Abstract
Objective
This study investigated the diagnostic performance of endobronchial ultrasound with Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra (Ultra) for detecting smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis (TB).
Methods
143 patients suspected of sputum smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis were enrolled in this study in Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, China. These patients underwent endobronchial ultrasound with a guide sheath (EBUS-GS) or endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) based on their chest CT manifestations. We assessed the sensitivity and specificity of tissue specimens with Ultra in the TB group and non-TB group. Culture and clinical diagnosis were used as gold-standard for TB.
Results
Among these 143 patients, 11 patients were culture-positive TB, 85 patients were diagnosed with culture-negative TB and 47 were with the non-TB diseases. Direct testing with microscopy (Acid-Fast Bacilli smear, AFB), liquid culture, pathology, Xpert MTB/RIF(Xpert) test and Ultra had a sensitivity of 8.3%, 11.5%, 42.7%, 64.6%, and 78.1% individually among all the TB patients. Ultra had a higher sensitivity than Xpert (P = 0.011). But Ultra had a specificity of 59.6% (95% CI 44.3–73.3), lower than that of Xpert (89.4%, 95% CI 76.1–96.0, P = 0.001). Ultra had the same sensitivity on specimens from EBUS-TBNA and EBUS-GS (P = 0.975). Ultra’s positive predictive value and negative predictive value were 79.8% and 57.1% respectively.
Conclusions
Tissue specimens from interventional bronchoscopy combined with Ultra provide a sensitive method for diagnosing smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis, but its specificity was lower than Xpert.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s12879-023-08073-7.
Keywords: Pulmonary tuberculosis, Smear-negative, Bronchoscopy, Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra
Background
As early as 2011, World Health Organization (WHO) issued a policy recommendation on using the Xpert MTB/RIF assay [1]. Xpert MTB/RIF was recommended by WHO as an initial diagnostic test in all adults suspected of having TB rather than conventional microscopy and culture in 2013 [2]. This test has greatly improved the diagnosis of tuberculosis globally. To further improve its sensitivity, Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra incorporates two different multi-copy amplification targets (IS6110 and IS1081) and has a larger DNA reaction chamber. Thus the limit of detection of tuberculosis reduces from 114 bacterial colony forming units (cfu) for Xpert MTB/RIF to 16 cfu per ml for Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra [3]. This is especially beneficial to smear-negative culture-positive tuberculosis patients as Ultra achieved the highest sensitivity increase in this group (+ 17%, 95% CI + 10, + 25) [3].
The bacteriologically confirmed pulmonary TB rate was 58% in China, lower than the average rate of 63% worldwide in 2021 [4]. However, more than one third of suspected TB patients cannot produce sufficient sputum for diagnosis [5]. Endobronchial ultrasound with biopsy techniques like EBUS-GS [6] and EBUS-TBNA [7] can play an important role in the collection of enough tissue specimens for TB diagnosis.
In this study, we combined the endobronchial ultrasound methods with Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra to evaluate their detection ability in smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis (PTB).
Methods
Study population
This was a single-center, prospective, diagnostic accuracy study. Participants were enrolled from September 2018 to December 2019 in Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, one of the top tuberculosis hospitals in China. Inclusion criteria: (1) Suspicion of pulmonary tuberculosis (with symptoms and radiological examination outcomes); (2) No contraindication for bronchoscopy; (3) Sputum smear negative twice; (4) Chest CT showed pulmonary lesions that could take tissue specimens by EBUS-TBNA or EBUS-GS; (5) HIV negative.
Bronchoscopy sampling
Patients with bronchial signs in the lesions were treated with EBUS-GS. They underwent bronchoscope to access the lesion via the planned path. After the lesion site was confirmed by an ultrasound probe through the guide sheath, the probe was removed. A forcep was inserted through the guide sheath to collect enough specimens. Then we brushed for the AFB test. EBUS-TBNA was performed on patients who had enlargement of mediastinal or hilar lymph nodes or centrally located peribronchial lesions. We used a curvilinear ultrasound bronchoscope (Olympus BF-UC 260 FW) to locate the lesion or lymph node and then punctured three times with a 22 gauge needle to aspirate enough specimens.
