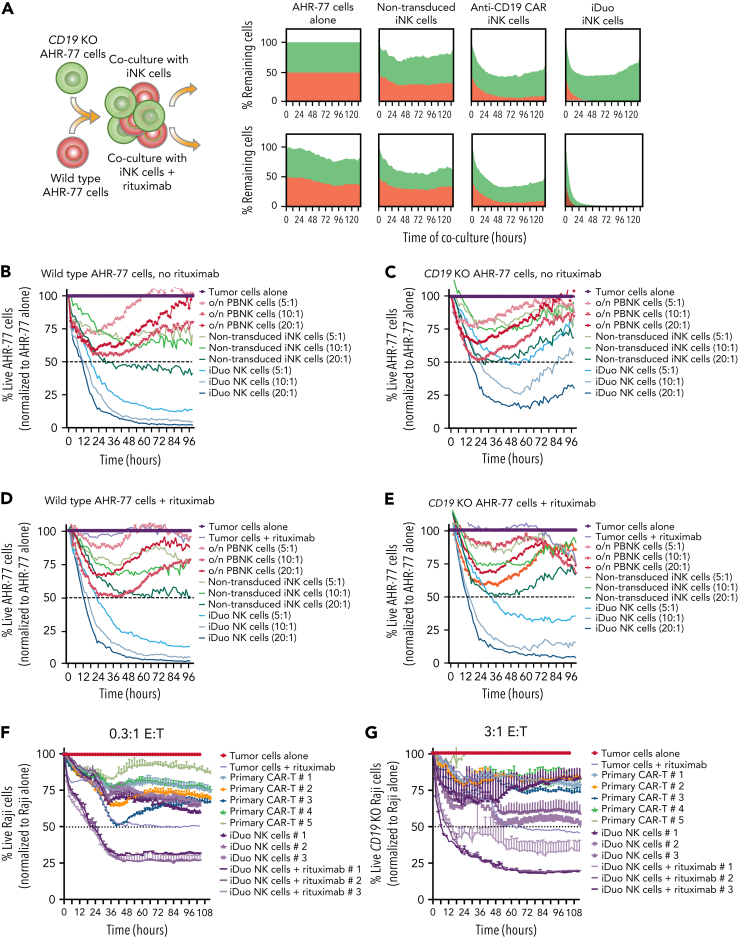
Figure 2.
iDuo NK cells eliminate CD19−B cells in models of antigen escape. (A) Wild-type AHR-77 cells transduced with NucLight Red and CD19 knockout AHR-77 cells transduced with NucLight green were mixed at a 1:1 ratio and cultured alone or cocultured with non-transduced iNK cells, anti-CD19 CAR iNK cells, or iDuo NK cells at a 10:1 E:T ratio in the presence or absence of 1 μg/mL rituximab. The percentages of live green and red cells were tracked over time in IncuCyte assays. Shown are overlaid killing curves from a representative experiment. IncuCyte assays were also performed using PBNK cells activated overnight with 10 ng/mL IL-15, non-transduced iNK cells, and iDuo NK cells as effectors at the indicated E:T ratios against (B) wild-type AHR-77 cells in the absence of rituximab, (C) CD19 knockout AHR-77 cells in the absence of rituximab, (D) wild-type AHR-77 cells in the presence of 1 μg/mL rituximab, and (E) CD19 knockout AHR-77 cells in the presence of 1 μg/mL rituximab. The percentages of live AHR-77 cells in each coculture condition were normalized to AHR-77 cells alone and graphed over time. All results are representative of two to three independent experiments. All conditions were run in triplicate. Primary anti-CD19 CAR T cells from five donors and iDuo NK cells from three different expansions were cocultured with NLR-transduced Raji cells at (F) low (0.3:1) and (G) high (3:1) E:T ratios in IncuCyte assays. iDuo NK cells were cocultured with targets in the presence or absence of 1 μg/mL rituximab. The percentages of live Raji cells in each coculture condition were normalized to Raji cells alone and graphed over time. All conditions were run in triplicate. Results are representative of two independent experiments.