Abstract
Background and study aims Credentialing, the process through which an institution assesses and validates an endoscopist’s qualifications to independently perform a procedure, can vary by region and country. Little is known about these inter-societal and geographic differences. We aimed to systematically characterize credentialing recommendations and requirements worldwide.
Methods We conducted a systematic review of credentialing practices among gastrointestinal and endoscopy societies worldwide. An electronic search as well as hand-search of World Endoscopy Organization members’ websites was performed for credentialing documents. Abstracts were screened in duplicate and independently. Data were collected on procedures included in each document (e. g. colonoscopy, ERCP) and types of credentialing statements (procedural volume, key performance indicators (KPIs), and competency assessments). The primary objective was to qualitatively describe and compare the available credentialing recommendations and requirements from the included studies. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize data when appropriate.
Results We screened 653 records and included 20 credentialing documents from 12 societies. Guidelines most commonly included credentialing statements for colonoscopy, esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), and ERCP. For colonoscopy, minimum procedural volumes ranged from 150 to 275 and adenoma detection rate (ADR) from 20 % to 30%. For EGD, minimum procedural volumes ranged from 130 to 1000, and duodenal intubation rate of 95 % to 100%. For ERCP, minimum procedural volumes ranged from 100 to 300 with selective duct cannulation success rate of 80 % to 90 %. Guidelines also reported on flexible sigmoidoscopy, capsule endoscopy, and endoscopic ultrasound.
Conclusions While some metrics such as ADR were relatively consistent among societies, there was substantial variation among societies with respect to procedural volume and KPI statements.
Introduction
Credentialing of endoscopic procedures is an essential component of high-quality endoscopic care 1 yet varies widely based on country and region. While clinical guidelines often provide recommendations based on procedural volume, procedure-specific performance indicators, and assessment of competence, these recommendations are not standardized 2 . With an increasing focus on quality and safety and an expanding array of complex endoscopic procedures, systematic knowledge regarding credentialing requirements and/or recommendations worldwide is needed.
Credentialing refers to the process designed to assess and validate independent practitioners’ qualifications to provide patient care 3 . Credentialing is contingent on determining competence, which requires demonstration of the minimum knowledge and skill to safely and effectively perform a task or procedure 4 , and can lead to authorization by an institution to perform said task or procedure independently. In endoscopy, competence requires cognitive, technical, and integrative skills and is attained independently for each procedure (e. g. colonoscopy, esophagogastroduodenoscopy [EGD]) 3 .
Competence and subsequent credentialing recommendations or requirements have traditionally been based on procedural volume 5 6 and procedure-specific key performance indicators (KPIs). For example, the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) recommends that credentialing for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) be considered after 200 ERCPs and a cannulation rate of 90 % 3 . More recently, competence assessment tools have been used to judge endoscopists’ readiness for independent practice 7 . For example, several American institutions and the Joint Advisory Group on Gastrointestinal (GI) Endoscopy (JAG) in the United Kingdom use the Assessment of Competence in Endoscopy (ACE) 8 9 and Direct Observation of Procedural Skills (DOPS) tools respectively for competence assessments in colonoscopy 10 11 .
A growing awareness of procedural quality and patient safety has spurred the implementation of competency-based education systems and a renewed focus on credentialing practices 12 . Despite this, widely accepted minimal standards for independent practice in endoscopy are lacking. Additionally, geographic and societal variations for such standards are not well described. To address these gaps, we systematically identified and qualitatively compared credentialing recommendations and requirements across a wide range of settings.
Methods
We conducted this systematic review in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement 13 . In addition, we registered our protocol on PROSPERO (ID: CRD42022321149).
Study definitions
We defined credentialing based on the ASGE definition: the process through which an institution assesses and validates an endoscopist’s qualifications to independently perform an endoscopic procedure in a manner that is safe and effective 3 . We will herein refer to credentialing requirements as statements which mandate meeting a threshold (e. g. procedure volume, adenoma detection rate) prior to the provision of clinical privileges to perform a procedure, and credentialing recommendations as statements which suggest meeting a threshold without an explicit or binding mandate. Key performance indicators refer to measures that reflect the quality of specific procedures (e. g. adenoma detection rate for colonoscopy, selective duct cannulation rate for ERCP).
