Abstract
Background/objective:
Spreading depolarization (SD) has been identified as a key mediator of secondary lesion progression after acute brain injuries and clinical studies are beginning to pharmacologically target SDs. While initial work has focused on the N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) antagonist ketamine there is also interest in alternatives that may be better tolerated. We recently showed that ketamine can inhibit mechanisms linked to deleterious consequences of SD in brain slices. The present study tested the hypothesis that memantine improves recovery of brain slices after SD and also explored the effects of memantine in a clinical case targeting SD.
Methods:
For mechanistic studies, electrophysiological and optical recordings were made from hippocampal area CA1 in acutely prepared brain slices from mice. SDs were initiated by localized microinjection of K+ in conditions of either normal or reduced metabolic substrate availability. Memantine effects were assessed from intrinsic optical signals (IOS) and extracellular potential recordings. For the clinical report, a subdural strip electrode was used for continuous electrocorticographic recording after surgical evacuation of a chronic subdural hematoma.
Results:
In brain slice studies, memantine (10–300μM) did not prevent initiation of SD, but impaired SD propagation rate and recovery from SD. Memantine reduced DC shift duration and improved recovery of synaptic potentials after SD. In brain slices with reduced metabolic substrate availability, memantine reduced evidence of structural disruption after passage of SD. In our clinical case, memantine did not noticeably immediately suppress SD, however it was associated with a significant reduction of SD duration, and a reduction in the ECoG suppression that occurs after SD. SD was completely suppressed with improvement in neurological examination with the addition of a brief course of ketamine.
Conclusions:
These data extend recent work showing that NMDAR antagonists can improve recovery from SD. These results suggest that memantine could be considered for future clinical trials targeting SD, in some cases as an adjunct or alternative to ketamine.
Keywords: Cortical spreading depression, excitotoxin, NMDA receptors, brain injury, ketamine, memantine, subdural hematoma
INTRODUCTION
Spreading depolarization (SD) was described long ago as a profound wave of depolarization that transiently silences brain activity1,2 but the phenomenon has only recently been identified as a key contributor to the secondary progression of a range of brain injuries.3 SD causes excitotoxic Ca2+ loading that is sufficient to rapidly injure metabolically compromised neurons4,5 and also leads to damaging spreading ischemia in injured brain6,7. SD can occur intermittently for days following the onset of stroke or brain trauma. This extended time course raises promising new opportunities for treatment, as SD can be recorded and potentially targeted in the intensive care unit8–10.
Clinical efforts to target SDs have been influenced by experience with sedatives used in the intensive care unit (ICU). Thus the dissociative anesthetic ketamine emerged a candidate treatment for SD, based on its mechanism of action and in vitro studies11–14, as well as clinical retrospective analyses15 and case reports16,17. A recent prospective pilot clinical trial established the ability of ketamine to inhibit SD in severe traumatic brain injury or subarachnoid hemorrhage18. Ketamine targeting of SD is now being considered in a number of centers10 and larger ketamine trials assessing long-term outcomes appear warranted10. Despite its promise, ketamine’s side effect profile19 may limit its use to target SD in conscious patients outside of the ICU setting. For example, SD has recently been implicated in fluctuating neurological deficits in subdural hematoma20 and in these conscious patients hallucinations and anxiety produced by ketamine are likely to be limiting.
Memantine is a use-dependent antagonist of N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDARs) that is approved for use in patients with moderate to severe dementia of the Alzheimer’s type, and is generally well tolerated21,22. Memantine has previously been demonstrated to inhibit the onset of SD in rodent neocortex23, brainstem24 and isolated chick retina25. It is also used in the prophylaxis of migraine with aura, whose underlying mechanism is SD26–28. The ability of memantine to improve recovery after SD is not well studied, particularly in compromised brain where SDs are generally more resistant to inhibition by NMDA antagonists29 Further, the potential of memantine to target SD in different brain injury conditions involving SD remains to be tested.
The goal of this study was to examine whether memantine might have potential as an intervention to improve outcomes after SD in injured brain. We tested the hypothesis that memantine improves recovery from SD in brain slices, including using recording conditions that model aspects of brain injury. These mechanistic studies were complemented by an initial demonstration using memantine in a clinical case with SD monitoring. Our observations support future prospective trials of memantine targeting of SD in a range of injury and neurological conditions.
METHODS
Animals and brain slice preparation
All animal procedures were performed in accordance with protocols approved by the UNM Health Sciences Center Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Brain slices were prepared from C57Bl/6 mice (6–8 weeks age) purchased from The Jackson Laboratory and Charles River Laboratories. Brain slices were prepared as previously described14. Briefly, animals were deeply anaesthetized with a ketamine-xylazine mixture and decapitated. Brains were quickly removed into ~150mL of oxygenated ice-cold cutting solution (in mM): sucrose, 220; NaHCO3, 26; KCl, 3; NaH2PO4, 1.5; MgSO4, 6; glucose, 10; CaCl2 0.2; equilibrated with 95% O2/5% CO2 supplemented with 0.2mL ketamine (100mg mL−1) to limit excitotoxicity during the cutting procedure. Ketamine washout and availability of NMDARs has been confirmed previously30. Coronal cortico-hippocampal slices (350μm) were prepared with a vibratome and hemisected. Slices were transferred to artificial cerebrospinal fluid (aCSF; containing (in mM): NaCl, 126; NaHCO3, 26; glucose, 10; KCl, 3; CaCl2, 2, NaH2PO4, 1.5; MgSO4, 1; equilibrated with 95% O2/ 5% CO2), at 35°C for 60 min. After this recovery period aCSF was replaced with chilled (20°C) aCSF and allowed to equilibrate to room temperature for 30 min prior to recording sessions.
Generation of SD and metabolic compromise in brain slices
Individual brain slices were transferred to a submersion recording chamber with nylon slice supports (RC-27, Warner Instruments, Hamden, CT). Moderate metabolic compromise was achieved by inverting the slice support and reducing superfusion of aCSF below the slice, as previously described14. For all recordings, slices were continuously superfused with aCSF at 2–2.4mL min−1 and bath temperature was maintained throughout experiments at 32°C by an inline heater assembly (TC-344B, Warner Instruments). This recording temperature was chosen because it improves viability for brain slice studies and allows for comparison with the body of brain slice SD literature recorded at similar temperatures from different groups31–34. To facilitate testing the effects of drug application onrepetitive SDs, aCSF was replaced with modified aCSF containing 8mM KCl ([K+]-aCSF) after slice and electrode placements and continued throughout the recording14. Following 15 minutes of warm up and equilibration, SD was generated in the hippocampal stratum radiatum of CA1 by localized microinjection (10–50ms, 30psi) of KCl (1M) via a glass micropipette (1.8–6 MΩ) using a picospritzer (Parker Hannifin, OH, USA). In experiments testing repetitive SDs in the standard recording chamber (Figures 1–3), each SD was generated (via KCl focal microinjection) at 15 minutes intervals to allow for recovery from the SD wave between events. Two control SDs prior to drug application were generated to enable in-slice comparison of SD characteristics. After the second control SD, memantine was washed in for 10 minutes prior to the next SD stimulation. For tests on memantine on preparations with reduced of metabolic substrate availability, (Figure 4), single SDs were generated in each preparation due to the lack of recovery (and thus ability to generate repetitive SD events) in these conditions.
