Abstract
Around 40–50% of all triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) patients achieve a pathological complete response (pCR) after treatment with neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC). The identification of biomarkers predicting the response to NAC could be helpful for personalized treatment. This systematic review provides an overview of putative biomarkers at baseline that are predictive for a pCR following NAC. Embase, Medline and Web of Science were searched for articles published between January 2010 and August 2022. The articles had to meet the following criteria: patients with primary invasive TNBC without distant metastases and patients must have received NAC. In total, 2045 articles were screened by two reviewers resulting in the inclusion of 92 articles. Overall, the most frequently reported biomarkers associated with a pCR were a high expression of Ki-67, an expression of PD-L1 and the abundance of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, particularly CD8+ T cells, and corresponding immune gene signatures. In addition, our review reveals proteomic, genomic and transcriptomic markers that relate to cancer cells, the tumor microenvironment and the peripheral blood, which also affect chemo-sensitivity. We conclude that a prediction model based on a combination of tumor and immune markers is likely to better stratify TNBC patients with respect to NAC response.
Keywords: TNBC, breast cancer, NAC, TILs, Ki-67, prediction, pCR
1. Introduction
Breast cancer is one of the most common malignancies among women worldwide [1]. Up to 15% of all breast cancers are triple-negative [2]. Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is defined by the lack of expression of the estrogen receptor (ER), the progesterone receptor (PR) and the absence of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression and/or gene amplification. According to the guidelines of the American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists (ASCO/CAP), ER and PR are considered negative when <1% of tumor cells show nuclear staining via immunohistochemistry [3,4]. TNBC is a biological and clinically heterogeneous disease and it tends to be more common among younger women and women carrying a BRCA1 gene mutation. Over the last decades, several gene-expression-based classifications have emerged for TNBC [5,6,7]. The majority of TNBC cases, as determined by immunohistochemistry, cluster within the basal-like intrinsic subtype, but a small group is identified as non-basal-like, including the luminal androgen receptor subtype and that which is HER2-enriched.
Patients with TNBC are not eligible for endocrine or HER2-targeted therapies, currently rendering chemotherapy as the most-used therapeutic option [8]. Anthracycline/taxane-containing chemotherapy regimens are widely used as adjuvant or neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and approximately 40 to 50% of patients with TNBC treated with chemotherapy achieve a pathologic complete response (pCR) [9,10,11,12]. Platinum salts can be added to taxane-containing neoadjuvant treatment, for example, carboplatin in combination with paclitaxel [13,14]. Currently, neoadjuvant treatment is the preferred treatment choice, based on the prognostic value of the treatment response and the possibility to treat the non-pCR group with novel promising adjuvant therapies. Achieving a pCR is correlated with a good prognosis, equal to that of other breast cancer subtypes, and is considered a surrogate marker for survival [15]. Unfortunately, there is also a subgroup of patients with TNBC that experience no or limited benefit from chemotherapy [8]. This chemo-resistant subgroup shows highly aggressive behavior with high recurrence rates, an increased risk of metastases and a lack of recognized molecular targets for therapy [16,17,18]. Moreover, these patients endure multiple cycles of chemotherapy with hardly any benefit, indicating the need for predictive biomarkers to prevent unnecessary toxicity and costs.
Many researchers have already investigated whether standard clinicopathologic characteristics at baseline, including tumor size, histologic grade, histologic subtype and lymph node involvement, can predict the response to NAC, albeit with contradictory results. For example, some articles found an association between the smaller, lower-grade, non-metastasized tumors (N0) and pCR rate, whereas other articles reported no association, indicating that these characteristics cannot be solely used for the prediction of a pCR [19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26]. Regarding histologic subtype, no significant associations with response to NAC have been reported [19,21,22,27,28,29,30,31,32].
Currently, no universally approved biomarker is available to predict the response to NAC. Novel biomarkers at baseline that enable the identification of good and poor responders would be critical for therapeutic decision making for TNBC patients [33]. Nowadays, the literature regarding the tumor microenvironment is growing exponentially since this has been recognized as a regulator of carcinogenesis as well as immune evasion [34]. However, using immune parameters in daily clinical practice has not yet been generally implemented [19].
The goal of this review was to provide a systematic overview of the existing literature regarding baseline biomarkers present in cancer cells, the tumor microenvironment or peripheral blood of TNBC patients and their potential for predicting the pCR rate.
2. Methods
2.1. Literature Search
The databases Embase, MEDLINE and Web of Science were searched from 2010 to August 2022 for articles with the use of the controlled terms TNBC and NAC (Supplementary file S1). Only papers written in English were considered for inclusion. Reviews were excluded. The authors N.S. van den Ende and A.H. Nguyen independently reviewed the titles and abstracts of the identified articles. The full text of potentially relevant articles was evaluated independently by both N.S. van den Ende and A.H Nguyen. Disagreement was solved by discussion and reaching consensus.
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion
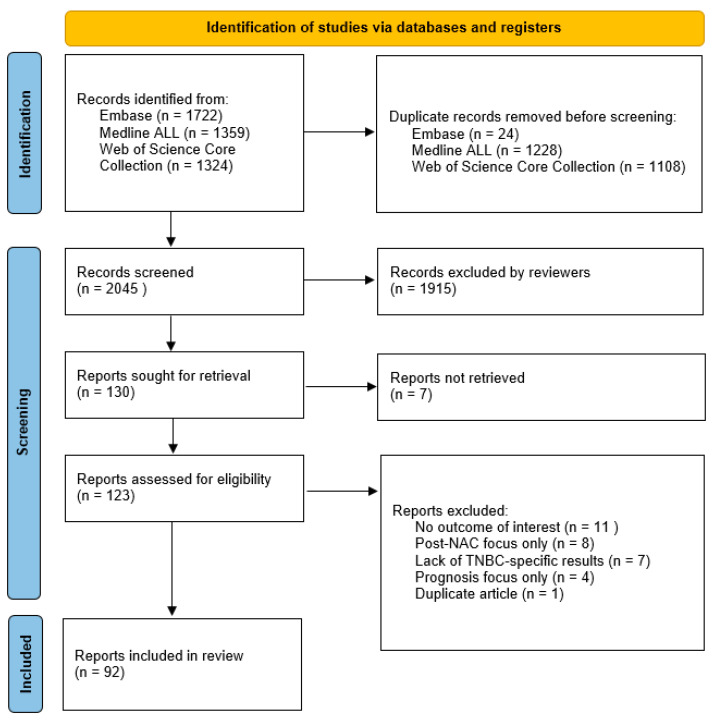
To be included in this review, the articles had to meet the following criteria: patients had to have primary invasive breast cancer without distant metastases and patients must have received NAC. A total of 2045 papers were screened and the papers that focused on the prediction of a pCR were of interest. The final exclusion of papers was based on the following criteria: no results for the outcome of interest, post-NAC focus only, lack of TNBC-specific results and focus on prognosis only. One duplicate article was discovered. In total, 92 papers were selected, revised and summarized for this article. Figure 1 illustrates the method of article selection.
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of inclusion and exclusion of papers for this review. NAC = neoadjuvant chemotherapy; TNBC = triple-negative breast cancer.
2.3. Synthesis Method
Following the Preferred Reporting Items for the Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) 2020 statement, this review was written and subdivided into 4 parts: proteomic (divided into 2 sections: tumor cells and tumor microenvironment), genomic and transcriptomic features [35]. The PRISMA 2020 checklist can be found in Supplementary File S2.
3. Results
3.1. Proteomic Profile of Tumor Cells
Protein expression determined by immunohistochemistry is the method that is used mostly in daily diagnostics for tumor subtyping, because it is quick and relatively cheap. Many protein markers at baseline have been analyzed for their ability to predict the response rate to NAC.
TNBC is a highly proliferative breast cancer subtype, often associated with high Ki-67 expression [18]. The Ki-67 index is an indicator of proliferation activity and has been extensively investigated as a predictive marker for therapy response. Table 1 provides an overview of the literature regarding baseline Ki-67 protein levels and response to NAC in TNBC patients. In summary, various studies showed a statistically significant higher expression of Ki-67 in patients achieving a pCR versus patients without a pCR [20,25,32,36,37,38,39]. On the other hand, several other studies showed no statistically significant difference in Ki-67 expression levels between the pCR and non-pCR groups [19,24,26,40,41]. In addition, some studies reported that solely using Ki-67 expression is not sufficient to predict a pCR, suggesting that other markers are also needed for a robust prediction model [38,42,43]. Notably, it is important to consider that these studies used different cut-off values for what is considered a high Ki-67 protein expression (Table 1). All studies performed the Ki-67 staining on whole tissue slides, expect for the study by Kraus et al. that used tissue microarrays [41].
Table 1.
Overview of articles regarding Ki-67 expression at baseline and the association with a pCR after NAC in TNBC patients.
| Author | Year of Publication | Study Size | Cut-Off Value High vs. Low | p-Value of the Association between Ki-67 and pCR | General Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Masuda et al. [25] | 2011 | N = 33 | 50% | p = 0.03 | The percentage of patients with a pCR who had high Ki-67 expression was 50%, whereas 15% had low Ki-67 expression |
| Sakuma et al. [43] | 2011 | N = 44 | 50% | p > 0.9999 | The percentage of patients with a high Ki-67 expression who had a pCR was 39%, compared to 36% of patients with a low Ki-67 expression |
| Kraus et al. [41] | 2012 | N = 56 | 25% | p = 0.542 | Patients with a pCR had a mean Ki-67 expression of 61% (range 35–90%), compared to 58% (range 5–95%) in patients without a pCR |
| Kawate et al. [42] | 2013 | N = 205 | 14% | p = 0.1011 | The percentage of patients with a high Ki-67 expression who had a pCR was 28%, compared to 16% of the patients with a low Ki-67 expression |
| Miyashita et al. [37] | 2014 | N = 110 | 57.5% | p = 0.002 | High Ki-67 expression was associated with a pCR rate of 70%, while low Ki-67 expression was associated with a pCR rate of 5% |
| Kim et al. [19] | 2015 | N = 198 | 10% | p = 0.056 | High Ki-67 expression was associated with a pCR rate of 19.5%, while low Ki-67 expression was associated with a pCR rate of 6% |
| Baba et al. [40] | 2016 | N = 34 | 35% | p = 0.66 | In patients with a pCR, the mean Ki-67 expression was 55% ± 30 standard deviation. In patients without a pCR, the mean Ki-67 expression was 80% ± 12 standard deviation for partial response, 73% ± 8 standard deviation for stable disease and 55% ± 41 standard deviation for progressive disease |
| Garcia-Vazquez et al. [36] | 2017 | N = 18 | Mean expression of Ki-67 | 64% expression of Ki-67 in pCR vs. 51% expression of Ki-67 in non-pCR | In patients with a pCR, the median Ki-67 expression was 71% (range 30–90), compared to 62% in the non-pCR group (range 15–90) |
| Bignon et al. [24] | 2018 | N = 53 | Mean pCR vs. non-pCR | p = 0.48 | The mean Ki-67 expression in the pCR group was 68%, compared to 64% in the non-pCR group |
| Guestini et al. [20] | 2019 | N = 148 | 53% | p = 0.023 | Patients with a pCR had higher expression levels of Ki-67 |
| Gluz et al. [38] | 2020 | N = 336 | Not mentioned | p < 0.001 | n/a |
| Kong et al. [32] | 2020 | N = 280 | 20% | p = 0.451 | n/a |
| Van Bockstal et al. [26] | 2020 | N = 35 | 20% | p = 1.000 | In the pCR group, no patients had a low Ki-67 expression. In the non-pCR group, 4% had low Ki-67 expression, while 96% had high Ki-67 expression |
| Zuo et al. [39] | 2022 | N = 127 | 40% | p = 0.028 | n/a |
Another protein marker often investigated for its association with a pCR is the androgen receptor (AR). Approximately 65 to 85% of all TNBCs lack AR expression [21]. Multiple studies found that TNBC with a negative AR is correlated with a higher pCR rate than the TNBC AR+ subtype, indicating that the presence of AR decreases the chance of achieving a pCR [21,22,44]. There is a possibility that the lower pCR rate for AR-expressing tumors could be caused by a lower proliferation rate, which could make this subgroup more chemo-resistant. Mohammed et al. described that TNBC AR+ tumors showed a lower proliferation rate compared to TNBC AR- tumors [21]. In contrast, two other studies did not find an association between the AR status and the pCR rate [25,45]. Lately, it has also been suggested that the AR is involved in tumor cell immune evasion, resulting in a lower immune response and thus a lower chance of achieving a pCR [46].
