Abstract
Introduction
Chlorhexidine (CHX) and essential oil containing mouthwashes like Listerine® can improve oral hygiene via suppressing oral microbes. In hospitalized patients, CHX mouthwash reduces the incidence of ventilator-associated pneumonia. However, CHX use was also associated with increased mortality, which might be related to nitrate-reducing bacteria. Currently, no study determines oral bacteria targeted by essential oils mouthwash in hospitalized patients using a metagenomic approach.
Methods
We recruited 87 hospitalized patients from a previous randomized control study, and assigned them to three mouthwash groups: CHX, Listerine, and normal saline (control). Before and after gargling the mouthwash twice a day for 5-7 days, oral bacteria were examined using a 16S rDNA approach.
Results
Alpha diversities at the genus level decreased significantly only for the CHX and Listerine groups. Only for the two groups, oral microbiota before and after gargling were significantly different, but not clearly distinct. Paired analysis eliminated the substantial individual differences and revealed eight bacterial genera (including Prevotella, Fusobacterium, and Selenomonas) with a decreased relative abundance, while Rothia increased after gargling the CHX mouthwash. After gargling Listerine, seven genera (including Parvimonas, Eubacterium, and Selenomonas) showed a decreased relative abundance, and the magnitudes were smaller compared to the CHX group. Fewer bacteria targeted by Listerine were reported to be nitrate-reducing compared to the CHX mouthwash.
Discussion
In conclusion, short-term gargling of the CHX mouthwash and Listerine altered oral microbiota in our hospitalized patients. The bacterial genera targeted by the CHX mouthwash and Listerine were largely different and the magnitudes of changes were smaller using Listerine. Functional alterations of gargling CHX and Listerine were also different. These findings can be considered for managing oral hygiene of hospitalized patients.
Keywords: mouthwash, Chlorhexidine, essential oil, oral microbiome, Listerine antiseptic mouth rinse
1. Introduction
Therapeutic mouthwash can improve oral hygiene, e.g., by reducing dental plaque and gingivitis (Araujo et al., 2015; Van der Weijden et al., 2015; Brookes et al., 2020). Dental plaque is a biofilm of oral microbes, mostly bacteria that grow on teeth. Build-up of plaque can lead to dental decay and gingival inflammation (Loesche, 1996).
The anti-plaque activity of mouthwash is partly attributed to its antimicrobial capability, and the antiseptic ingredients include chlorhexidine (CHX) and essential oils. CHX is a potent antimicrobial agent and is widely used as disinfectant in various medical fields, such as dermatology and surgery (Lim and Kam, 2008). CHX kills bacteria via binding and perforating cell membranes (Cheung et al., 2012). Antimicrobial activity of essential oils mouthwash has also been documented (Chouhan et al., 2017). The popular mouthwash brand Listerine® (LIS), which contains four plant-derived essential oils (eucalyptol, menthol, methyl salicylate, thymol), has also been shown to reduce plaque and gingivitis (Alshehri, 2018).
Besides its dental application, CHX mouthwash was suggested to reduce the risk of developing ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically ill patients (Hua et al., 2016). The benefit, however, might apply only to cardiac surgery patients (Klompas et al., 2014), and was further argued in a study of hospitalized patients that CHX mouthwash was associated with increased mortality (Deschepper et al., 2018). The association was hypothesized to stem from an obliteration of oral nitrate-reducing bacteria (such as Veillonella, Prevotella, Neisseria, and Haemophilus), which might cause nitric oxide deficiency (Hyde et al., 2014; Blot, 2021) and the subsequent ischemic heart events or sepsis. Because of the uncertainty in risk-benefit balance, current guidelines provide no formal recommendation for using CHX for oral care of hospitalized patients (Tran and Butcher, 2019). The pros and cons of using other mouthwash for the patients’ oral care is not yet reported to our knowledge. These show the importance of identifying bacterial species targeted by different mouthwashes.
Bacterial species altered by CHX mouthwash have been studied via examining in vitro communities of oral microbes (McBain et al., 2003; Eick et al., 2011). For example, exposing an in vitro community of ten oral bacterial species to CHX resulted in marked reductions in Prevotella sp. and Selenomonas infelix, while other species were reduced to a lesser degree (McBain et al., 2003). The effect of LIS on bacterial species has also been examined using a culturing approach for quantifying bacterial levels (Fine et al., 2007). In the study, Veillonella sp., Capnocytophaga sp., and Fusobacterium nucleatum in subgingival plaque were reduced significantly after gargling LIS for two weeks. In another in vitro study of 40 oral bacterial species, CHX mouthwash was more effective than LIS mouthwash in reducing all the species (Haffajee et al., 2008).
Although these in vitro studies were informative, the results may not reflect the in vivo dynamics of all oral microbes. A metagenomic approach, e.g., via examining 16S rRNA genes, is powerful for exploring environmental microbes. The approach, however, has only been applied in a few studies investigating oral microbes in the context of mouthwash. Tribble et al. studied tongue microbiome and found that Leptotrichia sp. and Veillonella rogosae were reduced on tongue after gargling CHX mouthwash for a week (Tribble et al., 2019). Bescos et al. examined the effects of CHX mouthwash on salivary microbiome of healthy individuals (Bescos et al., 2020). After gargling the mouthwash for a week, several bacterial genera, including Prevotella, Antinomyces, and Fusobacterium, were reduced, while the genera Neisseria, Streptococcus, etc., were increased. To our best knowledge, the effects of LIS on salivary microbiome using a 16S approach have not been reported, although the long term (12 weeks) effects of LIS on oropharyngeal microbiome was recently described (Plummer et al., 2022).
Here, we study the short-term effects of CHX mouthwash and LIS on oral microbiome of hospitalized patients using a 16S approach. We ask if the CHX and LIS mouthwash lead to different dysbiosis of oral bacteria. The findings can be considered for managing oral hygiene of patients at the internal medicine ward.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Study design and oral sample collection
Hospitalized patients were recruited for a clinical trial about the effects of CHX oral rinse on preventing hospital-acquired pneumonia in a general ward (Clinical Trials IRCT ID: NCT04403971)(Chen et al., 2022). In the trial, only patients who were aged ≧50 years, could rinse orally, and communicated well were included. The exclusion criteria were: an inpatient hospital stay of less than three consecutive calendar days and admission for routine or quick examination of acute psychiatric syndromes, chlorhexidine allergy, and cardiac catheterization. The main admission diagnoses were infectious diseases (44%) and gastrointestinal diseases (32%).
Patients were randomly assigned to three mouthwash groups: CHX (0.12%; aseptic innovative medicine co., ltd, Taipei, Taiwan), LIS (total care anticavity fluoride mouthwash), and normal saline. One research investigator who qualified for oral care training was blind to the group allocation evaluated the oral health status by using the oral health assessment tool (Chalmers et al., 2005).The tool included the eight subscales of lips, tongues, gums and tissues, saliva, natural teeth, dentures, oral cleanliness, and dental pain. The intraclass correlation coefficients for oral health assessment tool were set as 0.78 for intra-carer and 0.74 for inter-carer reliability (Chalmers et al., 2005).
