Abstract
Introduction
Many countries have reported severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infections in mink, and transmission back to humans has raised the concern of novel variants emerging in these animals. The monitoring system on Polish mink farms detected SARS-CoV-2 infection first in January 2021 and has been kept in place since then.
Material and Methods
Oral swab samples collected between February 2021 and March 2022 from 11,853 mink from 594 farms in different regions of Poland were screened molecularly for SARS-CoV-2. Isolates from those with the highest loads of viral genetic material from positive farms were sequenced and phylogenetically analysed. Serological studies were also carried out for one positive farm in order to follow the antibody response after infection.
Results
SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected in mink on 11 farms in 8 out of 16 Polish administrative regions. Whole genome sequences were obtained for 19 SARS-CoV-2 strains from 10 out of 11 positive farms. These genomes belonged to four different variants of concern (VOC) – VOC-Gamma (20B), VOC-Delta (21J), VOC-Alpha (20I) and VOC-Omicron (21L) – and seven different Pango lineages – B.1.1.464, B.1.1.7, AY.43, AY.122, AY.126, B.1.617.2 and BA.2. One of the nucleotide and amino acid mutations specific for persistent strains found in the analysed samples was the Y453F host adaptation mutation. Serological testing of blood samples revealed a high rate of seroprevalence on the single mink farm studied.
Conclusion
Farmed mink are highly susceptible to infection with SARS-CoV-2 of different lineages, including Omicron BA.2 VOC. As these infections were asymptomatic, mink may become an unnoticeable virus reservoir generating new variants potentially threatening human health. Therefore, real-time monitoring of mink is extremely important in the context of the One Health approach.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, surveillance, mink, whole-genome sequencing, Poland.
Introduction
Since the emergence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in humans, reverse zoonotic transmission has been identified in 23 different animal species in the Americas, Africa, Asia and Europe. Among these species are domestic animals (including cats, dogs and hamsters), farmed animals (mink), wild animals kept in zoos (gorillas, lions, snow leopards and hippopotamuses), and wild animals in their natural habitat (white-tailed deer) (29). The detection of the virus in wildlife populations is particularly alarming (12, 26). Although the exact routes of introduction remain to be determined, the observations raise concern about the establishment of new reservoirs in which SARS-CoV-2 can mutate during repeated passages leading to the emergence of further variants (21). There is also a risk that it could recombine with other species-specific coronaviruses and then spread to other animals or even humans (18).
The American mink (Neovison vison) is the animal species with the highest number of documented individual SARS-CoV-2 introductions and the only non-human species for which SARS-CoV-2 infection was recorded as associated with significant morbidity and mortality (5, 9, 17, 19, 20, 22). Thorough molecular and epidemiological studies in the Netherlands revealed that the virus was transmitted to mink from humans and then spread between mink and spilled back to humans, but that cats and dogs on mink farms were also infected with SARS-CoV-2 (19). Shortly thereafter, a so-called cluster 5 variant was identified on mink farms in Denmark containing a combination of a some number of mutations in the S protein that were considered to threaten the potential efficacy of vaccine-induced antibody therapy (13). Following these observations, all mink farmed in Denmark (>15,000,000) and in the Netherlands were culled (15).
The events in these countries have raised concern about the potential of mink as a SARS-CoV-2 reservoir and source of viral mutations that may thwart medical countermeasures in the global battle against COVID-19. Therefore, international organisations have called for mink to be an animal species monitored for SARS-CoV-2 in order to make early detection of the virus and the taking of appropriate preventive measures possible (8). Since the beginning of the pandemic, the Polish State Veterinary Inspectorate and the laboratories of the National Veterinary Research Institute in Puławy have implemented monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 infections in mink as part of the SARS-CoV-2 elimination programme. This brought about the first detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection in mink in Poland in January 2021 (4). The infected farm was located in the Pomorskie voivodeship in the north of Poland and kept about 5,850 healthy breeder mink. Phylogenetic analysis of full-length nucleotide sequences of two SARS-CoV-2 isolates revealed that they belonged to the B.1.1 Pango lineage. Moreover, subsequent studies revealed SARS-CoV-2 infection in a farm worker, and whole genome sequencing (WGS) identified several mutations in the S gene suspected of adapting the virus to mink. The most probable source of the infection detected in a farm worker was SARS-CoV-2 transmission from mink (23). We report the results of further SARS-CoV-2 monitoring on mink farms in Poland conducted during the 14-month period of February 2021 to March 2022.
Material and Methods
Sample collection. From February 2021 until the end of March 2022, 11,853 oral swabs collected from mink housed on a total of 594 farms located in different regions of Poland were tested. These farms were mainly in the northeastern and central parts of the country, where more than 80% of the Polish mink industry is located. Detailed information on the tested animal farms is provided in Table 1. In abidance with the monitoring rules in the Polish legislation of the time, 20 swabs from any symptomatic mink, supplemented by samples from asymptomatic ones if required, were taken from each farm in 2021. From 2022, EU legislation was adopted and samples were collected for testing according to the scheme in EU Commission Decision 2021/788 (usually the first alternative plan involving sampling of dead or diseased animals). When positive farms were retested after a 90-day quarantine period, swabs from 60 or 90 mink were taken. The samples were collected using dry swabs or swabs with viral transport medium. The swabs were transported to the laboratory at the National Veterinary Research Institute in the shortest possible time under temperature-controlled conditions. Additionally, 60 serum samples from one positive mink farm were included for screening for antibodies against SARS-CoV-2.
Table 1.