The HER2 protein is a member of the ERBB ontology family [47]. Signaling through this family of receptors promotes cell proliferation and prevents apoptosis. TNBC lacks overexpression of the HER2 protein and HER2 negativity is classified, through immunohistochemistry, as score 0, score 1+ or score 2+ with negative in situ hybridization. Gluz et al. reported that a higher HER2 score (1+ or 2+ versus 0) was unfavorable for the pCR rate (p = 0.03) [38]. However, this result was dependent on the type of NAC and the association was only found in a subgroup treated with a nab-paclitaxel/carboplatin and not in the subgroup receiving nab-paclitaxel/gemcitabine. In a study by Denkert et al., there was no statistically significant difference in pCR rate between HER2-low cases (immunohistochemistry score of 1+ or 2+ without amplification) versus HER2-0 cases within the hormone receptor negative cohort [48]. Recently, there has been increased interest in revising the HER2 classification and implementing a HER2-low category, since these patients could benefit from novel therapeutic agents [49,50]. Moreover, this HER2-low subgroup has been reported to have a lower immune response, which is in concordance with the lower pCR rate reported by Gluz et al. [38,49].
The most common genetic mutation in TNBC is in the TP53 gene, with a frequency of 84% [51,52]. The tumor suppressor protein p53 is involved in DNA repair mechanisms. Masuda et al. reported that tumor cells with a non-functional p53, determined by immunohistochemistry, do not respond to systemic therapy, due to a failure in apoptosis [25]. Several studies investigated the possible relation between p53 and a pCR. Most of these studies showed no significant association between immunohistochemical p53 expression or TP53 mutation status and the response to NAC [20,25,26,53,54]. However, two studies did find a correlation between overexpression of p53 and a high pCR rate [19,43].
EGFR is a transmembrane glycoprotein, which is a member of the ErbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases [55]. It plays a role in cell proliferation, cell motility, tissue invasion, cell survival and angiogenesis [56]. Tang et al. reported that, within 40 TNBC patients, the overexpression of EGFR was significantly associated with a high pCR rate [55]. Another study reported no association between EGFR and a pCR [41]. Furthermore, Abdelrahman et al. analyzed the predictive impact of EGFR and reported that high EGFR expression was a negative predictor for achieving a pCR [56]. These contradictory results indicate that EGFR is not a robust marker for predicting the pCR rate.
For VEGFR2, vimentin and HAGE, a higher expression of these individual markers was associated with a higher likelihood of achieving a pCR [20,57,58]. VEGFR2 is a signaling protein involved in angiogenesis, vimentin is a cytoskeletal component of mesenchymal cells and HAGE is a helicase antigen. Various other biomarkers including FGFR4, NUP98, E-cadherin, Bcl2, ALDH1, tumor-associated stromal clusterin, TOPK, YAP1 and MMP7 were also correlated with the pCR rate [38,41,59,60,61,62,63,64]. A high expression of these markers was associated with an unfavorable response to NAC. It is important to note that the study that reported tumor-associated stromal clusterin in relation to therapy response also considered patients with a limited amount of residual tumor (residual cancer burden (RCB) score 1) as good responders [62]. FGFR4 is a fibroblast growth factor receptor and NUP98 is involved in nuclear import and export [38,59]. Notably, the association for FGFR4 was only found in the subgroup treated with a nab-paclitaxel/gemcitabine regimen and not in the subgroup treated with nab-paclitaxel/carboplatin [38]. In a subsequent validation set for E-cadherin, a tumor suppressor protein, no difference in expression level was found between good and poor responders [41,65]. Therefore, it remains unclear whether reduced E-cadherin staining can predict a pCR. Moreover, three other studies found no significant association between Bcl2 expression and the pCR rate [19,20,40]. ALDH1 is a marker of breast cancer stem cells, which are multipotent cells that are able to renew themselves [61]. TOPK plays a role in the growth of breast cancer cells, cell migration and invasion [63]. YAP1 is a protein that promotes transcription and MMP7 regulates and supports tumor proliferation and the inhibition of apoptosis [66,67].
Finally, for a number of other tumor-related biomarkers, such as GCS, CYP1A1, SOX10, GATA3, NF-κB, p63, CK5, CK5/6, CK14 and CK17, no association was found across several studies between expression levels and pCR rate [26,33,40,41,56].
3.2. Proteomic Profile of Tumor-Associated Immune Cells
The tumor microenvironment is of great importance for the survival, growth and metastasis of breast cancer cells [68]. Several immune parameters from the tumor microenvironment or from the circulation have been shown to have predictive and/or prognostic value.
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) are lymphocytes that are present in and around the invasive tumor and they play a role in the tumor microenvironment where they can mediate adaptive immune responses against the tumor [69,70]. Overall, CD8+ T cells, CD4+ T cells and B cells are seen as TIL components. The scoring of TILs can be performed on H&E slides based on international guidelines by the International Immuno-Oncology Working Group for TIL assessment [71]. This working group has shown that TIL scores are reproducible with a high concordance among pathologists. Furthermore, TILs have also been reported to be prognostic markers, especially in TNBC, where a high density of TILs is associated with a survival benefit [72,73,74,75]. A high abundance of TILs has robustly been associated with a greater likelihood of achieving a pCR and a lower RCB score post-treatment in multiple studies [26,34,54,58,64,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88] (Table 2). It is important to note, however, that in these studies, different cut-off values were used for TIL assessment, varying from ≥20% to ≥40%, ≥50% and even ≥60%. The RCB is a standardized approach to evaluate the pathologic response to chemotherapy, ranging from RCB-0 (equal to a pCR) to RCB-III (no response) [89,90]. In addition to the density of TILs, the phenotype of TILs and the location are also seen as important factors for the predictive value of TILs [91]. Most of the studies reported in this review did mention whether they analyzed stromal TILs or intratumoral TILs. However, there was a lack of mentioning whether the tumors have an immune-desert, immune-excluded or immune-inflamed appearance [91,92]. Zhang et al. also proposed TIL volume (TILV = % stroma in tumor x % stromal TILs) as a predictor for a pCR and showed that high TILV (≥1600) was associated with a pCR [34].
Table 2.
Overview of articles regarding density of TILs at baseline and the association with a pCR after NAC in TNBC patients.
| Author | Year of Publication | Study Size | Cut-Off Value High vs. Low | Location of TILs: Stromal (s) or Tumoral | p-Value of the Association between pCR and Density of TILs | General Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ono et al. [81] | 2012 | N = 102 | 50% | sTILs | p = 0.05 | TIL-high patients had a pCR rate of 37%, compared to 16% in TIL-low patients |
| Abdel-Fatah et al. [58] | 2016 | N = 110 | 60% | sTILs and intratumoral TILs | p = 0.005 | TIL-high patients had a pCR rate of 53%, compared to 15% in TIL-low patients |
| Castaneda et al. [82] | 2016 | N = 98 | Continuous scale (per 10% increment) | sTILs | p = 0.0251 | A higher median TIL percentage of 40% ± 17.5 interquartile deviation was associated with a pCR, compared to a median of 30% ± 20 interquartile deviation TIL percentage in the non-pCR patients. When a cut-off of 50% was used for TIL-high vs. TIL-low, no significant association was found for pCR rate (p = 0.16) |
| Rao et al. [79] | 2017 | N = 52 | 35% (CD4) and 15% (CD8) | sTILs | p = 0.004 (CD4+ TILs) and p = 0.006 (CD8+ TILs) | When CD4+ TILs were high, 41.9% achieved a pCR, compared to 4.8% in cases with low CD4+ TILs. When CD8+ TIL levels were high, 47.6% achieved a pCR, compared to 12.9% of cases with low CD8+ TIL levels. Patients with both high CD4+ and CD8+ TIL levels had a pCR rate of 71.4% |
| Herrero-Vicent et al. [80] | 2017 | N = 164 | 40% | sTILs | p = 0.001 | TIL-high cases had a pCR rate of 88%, compared to 9% of the TIL-low cases |
| Würfel et al. [85] | 2018 | N = 146 | 50% | sTILs | p < 0.01 | TIL-high cases had a pCR rate of 67%, compared to 33% of the TIL-low cases |
| Ruan et al. [86] | 2018 | N = 166 | 20% for sTIL and 10% for intratumoral TILs | sTILs and intratumoral TILs | p = 0.006 (stromal) and p = 0.04 (intratumoral) | n/a |
| Zhang et al. [34] | 2018 | N = 58 | 60% | sTILs | p = 0.01 | The percentage of the pCR cases that were TIL-high was 46%, compared to 16% in the non-pCR group |
| Ochi et al. [78] | 2019 | N = 80 | 9% | sTILs | p < 0.001 | TIL-high cases had a pCR rate of 44%, compared to 4% of TIL-low cases |
| Van Bockstal et al. [26] | 2020 | N = 35 | 40% | sTILs |
p = 0.002 (2-tier) p = 0.013 (continuous percentage) |
The percentage of the pCR cases that were TIL-high was 62%, compared to 9% in the non-pCR group |
| Cerbelli et al. [83] | 2020 | N = 75 | Low: ≤9% Intermediate: ≥10–49% High: ≥50% |
sTILs | p = 0.037 | TIL-high cases had a pCR rate of 76.5%, compared to 16% in the TIL-intermediate cases and 42% in the TIL-low cases |
| Foldi et al. [76] | 2021 | N = 69 | Low: ≤9% Intermediate: ≥10–29% High: ≥30% |
sTILs | p = 0.0167 | TIL-high cases has a pCR rate of 57%, compared to 60% in the TIL-intermediate cases and 29% in the TIL-low cases |
| Abdelrahman et al. [84] | 2021 | N = 50 | 50% | sTILs | p < 0.02 | TIL-high cases had a pCR rate of 71%, compared to 28% of TIL-low cases |
| Ademuyiwa et al. [54] | 2021 | N = 127 | Continuous scale (per 10% increment) | sTILs | p = 0.05 | n/a |
| Lusho et al. [77] | 2021 | N = 120 | 30% | Not mentioned | p = 0.007 | TIL-high cases had a pCR rate of 54%, compared to 24% in TIL-low cases |
| Yuan et al. [64] | 2021 | N = 433 | 20% | sTILs | p = 0.014 | n/a |
| Goda et al. [88] | 2022 | N = 20 | 50% | sTILs | p = 0.002 | The percentage of the pCR cases that were TIL-high was 67%, and 18% of the non-pCR cases were TIL-high |
| Khoury et al. [87] | 2022 | N = 129 | Mean pCR vs. non-pCR | sTILs | p = 0.0003 | n/a |
Zooming in on TILs, specifically high levels of CD8+ cells and a high CD8/CD4 ratio were reported to be associated with achieving a pCR [37,54,64,82,93,94,95]. These studies used immunohistochemical staining on whole tissue slides. High intratumoral and stromal CD4+ T cell density was also shown to be a significant predictor for a pCR, independent of the treatment [95,96]. T regulator cells (Tregs) are a subset of CD4+ T cells that keep the function of CD8+ T cells in-check [84]. The transcription factor FOXP3 is known for its involvement in suppressing CD8+ T cell immunity. A study by Abdelrahman et al. showed that the absence of FOXP3+ Tregs is associated with a pCR, likely as a consequence of an adaptive response in which the numbers and function of Tregs increase following an initial anti-TNBC CD8+ T cell response [84,97]. In agreement, Miyashita et al. found a higher pCR rate in patients with a high CD8+/FOXP3+ ratio compared to a low CD8+/FOXP3+ ratio [37]. However, the FOXP3 marker individually was not found to be associated with the pCR rate.
