) | 0.0424 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.417288 | 0.072482 | 0.468641 | 0.051* | |
| C1 | 0.28014 (15) | 0.1311 (3) | 0.50632 (15) | 0.0361 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.25666 (15) | 0.0868 (3) | 0.60614 (15) | 0.0374 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.40774 (16) | −0.0157 (3) | 0.59400 (16) | 0.0395 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.3411 (2) | −0.0664 (3) | 0.74680 (19) | 0.0549 (6) | |
| H4A | 0.349683 | −0.177478 | 0.743311 | 0.066* | |
| H4B | 0.279528 | −0.047609 | 0.770075 | 0.066* | |
| C5 | 0.4249 (3) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.8179 (2) | 0.0752 (9) | |
| H5A | 0.487132 | −0.031874 | 0.799497 | 0.090* | |
| H5B | 0.422518 | −0.044378 | 0.880776 | 0.090* | |
| C6 | 0.20839 (17) | 0.0547 (3) | 0.42505 (16) | 0.0412 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.12239 (18) | −0.0173 (3) | 0.4386 (2) | 0.0513 (6) | |
| H7 | 0.104522 | −0.017699 | 0.499314 | 0.062* | |
| C8 | 0.0619 (2) | −0.0895 (4) | 0.3625 (3) | 0.0659 (8) | |
| H8 | 0.003723 | −0.137210 | 0.372572 | 0.079* | |
| C9 | 0.0871 (3) | −0.0910 (4) | 0.2741 (3) | 0.0803 (10) | |
| H9 | 0.046718 | −0.140238 | 0.223419 | 0.096* | |
| C10 | 0.1722 (4) | −0.0197 (6) | 0.2595 (3) | 0.1016 (15) | |
| H10 | 0.189448 | −0.020397 | 0.198523 | 0.122* | |
| C11 | 0.2333 (3) | 0.0538 (5) | 0.3343 (2) | 0.0772 (10) | |
| H11 | 0.290963 | 0.102283 | 0.323391 | 0.093* | |
| C12 | 0.28154 (17) | 0.3076 (3) | 0.49925 (17) | 0.0406 (5) | |
| C13 | 0.3654 (2) | 0.3905 (3) | 0.5354 (3) | 0.0680 (8) | |
| H13 | 0.422881 | 0.338705 | 0.562487 | 0.082* | |
| C14 | 0.3647 (3) | 0.5504 (4) | 0.5316 (3) | 0.0851 (11) | |
| H14 | 0.421780 | 0.605165 | 0.556105 | 0.102* | |
| C15 | 0.2814 (3) | 0.6282 (4) | 0.4925 (3) | 0.0778 (10) | |
| H15 | 0.281492 | 0.735614 | 0.489416 | 0.093* | |
| C16 | 0.1985 (3) | 0.5476 (4) | 0.4581 (3) | 0.0750 (9) | |
| H16 | 0.141001 | 0.600601 | 0.432518 | 0.090* | |
| C17 | 0.1975 (2) | 0.3870 (3) | 0.4603 (2) | 0.0598 (7) | |
| H17 | 0.140013 | 0.333439 | 0.435486 | 0.072* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.1041 (4) | 0.0862 (3) | 0.0912 (3) | −0.0175 (2) | −0.0107 (2) | −0.0181 (2) |
| O1 | 0.0413 (9) | 0.0627 (11) | 0.0519 (9) | 0.0039 (8) | 0.0162 (7) | −0.0076 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0477 (9) | 0.0542 (10) | 0.0584 (10) | 0.0179 (8) | 0.0137 (8) | 0.0165 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0412 (9) | 0.0405 (10) | 0.0407 (9) | 0.0009 (7) | 0.0112 (7) | 0.0045 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0378 (9) | 0.0478 (11) | 0.0440 (10) | 0.0112 (8) | 0.0138 (7) | 0.0076 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0328 (9) | 0.0361 (10) | 0.0399 (10) | 0.0045 (8) | 0.0074 (8) | −0.0002 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0359 (10) | 0.0365 (11) | 0.0402 (10) | −0.0016 (8) | 0.0076 (8) | −0.0051 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0393 (11) | 0.0347 (11) | 0.0458 (11) | 0.0024 (8) | 0.0108 (9) | 0.0030 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0610 (15) | 0.0567 (15) | 0.0492 (13) | −0.0017 (12) | 0.0155 (11) | 0.0142 (12) |