According to a previous study (Chen et al., 2022), a sample size about 30 individuals is sufficient for studying oral microbiota. We recorded the incidence of hospital-acquired pneumonia and changes in clinical pulmonary infection score among the three groups (Chen et al., 2022). The patients who provided oral microbial samples on Day 0 and Day 5-7 were included in this study. The mouthwash was placed in a cloudy container and each patient gargled the mouthwash twice a day (30-60 seconds with 10 ml) for 5-7 days under the supervision of a nurse. The first oral microbial samples were collected from each patient before intervention (Day 0) and the second sample was collected on the day after the last day of the intervention (5-7 days after the first use of mouthwash). We collected the samples before breakfast and brushing teeth in the early morning. To collect a sample, the patient gargled 20 mL of 0.9% saline and then spat the fluid into a sterile container. We did not intervene in the toothpaste use and the method of brushing teeth.
2.2. DNA extraction and 16S rDNA sequencing
Collected liquid was processed by centrifugation at 1000 × g for 10 minutes to separate the cellular pellet from cell-free suspension (Lim et al., 2017). From the oral samples pellets, total DNA were extracted and preserved using the DNA/RNA Shield Saliva Collection Kit (Zymo Research), and the extracts was stored at -70∘C. Total genomic DNA from samples was extracted using the column-based method (QIAamp PowerFecal DNA Kit, Qiagen). For the 16S rRNA gene sequencing, V3-V4 region was amplified by specific primer set (319F: 5’-CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3’, 806R: 5’-GACTACHVGGGTAT CTAATCC -3’) according to the 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library Preparation procedure (Illumina). In brief, 12.5 ng of gDNA was used for the PCR reaction carried out with KAPA HiFi HotStart ReadyMix (Roche) under the PCR condition: 95°C for 3 minutes; 25 cycles of: 95°C for 30 seconds, 55°C for 30 seconds, 72°C for 30 seconds; 72°C for 5 minutes and hold at 4°C. The PCR products were monitored on 1.5% agarose gel. Samples with bright main strip around 500bp were chosen and purified by using the AMPure XP beads for the following library preparation. The Sequencing library was prepared according to the 16S Metagenomic Sequencing Library Preparation procedure (Illumina). A secondary PCR was performed by using the 16S rRNA V3-V4 region PCR amplicon and Nextera XT Index Kit with dual indices and Illumina sequencing adapters (Illumina). The indexed PCR product quality was assessed on the Qubit 4.0 Fluorometer (Thermo Scientific) and Qsep100TM system. Equal amount of the indexed PCR product was mixed to generate the sequencing library. At last, the library was sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq platform and paired 300‐bp reads were generated.
2.3. Ethics approval
The study was approved by the institutional review board of the National Cheng Kung University Hospital (no: A-ER-108-397). All patients provided informed consent.
2.4. Data preprocessing and clustering
Raw paired-end reads were merged using FLASH (v1.2.11; option: -M 300) (Magoc and Salzberg, 2011), and short (<400 bp) merged reads were discarded. The preprocessed reads of all samples were clustered into zero-radius operation taxonomy units (ZOTUs) using UNOISE3 with default options (in USEARCH v11.0.667) (Edgar, 2010; Edgar, 2016). In the UNOISE3 pipeline, reads were quality filtered and dereplicated. Dereplicated reads were clustered into ZTOU sequences with sequencing errors corrected and chimera removed. Merged reads were then aligned to the ZTOU sequences to obtain a ZOTU table showing ZOTU abundances of all samples.
2.5. Taxonomy annotation
ZOTU sequences were annotated by RDP classifier (v2.13) (Wang et al., 2007), which was retrained to include species information. Specifically, the reference data of trainset 18 from RDP classifier were preprocessed to remove redundant sequences and unite the annotation format (e.g., setting species name of uncultured or unspecified bacteria as “genus_name sp.”) for a retrain. An annotation with a confidence score <0.8 was considered unclassified. Based on the annotations by RDP classifier, eukaryotic ZOTUs were filtered. ZOTU table was also converted into taxon abundance and percentage table at different taxonomy levels. Percentages of the top 30 abundant taxa were visualized in a heatmap using “clustermap()” in the python package seaborn (v0.9), in which the hierarchical clustering was done with the average linkage method and braycurtis dissimilarity as the metric.
2.6. Diversity and statistical analysis
For a fair comparison, ZOTU abundances of all samples were rarefied to the lowest total read count for diversity analyses. Alpha diversity indices (e.g., Chao1, Shannon, and Simpson) were calculated based on taxon percentages at different levels using “alpha_diversity.py” of QIIME (v1.9) (Caporaso et al., 2010). The alpha diversities before and after gargling were compared using paired Wilcoxon rank test in R. For beta diversity analysis by QIIME (v2-2022.2) (Caporaso et al., 2010), the ZOTU sequences were aligned using the “phylogeny” plugin and “align-to-tree-mafft-fasttree” method, which produced a rooted tree. With the tree, ZOTU abundance table, and clinical descriptions of samples, beta diversity was calculated using the “diversity” plugin and “core-metrics-phylogenetic” method. The command generated UniFrac distances (Lozupone and Knight, 2005) for all pairs of samples, and the resulting principal coordinate analysis was visualized using R (v4.0.2).
Differences in microbial communities between groups of samples were tested using permutational multivariate ANOVA (PERMANOVA) in the vegan package (v2.5) of R based on the UniFrac distances (option: permutations=9999). Differentially abundant microbes after gargling were identified using MaAsLin2 (Mallick et al., 2021) in a paired manner. Before the analysis, taxa present in less than 10% of the samples were filtered. For paired analysis, taxa fractions after gargling were subtracted from those before gargling and the fractions before gargling were set zero. Each difference (d) in taxon frequency was further rescaled into range [0,1] (i.e., via (d+1)/2). For consistency, the taxa frequencies before gargling were shifted to 1/2. The processed frequencies were input into MaAsLin2 for analysis with the options: –normalization=NONE –transform=AST –analysis_method=LM –fixed_effects=“gargling” –random_effect=NONE –reference=“gargling,before” –correction=BH. An association with a q-value<0.1 was considered significant. Association between microbes and clinical features was also analyzed using MaAsLin2, and only samples before gargling were examined. The options remained similar except that all clinical features (i.e., sex, age, smoking, alcohol, BMI, diabetes, cancer, cirrhosis, ESRD) were set as fixed effects and the values of age and BMI were standardized.
2.7. Functional prediction and comparison
PICRUSt2 (v2.4.1) (Douglas et al., 2020) was used to predict microbiota function for each sample. First, ZOTU sequences were placed in the phylogenetic tree using EPA-NG (Barbera et al., 2019). For each ZOTU, gene family abundances and copy number of 16S genes were then predicted by the castor R package (Louca and Doebeli, 2018) using default options. With the predicted abundances and ZOTU abundances, functional gene abundances in the community were then estimated. Abundances of KEGG pathways (Kanehisa and Goto, 2000) identified as present by MinPath (Ye and Doak, 2009) were then inferred for the subsequent statistical analysis. We compared pathway abundance before and after gargling in a paired manner. Specifically, samples before and after gargling of the same individual were compared using STAMP (v2.1.3) (Parks et al., 2014). Differential abundance was tested using “G-test (w/Yate’s) + Fisher’s” and the p-values were corrected by Benjamin-Hochberg FDR. Abundance of a pathway was considered different if the q-value was <0.1, and the effect size was recorded for subsequent analysis.