Recent reports have indicated that programmed cell death protein ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression can be used as a predictive marker of pCR rate [76,93,98,99,100]. Different PD-L1 antibodies with different scoring methods were used (SP142 Ventana, based on an immune cell score only, and 22C3 and SP263, based on a combined score of tumor cells and immune cells). Based on a cut-off of ≥1% on immunohistochemical staining for any of these three antibodies, between 50 and 80% of all TNBC tumors were PD-L1 positive and PD-L1 is known to be involved in the mechanism of immune escape and correlates with the overall immune cell infiltration [11,12,76]. Multiple studies indicated that a higher PD-L1 expression, for SP142, 22C3 and SP263, is associated with a higher likelihood of achieving a pCR [38,54,93,99,100]. In the study of Gluz et al., this association was only found in the carboplatin-treated group. The additional value of immunotherapy, combined with chemotherapy, in combination with the PD-L1 marker and pCR rate has been investigated recently. Mittendorf et al. reported that chemotherapy combined with pembrolizumab was beneficial for both PD-L1 positive and negative patients [12], whereas in the study by Schmid et al., the effect of the PD-L1 inhibitor was only seen in the PD-L1 positive subgroup [11]. Other studies have reported more contradictory results, which could partly be the result of the variation in PD-L1 assays, as reported by Savas et al. [70]. For example, Abdelrahman et al. found an association between negative PD-L1 status and achieving a pCR [84]. Studies by Foldi et al. and Ghosh et al. both found no association between PD-L1 expression and a pCR [76,98]. It has been reported that on a biologic level, PD-L1 expression is a marker for activated CD8+ TILs, indicating that elevated levels are correlated to an enhanced immune response [101], whereas on the therapeutic level, T cells that were originally inhibited by PD-L1 would reactivate again after a PD-L1 blockade, inducing an anti-tumor immune response.
CD73 plays a role in the catabolism of extracellular ATP to adenosine and is upregulated in regulatory T-cells in response to adenosine signaling [83]. It is highly expressed on mesenchymal stromal cells and infiltrating immune cells. Cerbelli et al. reported that low levels of CD73 expression on tumor cells correlate with an increased pCR rate. Another study by Cerbelli et al. analyzed whether a combination of TILs, PD-L1 and CD73 could better predict the pCR rate in 60 patients [31]. Twenty of the cases were TILs ≥ 50%, PD-L1 ≥ 1% and CD73 ≤ 40%, and after multivariate analysis these patients showed a significantly higher rate of response compared to the patients not reaching these cut-offs. Furthermore, the combination of these three markers was better at predicting a pCR than the individual biomarkers. Collectively, these results suggest that a combination of immune markers enables a more accurate prediction of a pCR.
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) play an important role in tumor growth, angiogenesis, metastasis and treatment resistance. A high infiltration of CD163+ TAMs has been correlated with lower pCR rates after NAC [30,93]. In addition, Ye et al. found that a high infiltration of TAMs was associated with aggressive behavior (advanced stage, nodal metastasis, lymphovascular invasion) and poor prognosis [30]. Yam et al. assessed T cell receptor (TCR) clonality and found higher TCR clonality in TNBC patients who experienced a pCR [99]. They further reported that the ratio of CD8+ T cells and CD68+ TAMs in pre-treatment biopsies was higher in the NAC-sensitive group versus the NAC-resistant group (defined as RCB I-III). These findings suggest that a relative overabundance of T cells compared to TAMs in TNBC is associated with a pCR. Notably, spatial analysis showed that tumor cells in NAC-sensitive tumors were in closer proximity to CD8+ T cells compared to NAC-resistant tumors. Furthermore, it was found that NAC-sensitive tumors had a higher TCR clonality compared to NAC-resistant tumors, and this clonal expansion of TILs, particularly the CD8+ T cells, is suggestive of anti-tumor reactivity, based on the NAC response.
Furthermore, recent research suggests that Ki-67 expressed on immune cells could also be important for immune oncology benefits (Bianchini et al. [102]).
Besides lymphocytes and macrophages, other immune cell subpopulations show aberrant abundance in TNBC. Neutrophils are known to promote tumor cell proliferation, angiogenesis and distant metastasis [103]. Normally, the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is low in tumors with high lymphocyte activity, which is often found in TNBC [29]. Chemotherapy could activate innate and adaptive immune cells and particularly evoke immune responses in patients with a low NLR. Neutrophil counts in tumor tissue and intratumoral NLR did not show a significant difference between the pCR and the non-pCR group [29,104]. Interestingly, in the study by Tokumaru et al., different regimens in five independent cohorts were studied, which all showed that high intratumoral NLR levels were associated with worse prognosis.
3.3. Immune Cells in Peripheral Blood
Frequencies of circulating immune cells are also linked to the response to NAC. The examination of circulating immune cells is simple, less invasive and less expensive compared to obtaining tissue-based immune parameters. A significant association was reported between a low NLR in circulating blood and the ability to achieve a pCR in several studies [104,105,106,107,108]. However, other studies did not find a significant association between the pCR rate and NLR levels [77,98,104,109]. Low hemoglobin levels, albumin levels, lymphocyte counts and platelet counts (HALPs) and a high platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio were also reported as markers of a poor efficacy of NAC [108]. However, multiple other studies found no significant association between a pCR or distant recurrence rate and absolute or relative baseline blood cell counts of neutrophils, eosinophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, platelets and the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio [77,98,110]. Currently, markers in peripheral blood are not robust enough to solely predict the pCR rate.
3.4. Genomic Profile
Genetic mutations in the DNA of the tumor cell have extensively been analyzed for their role in the response rate.
Besides the common TP53 mutation, other genes are also often dysregulated in breast cancer. For example, the PIK3CA gene is mutated in 16% of primary TNBCs and mutations in PIK3CA reduce the dependency of tumor cells on growth factors, promoting cell growth and transformation [111]. Research thus far suggests that patients with a PIK3CA-enhancing mutation are less likely to achieve a pCR compared to PIK3CA wild-type tumors, indicating that PI3K inhibitors could possibly enhance chemotherapeutic sensitivity [28,111,112]. However, this association has shown to be dependent on the specific type of PIK3CA mutation and NAC regimen.
On average, 10% to 15% of all TNBC patients carry a BRCA1 or BRCA2 germline mutation and BRCA1 mutation carriers are more likely to develop TNBC [15,113]. BRCA1/BRCA2 proteins play an important role in DNA repair via homologous recombination. Therefore, these mutations generally lead to a homologous recombination deficiency. Currently, most TNBC patients, BRCA mutation carriers or not, are treated with NAC. The pCR rate has been reported to be between 35% and 70% for TNBC patients with a BRCA mutation, receiving the standard NAC regimen [114,115]. Due to the mutation in the DNA damage repair mechanism, it could be possible that these patients show a difference in response to treatment. Indeed, two studies reported that patients with a germline BRCA1 mutation achieved a higher pCR rate than patients without the BRCA mutation [15,116]. However, in one study, this was only significant in the anthracycline (with or without taxane) regimen and not in the taxane-based regimen where it showed a similar pCR rate between germline BRCA1 mutation carriers and non-carriers. However, several other studies did not find a statistically significant difference between the pCR rates of good versus poor responders based on the germline or somatic BRCA1/2 mutation status [23,114,117,118]. This is possibly due to a small sample size of the mutation carriers or differences in chemotherapy regimen.
Watanabe et al. found that on the epigenetic DNA level, BRCA1 methylation levels are higher in patients with a pCR than those without a pCR [119]. Germline mutations of homologous recombination genes such as ATM are involved in breast cancer susceptibility. It was found that there were lower levels of DNA methylation in the ATM gene in cases with a pCR than in cases with a poor response. Another study by Meyer et al. reported nine differentially methylated regions to be associated with the response to NAC [120].
Besides the BRCA mutation status, homologous recombination deficiency itself has also been associated with pCR rates. This group of tumors is also called BRCAness or BRCA-like. These sporadic cancers share phenotypic overlap with BRCA1/2 germline-mutated tumors. However, these patients lack a detectable germline mutation but do have a homologous recombination error. In contrast to the positive predictive value of the BRCA mutation status, Akashi-Tanaka et al. reported that those with non-BRCAness tumors achieved a pCR more often than those with BRCAness tumors [121]. On the contrary, Telli et al. mentioned that homologous recombination-deficient patients are associated with achieving a pCR more often than patients without homologous recombination deficiency [117]. Moreover, also within wild-type BRCA patients, homologous recombination deficiency was correlated with a higher pCR rate. A study by Huang et al. found that the mutation status of 10 DNA repair genes involved in homologous recombination could predict the response to NAC [114]. Tumors with a positive mutation status for such genes would achieve a pCR more often than tumors with a negative mutation status.
Topoisomerase IIa (TOP2A) is a nuclear DNA-binding enzyme which is critical for obtaining a relaxed DNA structure, important for replication [122]. Data regarding TOP2A are inconsistent. No significant correlation between TOP2A overexpression and response rate to NAC was reported by Sakuma et al. [43]. The study of Loibl et al. found that tumors with amplification of TOP2A showed a decreased pCR rate compared with tumors without amplification of TOP2A [112]. In contrast, Rao et al. described that patients with high TOP2A expression were more likely to achieve a pCR [79].
3.5. Transcriptomic Profile
Some studies developed a gene signature consisting of coding genes and/or long non-coding RNAs (lncRNA), to predict the response to NAC. It is noteworthy that half of the genome is transcribed through lncRNAs, which are RNA transcripts of more than 200 nucleotides without coding capacity. Normally, lncRNAs are regulatory molecules that have been associated with the pathology of breast cancer. A study by Wang et al. investigated whether a specific RNA signature, based on lncRNA and coding gene expression, could predict the pCR rate and demonstrated that a response score signature consisting of one lncRNA (BPESC1) and two coding genes (WDR72 and GADD45A) could significantly distinguish between patients achieving a pCR and non-pCR [123]. When the response score was higher, patients were more likely to achieve a pCR. GADD45A is involved in growth arrest and DNA damage pathways [124]. Zheng et al. found that a gene signature of three coding genes (TCF3, CREB1 and CEP44) and two lncRNAs (NR 023392.1 and NR 048561.1) could predict the pCR to NAC [125]. TCF3 is part of the Wnt pathway-associated TCF/LEF transcription factor family and TCF3 is upregulated in cancers where it promotes proliferation and metastasis. CREB1 is a DNA-binding protein which stimulates transcription and it is also involved in tumor proliferation and metastasis [125,126].