Summary of mink farm SARS-CoV-2 monitoring data amassed during a period of 14 months
| Voivodeship | 2021 (February–December) | 2022 (January–March) | Total | Number of positive farms | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of farms | No. of swabs | No. of farms | No. of swabs | No. of farms | No. of swabs | ||
| Mazowieckie | 58 | 1,160 | 28 | 420 | 86 | 1,580 | 0 |
| Podkarpackie | 8 | 160 | 5 | 75 | 13 | 235 | 1 |
| Lubuskie | 35 | 700 | 19 | 295 | 54 | 995 | 0 |
| Wielkopolskie | 117 | 2,340 | 87 | 1,472 | 204 | 3,812 | 1 |
| Zachodniopomorskie | 54 | 1,080 | 8 | 420 | 62 | 1,500 | 3 |
| Pomorskie | 19 | 380 | 1 | 20 | 20 | 400 | 1 |
| Dolnośląskie | 14 | 280 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 280 | 0 |
| Kujawsko-Pomorskie | 24 | 480 | 0 | 0 | 24 | 480 | 1 |
| Lubelskie | 36 | 1,120 | 22 | 356 | 58 | 1,476 | 2 |
| Łódzkie | 6 | 120 | 1 | 15 | 7 | 135 | 1 |
| Małopolskie | 7 | 140 | 1 | 15 | 8 | 155 | 0 |
| Opolskie | 6 | 120 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 120 | 0 |
| Podlaskie | 10 | 200 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 200 | 1 |
| Świętokrzyskie | 6 | 120 | 13 | 185 | 19 | 305 | 0 |
| Warmińsko-Mazurskie | 1 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 20 | 0 |
| Śląskie | 8 | 160 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 160 | 0 |
| Total | 409 | 8,580 | 185 | 3,273 | 594 | 11,853 | 11 |
Molecular and serological tests. Dry swabs were immersed in 1 mL of phosphate-buffered saline (Biomed, Lublin, Poland) and incubated for 30 min at room temperature. Oral swabs immersed in viral transport medium were processed immediately without any pre-treatment. Five swab liquid samples per farm were pooled prior to RNA isolation; however, in the case of a positive result, the samples were retested individually as described below. RNA was extracted manually using the QIAamp Viral RNA Mini Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) following the manufacturer’s protocol or automatically using the IndiMaq Pathogen Kit, for extraction of viral RNA/DNA with an IndiMag 48 magnetic particle processor (Indical Bioscience, Leipzig, Germany). The samples were tested for SARS-CoV-2 RNA presence by a real-time RT-PCR assay with primers and a probe targeting E gene fragments of sarbecoviruses, in the case of positive samples followed by testing by assays targeting N and RdRp gene fragments (3). The QuantiTect Probe RT-PCR Kit (Qiagen) was used for all real-time RT-PCR assays on an ABI 7500 or QuantStudio 6 instrument (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). For serological testing of commercially available serum samples, the INgezim COVID 19 S VET indirect ELISA was utilised (Eurofins-Ingenasa, Madrid, Spain). To confirm positive serological results, virus neutralisation (VN) tests based on pseudovirus were carried out (cPass SARS-CoV-2 Neutralization Antibody Detection Kit; GenScript Biotech., Nanjing, China).
Virus sequencing and analysis. Whole-genome sequencing of SARS-CoV-2 strains detected in June in Wisznice in the Lubelskie voivodeship in eastern Poland was performed at the Erasmus Medical Centre, Rotterdam, the Netherlands with the support of the World Health Organisation. Viral RNA extracted directly from positive throat swab samples was reverse transcribed into cDNA using a Superscript IV First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA). Then the second strand was synthesised with the Klenow fragment of polymerase (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA). The quantity and quality of dsDNA were verified with a Qubit 3.0 fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) and capillary electrophoresis in a 5200 Fragment Analyzer System, (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), respectively. Sequencing libraries were prepared via KAPA HyperPrep with KAPA HyperCap (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Pair-end sequencing (2×150 bp) was performed on a NextSeq 550 System (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) with the Midi V2.5 kit (Illumina). Quality control was carried out using fastp software (2). The reads were deduplicated via the MarkDuplicates Picard tool (https://gatk.broadinstitute.org/hc/en-us/articles/360037052812-MarkDuplicates-Picard-). Sequences were mapped to MN996528.1 (Wuhan-Hu-1) with the Burrows–Wheeler Aligner (16). Sequences of SARS-CoV-2 were analysed with use of online tools: the Nextstrain database (https://nextstrain.org), Pangolin (https://Pangolin.cog-uk.io/), the Global Initiative on Sharing All Influenza Data (GISAID – https://www.gisaid.org/) and the University of California Santa Cruz Genome Browser (https://hgwdev.gi.ucsc.edu/index.html). Phylogenetic analysis, determination of the clade and lineage affiliation of individual virus strains and matching of the most closely related genomes were performed in the GISAID EpiCoV database (https://www.epicov.org/,version 2022-04-05) and verified in Nextstrain (https://clades.nextstrain.org/) databases (v1.14.0).
Results
During the 14-month period, 11,853 samples collected from 594 farms located in different regions of Poland were examined. On average, every farm was examined twice (236 farms registered as active in September 2021, personal information from the State Veterinary Inspectorate) and the largest numbers of farms were examined in the Wielkopolskie, Mazowieckie and Zachodniopomorskie voivodeships, where over 43%, 13% and 10% of all mink farms in Poland are located, respectively. The presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected on 11 farms (Table 1).
These positive farms were located in 8 out of 16 voivodeships (Fig. 1). The highest numbers of positive mink farms were located in Zachodniopomorskie (n = 3) and Lubelskie (n = 2). Taking into account all farms screened and found positive since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, two such farms were also identified in Pomorskie, the detection on the first farm predating the period of this report. In Zachodniopomorskie, all three farms were located in the same county, approximately 10–13 km apart, and were sampled at the same time. On the other hand, the positive farms in Lubelskie were identified six months apart and were more than 85 km distant from each other (Fig. 1). Single SARS-CoV-2–positive mink farms were located in the Podkarpackie, Wielkopolskie, Kujawsko-Pomorskie, Podlaskie and Łódzkie voivodeships. The animals on all these farms were healthy. The number of positive animals and the obtained threshold cycle (Ct) value ranges on individual farms are given in Table 2. The totals of positive animals per house on the farms varied, ranging from 1 to 19–20 minks per 20 tested animals in Wisznice (house 2) in Lubelskie or Zieleniewo in Zachodniopomorskie and Kościuki (Podlaskie) and Ołużna (Zachodniopomorskie) or Janowiec (Podkarpackie), respectively. The Ct values obtained also varied over a wide range. On some farms, they were higher than 30, indicating low viral loads in positive samples (Kościuki in Podlaskie or Wisznice (house 2) in Lubelskie), but on most farms the Ct values were low, indicating an active viraemic state of infection.