Differentially abundant pathways were further labeled by sign of the effect size, where minus and plus signs indicated lower and higher relative abundance after gargling, respectively. For each mouthwash group, we first picked the pathways that showed a preferred direction of change in the abundance among all the individuals. Specifically, each pathway was subjected to two-tailed binomial test for a biased distribution of individuals showing a lower and higher abundance under a null hypothesis of equal probabilities in both directions. The binomial test p-values were corrected by FDR and pathways with a corrected q-value <0.2 were considered differentially abundant with consistency.
3. Results
3.1. Sample collection and microbiome sequencing
Eighty-seven hospitalized patients were recruited and their clinical features were documented ( Table S1 ). Of the patients, 28, 29, and 30 were randomly assigned into three mouthwash groups: CHX (abbreviated as C), LIS (L), and normal saline (N; control group), respectively. In the previous trial data (Chen et al., 2022), the CHX group had a significant improvement in oral health assessment tool scores than the LIS and normal saline group after mouthwash (−1.20 in CHX group, −0.75 in Group LIS group, and 0.25 in control group). The incidence of hospital-acquired pneumonia and changes in clinical pulmonary infection score did not differ among the three groups (Chen et al., 2022).
From each patient, two oral samples were collected before and after gargling the mouthwash respectively, and the samples were subjected to 16S rDNA sequencing. MiSeq sequencing of the 174 samples generated 14.2 million raw paired-end reads; 95.6% of which could be merged into single reads ( Table S2 ). Among the merged reads, the 13.5M reads longer than 400 bp were clustered into 49,190 ZOTUs. Of those, 189 belonged to Zea mays and were discarded. The 174 samples had 37k~130k reads for community analysis.
3.2. Overall oral microbiota
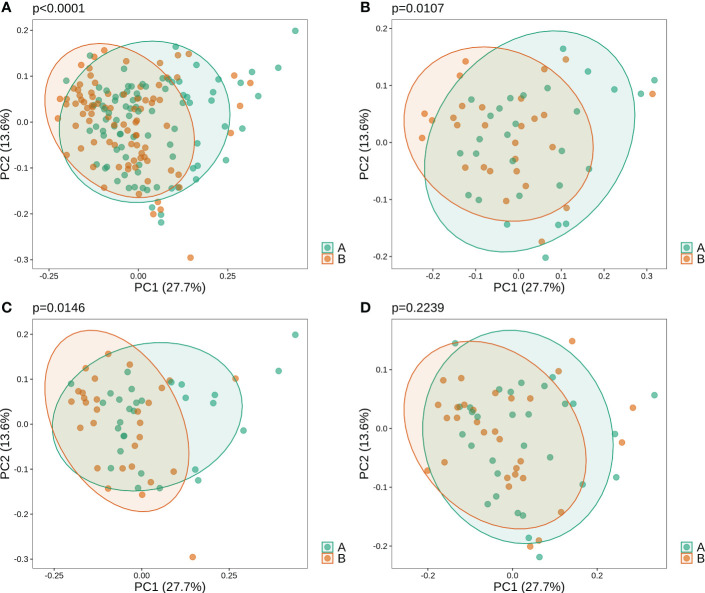
Beta diversity analysis revealed that oral microbiota before and after gargling were significantly different ( Figure 1A ; PERMANOVA p-value<1*10-4). The difference in microbiota after gargling was also significant for mouthwash groups C and L respectively, but not for group N ( Figures 1B–D ). This shows that CHX and LIS mouthwashes altered oral microbiota. The alternation, however, was not strong enough to separate the microbiota before and after gargling, which still overlapped to a large extent.
Figure 1.
Weighted principal component analysis (PCoA) of oral microbiota for (A) all samples, and samples in three mouthwash groups: (B–D) C, L, and N. For each set of samples, the PERMANOVA p-value shows significance of difference in microbiota of samples before (B) and after (A) gargling.
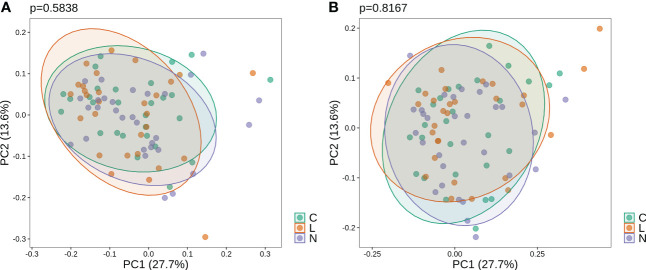
Before gargling, oral microbiota between three mouthwash groups were not different ( Figure 2A ), which echoed our random assignment of patients into groups. After gargling, oral microbiota of the three groups were still not different ( Figure 2B ). This indicates that the microbial alternations after gargling were not strong enough to stand out from the overall difference among the three groups.
Figure 2.
Weighted PCoA analysis of oral microbiota for samples (A) before and (B) after gargling. For each set of samples, the difference between the three mouthwash groups is quantified by the p-value.
At the phylum level, the top three abundant taxa across all oral samples were Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Proteobacteria ( Figure S1 ). In terms of phyla composition, again we observed no clear distinction between the three groups, both before and after gargling. In the following, oral microbiota in samples of each mouthwash group were examined.
3.3. Oral microbiota of the CHX group
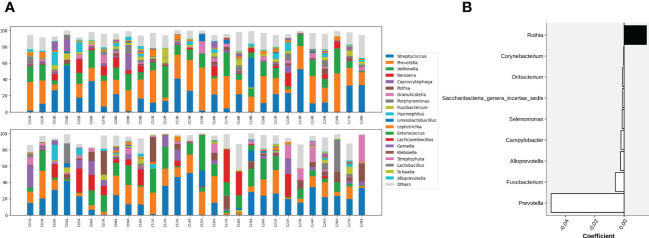
At the genus level, microbial composition across individuals spanned a large spectrum both before and after gargling ( Figure 3A ), which indicates substantial individual differences. A relatively large change in microbial composition after gargling was observed for several individuals.
Figure 3.
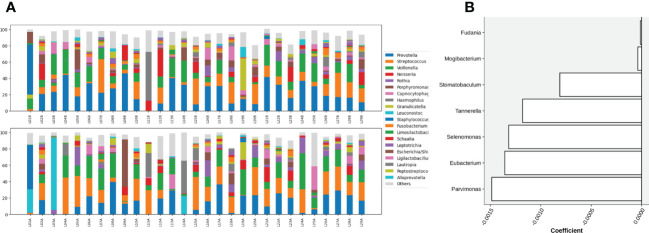
(A) Compositions of top 20 abundant genera in oral samples of group C before (top) and after (bottom) gargling. Rest genera are combined in the “Others” category. The space between 100% and height of each stacked bar shows the fraction of unclassified bacteria. (B) Differentially abundant genera; the +/- sign of a coefficient indicates an increase/decrease in the fraction after gargling and the value indicates the magnitude of change.
