Figure 3. Spirometry- and Symptom-Based Classification of Patients With a Positive or Negative Screening Result for Detecting Clinically Significant Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD).
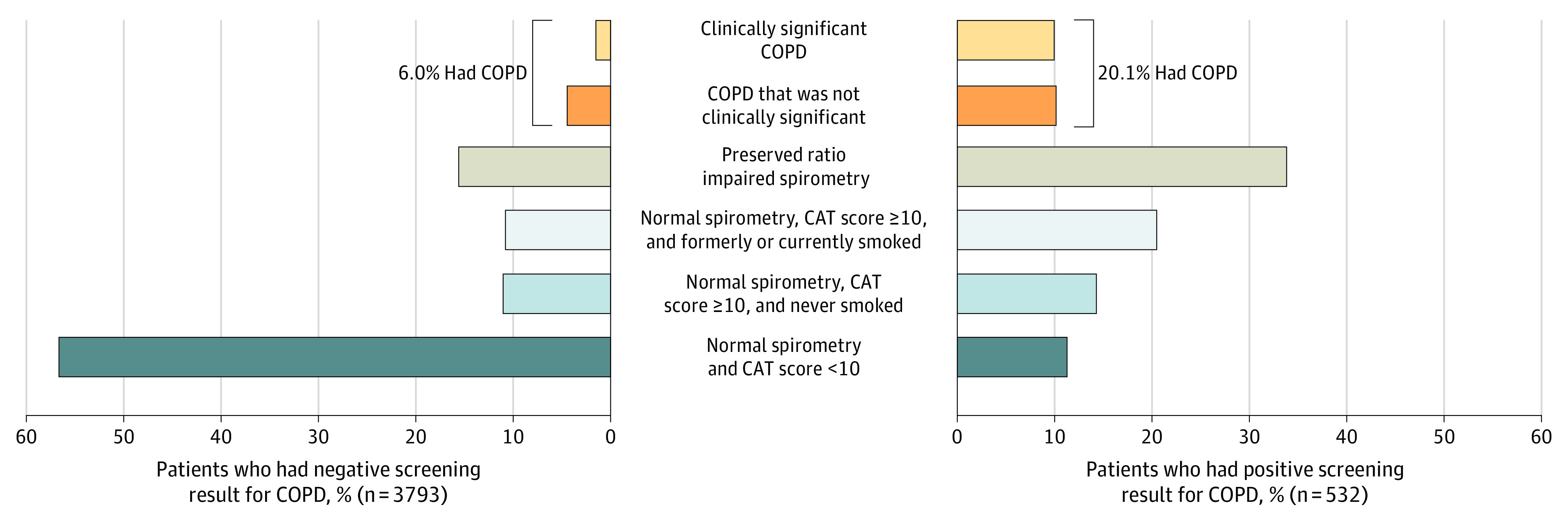
COPD was defined a postbronchodilator ratio of forced expiratory volume in the first second of expiration to forced vital capacity (FEV1:FVC) less than 0.70 or a prebronchodilator FEV1:FVC less than 0.65 in patients who did not complete postbronchodilator spirometry, and was considered clinically significant if the patient also had either 1 or more acute respiratory illnesses within the past 12 months or an FEV1 less than 60% of the predicted value. Clinically significant COPD was measured using spirometry with an FEV1 less than 60% of the predicted value or a history of acute respiratory illness within the past 12 months. A preserved ratio impaired spirometry result indicates no spirometry-defined COPD and an FEV1 less than 80% of the predicted value. A normal spirometry result indicates no spirometry-defined COPD or a preserved ratio impaired spirometry result. CAT indicates COPD Assessment Test.