| C5 | 0.080 (2) | 0.088 (3) | 0.0543 (16) | 0.0110 (17) | 0.0019 (15) | 0.0095 (16) |
| C6 | 0.0456 (11) | 0.0348 (11) | 0.0421 (11) | 0.0037 (9) | 0.0038 (9) | −0.0017 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0402 (11) | 0.0536 (14) | 0.0587 (14) | 0.0015 (10) | 0.0038 (10) | −0.0107 (12) |
| C8 | 0.0479 (14) | 0.0576 (17) | 0.086 (2) | −0.0004 (12) | −0.0069 (13) | −0.0180 (15) |
| C9 | 0.089 (2) | 0.072 (2) | 0.069 (2) | −0.0047 (18) | −0.0169 (17) | −0.0243 (17) |
| C10 | 0.127 (3) | 0.131 (4) | 0.0463 (17) | −0.038 (3) | 0.0114 (19) | −0.022 (2) |
| C11 | 0.095 (2) | 0.092 (2) | 0.0469 (15) | −0.032 (2) | 0.0203 (15) | −0.0127 (16) |
| C12 | 0.0421 (11) | 0.0354 (11) | 0.0438 (11) | 0.0011 (8) | 0.0055 (9) | −0.0012 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0529 (15) | 0.0466 (15) | 0.095 (2) | −0.0047 (12) | −0.0158 (14) | 0.0038 (14) |
| C14 | 0.077 (2) | 0.0505 (17) | 0.117 (3) | −0.0192 (16) | −0.015 (2) | −0.0067 (18) |
| C15 | 0.094 (2) | 0.0365 (14) | 0.100 (3) | −0.0010 (15) | 0.007 (2) | −0.0063 (15) |
| C16 | 0.0706 (19) | 0.0417 (15) | 0.107 (3) | 0.0166 (14) | −0.0011 (18) | 0.0032 (16) |
| C17 | 0.0461 (13) | 0.0425 (13) | 0.085 (2) | 0.0069 (10) | −0.0042 (13) | −0.0032 (13) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C5 | 1.923 (4) | C7—H7 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C2 | 1.207 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.351 (5) |
| O2—C3 | 1.223 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C2 | 1.366 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.366 (6) |
| N1—C3 | 1.402 (3) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C4 | 1.455 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.386 (5) |
| N2—C3 | 1.333 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C1 | 1.461 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| N2—H2 | 0.8899 | C12—C17 | 1.374 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.529 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.378 (4) |
| C1—C12 | 1.530 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.384 (5) |
| C1—C2 | 1.546 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.502 (5) | C14—C15 | 1.360 (5) |
| C4—H4A | 0.9700 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4B | 0.9700 | C15—C16 | 1.352 (5) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9700 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C5—H5B | 0.9700 | C16—C17 | 1.389 (4) |
| C6—C7 | 1.375 (4) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C11 | 1.381 (4) | C17—H17 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.390 (4) | ||
| C2—N1—C3 | 111.28 (18) | C6—C7—C8 | 120.6 (3) |
| C2—N1—C4 | 125.0 (2) | C6—C7—H7 | 119.7 |
| C3—N1—C4 | 123.6 (2) | C8—C7—H7 | 119.7 |
| C3—N2—C1 | 113.63 (18) | C9—C8—C7 | 120.5 (3) |
| C3—N2—H2 | 121.6 | C9—C8—H8 | 119.8 |
| C1—N2—H2 | 124.8 | C7—C8—H8 | 119.8 |
| N2—C1—C6 | 110.32 (18) | C8—C9—C10 | 119.5 (3) |
| N2—C1—C12 | 112.45 (18) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.2 |
| C6—C1—C12 | 113.30 (17) | C10—C9—H9 | 120.2 |
| N2—C1—C2 | 99.99 (16) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.9 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 111.75 (18) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.5 |
