Figure 2 -. Genetic deletion of Pcdhγc4 increased cell death in MGE-derived cINs.
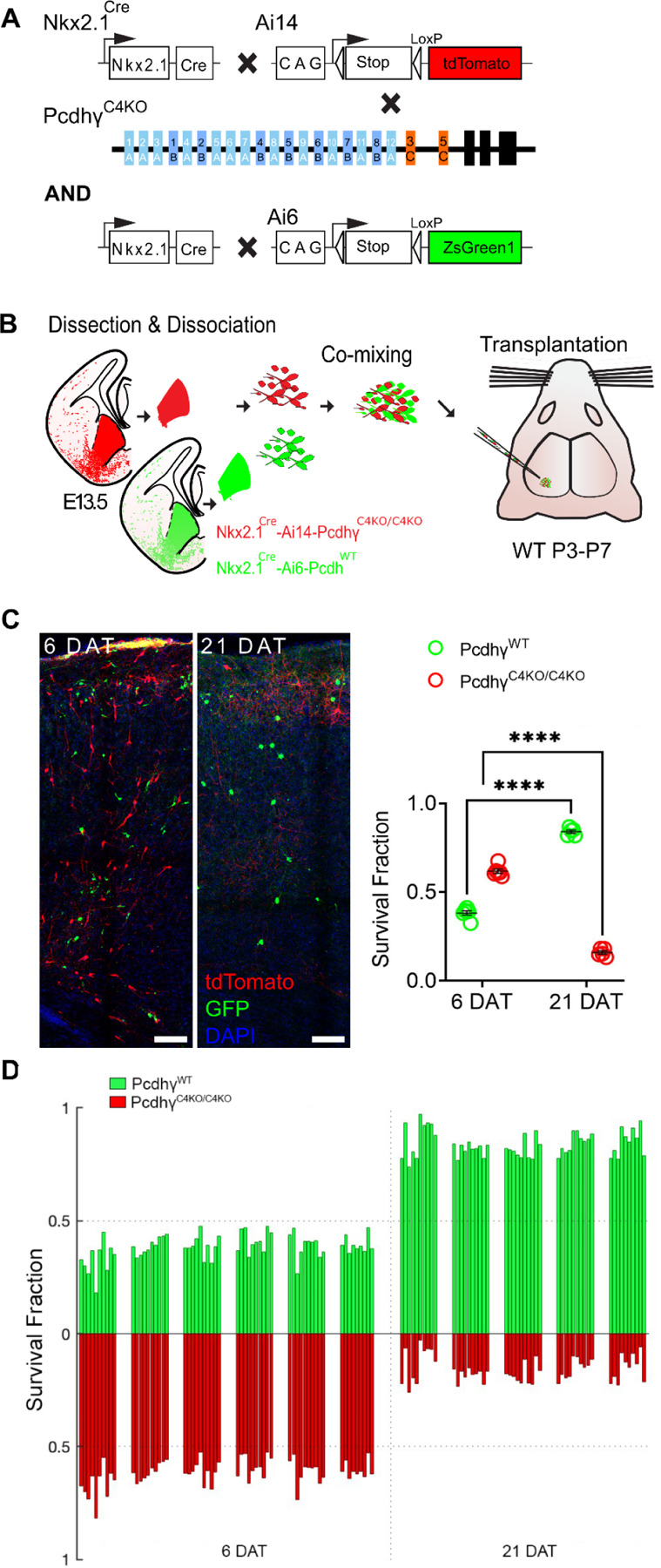
A. Diagram of genetic crosses between MGE/POA-specific reporter and PcdhγC4KO mice. PcdhγC4KO homozygous MGE cells were obtained from the Nkx2.1Cre; Ai14;PcdhγC4KO/C4KO embryos, whereas control cells were obtained from Nkx2.1Cre; Ai6 embryos.
B. Schematics of transplantation protocol. The MGEs from E13.5 PcdhγC4KO homozygous mutant or control embryos were dissected, dissociated, and mixed in similar proportions. The mixture of GFP+ (PcdhγWT) and tdTomato+ (PcdhγC4KO/C4KO) cells was grafted into the cortex of WT neonate mice.
C. Left - Confocal images from the cortex of 6 and 21 DAT mice. The transplanted cells are labeled with GFP (PcdhγWT) or tdTomato (PcdhγC4KO/C4KO). Right - Quantifications (shown as survival fraction) of surviving MGE-derived cINs at 6 and 21 DAT. Both the transplanted GFP and tdTomato-labeled cells undergo programmed cell death between 6 and 21 DAT, but the PcdhγC4KO/C4KO cells are eliminated at significantly higher rates.
D. Survival fraction quantification from (C) shown by the brain section (each bar) and separated by animals at 6 and 21 DAT.
Scale bar = 50 um, Nested-ANOVA, ****p =3.147e-10, n = 5 mice per time point and 10 brain sections quantified per mouse