Figure 1:
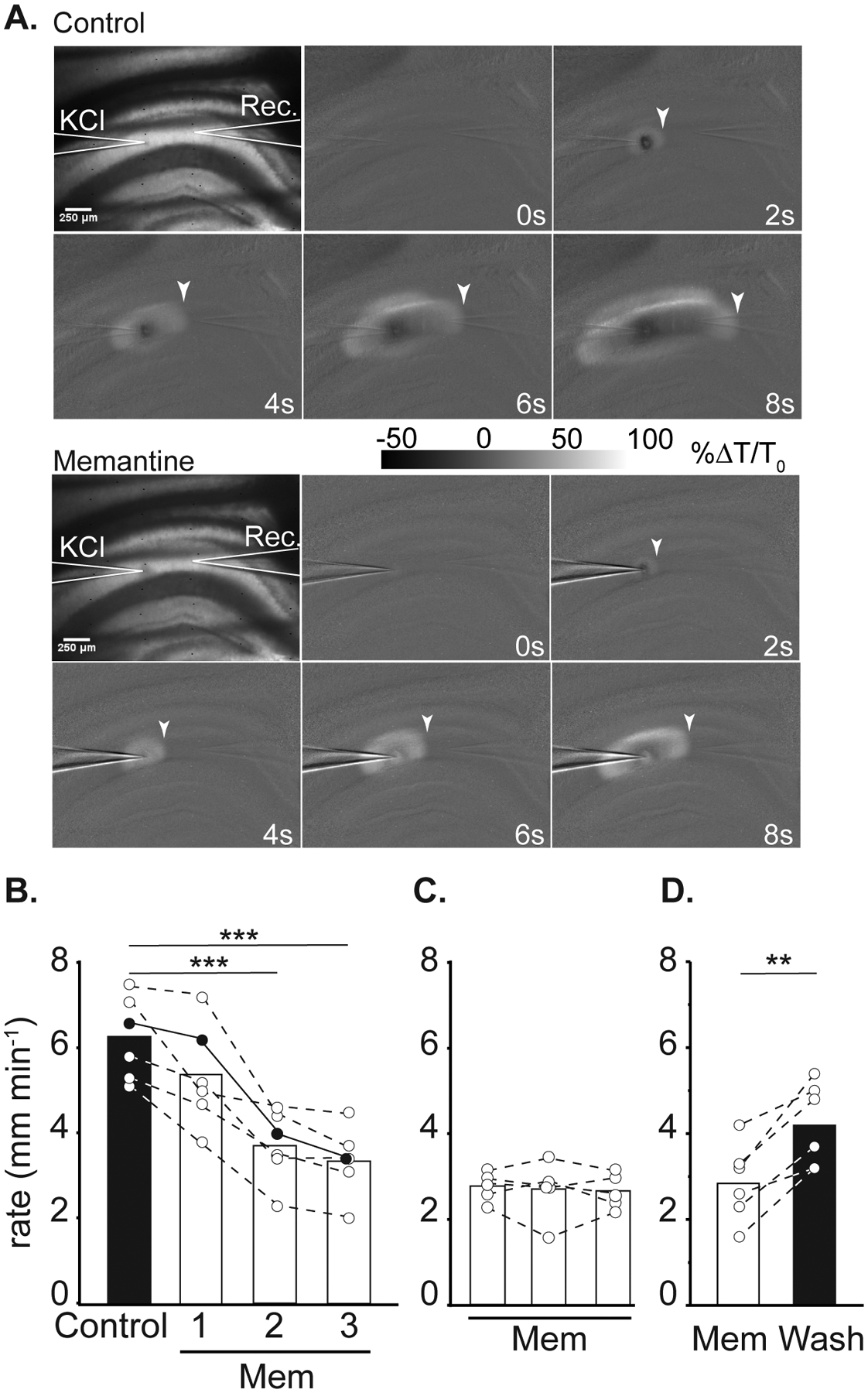
Effect of memantine on SD propagation rate. A: Representative images demonstrating electrode placements (KCl, Rec.) and changes in transmitted light during SD propagation in control (top panel) and in memantine (below, 3rd SD in mem) within the same slice. Arrowheads indicate the wavefront of SD, scale bar = 250μm. B: Summary data showing SD propagation rates during successive SD stimulations from three separate sets of experiments. Left: effect of acute memantine wash in (n = 6) on SD rate, filled symbols are values measured from the preparation shown in A. *** P<0.001 compared to the second control SD. Middle: slower propagation rates during the first SD following extended memantine exposure (≥ 3h, n = 5). Right: faster SD propagation could be observed following extensive memantine wash out (n = 6). **P<0.01 third SD in memantine compared to wash out.
Figure 3:
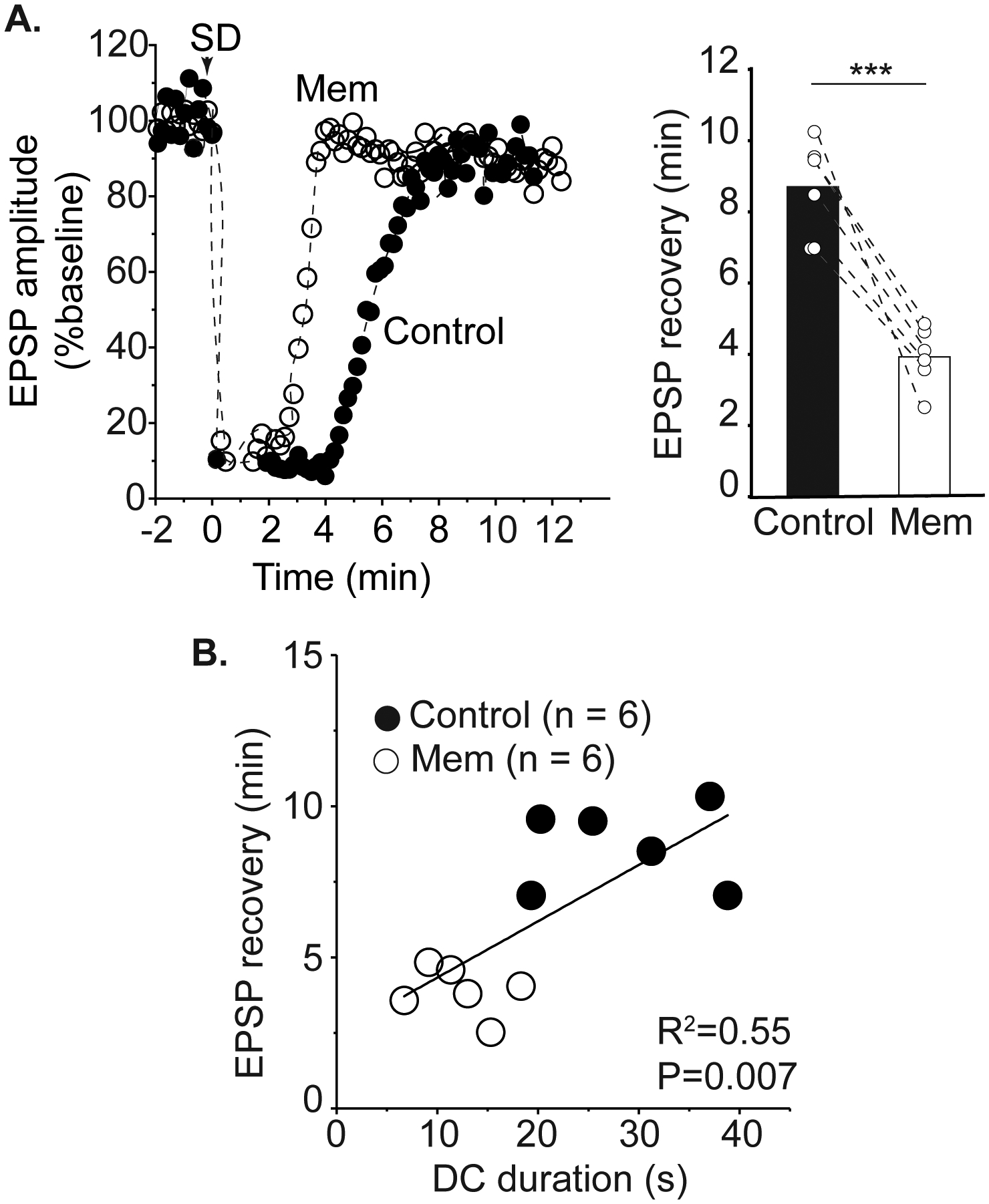
Memantine accelerates recovery of postsynaptic potentials after SD. A: Left panel shows a representative time course of EPSP amplitude recovery after SD in control and then in memantine within the same slice. Mean data of 6 preparations (right) demonstrates that acute memantine exposure reduces the duration of synaptic depression after SD. B: Shorter DC durations during the third SD in memantine were associated with accelerated recovery of postsynaptic potentials compared to the control SD in the same slice. *** P<0.001
Figure 4:
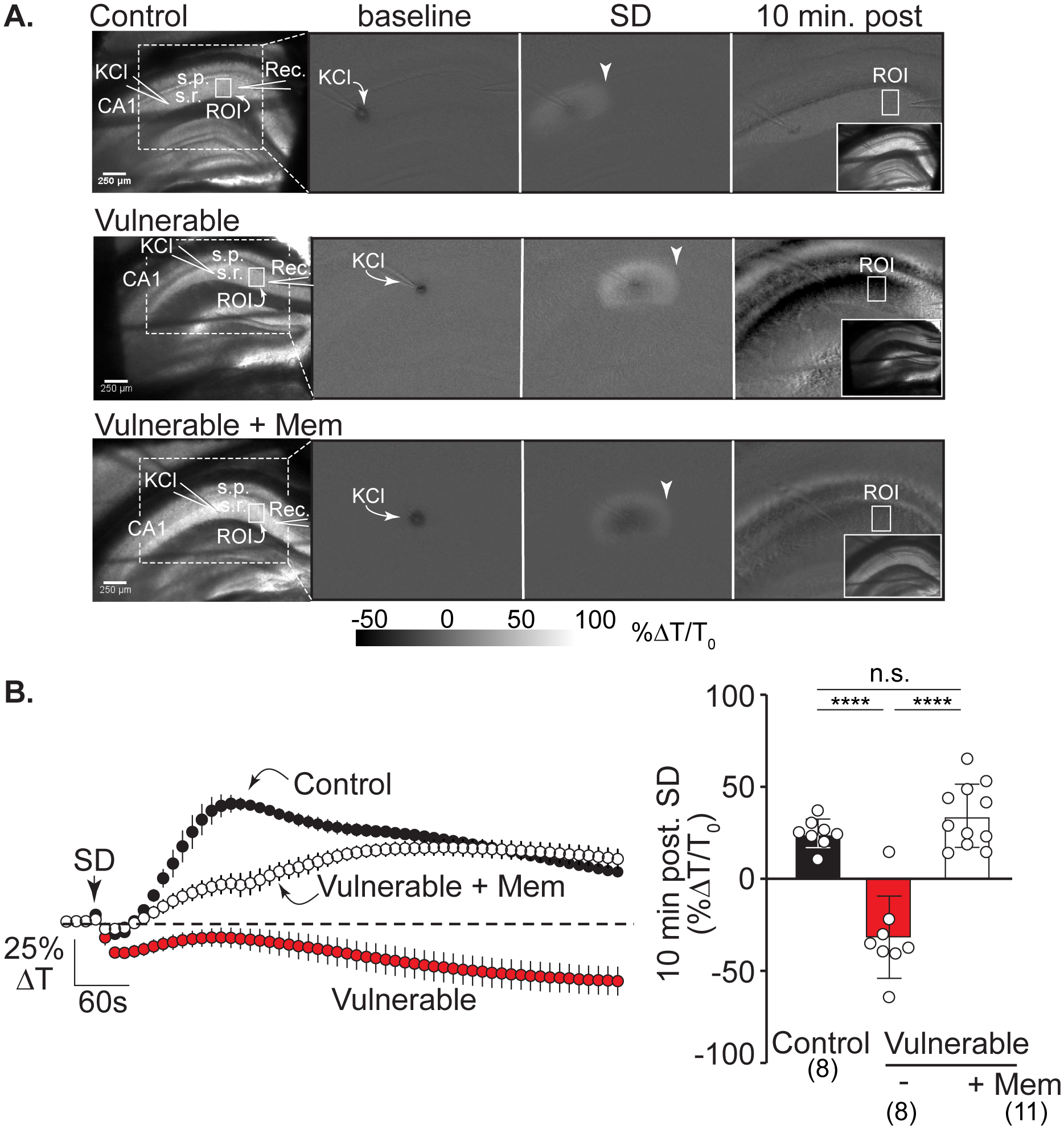
Memantine protects against IOS decreases after SD in vulnerable brain slices. A: Left hand panel shows the arrangement of KCl and recording electrodes in transmitted light images from representative slices in the three experimental conditions: control, vulnerable, and vulnerable + memantine (>2h). Solid white boxes show the regions of interest (ROIs) positioned in CA1 stratum radiatum and used for analyses; s.r.: stratum radiatum, s.p.: stratum pyramidale, scale bar = 250μm. The white dotted box outlines the imaging area shown in subsequent panels demonstrating changes in intrinsic optical signals (IOS, light transmittance) at baseline (during KCl microinjection), during SD propagation (arrowheads), and at the 10-minute time point