Abstract
Background
Open laparotomy with gastroenterological surgery is a surgical procedure results in a relatively high rate (about 10% or more) of incisional surgical site infection (SSI). To reduce incisional SSI after open laparotomy, mechanical preventors, such as subcutaneous wound drainage or negative-pressure wound therapy (NPWT), have been tried; however, conclusive results have not been obtained. This study evaluated the prevention of incisional SSI by first subfascial closed suction drainage after open laparotomy.
Methods
A total of 453 consecutive patients who underwent open laparotomy with gastroenterological surgery by one surgeon in one hospital (between August 1, 2011, and August 31, 2022) was investigated. Same absorbable threads and ring drapes were used in this period. Subfascial drainage was used in consecutive 250 patients in the later period (between January 1, 2016, and August 31, 2022). The incidences of SSIs in the subfascial drainage group were compared to those of in the no subfascial drainage group.
Results
(a) No incisional SSI (superficial and deep) occurred in the subfascial drainage group (superficial = 0% [0/250] and deep = 0% [0/250]). As a result, incidences of incisional SSI of the subfascial drainage group were significantly lower than those of the no subfascial drainage group (superficial = 8.9% [18/203]; deep = 3.4% [7/203]) (p < 0.001 and p = 0.003, respectively). (b) Four out of seven deep incisional SSI patients in the no subfascial drainage group underwent debridement and re-suture under lumbar or general anesthesia. (c) There was no significant difference in the incidences of organ/space SSI of the two groups (3.4% [7/203] in the no subfascial drainage group and 5.2% [13/250] in the subfascial drainage group) (P = 0.491).
Conclusion
Subfascial drainage was associated with no incisional SSI after open laparotomy with gastroenterological surgery.
Keywords: Incisional surgical site infection, Laparotomy, Gastroenterological surgery, Subfascial closed suction drainage, Surgical site infection
Introduction
Incisional surgical site infection (SSI) [1] is a troublesome postoperative complication. It is rarely fatal but leads to long-term hospitalization and physical and mental distress.
Open laparotomy with gastroenterological surgery is a surgical procedure that is performed with a clean-contaminated wound by wound classification [1, 2]. Thus, it often results in a relatively high rate (about 10% or more) of incisional SSI [3–5].
Numerous risk factors for developing an incisional SSI have been identified. Currently, to reduce incisional SSI after open laparotomy, mechanical preventors, such as subcutaneous wound drainage [6–10] or negative-pressure wound therapy (NPWT) [11–14], have been tried; however, conclusive results have not been obtained [15, 16].
Incisional SSI after laparotomy often occur after colorectal surgery or abdominal cavity contamination [3, 17, 18], and it is often accompanied by organ/space SSI [18, 19].
Under the hypothesis that incisional SSI might be prevented by shutout contaminated fluid raising from abdominal cavity, we started the subfascial closed suction drainage in all patient after open laparotomy from about halfway through this retrospective study period.
Herein, we report the first subfascial closed suction drainage to prevent incisional SSI after open laparotomy.
Methods
For this retrospective cohort study, a total of 453 consecutive surgical patients who underwent open laparotomy (length of incision was 10 cm or more) by one surgeon in Oomoto hospital (between August 1, 2011, and August 31, 2022) was investigated. Patients who underwent laparoscopic surgery (n = 71 [6 stomach, 30 colorectum, and 35 gallbladder]) were excluded. The same absorbable threads, ring drape wound protector, and technical procedures of wound closure for fascia, subcutaneous tissue and skin, were used in this period.
Patients who died before the 30th operative day were excluded from this study (n = 2; an 87-year-old gastric cancer patient who underwent fundectomy died of cardiopulmonary failure, and a 91-year-old advanced colonic cancer patient who underwent bypass operation died of uncontrollable bleeding from the tumor).
Surgical technique
The surgeon performed all the surgical procedures from skin incision to skin closure. A skin incision was made by a scalpel, and subcutaneous fat, fascia, and peritoneum were separated with electrocautery. Wound protection during the operation was performed by ring drape.