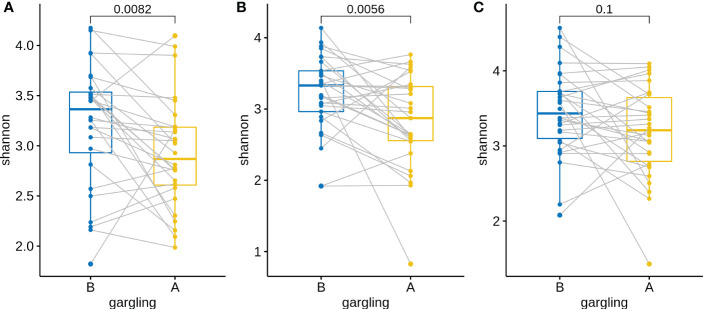
For identifying differentially abundant microbes after gargling, paired analysis was conducted to eliminate individual differences. The paired comparison revealed four differentially abundant phyla ( Table S3 ) and nine differentially abundant genera ( Figure 3B ). Relative abundance of the four phyla (Fusobacteria, Campilobacterota, Candidatus Saccharibacteria, and Bacteroidetes) decreased after gargling. Of the nine genera, eight showed a decreased fraction and only Rothia increased after gargling. Among the decreased genera, the magnitude of decrement (i.e., the coefficient value in Figure 3B ) was the largest for Prevotella. The species composition revealed that Rothia mulcilaginosa was the major species within the Rothia genus ( Figure S2 ). In contrast, the Prevotella genus was composed of several species, e.g., Prevotella melaninogenica, veroralis, oris, salivae, etc. Note that only four of the nine differentially abundant genera were among the top 20 abundant genera, thus the rest five were absent from the figures. In the paired comparison, the diversity of genus composition decreased after gargling for 21 of the 28 patients in group C ( Figure 4A ) and the overall decrease was significant.
Figure 4.
Shannon indices of oral microbiota in paired samples before (B) and after (A) gargling of mouthwash groups (A) C, (B) L, and (C) N. For each group, paired Wilcoxon rank test p-value is shown.
3.4. Oral microbiota of the LIS group
Substantial individual differences were again observed for patients in group L ( Figure 5A ). Paired analysis revealed that Firmicutes increased while Bacteroidetes, Spirochaetes, and Candidatus Saccharibacteria decreased after gargling ( Table S3B ). Seven differentially abundant genera were observed and all of them showed a decreased fraction after gargling ( Figure 5B ). Among the seven genera, only Selenomonas was also identified in group C. This indicates that bacterial species targeted by LIS were largely different from those by CHX. For the genera suppressed by LIS, the magnitudes of fractional changes were smaller compared to CHX (note the different scales of coefficients in Figures 3B , 5B ; the coefficients of Selenomonas were similar in the two). None of the seven differentially abundant genera were among the top 20 abundant ones. Therefore, the effect of LIS on the differentially abundant microbes was smaller compared to CHX. At the species level, only two species (Corynebacterium matruchotii and Leptotrichia wadei) showed different abundance after gargling ( Figure S3 ). Like CHX, the genus level diversities decreased significantly after gargling LIS ( Figure 4B ).
Figure 5.
(A) Compositions of the top 20 abundant genera in oral samples of group L before (top) and after (bottom) gargling, and (B) differentially abundant genera. Note that the scale of coefficients is different from that in Figure 3B .
3.5. Oral microbiota of the control group
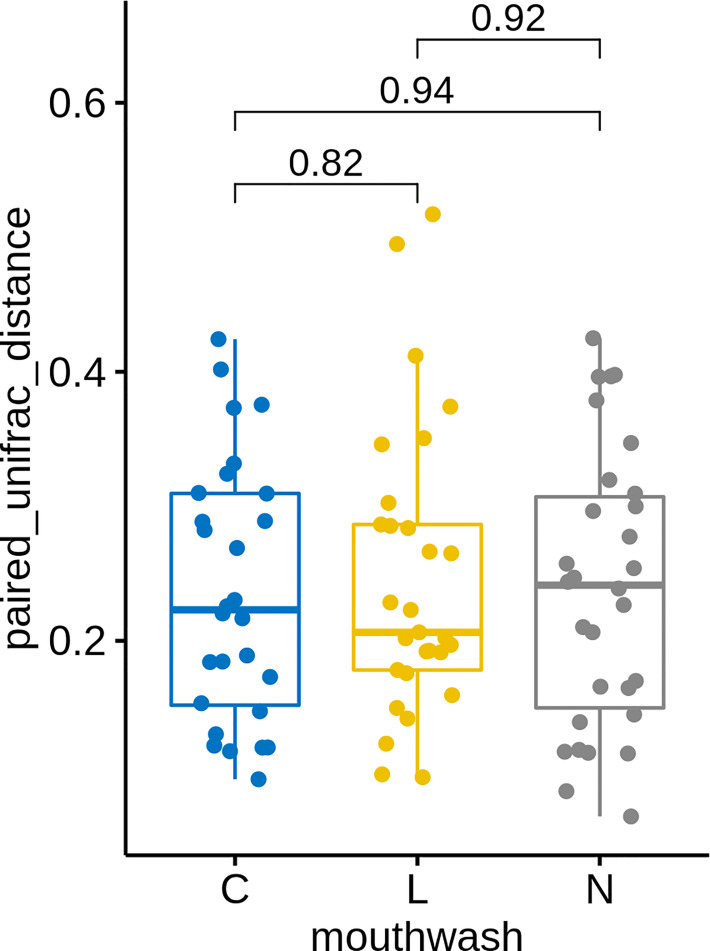
Similar to groups C and L, a large change in microbial composition was observed for several individuals in this control group ( Figure S4A ). In fact, the magnitudes of change in microbiota after gargling were not different for the three groups ( Figure 6 ). This suggests that oral microbiota could be altered largely because of the act of gargling. Paired analysis revealed only one differentially abundant genus ( Figure S4B ), and the magnitude of change was relatively small. Taken together, only CHX and LIS resulted in consistent fractional changes of some bacterial genera. Gargling normal saline decreased the genus level diversities, but not significantly ( Figure 4C ).
Figure 6.
UniFrac distances between microbiota before and after gargling of the same individuals in three mouthwash groups. Differences between groups are tested by Wilcoxon rank test.
