Abstract
Background and Purpose:
Heart failure is associated with high morbidity and mortality, and new therapeutic targets are needed. Preclinical data suggest that pharmacological activation of protein kinase G (PKG) can reduce maladaptive ventricular remodeling and cardiac dysfunction in the stressed heart. However, clinical trial results have been mixed, and the effects of long-term PKG activation in the heart are unknown.
Experimental Approach:
We characterized the cardiac phenotype of mice carrying a heterozygous knock-in mutation of PKG1 (Prkg1R177Q/+), which causes constitutive, cGMP-independent activation of the kinase. We examined isolated cardiac myocytes and intact mice, the latter after stress induced by surgical transaortic constriction or angiotensin II infusion.
Key Results:
Cardiac myocytes from Prkg1R177Q/+ mice showed altered phosphorylation of sarcomeric proteins and reduced contractility in response to electrical stimulation, compared to cells from wild type mice. Under basal conditions, young PKG1R177Q/+ mice exhibited no obvious cardiac abnormalities, but aging animals developed mild increases in cardiac fibrosis. In response to angiotensin II infusion or fixed pressure overload induced by transaortic constriction, young PKGR177Q/+ mice exhibited excessive hypertrophic remodeling with increased fibrosis and myocyte apoptosis, leading to increased left ventricular dilation and dysfunction compared to wild type litter mates.
Conclusion and Implications:
Long-term PKG1 activation in mice may be harmful to the heart, especially in the presence of pressure overload and neurohumoral stress.
Keywords: cGMP-dependent protein kinase, phosphorylation of sarcomeric proteins, cardiac hypertrophy, fibrosis, stress-induced dilated cardiomyopathy
INTRODUCTION
Protein kinase G1 (PKG1) is an important pharmacological target in the heart, with a wealth of preclinical data suggesting that PKG activation is cardio-protective, e.g., in models of ischemia/reperfusion injury and pressure overload-induced heart failure (Blanton, 2020; Preedy, Baliga & Hobbs, 2020). Some clinical trials of cGMP-elevating, PKG activating agents in heart failure have shown promising results, but the outcomes of other trials have been disappointing (Blanton, 2020). The discrepancy between preclinical and clinical data suggest that much still needs to be learned about long-term effects of PKG activation in the heart.
As in other cell types, PKG activity in cardiac myocytes is regulated by the balance between cGMP synthesis and breakdown. cGMP is generated by two types of guanylyl cyclases (GCs), NO-stimulated GC-1 and natriuretic peptide (NP)-stimulated GC-A and GC-B (Kuhn, 2016). It is hydrolysed predominantly by phosphodiesterases(PDEs)-5 and −9 in the heart, and expression of both PDEs appears to increase in failing hearts (Lee et al., 2015; Takimoto et al., 2005). In normal hearts, PDE-5 localizes to the Z-band of the myocyte contractile filaments and regulates NO/GC-1-generated cGMP, while PDE-9 localizes to the T-tubular invaginations of the sarcolemma and mainly degrades cGMP generated by the ANP/GC-A pathway (Lee et al., 2015). This subcellular compartmentalization of cGMP signaling appears to be disrupted in heart failure (Cuello & Nikolaev, 2020). Both clinical and preclinical data suggest that NO/cGMP and natriuretic peptide/cGMP signaling are reduced in heart failure, and restoring PKG activity pharmacologically may have beneficial effects (Cuello & Nikolaev, 2020; Preedy, Baliga & Hobbs, 2020).
PKG phosphorylates multiple target proteins in cardiac myocytes, which can result in reduced or increased contractility, or improved relaxation and reduced myocardial stiffness, depending on the mode of PKG activation (Adler, Kuret, Langst & Lukowski, 2020; Preedy, Baliga & Hobbs, 2020). PKG targets include sarcomeric proteins (e.g., titin, cardiac myosin-binding protein C, and troponin I), calcium regulatory proteins (e.g., phospholamban and several calcium channels), mitochondrial K channels, and the mammalian target of rapamycin regulator tuberous sclerosis complex-2 (TSC2) (Adler, Kuret, Langst & Lukowski, 2020).
Mice with cardiomyocyte)-specific knockout of GC-B or PKG1 show normal basal cardiac morphology and function (Frantz et al., 2013; Lukowski, Rybalkin, Loga, Leiss, Beavo & Hofmann, 2010; Michel et al., 2020), while cardiomyocyte-specific knockout of GC-A leads to blood pressure-independent cardiac hypertrophy (Holtwick et al., 2003). All three genotypes respond to pressure overload and neurohumoral stressors (e.g., angiotensin II) with impaired cardiac remodeling and contractile dysfunction, although controversy exists over the degree of dysfunction (Frantz et al., 2013; Holtwick et al., 2003; Lukowski, Rybalkin, Loga, Leiss, Beavo & Hofmann, 2010; Michel et al., 2020). Similarly, mice with mutations in the PKG1 leucine zipper domain that disrupt homodimerization and subcellular targeting (PKG1-LZM mice) are more susceptible to pressure-overload-induced heart failure than wild type litter mates (Blanton et al., 2012). In contrast, PKG1C42S mutant mice that express a “redox-dead” kinase, which also exhibits reduced cGMP affinity, adapt better to severe pressure overload (Nakamura et al., 2015).
A gain-of-function mutation in PKG1 (Prkg1, pArg177Gln) causes early onset thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections in humans, and we showed that mice heretozygous for this mutation (Prkg1RQ/+) develop age-related aortic dilation without spontaneous dissections (Schwaerzer et al., 2019). The mutation is located in the first cGMP binding domain of PKG1 and causes both PKG1α and PKG1β isoforms to assume an active conformation with constitutive, cGMP-independent activity (Chan et al., 2020). Here we report that the mutant mice, which express one copy of the constitutively-active, cGMP-independent PKG1, exhibit detrimental cardiac effects during aging and hypertension-induced stress, possibly providing some explanation for the mixed results of cGMP-elevating agents in clinical trials.
METHODS
Animal experiments and Prkg1RQ/+ knock-in mice
All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Care and Use Committee of the University of California, San Diego, and complied with ethical guideleines for the use of animals in research according to policies of the University of California. The use of genetically-modified mice was necessary to study the effects of constitutive PKG1 activation on the heart under basal and stressed conditions. Mice were housed in groups of 2–4 littermates, in a temperature-controlled environment with 12/12 h light/dark cycle and ad libitum access to food and water. Prkg1RQ/+ knock-in mice were generated as described before (Schwaerzer et al., 2019). Mice backcrossed for at least six generations with 129S1/SvImJ mice (JAX mouse stock #002448) were used in all experiments, except the thoracic aorta constriction (TAC) experiments, where we used mice backcrossed into a C57BL/6NHsd background (Envigo catalog #044) for at least 8 generations, because TAC is most established in this background (Moore-Morris et al., 2014). Results are shown for mixed gender, unless stated otherwise; for uniformity of results, angiotensin II (Ang II) infusion and TAC were performed in male mice only. Animal welfare checks were carried out weekly, except after TAC surgery and Ang II pump implantation, when the animals were monitored daily.
PKG1 activity assay
PKG activity was measured using an optimized PKG peptide (TQAKRKKSLAMA, 30 μM) in the presence of 1.25 μM protein kinase inhibitor peptide to inhibit cAMP-dependent protein kinase (Schwaerzer et al., 2019). Assays were performed with [γ−32PO4]ATP (1.3 Ci/mmol; 50 μM) in the presence and absence of 3 μM cGMP, and were linear with time and protein concentration.
Western blotting
Western blots were developed with antibodies specific for: PKG1 (1:2000; Cell Signaling #C8A4), Ser239 – phosphorylated vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP, 1:1000, Cell Signaling #3114), Ser23/24-phosphorylated troponin I (1:1000, Cell Signaling #4004), Ser16/Thr17-phosphorylated phospholamban (1:1000, Cell Signaling #8496), and β-actin (1:3000, Santa Cruz #sc47778). Proteins were quantified by chemiluminescence using a Li-COR Odyssey Scanner and Image Studio Version 5.2 software.
Isolation of murine adult cardiac myocytes
Adult cardiac myocytes were isolated as described previously (Hu, Jones & Dillmann, 2005). Briefly, mice were deeply anesthetized with ketamine (100 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg), and the heart was removed through a midline sternotomy. The heart was perfused at 2 ml/min in a modified Langendorff perfusion apparatus with nominally Ca2+-free perfusion solution (126 mM NaCl, 4.4 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 0.12 mM NaH2PO4, 4 mM NaHCO3, 30 mM 2,3-butadione monoxime, 1.8 mM pyruvate, 5 mM taurine, 5.5 mM glucose, 10 mM HEPES, pH 7.4 at 37°C), bubbled with oxygen. After 5 min, the perfusion solution was switched to the same buffer supplemented with 25 μM Ca2+ and 1 mg/ml collagenase (Worthington) for 20 min. The left ventricular free wall was dissected and myocytes were gently dispersed by passing through a cell dissociation cup (pore size 100 μm), to remove undigested myocytes, and connective and fatty tissue. Serial washes with fresh perfusion solution slowly increased [Ca2+] to 2 mM.