Fig. 1.
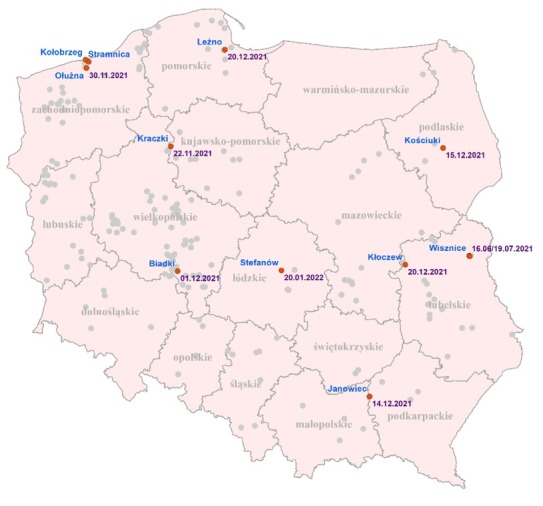
Locations of inspected mink farms (marked as grey dots) and those which were SARS-CoV-2 positive (marked as red dots)
Table 2.
A summary of the analysis of positive mink farms
| rRT-PCR | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No | Date of sample collection | Voivodeship | Location | Positive/Tested | Ct value range* |
| Wisznice (house 1) | 2/20 | 21.8–25.5 | |||
| 1 | 16/06/2021 | Lubelskie | Wisznice (house 2) | 1/20 | 28.9 |
| 2 | 22/11/2021 | Kujawsko-Pomorskie | Kraczki | 1/20 | 28.9 |
| 3 | Zieleniewo1 | 1/20 | 30.5 | ||
| 4 | 30/11/2021 | Zachodniopomorskie | Zieleniewo2 | 13/20 | 24.7–36.8 |
| 5 | Ołużna | 19/20 | 18.9–37.3 | ||
| 6 | 01/12/2021 | Wielkopolskie | Biadki | 18/20 | 17.6–36.4 |
| 7 | 14/12/2021 | Podkarpackie | Janowiec | 20/20 | 28.1–30.4 |
| 8 | 15/12/2021 | Podlaskie | Kościuki | 2/20 | 32.1–35.3 |
| 9 | 20/12/2021 | Pomorskie | Leźno | 10/20 | 19.1–26.3 |
| 10 | 20/12/2021 | Lubelskie | Kłoczew | 5/20 | 28.9–30.2 |
| 11 | 20/01/2022 | Łódzkie | Stefanów | 2/20 | 20.5–21.8 |
Ct – threshold cycle; * – results for E gene rRT-PCR
In compliance with the newly adopted rules, the positive farms were left for observation and tested after 90 days and 104 days for the presence of viral RNA in samples from the animals kept there. During this time, these farms were isolated and closely monitored, as were all contacts with them. Strict biosecurity and hygiene measures were implemented for people in contact with the animals (mandatory use of personal protective equipment (coverings, masks, goggles and gloves), frequent disinfection of tools, hands, etc.). The farms’ owners, workers, and visitors were also tested, regardless of health status, for the presence of SARS-CoV-2. No SARS-CoV-2 RNA was detected in any of the subsequent tests. One of the positive farms was subjected to testing with a shorter interval to monitor the evolution of the outbreak (Wisznice in Lubelskie) (Table 3). Here, the virus could still be detected during the second testing round after one month, but only in one animal house. An ELISA test performed two weeks later showed the presence of specific antibodies in all kittens and in more than 93% of mink dams screened (Table 3). Almost complete concordance between ELISA and VN tests was obtained (one serum negative in the ELISA was positive in the VN test). Interestingly, the serological response to virus infection was visibly stronger in adult than in young animals. The mink on the farm were skinned in late autumn and the mothers were left to breed. The animals in both buildings were then tested repeatedly. None of the biweekly samples collected over a three-month period between January and March 2022 showed the presence of the virus.
Table 3.
Results of oral swab and serum sample analysis collected in two houses in Wisznice in the Lubelskie voivodeship
| House | Date of sample collection | Sample | Number |
Results* | Prevalence (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Collected | Positive | |||||
| 16/06/2021 | 20 | 2 | 21.8–25.5 | 10 | ||
| 1 | 19/07/2021 | Oral swab | 90 | 1 | 28.8 | 1.1 |
| 02/08/2021 | Serum of kitten | 15 | 15 | 1.25 | 100 | |
| Serum of adult | 15 | 14 | 1.64 | 93.3 | ||
| 16/06/2021 | 20 | 2 | 28.5–30.7 | 10 | ||
| 19/07/2021 | Oral swab | 60 | 0 | - | 0 | |
| 2 | Serum of kitten | 15 | 15 | 1.04 | 100 | |
| 02/08/2021 | Serum of adult | 15 | 14 | 1.25 | 93.3 | |
* – results for E gene rRT-PCR/mean OD values obtained using Ingezim ELISA test
Nineteen full-length SARS-CoV-2 genomes of positive samples were successfully obtained and deposited in the GISAID EpiCoV database (www.gisaid.org) (Table 4). In addition, the raw reads from the NextSeq 550 System (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) were deposited in the ENA database. Unfortunately, the sequences of viruses detected in houses 1 and 2 from the second sampling on the farm in Wisznice, and from the Zieleniewo2 farm were not obtained. As shown in Table 4 and Fig. 2, molecular analysis indicates that SARS-CoV-2 isolated from ten Polish mink farms belonged to 4 different lineages – Gamma (GR-20B), Delta (GK-21J), Alpha (GRY-20I) and Omicron (GRA-21L) – and seven different Pango lineages – B.1.1.464, B.1.1.7, AY.43, AY.122, AY.126, B.1.617.2 and BA.2. It should be added that currently B.1.617.2 and BA.2 are variants of concern (VOC) and all of them have been identified as such, although some of them are in the state of de-escalation (B.1.1.7). The most frequently detected lineage was Delta, which included four Pango lineages: AY.43 identified on four farms (two in Zachodniopomorskie and one each in Wielkopolskie and Kujawsko-Pomorskie), AY.122 and AY.126 identified on individual farms in Lubelskie and Podkarpackie, respectively, and B.1.617.2 detected on a farm in Pomorskie. Subsequent clades were represented by single Pango lineages detected on single farms, the Gamma lineage represented by B.1.1.464 (Lubelskie), the Alpha lineage represented by B.1.1.7 (Podlaskie), and the Omicron lineage represented by BA.2 (Łódzkie). When analysing the emergence in Poland of the different lineages over time, it should be noted that the Gamma lineage emerged in June 2021, while the viruses belonging to the Delta lineage emerged between November and December 2021. The next SARS-CoV-2 lineage detected in January 2022 was classified as the Omicron clade. Interestingly, a virus from the Alpha clade was identified in mid-December 2021, while the last detection of the Alpha lineage in Poland in humans was confirmed three months earlier. Admittedly, the Alpha lineage was detected four further times in humans in Poland but the viruses from these cases were genetically distinct from the virus found in mink.