Between August 1, 2011, and December 31, 2015, wound closure was performed by interrupted sutures using 1–0 Coated Vicryl*Plus (Antibacterial)® for the fascia together with peritoneum in 203 patients. After closure, the wound was irrigated with 500 ml of saline solution, and the subcutaneous fat tissue was closed by interrupted sutures using 3–0 Coated Vicryl®. Skin closure was made by continuous intradermal suture using 4–0 Monocryl®.
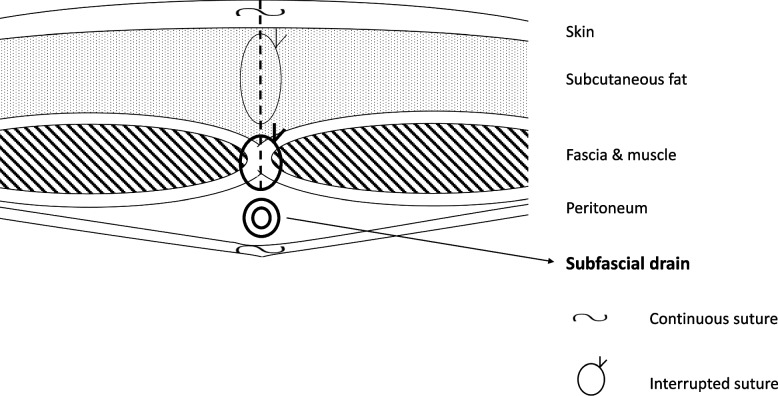
Between January 1, 2016, and August 31, 2022, wound closure was performed using the following procedure in 250 patients. Continuous suture of the peritoneum by 3–0 Coated Vicryl® was performed, and the wound was irrigated with 500 ml of saline solution. Then, a 7F conventional drain tube with discontinuous small holes (tkb SurgicalProducts, TOKIBO)® (Fig. 1) was placed between the peritoneum and fascia (under-muscle if the incision is subcostal or sub-umbilical) along the full length of the subfascial incision. The exit of the drain was placed separate from the incision at the caudal site. After this, the fascia was closed by interrupted sutures using 1–0 Coated Vicryl*Plus (Antibacterial)®. The same procedure as the no subfascial drainage group was performed for the closure of subcutaneous tissue and skin (Fig. 2). Finally, a drain tube was connected to a low-pressure (30–80 mmHg), continuous-aspiration portable reservoir (Bulb-type 100 ml) to allow the full length of the wound to be drained (Fig. 3). After the suturing of the wound, conventional gauze dressing was used in both groups.
Fig. 1.
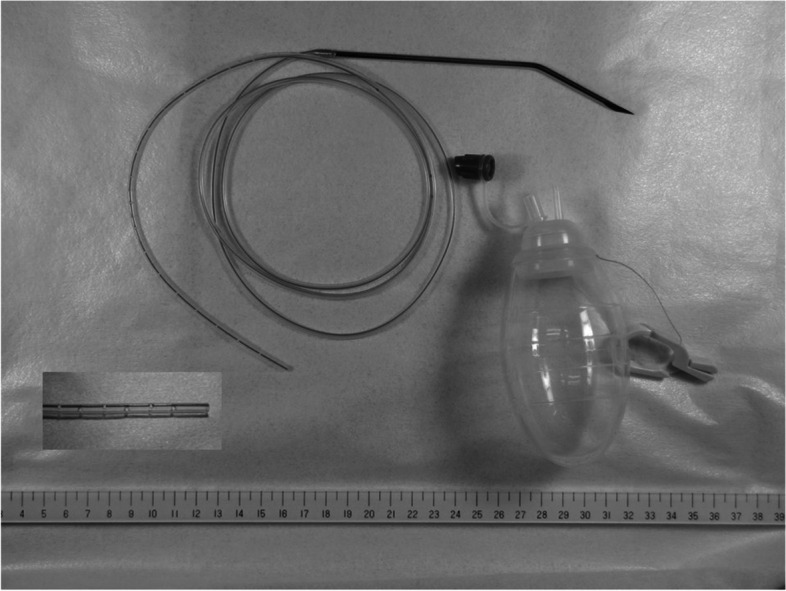

7F conventional drain tube with discontinuous small holes (tkb SurgicalProducts, TOKIBO)® and a low-pressure (30–80 mmHg), continuous-aspiration portable reservoir (Bulb-type 100 ml)
Fig. 2.