Multiple other gene signatures, scores and (random forest) models investigated in different studies have also been reported to be predictive for pCR rate [39,95,127]. Multiple favorable gene signatures are correlated with an immunogenic tumor microenvironment, further indicating the essential role of an immune-active tumor microenvironment for achieving a pCR.
Furthermore, higher expression levels of TMBS15A, SIRT5, SPARC, LAG-3, SFRP1, CCND1, SCD5, ILF2, IDO1, CTLA4, NFKB1, MAPK1, TRAF1, CXCL13, CXCL16, GZMK, IL7R, CR2, CD19, MS4A1, IL33 and MELK are associated with a higher likelihood of achieving a pCR [8,29,54,64,94,128,129,130,131,132]. Many of these genes, such as LAG-3, IDO1, CTLA4, CXCL13, CXCL16, GZMK, IL7R, CD19 and IL33 have reported immune functions, and their putative relation with a pCR is in line with findings on the immune profile, as discussed above. Patients with low expression levels of ITPKC and HO-1 and a lack of PCDH17 methylation showed higher pCR rates [18,27,32]. Furthermore, an increased expression of the neutrophil-associated genes DEFB1, DEFB103A, DEFB4A and FCAR was seen in patients who failed to achieve a pCR [29]. These findings are in concordance with the previously reported results about the negative association between a high NLR and achieving a pCR [104,105,106,107,108]. Gene expression profiles have been reported to be of importance for therapy responses by Lehmann et al. [5]. It was reported that there are six TNBC subtypes, based on gene expression profiles, and that these subtypes not only have a distinct phenotype but also have variable chemo-sensitivity and pCR rate [5,95]. Echavarria et al. reported that the pCR rate was significantly different between the different TNBC subtypes (Echavarria et al. [133]). The basal-like subtype has been associated with the highest pCR rate and is characterized by the high expression of DNA damage response genes and a high mRNA expression of Ki-67 [5]. Moreover, the immunomodulatory subtype is characterized by genes involved in immune cell processes, of which many have been reported earlier in this review, and is associated with a favorable prognosis. Furthermore, an immune gene signature of the combination IDO1, LAG3, STAT1 and GZMB did not show an association with pCR rate [134].
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are considered to influence the development and progression of breast cancer and are small non-coding RNAs of 25 nucleotides in length. Gene expression can be negatively regulated by miRNAs by inhibiting the translation or degradation of the target messenger RNA (mRNA). Lately, the role of several microRNAs in the chemo-resistance of TNBC tumors and their predictive value for the rate of response to NAC has been studied extensively. The miR-143-5p, miR-30a, miR-9-3p, miR-770 and miR-18a showed differential expressions between good and poor responders to NAC [36,135,136]. MiR-143-5p was significantly less expressed in patients who reached a pCR compared with patients who did not reach a pCR [136]. A high expression of miR-18a was shown in patients that were chemo-resistant to paclitaxel [135]. Some of these discriminatory miRNAs were deregulated in patients achieving a pCR, indicating that alterations in the miRNAs could be involved in the achievement of a pCR through the stimulation of particular oncogenic signaling pathways such as TGFB, PI3K/AKT, ErbB, VEGF/MAPK, FOXO, FAK, JAK/STAT and mTOR [136]. Not all miRNAs are associated with the response rate to NAC. Kolacinska et al. analyzed different miRNAs and identified that 3 out of 19 miRNAs, miR-200b-3p, miR-190a and miR-512-5p, could distinguish patients with a pCR from patients not achieving a pCR based on expression levels. They also observed that higher miR-200b-3p, higher miR-190a and lower miR-512-5p expression levels showed a trend towards reaching a higher pCR rate, but there was no statistically significant difference compared to the non-pCR group [137].
Exosomes are small membranous vesicles of around 30 to 100 nanometers that can contain lipids, proteins or miRNAs secreted by cells into the blood [138]. Exosomal miRNA can transmit information to the surrounding microenvironment. Sueta et al. reported that 16 exosomal miRNAs were expressed significantly differently between patients achieving a pCR and non-pCR. A signature of four of these upregulated miRNAs, miR-4448, miR-2392, miR-2467-3p and miR-4800-3p, was the most optimal to distinguish between patients with and without a pCR.
4. Discussion
This review focused on comprehensively charting and describing biomarkers at baseline that could predict a pCR following NAC treatment for TNBC, on proteomic, genomic and transcriptomic levels. Various biomarkers have been investigated for their correlation with pCR rate (Figure 2). Despite the large number of studies investigating which biomarkers are associated with a pCR, no ideal marker has reached the robustness and confidence to become widely implemented in clinical practice.
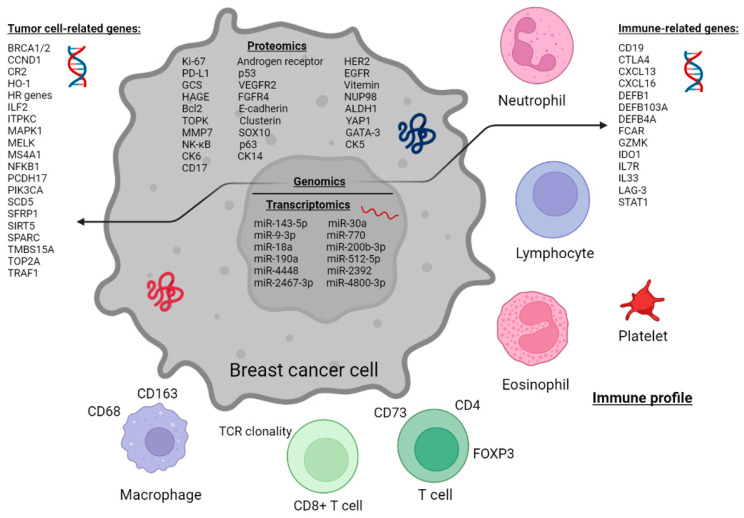
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of putative predictive markers linked to pCR after NAC in TNBC patients.
Based on this review, it has become clear that the immune microenvironment is critical for the response to NAC. The higher density of TILs, particularly CD8+ T cells, has been shown to be associated with achieving a pCR, indicating the predictive value of TILs as reported in a total number of 18 articles. The favorable involvement of CD4+ T regulatory cells and the unfavorable involvement of CD163+ TAMs and CD73+ tumor cells were also presented to correlate with the pCR rate. Thus, the pre-treatment activation of the CD8+ T cells against TNBC or their control via adaptive feedback mechanisms (such as evidenced by Tregs and TAMs) likely positively influences the response to NAC. The presence of CD8+ T cells is known to induce apoptosis of cancer cells, and CD4+ T cells are known for their helping function in maintaining the anti-tumor role of CD8 [139]. Chemotherapy can alter the microenvironment and with higher numbers of CD8+ and CD4+ T cells at baseline, these responses could be further enhanced. Indeed, a study by Emens et al. has shown that cyclophosphamide can assist immune cells to develop and mature, leading to better responses to treatment [140]. Furthermore, Voorwerk et al. reported in preclinical research that chemotherapy renders immunomodulatory properties through the upregulation of genes associated with T cell cytotoxicity, inflammation and PD-L1 pathways [141]. PD-L1 has also been reported as a predictive marker, but results were contradictory, which could partially be due to the variations in PD-L1 antibodies. CD163+ TAMs have an M2-like macrophage phenotype and CD73 is an enzyme that produces immunosuppressive extracellular adenosine [93,142,143]. A study by Jinushi et al. suggested that CD163+ TAMs can produce milk-fat globule epidermal growth factor-8, which in turn can mediate drug resistance through STAT3 and hedgehog signals [144]. For the other immune markers, such as eosinophil count, the platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio and NLR, results varied, and no clear association was found.
On the tumor cell level, Ki-67 and AR seem to be fairly robust predictive markers of a pCR. Nevertheless, for Ki-67, the results reported are somewhat contradictory, but there were more studies (n = 7) that found an association between a high Ki-67 expression and pCR rate compared to the studies that did not find a significant association (n = 5). In addition, the studies reporting an association were based on larger cohorts compared to the studies without an association. On the genomic level, PIK3CA seems to be the only biomarker that has shown an association with a pCR in multiple articles. Furthermore, various biomarkers have been found to be associated with a pCR but have only been reported infrequently. For these biomarkers, additional research is needed to validate the association with a pCR.
To our knowledge, this is the first systematic review giving an exhaustive overview of all reported biomarkers of a pCR in NAC-treated TNBC at the proteomic, genomic and transcriptomic levels. This review was written as a narrative (qualitative) approach aiming to achieve a better understanding of the potential biological effects of individual markers on the pCR rate. A quantitative approach meta-analysis was not possible because of the heterogeneity of the articles in this search. The studies varied in biomarkers, patient populations, sample size, treatment regimen and other study settings, which makes it difficult to generalize the results found in these studies. Moreover, a lack of standardized threshold settings for immunohistochemical stains and scoring methods, and peripheral blood cell counts, increases the variety between the studies.
Most of the studies included in this review followed the ASCO/CAP guidelines for ER and PR scoring, using a cut-off of <1%. However, nine studies used a cut-off of <10% for an ER negative status [24,25,43,55,77,106,119,122,130]. Four studies used the Allred score to determine ER status and one study used the H-score [26,41,61,78,81]. The definition of a pCR also differed across the studies included in this review. Mainly, a pCR was defined as being where no invasive residual tumor cells were present in the breast and axillary lymph nodes [145]. Other used definitions were the absence of invasive and in situ carcinoma in the breast and axillary lymph nodes after completing the NAC regimen, and in one study an RCB1 score was seen as a pCR [62,90]. However, the definitions are very comparable, so it is unlikely that the difference in pCR definition affected the outcome of results.
Currently, treatment decisions are based on baseline prognostic clinicopathologic features, so the additional value of predictive biomarkers should be studied on top of this. Given the rapid developments in the field of neoadjuvant treatment of TNBC patients, including the addition of neoadjuvant pembrolizumab, it becomes even more important to select those patients that could be treated with chemotherapy alone, to keep the health care system affordable. In addition, TIL-high TNBC patients have been reported to have a good prognosis without any systemic treatment [74]. Therefore, there is a need for a reproducible predictive biomarker to be used on top of the baseline prognostic features.
