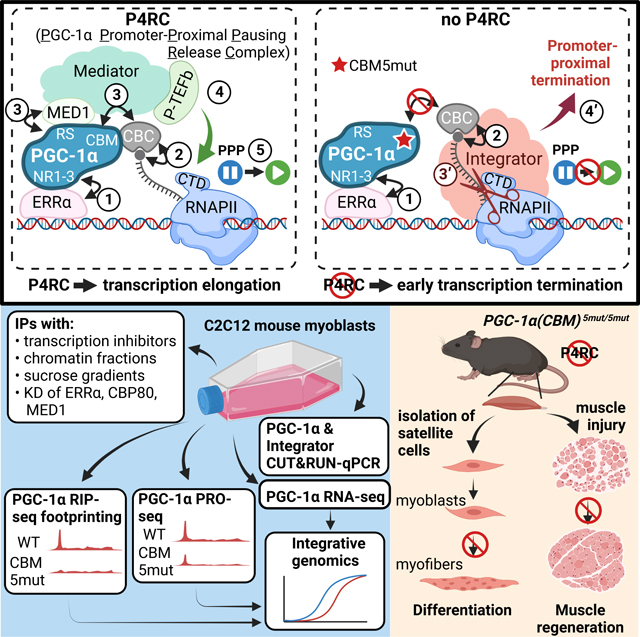
SUMMARY
PGC-1α is well-established as a metazoan transcriptional coactivator of cellular adaptation in response to stress. However, the mechanisms by which PGC-1α activates gene transcription are incompletely understood. Here, we report that PGC-1α serves as a scaffold protein that physically and functionally connects the DNA-binding protein estrogen-related receptor α (ERRα), cap-binding protein 80 (CBP80), and Mediator to overcome promoter-proximal pausing of RNAPII and transcriptionally activate stress-response genes. We show that PGC-1α promotes pausing release in a two-arm mechanism: by recruiting the positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb), and by outcompeting the premature transcription termination complex Integrator. Using mice homozygous for five amino-acid changes in the CBP80-binding motif (CBM) of PGC-1α that destroy CBM function, we show that efficient differentiation of primary myoblasts to myofibers and timely skeletal-muscle regeneration after injury require PGC-1α binding to CBP80. Our findings reveal how PGC-1α activates stress-response gene transcription in a previously unanticipated pre-mRNA quality-control pathway.
Keywords: PGC-1α, ERRα, gene transcription, cap-binding complex, CBP80, Mediator, P-TEFb, promoter-proximal pausing, Integrator, pre-mRNP quality control, myogenesis, skeletal-muscle regeneration, interferon signaling
Graphical Abstract
eTOC Blurb
PGC-1α is a major regulator of the cellular adaptation to stress. Rambout, Cho et al. show that PGC-1α activates the transcription of stress-response genes in a pre-mRNA quality-control mechanism. This mechanism involves release of RNAPII from pausing after PGC-1α senses 5´-cap-bound CBP80, thereby ensuring that downstream steps promote gene expression.
INTRODUCTION
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARɣ) coactivator-1 alpha (PGC-1α) is a master transcriptional coactivator that induces gene-expression programs typically activated in response to physiological or pathological stresses.1,2 PGC-1α has been mainly characterized as a positive regulator of cellular metabolism in energy-demanding tissues, including skeletal muscle. Musculoskeletal PGC-1α has also emerged as an anti-inflammatory3 and pro-differentiation factor4. For example, transgenic expression of the canonical PGC-1α isoform, PGC-1α1/-a, within skeletal myofibers of mice promotes the formation of oxidative fibers at the expense of glycolytic fibers5 and improves exercise performance.6 We refer to PGC-1α1/–a as PGC-1α in this manuscript for simplicity. By comparison, transgenic expression of PGC-1α4, a C-terminal truncated isoform of PGC-1α, which notably does not contribute to the molecular mechanism described in this paper because it lacks the requisite regulatory motifs (see below), increases muscle mass and strength as well as resistance to muscle wasting.7 Muscle-specific expression of PGC-1α also augments activation and proliferation of adult muscle stem cells, i.e. satellite cells (SCs),8 which drive the growth, maintenance and repair of adult skeletal muscle in a multi-step differentiation process. This process involves the activation of SCs to form myoblasts (MBs), the proliferation and commitment of MBs to form myocytes, and the fusion of myocytes to form multinucleated myofibers.9
PGC-1α is recruited to target genes via direct binding to transcription factors, which include myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2 (MEF2) and the nuclear receptors (NRs) estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) and estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRα).10–12 PGC-1α is then able to activate gene transcription through different mechanisms that may not be mutually exclusive. One mechanism involves chromatin remodeling whereby the PGC-1α N-terminal activation domain recruits a histone acetyltransferase, e.g. steroid receptor coactivator 1 (SRC-1) or cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB)-binding protein (CBP)/p300.13,14 A second, which requires prior chromatin remodeling by, e.g., CBP/p300 has been proposed to involve assembly and/or activation of the transcription preinitiation complex (PIC) by direct binding of the PGC-1α C-terminal arginine-serine (RS) domain to the MED1 subunit of Mediator.14,15 In another, PGC-1α interacts directly, at least in vitro, with the ménage-à-trois 1 (MNAT1) constituent of the cyclin-dependent kinase 7 (CDK7)-containing module of the general transcription factor TFIIH.16 In a fourth, we