Search strategy
We conducted a systematic search in MEDLINE, EMBASE and PUBMED for published credentialing recommendations or requirements in endoscopy training by gastroenterology and endoscopy societies, or affiliated training committees up to January 31, 2022 (Supplemental Fig. 1). We also conducted a gray literature search through the World Gastroenterology Organization (WGO) website ( https://www.worldgastroenterology.org/ ). This organization is a global body with over 100 member societies in gastroenterology, hepatology, and endoscopy. Through the WGO website, which contains hyperlinks to member societies’ websites, we searched for all credentialing recommendations and/or requirements within each of the individual member societies. We used our web browser’s (Google Chrome, Alphabet Inc, Mountain View, California, United States) automatic web-based language detection and translation services for websites in non-English languages.
Study selection
Two reviewers (N.S. and S.S.) independently screened all titles and abstracts. A third author (S.C.G.) adjudicated disagreements for study inclusion. Records were included if they provided any credentialing recommendations or requirements regarding colonoscopy, EGD, flexible sigmoidoscopy, capsule endoscopy, ERCP, and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS). We excluded other endoscopic procedures such as balloon enteroscopy. We anticipated that some societies would provide credentialing statements that were not peer-reviewed, so we decided a priori to include sources such as white papers and webpage-based recommendations. If there were multiple versions of guidelines from specialty societies that provided credentialing statements for the same procedures, we only included the most updated version.
Data extraction
N.S. independently extracted the data using a standardized data collection form. R.K. and S.C.G reviewed all data collected to ensure accuracy. For each record, we collected the year of issuing (if available), the authors, the corresponding society, conflicts of interest (COI), and funding sources. We identified the procedures included in each study and categorized credentialing statements for each procedure as related to a) procedural volume, b) KPIs, and c) observational assessment using a tool such as the DOPS.
Statistical analysis
Our primary aim was to qualitatively describe and compare the available credentialing recommendations and requirements from the included studies. We used descriptive statistics to summarize the data from individual studies. We did not conduct pooled analyses as this was not the aim of this study.
Results
We identified 653 records from our electronic search, with 646 remaining after de-duplication. We assessed 51 full-text studies from the electronic search along with seven from the gray literature hand search, with 20 studies included in the final sample 2 3 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 (Supplementary Fig. 1). Some of these guidelines commented on a single procedure, such as colonoscopy, while others offered credentialing recommendations for multiple procedures.
Of the 20 credentialing guidelines, five were from Canada 18 19 20 21 22 , three from the United States 2 3 27 , three from the United Kingdom 28 29 30 , two from Singapore 14 15 , two from Korea 25 26 , one from international societies 31 , one from Australia 17 , one from New Zealand 16 , one from Switzerland 23 , and one from Poland 24 . Guidelines were reported between 2001 and 2022. Five guidelines were identified through the gray literature search of GI society websites 16 17 23 24 30 . Four guidelines reported on the presence or absence of conflicts of interest 26 28 29 31 . Guidelines contained credentialing statements for one or more of the included procedures (Supplementary Table 5).
Colonoscopy
Six colonoscopy guidelines 3 16 17 19 26 30 recommended a minimum procedural volume ranging from 150 to 275 procedures, with 100 to 180 of these being unassisted ( Fig. 1 ). With respect to KPIs, the minimum cecal intubation rate (CIR) and the minimum ADR ranged from 85–90 % and 20 %-30 % respectively ( Table 1 ). The minimum volume for snare polypectomy ranged from 10 to 50, however there was minimal guidance as to threshold polyp detection rates ( Table 1 ). The New Zealand Conjoint Committee for Recognition of Training in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (NZCCRTGE), the Australian Conjoint Committee for the Recognition of Training in GI endoscopy (CCRTGE), and the JAG recommended the use of the lower GI DOPS tool in credentialing 16 17 30 .
Fig. 1.