after SD. Right hand inset panels show transmitted light images of each slice 10 minutes post SD. In control recording conditions (top row) SD led to a persistent IOS increase in stratum radiatum regions, consistent with full recovery in these nominally healthy conditions. In contrast, in the vulnerable conditions (middle row) there was persistent decrease IOS after SD, characteristic of lack of recovery. Pre-exposure to memantine (bottom row) prevented the decrease in IOS signal, consistent with improved recovery of SD in these metabolically compromised conditions. B: Average IOS traces (left; from n = 27 preparations) extracted from regions in CA1 (ROIs in stratum radiatum shown in A) during experiments shown in A. Summary data (right) confirm substantial decreases in CA1 light transmittance 10 minutes after passage of the SD wavefront in vulnerable slices (red symbols, n = 8) compared to control conditions (black symbols n = 8) with prevention by memantine pretreatment (>2h, white symbols, n = 11). ****P<0.0001
Brain slice electrophysiology and imaging
Extracellular recordings were made using glass microelectrodes filled with aCSF (tip resistance 1.8–6MΩ) placed at a depth of 50μm in the CA1 stratum radiatum >200μm from the KCl micropipette. Extracellular DC potential was acquired at 1 kHz with an Axon MultiClamp 700A amplifier and Clampex 9.2 (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA), and digitized with a Digidata 1332 digitizer. For extracellular excitatory postsynaptic potential (EPSP) recordings, a concentric bipolar electrode (FHC) was positioned 50μm deep into the CA1 stratum radiatum between the KCl micropipette and recording electrode for stimulation of Schaffer collateral inputs. After electrode placements, slices were allowed to equilibrate for 15 min during which an input-output curve was generated. Test pulses were delivered at intensities that gave 50–60% of maximum EPSP responses (150 – 600μ, 50μs, 0.1Hz). Responses were recorded at 10kHz and SD was generated after stabilization of baseline EPSPs. All analyses were performed using Clampfit 10.4 software and DC shift durations during SD were measured as the width between 20% of the initial downward deflection of the peak amplitude to 80% of recovery to baseline levels.