Schema of closure of abdominal wall and placement of subfascial drain tube
Fig. 3.
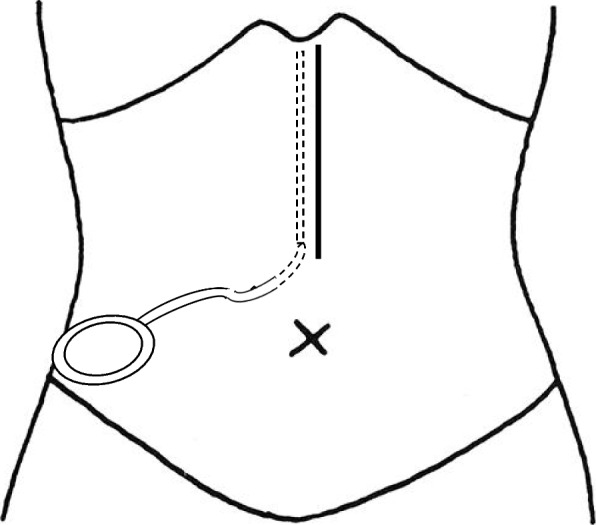
Subfascial drainage along the full length of the subfascial incision. Exit of the drain was placed separate from the incision at the caudal site, and connected to a low-pressure (30–80 mmHg), continuous-aspiration portable reservoir (Bulb-type 100 ml)
Outcome measures
The patient’s individual clinical items were recorded from their medical chart.
The following factors in relation to SSI were recorded: sex, age, body mass index, serum albumin, smoking, diabetes mellitus, previous laparotomy, emergency operation, blood transfusion, stoma-related, American Society of Anesthesiology score, organs of disease, malignancy, types of operations, sites of incision, wound classification, drainage from abdominal cavity, re-operation, and postoperative hospital stay. Hepatobiliary pancreatic diseases consisted of: liver cancer (n = 6), biliary tract cancer (n = 4), and pancreatic cancer (n = 4) in the no subfascial drain group; and liver cancer (n = 5), biliary tract cancer (n = 2), gallstones (n = 6), pancreatic cancer (n = 8), and pancreatitis (n = 1) in the subfascial drainage group.
The diagnosis of SSI was made by surgeons according to the criteria of the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (Table 1).
Table 1.
Criteria of surgical site infection (summarized)
| Surgical Site Infections (SSI) |
|---|
| Incisional SSI |
| Superficial incisional SSI |
| 1. Purulent drainage, with or without laboratory conformation, from the superficial incision |
| 2. Organisms isolated from an aseptically obtained culture of fluid or tissue from the superficial incision |
| 3. At least one of the following signs or symptoms of infection: pain or tenderness, localized swelling, redness or heat, which requre the superficial incision to be deliberately opened by a surgeon,unless the incision is culture negative |
| 4. Diagnosis of superficial incisional SSI made by the surgeon |
| Deep incisional SSI |
| 1. Purulent drainage from the deep incision but not from the organ/space component of the surgical site |
| 2. Diagnosis of a deep incisional SSI made by the surgeon |
| Organ/space SSI |
| 1. Purulent drainage from a drain that is placed though a cut |
| 2. Organisms isolated from an aseptically obtained culture of fluid or tissue in the organ/space |
| 3. An abscess or other evidence of infection involving the organ/space that is found on direct examination, during reoperation, or by histopathologic or radiologic examination |
| 4. Diagnosis of an organ/space SSI by the surgeon |
SSIs were defined according to these definitions and occurring within 30 days after surgery
For the elective colorectal surgery, mechanical bowel preparation was performed two days before surgery. Preoperative oral antibiotics consisting of oral antibiotic mechanical bowel preparation were administered 2 days before surgery and the day of surgery.