AFB, culture, Xpert, Ultra and pathological examination
Both pathological and microbiological (AFB smear, culture, Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra) tests were conducted. Each biopsy specimen was fixed in formalin, embedded, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin for pathological examination. Brushing and aspiration smears were prepared and stained with the Ziehl–Neelsen method [6]. The results were graded as negative or positive (scanty, 1+, 2+, 3+, 4+). The rest of the samples were ground and homogenized with PBS buffer. After centrifugation and resuspended the sediments in 2 ml PBS buffer via vortexing. Part of the specimens was used for liquid culture (BACTEC MGIT, Becton Dickinson, Cockeysville, MD, USA). The supernatant of the culture-positive strain was tested by MPT64 antigen detection (SD Bioline Kit, Standard Diagnostics, Korea) [8] to rule out nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) infection. The remaining specimens were used for Xpert MTB/RIF (Cepheid, USA) [9] and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra (Cepheid, USA) [10] according to the manufacturer’s instructions. GeneXpert sample reagent was added to the remaining specimen, vortexed and incubated at room temperature for 15 min. Then the digested sample was transferred to one Xpert and one Ultra cartridge and loaded onto instruments. The results of the detection of MTB can be automatically generated by instruments.
Diagnosis and grouping
Culture and clinical diagnosis were used as gold-standard for TB. Patients were divided into three categories for analysis according to their diagnosis: those with culture-positive pulmonary tuberculosis (culture-positive TB); those with culture-negative pulmonary tuberculosis who had improvement with anti-tuberculous treatment based on clinical and radiologic findings (culture-negative TB); and those with no evidence of TB and diagnosed with other pulmonary diseases based on pathological and laboratory findings (non-TB). Smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis was defined as two sputum smear negative. The histopathological diagnosis criteria for TB was granuloma with cheesy necrosis. Patients were all followed-up in the outpatient department to correct diagnosis.
Statistical method
The median and range were calculated to determine the study population. The χ2 test, Fisher test, and t-test were used to verify whether there were significant differences between enrolled TB patients and non-TB patients. Two-sided P value < 0.05 was set as statistically significant. For binomial distribution data, we used 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) to report the number of positive samples and the corresponding proportion. All analysis and graphs were performed by SPSS® 26.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) and prism 7.0 software (Graphpad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA).
Results
Patients
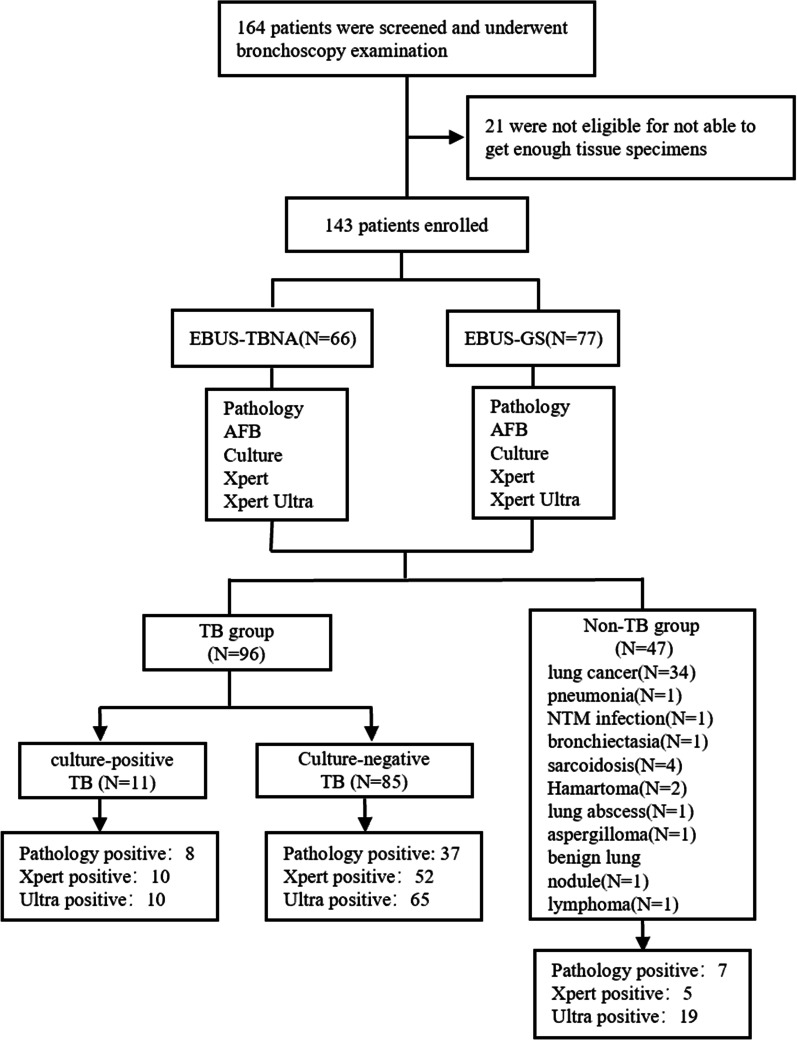
A total of 164 smear-negative patients with suspected smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis were screened in this study (Fig. 1). 21 were excluded for not able to get tissue specimens by EBUS-TBNA or EBUS-GS. Then 143 patients enrolled in the final analysis. Among these patients, 96 (67.1%) were diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis (TB group); In the TB group, 11 patients were culture-positive TB and 85 patients were diagnosed with culture-negative TB; 47 (32.9%) were in the non-TB group. The TB group had 50 (50.1%) patients undergo EBUS-TBNA while the non-TB group had 16 (34.0%) patients to do the same test.