SD initiation and propagation were examined IOS generated by trans-illuminated with visible light (≥600nm) and recorded using a 4x objective (Olympus 0.10 NA). Signals were captured (0.5Hz, 2Hz) using a cooled CCD camera (TILL IMAGO CCD Camera, Sensicam PCO) and analyzed with TillVision software (TillPhotonics, version 4.5). Data analysis involved normalizing to baseline transmitted light and expressing IOS as percent change in transmission (ΔT/T0 × 100).
Reagents
All chemicals were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) unless otherwise stated. Memantine-HCl (Sigma M9292) was prepared as a 100mM stock in deionized water and stored in aliquots at −20°C until daily use.
Clinical recordings
Clinical SD recordings were performed using a 1×6 electrode (Auragen platinum electrode, Integra Life Sciences, Princeton NJ) connected to a full band DC amplifier and data management system (Moberg component neuromonitoring system, Ambler, PA) as previously published9. Strip electrodes are placed as standard clinical care to direct therapy for seizure and SD at our institution. Data were collected and stored with prospective informed consent under local IRB (UNM HRPO #17–297). DC ECog was reviewed for both seizure using standard neuromonitoring as spreading depolarization as previously reported35. These were recorded in real time in order to assist in clinical management.
After scoring all SDs, a single channel was used for further analysis to decrease variability of DC shift and depression duration. Each DC shift was scored for total duration, maximum amplitude, and depression duration of high frequency activity if measurable.
Data analysis
All data analyses and statistical tests were performed using GraphPad Prism 8.4.3. Unless otherwise stated, all data are represented as mean ± SEM. One way repeated measures ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons was used in Figures 1 and 2. Based on those findings (that maximum effects of memantine were achieved by the third SD in memantine), paired t-tests were used for Figure 3 analyses. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons was used in Figure 4. Two-tailed paired t-tests were used to analyze SD characteristics before the first dose of memantine compared to those after memantine treatment in a clinical case study. P values <0.05 was considered significant.
Figure 2:
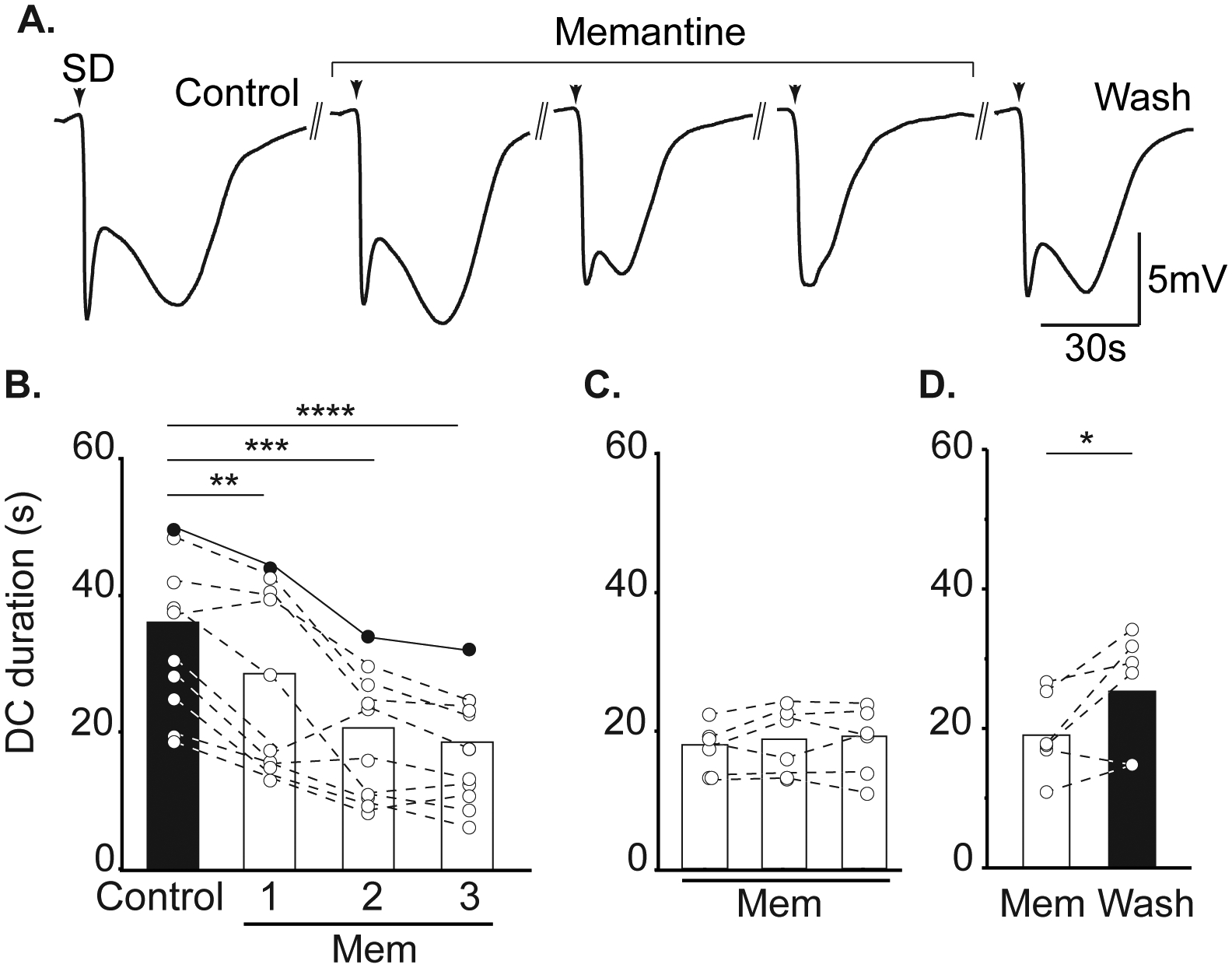
Memantine reduces SD duration. A. Example traces demonstrating the effect of memantine on DC shift duration during successive SDs in a single slice. Return to a biphasic waveform could be achieved following memantine wash out. Arrowheads indicate SD onset and double lines represent 15 minute intervals between successive SDs. B: Summary data showing effect on DC duration during acute memantine exposure (left, n = 10), following extended memantine treatment (middle, ≥ 3h, n = 6), and after memantine wash out (right, n = 6). Filled symbols show DC durations from the same preparation shown in A. **P<0.01, ***P<0.005,****P<0.0001 compared to second control SD; *P<0.05 third SD in memantine compared to wash out.
RESULTS
Memantine slows SD and reduces DC shift duration
Memantine exposures (up to 300μM) did not prevent initiation of SD in any preparation (data not shown), but reliably slowed propagation rate. Figure 1A shows an example of slowed progression of SD in 100 μM memantine, compared to the control SD within the same slice. Figure 1B demonstrates that significant effects took time to develop during acute memantine exposures. The first SD in memantine (Mem1) was not significantly slower compared to controls (P=0.16). The maximum effect was achieved during the 2nd SD in memantine (Mem2), with no change in rate between Mem2 and Mem3 (p=0.16). When slices were pre-exposed to memantine prior to recordings (≥ 3 hours), SD propagation rates were immediately slower and did not require successive SDs to achieve the maximum effect (Figure 1C). Figure 1D shows recovery following memantine washout.