Routine use of prophylactic antibiotics was as follows. For stomach disease, a first-generation cephalosporin (cefazoline sodium), and for the other diseases, a second-generation cephalosporin (flomoxef sodium) was administered by intravenous injection within 30 min before skin incision. In patients who underwent operations lasting longer than 3 h, additional doses of the same antibiotics were injected intravenously. These agents were also administered twice a day up to POD 3, according to the surgeon’s routine use.
All statistical analyses were performed using EZR (Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University, Saitama, Japan), which is a graphical user interface for R (The R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) [20]. P-values < 0.05 by Fisher's exact test and unpaired t-test were considered significant.
Results
The mean retention period of the subfascial drain was 5.9 days after surgery. Usually, the subfascial drain was removed simultaneously when the drain from the abdominal cavity was removed (mean = 6.0 days), and if no abdominal drain was inserted, the subfascial drain was removed (mean = 4.9 days) after surgery. The mean of the total volume of the subfascial drainage was 29.8 ml.
Table 2 shows the clinical items and incidences of the incisional SSI and the organ/space SSI in the no subfascial drainage group and the subfascial drainage group.
Table 2.
Clinical items and incidences of the incisional SSI and the organ/space SSI in the no subfascial drainage group and the subfascial drainage group
| Subfascial suction drainage | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | p value | ||
| Number of patients | 203 | 250 | ||
| Sex | Male | 115 (56.7%) | 146 (58.4%) | 0.774 |
| Female | 88 (43.3%) | 104 (41.6%) | ||
| Age | 68.84 (10.62) | 69.77 (11.48) | 0.374 | |
| Body mass index | 21.80 (3.84) | 22.44 (4.07) | 0.089 | |
| Serum albumin (g/dl) | 3.87 (0.52) | 3.94 (0.49) | 0.112 | |
| Smoking | 37 (18.2%) | 78 (31.2%) | 0.002 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 10 (5.0) | 15 (6.0) | 0.684 | |
| Previous laparotomy | 30 (14.8) | 53 (21.2) | 0.088 | |
| Emergency | 10 (5.0) | 32 (12.8) | 0.005 | |
| Blood transfusion | 45 (22.2) | 49 (19.7) | 0.561 | |
| Stoma-related | 11 (5.4) | 13 (5.2) | 1 | |
| Organs of disease | Stomach | 117 (57.6) | 111 (44.4) | 0.133 |
| Small Bowel | 7 (3.4) | 15 (6.0) | ||
| Colon | 36 (17.7) | 60 (24.0) | ||
| Rectum | 26 (12.8) | 37 (14.8) | ||
| Hepatobiliary pancreas | 14 (6.9) | 22 (8.8) | ||
| Others | 3 (1.5) | 5 (2.0) | ||
| Malignancy | 193 (95.1) | 220 (88.0) | 0.012 | |
| ASA score | 1 | 88 (43.3) | 89 (35.6) | 0.103 |
| 2 | 96 (47.3) | 124 (49.6) | ||
| 3 | 19 (9.4) | 37 (14.8) | ||
| Types of operations | Gastrectomy (partial) | 79 (38.9) | 81 (32.4) | NA |
| Gastrectomy (total) | 36 (17.7) | 26 (10.4) | ||
| Colectomy | 36 (17.7) | 56 (22.4) | ||
| Rectal anterior resection | 21 (10.3) | 33 (13.2) | ||
| Miles or Hartmann | 4 (2.0) | 5 (2.0) | ||
| Total pelvic exenteration | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.4) | ||
| Ileus (adhesiolysis) | 3 (1.5) | 3 (1.2) | ||
| Ileus (anastomosis) | 3 (1.5) | 9 (3.6) | ||
| Hepatobiliary pancreatic | 14 (6.9) | 22 (8.8) | ||
| Others | 6 (3.0) | 14 (5.6) | ||
| Sites of Incision | 1 Median (supra-umblical) | 113 (55.7) | 112 (44.8) | 0.079 |
| 2 Median (Median) | 28 (13.8) | 47 (18.8) | ||
| 3 Median (sub-umbilical) | 37 (18.2) | 54 (21.6) | ||
| 4 Subcostal | 2 (1.0) | 9 (3.6) | ||
| 5 Subcostal + median | 20 (9.9) | 20 (8.0) | ||