Phosphoproteomics analysis
Freshly-isolated cardiac myocytes were lysed, trypsin-digested, and the lysates analyzed by ultra-high pressure liquid chromatography (UHPLC) coupled with tandem mass spectroscopy (LC-MS/MS) using nano-spray ionization (Guttman, Betts, Barnes, Ghassemian, van der Geer & Komives, 2009). Phospho-peptides were enriched using TiO2 (High-Select™ TiO2 Phosphopeptide Enrichment Kit, ThermoFisher) and metal-based resins (IMAC, High-Select™ Fe-NTA Phosphopeptide Enrichment Kit, ThermoFisher) as described in the manufacturers’ protocols. Peptides not retained by TiO2 and IMAC were pooled and analyzed separately. Peptides were eluted into the mass spectrometer with charge state set to include only +2–5 ions. Protein identification and label-free quantification was carried out using Peaks Studio 8.5 (Bioinformatics Solutions Inc.). Phosphopeptides were identified as those retained by the TiO2 and IMAC resins, displaying at least one phosphate residue (mol mass=+79.97) per peptide. Only phospho-peptides that were detected in every sample for each biological group were considered. The quantity of each phosphopeptide was normalized to the amount of the peptide not retained by the TiO2 and IMAC resins. Phosphopeptides detected multiple times were averaged, and normalized phosphopeptides were averaged between biological groups. Analysis of the most abundant serine-centered-phospho-motifs was performed using a probability logo generator (O’Shea, Chou, Quader, Ryan, Church & Schwartz, 2013). The complete list of phospho-peptides is shown in Supplemental Table 1. The data have been deposited in the PRIDE (Perez-Riverol et al., 2019) partner repository with dataset identifier PXD022600.
Cardiac myocyte contractility measurements
Freshly isolated cardiac myocytes were plated onto mouse laminin-coated coverslips (Invitrogen) in 4.5 g glucose DMEM. After 30 min, coverslips were mounted in an Motic AE-31E light-inverted microscope equipped with a 40 × objective and a high resolution CMOS sensor camera. Cells were induced to contract by electrical field stimulation (0.3 Hz), while perfused with respiratory buffer [126 mM NaCl, 4.4 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 0.12 mM NaH2PO4, 4 mM NaHCO3, 5.5. mM glucose, 1 mM pyruvate, 1 mM malate, 0.2% BSA, 2 mM CaCl2, 10 mM Hepes pH 7.4]. SarcLem PMT software (IonOptix) was used to determine average sarcomere length, fractional shortening, and speed of contraction and relaxation.
Cytosolic Ca2+ analysis
Freshly isolated cardiac myocytes plated on laminin-coated coverslips (in 4.5 g glucose DMEM for 30 min) were loaded with Indo-1 AM (0.02 mg/ml) for an additional 30 min at room temperature. Coverslips were mounted in an epi-fluorescence microscope equipped with a 100 × objective interfaced to a dual excitation lamp system (Photon Technologies International, Inc). Transient increases in fluorescence upon electric stimulation at 0.3 Hz were collected by an aperture mechanism from a selected portion of the field, positioned over the cytosolic region of individual cells. Cells were perfused with respiratory buffer, and cytosolic Ca2+ transients were analyzed as described (Suarez et al., 2004).
Immunofluorescent microscopy
Isolated cardiac myocytes were plated on laminin-coated coverslips. After 30 min, cells were fixed in 99.6% acetone cooled to −20 °C, permeabilized in 0.025% Triton X-100 in PBS, and incubated at 4°C overnight with 1:50 diluted primary antibodies (in PBS, 2% BSA) specific for PKG1 (Sigma HPA-007699), and either cardiac myosin heavy chain (Abcam Ab50967), α-actinin (Santa Cruz sc17829) or cytochrome c oxidase subunit Cox-1 (Abcam Ab14705). After washing in 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% Tween 20, cells were incubated with the corresponding FITC- or TRITC-labeled secondary antibodies (Alexa anti-rabbit-488 for PKG, and Alexa anti-mouse-561 for other antibodies). DNA was counter-stained with Hoechst 33342 (Invitrogen), and coverslips were mounted with ProLong Diamond Antifade Mountant (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Photographs were acquired using a 60 X objective on a Zeiss LSM880 fluorescent confocal microscope.
Transthoracic echocardiography
Transthoracic echocardiography was performed on mice that were anesthetized for 15 sec with 5% isoflurane and maintained on 0.5% isoflurane. Electrocardiograms were recorded with small needles inserted into one front and one hind limb. Cardiac function was recorded with a VisualSonics, SonoSite FUJIFILM, Vevo 2100 ultrasound system with a linear transducer 32–55 MHz by a single, highly experienced operator who was blinded to the genotype and treatment of the mice as described (Schwaerzer et al., 2019).
Subcutaneous angiotensin II infusion
Four month-old male mice were anesthetized with 1.5% isoflurane and an Alzet osmotic minipump releasing 1 μg/min/kg of Ang II was implanted subcutaneously. Some of the mice received additionally an implantable wireless transmitter/receiver system (Datasciences International, Ponemah, PA-C10 pressure transmitter) to measure blood pressure and heart rate. Two weeks after implantation, data were recorded for three days. After three weeks of Ang II infusion, echocardiography was performed and the mice were euthanized.
Transverse aortic constriction (TAC)
TAC was performed on four- to five-month-old male mice under deep anesthesia as described (Schwaerzer et al., 2019). Briefly, aortas were banded with a 27.5-gauge needle for mice < 25 g or a 27-gauge needle for mice ≥ 25 g to yield a constriction with an opening of about 0.4 mm diameter, as previously described (Schwaerzer et al., 2019). Buprenorphine was given for pain control for three days post-operatively. Fourteen days after the procedure, echocardiography was performed on lightly-anesthetized mice as described above. The mice were then deeply anesthetized with ketamine/xylazine, and blood pressure was invasively measured proximal and distal to the constriction; the mice were then euthanasized by exsanguination and cervical dislocation. Peri-operative mortality was 13% for both genotypes; 36% of Prkg1RQ/+ mice died between post-operative day 2 and 14 from aortic rupture, and were excluded from analysis.
Histological analysis
Following anesthesia with ketamine (100 mg/kg) and xylazine (10 mg/kg), mice were perfusion-fixed with 10 ml of 4% paraformaldehyde for 3 min under physiological pressure. Hearts were excised and further fixed overnight. Five μm-thick cross-sections from paraffin-embedded hearts were stained with Masson’s Trichrome stain or wheat germ agglutinin (WGA). Slides were scanned with a Hamamatsu NanoZoomer 2.0 HT System and analyzed using Digital Pathology NDP.view2 software. Collagen content was measured on five non-overlapping left ventricular sections (0.2 μm2 each) stained with Masson’s Trichrome using Image-Pro Premier software (V 9.0, Media Cybernetics). Cardiomyocyte cross-sectional areas were measured on WGA-stained left ventricle cross sections, assessing at least 40 myocytes with a central nucleus per section. Apoptosis was assessed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick end-labeling (TUNEL) of deparaffinized sections, using the Apoptag Peroxidase In-situ Apoptosis Detection Kit (Millipore EMD; S7100). Histomorphometric analysis was performed with the observer blinded to the genotype of the mice, and results were confirmed by an independent observer.
Quantitative qPCR
Hearts were snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and pulverized and immersed in Trizol (Molecular Research Center, TR118). Total RNA was isolated, and reverse-transcribed using iScript cDNA synthesis kit (Bio-Rad). Quantitative PCR was performed using Brilliant II SYBR Green (Agilent Technologies) (Schwaerzer et al., 2019). All primers were intron-spanning (except for 18S rRNA), and were tested with serial cDNA dilutions. Relative changes in mRNA expression were analyzed using the comparative 2−ΔΔCt method, with 18S rRNA as internal control.
Statistics
Most data are presented as dot plots with means ± SD or as box-and whiskers plots, where the upper and lower margins of the box define the 75th and 25th percentiles, respectively, the internal line defines the median, and the whiskers show the total range. qRT-PCR results were normalized to the wild type control group (the mean of this group was assigned a value of one). Where appropriate (for n>7), the data were tested for normality using the D’Agostino-Pearson omnibus normality test, and for equal variance using an F test (to compare the variances of two groups), or the Browne and Forsythe test (for 3 or more groups). For comparison of two groups, P values refer to unpaired, 2-tailed Student’s t test. For multiple comparisons, P values refer to 2-way ANOVA with Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparison test; the post-hoc test was only performed if F was significant and there was no variance inhomogeneity. When the assumptions of normal distribution and/or equal variances were not met, a non-parametric test was chosen (Mann-Whitney test for two groups and Kruskal-Wallis test for three or more groups). P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. Data analysis was performed using GraphPad Prism 8 software.
RESULTS
Prkg1RQ/+ mice show increased basal PKG activity in heart extracts and altered phosphorylation of sarcomeric proteins in isolated cardiac myocytes
Since homozygous Prkg1RQ/RQ mice have a high mortality within the first 6 weeks of life due to severe gastro-intestinal dysfunction (Schwaerzer et al., 2019), we concentrated on heterozygous Prkg1RQ/+ mice. The latter mice appear healthy and have normal body weights, but they are mildly hypotensive, with a mean arterial pressure about 10 mmHg below that of wild type litter mates (Schwaerzer et al., 2019).