Figure 2A demonstrates effects of memantine on the characteristics of DC potential shifts recorded during SD. Consistent with effects of other NMDAR antagonists4 12 14, the most significant effect of memantine was on the duration of SD, and in particular the late phase of the DC shift present after passage of the wave front. Like the effects on SD propagation rate (Figure 1), maximum effects of memantine effects required either repetitive SDs (Figure 2B) or extended pre-exposures prior to recordings (Figure 2C,). Figure 2D shows recovery after memantine washout. There was a 13.1% decrease in peak SD amplitude, comparing control and the third SD recorded in memantine (6.93 ± 0.78 vs. 6.025±0.86mV, control and memantine respectively, P=0.0080). This is attributed in part to run down of SD amplitude with successive SDs, being similar to decreases described in time control studies conducted in parallel and reported previously14.
Memantine accelerates recovery of postsynaptic potentials after SD
To determine the physiological significance of shorter extracellular DC shifts, we monitored adenosine-A1 receptor (A1R) -mediated suppression of EPSPs as a read-out of the metabolic demand of SD36,37. Memantine accelerated recovery of EPSPs. Figure 3A shows a representative time course of EPSP recovery in control conditions SD and then following memantine exposure in the same slice. As for figures 1B and 2B, three successive SDs were generated in memantine to generate a maximal effect of the antagonist. Mean data from such experiments are shown in the right panel of Figure 3A demonstrating the acceleration of EPSP recovery by memantine in each slice (P= 0.0008, n=6). Time control studies conducted in parallel confirmed that the change in recovery time was an effect of memantine, rather than spontaneous changes occurring during the series of SDs (n=5). In the same preparations, shorter DC durations were correlated with shorter durations of EPSP suppression (Figure 3B). This results show that memantine accelerates recovery of normal synaptic transmission in the wake of SD.
Memantine improves recovery after SD in vulnerable brain slices
We next examined whether memantine can improve recovery from SD in metabolically vulnerable brain slices. The experimental approach was as described recently using partial reduction in metabolic substrate availability by restriction of aCSF flow under brain slices (see Methods). This partial metabolic compromise does not spontaneously initiate SD but greatly impairs recovery after SD14. In the current study we selected intrinsic optical signals (IOS) as a robust measure of recovery, as described previously for ketamine14 IOS decreases after SD in metabolically compromised conditions have been attributed to a combination of factors, including dendritic disruption and swelling of intracellular organelles38 39 and persistent astrocyte swelling observed in vulnerable tissues could also contribute40 (Figure 4 shows that under control conditions, a prominent IOS increase is observed that recovers towards baseline. In contrast, SD in metabolically compromised conditions was invariably followed by sustained IOS decreases (~25% ΔT/T0; Figure 4A&B) that could be attributed to injury (see Discussion). Memantine (100μM, ≥3 hours pre-exposure) effectively prevented decreased IOS signals, consistent with improved recovery from SD under these conditions.
Memantine administration is associated with apparent improvement on SD morphology in a human subject
Following brain slices observations, we tested the feasibility of targeting SD in clinical settings. Figure 5 shows results from a case of a 72 year old male reported to have had a ground level fall one month prior to presentation. He was found to have large bilateral mixed density chronic subdural hematoma (Figure 5A), left greater than right with progressive right sided weakness and headache. He was taken to the operating room for evacuation of both hematomas via burrholes with normalization of his neurological examination after surgery despite a small amount of residual hematoma. On postoperative day #3, he was found to have right-sided weakness despite no significant change in imaging. A short-term EEG showed no evidence of seizure. Given the residual hematoma on the left, and lack of other explanation for the deficit, the patient was taken for re-do evacuation with a small craniotomy and placement of ECoG electrode in order to monitor for seizures or SD given recently published findings (Figure 5B)20. He was found to have frequent SD and clusters of SD with progressively worsening weakness and mental status. The ECoG recordings were reviewed and integrated in to the multidisciplinary care of the patient. Due to these concerning findings, the patient was started on memantine 30 mg enterally BID on POD 2 from the second surgery. We are increasingly treating symptomatic patients with SD ketamine based on previous published data at our institution. In patients who are not intubated, we have started using memantine as an alternate agent without risk of respiratory suppression. This high dose is based on a published RCT in moderate TBI patients (Mokhtari, 2018) and preclinical data showing efficacy against SD. Figure 5C shows analysis of SDs recorded prior to initiation of memantine followed by SDs in the presence of memantine alone. In the 37 events recorded on memantine alone, there was a significant decrease in the duration of SD events (Figure 5C), amplitude of individual events (Figure 5D) and the duration of ECoG suppression following each SD (Figure 5E) compared to 39 events prior to memantine. These findings are in concurrence with the effects of memantine on the DC shift duration and synaptic suppression after SD observed in the brain slice model.
Figure 5:
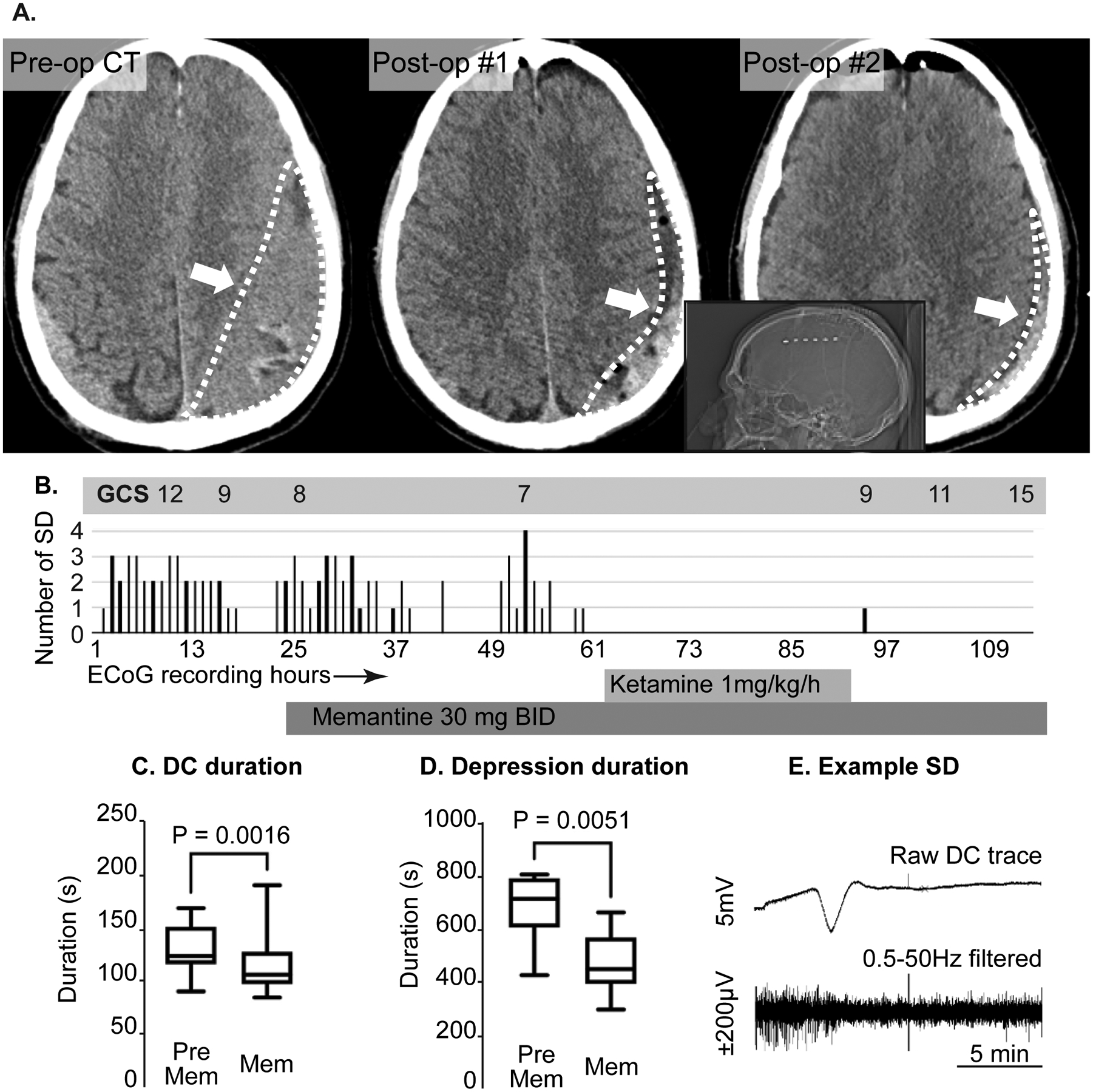