| 6 Right para-rectal | 3 (1.5) | 8 (3.2) | ||
| Wound classification | 2 | 202 (99.5) | 243 (97.2) | 0.08 |
| 3 | 1 (0.5) | 9 (3.6) | ||
| Operative time (min) | 135.8 (56.67) | 165.5 (76.8) | < 0.001 | |
| Blood loss (ml) | 138.1 (214.00) | 143.7(221.7) | 0.787 | |
| Drainage from abdominal cavity | 161 (79.3) | 214 (85.6) | 0.081 | |
| Re-operation | 6 (3.0) | 11 (4.4) | 0.467 | |
| Incisional SSI | Superficial | 18 (8.9) | 0 (0.0) | < 0.001 |
| Deep | 7 (3.4) | 0 (0.0) | 0.003 | |
| Organ/space SSI | 7 (3.4) | 13 (5.2) | 0.491 | |
| Abscess | 3 (42.9) | 3 (23.1) | 4 (30.8) | |
| Leakage | 4 (57.1) | 5 (38.5) | ||
| Bowel Perforation | 0 (0.0) | 1 (7.7) | ||
| Others | 0 (0.0) | 4 (30.8) | ||
| Postoperative hospital stay (days) | 26.8 (14.3) | 24.52 (14.7) | 0.093 | |
SSI Surgical Site Infections
ASA American Society of Anesthesiology score
Comparing the two groups, the subfascial drainage group included more smokers and more emergency operations than the no subfascial drainage group. The rate of malignancy in the no subfascial drainage group was higher (95.1%) than that in the subfascial drainage group (88.0%). Moreover, the operative time (165.5 min) of the subfascial drainage group was longer than that of the no subfascial drainage group (135.8 min).
The incidences of re-operation were similar in the two groups (3.0% [6/203] in the no subfascial drainage group and 4.4% [11/250] in the subfascial drainage group) (P = 0.467).
Surgical site infection
Incisional surgical site infection
A total of 18 incisional SSI was diagnosed at 10.5 postoperative days on average (5-18 days) in the no subfascial drainage. Diagnosis of incisional SSI was made by the surgeon himself in 5 patients and made by 5 other surgeons in 13 patients during routine doctor rounds. Then, the wounds were opened by those surgeons.
As a result of this study, no incisional SSI (superficial and deep) occurred in the subfascial drainage group (superficial 0% [0/250] and deep 0% [0/250]). Therefore, the incidences of incisional SSI of the subfascial drainage group were significantly lower than those of the no subfascial drainage group (superficial 8.9% [18/203] and deep 3.4% [7/203]) (p < 0.001 and p = 0.003).
In all seven deep incisional SSI patients in the no subfascial drainage group, superficial SSIs were found. Furthermore, four out of seven patients with deep SSI underwent debridement and re-suture under lumbar or general anesthesia. Re-suturing of the wound was performed by interrupted transdermal vertical mattress sutures with 2.0 monofilament nylon.
Bacterial test performed in ten patients with incisional SSI: Enterococcus faecalis (n = 2), Staphylococcus aureus (n = 1), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (n = 4) and Negative (n = 3).
Organ/space surgical site infection
There was no significant difference in the incidences of organ/space SSI of the two groups (3.4% [7/203] in the no subfascial drainage group and 5.2% [13/250] in the subfascial drainage group) (P = 0.491). Four of 7 patients with organ/space SSI in the no subfascial drainage group was accompanied by incisional SSI. On the other hand, none of the 13 organ/space SSI patients in the subfascial drainage group was accompanied by incisional SSI (p = 0.007).
Table 3 shows incidences of incisional SSI according the organs of disease in the no subfascial drainage group and the subfascial drainage group. In colon or rectum group, the incidence of incisional SSIs was significantly different between the two groups.
Table 3.