PKG1 protein and cGMP-stimulated PKG activity were the same in hearts from heterozygous Prkg1RQ/+ mice and their wild type litter mates (Fig. 1a and 1b), but basal PKG activity was about two-fold higher in hearts from mutant mice, when measured with an optimized peptide substrate (Fig. 1a) or assessed by phosphorylation of the preferred PKG1 substrate vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein (pVASP, Fig. 1b and 1c). Basal PKG activity in the hearts of the mutant mice was ~45 % of maximal cGMP-stimulated activity, compared to ~20 % of maximal activity in the wild type mice (Fig. 1a). Phosphorylation of the known PKG1 substrates phospholamban (Ser16) and troponin I (Ser23/24) was similar in Prkg1RQ/+ and wild type hearts, suggesting that the mutant PKG1 may not equally target all known PKG substrates in the heart (Fig. 1b).
Fig. 1: PKG activity in heart extracts and phosphoproteomic anaylsis of cardiac myocytes isolated from Prkg1RQ/+ mice and control litter mates.
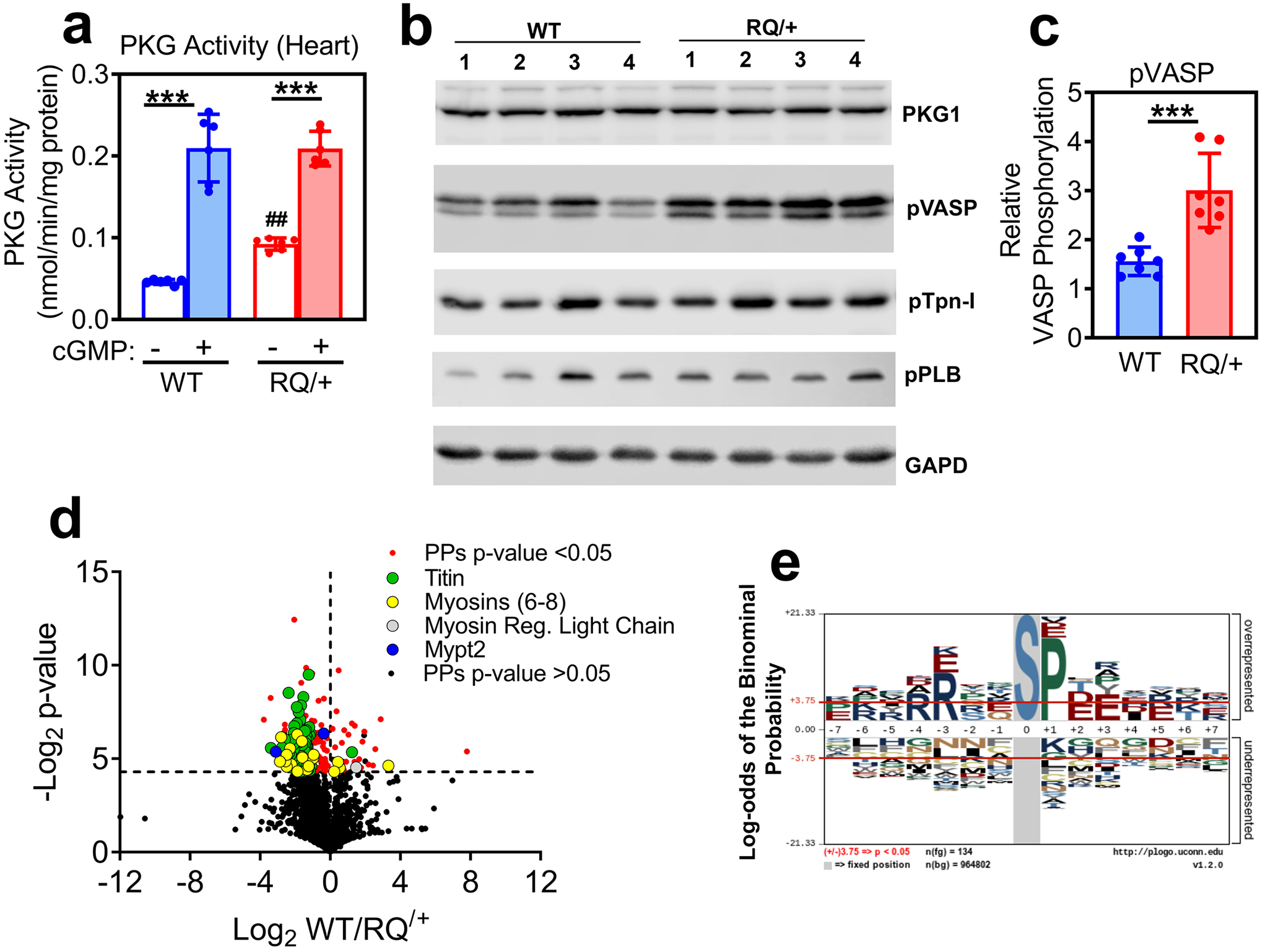
(a) PKG activity was measured in heart extracts from wild type (WT) and Prkg1RQ/+ (RQ/+) mice using an optimized peptide substrate in the absence and presence of cGMP (n=6 mice per genotype; means +/− SD, ***p<0.001 for comparison +/− cGMP and ##p<0.01 for comparison to wild type). (b) Western blots of heart extracts from four wild type and four Prkg1RQ/+ mice were developed with antibodies specific for PKG1, Ser239-phospho-VASP (a preferred PKG substrate site), Ser23/24-phosphorylated troponin I (pTpn-I), Ser16/Thr17-phosphorylated phospholamban (pPLB), or GAPD (loading control). (c) VASP phosphorylation (assessed as in panel b) was quantified using a Li-COR Odyssey Scanner, and normalized to GAPD (n=7 mice per genotype, ***p<0.001). (d) The phosphoproteome of adult cardiac myocytes freshly isolated from WT and RQ/+ mice (n=4 per genotype) was analyzed, and the Log2 differences between WT and RQ/+ were plotted over Log2 t-test values (Volcano plot) for all peptides identified at least once in every sample. Significantly different phospho-peptides (PPs, −Log2 t-test p-values >4.3) are shown in red, with peptides from some sarcomeric proteins highlighted in green (titin), yellow (myosin 6, 7, 8), grey (myosin regulatory light chain) and blue (Mypt2). (e) A graphical representation of the most frequently encountered serine (S)-centered phosphorylation consensus motifs is shown for cardiac myocytes from RQ/+ mice.
To determine if chronic PKG activation increases steady-state serine/threonine phosphorylation of specific proteins, we performed an unbiased proteomic analysis, comparing phosphoproteins in adult cardiac myocytes isolated from 6 month-old Prkg1RQ/+ mice to those in wild type litter mates (Fig. 1d and Supplemental Table 1). Based on exploratory data from n=4 mice per genotype, 48 unique proteins showed increased serine/threonine phosphorylation in the mutant cardiomyocytes, including 22 sarcomere-associated proteins, most notably titin (65 unique phosphorylation sites), myosins 6/7/8, and myosin phosphatase targeting subunit-2 (MYPT2, also known as protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 12B). In contrast, only seven unique proteins showed decreased phosphorylation in mutant compared to wild type myocytes, most notably the myosin regulatory light chain-2 (MLC2, gene name Myl2). The most frequently encountered phosphorylation motif in cardiac myocytes from Prkg1RQ/+ mice corresponded to the known PKG consensus site RRXXS/T (Fig. 1e for serine-centered sites, with similar results obtained for threonine-centered sites).
Cardiac myocytes isolated from Prkg1RQ/+ mice exhibit decreased contractility compared to cells from wild type litter mates, but cytosolic Ca++ transients are unchanged
To evaluate the effect of constitutively-active PKG1 on contractile function, cardiac myocytes were isolated from 8–12 month-old Prkg1RQ/+ mice and wild type litter mates. Cell contraction was induced by field electrical stimulation and sarcomere lengths were analyzed using fast Fourier transform analysis. Freshly-isolated cardiac myocytes from Prkg1RQ/+ mice exhibited contractile dysfunction, represented by a 38% reduction in fractional shortening and a 39% reduction in the rate of contraction compared to wild type myocytes (Fig. 2a–c). The myocytes from Prkg1RQ/+ mice also showed a slower relaxation rate, but this did not reach statistical significance (Fig. 2d).
Fig. 2: Contractility and cytosolic Ca++ transients in adult cardiac myocytes isolated from Prkg1RQ/+ mice and control litter mates.