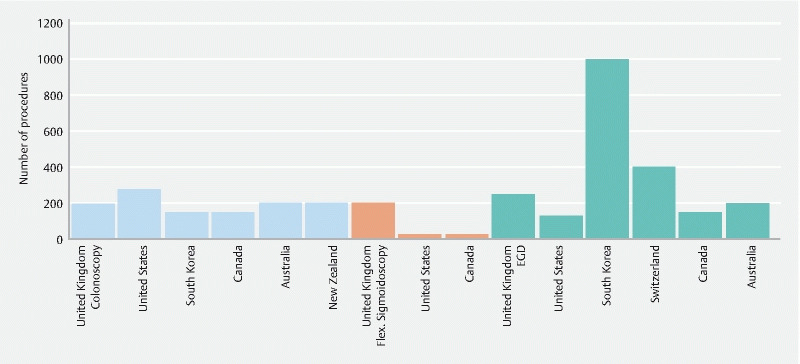
Minimum number of procedures prior to credentialing for colonoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy, and EGD by country of society.
Table 1. Key performance indicators for colonoscopy.
|
Society or training committee, country/region
(year) |
Assessment tool | Key performance indicators | |||||
| Minimum procedures | Min. adenoma detection | Min. cecal intubation rate | Withdrawal time | Min. polypectomy/polyp detection | Max complication rate | ||
| JAG, United Kingdom | > 20 lower gastrointestinal DOPS, competent as per 5 most recent | 200 (incl. 180 unassisted, 15 in last 3 months) + 100 for full certification | – | 90 % | – | Polyp detection and removal > 10 % | ≤ 0.5 % |
| ASGE, United States (2017) | – | 275 | ‘Above recommended threshold’ but not specified | 90 % | – | – | – |
| KSGE, Korea (2017) |
– | 150 | 30 % at-risk men, 20 % women (mean age > 50) | 90 % | > 6 minutes | 10 supervised, 10 unassisted | – |
| CAG, Canada (2008) | – | 150 (incl. 100 unassisted) | 25 % men; 15 % women (mean age > 50) | > 85 %–90 % | > 7 minutes | 30 unassisted snare polypectomies | 0.2; ≤ 1 % post polypectomy bleeding |
| Conjoint Committee, Australia 1 (2015) | DOPS required | 200 (incl. Flex sigmoidoscopy) | – | 90 % | – | 50 successful snare polypectomies | – |
| NZCCRTGE, New Zealand 2 (2022) | 4 DOPS recommended by at least 2 different assessors | 200 (incl. Flex sigmoidoscopy, supervised) | – | 90 % | – | 40 successful snare polypectomies, 10 larger polypectomies with hot or cold snare | – |
–, not reported; ASGE, American Society of Gastroenterology; JAG, Joint Advisory Group on Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; KSGE, Korea Association of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; CAG, Canadian Association of Gastroenterology; NZCCRTGE, New Zealand Conjoint Committee for Recognition of Training in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
Conjoint committee for recognition of training in gastrointestinal endoscopy (including the Royal Autralasian College of Surgeons, Gastroenterological Society of Australia and Royal Australasian College of Physicians)
New Zealand Conjoint Committee for Recognition of Training in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (including the New Zealand Society of Gastroenterology, the New Zealand Committees of the Royal Australasian College of Physicians and Royal Australasian College of Surgeons)
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Seven EGD guidelines recommended a minimum procedural volume ranging from 130–1000 procedures 3 16 17 20 23 26 30 and four guidelines recommended a minimum GI bleeding management volume of 20 to 45 cases 3 20 23 26 ( Fig. 1 ). With respect to KPIs, four guidelines recommended a minimum duodenal or pylorus intubation rate ranging from 95%-100 % 3 16 20 29 ( Table 2 ). The NZCCRTGE, CCRTGE, and the JAG recommended the use of the EGD DOPS tool in credentialing 16 17 28 .