Table 4.
Molecular characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 detected in farmed mink in Poland in the studied period
| No | Mink farm | Gisaid_ID | Clade | Pango lineage | Nucleotide | Frame shifts | Amino acid | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| substit. | delet. | substit. | delet. | ||||||
| 1 | Wisznice, house 2, | EPI_ISL_3218555 | GR/20B | B.1.1 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 0 |
| Lubelskie | EPI_ISL_3218557 | 31 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 0 | |||
| 2 | Kraczki, Kujawsko-Pomorskie | EPI_ISL_7721854 | GK/21J (Delta) | AY.43 | 44 | 13 | 0 | 34 | 4 |
| EPI_ISL_8693906 | 38 | 13 | 0 | 33 | 4 | ||||
| 3 | Ołużna, Zachodniopomorskie | EPI_ISL_8693911 | GK/21J (Delta) | AY.43 | 40 | 14 | 1 | 34 | 4 |
| EPI_ISL_8693912 | 38 | 13 | 0 | 33 | 4 | ||||
| 4 | ZieleniewoZachodniopomorskie 1, | EPI_ISL_8693816 | GK/21J (Delta) | AY.43 | 38 | 13 | 0 | 33 | 4 |
| EPI_ISL_8693913 | 41 | 13 | 0 | 34 | 4 | ||||
| 5 | Biadki, Wielkopolskie | EPI_ISL_8693914 | GK/21J (Delta) | AY.43 | 41 | 13 | 0 | 34 | 4 |
| EPI_ISL_8693915 | 41 | 13 | 0 | 34 | 4 | ||||
| EPI_ISL_9640028 | 51 | 104 | 1 | 37 | 34 | ||||
| 6 | Janowiec, Podkarpackie | EPI_ISL_9640033 | GK/21J (Delta) | AY.126 | 50 | 107 | 1 | 37 | 34 |
| EPI_ISL_9640052 | 50 | 107 | 1 | 37 | 34 | ||||
| 7 | Kościuki, Podlaskie | EPI_ISL_9640055 | GRY/20I (Alpha, V1) | B.1.1.7 | 52 | 37 | 0 | 30 | 11 |
| 8 | Leźno, Pomorskie | EPI_ISL_9640059 | GK/21J (Delta) | B.1.617.2 | 47 | 16 | 0 | 37 | 5 |
| EPI_ISL_9640062 | 45 | 47 | 1 | 36 | 12 | ||||
| 9 | Kłoczew, Lubelskie | EPI_ISL_9640065 | GK/21J (Delta) | AY.122 | 41 | 16 | 0 | 32 | 4 |
| EPI_ISL_10337406 | 74 | 53 | 0 | 51 | 12 | ||||
| 10 | Stefanów, Łódzkie | EPI_ISL_10337127 | GRA/21L (Omicron) | BA.2 | 72 | 53 | 0 | 51 | 12 |
Fig. 2.
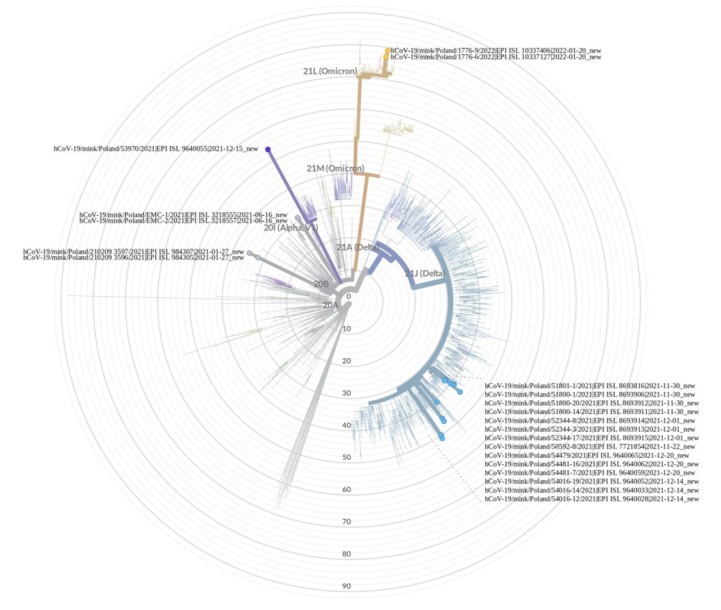
Maximum-likelihood phylogenic tree constructed using the SARS-CoV-2 sequences from all Polish mink farms obtained in this and previous studies. The tree was processed with the Nextclade open source tool (https://clades.nextstrain.org/tree)
Analysis of whole genome SARS-CoV-2 sequences revealed many nucleotide and amino acid mutations compared to the genome sequence of the Wuhan-Hu1 reference strain (NC_045512). A summary of nucleotide and amino acid mutation is given in Tables 4 and 5. The highest numbers of mutations were found in Pango lineage AY.126 Delta clade viruses (Janowiec, Podkarpackie) and lineage BA.2 Omicron clade viruses (72–74 substitutions and 53 deletions), and the lowest in clade GR/20B viruses of June 2021 (only 31 substitutions, no deletions). The Delta clade viruses presented 50–51 substitutions and 104–107 deletions. Most changes were identified within the S protein; however, these changes seemed to be clade-specific. The substitution at position 681 was present in 17 SARS-CoV-2 isolates, albeit with different amino acids substituted in the different clades, P681R in Delta viruses and P681H in Alpha and Omicron viruses. Interestingly, the “mink” mutation at Y453F position was only found in three isolates in two different SARS-CoV-2 lineages: WT and Alpha.