3.6. Functional difference after gargling
Functional pathways in each microbial sample were predicted and the abundances of each pathway before and after gargling were compared for each individual. As the abundance change is bi-directional, we first selected differentially abundant (DA) pathways that showed a preferred direction of change (called consistent DA pathway) in all individuals of each mouthwash group. Of the 153 functional pathways, 26 and 6 were consistent DA in the groups C and L, respectively ( Table S4 ). This is consistent with the observed smaller magnitudes of changes in microbial relative abundances after gargling LIS than CHX. There were no common consistent DA pathways in the two groups, suggesting different functional impacts of the CHX and LIS. No consistent DA pathway was found in the control group, which echoes the random alteration in microbial abundance after gargling normal saline. Several functional pathways (e.g., flagellar assembly, and lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis) were decreased after gargling CHX. This suggests a preference of CHX on targeting certain types of bacteria. Preference of LIS on target bacteria is also hinted in the pathway analysis. After gargling LIS, the relative abundance of “vitamin B6 metabolism” decreased and there was an increase of relative abundance of “glycerolipid metabolism” after gargling LIS ( Table S4 ).
3.7. Microbial association with clinical features
Oral microbiota might be affected by physiological or pathological status of individuals, e.g., with drinking habit or diagnosis with cancer. Therefore, we searched for microbes associated with various clinical features. As the clinical features were expected to affect only the baseline levels of microbes, only samples before gargling were analyzed. Among the clinical features, a significant association was found for ten genera and eight of them were associated with alcohol consumption ( Figure S5 ). One genus was associated with age and one was with smoking. None of the ten genera were differentially abundant for the three mouthwash groups. Thus, bacterial genera targeted by the mouthwashes differed from those associated with the clinical features. This supports our assumption that the clinical features only affect the baseline levels of microbes, while gargling was expected to pose a short-term impact.
4. Discussion
In this randomized clinical study on hospitalized patients, we explored the short-term effects of CHX mouthwash and LIS on salivary microbiome using a 16S approach. The short-term design was motivated by the usual length of hospital stay (Moloney et al., 2005), which is about one week, and is similar to several related studies (Tribble et al., 2019; Bescos et al., 2020). Compared to the in vitro studies, our 16S approach allows a more comprehensive and less biased investigation of oral microbes regarding the effects of mouthwash. To our knowledge, this is the first metagenomic study about the effect of LIS on salivary microbes. Including CHX mouthwash ensures a fair comparison of the two mouthwashes under the same experimental procedure. Including normal saline allows us to discern the effect of mouthwash from the act of gargling, thus strengthens validity of the identified bacteria targeted by the mouthwashes. In addition, paired analysis reduces noises from individual differences as many microbial taxa were not identified using unpaired analysis (data not shown).
In response to CHX mouthwash, our differentially abundant bacterial genera were consistent with the results of Bescos et al. (Bescos et al., 2020). Specifically, four of our eight decreased genera (Prevotella, Fusobacterium, Campylobacter, and Corynebacterium) were also decreased in the previous study, and Prevotella showed the largest decrease in both studies. Although not yet significant, Rothia had a high positive score in the previous work. The consistency is reasonable because we and Bescos et al. studied salivary microbiome using a 16S approach. Some of our differentially abundant genera had also been reported in previous in vitro studies. For example, Prevotella and Selenomonas were the two most suppressed bacteria by CHX in the study of McBain et al. (McBain et al., 2003), and the levels of both genera decreased in our study. Note that as the 16S approach only reveals relative abundance, it is possible that Rothia was also suppressed by the CHX mouthwash, but to a lesser degree compared to other genera, which ended up with an increased relative abundance.
Seven bacterial genera were found to be targeted by LIS, and only Selenomonas was also suppressed by the CHX mouthwash. This indicates that the bacterial species targeted by CHX and LIS were largely different. Of our seven genera targeted by LIS, Parvimonas, Eubacterium, and Tannerella were also mentioned in a previous study where bacterial levels were quantified using PCR (Hwang et al., 2021). The most suppressed Parvimonas has also been reported to be suppressed by LIS in a previous in vitro study (Filipovic et al., 2020).
While both the CHX mouthwash and LIS targeted certain bacterial genera, the magnitudes of changes in relative abundance were smaller using LIS in general. This suggests a milder effect of LIS against the target microbes. However, we note that as the 16S approach only reveals relative abundance, the effects in absolute abundance cannot be inferred. CHX has been shown to suppress oral bacteria more effectively than LIS (Haffajee et al., 2008; Thomas et al., 2015), but the higher efficiency is still controversial (Quintas et al., 2015). LIS are generally considered less harmful than CHX (Tsourounakis et al., 2013), however, the statement varies between different settings (Park et al., 2014). Although the physiological impact of mouthwashes still needs further investigation, their functional role can be inferred via the identified target bacteria.
The dysbiosis of the upper respiratory tract microbiome has been associated with pneumonia (de Steenhuijsen Piters et al., 2016). In oropharyngeal microbiota, the genera Rothia and Prevotella were found more and less abundant in pneumonia patients respectively compared to healthy individuals. The two genera showed the largest change in relative abundance, with Rothia increased while Prevotella decreased, after gargling CHX. Therefore, gargling CHX likely moved the oral microbiota toward the profiles in pneumonia patients. Several Prevotella species (P. melaninogenica, buccae, tannerae, and nanceiensis) in the airway have been associated with the clearance of Streptococcus pneumoniae (Horn et al., 2022), a bacterial pathogen causing community-acquired pneumonia. P. melaninogenica was the most abundant Prevotella species in our data. However, its relative abundance did not change significantly after gargling CHX, neither did the three other Prevotella species. In our hospitalized patients, P. nigrescens was decreased after gargling CHX, but it was not associated with the clearance of S. pneunomiae. Therefore, the impact of CHX on pneumonia via altering oral microbes still needs further investigation.
Oral nitrate‐reducing bacteria are beneficial to vascular health and linked to blood pressure regulation and insulin resistance (Goh et al., 2019; Pignatelli et al., 2020). In our hospitalized patients, Prevotella spp. were reduced the most after gargling the CHX mouthwash while not suppressed after gargling LIS and normal saline. Prevotella is the most abundant genus of oral nitrate-reducing bacteria in healthy adults (Burleigh et al., 2018). Consistently, CHX mouthwash eliminated nitrate-nitrite conversion markedly, which resulted in lower plasma and salivary concentration of nitrite, while no difference was found after gargling LIS (Woessner et al., 2016). Other oral nitrate-reducing bacteria include Neisseria, Rothia, Veillonella, Antinomyces, Corynebactrium, and Haemophilus (Rosier et al., 2020), among which Corynebacterium were decreased and Rothia were increased in our hospitalized patients after gargling the CHX mouthwash. Many of the mentioned nitrate-reducing bacteria were not reduced after gargling LIS. A common genus reduced by CHX and LIS in our data was Selenomonas, which capability to reduce nitrate has been reported (Asanuma et al., 2015). The degrees of suppression using the two mouthwashes were similar. Taken together, LIS could also reduce some nitrate-reducing bacteria. However, CHX targeted more nitrate-reducing bacteria and to a greater degree.