Table 2. Key performance indicators for esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD).
|
Society or training committee, country/region
(year) |
Assessment tool | Key performance indicators | ||||
| Minimum procedures | Min. duodenal (or pylorus) intubation rate | Min. endoscopic hemostasis | Min. number of other therapeutic procedures | Max complication rate | ||
| JAG, United Kingdom 1 (2022) | > 25 EGD DOPS, competent as per 5 most recent (90 % + ) | 250 (incl. 190 unassisted, 15 in last 3 months) | 95 % D2 intubation, with J maneuver for 95 % of cases | – | – | – |
| ASGE, United States (2017) | – | 130 | 95 % pylorus intubation | 45 procedures (20 variceal and 25 non-variceal hemorrhages) | – | – |
| KSGE, Korea (2017) | – | 1000 | – | 20 procedures (10 supervised and 10 unassisted) | 10 foreign body removals (5 supervised and 5 independent) | – |
| SSG, Switzerland (2013) | – | 400 supervised | – | 20 procedures | – | – |
| CAG, Canada (2008) | – | 150 (incl. 100 unassisted) | 100 % D2 intubation | 40 supervised procedures (20 variceal and 20 non-variceal hemorrhages) | 20 supervised stricture dilations 200 supervised PEG Tube insertions |
< 0.1 % |
| Conjoint Committee, Australia 1 (2015) | DOPS required for gastroscopy | 200 supervised (unassisted) | – | – | 20 non–specified additional procedures (i. e., banding, clipping, adrenaline injection, etc.) | – |
| NZCCRTGE, New Zealand 2 (2022) | 4 DOPS by 2 different assessors | 200 supervised | 95 % D2 intubation (in last 100 procedures) | – | 20 non–specified additional procedures (i. e., banding, clipping, adrenaline injection, etc.) | – |
–, not reported; ASGE, American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; JAG, Joint Advisory Group on Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; KSGE, Korea Association of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; CAG, Canadian Association of Gastroenterology; SSG, Swiss Society of Gastroenterology; NZCCRTGE, New Zealand Conjoint Committee for recognition of Training in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
Siau et. Al have recently published a JAG consensus statement for EGD credentialing in January, 2022, which have increased the minimum number of EGD’s from 200 to 250 and the minimum number of DOPS from 20 to 25.
New Zealand Conjoint Committee for Recognition of Training in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (including the New Zealand Society of Gastroenterology, the New Zealand Committees of the Royal Australasian College of Physicians and Royal Australasian College of Surgeons).
Flexible sigmoidoscopy
Three flexible sigmoidoscopy guidelines recommended a minimum procedural volume ranging from 30 to 100 procedures 3 21 30 ( Fig. 1 ). With respect to KPIs, the ASGE recommended a depth of insertion of 50 cm 3 and the Canadian Association of Gastroenterology (CAG) recommended a depth of insertion sufficient to examine the rectum and sigmoid colon 21 (Supplementary Table 3). The JAG recommended the use of lower GI DOPS tool 30 .
Capsule endoscopy
Five capsule endoscopy guidelines recommended a minimum procedural volume ranging from 15 to 50 cases 2 3 17 25 30 and one guideline recommended formal training in capsule endoscopy during gastroenterology fellowship or 8 hours of continuing medical education with 10 supervised capsule studies (Supplementary Table 2) 5 . There were no credentialing statements with respect to KPIs. The JAG recommended the use of the capsule endoscopy DOPS tool 16 30 .
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
There were 10 ERCP guidelines 3 14 16 17 22 23 24 26 30 31 Nine guidelines recommended a minimum procedural volume ranging from 100 to 300 procedures 3 14 16 17 22 23 24 29 31 ( Fig. 2 ). With respect to KPIs, eight guidelines recommended a duct cannulation success rate ranging from 80 % to 90 % 3 14 16 22 24 29 31 ( Table 3 ). The JAG recommended the use of the ERCP DOPS tool and the European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) recommended the use of the DOPS tool and The EUS and ERCP Skills Assessment Tool (TEESAT) 29 31 .
Fig. 2.
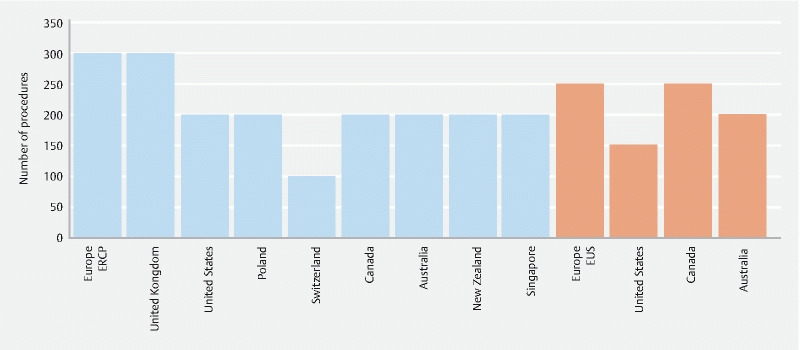
Minimum number of procedures prior to credentialing for ERCP and EUS by country of society.