| C12—C1—C2 | 108.26 (17) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.5 |
| O1—C2—N1 | 126.1 (2) | C6—C11—C10 | 119.8 (3) |
| O1—C2—C1 | 126.7 (2) | C6—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| N1—C2—C1 | 107.18 (17) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.1 |
| O2—C3—N2 | 128.5 (2) | C17—C12—C13 | 118.6 (2) |
| O2—C3—N1 | 123.8 (2) | C17—C12—C1 | 120.4 (2) |
| N2—C3—N1 | 107.71 (18) | C13—C12—C1 | 120.9 (2) |
| N1—C4—C5 | 114.0 (2) | C12—C13—C14 | 120.4 (3) |
| N1—C4—H4A | 108.8 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.8 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 108.8 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.8 |
| N1—C4—H4B | 108.8 | C15—C14—C13 | 120.7 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4B | 108.8 | C15—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 107.7 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.6 |
| C4—C5—Br1 | 113.0 (2) | C16—C15—C14 | 119.2 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 109.0 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.4 |
| Br1—C5—H5A | 109.0 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.4 |
| C4—C5—H5B | 109.0 | C15—C16—C17 | 121.2 (3) |
| Br1—C5—H5B | 109.0 | C15—C16—H16 | 119.4 |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 107.8 | C17—C16—H16 | 119.4 |
| C7—C6—C11 | 118.6 (2) | C12—C17—C16 | 119.9 (3) |
| C7—C6—C1 | 123.3 (2) | C12—C17—H17 | 120.1 |
| C11—C6—C1 | 118.0 (2) | C16—C17—H17 | 120.1 |
| C3—N2—C1—C6 | −113.5 (2) | N2—C1—C6—C11 | −54.9 (3) |
| C3—N2—C1—C12 | 119.0 (2) | C12—C1—C6—C11 | 72.1 (3) |
| C3—N2—C1—C2 | 4.3 (2) | C2—C1—C6—C11 | −165.2 (3) |
| C3—N1—C2—O1 | −176.7 (2) | C11—C6—C7—C8 | 0.0 (4) |
| C4—N1—C2—O1 | −0.6 (4) | C1—C6—C7—C8 | −177.7 (2) |
| C3—N1—C2—C1 | 3.1 (2) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 0.4 (5) |
| C4—N1—C2—C1 | 179.1 (2) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.6 (6) |
| N2—C1—C2—O1 | 175.5 (2) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.2 (7) |
| C6—C1—C2—O1 | −67.8 (3) | C7—C6—C11—C10 | −0.4 (6) |
| C12—C1—C2—O1 | 57.7 (3) | C1—C6—C11—C10 | 177.4 (4) |
| N2—C1—C2—N1 | −4.3 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C6 | 0.3 (7) |
| C6—C1—C2—N1 | 112.5 (2) | N2—C1—C12—C17 | 157.7 (2) |
| C12—C1—C2—N1 | −122.08 (19) | C6—C1—C12—C17 | 31.7 (3) |
| C1—N2—C3—O2 | 177.4 (2) | C2—C1—C12—C17 | −92.8 (3) |
| C1—N2—C3—N1 | −2.8 (3) | N2—C1—C12—C13 | −25.2 (3) |
| C2—N1—C3—O2 | 179.4 (2) | C6—C1—C12—C13 | −151.1 (3) |
| C4—N1—C3—O2 | 3.3 (4) | C2—C1—C12—C13 | 84.3 (3) |
| C2—N1—C3—N2 | −0.4 (3) | C17—C12—C13—C14 | −0.5 (5) |
| C4—N1—C3—N2 | −176.5 (2) | C1—C12—C13—C14 | −177.7 (3) |
| C2—N1—C4—C5 | −113.9 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.1 (7) |
| C3—N1—C4—C5 | 61.7 (4) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.8 (7) |
| N1—C4—C5—Br1 | 55.0 (3) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | −1.3 (7) |
| N2—C1—C6—C7 | 122.8 (2) | C13—C12—C17—C16 | 0.0 (5) |
| C12—C1—C6—C7 | −110.1 (3) | C1—C12—C17—C16 | 177.2 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 12.5 (3) | C15—C16—C17—C12 | 0.9 (6) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
Cg3 is the centroid of the C12–C17 benzene ring.