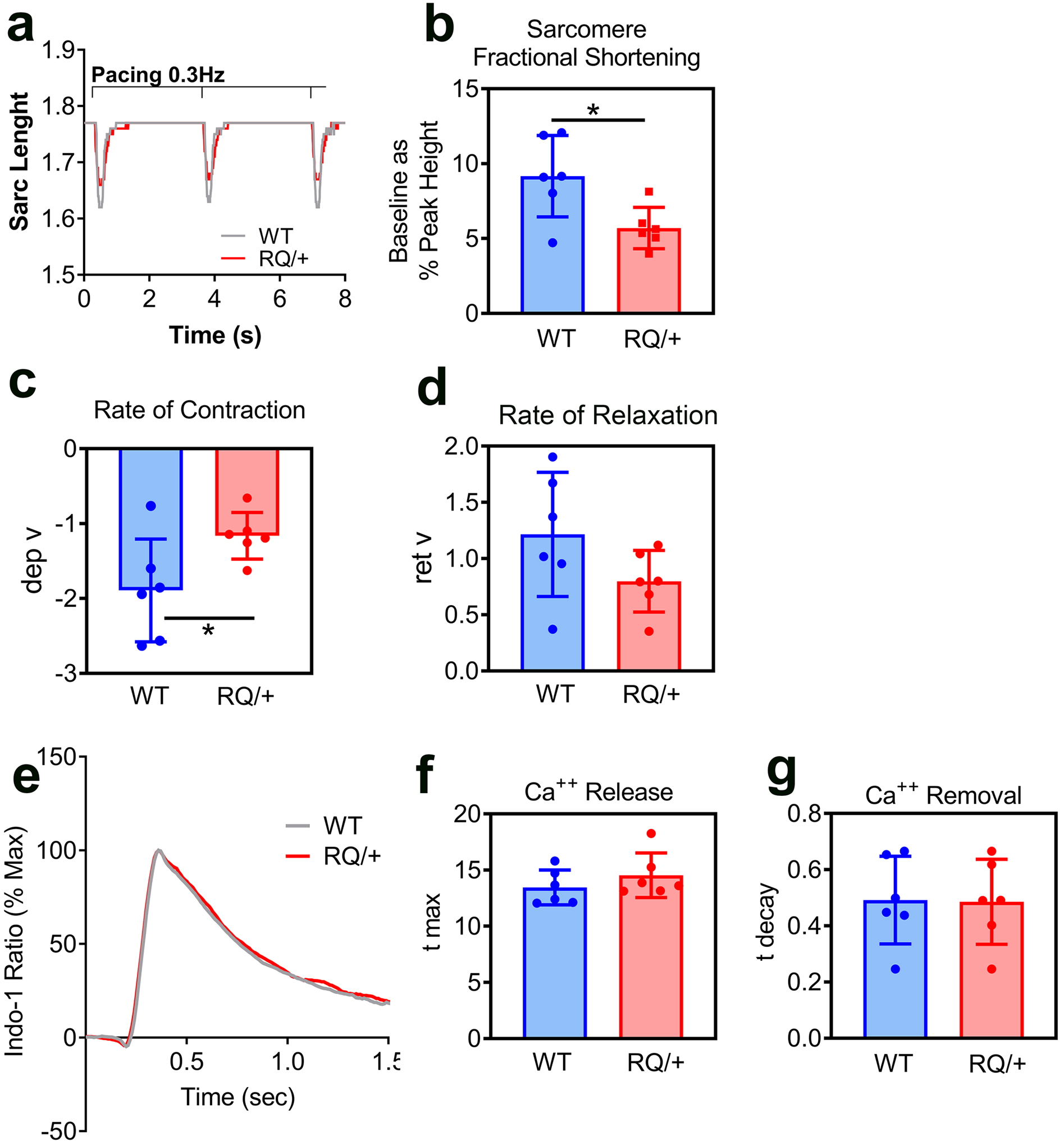
(a-d) Cardiac myocyte contractility was assessed by monitoring sarcomere length upon electrical stimulation (20V, 0.3 Hz). Representative traces (a) from three consecutive contractions are shown for wild type (WT, grey) and Prkg1RQ/+ (RQ/+, red) myocytes. Sarcomere fractional shortening (b) was measued as a percent of sarcomere length change during contraction (baseline as a percent of peak height). Rate of contraction (c) is expressed as departure velocity (dep v). Rate of relaxation (d) is expressed as return velocity (ret v), i.e. velocity of the return phase of the transient. (e-g) Representative cytosolic Ca++ transients (e) were recorded in paced-contracting myocytes from wild type (WT, grey) and Prkg1RQ/+ (RQ/+, red) mice; cells were pre-loaded with Indo-1 for 30 min. Rates of Ca++ release into the cytosol (f, t max) and rates of Ca++ removal from the cytosol (g, t decay) were measured. The data in panels b-d and f-g represent n=6 mice per genotype with ≥20 cells analyzed per mouse; means +/− SD with *p<0.05 for the indicated comparisons by two-sided t-test.
To determine whether the reduced contractility of Prkg1RQ/+ cardiac myocytes was due to changes in calcium handling, electrical stimulation-induced changes in the cytoplasmic calcium concentration was measured in Indo-1-loaded myocytes. Intracellular calcium transients from wild type and Prkg1RQ/+ cardiac myocytes were essentially identical (Fig. 2e), and neither the rate of Ca++ release nor removal differed between the two genotypes (Fig. 2f,g). Thus, the reduced cardiac myocyte contractility appeared to be calcium-independent, and likely due to changes in phosphorylation of sarcomeric proteins (discussed below).
Wild type and mutant PKG1RQ co-localize with myosin heavy chain and α-actinin
To determine if the subcellular localization of the constitutively-active mutant PKG1 in cardiac myocytes differed from that of the wild type enzyme, we identified PKG1 by immunofluorescent staining using an antibody that showed no non-specific staining in PKG1-deficient H9C2 myoblasts (Suppl. Fig. 1a). PKG1 showed a similar striated pattern in cardiac myocytes isolated from Prkg1RQ/+ and wild type mice, with brightly-stained bands alternating with less brightly-stained bands (Fig. 3a, negative controls are shown in Suppl. Fig. 1b). The brightly-stained PKG1 bands co-localized with myosin heavy chain, which marks the sarcomere M-band (Lange, Pinotsis, Agarkova & Ehler, 2020) (Fig. 3a). The less intense PKG1 bands co-localized with α-actinin, which marks the Z-band (Cai et al., 2019) (Fig. 3b). PKG1 was not detected in mitochondria, which were stained with an antibody recognizing cytochrome oxidase-1 (Fig. 3c). Thus, both wild type and mutant PKG1 were localized predominantly at the M- and Z-bands of the sarcomere, and no difference in the staining pattern was discernable between wild type and mutant enzyme.
Fig. 3: Subcellular localization of wild type and mutant PKG1RQ in cardiac myocytes.
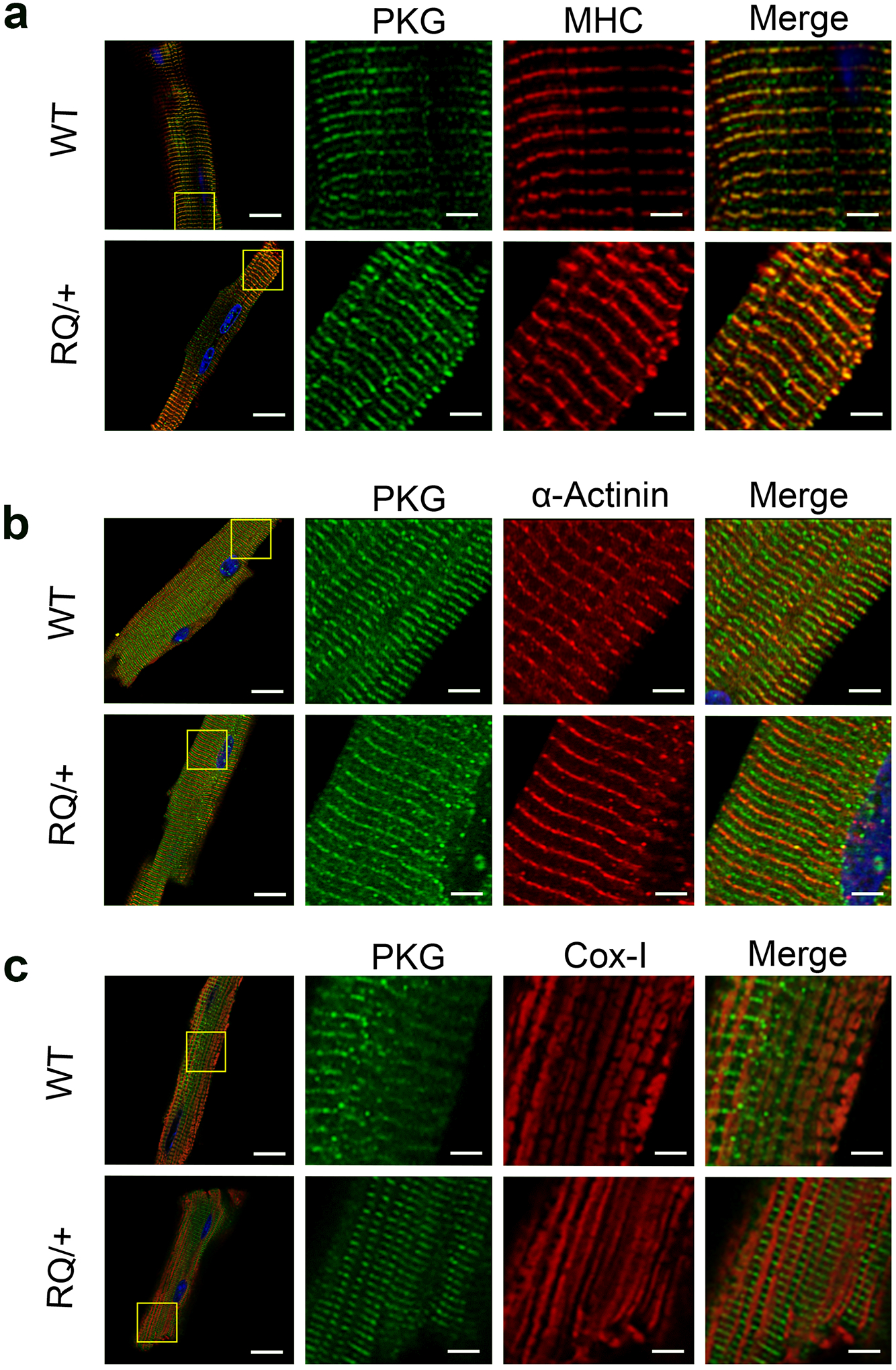
Cardiac myocytes were isolated from adult (6 mo old) wild type (WT) and Prkg1RQ/+ (RQ/+) mice, and were allowed to adhere to laminin-coated glass coverslips. The cells were fixed and stained, and proteins were visualized by immunofluorescence. Green staining represents PKG1; cells were co-stained (red) for either myosin heavy chain (MHC) representing the M-band (a), α-actinin representing the Z-band (b), or cytochrome oxidase-1 (Cox-1) highlighting mitochondria (c). Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). Images were acquired on a Zeiss LSM880 fluorescent confocal microscope with Airyscan using a 60x objective, and are representative for cardiomyocyte preparations from n=3 mice per genotype, with at least 5–10 cells analyzed per mouse. (bars in left column represent 20 μm, in magnified views 4 μm).