Table 5.
Sequence mutations in SARS-CoV-2 detected in farmed mink in Poland in the studied period
| No | Mink farm | Pango lineage | Nonsynonymous mutations in the S protein in comparison to the Wuhan reference strain |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Wisznice, Lubelskie house 2, | B.1.1 | Q183R, Y453F, K558N, D614G, C1236F |
| 2 | Kraczki, Kujawsko- Pomorskie | AY.43 | T19R, E96A, G142D, R158G, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R, D950N, E156-, F157- |
| 3 | Ołużna, Zachodniopomorskie | AY.43 | T19R, G142D, R158G, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R, D950N, E156-, F157- |
| 4 | Zieleniewo1, Zachodniopomorskie | AY.43 | T19R, G142D, R158G, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R, D950N, E156-, F157- |
| 5 | Biadki, Wielkopolskie | AY.43 | T19R, G142D, R158G, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R, D950N, E156-, F157- |
| 6 | Janowiec, Podkarpackie | AY.126 | T19R, T95I, G142D, R158G, G181V, L452R, T478K, N532S, D614G, P681R, I850L, D950N, K1045N E156-, F157- |
| 7 | Kościuki, Podlaskie | B.1.1.7 | S94F, Y453F, N501Y, A570D, D614G, P681H, T716I, S982A, D1118H H69-, Y144-, H245-, S247-, V70-, L244-, R246-, Y248- |
| 8 | Leźno, Pomorskie | B.1.617.2 | T19R, T95I, G142D, R158G, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R, D950N, E156-, F157- |
| 9 | Kłoczew, Lubelskie | AY.122 | T19R, G142D, R158G, L452R, T478K, D614G, P681R, D950N E156-, F157- |
| 10 | Stefanów, Łódzkie | BA.2 | T19I, A27S, G142D, V213G, G339D, S371F, S373P, S375F, T376A, D405N, R408S, K417N, N440K, S477N, T478K, E484A, Q493R, Q498R, N501Y, Y505H, D614G, H655Y, N679K, P681H, N764K, D796Y, Q954H, N969K L24-, P25-, P26- |
bold – Y453F mutation; italic and bold – D614G mutation; underlined – substitutions in position 681
Subsequently, the GISAID database was searched using the AudacityInstant tool in an analysis performed on 04/05/2022 for the most similar genomes to help to determine the likely source of the mink farms’ infection. Probable sources were determined for five farms (Kraczki, Ołużna, Zieleniewo, Biadki and Janowiec). In these cases, a minimum genetic distance of 0–2 as found by the AudacityInstant tool was observed with human SARS-CoV-2 isolates detected at a given time and in a close location in the same district as the positive mink farm. On the other hand, for three subsequent farms (Leźno, Kłoczew and Stefanów) the identified virus strains with the closest genetic relationships were collected from people in sometimes very distant places, e.g. in Germany, the UK, the Netherlands or even the USA. In the cases of the two SARS-CoV-2 strains identified on the farm in Wisznice and Kościuki, even the most permissive parameters of the search criterion did not detect related genomes. It should be noted, however, that in the period from the beginning of the pandemic to the end of March 2022, there were 82,146 SARS-CoV-2 sequences from Poles in the GISAID database (including 29,341 Delta and 13,463 Alpha variants). In comparison, in the Netherlands, a country 7.5 times smaller and 2.1 times less populous than Poland, the total of all sequences was 115,614 (44,741 Delta and 28,115 Alpha variants). Thus, it seems that the number of human samples tested in Poland may not reflect the real epidemiological situation, and the search for the origin of these viruses may yield a misleading answer.
Discussion
In this report we describe the findings of the SARS-CoV-2 surveillance of mink farms in Poland conducted during a 14-month period. With the culling of all mink in Denmark and the Netherlands, Poland has become the leading producer of mink in Europe and the second in the world after China, although it should be noted that the COVID-19 pandemic has stifled mink production in Poland, as only 236 farms were active in August 2021 compared to 350 farms at the end of 2019. Reports on the possibility of SARS-CoV-2 infection in animals, but especially reports from several countries concerning the spread of SARS-CoV-2 between mink on farms as well as human-to-animal and animal-to-human transmission alerted the Polish veterinary services to the danger. Since the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, the State Veterinary Inspectorate in Poland has been monitoring the SARS-CoV-2 infection situation in animals, paying particular attention to farmed mink (6, 10), doing so by means of the SARS-CoV-2 detection and analysis system implemented at the National Veterinary Research Institute in Puławy. In October 2020, a pilot study of SARS-CoV-2 presence in mink populations was undertaken in areas with a high density of breeding farms (Wielkopolskie, Lubuskie, Mazowieckie and Podkarpackie). In the following months, monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 infections on mink farms was introduced, through the issuance of relevant ordinances by the Polish Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Development detailing the principles of surveillance of the country’s mink farms (11). Changes in these regulations resulted from new scientific reports on SARS-CoV-2 infections in animals of this species and also took into account EU legislation (7, 8). The monitoring rules in place resulted in the detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection on 12 farms.