Incidences of the incisional SSI acccording to organs of disease in the no subfascial drainage group and the subfascial drainage group
| Subfascial suction drainage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Yes | p value | |||
| Organs | Number of patients | Incisional SSI | Number of patients | Incisional SSI | |
| Stomach | 117 (117) | 5(5) | 111(110) | 0 | 0.06 |
| Small Bowel | 7(1) | 1(1) | 15(6) | 0 | 0.318 |
| Colon | 36(34) | 5(4) | 60(49) | 0 | 0.007 |
| Rectum | 26(26) | 5(5) | 37(36) | 0 | 0.009 |
| Hepatobiliary pancreas | 14(13) | 2(2) | 22(15) | 0 | 0.144 |
| Others | 3(2) | 0 | 5(4) | 0 | 1 |
SSI Surgical Site Infections
() Malignant disease
Discussion
Various risk factors associated with SSI have been reported. Fukuda reported that intra-operative blood transfusion, diabetes, and use of steroids were risk factors for SSI following gastrointestinal surgery [21].
Although prophylactic antibiotics were administered up to POD 3 according to the surgeon’s routine use, in the period of the present study, we administered the following treatments according to the common recommendations: Oral antibiotic mechanical bowel preparation for elective colorectal surgery [22], a ring drape as a wound protector [3], an absorbable 1–0 Coated Vicryl*Plus (Antibacterial)® [23] for interrupted suture of the fascia [24], an absorbable 3–0 coated Vicryl for continuous suture of the peritoneum in the subfascial drainage group, an absorbable 3–0 coated Vicryl for interrupted suture of subcutaneous fat mass, and an absorbable 4–0 Monocryl® for continuous intradermal suture of skin closure [25].
As mentioned before, open laparotomy with gastroenterological surgery is an operation performed with a clean-contaminated wound, resulting in relative high rate (over 10%) of incisional SSI.
In the present study, our hypothesis was that incisional SSI might be prevented by shutout of contaminated fluid raising from the abdominal cavity; however, there has been no report of subfascial closed suction drainage to prevent incisional SSI after open laparotomy. On the other hand, there have been many reports concerning subcutaneous drainage after laparotomy to prevent incisional SSI; however, conclusive results have not been obtained.
In a previous review of subcutaneous drainage, the advantage of closed suction drainage over passive drainage was not shown [15]. Moreover, among studies of subcutaneous closed suction drainage, the results varied [8, 15]. In a review of subcutaneous wound drainage in reducing surgical infection after laparotomy, Manzoor et al. [15] stated that: “There seems to be no benefit in using it in clean and clean contaminated wounds. However, there may be benefit in using drains in patients who are at high risk, including patients who are obese and/or have contaminated wound types.” A recent systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrated that the use of subcutaneous suction drains did not exhibit any significant differences between drained and undrained patients in developing SSI (odds ratio 0.76, 95% CI 0.56–1.02; p = 0.07) [26].
NPWT as a mechanical preventor has been tried, as well as open dirty wound, to reduce incisional SSIs of closed incisions after laparotomy. NPWT has several possible mechanisms, including the prompt removal of exudation to avoid fluid on the inter-stitched face and tissue layers [13]. However, similar to subcutaneous closed suction drainage, conclusive results have not been obtained [14, 16]. Recently, a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials of prophylactic NPWT for closed laparotomy wounds showed that the overall SSI rate in NPWT groups (18.6%, 87/467) was significantly lower than that of standard dressing groups (23.9%, 111/464) (Odds ratio 0.71, 95% CI 0.52–0.99, p = 0.04*) [27].
Subcutaneous suction drainage and NPWT were performed under the hypothesis that the elimination of dead space and fluid collection by active suctioning may prevent wound infection. However, our findings suggest that the beneficial effect of only subcutaneous suctioning remains to be shown.
In the present study, subfascial drainage resulted in no incisional SSIs (0/250) after open laparotomy with gastroenterological surgery. In comparison to the no subfascial drainage group, the subfascial drainage group consisted of more smokers, more previous laparotomies, more emergency operations, worse wound classification, and longer operative time.
Now, we could not understand the preventing mechanism of incisional SSI by the subfascial suction drainage which yielded this striking result. However, the following mechanism might be caused: contaminated fluid from the abdominal cavity sucked below the fascial space; in addition, the exudate under the subcutaneous space sucked through the gap between sutures of the facia.