Table 3. Key performance indicators for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).
|
Society or training committee, country/region
(Year) |
Assessment tool | Key performance indicators | ||||||
| Minimum procedures | Min. number of stents placed | Min. number of stone extractions | Min. rate of duct cannulation | Min. success rate for stent placement | Min. success rate for stone extraction | Post-ERCP pancreatitis | ||
| ESGE, Europe (2021) | DOPS and TEESAT recommended to track competency | 300 | – | – | 80 % (in native papilla) | 90 % (for distal biliary strictures) | 85 % | 10 % post-ERCP pancreatitis |
| JAG, United Kingdom | Min. 30 formative DOPS, “ready of independent practice” in at least 85 % of items as per 5 most recent | 300 (incl. 240 unassisted in last 3 months) | – | – | 80 % (native papilla) | 75 % (for distal biliary strictures) | 70 % | 5 % post–ERCP pancreatitis (Schutz 1 or 2 cases) |
| ASGE, United States (2017) | – | 200 (supervised, unassisted) & 80 sphincterotomies (unassisted) | 60 biliary stents | – | 90 % | – | – | – |
| KSGE, Korea (2017) | – | – | – | – | 80 % | – | 85 % | – |
| PSG, Poland | – | 200 ‘with therapeutic intention’ | – | – | 80 % (past 50 cases) | 80 % | 80 % | – |
| SSG, Switzerland (2015) | – | 100 (incl. 50 sphincterotomies) | 25 drainages (stents, plastic endoprosthesis, nobiliary tubes, etc.) | 25 | – | – | – | – |
| CAG, Canada (2008) | – | 200 (incl. 80 supervised) | 60 biliary stents or nobiliary drains | – | 80–85 % | 85 % | 85 % | – |
| Conjoint Committee, Australia 1 (2015) | – | 200 unassisted (incl. 80 sphincterotomies) | 60 biliary stents | – | – | – | – | – |
| NZCCRTGE, New Zealand 2 (2022) | – | 200 supervised (incl. 80 sphincterotomies) | 60 biliary stents | – | 80 % (in last 50 cases) | – | – | – |
| ERCP working group (under the auspices of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore) (2011) | – | 200 | – | – | 85 % (in native papilla) | 85 % | 85 % | – |
–, not reported; ASGE: American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; JAG, Joint Advisory Group on Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; KSGE, Korea Association of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; ESGE, European Association of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; CAG, Canadian Association of Gastroenterology; SSG, Swiss Society of Gastroenterology; NZCCRTGE: New Zealand Conjoint Committee for Recognition of Training in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy; PSG, Polish Society of Gastroenterology.
Endoscopic ultrasound
There were 7 EUS guidelines 3 15 17 18 26 27 . Four guidelines recommended a minimum procedural volume ranging from 150 to 250 EUS procedures 17 18 27 31 and six guidelines recommended an EUS fine needle aspiration (FNA) volume of 50 to 75 procedures. (Supplementary Table 1) 3 14 17 18 27 31 . There were no credentialing statements with respect to KPIs. The ESGE recommended the use of the DOPS tool and the TEESAT 31 .
Discussion
We systematically identified and compared 20 endoscopy credentialing guidelines covering colonoscopy, EGD, flexible sigmoidoscopy, capsule endoscopy, ERCP, and EUS. Credentialing statements that referenced minimum procedural volume and KPIs were most common, with some guidelines also issuing statements recommending the use of validated endoscopy assessment tools. Colonoscopy, EGD, and ERCP were the most commonly reported on procedures with relatively sparse recommendations for sigmoidoscopy, capsule endoscopy, and EUS. While we identified some consistency among guidelines, such as recommendations for ADR in colonoscopy and bile duct cannulation success rate in ERCP, there was substantial variation among societies with respect to number of recommended procedures and KPI metrics.