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram of the study population
The demographic characteristics of both groups were showed in Table 1. We collected demographic information of both groups, including: sex, age, tuberculosis history, T-SPOT.TB (T-SPOT) result, complication, and chest CT manifestation. Among all the enrolled patients, 56.6% were males. The age range was from 11 to 82 years old with a median of 45 years old. The TB group was younger than the non-TB group (33.5 vs 56, P = 0.000). The tuberculosis history and complication were no difference between these two groups. But the TB group had a higher rate of T-SPOT positive results (86.4% vs 22.5%, P = 0.000) and fever symptoms (24.0% vs 8.7%, P = 0.027). The differences were also seen in the imaging findings. The non-TB group tended to have lesions in single lobe (70.2% vs 46.9%, P = 0.008) and have less shadow in the CT scan (25.5% vs 74.0%, P = 0.000).
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics of the TB group and non-TB group
| Clinical characteristics | All patients (N = 143) | TB group (N = 96) | Non-TB group (N = 47) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, male (no, %) | 81 (56.6) | 55 (57.3) | 26 (55.3) | 0.823 |
| Age, median (range) | 45 (11–82) | 33.5 (16–82) | 56 (11–74) | 0.000 |
| Had tuberculosis history | 12 (8.4) | 5 (5.2) | 7 (14.9) | 0.06 |
| T-spot positive (no/total no, %) | 85/126 (67.5) | 76/86 (86.4) | 9/40 (22.5) | 0.000 |
| Complication (no, %) | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 5 (3.5) | 4 (4.2) | 1 (2.1) | 1.000 |
| Chronic respiratory diseasesa | 3 (2.1) | 1 (1.0) | 2 (4.3) | 0.251 |
| Symptoms (no, %) | ||||
| Cough | 59 (41.3) | 39 (40.6) | 20 (42.6) | 0.826 |
| Hemoptysis | 8 (5.6) | 4 (4.2) | 4 (8.5) | 0.288 |
| Fever | 27 (18.9) | 23 (24.0) | 4 (8.7) | 0.027 |
| Range of lung lesions | 0.008 | |||
| In single lobe | 78 (54.5) | 45 (46.9) | 33 (70.2) | |
| In multiple lobes | 65 (45.5) | 51 (53.1) | 14 (30.0) | |
| Chest CT manifestation | ||||
| Nodule | 113 (79.0) | 74 (77.1) | 39 (83.0) | 0.416 |
| Cavitation | 11 (7.7) | 7 (7.3) | 4 (8.5) | 0.797 |
| Shadow | 83 (58.0) | 71 (74.0) | 12 (25.5) | 0.000 |
aChronic respiratory diseases included chronic bronchitis, asthma, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
The common side effects of bronchoscopy are airway bleeding and fever which occurred in 12 (8.4%) cases and 3 (2.1%) cases separately.