In a previous study (de Steenhuijsen Piters et al., 2016), the domination of Rothia was strongly associated with pneumonia. And iron-chelating enterobactin might explain Rothia mucilaginosa’s successful oral colonization in both healthy and diseased individuals (Uranga et al., 2020). However, a recent literature showed that Rothia mucilaginosa abundance inversely correlated with sputum pro-inflammatory markers in chronic lung disease, which implies a beneficial role in the respiratory tract (Rigauts et al., 2022). Therefore, the role of Rothia mulcilaginosa in pneumonia is still controversial.
Our pathway analysis reveals a decreased relative abundance in several bacterial activities after gargling CHX, e.g., bacterial chemotaxis, flagellar assembly, and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) biosynthesis. This suggests preference of CHX on targeting certain types of bacteria. For example, CHX may prefer to target gram-negative bacteria because LPS is a major component of their outer membrane. Indeed, CHX binds to LPS and suppresses the LPS-induced inflammation after the bacteria are destroyed (Zorko and Jerala, 2008). Preference of LIS on target bacteria is also hinted in the pathway analysis. After gargling LIS, the relative abundance of “vitamin B6 metabolism” decreased. Many bacteria in the Bacteroidetes phylum possess a vitamin B6 biosynthesis pathway, while most Firmicutes lack such the pathway (Yoshii et al., 2019). After gargling LIS, Bacteroidetes decreased while Firmicutes increased, which could explain the decreased “vitamin B6 metabolism”.
We also observed an increase of relative abundance of “glycerolipid metabolism” after gargling LIS. This may also suggest a preference of LIS on target bacteria because bacterial membranes are diverse in the contents of various lipids (Sohlenkamp and Geiger, 2016). However, we give a caveat to the functional interpretation. Glycerolipid is also a major component of plant membrane (Reszczynska and Hanaka, 2020) and could be in the essential oil. Therefore, bacteria might engage in processing the glycerolipid in the LIS. Similarly, the increase of “sulfur metabolism” after gargling LIS seems reasonable because volatile sulfur compounds produced by bacteria are the source of oral malodor (Foo et al., 2021) and LIS may target those bacteria. However, CHX has been shown to reduce volatile sulfur compounds more effectively than essential oil mouthwash (Malhotra and Yeltiwar, 2011), but the pathway was not consistently different after gargling CHX.
We examined the correlation between the baseline (i.e., before gargling) oral microbes and the clinical features, including alcohol drinking and smoking habits. The correlation analysis was performed using multiple regression, that is, all variables were examined simultaneously. The result suggests a correlation between some genera and alcohol drinking, smoking, and age. No correlation was observed for all other variables. Therefore, we found no bacterial genera associated with BMI, diabetes, cancer, cirrhosis, infections, and end-stage renal disease. In our analysis of the correlation between baseline (i.e., before gargling) bacterial genera and alcohol drinking, we found that Desulfobulbus was more abundant in alcohol users than non-alcoholic individuals. A similar finding was reported (Barb et al., 2022). As for the smoking-associated Bulleidia, the genus was also reported to be more abundant in smoking than non-smoking individuals (Jia et al., 2021). The Parascardovia genus was found associated with age in our study. Parascardovia has been shown to be predominant in diabetic salivary microbiome in another study (Liu et al., 2021). But the association was not found in the elderly in the published literature.
There are limitations of this study. First, an observed alteration in relative abundance did not guarantee a change in absolute abundance in the same direction. Therefore, one needs to be cautious about linking the altered microbiota to potential functional impacts, e.g., the susceptibility to pneumonia and nitrate reduction, which were not measured in this work. Second, we did not intervene the patients’ oral cleaning such as toothbrushing and the toothpaste use, which might impact the oral microbiome (Chhaliyil et al., 2020; Shang et al., 2020). However, we expect that toothpaste use and brushing method posed a long-term impact on the baseline (i.e., before gargling) oral microbiota in the recruited individuals. In this study, we examined the short-term effects of mouthwashes on oral microbiota. By checking microbial differences before and after gargling, the baseline microbiota only served as a reference point. We thus do not expect that the long-term habit of toothpaste use and brushing method posed a noticeable impact on the short-term alteration in oral microbiota. In a previous study, short term use (~2 weeks) of toothpastes with different active components did not lead to different relative abundance of the dominating genera in oral microbiome (Shang et al., 2020). Although we did not control the toothpaste use and brushing method, the random assignment of subjects to groups should alleviate the impact if there is any. Besides, the consistent findings with the literature suggests a good randomization. Third, it may not be appropriate to extrapolate our findings for long-term alteration of oral microbiota. For example, no differentially abundant oropharyngeal bacteria were observed after using LIS for 12 weeks. It is possible that certain bacteria develop resistance to mouthwash in the long run (Cieplik et al., 2019). Therefore, long-term effects of mouthwash on oral microbiome still need further investigation. Fourth, neither a dentist nor a stomatologist performed a clinical examination and registered the oral hygiene indices. And the sole “inspection” of the oral cavity without the proper light, instruments, and operator can underestimate any differences in the baseline oral conditions. This might lead to variations in baseline oral hygiene among the recruited individuals. However, the potential difference between groups of individuals could be addressed by randomization.
In conclusion, this is the first metagenomic study about the effects of LIS on oral microbes. Both the CHX mouthwash and LIS altered oral microbiota in our hospitalized patients. Bacterial genera targeted by the CHX mouthwash and LIS were largely different, and the magnitude of suppression by LIS was also smaller. Moreover, fewer bacterial genera targeted by LIS were reported to be nitrate-reducing compared to CHX mouthwash.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA834608.
Ethics statement
The studies involving human participants were reviewed and approved by Institutional review board of the National Cheng Kung University Hospital (no: A-ER-108-397). The patients/participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
Y-CC, TL, and J-LW: conceptualization. TL, S-LJ, and J-JC: methodology. K-NY and W-CK: validation C-HL and TL: formal analysis. Y-CC, P-FT and J-LW: investigation. Y-CC and J-LW: writing—original draft preparation. TL, and W-CK: writing—review and editing. J-YW and K-NY: supervision. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank all the patients, family members and staff from all the units that participated in the study. Thank Dr. Meng-Ru Shen for encouraging this research.