Credentialing guidelines recommended 150 to 275 colonoscopies, 130 to 1000 EGDs, and 100 to 300 ERCPs. While guidelines generally included KPIs for the above procedures, the Swiss Society of Gastroenterology (SSG) and the CCRTGE recommended minimum procedural volumes of 400 supervised EGDs and 200 unassisted ERCPs respectively with no KPI recommendations. Relying on procedural volume alone may jeopardize quality of care, given the wide variation in skills among endoscopists with similar experience. For example, some endoscopists may struggle to reach 90 % CIR despite having performed over 500 colonoscopies 32 . Indeed, large societies such as the ASGE and JAG recommend crossing a threshold of minimum colonoscopies, EGDs, and ERCPs in addition to adequate performance with respect to the KPIs 3 30 .
We identified several important KPIs in the included credentialing guidelines. KPIs for colonoscopy, which include ADR, CIR, and withdrawal time, are grounded in robust evidence demonstrating their association with detection of colorectal cancer 33 34 . For ERCP, the KPI of selective duct cannulation is consistent across guidelines and is a useful adjunct to mitigate dissonant estimates of minimum procedural volume, as studies on ERCP learning curves have reported a range of less than 100 to greater than 400 ERCPs to attain proficiency 35 36 . Several guidelines also included KPIs related to biliary stent insertion and stone extraction success rates 16 22 24 29 31 , reflecting the transition of ERCP to an almost exclusively therapeutic modality 37 . In contrast to colonoscopy and ERCP, EGD has sparse data on clinically relevant KPIs, with the duodenal (D2) intubation rate being the only consistent indicator in most guidelines 3 16 20 28 . Moving forward, credentialing guidelines may consider the addition of measures such as EGD duration 38 and mucosal visualization 39 , akin to withdrawal time and bowel preparation in colonoscopy respectively, which are being explored for their relevance to clinical outcomes.
The JAG, NZCCRTGE, CCRTGE, and ESGE recommended the use of validated observational assessment tools in addition to procedural volume and KPIs 16 17 30 31 , wherein an endoscopist is observed and graded on a set of items specific to the procedure by an expert assessor. When tools with strong evidence of clinical validity, such as the DOPS and TEESAT, are used, they can provide a more rounded assessment of individuals’ endoscopic skills, help identify areas where endoscopists need additional support, guide ongoing development, and inform decisions regarding readiness for independent practice 7 . In contrast to number of procedures performed and KPIs, assessment tools encompass the full breadth of technical, cognitive, and non-technical skills needed for high-quality endoscopy 7 , the latter of which are associated with patient safety 40 . While specific barriers have not been studied, widespread implementation of these tools may be limited by lack of time, data collection and storage infrastructure, and financial resources.
Our study has several important limitations. First, systematic reviews and their conclusions are contingent on the underlying primary literature, some of which was not peer-reviewed and largely based on expert opinion and low-quality evidence. Second, we only identified qualitative trends in the data, and were not able to conduct meaningful pooled analyses. Third, there was substantial variability with respect to year of guideline publication. This is an important factor considering the advancements made in endoscopic care over time. Finally, we may have missed sources that were not indexed in the databases included in our electronic search or from organizations that are not a part of the WEO. Despite these limitations, we present the first systematic review on credentialing recommendations and requirements for six endoscopic procedures. These data are crucial in understanding trends in global credentialing practices and identifying deficiencies.
Conclusions
Many national or international guidelines provide recommendations and leave credentialing and granting clinical privileges to institutions at which procedures are performed. Inconsistent implementation of these recommendations can create challenges in ensuring endoscopists’ competence and may jeopardize patient safety. For example, in the US, hospital participation in ASGE credentialing recommendations for ERCP is less than 50 % 41 . In contrast, credentialing in the UK is largely managed by the JAG 43 . While adoption of JAG credentialing guidelines is not mandatory, it is strongly incentivized as it is required for endoscopy units to have trainees or participate in the national bowel screening program 42 . Similarly in Australia, the CCRTGE provides credentialing thresholds and recognizes endoscopists who meet those thresholds 43 . Many endoscopy facilities require that their practitioners carry CCRTGE recognition. The merits of local versus national or regional credentialing are not clear. Moving forward, societies that produce credentialing guidelines should continuously evaluate and update their statements to ensure they are grounded in evidence and support their implementation at individual facilities. Future research should be aimed at clarifying the impact of credentialing practices on quality of care.