Diagnostic performance of AFB, culture, pathology, Xpert and Ultra
Among 11 culture-positive TB, Ultra detected positive results in 10 cases (90.9%), the same sensitivity as Xpert. Among all the 96 smear-negative TB patients, EBUS-TBNA and EBUS-GS combined had reached an AFB positive rate of 8.3% (8/96) and a culture positive rate of 11.5% (11/96) (Table 2). The pathological diagnosis provided by tissue specimens had a higher positive rate of 42.7%, and its specificity was 85.1%. The Xpert positive rate on the tissue specimen was 64.6%, and its specificity was 89.4%. Ultra had the highest sensitivity of 78.1% among these methods, statistically higher than Xpert (P = 0.011). But its specificity was the lowest (59.6%), statistically lower than Xpert (P = 0.001). Ultra’s positive predictive value and negative predictive value were 79.8% and 57.1% respectively.
Table 2.
The diagnostic performance of AFB, culture, pathological examination, Xpert and Ultra, using culture or final diagnosis as gold-standard
| Method | % (correct no./total no.) 95% CI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV | ||
| For culture-positive TB patients (n = 11) | AFB |
63.6 (7/11) 31.6–87.6 |
100 (47/47) 90.6–100 |
100 (7/7) 56.1–100 |
92.2 (47/51) 80.3–97.5 |
| Pathology |
72.7 (8/11) 39.3–92.7 |
85.1 (40/47) 71.1–93.3 |
53.3 (8/15) 27.4–77.8 |
93.0 (40/43) 79.9–98.2 |
|
| Xpert |
90.9 (10/11) 57.1–99.5 |
89.4 (42/47) 76.1–96.0 |
66.7 (10/15) 38.7–87.0 |
97.7 (42/43) 86.2–99.9 |
|
| Ultra |
90.9 (10/11) 57.1–99.5 |
59.6 (28/47) 44.3–73.3 |
34.5 (10/29) 18.6–54.3 |
96.6 (28/29) 80.4–99.8 |
|
| For culture-positive and negative TB patients (n = 96) | AFB |
8.3 (8/96) 3.9–16.2 |
100 (47/47) 90.6–100 |
100 (8/8) 59.8–100 |
34.8 (47/135) 27.0–43.5 |
| Culture |
11.5 (11/96) 6.1–20.0 |
100 (47/47) 90.6–100 |
100 (11/11) 67.9–100 |
35.6 (47/132) 27.6–44.5 |
|
| Pathology |
42.7 (41/96) 32.8–53.2 |
85.1 (40/47) 71.1–93.3 |
85.4 (41/48) 72.8–92.8 |
42.1 (40/95) 32.2–52.7 |
|
| Xpert |
64.6 (62/96)a 54.1–73.9 |
89.4 (42/47) 76.1–96.0 |
92.5 (62/67) 86.1–99.0 |
55.3 (42/76) 43.8–66.7 |
|
| Ultra |
78.1 (75/96)a 68.3–85.7 |
59.6 (28/47) 44.3–73.3 |
79.8 (75/94) 71.5–88.1 |
57.1 (28/49) 42.8–71.5 |
|
SE sensitivity, SP specificity, PPV positive predictive value, NPV negative predictive value
aMcNemar test P = 0.011 (Ultra vs. Xpert)
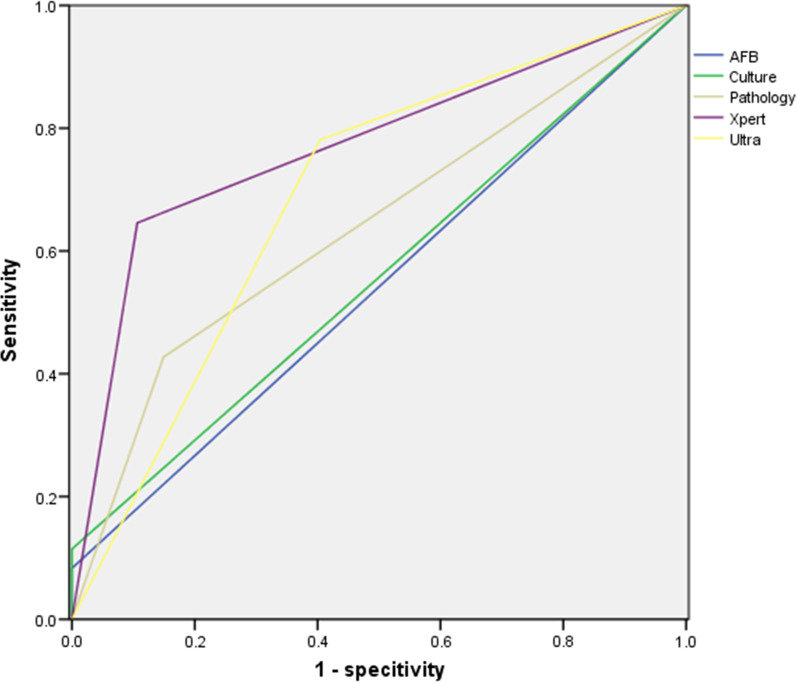
The corresponding receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves for AFB, culture, pathology, Xpert and Ultra on tissue specimen are shown in Fig. 2. The areas under the curve (AUC) for AFB, culture, pathology, Xpert and Ultra were 0.542, 0.557, 0.639, 0.770 and 0.688.