The first infection reported earlier and not included in this study occurred in January 2021 on a farm in Leźno (Pomorskie) (4). According to the current Pango classification, the strains detected were the B.1.1.464 Gamma lineage (amended from the B.1.1.279 lineage defined in March 2021). This farm had already been diagnosed in November 2020 in a study outside the official monitoring of infections with SARS-CoV-2 in mink (24). A subsequent epidemiological investigation resulted in the detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection in one of the farm’s employees, and based on thorough molecular testing, the detected virus was determined to be of mink origin (23). This is the third report of the spillover of viral infections from mink to humans, following reports from the Netherlands and Denmark (13, 19). As required under the legislation enforced at that time in Poland, all animals on the farm were culled in February 2021. Further SARS-CoV-2–infected farms were identified at 11 locations as monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 infections continued. One of them was detected in the Leźno region again on 20 December, 2021, i.e. one year after the first infection. Both positive farms were located a few kilometres from each other and the owners were in the same family. However, the virus detected in December belonged to the Delta lineage (lineage B.1.1.617.2), indicating that this was a new introduction from the human population. Detection of a subsequent infection on a farm in the same locality indicated inadequate implementation of the biosecurity system, despite previous infections in the area. Of the three consecutive Delta variant lineages, the same one – AY.43 – was identified on four farms, two in Zachodniopomorskie and one each in Wielkopolskie and
Kujawsko-Pomorskie. The farms in Zachodniopomorskie were in close proximity to each other (a few kilometres) and while no direct links were shown, they cannot be completely ruled out and may possibly have been feral cats, escaped mink or other animals. On the other hand, two other farms infected with this virus lineage were 160 km apart and at a distance of 350 km from the two farms in Zachodniopomorskie, and no links to other farms were identified.
As in the rest of the world, the Delta variant viruses were dominant in Poland’s human patients from June to almost the end of December (https://mocos.pl/pl/variants.html). According to the GISAID database, the Pango lineage B.1.1.617.2 VOC strains were some of the dominant variants causing human disease in Poland with a cumulative count of approximately 2,250 sequences. Most variants detected on Polish mink farms in December also belonged to the Delta lineage, namely AY.122, AY.126 and AY.43, which are all regarded as VOC. These SARS-CoV-2 variants were also dominant in Poland in people in this period, with cumulative counts of 4,177, 853 and 3,192 sequences, respectively. Moreover, a GISAID database search for the most related genomes found them at an appropriate time in a close location, i.e. in the same area as the one associated with a positive mink farm. Additionally, the genetic distance between these SARS-CoV-2 strains identified in mink and humans was 0, which means 100% identical sequences.
In samples collected in Kościuki (Podlaskie) on 15 December, 2021, the detected strain belonged to the Alpha virus B.1.1.7. This Alpha variant emerged in September 2020 and was originally treated as a VOC because of increased disease transmissibility and severity, but it is now considered a de-escalated variant, the circulation of which in the EU has significantly reduced. Although the number of strains of this variant identified recently in Poland has also definitely decreased and other mainly Delta-clade VOCs have overtaken it, its detection level in Poland seems to be high. Interestingly, no similar sequence to that detected in mink was found in the GISAID database. The reason for this may be that not all human infections are reported to medical services. This implies that the search for the origin of SARS-CoV-2 in mink may yield a misleading answer. Only scaling up of human sampling and deep analysis of sample isolates can take epidemiological investigations forward, which is why the One Health approach is important. However, it also cannot be ruled out that the infection occurred earlier, when this virus variant was prevalent in humans, and persisted on a mink farm for almost a year. A similar situation was recently suggested in deer in Michigan (18). This may also suggest insufficient sensitivity in the ongoing monitoring of virus infection in mink. Perhaps the introduction of additional serological tests having a longer window of detection would allow identification of older SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The last SARS-CoV-2 isolates identified in Polish farmed mink in January 2022 belong to the Omicron clade and Pango lineage BA.2. The detection of the Omicron VOC in animals is of particular importance. Some mutations in the Omicron spike protein seem to be associated with adaptation in mice and, based on in silico investigations, it has been suggested that this clade of viruses evolved in mice before spilling back into humans (28). The detection of Omicron strains in Polish farmed mink is the first such to be reported in animals. Another Omicron virus was identified in deer on New York’s Staten Island in February 2022, and this is in turn the first time the strain has been found in a wild animal (27). Therefore, the Advisory Group of the World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) encourages the surveillance of potential hosts for SARS-CoV-2 infection and continuous monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 mutations in animals. Such studies have allowed the identification of different SARS-CoV-2 variants in deer populations in the USA and Canada and in hamsters in Hong Kong.
In this study, mink SARS-CoV-2 infections were traced back to dominant variants in human samples during the COVID-19 epidemic in Poland, but one of the Alpha variants was detected many months after the epidemic’s peak. Careful tracing of the S protein amino acid sequences of the strains identified in mink showed that only mutations specific to individual SARS-CoV-2 variants were observed. A low number of mutations were found in some strains, and they were mutations which had previously been detected in other mink samples and were indicated to be possibly related to adaptation from the human to the mink ACE2 receptor (1, 14, 17, 26). The Y453F mutation was identified in only three strains, while the F486L and F452M mutations were not found. In contrast, a change was identified at position 501 of the S protein in three strains, but it was an N to Y change rather than an N to T change, a feature that likely increases the affinity for mink.
The only serological tests carried out on the farm in Wisznice revealed that almost all mink showed SARS-CoV-2 specific antibodies, and the absence of the virus in sporadic samples collected after this time point suggested effective elimination of the virus from the body and from the herds. The stronger serological response observed in dams than in kittens could be a consequence of a more mature immune system or a more extensive infection, similar to what has been observed in humans. Subsequent tests over several months also failed to detect the presence of the virus, unlike the reprised tests on the only surviving farm in Denmark, where a second round of infection was observed (25).
In conclusion, farmed mink are highly susceptible to infection with SARS-CoV-2 belonging to different clades and lineages. Although we found SARS-CoV-2 on several different mink farms in the same region, we did not observe transmission of the virus from one farm to another, in contrast to what has been observed in the Netherlands, for instance. This indicates that the biosecurity controls put in place have been effective. Only a few Polish mink isolates of the virus possessed molecular features in the S protein which potentially increased the virus’ affinity to mink. The infections identified on farms in Poland were asymptomatic. One mink farm was infected with a variant that was prevalent in humans more than a year earlier, which may suggest the persistence of the infection over a long period of time. This in turn confirms that mink may become a virus reservoir generating new, potentially dangerous variants. Only continuous monitoring of these farms allows rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 infections; however, it seems the surveillance strategy might have to be strengthened and additional serology included.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Agnieszka Stolarek for her help in designing the map with the locations of the mink farms. The raw reads from the WGS performed at the Erasmus Medical Centre, Rotterdam, the Netherlands have been deposited in the ENA under accession numbers ERS13444963 and ERS13444964. The rest of WGS results have been deposited in a common bioproject under the number PRJEB56174 (accession numbers ERS13476009-ERS13476025).