Aging male Prkg1RQ/+ mice show mild cardiac structural changes with increased interstitial fibrosis
In 4 month-old male and female Prkg1RQ/+ mice, basal cardiac parameters, including heart weight normalized to body weight, and left ventricular (LV) mass, fractional shortening, septum thickness, and LV inner diameter in diastole were similar to wild type mice; the LV posterior wall thickness was less in male mutant mice than wild type mice (Fig. 4a–f; body weights for males and females and ECHO data for female mice are shown in Suppl. Fig. 2a–g). At the age of 12 months, male Prkg1RQ/+ mice showed a modest reduction in LV mass, LV posterior wall thickness, and septum thickness compared to wild type litter mates (Fig. 4a–f), possibly related to their mild hypotension (Schwaerzer et al., 2019). However, this modest reduction in age-related LV hypertrophy was not apparent in female mutant mice (Suppl. Fig. 2c–g). Histological analysis of the hearts from 12 month-old mice showed increased interstitial fibrosis in both male and female Prkg1RQ/+ mice compared to wild type litter mates (Fig. 4g shows male mice). No interstitial fibrosis was observed in young mice (data not shown).
Fig. 4: Basal cardiac phenotype of aging Prkg1RQ/+ mice and control litter mates.
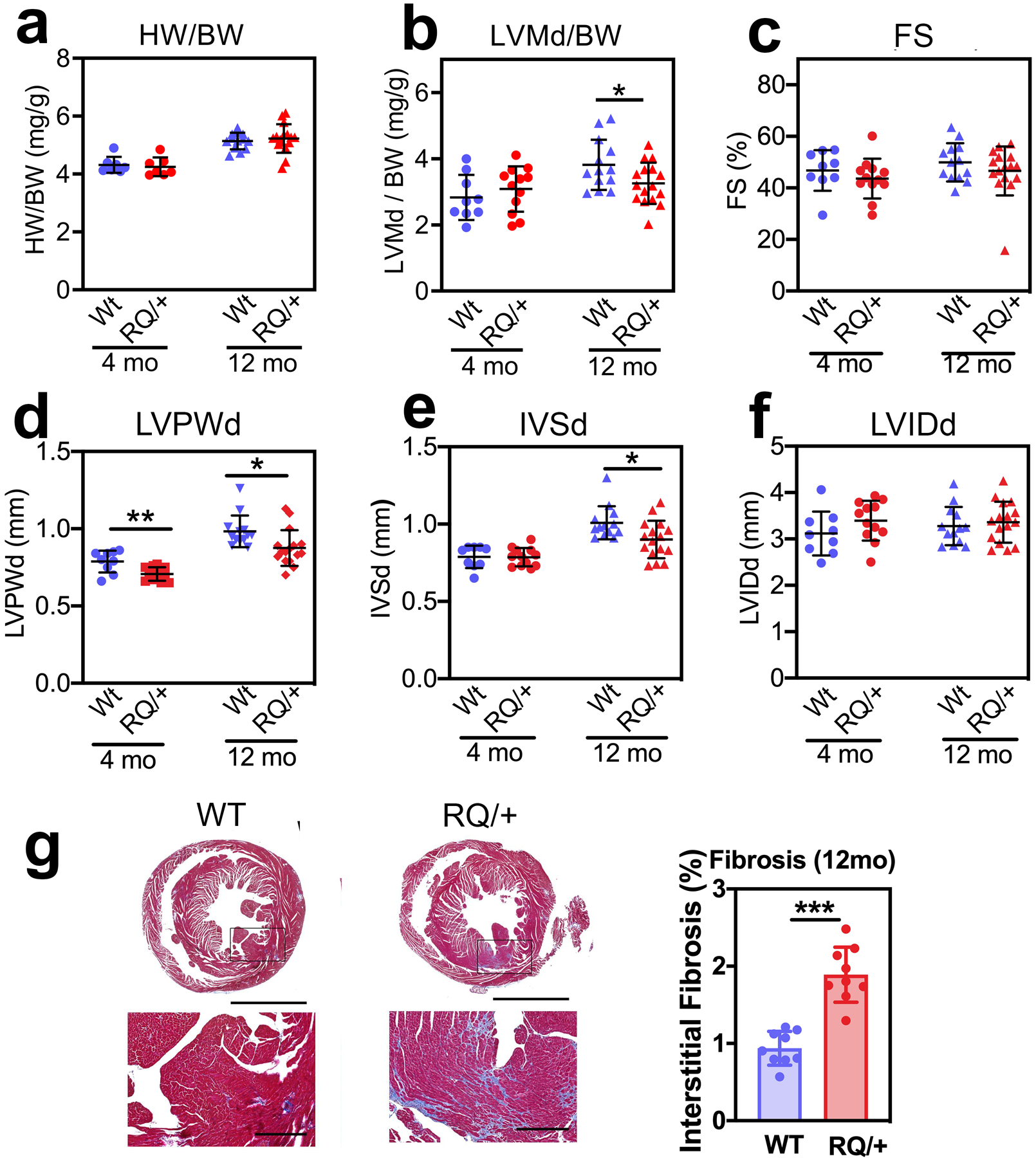
(a,b) Heart weight (HW) and left ventricular mass in diastole (LVMd) were normalized to body weight (BW) in 4-month and 12-month-old male Prkg1RQ/+ (RQ/+) mice and wild type (WT) litter mates. (c-f) Cardiac parameters were measured by echocardiography in 4-month and 12-month-old male WT and RQ/+ mice: (c) LV fractional shortening (FS); (d) LV posterior wall thickness in diastole (LVPWd); (e) inter-ventricular septum thickness in diastole (IVSd); (f) LV inner diameter in diastole (LVIDd). (g) Cross-sections of the hearts from 12-month-old male mice stained with trichrome to highlight collagen in blue. Interstitial fibrosis was quantified using Image-Pro Premier software and is expressed as percent of cross-sectional area. Data are shown as mean ± SD for n=9 and 13 WT mice and n=12 and 16 RQ/+ mice in the 4- and 12-month-old groups, respectively, except for panel a with seven 4-month-old mice and panel g with nine 12-month-old mice per genotype. *p<0.05 for the indicated comparisons by 2-Way ANOVA (panels a-f), ***p<0.001 by two-sided t-test (panel g).
Prkg1RQ/+ mice develop a dilated cardiomyopathy in response to angiotensin II
Since cardiac myocyte-specific Prkg1 knockout mice have normal cardiac function at baseline, but develop cardiac dysfunction and increased fibrosis in response to Ang II infusion, it has been suggested that PKG1 may attenuate Ang II- (Gαq-mediated) cardiac hypertrophy (Frantz et al., 2013). To test this hypothesis, we subjected four month-old male wild type and Prkg1RQ/+ mice to Ang II infusion (1 μg/kg/min) for three weeks. Both wild type and mutant mice became hypertensive in response to the drug, but the average systolic blood pressure of Prkg1RQ/+ mice was almost 20 mmHg lower than that of the wild type mice (Fig. 5a, telemetric blood pressure measurements; Fig. 5b, systolic pressures obtained by tail cuff plethysmography; both measurements in conscious mice). Ang II increased total LV mass by echocardiographic estimation in wild type and mutant mice to a similar degree, but LV posterior wall thickness and septum thickness increased less in Prkg1RQ/+ mice compared to wild type mice, perhaps because Ang II-induced hypertension was less severe in the mutant mice (Fig. 5c–e). After Ang II treatment, Prkg1RQ/+ mice showed more interstitial fibrosis, and larger cardiac myocyte cross-sectional area compared to wild type mice (Fig. 5f,g). These structural changes were associated with functional changes: fractional shortening remained the same in wild type mice pre and post-AngII, but the Prkg1RQ/+ mice exhibited decreased fractional shortening post-Ang II associated with mild LV dilation (Fig. 5h,i). Thus, Prkg1RQ/+ mice developed a dilated cardiomyopathy under the stress of Ang II, despite lower blood pressures in response to the drug.