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N2—H2···O2i | 0.89 | 1.98 | 2.862 (3) | 174 |
| C4—H4A···O1ii | 0.97 | 2.49 | 3.175 (3) | 128 |
| C8—H8···O1iii | 0.93 | 2.56 | 3.387 (3) | 148 |
| C10—H10···Cg3iv | 0.93 | 2.85 | 3.771 (5) | 173 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+3/2; (iii) −x, −y, −z+1; (iv) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Funding Statement
JTM thanks Tulane University for support of the Tulane Crystallography Laboratory.
References
- Akrad, R., Mague, J. T., Guerrab, W., Taoufik, J., Ansar, M. & Ramli, Y. (2017). IUCrData, 2, x170033.
- Brandenburg, K. & Putz, H. (2012). DIAMOND, Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2016). APEX3 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Guerrab, W., Akachar, J., El Jemli, M., Abudunia, A. M., Ouaabou, R., Alaoui, K., Ibrahimi, A. & Ramli, Y. (2022a). J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. https://doi.org/10.1080/07391102.2022.2069865 [DOI] [PubMed]
- Guerrab, W., Chung, I. M., Kansiz, S., Mague, J. T., Dege, N., Taoufik, J., Salghi, R., Ali, I. H., Khan, M. I., Lgaz, H. & Ramli, Y. (2019). J. Mol. Struct. 1197, 369–376.
- Guerrab, W., El Jemli, M., Akachar, J., Demirtaş, G., Mague, J. T., Taoufik, J., Ibrahimi, A., Ansar, M., Alaoui, K. & Ramli, Y. (2022b). J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 40, 8765–8782. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Guerrab, W., Lgaz, H., Kansiz, S., Mague, J. T., Dege, N., Ansar, M., Marzouki, R., Taoufik, J., Ali, I. H., Chung, I. & Ramli, Y. (2020a). J. Mol. Struct. 1205, 127630.
- Guerrab, W., Mague, J. T. & Ramli, Y. (2020b). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 235, 1425–1427.
- Guerrab, W., Mague, J. T., Taoufik, J. & Ramli, Y. (2018). IUCrData, 3, x180057.
- Havera, H. J. & Strycker, W. G. (1976). US Patent 3 904 909.
- Khodair, A. I., el-Subbagh, H. I. & el-Emam, A. A. (1997). Boll. Chim. Farm. 136, 561–567. [PubMed]
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ramli, Y., Akrad, R., Guerrab, W., Taoufik, J., Ansar, M. & Mague, J. T. (2017a). IUCrData, 2, x170098.
- Ramli, Y., Guerrab, W., Moussaif, A., Taoufik, J., Essassi, E. M. & Mague, J. T. (2017b). IUCrData, 2, x171041.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Thenmozhiyal, J. C., Wong, P. T. H. & Chui, W.-K. (2004). J. Med. Chem. 47, 1527–1535. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Weichet, B. L. (1974). Czech Patent 151,744-747.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623000603/tk4088sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623000603/tk4088Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2414314623000603/tk4088Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 2235944
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report