Funding Statement
This research was supported in part by Higher Education Sprout Project, Ministry of Education to the Headquarters of University Advancement at National Cheng Kung University (NCKU), and Ministry of Science, Taiwan MOST 110-2314-B-006 -093 -MY2 and MOST 110-2221-E-006-142-MY2.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2023.1056534/full#supplementary-material
References
- Alshehri F. A. (2018). The use of mouthwash containing essential oils (LISTERINE(R)) to improve oral health: A systematic review. Saudi Dent. J. 30, 2–6. doi: 10.1016/j.sdentj.2017.12.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Araujo M. W. B., Charles C. A., Weinstein R. B., Mcguire J. A., Parikh-Das A. M., Du Q., et al. (2015). Meta-analysis of the effect of an essential oil-containing mouthrinse on gingivitis and plaque. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 146, 610–622. doi: 10.1016/j.adaj.2015.02.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asanuma N., Yokoyama S., Hino T. (2015). Effects of nitrate addition to a diet on fermentation and microbial populations in the rumen of goats, with special reference to selenomonas ruminantium having the ability to reduce nitrate and nitrite. Anim. Sci. J. 86, 378–384. doi: 10.1111/asj.12307 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barb J. J., Maki K. A., Kazmi N., Meeks B. K., Krumlauf M., Tuason R. T., et al. (2022). The oral microbiome in alcohol use disorder: a longitudinal analysis during inpatient treatment. J. Oral. Microbiol. 14, 2004790. doi: 10.1080/20002297.2021.2004790 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbera P., Kozlov A. M., Czech L., Morel B., Darriba D., Flouri T., et al. (2019). EPA-Ng: Massively parallel evolutionary placement of genetic sequences. Syst. Biol. 68, 365–369. doi: 10.1093/sysbio/syy054 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bescos R., Ashworth A., Cutler C., Brookes Z. L., Belfield L., Rodiles A., et al. (2020). Effects of chlorhexidine mouthwash on the oral microbiome. Sci. Rep. 10, 5254. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-61912-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blot S. (2021). Antiseptic mouthwash, the nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway, and hospital mortality: a hypothesis generating review. Intensive Care Med. 47, 28–38. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06276-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brookes Z. L. S., Bescos R., Belfield L. A., Ali K., Roberts A. (2020). Current uses of chlorhexidine for management of oral disease: a narrative review. J. Dent. 103, 103497. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2020.103497 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burleigh M. C., Liddle L., Monaghan C., Muggeridge D. J., Sculthorpe N., Butcher J. P., et al. (2018). Salivary nitrite production is elevated in individuals with a higher abundance of oral nitrate-reducing bacteria. Free Radical Biol. Med. 120, 80–88. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.03.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso J. G., Kuczynski J., Stombaugh J., Bittinger K., Bushman F. D., Costello E. K., et al. (2010). QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 7, 335–336. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.f.303 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers J. M., King P. L., Spencer A. J., Wright F. A., Carter K. D. (2005). The oral health assessment tool–validity and reliability. Aust. Dent. J. 50, 191–199. doi: 10.1111/j.1834-7819.2005.tb00360.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. C., Ku E. N., Tsai P. F., Ng C. M., Wang J. L., Lin C. W., et al. (2022). Effect of 0.12% chlorhexidine oral rinse on preventing hospital-acquired pneumonia in nonventilator inpatients. J. Nurs. Res 30, e248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung H. Y., Wong M. M., Cheung S. H., Liang L. Y., Lam Y. W., Chiu S. K. (2012). Differential actions of chlorhexidine on the cell wall of bacillus subtilis and escherichia coli. PloS One 7, e36659. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036659 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chhaliyil P., Fischer K. F., Schoel B., Chhalliyil P. (2020). A novel, simple, frequent oral cleaning method reduces damaging bacteria in the dental microbiota. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 10, 511–519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouhan S., Sharma K., Guleria S. (2017). Antimicrobial activity of some essential oils-present status and future perspectives. Medicines (Basel) 4, 58. doi: 10.3390/medicines4030058 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cieplik F., Jakubovics N. S., Buchalla W., Maisch T., Hellwig E., Al-Ahmad A. (2019). Resistance toward chlorhexidine in oral bacteria - is there cause for concern? Front. Microbiol. 10, 587. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00587 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Steenhuijsen Piters W. A., Huijskens E. G., Wyllie A. L., Biesbroek G., Van Den Bergh M. R., Veenhoven R. H., et al. (2016). Dysbiosis of upper respiratory tract microbiota in elderly pneumonia patients. ISME J. 10, 97–108. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.99 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschepper M., Waegeman W., Eeckloo K., Vogelaers D., Blot S. (2018). Effects of chlorhexidine gluconate oral care on hospital mortality: a hospital-wide, observational cohort study. Intensive Care Med. 44, 1017–1026. doi: 10.1007/s00134-018-5171-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas G. M., Maffei V. J., Zaneveld J. R., Yurgel S. N., Brown J. R., Taylor C. M., et al. (2020). PICRUSt2 for prediction of metagenome functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 38, 685–688. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0548-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar R. C. (2010). Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26, 2460–2461. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgar R. C. (2016). UNOISE2: improved error-correction for illumina 16S and ITS amplicon sequencing. bioRxiv. doi: 10.1101/081257 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Eick S., Goltz S., Nietzsche S., Jentsch H., Pfister W. (2011). Efficacy of chlorhexidine digluconate-containing formulations and other mouthrinses against periodontopathogenic microorganisms. Quintessence Int. 42, 687–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipovic G., Stevanovic M. D., Stojanovic-Radic Z., Obradovic R., Randjelovic P. J., Radulovic N. S. (2020). Choosing the right essential oil for a mouthwash: Chemical, antimicrobial and cytotoxic studies. Chem. Biodivers 17, e2000748. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202000748 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. H., Markowitz K., Furgang D., Goldsmith D., Charles C. H., Lisante T. A., et al. (2007). Effect of an essential oil-containing antimicrobial mouthrinse on specific plaque bacteria in vivo . J. Clin. Periodontol 34, 652–657. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2007.01096.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foo L. H., Balan P., Pang L. M., Laine M. L., Seneviratne C. J. (2021). Role of the oral microbiome, metabolic pathways, and novel diagnostic tools in intra-oral halitosis: a comprehensive update. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 47, 359–375. doi: 10.1080/1040841X.2021.1888867 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh C. E., Trinh P., Colombo P. C., Genkinger J. M., Mathema B., Uhlemann A. C., et al. (2019). Association between nitrate-reducing oral bacteria and cardiometabolic outcomes: Results from ORIGINS. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 8, e013324. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.013324 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haffajee A. D., Yaskell T., Socransky S. S. (2008). Antimicrobial effectiveness of an herbal mouthrinse compared with an essential oil and a chlorhexidine mouthrinse. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 139, 606–611. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2008.0222 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn K. J., Schopper M. A., Drigot Z. G., Clark S. E. (2022). Airway prevotella promote TLR2-dependent neutrophil activation and rapid clearance of streptococcus pneumoniae from the lung. Nat. Commun. 13, 3321. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31074-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua F., Xie H., Worthington H. V., Furness S., Zhang Q., Li C. (2016). Oral hygiene care for critically ill patients to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 10, CD008367. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008367.pub3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang S.-H., Hwang I., Lee J.-Y. (2021). Antibiotic effects of a natural extracts mouthwash. Int. J. Clin. Prev. Dentistry 17, 6–11. doi: 10.15236/ijcpd.2021.17.1.6 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde E. R., Andrade F., Vaksman Z., Parthasarathy K., Jiang H., Parthasarathy D. K., et al. (2014). Metagenomic analysis of nitrate-reducing bacteria in the oral cavity: implications for nitric oxide homeostasis. PloS One 9, e88645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088645 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jia Y. J., Liao Y., He Y. Q., Zheng M. Q., Tong X. T., Xue W. Q., et al. (2021). Association between oral microbiota and cigarette smoking in the Chinese population. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 11, 658203. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.658203 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanehisa M., Goto S. (2000). KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28, 27–30. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.27 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klompas M., Speck K., Howell M. D., Greene L. R., Berenholtz S. M. (2014). Reappraisal of routine oral care with chlorhexidine gluconate for patients receiving mechanical ventilation: systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Intern. Med. 174, 751–761. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2014.359 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim K. S., Kam P. C. (2008). Chlorhexidine–pharmacology and clinical applications. Anaesth Intensive Care 36, 502–512. doi: 10.1177/0310057X0803600404 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim Y., Totsika M., Morrison M., Punyadeera C. (2017). The saliva microbiome profiles are minimally affected by collection method or DNA extraction protocols. Sci. Rep. 7, 8523. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07885-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y.-K., Chen V., He J.-Z., Zheng X., Xu X., Zhou X.-D. (2021). A salivary microbiome-based auxiliary diagnostic model for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Arch. Oral. Biol. 126, 105118. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2021.105118 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. (1996). “Microbiology of dental decay and periodontal disease,” in Medical microbiology (Galveston (TX: Th & S. Baron; ). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louca S., Doebeli M. (2018). Efficient comparative phylogenetics on large trees. Bioinformatics 34, 1053–1055. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx701 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozupone C., Knight R. (2005). UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71, 8228–8235. doi: 10.1128/AEM.71.12.8228-8235.2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magoc T., Salzberg S. L. (2011). FLASH: fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27, 2957–2963. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btr507 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra S., Yeltiwar R. K. (2011). Evaluation of two mouth rinses in reduction of oral malodor using a spectrophotometric technique. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol 15, 250–254. doi: 10.4103/0972-124X.85669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallick H., Rahnavard A., Mciver L. J., Ma S., Zhang Y., Nguyen L. H., et al. (2021). Multivariable association discovery in population-scale meta-omics studies. PloS Comput. Biol. 17, e1009442. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009442 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBain A. J., Bartolo R. G., Catrenich C. E., Charbonneau D., Ledder R. G., Gilbert P. (2003). Effects of a chlorhexidine gluconate-containing mouthwash on the vitality and antimicrobial susceptibility of in vitro oral bacterial ecosystems. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 4770–4776. doi: 10.1128/AEM.69.8.4770-4776.2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moloney E. D., Smith D., Bennett K., O'riordan D., Silke B. (2005). Impact of an acute medical admission unit on length of hospital stay, and emergency department ‘wait times’. QJM: Int. J. Med. 98, 283–289. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hci044 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. B., Lee G., Yun B. G., Kim C. H., Ko Y. (2014). Comparative effects of chlorhexidine and essential oils containing mouth rinse on stem cells cultured on a titanium surface. Mol. Med. Rep. 9, 1249–1253. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.1971 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks D. H., Tyson G. W., Hugenholtz P., Beiko R. G. (2014). STAMP: statistical analysis of taxonomic and functional profiles. Bioinformatics 30, 3123–3124. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli P., Fabietti G., Ricci A., Piattelli A., Curia M. C. (2020). How periodontal disease and presence of nitric oxide reducing oral bacteria can affect blood pressure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 7538. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207538 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer E. L., Maddaford K., Murray G. L., Fairley C. K., Pasricha S., Mu A., et al. (2022). The impact of mouthwash on the oropharyngeal microbiota of men who have sex with men: a substudy of the OMEGA trial. Microbiol. Spectr. 10, e0175721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintas V., Prada-Lopez I., Donos N., Suarez-Quintanilla D., Tomas I. (2015). Antiplaque effect of essential oils and 0.2% chlorhexidine on an in situ model of oral biofilm growth: a randomised clinical trial. PLoS One 10, e0117177. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117177 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reszczynska E., Hanaka A. (2020). Lipids composition in plant membranes. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 78, 401–414. doi: 10.1007/s12013-020-00947-w [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigauts C., Aizawa J., Taylor S. L., Rogers G. B., Govaerts M., Cos P., et al. (2022). R othia mucilaginosa is an anti-inflammatory bacterium in the respiratory tract of patients with chronic lung disease. Eur. Respir. J. 59, 2101293. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01293-2021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosier B. T., Moya-Gonzalvez E. M., Corell-Escuin P., Mira A. (2020). Isolation and characterization of nitrate-reducing bacteria as potential probiotics for oral and systemic health. Front. Microbiol. 11, 555465. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.555465 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shang Q., Gao Y., Qin T., Wang S., Shi Y., Chen T. (2020). Interaction of oral and toothbrush microbiota affects oral cavity health. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 10, 17. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00017 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sohlenkamp C., Geiger O. (2016). Bacterial membrane lipids: diversity in structures and pathways. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 40, 133–159. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuv008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas A., Thakur S., Mhambrey S. (2015). Comparison of the antimicrobial efficacy of chlorhexidine, sodium fluoride, fluoride with essential oils, alum, green tea, and garlic with lime mouth rinses on cariogenic microbes. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 5, 302–308. doi: 10.4103/2231-0762.161759 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tran K., Butcher R. (2019). Chlorhexidine for oral care: A review of clinical effectiveness and guidelines. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tribble G. D., Angelov N., Weltman R., Wang B. Y., Eswaran S. V., Gay I. C., et al. (2019). Frequency of tongue cleaning impacts the human tongue microbiome composition and enterosalivary circulation of nitrate. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 9, 39. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00039 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsourounakis I., Palaiologou-Gallis A. A., Stoute D., Maney P., Lallier T. E. (2013). Effect of essential oil and chlorhexidine mouthwashes on gingival fibroblast survival and migration. J. Periodontol 84, 1211–1220. doi: 10.1902/jop.2012.120312 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uranga C. C., Arroyo P., Duggan B. M., Gerwick W. H., Edlund A. (2020). Commensal oral rothia mucilaginosa produces enterobactin, a metal-chelating siderophore. mSystems 5, e00161–e00120. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.00161-20 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Weijden F. A., van der Sluijs E., Ciancio S. G., Slot D. E. (2015). Can chemical mouthwash agents achieve Plaque/Gingivitis control? Dent. Clin. North Am. 59, 799–829. doi: 10.1016/j.cden.2015.06.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Q., Garrity G. M., Tiedje J. M., Cole J. R. (2007). Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 73, 5261–5267. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00062-07 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner M., Smoliga J. M., Tarzia B., Stabler T., Van Bruggen M., Allen J. D. (2016). A stepwise reduction in plasma and salivary nitrite with increasing strengths of mouthwash following a dietary nitrate load. Nitric. Oxide 54, 1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2016.01.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ye Y., Doak T. G. (2009). A parsimony approach to biological pathway reconstruction/inference for genomes and metagenomes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 5, e1000465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000465 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshii K., Hosomi K., Sawane K., Kunisawa J. (2019). Metabolism of dietary and microbial vitamin b family in the regulation of host immunity. Front. Nutr. 6, 48. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00048 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorko M., Jerala R. (2008). Alexidine and chlorhexidine bind to lipopolysaccharide and lipoteichoic acid and prevent cell activation by antibiotics. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 62, 730–737. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkn270 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found below: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, PRJNA834608.