Fig. 5: Cardiac remodeling and function in response to angiotensin II.
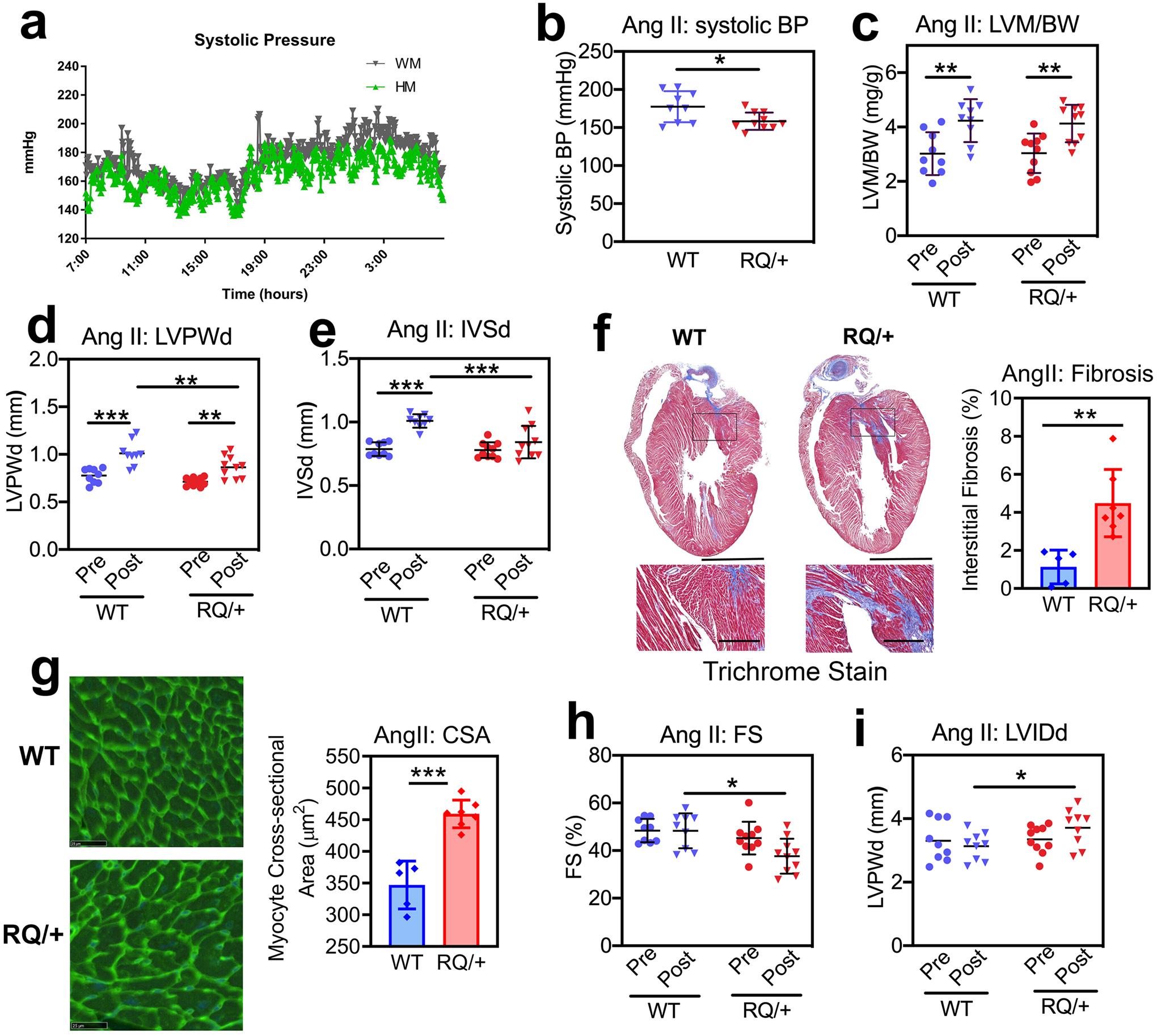
Four month-old male Prkg1RQ/+ (RQ/+) mice and wild type (WT) litter mates received Ang II at 1 μg/kg/min subcutaneously per osmotic minipump for three weeks. (a) Systolic blood pressure was measured by telemetry over 24 h, starting after 2 weeks of Ang II infusion (n=4 mice per genotype). (b) Systolic blood pressure was measured by tail cuff plethysmography after 2 weeks of Ang II infusion in mice that underwent echocardiography after 3 weeks (n=9 WT and n=10 RQ/+). (c-e, h-i) Cardiac parameters were measured by echocardiography after three weeks of Ang II infusion (n=9 WT and n=10 RQ/+): (c) LV mass (LVM) normalized to body weight (BW); (d) LV posterior wall thickness in diastole (LVPWd); (e) inter-ventricular septum thickness in diastole (IVSd); (h) LV fractional shortening (FS); and (i) LV inner diameter in diastole (LVIDd). (f) Collagen content was quantified on trichrome-stained sections as in Fig. 4g (n=5 WT and n=7 RQ/+ mice). (g) Cardiac myocyte cross-sectional area (CSA) was measured on wheat germ agglutinin-stained cross sections (n=5 WT and n=7 RQ/+ mice). Graphs represent means ± SD; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 for the indicated comparisons by 2-Way ANOVA (panels c-e, h,i), or by two-sided t-test (panels b, f, g).
Prkg1RQ/+ mice develop more severe cardiac remodeling, dilation, and decompensation after TAC than wild type mice
To study another form of cardiac stress, we subjected four to five month-old male Prkg1RQ/+ mice and their wild type littermates to pressure overload by transaortic constriction. As previously reported, about one-third of the Prkg1RQ/+ mice succumbed to aortic rupture within 2 weeks after TAC, while none of the wild type mice died (Schwaerzer et al., 2019). TAC produced similar aortic pressure gradients in both genotypes (Fig. 6a). On analyzing the cardiac phenotype of surviving mutant mice, TAC induced a greater increase in heart weight and LV mass compared to that observed in wild type mice, with a similar increase in LV posterior wall thickness and septum thickness in both genotypes (Fig. 6 b–e). Moreover, Prkg1RQ/+ mice developed more interstitial fibrosis, cardiomyocyte enlargement, and cardiomyocyte apoptosis after TAC compared to wild type mice (Fig. 6 f–h). As in the AngII-treated mice, these structural changes were associated with more adverse functional changes than occurred in wild type mice, with the Prkg1RQ/+ mice exhibiting a greater decrease in fractional shortening and more cardiac dilation after TAC (Fig. 6 i–j). Prior to TAC, expression of cardiac hypertrophy markers (ANP, BNP, and myosin heavy chain-7) was similar in the hearts of wild type and Prkg1RQ/+ mice, as was the expression of the housekeeping genes β-actin (Actb), hypoxanthine phosphoribosyl transferase (Hprt), and β2-microglobulin (B2m) (Fig. 6k, left panel). However after TAC, Nppa (ANP), Nppb (BNP), Myh7, and Actb gene expression was higher in hearts from the mutant mice than from wild type mice, whereas Hprt and B2m remained the same (Fig. 6k, right panel). Thus, after TAC-induced pressure overload, Prkg1RQ/+ mice develop more severe pathological cardiac remodeling, contractile dysfunction, and cell death than wild type mice.
Fig. 6: Cardiac remodeling and function in response to transaortic constriction (TAC).