Clinical management of patient with recurrent SD after chronic subdural hematoma evacuation. A: axial non-contrast CT scans demonstrating a large isodense/ mixed density chronic subdural hematoma (left panel, white arrow and outline). The center panel shows the result of the initial drainage with a small amount of residual blood product but improved mass effect (arrow, outline). The right panel demonstrates further decrease in residual volume after the second surgery with electrode placement. The inset shows the position of the electrode strip (white dots) on the lateral CT scout film. All these occurred prior to SD recordings. B: time course of neurological examination (Glasgow coma scale[GCS]),_SD frequency, and memantine and ketamine use during >100 hours of ECoG monitoring. Note that the GCS progressively deteriorated with recurrent SD and improved after cessation of SD. Overall rate of SD did not immediately decrease after memantine administration, but were completely abolished after initiation of ketamine. After ketamine was discontinued, memantine was continued with only one isolated SD during the monitoring period. C, D: Box plots of C) DC duration and D) Depression duration before and after memantine administration in this subject. E: Example SD from this subject. This SD is from the single electrode where the events were most prominent. The top trace is the raw DC (direct current) trace, the bottom is the same data with 0.5–50Hz band pass filter to display the high frequency data only. Note the depression of the high frequency activity lasting ~10 minutes.
At the concentration tested, memantine alone did not abolish SDs and the patient further deteriorated, requiring intubation so a ketamine infusion was initiated (again as a clinically targeted therapy). Figure 5 shows the onset of ketamine infusion at 1mg/kg/h at which point SD stopped completely. The patient was also monitored with continuous EEG during this entire period. There were no seizures for the first two days of monitoring. There was one generalized seizure approximately 30 hours after starting memantine (prior to ketamine initiation), which initiated on the strip electrode and generalized to the surface electrodes. There were several additional brief seizures noted only on the strip and so the patient’s levetiracetam dosing was increased from 1000mg BID to 1500mg BID. All these events occurred after the patient deteriorated to the point of requiring intubation. Other findings from the EEG included periodic discharges and diffuse brain slowing.
The neurologic exam slowly began to improve over several days (Figure 5B) to following simple commands and symmetric motor examination. The ECoG strip was removed after two further days where no SD was noted. Memantine was stopped after 10 days with no notable clinical side effects and improving mental status. By 1-week clinic follow-up, the patient had returned to a normal examination (fully oriented and normal motor examination). The intent of this approach was to continue the more tolerable drug subacutely in hopes of avoiding any rebound effect after discontinuation of the ketamine.
DISCUSSION
The main findings of this study are that memantine can improve recovery from SD, and could be considered a candidate for future prospective clinical studies targeting SD in the ICU. In mechanistic studies in brain slices, memantine did not block SD, but significantly slowed SD and reduced DC shift duration. Importantly, memantine was shown to improve recovery as measured by IOS in metabolically vulnerable brain slices. Finally, an example of initial targeting of SD with memantine in a clinical setting showed results fully consistent with the brain slice studies. Thus, SDs recorded from a subdural hematoma patient were not immediately abolished by memantine, but the duration of SDs and the suppression of ECoG activity following SDs occurring in the presence of memantine were significantly reduced. These findings provide a basis for future clinical studies examining effects of targeting SD with memantine on neurological outcomes. They also raise the possibility of using memantine and ketamine in combination, using the advantages of each (potency for ketamine, tolerability for memantine) when clinically appropriate.
With the recent recognition of the involvement of SD in a range of clinical settings, there is much renewed interest in pharmacologic approaches to manipulate SD.10 Ketamine has emerged as a leading candidate, partly because of its efficacy use as a sedative in the ICU with patients undergoing monitoring for SD and associated case reports16,17 and a comprehensive retrospective analysis supporting efficacy in reducing the number of SD events15. Preclinical studies11,12,14, and an initial prospective clinical study supports efficacy18, and there is currently an important larger clinical trial to evaluate efficacy of ketamine along with targeted physiologic interventions in subjects with severe traumatic brain injury undergoing surgical decompression. While suppression of SDs with ketamine is a very promising approach, it is appreciated that in some patient populations, ketamine may not be well tolerated. In addition, SD may have different roles across different spectrum of disease3 which has impact on the goals for treatment. A comatose patient at risk for secondary ischemic progression may require complete suppression to limit further damage and a sedating agent may be reasonable. In cSDH, the concern is usually that the SD is causing transient neurologic deficits which delay or impair recovery and rehabilitation and so this scenario generally requires an agent that would not further sedate the patient. The case we present here was an unusually severely affected subject who eventually required intubation due to these deficits, thus warranting the more aggressive approach with addition of ketamine, however the “typical” SD after cSDH are more sporadic20 and an agent such as memantine that would not sedate the patient, but improve recovery from SD and potentially suppress these sporadic events is worth testing further.
Memantine is well tolerated in elderly populations treated for dementia of the Alzheimer type41 and has been proposed as an attractive candidate for clinical translation for stroke treatment42. Preliminary data have also supported improving clinical recovery and neuron specific enolase levels after moderate traumatic brain injury43. Memantine is effective in reducing both aura and headache in migraine with aura, a condition where SD occurs26–28 and previous preclinical data have also demonstrated a dose dependent suppressive effect of memantine on SD44. Like ketamine, memantine is an NMDAR antagonist, and our preclinical results here confirm that it is less potent than ketamine at inhibiting the initiation or propagation of SD. The time course of inhibition is similar to prior studies of NMDAR-mediated synaptic currents, which identified a slow time course of 100 μM memantine inhibition (as well as recovery) of EPSCs.45 This suggests that memantine does not require the presence of large depolarizations in order to reduce the spread of SD but does not rule out the possibility of use-dependency of memantine block being contributed to by ongoing synaptic activity during long pre-exposures.