Footnotes
Competing interests R Khan has received research grants from AbbVie (2018) and Ferring Pharmaceuticals (2019) and research funding from Pendopharm (2019). S. C. Grover has received research grants and personal fees from AbbVie and Ferring Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from Takeda, education grants from Janssen, and has equity in Volo Healthcare. The remaining authors disclose no conflicts.
Supplementary material :
References
- 1.Adler D G, Bakis G, Coyle W J et al. Principles of training in GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75:231–235. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Faigel D O, Baron T H, Adler D G et al. ASGE guideline: guidelines for credentialing and granting privileges for capsule endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61:503–505. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(04)02781-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Faulx A L, Lightdale J R, Acosta R D et al. Guidelines for privileging, credentialing, and proctoring to perform GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;85:273–281. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2016.10.036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Powell D E, Carraccio C. Toward competency-based medical education. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:3–5. doi: 10.1056/nejmp1712900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Faigel D O, Baron T, Lewis B Ensuring competence in endoscopy. ASGE policy and procedures manual for gastrointestinal endoscopy: guidelines for training and practice 2005
- 6.Ekkelenkamp V E, Koch A D, de Man R A et al. Training and competence assessment in GI endoscopy: a systematic review. Gut. 2016;65:607–615. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Khan R, Zheng E, Wani S et al. Colonoscopy competence assessment tools: A systematic review of validity evidence. Endosc. 2021;53:1235–1245. doi: 10.1055/a-1352-7293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.ACE Research Group . Sedlack R E, Coyle W J. Assessment of competency in endoscopy: establishing and validating generalizable competency benchmarks for colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;83:516–523. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2015.04.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sedlack R E, Coyle W J, Obstein K L et al. ASGE’s assessment of competency in endoscopy evaluation tools for colonoscopy and EGD. Gastrointest Endosc. 2014;79:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2013.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Siau K, Crossley J, Dunckley P et al. Colonoscopy Direct Observation of Procedural Skills assessment tool for evaluating competency development during training. The Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:234–243. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000000426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Siau K, Hodson J, Valori R M et al. Performance indicators in colonoscopy after certification for independent practice: outcomes and predictors of competence. Gastrointest Endosc. 2019;89:482–482. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2018.07.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Taber S, Frank J R, Harris K A et al. Identifying the policy implications of competency-based education. Med Teacher. 2010;32:687–691. doi: 10.3109/0142159X.2010.500706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6:e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ang T, Cheng J, Khor J et al. Guideline on training and credentialing in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Singapore Med J. 2011;52:654–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mesenas S, Ang T L, Khor C et al. Guidelines for endoscopic ultrasonography. Ann Acad Med Singapore. 2010;39:489–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Endoscopy Guidance Group for New Zealand . Guidelines for Local Credentialing in Adult Endoscopy. Wellington, New Zealand. 2021.
- 17.Conjoint Committee For Recognition of Training in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy . Melbourne, Australia: Gastroenterological Society of Australia, Royal Australasian College of Surgeons, Royal Australasian College of Physicians; 2015. Information for Applicants. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Arya N, Sahai A V, Paquin S C. Credentialing for endoscopic ultrasound: A proposal for Canadian guidelines. Endosc Ultrasound. 2016;5:4. doi: 10.4103/2303-9027.175875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Romagnuolo J, Enns R, Ponich T et al. Canadian credentialing guidelines for colonoscopy. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008;22:17–22. doi: 10.1155/2008/837347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ponich T, Enns R, Romagnuolo J et al. Canadian credentialing guidelines for esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Can J Gastroenterol. 2008;22:349–354. doi: 10.1155/2008/987012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Enns R, Romagnuolo J, Ponich T et al. Canadian credentialing guidelines for flexible sigmoidoscopy. Can J Gastroenterol. 2008;22:115–119. doi: 10.1155/2008/874796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Springer J, Enns R, Romagnuolo J. Canadian credentialing guidelines for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Can J Gastroenterol. 2008;22:547–551. doi: 10.1155/2008/582787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Swiss Society of Gastroenterology . Bern, Switzerland: Schweizerisches Institut für ärztliche Weiter- und Fortbildung, Institut suisse pour la formation médicale postgraduée et continue; 2015. Cholangio-pancréatographie endoscopique rétrograde ERCP (SSG) [Google Scholar]
- 24.Polskie Towarzystwo Gastroenterologii . Przyznawanie dyplomu potwierdzającego umiejętności wykonywania badań endoskopowych. Warsaw, Poland. 2021.