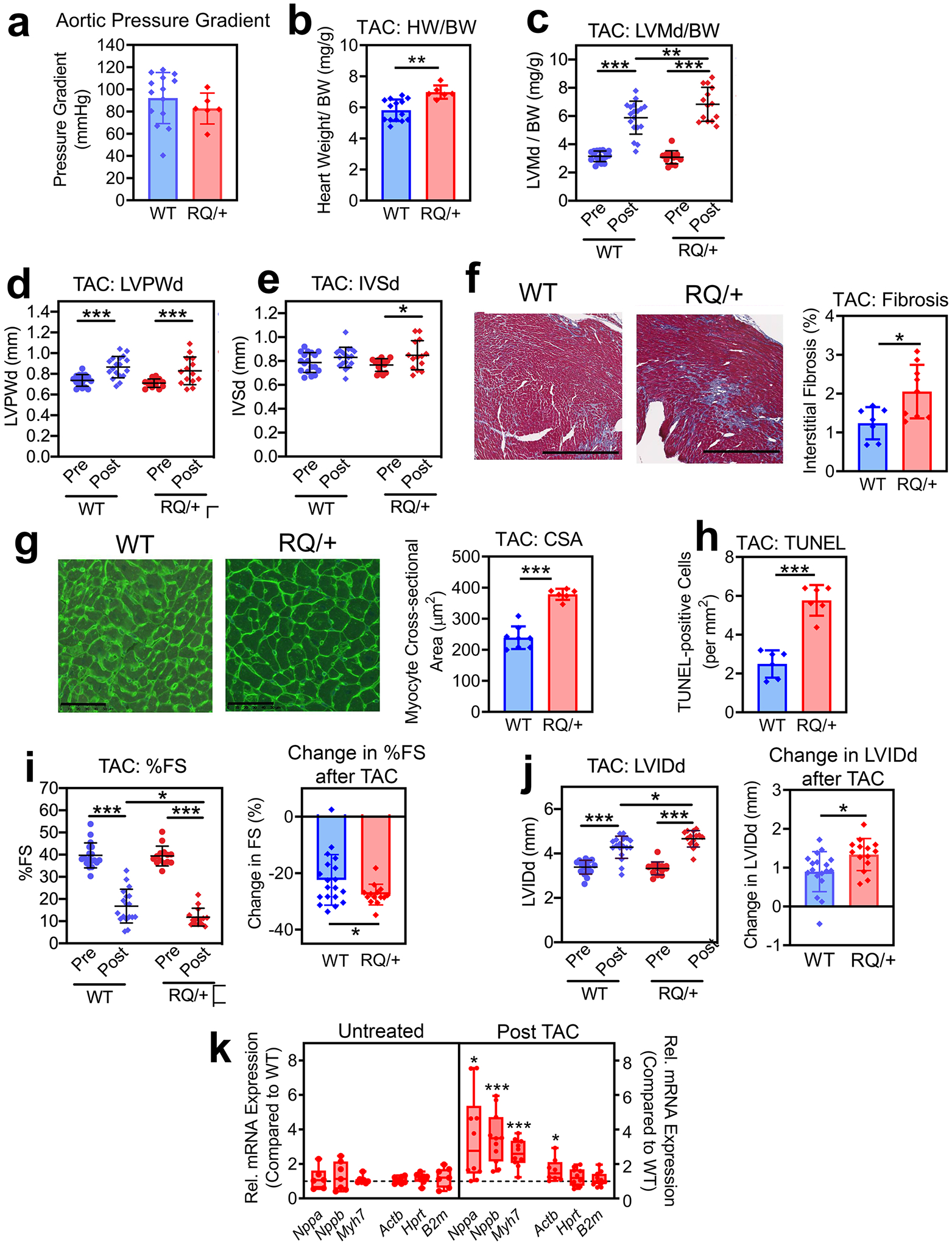
Four to five month-old male Prkg1RQ/+ (RQ/+) mice and wild type (WT) litter mates were subjected to transaortic constriction and were euthanized 2 weeks later. (a) The aortic pressure gradient generated by TAC was measured proximal and distal to the constriction by invasive blood pressure monitoring at the time of euthanasia. (b) Heart weight (HW) was normalized to body weight (BW). (c-e, i,j) Cardiac echocardiography was performed two days before (Pre) and 14 d after TAC (Post) in n=18 WT and n=14 RQ/+ mice: (c) LV mass in diastole (LVMd) normalized to body weight (BW); (d) left ventricular posterior wall thickness in diastole (LVPWd); (e) inter-ventricular septum thickness in diastole (IVSd);); (i) left ventricular fractional shortening (FS); and (j) left ventricular inner diameter in diastole (LVIDd). (f) Collagen content was quantified on trichrome-stained sections as in Fig. 4g (n=7 mice per genotype). (g) Cardiac myocyte cross-sectional area (CSA) was measured on wheat germ agglutinin-stained cross sections (n=7 mice per genotype). (h) Cardiac myocyte apoptosis was assessed by TUNEL staining (n=6 mice per genotype). (k) Expression of hypertrophic genes and house-keeping genes in hearts from RQ/+ mice was compared to WT mice under basal conditions (untreated) and after TAC. Gene expression was measured by quantitative RT-PCR, and was normalized to 18S RNA. For each gene, mean ΔCT values in the wild type group were assigned a value of one (n= 10 mice per genotype). Data in a-j are plotted as means ± SD; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 for the indicated comparisons by two-tailed t-test (b, f-h), one-spample t-test (k), or 2-Way ANOVA (c-e, i,j).
DISCUSSION
We previously showed that Prkg1R177Q/+ mice are mildly hypotensive and develop age-related aortic dilation due to aortic media degeneration, similar to humans who are heterozygous for the mutation (Schwaerzer et al., 2019). Among the ~ 50 reported patients who carry the Prkg1R177Q/+ mutation, no consistent cardiac abnormalities have been described, but a few of the patients have LV hypertrophy and systemic hypertension (Gago-Diaz et al., 2016; Guo et al., 2013).
We now report that young Prkg1R177Q/+ mice have normal basal cardiac function. However, age-related physiological hypertrophy of the LV posterior wall and septum appears to be mildly reduced–perhaps related to mild hypotension–while interstitial fibrosis is increased in 12 month-old mutant mice. Moreover, we found that the stress of Ang II infusion or TAC induced more severe cardiac remodeling and functional impairment in Prkg1R177Q/+ mice compared to wild type litter mates. These results are similar to those found in PKG1-LZM mice, which show increased basal PKG activity with abnormal targeting (Michael et al., 2008), and in mice with cardiac myocyte-specific PKG1: these mice show no basal cardiac abnormalities, but develop cardiac dysfunction after Ang II infusion and/or TAC (Blanton et al., 2013; Frantz et al., 2013). Thus, either too much (PKG1RQ), too little (PKG1 knockout), or untargeted (PKG1-LZM) PKG1 activity interferes with cardiac adaptation to stress. Since Prkg1RQ/+ and PKG1-LZM mice are global knock-in mice, it is possible that mutant PKG1 in cells other than cardiac myocytes contributes to the phenotype.
Cardiac myocytes isolated from the Prkg1R177Q/+ mice exhibited impaired contractility when electrically paced, similar to depressed contractility in murine and rat ventricular cardiomyocytes treated with activators of the NO/GC-1 and NP/GC-A/B pathways (Preedy, Baliga & Hobbs, 2020). cGMP generated via NO/GC-1 may act as a negative inotrope by way of PKG1 phosphorylating Cav1.2 and regulating L-type calcium channels, while BNP and CNP can attenuate myocyte shortening via PKG1 phosphorylation of phospholamban and regulation of SERCA (Preedy, Baliga & Hobbs, 2020). However, we did not observe increased phosphorylation of these calcium-regulatory proteins in Prkg1R177Q/+ cardiac myocytes, and calcium transients after electrical stimulation were the same in wild type and mutant myocytes. Instead, we observed decreased MLC2 phosphorylation in Prkg1R177Q/+ myocytes, which may at least partly explain the decrease in single cell contractility. PKG1 is known to activate MLC phosphatase (PP1cδ) in vascular smooth muscle cells via phosphorylation of the MLC phosphatase regulatory subunit MYPT1 (Yuen, Ogut & Brozovich, 2014). We found increased phosphorylation of the homologous protein MYPT2 in Prkg1R177Q/+ cardiac myocytes, but more work is required to determine if MYPT2 phosphorylation by PKG1 can activate MLC phosphatase to explain decreased MLC2 phosphorylation and a consequent decrease in contractility in Prkg1R177Q/+ cardiac myocytes. MLC phosphorylation is critical for cardiac contractility and adaptation to stress, as demonstrated in mice with targeted deletion of cardiac MLC kinase-3 or mice overexpressing MYPT2, which both show decreased MLC2 phosphorylation and CM contractility (Mizutani et al., 2010; Warren et al., 2012).
Localization of PKG1 at the sarcomere M-band suggests that some important PKG1 targets are associated with the myosin complex. While a striated pattern of PKG1 staining in isolated adult cardiac myocytes has been described (Takimoto et al., 2009), co-localization of PKG1 with myosin heavy chain at the M-band and α-actinin at the Z-band of the sarcomere has not been previously reported to our knowledge. We found increased phosphorylation of the giant sarcomere protein titin on multiple sites in cardiac myocytes from Prkg1R177Q/+ mice compared to cells from wild type mice. Titin is anchored at the Z-disc and spans all the way to the M-band, and titin phosphorylation at specific PKG1 target sites regulates cardiac myocyte stiffness (Kotter et al., 2013; Michel et al., 2020); however, we did not observe differential titin phosphorylation on these sites within the “elastic” N2-Bus domain. It will be interesting to decipher the functional consequences of the numerous PKG1 phosphorylation sites in the C-terminus of titin.
Preclinical data support a beneficial effect of PKG activation via PDE5 or PDE9 inhibition, mitigating TAC-induced hypertrophic heart disease (Takimoto 2005 +2009, Lee 2015). It is controversial, however, whether PDE5 inhibition also ameliorates LV dysfunction and cardiac fibrosis induced by Ang II (Westerman 2012, Straubinger 2015). Our results contrast with the cardio-protective effects of PKG activation by PDE5 and 9 inhibitors, but short-term drug administration could yield very different results from constitutive enzyme activation. It is also possible that the PKG1RQ mutant enzyme becomes mislocalized after TAC or Ang II challenge, even though we found no evidence of mislocalization in cardiac myocytes isolated from non-stressed hearts.
We found similar protein phosphorylation patterns in Prkg1RQ/+ cardiac myocytes as reported in myocytes treated with PDE5 or PDE9 inhibitors (Lee et al., 2015). For example, myosin-6, tensin-1, junctophilin-2, connexin-43, serum deprivation-response factor, and elongation factor-1β are all phosphorylated in cardiac myocytes after PDE5 and/or PDE9 inhibition (Lee et al., 2015), as well as in Prkg1RQ/+ myocytes. These results suggest that some PKG1 target proteins are phosphorylated under conditions where PKG1 activation is cardio-protective, but also under conditions where it leads to reduced stress resistance.