Memantine effectively reduced the duration of individual SD events, as measured by the extracellular DC potential shifts. The late phase of SD involves an unusual surge of damaging Ca2+ loading, as presynaptic terminals release a barrage of glutamate that coincides with sustained postsynaptic depolarization and release of Mg2+ block from NMDA receptors4. Reducing the duration of SD by memantine likely prevents this deleterious Ca2+ loading, and promotes recovery from SD. Figure 3B shows the correlation between the duration of extracellular DC shift duration and recovery of evoked synaptic potentials. With shorter DC potential shifts in memantine, accelerated recovery of postsynaptic potentials after SD is consistent with more rapid restoration of ionic balance, and thus reduced adenosine-mediated suppression of presynaptic release, to allow neurons to reengage more rapidly in coordinated communicative activity. In the clinical recordings, suppression of ECoG activity was used to monitor recovery of circuit activity, rather than by testing evoked synaptic potentials. However, ECoG in vivo is mediated in part by the same adenosine A1 mechanisms as EPSP inhibition after SD46, allowing comparison of synaptic recovery in both preclinical and clinical studies (see below).
We exploited a brain slice model of metabolically vulnerable tissue to test protective effects of memantine. The model involves moderately restricting diffusion of metabolic substrates. This weakens the tissue, but unlike more common models of extreme metabolic depletion (such as complete anoxia or oxygen-glucose-deprivation) SD is not generated and evoked synaptic transmission can continue for hours without interruption. SDs evoked on this background of metabolic compromise lead to persistent suppression of synaptic transmission and other evidence of tissue stress or damage. As shown in Figure 4, one measure of deleterious outcome is persistent decreases in IOS after SD. IOS decreases after SD in metabolically compromised conditions have been attributed to a combination of factors, including dendritic disruption and swelling of intracellular organelles38,39 and persistent astrocyte swelling observed in vulnerable tissues could also contribute40. As shown here, memantine pre-exposure effectively prevented signs of impairment in the vulnerable conditions, similar to that previously reported with ketamine14. This is important, because it shows that overt SD suppression is not necessary for memantine to have a predicted protective effect, by improving recovery from SD.
The clinical case illustrates the close temporal association of SD with severe, reversible, non-epileptic neurological deficit after cSDH evacuation. The cause of SD in such cases is not known, but in the absence of ischemia, we hypothesize that the combination of mass effect and inflammatory changes from blood products and membranes is adequate to trigger these events. In the ~40 hours of treatment with memantine alone (i.e. prior to co-administration with ketamine), SD were not abolished but those SDs that were recorded showed a significant decrease in the DC duration, SD amplitude and ECoG depression duration as compared with SDs recorded in the absence of memantine. These observations are consistent with the main results of the brain slice studies, and suggest value of future prospective trials aimed at reducing deleterious effects of SD. These observations make memantine a potentially attractive agent in conditions such as cSDH where patients may have minor symptoms and minimally invasive treatments are emerging. Such therapies could potentially decrease the perceived need for surgical intervention if the symptoms could be improved while the cSDH resolves.
There are limitations to the study. The brain slice studies were conducted at 32°C, as is commonly utilized for studies of SD by different groups, and indeed many valuable mechanistic SD studies are conducted with slices at room temperature. Hypothermia reduces SDs47 and it is not yet known whether high recording temperatures will increase vulnerability to SD in the current model, and amplify (or reduce) effects of memantine. Intrinsic optical signals provide a straightforward method to assess disruption of slice integrity following SD, but they do not provide a direct measure of neuronal viability. Future studies would be required to directly test whether memantine prevents injury produced by SD in metabolically compromised tissues. With regard to our clinical observations, we acknowledge that these are very preliminary and alone do not provide evidence for the clinical use of memantine to target SD. Though we did not note seizures during the time the patient was deteriorating, the patient did ultimately have several seizures and so it is possible that other electrophysiological events contributed to the deterioration. In addition, the optimal dose for memantine to target SD clinically is not known. It is proven safe at lower doses of 10mg BID for dementia and migraine, though potential additional risk of higher doses is unknown. Finally the natural history of the clinical recovery without the memantine or ketamine is unknown, and it seems likely that the co-administration of ketamine at later time points could underlie abolition of SD.
Conclusions:
Together, these data extend recent work showing that NMDA antagonists can improve recovery from SD, without outright blocking propagation of the events. These results suggest that memantine could be considered for future clinical trials targeting SD, in some cases as an adjunct or alternative to ketamine and that assessing characteristics of SD events should be assessed. In addition, memantine may be attractive in settings where outpatient therapy (such as minimally symptomatic cSDH) is needed.
Manuscript Details.
We confirm that the manuscript complies with all instructions to authors
-
We confirm that authorship requirements have been met and the final manuscript was approved by all authors, as follows:
KMR: Experimental design, acquisition & interpretation of data, drafting and revision of manuscript, final approval of version to be published
AH: Experimental design, acquisition and analysis of data, revising manuscript and final approval of version to be published.
KCB: Conception and design, critically revising manuscript, final approval of version to be published
APC: Conception and design, acquisition and interpretation of data, drafting and revision of manuscript, final approval of version to be published.
CWS: Conception and design, interpretation and analysis of data, drafting and critically revising manuscript, final approval of version to be published
We confirm that this manuscript has not been published elsewhere and is not under consideration by another journal
We confirm that the research reported here adheres to ethical guidelines, with animal procedures for preparation of in vitro brain slices being approved by the UNM Health Sciences Center Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (protocol # 19–200973-HSC) and the example of clinical monitoring approved by prospective informed consent under local IRB (protocol # UNM HRPO #17–297).
Drs. Shuttleworth, Reinhart, Brennan and Carlson report grants from NIH during the conduct of the study. NS106901 (Shuttleworth), T32 HL007736 (Reinhart), GM109089 (Carlson), NS102978, NS104742 (Brennan). There are no other conflicts of interest to declare.
There were no in vivo animal studies and thus the ARRIVE checklist was not included for the in vitro brain slice studies. Other checklists were not appropriate for the single illustrative clinical case.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Supported by NIH grants NS106901, GM109089, T32 HL007736, NS102978, NS104742.