Fig. 2.
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of AFB, culture, pathology, Xpert and Ultra on tissue specimens
Comparison of detection rates among specimens from EBUS-TBNA and EBUS-GS by Ultra
There was no significant difference in the diagnostic performance of Xpert Ultra tested on specimens from different methods (P = 0.975). Ultra had a detection rate of 78.0% (23/50) on EBUS-TBNA specimens and 78.3% (18/46) on EBUS-GS specimens, respectively. The detection rate of Ultra on EBUS-TBNA specimens and EBUS-GS specimens were both higher than those of Xpert, but they were not statistically significant (Additional file 1: Table S1).
Discussion
Diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis is a challenge for society. With limited laboratory resources and understaffed situations, the diagnosis in low-income countries depends mostly on clinical and radiological indicators [11]. The most common radiographic manifestation of PTB is parenchymal opacities in the apical and posterior segments of the upper lobes and the superior segments of the lower lobes, usually more than one segment [12]. The most common CT manifestation is the bronchogenic spread of infection (tree-in-bud), which can be identified in 95% of pulmonary TB [13]. Single or multiple cavitations, the radiological hallmark of PTB, can be found in 40% to 45% cases [12, 13]. But some atypical CT manifestations like intrathoracic lymphadenopathy, mediastinal lesions, single pulmonary nodule or unconventional lesion site of pulmonary tuberculosis also increase difficulties of diagnosis for clinicians. An atypical distribution of parenchymal opacities in uncommon segments accounts for approximately 5% of cases [13]. Hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathy also occur in approximately 5% of cases [13]. The atypical CT manifestations occur more frequently in people living with HIV and other immunosuppressed populations like patients with diabetes mellitus and the elderly. They may be misdiagnosed or missed diagnosed for lack of effective diagnostic methods.
In this situation, the pathological examination is quite important in the field of differential diagnosis. EBUS-GS with a flexible catheter guided by ultrasound probe is helpful and has minimal invasive in accessing the tissue specimens with reachable bronchial signs in the lesions [6, 14]. Among patients with intrathoracic lymphadenopathy, EBUS-TBNA is a technique that allows direct sampling to increase the sensitivity and culture yield of tuberculosis [15–17]. Cytopathological or pathological findings alone revealed TB in 72.7% [15] to 84.2% of patients [17]. So compared with smear and culture, pathological diagnosis is quite sensitive but its specificity was lower in our study. Granulomatous inflammation can be found in many other diseases like sarcoidosis, nontuberculous mycobacterial disease, parasites, fungi, autoimmune disease, and even lymphoma [18]. So pathological examination alone may cause a false positive result.
Tissue samples with bacteriological examinations have some advantages over simply pathological diagnosis. Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra has 5% higher sensitivity than Xpert MTB/RIF [3], and it has been recommended as an initial diagnostic test in adults with signs and symptoms of pulmonary TB and without a prior history of TB (≤ 5 years) or with a remote history of TB treatment (> 5 years since end of treatment) or with a prior history of TB and an end of treatment within the last 5 years in the latest WHO policy [19]. Ultra has already been applied to diagnose extrapulmonary tuberculosis. In the diagnosis of pleural TB, Ultra using pleural fluids is better than Xpert [20, 21], but using biopsy samples maybe even better [22–24]. One study combining pathological examination for biopsy with Ultra increased the sensitivity to 92.59% (25/27) [25]. It is the same on other types of tissue samples, like lymph node aspirate or lymph node biopsy [21, 26] and bone or joint aspirate [27, 28]. However, the increased sensitivity of Ultra reduces the overall specificity in high-burden TB settings for detecting of dead bacilli in patients with recent history of TB [3]. In this study, the non-TB group had a 14.9% of tuberculosis history and 22.5% of T-spot positive rate, which may contribute to the low specificity of Ultra.