A clinical useful predictive biomarker is analytically valid, reproducible and able to select patients with a high or low chance of a pCR after NAC (for example >90% or <10%) [146,147,148]. As described in this review, there is plenty of literature reporting significant associations between biomarkers and therapy response, mainly the TILs and the expression of Ki-67. Based on the literature, the abundance of TILs is the most robust biomarker so far. Since both TILs and Ki-67 are relatively easy to implement in daily clinical practice, it could be considered that Ki-67 be reported as well as the density and location of TILs. However, the pCR rate varies substantially across studies in TIL-high and Ki-67-high cases, so the predictive value of these markers by themselves does not seem to be sufficiently strong enough yet to guide clinical decision making. Artificial intelligence techniques, such as deep learning, are being developed to assess the H&E slides for the density of TILs and spatial information [149]. Future research on early readouts for therapy response, during the NAC period, could also contribute to the optimization of the treatment schedule.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, several markers have been associated with the pCR rate, with immune markers being the most promising. However, several other markers that relate to cancer cells, the tumor microenvironment and the peripheral blood also affect chemo-sensitivity. The combination of tumor cell and immune markers, such as Ki-67 expression and TIL density, in a prediction model is likely to yield the best stratification of TNBC patients with respect to response to NAC.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Wichor M. Bramer from the Erasmus MC Medical Library for developing and updating the search strategies.
Abbreviations
| ALDH1 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 family member A1 |
| AR | Androgen receptor |
| ATM | Ataxia telangiectasia-mutated |
| ATP | Adenosine 5′-triphosphate |
| Bcl2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| BPESC1 | Blepharophimosis, epicanthus inversus and ptosis candidate 1 |
| BRCA | Breast cancer |
| CCND1 | Cyclin D1 |
| CK | Cytokeratine |
| CD19 | Cluster of differentiation 19 |
| CEP44 | Centrosomal protein 44 |
| CR2 | Complement component 3d receptor 2 |
| CREB1 | CAMP responsive element binding protein 1 |
| CTLA4 | Cluster of differentiation 152 |
| CXCL | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand |
| DEFB | Defensin beta |
| DFS | Disease-free survival |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ER | Estrogen receptor |
| FCAR | Fc fragment of IgA receptor |
| FOXP3 | Forkhead box P3 |
| FGFR4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 |
| GADD45A | Growth arrest and DNA damage inducible alpha |
| GATA3 | GATA binding protein 3 |
| GCS | Glucosylceramide synthase |
| GZMB | Granzyme B |
| GZMK | Granzyme K |
| HAGE | Helicase antigen |
| HER2 | Human epidermal growth factor 2 |
| HO-1 | Heme oxygenase 1 |
| IDO1 | Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 |
| IL7R | Interleukin-7 receptor |
| IL33 | Interleukin 33 |
| ILF2 | Interleukin enhancer binding factor 2 |
| ITPKC | Inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinase C |
| LAG-3 | Lymphocyte activation gene-3 |
| LncRNA | Long non-coding RNA |
| MAPK1 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 |
| MELK | Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase |
| MFS | Metastasis-free survival |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| MMP7 | Matrix metalloproteinase 7 |
| MS4A1 | Membrane spanning 4-domains A1 |
| NAC | Neoadjuvant chemotherapy |
| NFKB1 | Nuclear factor kappa B subunit 1 |
| NUP98 | Nucleoporin 98 and 96 precursor |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PCDH17 | Protocadherin 17 |
| pCR | Pathological complete response |
| PD-L1 | Programmed cell death protein ligand 1 |
| PIK3CA | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha |
| PR | Progesterone receptor |
| RCB | Residual cancer burden |
| RFS | Recurrence free survival |
| SCD5 | Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 5 |
| SFRP1 | Secreted frizzled related protein 1 |
| SIRT5 | Sirtuin 5 |
| SPARC | Secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine |
| SOX10 | SRY-box transcription factor 10 |
| STAT1 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 |
| (s)TIL | (Stromal) tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte |
| TCF3 | Transcription factor 3 |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| TMBS15A | Thymosin beta-15A |
| TRAF1 | TNF receptor-associated factor 1 |
| TILV | Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte volume |
| TP53 | Tumor protein 53 |
| TOP2A | Topoisomerase IIa |
| TOPK | T-LAK-cell originated protein kinase |
| Tregs | T regulator cells |
| VEGFR2 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 |
| WDR72 | WD repeat domain 72 |
| YAP1 | Yes1-associated transcriptional regulator |
Supplementary Materials
The supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms24032969/s1.
Author Contributions
N.S.v.d.E. and A.H.N. contributed equally to this work, and focused on the screening of the articles, inclusion and exclusion and writing of the manuscript. N.S.v.d.E. constructed all of the figures and tables. C.H.M.v.D., R.D., A.J. and M.K. reviewed and revised the manuscript and approved the final version. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest related to the submitted work.
Funding Statement
This research received funding from NWO. Grant number: 015.014.068.
Footnotes
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content.
References
- 1.International WCRF Worldwide Cancer Data. 2020. [(accessed on 3 November 2022)]. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/cancer-trends/worldwide-cancer-data/
- 2.Rakha E.A., El-Sayed M.E., Green A.R., Lee A.H., Robertson J.F., Ellis I.O. Prognostic markers in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer. 2007;109:25–32. doi: 10.1002/cncr.22381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Wolff A.C., Hammond M.E.H., Allison K.H., Harvey B.E., Mangu P.B., Bartlett J.M.S., Bilous M., Ellis I.O., Fitzgibbons P., Hanna W., et al. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Testing in Breast Cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists Clinical Practice Guideline Focused Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018;36:2105–2122. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.77.8738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Allison K.H., Hammond M.E.H., Dowsett M., McKernin S.E., Carey L.A., Fitzgibbons P.L., Hayes D.F., Lakhani S.R., Chavez-MacGregor M., Perlmutter J., et al. Estrogen and Progesterone Receptor Testing in Breast Cancer: ASCO/CAP Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020;38:1346–1366. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.02309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lehmann B.D., Bauer J.A., Chen X., Sanders M.E., Chakravarthy A.B., Shyr Y., Pietenpol J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011;121:2750–2767. doi: 10.1172/JCI45014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Parker J.S., Mullins M., Cheang M.C., Leung S., Voduc D., Vickery T., Davies S., Fauron C., He X., Hu Z., et al. Supervised Risk Predictor of Breast Cancer Based on Intrinsic Subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009;27:1160–1167. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.1370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Prat A., Pineda E., Adamo B., Galván P., Fernández A., Gaba L., Díez M., Viladot M., Arance A., Muñoz M. Clinical implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Breast. 2015;24:S26–S35. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2015.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bernemann C., Hülsewig C., Rückert C., Schäfer S., Blümel L., Hempel G., Götte M., Greve B., Barth P.J., Kiesel L., et al. Influence of secreted frizzled receptor protein 1 (SFRP1) on neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple negative breast cancer does not rely on WNT signaling. Mol. Cancer. 2014;13:174. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-13-174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhu M., Liang C., Zhang F., Zhu L., Chen D. A Nomogram to Predict Disease-Free Survival Following Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021;11:4399. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.690336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Abuhadra N., Stecklein S., Sharma P., Moulder S. Early-stage Triple-negative Breast Cancer: Time to Optimize Personalized Strategies. Oncologist. 2022;27:30–39. doi: 10.1093/oncolo/oyab003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Schmid P., Cortes J., Pusztai L., McArthur H., Kümmel S., Bergh J., Denkert C., Park Y.H., Hui R., Harbeck N., et al. Pembrolizumab for Early Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020;382:810–821. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1910549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Mittendorf E.A., Zhang H., Barrios C.H., Saji S., Jung K.H., Hegg R., Koehler A., Sohn J., Iwata H., Telli M.L., et al. Neoadjuvant atezolizumab in combination with sequential nab-paclitaxel and anthracycline-based chemotherapy versus placebo and chemotherapy in patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (IMpassion031): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2020;396:1090–1100. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31953-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lee J.S., Yost S.E., Yuan Y. Neoadjuvant Treatment for Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Recent Progresses and Challenges. Cancers. 2020;12:1404. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Holanek M., Selingerova I., Bilek O., Kazda T., Fabian P., Foretova L., Zvarikova M., Obermannova R., Kolouskova I., Coufal O., et al. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Evaluation of Early Clinical Response, Pathological Complete Response Rates, and Addition of Platinum Salts Benefit Based on Real-World Evidence. Cancers. 2021;13:1586. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Paluch-Shimon S., Friedman E., Berger R., Papa M., Dadiani M., Friedman N., Shabtai M., Zippel D., Gutman M., Golan T., et al. Neo-adjuvant doxorubicin and cyclophosphamide followed by paclitaxel in triple-negative breast cancer among BRCA1 mutation carriers and non-carriers. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016;157:157–165. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3800-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bianchini G., De Angelis C., Licata L., Gianni L. Treatment landscape of triple-negative breast cancer—Expanded options, evolving needs. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022;19:91–113. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00565-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dent R., Trudeau M., Pritchard K.I., Hanna W.M., Kahn H.K., Sawka C.A., Lickley L.A., Rawlinson E., Sun P., Narod S.A. Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Pt 1Clin. Cancer Res. 2007;13:4429–4434. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-06-3045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Oshi M., Newman S., Murthy V., Tokumaru Y., Yan L., Matsuyama R., Endo I., Takabe K. ITPKC as a Prognostic and Predictive Biomarker of Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2020;12:2758. doi: 10.3390/cancers12102758. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kim T., Han W., Kim M.K., Lee J.W., Kim J., Ahn S.K., Lee H.-B., Moon H.-G., Lee K.-H., Kim T.-Y., et al. Predictive Significance of p53, Ki-67, and Bcl-2 Expression for Pathologic Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Breast Cancer. 2015;18:16–21. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2015.18.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Guestini F., Ono K., Miyashita M., Ishida T., Ohuchi N., Nakagawa S., Hirakawa H., Tamaki K., Ohi Y., Rai Y., et al. Impact of Topoisomerase IIα, PTEN, ABCC1/MRP1, and KI67 on triple-negative breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2019;173:275–288. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4985-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mohammed A.A., Elsayed F.M., Algazar M., Rashed H.E., Anter A.H. Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Correlation between Androgen Receptor Expression and Pathological Response. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2020;21:563–568. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhu M., Yu Y., Shao X., Zhu L., Wang L. Predictors of Response and Survival Outcomes of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Receiving Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy. 2020;65:101–109. doi: 10.1159/000509638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kedzierawski P., Macek P., Ciepiela I., Kowalik A., Gozdz S. Evaluation of Complete Pathological Regression after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients with BRCA1 Founder Mutation Aided Bayesian A/B Testing Approach. Diagnostics. 2021;11:1144. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11071144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bignon L., Fricker J.P., Nogues C., Mouret-Fourme E., Stoppa-Lyonnet D., Caron O., Lortholary A., Faivre L., Lasset C., Mari V., et al. Efficacy of anthracycline/taxane-based neo-adjuvant chemotherapy on triple-negative breast cancer in BRCA1/BRCA2 mutation carriers. Breast J. 2018;24:269–277. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Masuda H., Masuda N., Kodama Y., Ogawa M., Karita M., Yamamura J., Tsukuda K., Doihara H., Miyoshi S., Mano M., et al. Predictive factors for the effectiveness of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer patients. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011;67:911–917. doi: 10.1007/s00280-010-1371-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Van Bockstal M.R., Noel F., Guiot Y., Duhoux F.P., Mazzeo F., Van Marcke C., Fellah L., Ledoux B., Berlière M., Galant C. Predictive markers for pathological complete response after neo-adjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2020;49:151634. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2020.151634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Tan Q., Qin Q., Huang Z., Lian B., Mo Q., Wei C. Predictive and prognostic effect of HO-1 expression in breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022;193:393–403. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06565-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Guo S., Loibl S., von Minckwitz G., Darb-Esfahani S., Lederer B., Denkert C. PIK3CA H1047R Mutation Associated with a Lower Pathological Complete Response Rate in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Anthracycline-Taxane-Based Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020;52:689–696. doi: 10.4143/crt.2019.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lee H.J., Lee J.J., Song I.H., Park I.A., Kang J., Yu J.H., Ahn J.H., Gong G. Prognostic and predictive value of NanoString-based immune-related gene signatures in a neoadjuvant setting of triple-negative breast cancer: Relationship to tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2015;151:619–627. doi: 10.1007/s10549-015-3438-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ye J.H., Wang X.H., Shi J.J., Yin X., Chen C., Chen Y., Wu H.-Y., Jiong S., Sun Q., Zhang M., et al. Tumor-associated macrophages are associated with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and poor outcomes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J. Cancer. 2021;12:2886–2892. doi: 10.7150/jca.47566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cerbelli B., Scagnoli S., Mezi S., De Luca A., Pisegna S., Amabile M.I., Roberto M., Fortunato L., Costarelli L., Pernazza A., et al. Tissue Immune Profile: A Tool to Predict Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2020;12:2648. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kong D.D., Fu R.Z., Li L., Wang W., Wang S.B. Association between the methylation status of PCDH17 and the efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020;20:1649–1656. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Liu J., Wang S., Wang C., Kong X., Sun P. Prognostic value of using glucosylceramide synthase and cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A1 expression levels for patients with triple-negative breast cancer following neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021;21:247. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.9678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang L., Wang X.I., Zhang S. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte volume is a better predictor of neoadjuvant therapy response and overall survival in triple-negative invasive breast cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2018;80:47–54. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2018.05.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Page M.J., McKenzie J.E., Bossuyt P.M., Boutron I., Hoffmann T.C., Mulrow C.D., Shamseer L., Tetzlaff J.M., Akl E.A., Brennan S.E., et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.García-Vazquez R., Ruiz-García E., Meneses Garcia A., Astudillo-De La Vega H., Lara-Medina F., Alvarado-Miranda A., Maldonado-Martínez H., González-Barrios J.A., Campos-Parra A.D., Rodriguez Cuevas S., et al. A microRNA signature associated with pathological complete response to novel neoadjuvant therapy regimen in triple-negative breast cancer. Tumor Biol. 2017;39:1010428317702899. doi: 10.1177/1010428317702899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Miyashita M., Sasano H., Tamaki K., Chan M., Hirakawa H., Suzuki A., Tada H., Watanabe G., Nemoto N., Nakagawa S., et al. Tumor-infiltrating CD8+ and FOXP3+ lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer: Its correlation with pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014;148:525–534. doi: 10.1007/s10549-014-3197-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gluz O., Kolberg-Liedtke C., Prat A., Christgen M., Gebauer D., Kates R., Paré L., Grischke E.M., Forstbauer H., Braun M., et al. Efficacy of deescalated chemotherapy according to PAM50 subtypes, immune and proliferation genes in triple-negative early breast cancer: Primary translational analysis of the WSG-ADAPT-TN trial. Int J Cancer. 2020;146:262–271. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zuo K., Yuan X., Liang X., Sun X., Liu S., Connell P.P., Li X., Yang W. qRT-PCR-based DNA homologous recombination-associated 4-gene score predicts pathologic complete response to platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022;191:335–344. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06442-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Baba M., Takahashi M., Yamashiro K., Yokoo H., Fukai M., Sato M., Hosoda M., Kamiyama T., Taketomi A., Yamashita H. Strong cytoplasmic expression of NF-κB/p65 correlates with a good prognosis in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Surg. Today. 2016;46:843–851. doi: 10.1007/s00595-015-1265-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kraus J.A., Beriwal S., Dabbs D.J., Ahrendt G.M., McGuire K.P., Johnson R.R., Badve P., Puhalla S.L., Bhargava R. Predictors of pathologic complete response after standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast carcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2012;20:334–339. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0b013e31823f4663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kawate T., Iwaya K., Kikuchi R., Kaise H., Oda M., Sato E., Hiroi S., Matsubara O., Kohno N. DJ-1 protein expression as a predictor of pathological complete remission after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013;139:51–59. doi: 10.1007/s10549-013-2523-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Sakuma K., Kurosumi M., Oba H., Kobayashi Y., Takei H., Inoue K., Tabei T., Oyama T. Pathological tumor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy using anthracycline and taxanes in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2011;2:257–264. doi: 10.3892/etm.2011.212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Di Leone A., Fragomeni S.M., Scardina L., Ionta L., Mulè A., Magno S., Terribile D., Masetti R., Franceschini G. Androgen receptor expression and outcome of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2021;25:1910–1915. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202102_25087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sridhar N., Glisch C., Jawa Z., Chaudhary L.N., Kamaraju S., Burfeind J., Charlson J., Chitambar C.R., Jorns J.M., Cheng Y.C. Androgen receptor expression in patients with triple negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A single institution study. J. Cancer. 2022;13:2472–2476. doi: 10.7150/jca.67536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wang Y., Li J., Li J., Li P., Wang L., Di L. An Enhancer-Based Analysis Revealed a New Function of Androgen Receptor in Tumor Cell Immune Evasion. Front. Genet. 2020;11:595550. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.595550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gutierrez C., Schiff R. HER 2, biology, detection, and clinical implications. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2011;135:55–62. doi: 10.5858/2010-0454-RAR.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Denkert C., Seither F., Schneeweiss A., Link T., Blohmer J.-U., Just M., Wimberger P., Forberger A., Tesch H., Jackisch C., et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of HER2-low-positive breast cancer: Pooled analysis of individual patient data from four prospective, neoadjuvant clinical trials. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:1151–1161. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00301-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Ende N.S.v.D., Smid M., Timmermans A., van Brakel J.B., Hansum T., Foekens R., Trapman A.M.A.C., Heemskerk-Gerritsen B.A.M., Jager A., Martens J.W.M., et al. HER2-low breast cancer shows a lower immune response compared to HER2-negative cases. Sci. Rep. 2022;12:12974. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16898-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Baez-Navarro X., Salgado R., Denkert C., Lennerz J.K., Penault-Llorca F., Viale G., Bartlett J.M., van Deurzen C.H. Selecting patients with HER2-low breast cancer: Getting out of the tangle. Eur. J. Cancer. 2022;175:187–192. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2022.08.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Duffy M.J., Synnott N.C., Crown J. Mutant p53 in breast cancer: Potential as a therapeutic target and biomarker. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018;170:213–219. doi: 10.1007/s10549-018-4753-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Liao G., Jiang Z., Yang Y., Zhang C., Jiang M., Zhu J., Xu L., Xie A., Yan M., Zhang Y., et al. Combined homologous recombination repair deficiency and immune activation analysis for predicting intensified responses of anthracycline, cyclophosphamide and taxane chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Med. 2021;19:190. doi: 10.1186/s12916-021-02068-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Bae S.Y., Lee J.H., Bae J.W., Jung S.P. Differences in prognosis by p53 expression after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2020;98:291–298. doi: 10.4174/astr.2020.98.6.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ademuyiwa F.O., Chen I., Luo J., Rimawi M.F., Hagemann I.S., Fisk B., Jeffers G., Skidmore Z.L., Basu A., Richters M., et al. Immunogenomic profiling and pathological response results from a clinical trial of docetaxel and carboplatin in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021;189:187–202. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06307-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Tang Y., Zhu L., Li Y., Ji J., Li J., Yuan F., Wang D., Chen W., Huang O., Chen X., et al. Overexpression of epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) predicts better response to neo-adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2012;10:S4. doi: 10.1186/1479-5876-10-S1-S4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Abdelrahman A.E., Rashed H.E., Abdelgawad M., Abdelhamid M.I. Prognostic impact of EGFR and cytokeratin 5/6 immunohistochemical expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2017;28:43–53. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2017.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Babyshkina N., Zavyalova M., Tarabanovskaya N., Dronova T., Krakhmal N., Slonimskaya E., Kzhyshkowska J., Choynzonov E., Cherdyntseva N. Predictive value of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor type 2 in triple-negative breast cancer patients treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018;444:197–206. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-3244-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Abdel-Fatah T.M., McArdle S.E., Agarwal D., Moseley P.M., Green A.R., Ball G.R., Pockley A.G., Ellis I.O., Rees R.C., Chan S.Y. HAGE in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Is a Novel Prognostic, Predictive, and Actionable Biomarker: A Transcriptomic and Protein Expression Analysis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016;22:905–914. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Mullan P.B., Bingham V., Haddock P., Irwin G.W., Kay E., McQuaid S., Buckley N.E. NUP98—A novel predictor of response to anthracycline-based chemotherapy in triple negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:236. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5407-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Abdel-Fatah T., Perry C., Dickinson P., Ball G., Moseley P., Madhusudan S., Ellis I., Chan S. Bcl2 is an independent prognostic marker of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) and predicts response to anthracycline combination (ATC) chemotherapy (CT) in adjuvant and neoadjuvant settings. Ann. Oncol. 2013;24:2801–2807. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdt277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kida K., Ishikawa T., Yamada A., Shimada K., Narui K., Sugae S., Shimizu D., Tanabe M., Sasaki T., Ichikawa Y., et al. Effect of ALDH1 on prognosis and chemoresistance by breast cancer subtype. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016;156:261–269. doi: 10.1007/s10549-016-3738-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Wang Y., Brodsky A.S., Xiong J., Lopresti M.L., Yang D., Resnick M.B. Stromal Clusterin Expression Predicts Therapeutic Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer. 2018;18:e373–e379. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2017.08.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wang K., Chai J., Xu J., Wei J., Li P., Liu Y., Ma J., Xu T., Zhao D., Yu K., et al. TOPK: A new predictor of the therapeutic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Pathol.-Res. Pract. 2021;226:153603. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Yuan J.-Q., Zhang K.-J., Wang S.-M., Guo L. YAP1/MMP7/CXCL16 axis affects efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy via tumor environment immunosuppression in triple-negative breast cancer. Gland Surg. 2021;10:2799–2814. doi: 10.21037/gs-21-612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Na T.-Y., Schecterson L., Mendonsa A.M., Gumbiner B.M. The functional activity of E-cadherin controls tumor cell metastasis at multiple steps. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2020;117:5931–5937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1918167117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Guo L., Chen Y., Luo J., Zheng J., Shao G. YAP1 overexpression is associated with poor prognosis of breast cancer patients and induces breast cancer cell growth by inhibiting PTEN. FEBS Open Bio. 2019;9:437–445. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Soleyman-Jahi S., Nedjat S., Abdirad A., Hoorshad N., Heidari R., Zendehdel K. Prognostic Significance of Matrix Metalloproteinase-7 in Gastric Cancer Survival: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0122316. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Hammerl D., Massink M.P., Smid M., van Deurzen C.H., Meijers-Heijboer H.E., Waisfisz Q., Debets R., Martens J.W. Clonality, Antigen Recognition, and Suppression of CD8(+) T Cells Differentially Affect Prognosis of Breast Cancer Subtypes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020;26:505–517. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Wang Y., Zong B., Yu Y., Wang Y., Tang Z., Chen R., Huang M., Liu S. Ki67 Index Changes and Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Levels Impact the Prognosis of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients with Residual Disease after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2021;11:668610. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.668610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Savas P., Salgado R., Loi S. Seeing the forest and the tree: TILs and PD-L1 as immune biomarkers. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021;189:599–606. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06287-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Salgado R., Denkert C., Demaria S., Sirtaine N., Klauschen F., Pruneri G., Wienert S., Van den Eynden G., Baehner F.L., Pénault-Llorca F., et al. The evaluation of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) in breast cancer: Recommendations by an International TILs Working Group 2014. Ann. Oncol. 2015;26:259–271. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Loi S., Drubay D., Adams S., Pruneri G., Francis P.A., Lacroix-Triki M., Joensuu H., Dieci M.V., Badve S., Demaria S., et al. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and Prognosis: A Pooled Individual Patient Analysis of Early-Stage Triple-Negative Breast Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019;37:559–569. doi: 10.1200/JCO.18.01010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Park J.H., Jonas S.F., Bataillon G., Criscitiello C., Salgado R., Loi S., Viale G., Lee H.J., Dieci M.V., Kim S.B., et al. Prognostic value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with early-stage triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) who did not receive adjuvant chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2019;30:1941–1949. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.de Jong V.M., Wang Y., ter Hoeve N.D., Opdam M., Stathonikos N., Jóźwiak K., Hauptmann M., Cornelissen S., Vreuls W., Rosenberg E.H., et al. Prognostic Value of Stromal Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Young, Node-Negative, Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Patients Who Did Not Receive (neo)Adjuvant Systemic Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022;40:2361–2374. doi: 10.1200/JCO.21.01536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Denkert C., von Minckwitz G., Darb-Esfahani S., Lederer B., Heppner B.I., Weber K.E., Budczies J., Huober J., Klauschen F., Furlanetto J., et al. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes and prognosis in different subtypes of breast cancer: A pooled analysis of 3771 patients treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:40–50. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30904-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Foldi J., Silber A., Reisenbichler E., Singh K., Fischbach N., Persico J., Adelson K., Katoch A., Horowitz N., Lannin D., et al. Neoadjuvant durvalumab plus weekly nab-paclitaxel and dose-dense doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide in triple-negative breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2021;7:9. doi: 10.1038/s41523-021-00219-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Lusho S., Durando X., Mouret-Reynier M.A., Kossai M., Lacrampe N., Molnar I., Penault-Llorca F., Radosevic-Robin N., Abrial C. Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Is Associated with Favorable Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Triple Negative Breast Cancer: A Study on 120 Patients. Front. Oncol. 2021;11:678315. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.678315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ochi T., Bianchini G., Ando M., Nozaki F., Kobayashi D., Criscitiello C., Curigliano G., Iwamoto T., Niikura N., Takei H., et al. Predictive and prognostic value of stromal tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes before and after neoadjuvant therapy in triple negative and HER2-positive breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer. 2019;118:41–48. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2019.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Rao N., Qiu J., Wu J., Zeng H., Su F., Qiu K., Wu J., Yao H. Significance of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes and the Expression of Topoisomerase IIα in the Prediction of the Clinical Outcome of Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer after Taxane-Anthracycline-Based Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Chemotherapy. 2017;62:246–255. doi: 10.1159/000470900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Herrero-Vicent C., Guerrero A., Gavilá J., Gozalbo F., Hernandez A., Sandiego S., Algarra M.A., Calatrava A., Guillem-Porta V., Ruiz-Simón A. Predictive and prognostic impact of tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ecancermedicalscience. 2017;11:759. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2017.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Ono M., Tsuda H., Shimizu C., Yamamoto S., Shibata T., Yamamoto H., Hirata T., Yonemori K., Ando M., Tamura K., et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are correlated with response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012;132:793–805. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1554-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Castaneda C.A., Mittendorf E., Casavilca S., Wu Y., Castillo M., Arboleda P., Nunez T., Guerra H., Barrionuevo C., Dolores-Cerna K., et al. Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes in triple negative breast cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2016;7:387–394. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v7.i5.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Cerbelli B., Botticelli A., Pisano A., Pernazza A., Campagna D., De Luca A., Ascierto P.A., Pignataro M.G., Pelullo M., Della Rocca C., et al. CD73 expression and pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple negative breast cancer. Virchows Arch. 2020;476:569–576. doi: 10.1007/s00428-019-02722-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Abdelrahman A.E., Rashed H.E., Toam M., Omar A., Abdelhamid M.I., Matar I. Clinicopathological significance of the immunologic signature (PDL1, FOXP3+ Tregs, TILs) in early stage triple-negative breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2021;51:151676. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2020.151676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Würfel F., Erber R., Huebner H., Hein A., Lux M.P., Jud S., Kremer A., Kranich H., Mackensen A., Häberle L., et al. TILGen: A Program to Investigate Immune Targets in Breast Cancer Patients—First Results on the Influence of Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes. Breast Care. 2018;13:8–15. doi: 10.1159/000486949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ruan M., Tian T., Rao J., Xu X., Yu B., Yang W., Shui R. Predictive value of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes to pathological complete response in neoadjuvant treated triple-negative breast cancers. Diagn. Pathol. 2018;13:66. doi: 10.1186/s13000-018-0743-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Khoury T., Aljabab S., Yao S., Ambrosone C., Omilian A., Attwood K., Ji W., Gandhi S. Tumor-associated mononuclear cells in the tumor bed of triple-negative breast cancer associate with clinical outcomes in the post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy setting. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022;194:531–540. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06641-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Goda N., Nakashima C., Nagamine I., Otagaki S. The Effect of Intratumoral Interrelation among FOXP3+ Regulatory T Cells on Treatment Response and Survival in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2022;14:2138. doi: 10.3390/cancers14092138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Symmans W.F., Yau C., Chen Y.Y., Balassanian R., Klein M.E., Pusztai L., Nanda R., Parker B.A., Datnow B., Krings G., et al. Assessment of Residual Cancer Burden and Event-Free Survival in Neoadjuvant Treatment for High-risk Breast Cancer: An Analysis of Data From the I-SPY2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2021;7:1654–1663. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.3690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Yau C., Osdoit M., van der Noordaa M., Shad S., Wei J., de Croze D., Hamy A.-S., Laé M., Reyal F., Sonke G.S., et al. Residual cancer burden after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and long-term survival outcomes in breast cancer: A multicentre pooled analysis of 5161 patients. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23:149–160. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00589-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Hammerl D., Martens J.W., Timmermans M., Smid M., Trapman-Jansen A.M., Foekens R., Isaeva O.I., Voorwerk L., Balcioglu H.E., Wijers R., et al. Spatial immunophenotypes predict response to anti-PD1 treatment and capture distinct paths of T cell evasion in triple negative breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2021;12:5668. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25962-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.El Bairi K., Haynes H.R., Blackley E., Fineberg S., Shear J., Turner S., de Freitas J.R., Sur D., Amendola L.C., Gharib M., et al. The tale of TILs in breast cancer: A report from The International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2021;7:150. doi: 10.1038/s41523-021-00346-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Arole V., Nitta H., Wei L., Shen T., Parwani A.V., Li Z. M2 tumor-associated macrophages play important role in predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2021;188:37–42. doi: 10.1007/s10549-021-06260-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Wang Y., Dong T., Xuan Q., Zhao H., Qin L., Zhang Q. Lymphocyte-Activation Gene-3 Expression and Prognostic Value in Neoadjuvant-Treated Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Breast Cancer. 2018;21:124–133. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2018.21.2.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Iwase T., Blenman K.R.M., Li X., Reisenbichler E., Seitz R., Hout D., Nielsen T.J., Schweitzer B.L., Bailey D.B., Shen Y., et al. A Novel Immunomodulatory 27-Gene Signature to Predict Response to Neoadjuvant Immunochemotherapy for Primary Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2021;13:4839. doi: 10.3390/cancers13194839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ueno T., Kitano S., Masuda N., Ikarashi D., Yamashita M., Chiba T., Kadoya T., Bando H., Yamanaka T., Ohtani S., et al. Immune microenvironment, homologous recombination deficiency, and therapeutic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer: Japan Breast Cancer Research Group (JBCRG)22 TR. BMC Med. 2022;20:136. doi: 10.1186/s12916-022-02332-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Spranger S., Spaapen R.M., Zha Y., Williams J., Meng Y., Ha T.T., Gajewski T.F. Up-regulation of PD-L1, IDO and T(regs) in the melanoma tumor microenvironment is driven by CD8(+) T cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013;5:200ra116. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Ghosh J., Chatterjee M., Ganguly S., Datta A., Biswas B., Mukherjee G., Agarwal S., Ahmed R., Chatterjee S., Dabkara D. PDL1 expression and its correlation with outcomes in non-metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) Ecancermedicalscience. 2021;15:1217. doi: 10.3332/ecancer.2021.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Yam C., Yen E.-Y., Chang J.T., Bassett J.R.L., Alatrash G., Garber H., Huo L., Yang F., Philips A.V., Ding Q.-Q., et al. Immune Phenotype and Response to Neoadjuvant Therapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021;27:5365–5375. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Cerbelli B., Pernazza A., Botticelli A., Fortunato L., Monti M., Sciattella P., Campagna D., Mazzuca F., Mauri M., Naso G., et al. PD-L1 Expression in TNBC: A Predictive Biomarker of Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy? BioMed Res. Int. 2017;2017:1750925. doi: 10.1155/2017/1750925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Sabatier R., Finetti P., Mamessier E., Adelaide J., Chaffanet M., Ali H.R., Viens P., Caldas C., Birnbaum D., Bertucci F. Prognostic and predictive value of PDL1 expression in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6:5449–5464. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Bianchini G. Single-cell spatial analysis by imaging mass cytometry and immunotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) in the NeoTRIPaPDL1 trial; Proceedings of the SABCS 2021; San Antonio, TX, USA. 8–11 December 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 103.Long W., Chen J., Gao C., Lin Z., Xie X., Dai H. Brief review on the roles of neutrophils in cancer development. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2021;109:407–413. doi: 10.1002/JLB.4MR0820-011R. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Tokumaru Y., Oshi M., Murthy V., Tian W., Yan L., Angarita F.A., Nagahashi M., Matsuhashi N., Futamura M., Yoshida K., et al. Low intratumoral genetic neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) is associated with favorable tumor immune microenvironment and with survival in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021;11:5743–5755. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Asano Y., Kashiwagi S., Onoda N., Noda S., Kawajiri H., Takashima T., Ohsawa M., Kitagawa S., Hirakawa K. Predictive Value of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio for Efficacy of Preoperative Chemotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016;23:1104–1110. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4934-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Chae S., Kang K.M., Kim H.J., Kang E., Park S.Y., Kim J.H., Kim S.H., Kim E.K. Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio predicts response to chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Curr. Oncol. 2018;25:e113–e119. doi: 10.3747/co.25.3888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Ocana A., Chacon J.I., Calvo L., Anton A., Mansutti M., Albanell J., Martinez M.T., Lahuerta A., Bisagni G., Bermejo B., et al. Derived Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Predicts Pathological Complete Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022;11:5834. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.827625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Lou C., Jin F., Zhao Q., Qi H. Correlation of serum, N.L.R.; PLR and HALP with efficacy of neoadjuvant chemotherapy and prognosis of triple-negative breast cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022;14:3240–3246. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Pang J., Zhou H., Dong X., Wang S., Xiao Z. Relationship Between the Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio, Stromal Tumor-infiltrating Lymphocytes, and the Prognosis and Response to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Triple-negative Breast Cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer. 2021;21:e681–e687. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2021.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Onesti C.E., Josse C., Poncin A., Frères P., Poulet C., Bours V., Jerusalem G. Predictive and prognostic role of peripheral blood eosinophil count in triple-negative and hormone receptor-negative/HER2-positive breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant treatment. Oncotarget. 2018;9:33719–33733. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Hu H., Zhu J., Zhong Y., Geng R., Ji Y., Guan Q., Hong C., Wei Y., Min N., Qi A., et al. PIK3CA mutation confers resistance to chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer by inhibiting apoptosis and activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021;9:410. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Loibl S., Treue D., Budczies J., Weber K., Stenzinger A., Schmitt W.D., Weichert W., Jank P., Furlanetto J., Klauschen F., et al. Mutational Diversity and Therapy Response in Breast Cancer: A Sequencing Analysis in the Neoadjuvant GeparSepto Trial. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019;25:3986–3995. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-3258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Atchley D.P., Albarracin C.T., Lopez A., Valero V., Amos C.I., Gonzalez-Angulo A.M., Hortobagyi G.N., Arun B.K. Clinical and pathologic characteristics of patients with BRCA-positive and BRCA-negative breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008;26:4282–4288. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2008.16.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Huang L., Lang G.T., Liu Q., Shi J.X., Shao Z.M., Cao A.Y. A predictor of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer patients with the DNA repair genes. Ann. Transl. Med. 2021;9:301. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-4852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Telli M.L., Hellyer J., Audeh W., Jensen K.C., Bose S., Timms K.M., Gutin A., Abkevich V., Peterson R.N., Neff C., et al. Pathological complete response rate and survival in patients with BRCA-associated triple-negative breast cancer after 12 weeks of de-escalated neoadjuvant chemotherapy: Translational results of the WSG-ADAPT TN randomized phase II trial ( NCT01815242) J. Clin. Oncol. 2021;39((Suppl. 15)):579. [Google Scholar]
- 116.Richters L.K.K., Gluz O., Weber-Lassalle N., Christgen M., Haverkamp H., Kuemmel S., Kayali M., Kates R.E., Grischke E.M., Braun M., et al. Prevalence of BRCA1 mutations and responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy among BRCA1 carriers and non-carriers with triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2015;26:523–528. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Telli M.L., Hellyer J., Audeh W., Jensen K.C., Bose S., Timms K.M., Gutin A., Abkevich V., Peterson R.N., Neff C., et al. Homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) status predicts response to standard neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with triple-negative or BRCA1/2 mutation-associated breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2018;168:625–630. doi: 10.1007/s10549-017-4624-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Li M., Zhang J., Ouyang T., Li J., Wang T., Fan Z., Fan T., Lin B., Xie Y. Incidence of BRCA1 somatic mutations and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in Chinese women with triple-negative breast cancer. Gene. 2016;584:26–30. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2016.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Watanabe Y., Maeda I., Oikawa R., Wu W., Tsuchiya K., Miyoshi Y., Itoh F., Tsugawa K.-I., Ohta T. Aberrant DNA methylation status of DNA repair genes in breast cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Genes Cells. 2013;18:1120–1130. doi: 10.1111/gtc.12100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Meyer B., Clifton S., Locke W., Luu P.-L., Du Q., Lam D., Armstrong N.J., Kumar B., Deng N., Harvey K., et al. Identification of DNA methylation biomarkers with potential to predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Clin. Epigenet. 2021;13:226. doi: 10.1186/s13148-021-01210-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Akashi-Tanaka S., Watanabe C., Takamaru T., Kuwayama T., Ikeda M., Ohyama H., Mori M., Yoshida R., Hashimoto R., Terumasa S., et al. BRCAness predicts resistance to taxane-containing regimens in triple negative breast cancer during neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Clin. Breast Cancer. 2015;15:80–85. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2014.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Nogi H., Uchida K., Kamio M., Kato K., Toriumi Y., Akiba T., Morikawa T., Suzuki M., Kobayashi T., Takeyama H. Triple-negative breast cancer exhibits a favorable response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy independent of the expression of topoisomerase IIα. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2016;4:383–389. doi: 10.3892/mco.2015.719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Wang Q., Li C., Tang P., Ji R., Chen S., Wen J. A Minimal lncRNA-mRNA Signature Predicts Sensitivity to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018;48:2539–2548. doi: 10.1159/000492698. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Liebermann D.A. Gadd45 in Normal Hematopoiesis and Leukemia. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022;1360:41–54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-94804-7_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Zheng T., Pang Z., Zhao Z. A gene signature predicts response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer patients. Biosci. Rep. 2019;39:BSR20190414. doi: 10.1042/BSR20190414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Hoeffler J.P., Meyer T.E., Yun Y., Jameson J.L., Habener J.F. Cyclic AMP-Responsive DNA-Binding Protein: Structure Based on a Cloned Placental cDNA. Science. 1988;242:1430–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.2974179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Park S., Yi G. Development of Gene Expression-Based Random Forest Model for Predicting Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Response in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers. 2022;14:881. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Darb-Esfahani S., Kronenwett R., von Minckwitz G., Denkert C., Gehrmann M., Rody A., Budczies J., Brase J.C., Mehta M.K., Bojar H., et al. Thymosin beta 15A (TMSB15A) is a predictor of chemotherapy response in triple-negative breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer. 2012;107:1892–1900. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2012.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Xu L., Che X., Wu Y., Song N., Shi S., Wang S., Li C., Zhang L., Zhang X., Qu X., et al. SIRT5 as a biomarker for response to anthracycline-taxane-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2018;39:2315–2323. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Lindner J., Loibl S., Denkert C., Ataseven B., Fasching P., Pfitzner B., Gerber B., Gade S., Darb-Esfahani S., Sinn B., et al. Expression of secreted protein acidic and rich in cysteine (SPARC) in breast cancer and response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Ann. Oncol. 2015;26:95–100. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdu487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Orozco J.I.J., Grumley J.G., Matsuba C., Manughian-Peter A.O., Chang S.-C., Chang G., Gago F.E., Salomon M.P., Marzese D.M. Clinical Implications of Transcriptomic Changes after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019;26:3185–3193. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-07567-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Oshi M., Gandhi S., Huyser M.R., Tokumaru Y., Yan L., Yamada A., Matsuyama R., Endo I., Takabe K. MELK expression in breast cancer is associated with infiltration of immune cell and pathological compete response (pCR) after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2021;11:4421–4437. doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.SABCS21-P1-08-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Echavarria Diaz-Guardamino I., Lopez-Tarruella Cobo S., Del Monte-Millan M., Alvarez E., Jerez Y., Moreno Anton F., Lopez-Tarruella Cobo J.Á., Massarrah T., Ocaña I., Cebollero M., et al. 141MO—Pathological response and early survival data according to TNBCtype4 classifier in operable triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) treated with neoadjuvant carboplatin and docetaxel; Proceedings of the ESMO Congress; Paris, France. 9–13 September 2022. [Google Scholar]
- 134.Pérez-Pena J., Tibor Fekete J., Páez R., Baliu-Piqué M., García-Saenz J.Á., García-Barberán V., Manzano A., Pérez-Segura P., Esparis-Ogando A., Pandiella A., et al. A Transcriptomic Immunologic Signature Predicts Favorable Outcome in Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy Treated Triple Negative Breast Tumors. Front. Immunol. 2019;10:2802. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Sha L.-Y., Zhang Y., Wang W., Sui X., Liu S.-K., Wang T., Zhang H. MiR-18a upregulation decreases Dicer expression and confers paclitaxel resistance in triple negative breast cancer. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016;20:2201–2208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.García-García F., Salinas-Vera Y.M., García-Vázquez R., Marchat L.A., Rodríguez-Cuevas S., López-González J.S., Carlos-Reyes Á., Ramos-Payán R., Aguilar-Medina M., Pérez-Plasencia C., et al. miR-145–5p is associated with pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy and impairs cell proliferation by targeting TGFβR2 in breast cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2019;41:3527–3534. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Kolacinska A., Morawiec J., Fendler W., Malachowska B., Morawiec Z., Szemraj J., Pawlowska Z., Chowdhury D., Choi Y.E., Kubiak R., et al. Association of microRNAs and pathologic response to preoperative chemotherapy in triple negative breast cancer: Preliminary report. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014;41:2851–2857. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3140-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Sueta A., Fujiki Y., Goto-Yamaguchi L., Tomiguchi M., Yamamoto-Ibusuki M., Iwase H., Yamamoto Y. Exosomal miRNA profiles of triple-negative breast cancer in neoadjuvant treatment. Oncol. Lett. 2021;22:819. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.13080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Graeser M., Feuerhake F., Gluz O., Volk V., Hauptmann M., Jozwiak K., Christgen M., Kuemmel S., Grischke E.M., Forstbauer H., et al. Immune cell composition and functional marker dynamics from multiplexed immunohistochemistry to predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the WSG-ADAPT-TN trial. J. Immunother. Cancer. 2021;9:e002198. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-002198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Emens L.A. Chemotherapy and tumor immunity: An unexpected collaboration. Front. Biosci. 2008;13:249–257. doi: 10.2741/2675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Voorwerk L., Slagter M., Horlings H.M., Sikorska K., van de Vijver K.K., de Maaker M., Nederlof I., Kluin R.J., Warren S., Ong S., et al. Immune induction strategies in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer to enhance the sensitivity to PD-1 blockade: The TONIC trial. Nat. Med. 2019;25:920–928. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0432-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Buisseret L., Pommey S., Allard B., Garaud S., Bergeron M., Cousineau I., Ameye L., Bareche Y., Paesmans M., Crown J.P.A., et al. Clinical significance of CD73 in triple-negative breast cancer: Multiplex analysis of a phase III clinical trial. Ann. Oncol. 2018;29:1056–1062. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Loi S., Pommey S., Haibe-Kains B., Beavis P.A., Darcy P.K., Smyth M.J., Stagg J. CD73 promotes anthracycline resistance and poor prognosis in triple negative breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:11091–11096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222251110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Jinushi M., Chiba S., Yoshiyama H., Masutomi K., Kinoshita I., Dosaka-Akita H., Yagita H., Takaoka A., Tahara H. Tumor-associated macrophages regulate tumorigenicity and anticancer drug responses of cancer stem/initiating cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:12425–12430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106645108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Von Minckwitz G., Untch M., Blohmer J.U., Costa S.D., Eidtmann H., Fasching P.A., Gerber B., Eiermann W., Hilfrich J., Huober J., et al. Definition and Impact of Pathologic Complete Response on Prognosis After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Various Intrinsic Breast Cancer Subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012;30:1796–1804. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.38.8595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Institute of Medicine Committee on Qualification of Biomarkers and Surrogate Endpoints in Chronic Disease . References. In: Micheel C.M., Ball J.R., editors. Evaluation of Biomarkers and Surrogate Endpoints in Chronic Disease. National Academies Press; Washington, DC, USA: 2010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Simon R. Sensitivity, Specificity, PPV and NPV for Predictive Biomarkers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015;107:djv153. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djv153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Brower V. Biomarkers: Portents of malignancy. Nature. 2011;471:S19–S20. doi: 10.1038/471S19a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Li F., Yang Y., Wei Y., He P., Chen J., Zheng Z., Bu H. Deep learning-based predictive biomarker of pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy from histological images in breast cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2021;19:348. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-03020-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.