Clinical trials targeting PKG1 in heart failure have not shown consistent benefit. In heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, benefits were observed with PDE5 inhibitors and with the GC-1 activator vericiguat in some, but not all trials (Armstrong et al., 2020; Blanton, 2020; Burnett, 2020; De Vecchis, Cesaro, Ariano, Giasi & Cioppa, 2017). It is not clear how much PKG activation contributes to the cardioprotection observed with the combinations of hydralazine/isosorbide dinitrate (an NO generating agent), and valsartan/sacubitril (a neprilysin inhibitor expected to inhibit natriuretic peptide degradation), since NO can have cGMP-independent effects and the neprilysin inhibitor can block degradation of peptides other than NPs (Blanton, 2020). Multiple trials in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction have failed to show improvements with cGMP-elevating agents. The somewhat disappointing results with cGMP modulating agents may be due to a number of reasons, including that too much cGMP elevation and PKG1 activation in the heart is detrimental, and that pharmacological activation of PKG in heart failure may have a narrow therapeutic window (Blanton, 2020). Thus, our study adds important new and clinically-relevant information about the effects of long-term PKG1 activation in the heart.
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS:
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health grants R01-HL132141 (to RBP) and P30-NS047101 (UCSD Microscopy Shared Facility), and the Merit Review Award BX003429 from the VHA Office of Research and Development (to WHD). GS was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemein-schaft.
Footnotes
Competing Interests: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
DATA AVAILABILITY:
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE (Perez-Riverol et al., 2019) partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD022600
REFERENCES
- Adler J, Kuret A, Langst N, & Lukowski R (2020). Targets of cGMP/cGKI in Cardiac Myocytes. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 75: 494–507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong PW, Pieske B, Anstrom KJ, Ezekowitz J, Hernandez AF, Butler J, et al. (2020). Vericiguat in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N Engl J Med 382: 1883–1893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton RM (2020). cGMP Signaling and Modulation in Heart Failure. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 75: 385–398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton RM, Takimoto E, Aronovitz M, Thoonen R, Kass DA, Karas RH, et al. (2013). Mutation of the protein kinase I alpha leucine zipper domain produces hypertension and progressive left ventricular hypertrophy: a novel mouse model of age-dependent hypertensive heart disease. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 68: 1351–1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanton RM, Takimoto E, Lane AM, Aronovitz M, Piotrowski R, Karas RH, et al. (2012). Protein kinase g ialpha inhibits pressure overload-induced cardiac remodeling and is required for the cardioprotective effect of sildenafil in vivo. J Am Heart Assoc 1: e003731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnett JC Jr. (2020). Vericiguat - Another Victory for Targeting Cyclic GMP in Heart Failure. N Engl J Med 382: 1952–1953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai LX, Tanada Y, Bello GD, Fleming JC, Alkassis FF, Ladd T, et al. (2019). Cardiac MLC2 kinase is localized to the Z-disc and interacts with alpha-actinin2. Sci Rep 9: 12580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan MH, Aminzai S, Hu T, Taran A, Li S, Kim C, et al. (2020). A substitution in cGMP-dependent protein kinase 1 associated with aortic disease induces an active conformation in the absence of cGMP. J Biol Chem 295: 10394–10405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuello F, & Nikolaev VO (2020). Cardiac cGMP Signaling in Health and Disease: Location, Location, Location. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 75: 399–409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vecchis R, Cesaro A, Ariano C, Giasi A, & Cioppa C (2017). Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitors Improve Clinical Outcomes, Exercise Capacity and Pulmonary Hemodynamics in Patients With Heart Failure With Reduced Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction: A Meta-Analysis. J Clin Med Res 9: 488–498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frantz S, Klaiber M, Baba HA, Oberwinkler H, Volker K, Gabetaner B, et al. (2013). Stress-dependent dilated cardiomyopathy in mice with cardiomyocyte-restricted inactivation of cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase I. Eur Heart J 34: 1233–1244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gago-Diaz M, Blanco-Verea A, Teixido G, Huguet F, Gut M, Laurie S, et al. (2016). PRKG1 and genetic diagnosis of early-onset thoracic aortic disease. Eur J Clin Invest 46: 787–794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo DC, Regalado E, Casteel DE, Santos-Cortez RL, Gong L, Kim JJ, et al. (2013). Recurrent gain-of-function mutation in PRKG1 causes thoracic aortic aneurysms and acute aortic dissections. Am J Hum Genet 93: 398–404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guttman M, Betts GN, Barnes H, Ghassemian M, van der Geer P, & Komives EA (2009). Interactions of the NPXY microdomains of the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1. Proteomics 9: 5016–5028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtwick R, van Eickels M, Skryabin BV, Baba HA, Bubikat A, Begrow F, et al. (2003). Pressure-independent cardiac hypertrophy in mice with cardiomyocyte-restricted inactivation of the atrial natriuretic peptide receptor guanylyl cyclase-A. J Clin Invest 111: 1399–1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y, Jones SV, & Dillmann WH (2005). Effects of hyperthyroidism on delayed rectifier K+ currents in left and right murine atria. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289: H1448–H1455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotter S, Gout L, Von Frieling-Salewsky M, Muller AE, Helling S, Marcus K, et al. (2013). Differential changes in titin domain phosphorylation increase myofilament stiffness in failing human hearts. Cardiovasc Res 99: 648–656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn M (2016). Molecular Physiology of Membrane Guanylyl Cyclase Receptors. Physiol Rev 96: 751–804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange S, Pinotsis N, Agarkova I, & Ehler E (2020). The M-band: The underestimated part of the sarcomere. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1867: 118440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee DI, Zhu G, Sasaki T, Cho GS, Hamdani N, Holewinski R, et al. (2015). Phosphodiesterase 9A controls nitric-oxide-independent cGMP and hypertrophic heart disease. Nature 519: 472–476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukowski R, Rybalkin SD, Loga F, Leiss V, Beavo JA, & Hofmann F (2010). Cardiac hypertrophy is not amplified by deletion of cGMP-dependent protein kinase I in cardiomyocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107: 5646–5651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michael SK, Surks HK, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Blanton R, Jamnongjit M, et al. (2008). High blood pressure arising from a defect in vascular function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105: 6702–6707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel K, Herwig M, Werner F, Spiranec Spes K, Abesser M, Schuh K, et al. (2020). C-type natriuretic peptide moderates titin-based cardiomyocyte stiffness. JCI Insight. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizutani H, Okamoto R, Moriki N, Konishi K, Taniguchi M, Fujita S, et al. (2010). Overexpression of myosin phosphatase reduces Ca(2+) sensitivity of contraction and impairs cardiac function. Circ J 74: 120–128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore-Morris T, Guimaraes-Camboa N, Banerjee I, Zambon AC, Kisseleva T, Velayoudon A, et al. (2014). Resident fibroblast lineages mediate pressure overload-induced cardiac fibrosis. J Clin Invest 124: 2921–2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T, Ranek MJ, Lee DI, Shalkey H, V, Kim C, Eaton P, et al. (2015). Prevention of PKG1alpha oxidation augments cardioprotection in the stressed heart. J Clin Invest. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O’Shea JP, Chou MF, Quader SA, Ryan JK, Church GM, & Schwartz D (2013). pLogo: a probabilistic approach to visualizing sequence motifs. Nat Methods 10: 1211–1212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Riverol Y, Csordas A, Bai J, Bernal-Llinares M, Hewapathirana S, Kundu DJ, et al. (2019). The PRIDE database and related tools and resources in 2019: improving support for quantification data. Nucleic Acids Res 47: D442–D450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preedy MEJ, Baliga RS, & Hobbs AJ (2020). Multiplicity of Nitric Oxide and Natriuretic Peptide Signaling in Heart Failure. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 75: 370–384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaerzer GK, Kalyanaraman H, Casteel DE, Dalton ND, Gu Y, Lee S, et al. (2019). Aortic pathology from protein kinase G activation is prevented by an antioxidant vitamin B12 analog. Nat Commun 10: 3533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez J, Belke DD, Gloss B, Dieterle T, McDonough PM, Kim YK, et al. (2004). In vivo adenoviral transfer of sorcin reverses cardiac contractile abnormalities of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286: H68–75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto E, Champion HC, Li M, Belardi D, Ren S, Rodriguez ER, et al. (2005). Chronic inhibition of cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase 5A prevents and reverses cardiac hypertrophy. Nat Med 11: 214–222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takimoto E, Koitabashi N, Hsu S, Ketner EA, Zhang M, Nagayama T, et al. (2009). Regulator of G protein signaling 2 mediates cardiac compensation to pressure overload and antihypertrophic effects of PDE5 inhibition in mice. J Clin Invest 119: 408–420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren SA, Briggs LE, Zeng H, Chuang J, Chang EI, Terada R, et al. (2012). Myosin light chain phosphorylation is critical for adaptation to cardiac stress. Circulation 126: 2575–2588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen SL, Ogut O, & Brozovich FV (2014). Differential phosphorylation of LZ+/LZ− MYPT1 isoforms regulates MLC phosphatase activity. Arch Biochem Biophys 562: 37–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE (Perez-Riverol et al., 2019) partner repository with the dataset identifier PXD022600