This retrospective cohort study of incisional SSI has the following limitations. First, this study was performed by one surgeon in one hospital; thus, it was not a randomized trial. Second, the period of study could be divided into early (no subfascial drainage) and late (with the subfascial drainage) periods. The main shortcomings related to historic controls is the introduction of "hidden bias" related the multiple additional standards in care. Although the same ring drape for wound protection and same absorbable threads for the closure of abdominal wall were used in both periods of this study, some changes of infection prevention protocols or gastrointestinal surgical procedures may have occurred. Third, this study may be the first report of the subfascial suction drainage after laparotomy; thus, randomized controlled trials are necessary to confirm the present findings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, subfascial drainage was associated with no incisional SSI (0/250) after open laparotomy with gastroenterological surgery. Based on the insights from this study, we recommend the placement of the subfascial suction drainage after open laparotomy, especially after colorectal surgery or abdominal cavity contamination, to prevent incisional SSI.
Acknowledgements
The author is grateful to all surgeons and nurses who helped the surgeon perform all of operations used in this study. The author also thanks Mrs. Murakami (nurse) and Ms. Fujino for her secretarial work.
Author Disclosure Statement
The author has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Abbreviations
- SSI
Surgical site infection
- NPWT
Negative-pressure wound therapy
Authors’ contributions
Isozaki carried out all surgical procedures as surgeon, input the data in the computer, performed the statistical analysis, and drafted the manuscript. The author(s) read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
No funding resources were used.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the ethics committee of Oomoto Hospital in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki as revised in 2013. Informed consent to participate in the analysis of anonymous data from the Oomoto Hospital database was received through our institutional form.
Consent for publication
We have consent to publish case reports through our institutional form.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Mangram AJ, Horan TC, Pearson ML, et al. Guideline for Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 1999. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Hospital Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Am J Infect Control. 1999;27(2):97–132. doi: 10.1016/S0196-6553(99)70088-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Garner JS. CDC guideline for prevention of surgical wound infections, 1985. Infect Control. 1986;7:193–200. doi: 10.1017/S0195941700064080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Itatsu K, Yokoyama Y, Sugawara G, et al. The Benefits of a Wound Protector in Preventing Incisional Surgical Site Infection in Elective Open Digestive Surgery. A Large-Scale Cohort Study. World J Surg. 2017;41(11):2715–2722. doi: 10.1007/s00268-017-4082-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Utsumi M, Yamada T, Yamabe K, et al. Differences in risk factors for surgical site infection between laparotomy and laparoscopy in gastrointestinal surgery. PLoS One. 2022;17(9):e0274887. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Imamura K, Adachi K, Sasaki R, et al. Randomized Comparison of Subcuticular Sutures Versus Staples for Skin Closure After Open Abdominal Surgery: a Multicenter Open-Label Randomized Controlled Trial. J Gastrointest Surg. 2016;20(12):2083–2092. doi: 10.1007/s11605-016-3283-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Watanabe J, Ota M, Kawamoto M, et al. A randomized controlled trial of subcutaneous closed-suction Blake drains for the prevention of incisional surgical site infection after colorectal surgery. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2017;32(3):391–398. doi: 10.1007/s00384-016-2687-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Numata M, Godai T, Shirai J, et al. A prospective randomized controlled trial of subcutaneous passive drainage for the prevention of superficial surgical site infections in open and laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2014;29(3):353–358. doi: 10.1007/s00384-013-1810-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tsujita E, Yamashita Y, Takeishi K, et al. Subcuticular absorbable suture with subcutaneous drainage system prevents incisional SSI after hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg. 2012;36(7):1651–1656. doi: 10.1007/s00268-012-1524-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Nakayama H, Takayama T, Okubo T, et al. Subcutaneous drainage to prevent wound infection in liver resection: a randomized controlled trial. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2014;21(7):509–517. doi: 10.1002/jhbp.