Limitation
The limitation of this study was the relatively small study population and the uneven distribution of enrolled patients in different groups. The non-TB group had a smaller size compared with the TB group. And the patients underwent EBUS-TBNA were less than half the number of patients underwent EBUS-GS, which made tissue specimens mainly come from EBUS-GS. So we need larger studies to further evaluate the performance of Xpert Ultra with tissue specimens from interventional bronchoscopy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, tissue specimens from interventional bronchoscopy combined with Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra could provide a sensitive method for diagnosing smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis, but its specificity was lower than Xpert MTB/RIF.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Table S1. The detection rate of culture, pathology, Xpert and Ultra on specimens from EBUS-TBNA and EBUS-GS.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author contributions
GY and SW contributed to the design of this study. GY performed the study and collected data. Data analysis was performed by both CSH and YL. The manuscript was written by YL. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by Shanghai Clinical Research Center for infectious disease (tuberculosis) (19MC1910800) and Clinical Research Plan of SHDC (SHDC2020CR6024).
Data availability
All data analyzed in this study are included in this published article.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in these studies were approved by the ethics review committee of Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, China (K19-121Y). All methods were carried out following relevant guidelines and regulations. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants upon enrollment. Participants below the age of 16 were obtained informed consent from their parents.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
None of the authors has a conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Lan Yao and Shanhao Chen contributed equally to this work
Contributor Information
Wei Sha, Email: shfksw@126.com.
Ye Gu, Email: drsymons@outlook.com.
References
- 1.World Health Organization. Automated real-time nucleic acid amplification technology for rapid and simultaneous detection of tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance: Xpert MTB/RIF system: policy statement. 2011; WHO/HTM/TB/2011.4:36. [PubMed]
- 2.World Health Organization . Using the Xpert MTB/RIF assay to detect pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance in adults and children. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 3.World Health Organization. 2017 (WHO/HTM/TB/2017.04). WHO meeting report of a technical expert consultation: non-inferiority analysis of Xpert MTF/RIF ultra compared to Xpert MTB/RIF. 2017; Geneva: World Health Organization.
- 4.World Health Organization . Global tuberculosis report 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Theron G, Peter J, Meldau R, Khalfey H, Gina P, Matinyena B, et al. Accuracy and impact of Xpert MTB/RIF for the diagnosis of smear-negative or sputum-scarce tuberculosis using bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Thorax. 2013;68:1043–1051. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2013-203485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gu Y, Wu C, Yu F, Gui X, Ma J, Cheng L, et al. Application of endobronchial ultrasonography using a guide sheath and electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy in the diagnosis of atypical bacteriologically-negative pulmonary tuberculosis. Ann Transl Med. 2019;7:567. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.09.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Geweniger A, Janda A, Eder K, Fressle R, Kannan CV, Fahnenstich H, et al. High diagnostic yield of endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) in the diagnosis of adolescent pulmonary tuberculosis. BMC Infect Dis. 2021;21:946. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06413-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kumar VG, Urs TA, Ranganath RR. MPT 64 antigen detection for rapid confirmation of M. tuberculosis isolates. BMC Res Notes. 2011;4:79. doi: 10.1186/1756-0500-4-79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Boehme CC, Nabeta P, Hillemann D, Nicol MP, Shenai S, Krapp F, et al. Rapid molecular detection of tuberculosis and rifampin resistance. N Engl J Med. 2010;363(11):1005–1015. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0907847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dorman SE, Schumacher SG, Alland D, Nabeta P, Armstrong DT, King B, et al. Xpert MTB/RIF ultra for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance: a prospective multicentre diagnostic accuracy study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2018;18:76–84. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30691-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Siddiqi K, Lambert M-L, Walley J. Clinical diagnosis of smear-negative pulmonary tuberculosis in low-income countries: the current evidence. Lancet Infect Dis. 2003;3:288–296. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(03)00609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Skoura E, Zumla A, Bomanji J. Imaging in tuberculosis. Int J Infect Dis. 2015;32:87–93. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2014.12.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Leung AN. Pulmonary tuberculosis: the essentials. Radiology. 1999;210:307–322. doi: 10.1148/radiology.210.2.r99ja34307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ma L, Fang Y, Zhang T, Xue P, Bo L, Liu W, et al. Comparison in efficacy and safety of forceps biopsy for peripheral lung lesions guided by endobronchial ultrasound-guided sheath (EBUS-GS) and electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy combined with EBUS (ENB-EBUS) Am J Transl Res. 2020;12:4604–4611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kiral N, Caglayan B, Salepci B, Torun Parmaksiz E, Fidan A, Comert SS, et al. Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in diagnosing intrathoracic tuberculous lymphadenitis. Med Ultrason. 2015;17:333–338. doi: 10.11152/mu.2013.2066.173.nki. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gupta N, Muthu V, Agarwal R, Dhooria S. Role of EBUS-TBNA in the diagnosis of tuberculosis and sarcoidosis. J Cytol. 2019;36:128–130. doi: 10.4103/JOC.JOC_150_18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hassan T, McLaughlin AM, O’Connell F, Gibbons N, Nicholson S, Keane J. EBUS-TBNA performs well in the diagnosis of isolated thoracic tuberculous lymphadenopathy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:136–137. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.183.1.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang X, Liu Y. Offense and defense in granulomatous inflammation disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022;12:797749. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.797749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.WHO consolidated guidelines on tuberculosis: module 3: diagnosis: rapid diagnostics for tuberculosis detection, 2021 update.
- 20.Wang G, Wang S, Yang X, Sun Q, Jiang G, Huang M, et al. Accuracy of Xpert MTB/RIF ultra for the diagnosis of pleural TB in a multicenter cohort study. Chest. 2020;157:268–275. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2019.07.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Christopher DJ, Coelho V, Ebby GS, Shankar D, Gupta R, Thangakunam B. Incremental yield of Xpert® MTB/RIF ultra over Xpert® MTB/RIF in the diagnosis of extrapulmonary TB. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 2021;25:939–944. doi: 10.5588/ijtld.21.0280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Thangakunam B, Christopher DJ. Xpert ultra is better than Xpert, but using biopsy samples may be even better. Chest. 2020;158:829–830. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.02.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Christopher DJ, Dinakaran S, Gupta R, James P, Isaac B, Thangakunam B. Thoracoscopic pleural biopsy improves yield of Xpert MTB/RIF for diagnosis of pleural tuberculosis. Respirology. 2018;23:714–717. doi: 10.1111/resp.13275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wu X, Tan G, Gao R, Yao L, Bi D, Guo Y, et al. Assessment of the Xpert MTB/RIF ultra assay on rapid diagnosis of extrapulmonary tuberculosis. Int J Infect Dis. 2019;81:91–96. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2019.01.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gao S, Wang C, Yu X, Teng T, Shang Y, Jia J, et al. Xpert MTB/RIF ultra enhanced tuberculous pleurisy diagnosis for patients with unexplained exudative pleural effusion who underwent a pleural biopsy via thoracoscopy: a prospective cohort study. Int J Infect Dis. 2021;106:370–375. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2021.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Antel K, Oosthuizen J, Malherbe F, Louw VJ, Nicol MP, Maartens G, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of the Xpert MTB/Rif ultra for tuberculosis adenitis. BMC Infect Dis. 2020;20:33. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4749-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sun Q, Wang S, Dong W, Jiang G, Huo F, Ma Y, et al. Diagnostic value of Xpert MTB/RIF ultra for osteoarticular tuberculosis. J Infect. 2019;79:153–158. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2019.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Perez-Risco D, Rodriguez-Temporal D, Valledor-Sanchez I, Alcaide F. Evaluation of the Xpert MTB/RIF ultra assay for direct detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex in smear-negative extrapulmonary samples. J Clin Microbiol. 2018;56:e00659-18. doi: 10.1128/JCM.00659-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Table S1. The detection rate of culture, pathology, Xpert and Ultra on specimens from EBUS-TBNA and EBUS-GS.
Data Availability Statement
All data analyzed in this study are included in this published article.