Footnotes
Conflict of Interest
Conflict of Interests Statement: The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this article.
Financial Disclosure Statement
This study was funded by the financial resources of the National Veterinary Research Institute, Puławy, Poland. Additionally, the study was also supported by funding from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation programme under grant agreement No. 773830: One Health European Joint Programme COVRIN, 2018-2022 science funding awarded for an international project co-financed by the Ministry of Education and Science, Poland.
Animal Rights Statement
Sampling was carried out by State Veterinary Inspectorate officers, who took samples in the ambit of veterinary inspection as legislated and with the permission of the farms’ owners. For this reason. sampling did not require the approval of an ethics committee.
References
- 1.Burkholz S., Pokhrel S., Kraemer B.R., Mochly-Rosen D., Carback R.T., Hodge T., Harris P., Ciotlos S., Wang L., Herst C.V., Rubsamen R.. Paired SARS-CoV-2 spike protein mutations observed during ongoing SARS-CoV-2 viral transfer from humans to minks and back to humans. Infect Genet Evol. 2021;93:104897. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104897.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chen S., Zhou Y., Chen Y., Gu J.. fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics. 2018;34:i884–i890. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Corman V.M., Landt O., Kaiser M., Molenkamp R., Meijer A., Chu D.K.W., Bleicker T., Brünink S., Schneider J., Schmidt M.L., Mulders D.G.J.C., Haagmans B.L., van der Veer B., van den Brink S., Wijsman L., Goderski G., Romette J.-L., Ellis J., Zambon M., Peiris M., Goossens H., Reusken C., Koopmans M.P.G., Drosten C.. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill. 2020;25:2000045. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.200004.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Domańska-Blicharz K., Orłowska A., Smreczak M., Niemczuk K., Iwan E., Bomba A., Lisowska A., Opolska J., Trębas P., Potyrało P., Kawiak-Sadurska M., Rola J.. Mink SARS-CoV-2 infection in Poland – short communication. J Vet Res. 2021;65:1–5. doi: 10.2478/jvetres-2021-0017.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Eckstrand C.D., Baldwin T.J., Rood K.A., Clayton M.J., Lott J.K., Wolking R.M., Bradway D.S., Baszler T.. An outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 with high mortality in mink (Neovison vison) on multiple Utah farms. PLoS Pathog. 2021;17:e1009952. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009952.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2020/2183 of 21 December 2020 concerning certain protective measures in relation to reporting infection with SARS-CoV-2 in minks and other animals of the family Mustelidae and in raccoon dogs. OJEU. 2020:L433. European Commission. 22/12/2020, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Commission Implementing Decision (EU) 2021/788 of 12 May 2021 laying down rules for the monitoring and reporting of infections with SARS-CoV-2 in certain animal species. OJEU. 2021:L173. European Commission. 17/5/2021, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Boklund A., Gortázar C., Pasquali P., Roberts H., Nielsen S.S., Stahl K., Stegeman A., Baldinelli F., Broglia A., Van Der Stede Y., Adlhoch C., Alm E., Melidou A., Mirinaviciute G.. Monitoring of SARS-CoV-2 infection in mustelids. EFSA J. 2021;19:e06459. doi: 10.2903/j.efsa.2021.6459.. European Food Safety Authority, European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fenollar F., Mediannikov O., Maurin M., Devaux C., Colson P., Levasseur A., Fournier P.-E., Raoult D.. Mink, SARS-CoV-2, and the Human-Animal Interface. Front Microbiol. 2021;12 doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.663815.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Rozporządzenie Ministra Rolnictwa i Rozwoju Wsi z dnia 4 grudnia 2020 r. zmieniające rozporządzenie w sprawie określenia jednostek chorobowych, sposobu prowadzenia kontroli oraz zakresu badań kontrolnych zakażeń zwierząt (Decree by the Minister of Agriculture and Rural Development of 4 December 2020 amending the decree on definitions of diseases, the means of conducting surveillance of them and the scope of screening tests for infections in animals – in Polish). Dz. U. z dnia 4 grudnia 2020, poz. 2162 (Official Journal of Laws of 4 December2020, item 2162) Government of the Republic of Poland.
- 11.Rozporządzenie Ministra Rolnictwa i Rozwoju Wsi z dnia 24 listopada 2021 r. zmieniające rozporządzenie w sprawie określenia jednostek chorobowych, sposobu prowadzenia kontroli oraz zakresu badań kontrolnych zakażeń zwierząt (Decree by the Minister of Agriculture and Rural Development of 24 November 2021 amending the decree on definitions of diseases, the means of conducting surveillance of them and the scope of screening tests for infections in animals – in Polish). Dz.U z dnia 3 grudnia 2021, poz. 2237 (Official Journal of Laws of 3 December 2021, item 2237) Government of the Republic of Poland.