- 25.Lim Y-J, Moon J-S, Chang D-K. Vol. 37. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc; 2008. Korean Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (KSGE) guidelines for credentialing and granting previleges for capsule endoscopy; pp. 393–402. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Moon H S, Choi E K, Seo J H et al. Education and training guidelines for the board of the Korean Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Clin Endosc. 2017;50:345. doi: 10.5946/ce.2017.106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Eisen G M, Dominitz J A, Faigel D O et al. Guidelines for credentialing and granting privileges for endoscopic ultrasound. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;54:811–814. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(01)70082-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Siau K, Beales I L, Haycock A et al. JAG consensus statements for training and certification in oesophagogastroduodenoscopy. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2022;13:193–205. doi: 10.1136/flgastro-2021-101907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Siau K, Keane M G, Steed H et al. UK Joint Advisory Group consensus statements for training and certification in endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Endosc Int Open. 2022;10:E37–E49. doi: 10.1055/a-1629-7540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Joint Advisory Group on Gastrointestinal Endoscopy . London, UK: Royal College of Physicians; JETS Certification Pathways: Trainee Certification Process. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Johnson G, Webster G, Boškoski I et al. Curriculum for ERCP and endoscopic ultrasound training in Europe: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) position statement. Endoscopy. 2021;53:1071–1087. doi: 10.1055/a-1537-8999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dafnis G, Granath F, Påhlman L et al. The impact of endoscopists’ experience and learning curves and interendoscopist variation on colonoscopy completion rates. Endoscopy. 2001;33:511–517. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-14964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lee T, Blanks R, Rees C et al. Longer mean colonoscopy withdrawal time is associated with increased adenoma detection: evidence from the Bowel Cancer Screening Programme in England. Endoscopy. 2013;45:20–26. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1325803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kaminski M F, Regula J, Kraszewska E et al. Quality indicators for colonoscopy and the risk of interval cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1795–1803. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0907667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wani S, Hall M, Wang A Y et al. Variation in learning curves and competence for ERCP among advanced endoscopy trainees by using cumulative sum analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;83:711–719. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2015.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Ekkelenkamp V E, Koch A D, Rauws E A et al. Competence development in ERCP: the learning curve of novice trainees. Endoscopy. 2014;46:949–955. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1377930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Huang R J, Thosani N C, Barakat M T et al. Evolution in the utilization of biliary interventions in the United States: results of a nationwide longitudinal study from 1998 to 2013. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86:319–326. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2016.12.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Park J M, Huo S M, Lee H H et al. Longer observation time increases proportion of neoplasms detected by esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2017;153:460–469. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.05.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Khan R, Gimpaya N, Vargas J I et al. The Toronto Upper Gastrointestinal Cleaning Score (TUGCS): a prospective validation study. Endoscopy. 2022 doi: 10.1055/a-1865-4180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Matharoo M, Haycock A, Sevdalis N et al. A prospective study of patient safety incidents in gastrointestinal endoscopy. Endoscopy international open. 2017;5:E83. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-117219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Cotton P B, Feussner D, Dufault D et al. A survey of credentialing for ERCP in the United States. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017;86:866–869. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.03.1530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Siau K, Green J T, Hawkes N D et al. Impact of the Joint Advisory Group on Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (JAG) on endoscopy services in the UK and beyond. Frontline gastroenterology. 2019;10:93–106. doi: 10.1136/flgastro-2018-100969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Thomson A. ERCP credentialing approaches in Australia and throughout the world. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. 2018;87:1365. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


