Fig. 2 |. Asymmetry in the PhyB dimer.
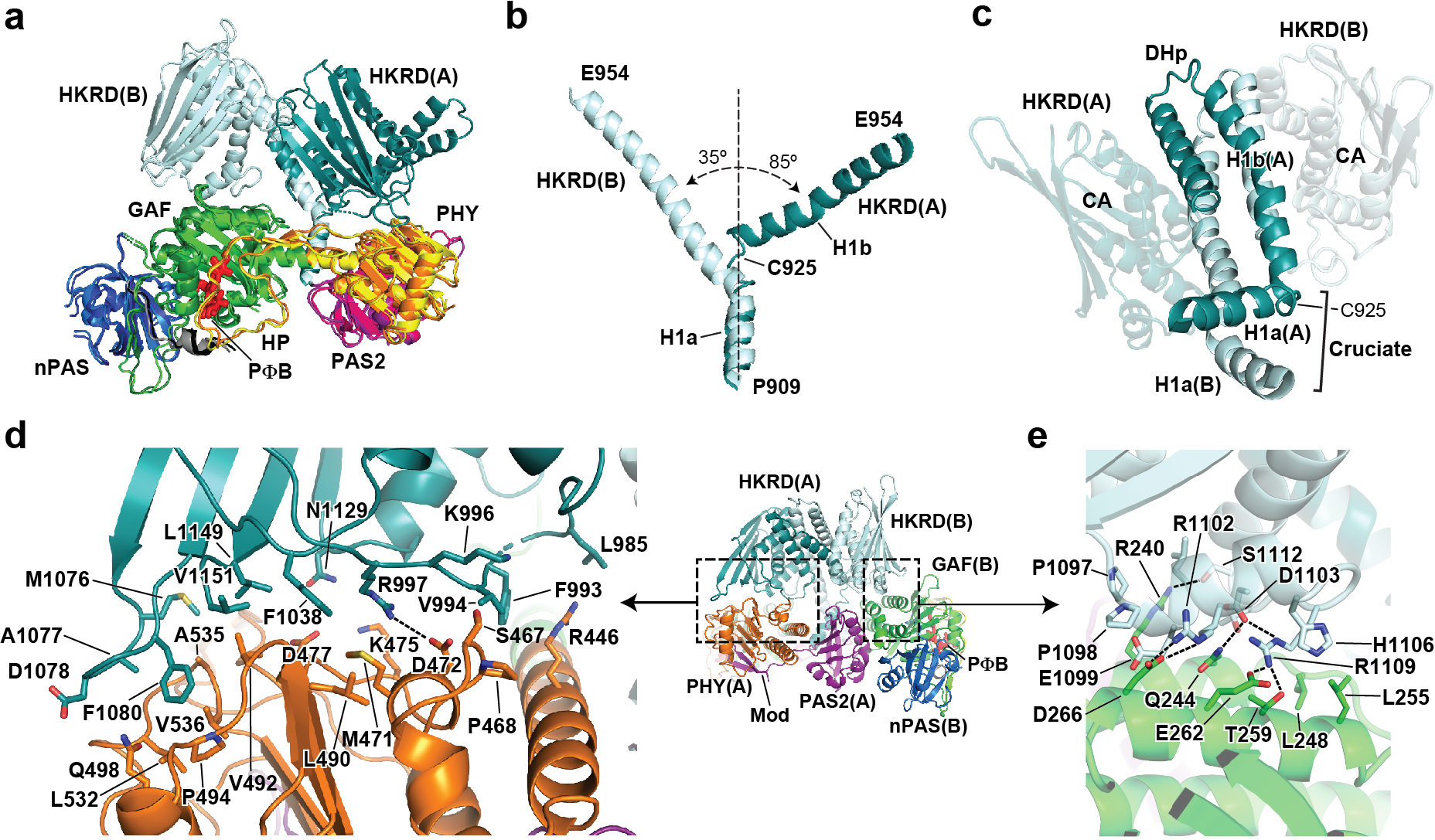
a, Superposition of protomers A and B based on the subtending PSM–PAS2 module, revealing the distinct HKRD positions in the two protomers. Domains are coloured as in Fig. 1e. b, Alignment of the DHp α1 helices to illustrate the distinct positions of the helical H1a and H1b segments in the DHp domain from protomers A and B that diverge at the cruciate. c, View of the DHp domains showing the intertwined H1a and H1b segments (protomers are coloured in dark and light cyan). The cruciate bend at Cys925 allows the switch from a head-to-tail orientation for the paired PSMs to a head-to-head orientation for the paired HKRDs. d, e, Focused views of the asymmetric connections between the HKRDs and the PSMs. d, Contacts between the HKRD from protomer A and the PHY domain in protomer A. e, Contacts between the HKRD of protomer B and the GAF domain of protomer B. Hydrogen bonds are indicated by the dashed lines.