- 12.Hale V.L., Dennis P.M., McBride D.S., Nolting J.M., Madden C., Huey D., Ehrlich M., Grieser J., Winston J., Lombardi D., Gibson S., Saif L., Killian M.L., Lantz K., Tell R.M., Torchetti M., Robbe-Austerman S., Nelson M.I., Faith S.A., Bowman A.S.. SARS-CoV-2 infection in free-ranging white-tailed deer. Nature. 2022;602:481–486. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04353-x.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hammer A.S., Quaade M.L., Rasmussen T.B., Fonager J., Rasmussen M., Mundbjerg K., Lohse L., Strandbygaard B., Jørgensen C.S., Alfaro-Núñez A., Rosenstierne M.W., Boklund A., Halasa T., Fomsgaard A., Belsham G., Bøtner A.. SARS-CoV-2 Transmission between Mink (Neovison vison) and Humans, Denmark. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021;27:547. doi: 10.3201/eid2702.203794.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hoffmann M., Zhang L., Krüger N., Graichen L., Kleine-Weber H., Hofmann-Winkler H., Kempf A., Nessler S., Riggert J., Winkler M.S., Schulz S., Jäck H.-M., Pöhlmann S.. SARS-CoV-2 mutations acquired in mink reduce antibody-mediated neutralization. Cell Rep. 2021;35:109017. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109017.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Larsen H.D., Fonager J., Lomholt F.K., Dalby T., Benedetti G., Kristensen B., Urth T.R., Rasmussen M., Lassaunière R., Rasmussen T.B., Strandbygaard B., Lohse L., Chaine M., Møller K.L., Berthelsen A.-S.N., Nørgaard S.K., Sönksen U.W., Boklund A.E., Hammer A.S., Belsham G.J., Krause T.G., Mortensen S., Bøtner A., Fomsgaard A., Mølbak K.. Preliminary report of an outbreak of SARS-CoV-2 in mink and mink farmers associated with community spread, Denmark, June to November 2020. Eurosurveillance. 2021;26:2100009. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2021.26.5.210009.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Li H., Durbin R.. Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:589–595. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp698.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lu L., Sikkema R.S., Velkers F.C., Nieuwenhuijse D.F., Fischer E.A.J., Meijer P.A., Bouwmeester-Vincken N., Rietveld A., Wegdam-Blans M.C.A., Tolsma P., Koppelman M., Smit L.A.M., Hakze-van der Honing R.W., van der Poel W.H.M., van der Spek A.N., Spierenburg M.A.H., Molenaar R.J., de Rond J., Augustijn M., Woolhouse M., Stegeman J.A., Lycett S., Oude Munnink B.B., Koopmans M.P.G.. Adaptation, spread and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in farmed minks and associated humans in the Netherlands. Nat Commun. 2021;12:6802. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-27096-9.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mallapaty S.. Could deer become a natural Covid reservoir? Nature. 2022;604:612–615. doi: 10.1038/d41586-022-01112-4.. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Munnink B.B.O., Sikkema R.S., Nieuwenhuijse D.F., Molenaar R.J., Munger E., Molenkamp R., van der Spek A.N., Tolsma P., Rietveld A., Brouwer M., Bouwmeester-Vincken N., Harders F., Honing R.H.-v.d., Wegdam-Blans M.C.A., Bouwstra R.J., GeurtsvanKessel C., van der Eijk A.A., Velkers F.C., Smit L.A.M., Stegeman A., van der Poel W.H.M., Koopmans M.P.G.. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 on mink farms between humans and mink and back to humans. Science. 2021;371:172–177. doi: 10.1126/science.abe5901.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Oreshkova N., Molenaar R.J., Vreman S., Harders F., Oude Munnink B.B., Hakze-van der Honing R.W., Gerhards N., Tolsma P., Bouwstra R., Sikkema R.S., Tacken M.G., de Rooij M.M., Weesendorp E., Engelsma M.Y., Bruschke C.J., Smit L.A., Koopmans M., van der Poel W.H., Stegeman A.. SARS-CoV-2 infection in farmed minks, the Netherlands, April and May 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020;25 doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.es.2020.25.23.2001005.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pickering B., Lung O., Maguire F., Kruczkiewicz P., Kotwa J.D., Buchanan T., Gagnier M., Guthrie J.L., Jardine C.M., Marchand-Austin A., Massé A., McClinchey H., Nirmalarajah K., Aftanas P., Blais-Savoie J., Chee H.-Y., Chien E., Yim W., Goolia M., Suderman M., Pinette M., Smith G., Sullivan D., Rudar J., Adey E., Nebroski M., Côté M., Laroche G., McGeer A.J., Nituch L., Mubareka S., Bowman J. Highly divergent white-tailed deer SARS-CoV-2 with potential deer-to-human transmission. bioRxiv. 2022. 2022.02.22.481551, doi. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 22.Pomorska-Mól M., Włodarek J., Gogulski M., Rybska M.. Review: SARS-CoV-2 infection in farmed minks – an overview of current knowledge on occurrence, disease and epidemiology. Animal. 2021;15:100272. doi: 10.1016/j.animal.2021.100272.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rabalski L., Kosinski M., Mazur-Panasiuk N., Szewczyk B., Bienkowska-Szewczyk K., Kant R., Sironen T., Pyrc K., Grzybek M.. Zoonotic spill-over of SARS-CoV-2: mink-adapted virus in humans. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2022;28:451. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2021.12.001.. e1–451.e4, [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Rabalski L., Kosinski M., Smura T., Aaltonen K., Kant R., Sironen T., Szewczyk B., Grzybek M.. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Farmed Mink (Neovison vison), Poland. Emerg Infect Dis. 2021;27:2333–2339. doi: 10.3201/eid2709.210286.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rasmussen T.B., Fonager J., Jørgensen C.S., Lassaunière R., Hammer A.S., Quaade M.L., Boklund A., Lohse L., Strandbygaard B., Rasmussen M., Michaelsen T.Y., Mortensen S., Fomsgaard A., Belsham G.J., Bøtner A.. Infection, recovery and re-infection of farmed mink with SARS-CoV-2. PLoS Pathog. 2021;17:e1010068. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010068.. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tan C.C.S., Lam S.D., Richard D., Owen C., Berchtold D., Orengo C., Nair M.S., Kuchipudi S.V., Kapur V., van Dorp L., Balloux F. Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 from humans to animals and potential host adaptation. bioRxiv. 2022. 2020.11.16.384743, doi. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 27.Vandegrift K.J., Yon M., Surendran-Nair M., Gontu A., Amirthalingam S., Nissly R.H., Levine N., Stuber T., DeNicola A.J., Boulanger J.R., Kotschwar N., Aucoin S.G., Simon R., Toal K., Olsen R.J., Davis J.J., Bold D., Gaudreault N.N., Richt J.A., Musser J.M., Hudson P.J., Kapur V., Kuchipudi S.V. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) infection of white-tailed deer. bioRxiv. 2022. 2022.02.04.479189, doi. [DOI]
- 28.Statement from the Advisory Group on SARS-CoV-2 Evolution in Animals concerning the origins of the Omicron variant. World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE); Paris: 2022. World Organisation for Animal Health. [Google Scholar]
- 29.SARS-CoV-2 in animals – Situation Report 12. World Organisation for Animal Health (OIE) Paris: 2022. World Organisation for Animal Health. [Google Scholar]