REFERENCES
- 1.Leao AAP. Spreading depression of activity in the cerebral cortex. J Neurophysiol 1944;7:359–90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Leao AAP. Further observations on the spreading depression of activity in the cerebral cortex. J Neurophysiol 1947;10:409–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hartings JA, Shuttleworth CW, Kirov SA, et al. The continuum of spreading depolarizations in acute cortical lesion development: Examining Leao’s legacy. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2017;37:1571–94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Aiba I, Shuttleworth CW. Sustained NMDA receptor activation by spreading depolarizations can initiate excitotoxic injury in metabolically compromised neurons. The Journal of physiology 2012;590:5877–93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hinzman JM, DiNapoli VA, Mahoney EJ, Gerhardt GA, Hartings JA. Spreading depolarizations mediate excitotoxicity in the development of acute cortical lesions. Experimental neurology 2015;267:243–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dreier JP. The role of spreading depression, spreading depolarization and spreading ischemia in neurological disease. Nature medicine 2011;17:439–47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hinzman JM, Andaluz N, Shutter LA, et al. Inverse neurovascular coupling to cortical spreading depolarizations in severe brain trauma. Brain : a journal of neurology 2014;137:2960–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dreier JP, Fabricius M, Ayata C, et al. Recording, analysis, and interpretation of spreading depolarizations in neurointensive care: Review and recommendations of the COSBID research group. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2017;37:1595–625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hartings JA, Li C, Hinzman JM, et al. Direct current electrocorticography for clinical neuromonitoring of spreading depolarizations. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2017;37:1857–70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Helbok R, Hartings JA, Schiefecker A, et al. What Should a Clinician Do When Spreading Depolarizations are Observed in a Patient? Neurocrit Care 2020;32:306–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hernandez-Caceres J, Macias-Gonzalez R, Brozek G, Bures J. Systemic ketamine blocks cortical spreading depression but does not delay the onset of terminal anoxic depolarization in rats. Brain Res 1987;437:360–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Marrannes R, Willems R, De Prins E, Wauquier A. Evidence for a role of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor in cortical spreading depression in the rat. Brain research 1988;457:226–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sanchez-Porras R, Santos E, Scholl M, et al. The effect of ketamine on optical and electrical characteristics of spreading depolarizations in gyrencephalic swine cortex. Neuropharmacology 2014;84:52–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Reinhart KM, Shuttleworth CW. Ketamine reduces deleterious consequences of spreading depolarizations. Exp Neurol 2018;305:121–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hertle DN, Dreier JP, Woitzik J, et al. Effect of analgesics and sedatives on the occurrence of spreading depolarizations accompanying acute brain injury. Brain : a journal of neurology 2012;135:2390–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sakowitz OW, Kiening KL, Krajewski KL, et al. Preliminary evidence that ketamine inhibits spreading depolarizations in acute human brain injury. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation 2009;40:e519–22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Schiefecker AJ, Beer R, Pfausler B, et al. Clusters of cortical spreading depolarizations in a patient with intracerebral hemorrhage: a multimodal neuromonitoring study. Neurocrit Care 2015;22:293–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Carlson AP, Abbas M, Alunday RL, Qeadan F, Shuttleworth CW. Spreading depolarization in acute brain injury inhibited by ketamine: a prospective, randomized, multiple crossover trial. Journal of neurosurgery 2018:1–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Peltoniemi MA, Hagelberg NM, Olkkola KT, Saari TI. Ketamine: A Review of Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics in Anesthesia and Pain Therapy. Clin Pharmacokinet 2016;55:1059–77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Mohammad LM, Abbas M, Shuttleworth CW, et al. Spreading depolarization may represent a novel mechanism for delayed fluctuating neurological deficit after chronic subdural hematoma evacuation. Journal of neurosurgery 2020:1–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bullock R Efficacy and safety of memantine in moderate-to-severe Alzheimer disease: the evidence to date. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 2006;20:23–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lipton SA. Pathologically activated therapeutics for neuroprotection. Nature reviews 2007;8:803–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Peeters M, Gunthorpe MJ, Strijbos PJ, Goldsmith P, Upton N, James MF. Effects of pan- and subtype-selective N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists on cortical spreading depression in the rat: therapeutic potential for migraine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2007;321:564–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jansen NA, Schenke M, Voskuyl RA, Thijs RD, van den Maagdenberg A, Tolner EA. Apnea Associated with Brainstem Seizures in Cacna1a (S218L) Mice Is Caused by Medullary Spreading Depolarization. J Neurosci 2019;39:9633–44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kertesz S, Kapus G, Gacsalyi I, Levay G. Deramciclane improves object recognition in rats: potential role of NMDA receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 2010;94:570–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Charles A, Flippen C, Romero Reyes M, Brennan KC. Memantine for prevention of migraine: a retrospective study of 60 cases. J Headache Pain 2007;8:248–50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bigal M, Rapoport A, Sheftell F, Tepper D, Tepper S. Memantine in the preventive treatment of refractory migraine. Headache 2008;48:1337–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Noruzzadeh R, Modabbernia A, Aghamollaii V, et al. Memantine for Prophylactic Treatment of Migraine Without Aura: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study. Headache 2016;56:95–103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Petzold GC, Windmuller O, Haack S, et al. Increased extracellular K+ concentration reduces the efficacy of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists to block spreading depression-like depolarizations and spreading ischemia. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation 2005;36:1270–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Vander Jagt TA, Connor JA, Shuttleworth CW. Localized loss of Ca2+ homeostasis in neuronal dendrites is a downstream consequence of metabolic compromise during extended NMDA exposures. J Neurosci 2008;28:5029–39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Frank R, Bari F, Menyhart A, Farkas E. Comparative analysis of spreading depolarizations in brain slices exposed to osmotic or metabolic stress. BMC Neurosci 2021;22:33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Petrin D, Gagolewicz PJ, Mehder RH, Bennett BM, Jin AY, Andrew RD. Spreading depolarization and neuronal damage or survival in mouse neocortical brain slices immediately and 12 hours following middle cerebral artery occlusion. J Neurophysiol 2019;121:1650–63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Zhou N, Gordon GR, Feighan D, MacVicar BA. Transient swelling, acidification, and mitochondrial depolarization occurs in neurons but not astrocytes during spreading depression. Cereb Cortex 2010;20:2614–24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Carter RE, Aiba I, Dietz RM, Sheline CT, Shuttleworth CW. Spreading depression and related events are significant sources of neuronal Zn2+ release and accumulation. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2011;31:1073–84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Dreier JP, Fabricius M, Ayata C, et al. Recording, analysis, and interpretation of spreading depolarizations in neurointensive care: Review and recommendations of the COSBID research group. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2017;37:1595–625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Lindquist BE, Shuttleworth CW. Adenosine receptor activation is responsible for prolonged depression of synaptic transmission after spreading depolarization in brain slices. Neuroscience 2012;223:365–76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Lindquist BE, Shuttleworth CW. Spreading depolarization-induced adenosine accumulation reflects metabolic status in vitro and in vivo. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 2014;34:1779–90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Obeidat AS, Andrew RD. Spreading depression determines acute cellular damage in the hippocampal slice during oxygen/glucose deprivation. Eur J Neurosci 1998;10:3451–61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fayuk D, Aitken PG, Somjen GG, Turner DA. Two different mechanisms underlie reversible, intrinsic optical signals in rat hippocampal slices. J Neurophysiol 2002;87:1924–37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Risher WC, Croom D, Kirov SA. Persistent astroglial swelling accompanies rapid reversible dendritic injury during stroke-induced spreading depolarizations. Glia 2012;60:1709–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Winblad B, Jones RW, Wirth Y, Stoffler A, Mobius HJ. Memantine in moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 2007;24:20–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Lopez-Valdes HE, Clarkson AN, Ao Y, et al. Memantine enhances recovery from stroke. Stroke 2014;45:2093–100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mokhtari M, Nayeb-Aghaei H, Kouchek M, et al. Effect of Memantine on Serum Levels of Neuron-Specific Enolase and on the Glasgow Coma Scale in Patients With Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury. J Clin Pharmacol 2018;58:42–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Peeters M, Gunthorpe MJ, Strijbos PJ, Goldsmith P, Upton N, James MF. Effects of pan- and subtype-selective N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists on cortical spreading depression in the rat: therapeutic potential for migraine. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics 2007;321:564–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Frankiewicz T, Potier B, Bashir ZI, Collingridge GL, Parsons CG. Effects of memantine and MK-801 on NMDA-induced currents in cultured neurones and on synaptic transmission and LTP in area CA1 of rat hippocampal slices. Br J Pharmacol 1996;117:689–97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lindquist BE, Shuttleworth CW. Evidence that adenosine contributes to Leao’s spreading depression in vivo. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2017;37:1656–69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ueda M, Watanabe N, Ushikubo Y, et al. [The effect of hypothermia on CSD propagation in rats]. No Shinkei Geka 1997;25:523–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