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kaya E, Paksoy E, Ozturk E, et al. Subcutaneous closed-suction drainage does not affect surgical site infection rate following elective abdominal operations: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Acta Chir Belg. 2010;110(4):457–462. doi: 10.1080/00015458.2010.11680655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zaidi A, El-Masry S. Closed-incision negative-pressure therapy in high-risk general surgery patients following laparotomy: a retrospective study. Colorectal Dis. 2017;19(3):283–287. doi: 10.1111/codi.13458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Javed AA, Teinor J, Wright M, et al. Negative Pressure Wound Therapy for Surgical-site Infections: A Randomized Trial. Ann Surg. 2019;269(6):1034–1040. doi: 10.1111/codi.13458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Li PY, Yang D, Liu D, et al. Reducing Surgical Site Infection with Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy After Open Abdominal Surgery: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Study. Scand J Surg. 2017;106:189–195. doi: 10.1177/1457496916668681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Shen P, Blackham AU, Lewis S, et al. Phase II Randomized Trial of Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy to Decrease Surgical Site Infection in Patients Undergoing Laparotomy for Gastrointestinal, Pancreatic, and Peritoneal Surface Malignancies. J Am Coll Surg. 2017;224(4):726–737. doi: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2016.12.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Manzoor B, Heywood N, Sharma A. Review of Subcutaneous Wound Drainage in Reducing Surgical Site Infections after Laparotomy. Surg Res Pract. 2015;2015:715803. doi: 10.1155/2015/715803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.De Vries FEE, Wallert ED, Solomkin JS, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis including GRADE qualification of the risk of surgical site infections after prophylactic negative pressure wound therapy compared with conventional dressings in clean and contaminated surgery. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(36):e4673. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Andrade EG, Guerra JJ, Punch L. A Multi-Modal Approach to Closing Exploratory Laparotomies Including High-Risk Wounds. Cureus. 2020;12(7):e9087–e9087. . doi: 10.7759/cureus.9087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Itatsu K, Sugawara G, Kaneoka Y, et al. Risk factors for incisional surgical site infections in elective surgery for colorectal cancer: focus on intraoperative meticulous wound management. Surg Today. 2014;44:1242–1252. doi: 10.1007/s00595-013-0677-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chida K, Watanabe J, Suwa Y, et al. Risk factors for incisional surgical site infection after elective laparoscopic colorectal surgery. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2019;3(2):202–208. doi: 10.1002/ags3.12229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kanda Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software 'EZR' for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013;48:452–458. doi: 10.1038/bmt.2012.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Fukuda H. Patient-related risk factors for surgical site infection following eight types of gastrointestinal surgery. J Hosp Infect. 2016;93(4):347–354. doi: 10.1016/j.jhin.2016.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Morris MS, Graham LA, Chu DI, et al. Oral Antibiotic Bowel Preparation Significantly Reduces Surgical Site Infection Rates and Readmission Rates in Elective Colorectal Surgery. Ann Surg. 2015;261(6):1034–1040. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rasić Z, Schwarz D, Adam VN, et al. Efficacy of antimicrobial triclosan-coated polyglactin 910 (Vicryl* Plus) suture for closure of the abdominal wall after colorectal surgery. Coll Antropol. 2011;35(2):439–443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Seiler CM, Bruckner T, Diener MK, et al. Interrupted or continuous slowly absorbable sutures for closure of primary elective midline abdominal incisions: a multicenter randomized trial (INSECT: ISRCTN24023541) Ann Surg. 2009;249(4):576–582. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e31819ec6c8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pauniaho SL, Lahdes-Vasama T, Helminen MT, et al. Non-absorbable interrupted versus absorbable continuous skin closure in pediatric appendectomies. Scand J Surg. 2010;99(3):142–146. doi: 10.1177/145749691009900308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Coletta D, Del Basso C, Giuliani G, et al. Subcutaneous suction drains do not prevent surgical site infections in clean-contaminated abdominal surgery-results of a systematic review and meta-analysis. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2019;404(6):663–668. doi: 10.1007/s00423-019-01813-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Boland PA, Kelly ME, Donlon NE, et al. Prophylactic negative pressure wound therapy for closed laparotomy wounds: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Ir J Med Sci. 2021;190(1):261–267. doi: 10.1007/s11845-020-02283-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and/or analyzed in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.