showed that PGC-1α promotes gene expression by directly binding cap-binding protein 80 (CBP80), itself bound to CBP20 to form the largely nuclear cap-binding complex (CBC), at the 5´-cap of target transcripts.4 While the CBC positively regulates numerous transcriptional and co-transcriptional aspects of gene metabolism (reviewed in Rambout and Maquat, 202017), which aspect is regulated by the CBP80-binding motif (CBM) of PGC-1α remains unknown. Embedded between the PGC-1α RS domain and CBM is a putative RNA-recognition motif (RRM). The RRM assists PGC-1α binding to 5´-cap-bound CBP80,4 possibly consistent with in vitro-crosslinking experiments using a GC-rich RNA probe that suggested the RRM does not bind RNA directly.18 In yet another unknown mechanism, PGC-1α promotes gene transcription through direct binding to proximal and distal introns of pre-mRNAs.19
After transcription initiates, CDK7 and, possibly, CDK12 and/or CDK1320,21 phosphorylate the RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) C-terminal domain (CTD) at serine 5 (Ser5 or S5), which recruits components of the pre-mRNA capping machinery.22 Notably, RNAPII(pS5) marks RNAPII at sites of promoter-proximal pausing (PPP). PPP generally occurs after 25–60 nucleotides of RNA have been synthesized.23,24 Recruitment of the dimeric positive transcription elongation factor P-TEFb, which is most often composed of Cyclin T1 and CDK9, induces phosphorylation of the RNAPII CTD at S2 as well as phosphorylation of other factors to stimulate the release of RNAPII from PPP and augment transcription elongation.24 PPP is viewed as a central point of gene regulation for most protein-encoding genes of higher eukaryotes.24 Pertinent to our studies, stress-response genes are typified by unstable RNAPII pausing and early transcription termination, both under stressed and unstressed conditions, in a mechanism that involves recruitment of the multi-protein termination complex Integrator.25,26
Here, we demonstrate that PGC-1α forms a complex in MBs that includes ERRα, the CBC, Mediator, P-TEFb, and transcriptionally engaged RNAPII. We refer to this complex as the PGC-1α Promoter-Proximal Pausing Release Complex (P4RC) since we show that it forms during PPP and promotes gene transcription in a two-arm mechanism. In the first arm, the P4RC recruits P-TEFb to release RNAPII from PPP into processive transcription elongation. In the second arm, the P4RC outcompetes Integrator, thereby preventing promoter-proximal termination of transcription. Our data suggest that the P4RC operates in a pre-mRNP surveillance mechanism to promote the expression of target transcripts with properly capped and CBP80-bound 5´-ends. Using CRISPR-Cas9-engineered mice in which the PGC-1α CBM harbors five amino-acid changes that destroy CBM function, we demonstrate that PGC-1α binding to CBP80 promotes the differentiation of primary MBs to myofibers and the regeneration of injured skeletal muscle.
RESULTS
PGC-1α binds the CBC during RNAPII PPP
Since the CBC is recruited to the cap of nascent pre-mRNAs co-transcriptionally (reviewed in Rambout and Maquat, 202017) we hypothesized that PGC-1α binding to CBP80 may require ongoing transcription. To test this hypothesis, we inhibited RNAPII transcription in mouse C2C12 MBs using α-amanitin, which blocks RNAPII translocation and promotes RNAPII degradation (Figure S1A),27 under conditions where MB viability was largely unperturbed (Figure S1B). We used C2C12 MBs because PGC-1α function in skeletal muscle biology has been and remains of a topic of great interest. We found that α-amanitin inhibited the co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) of CBP80 and CBP20 with PGC-1α (Figure S1C) as well as the reciprocal co-IP of PGC-1α with CBP80 (Figure S1D). Both IPs were performed in the presence of RNase I to eliminate protein–protein interactions that are bridged by RNA. In contrast, the co-IP of the transcription factors MEF2, ERα and ERRα with PGC-1α (Figure S1C), and the co-IP of CBP20 with CBP80 (Figure S1D), were unaffected by α-amanitin treatment.
Pre-mRNA capping and recruitment of the CBC are temporally associated with PPP (Rambout and Maquat, 2020 and references therein). Thus, we next tested whether PGC-1α binding to CBP80 is influenced by (i) inhibiting the establishment of paused RNAPII and pre-mRNA capping using the CDK inhibitor THZ1,28,29 or (ii) inhibiting the release from PPP using the CDK inhibitor 5,6-Dichlorobenzimidazole 1-b-D-ribofuranoside (DRB) (Nechaev and Adelman, 2011 and references therein) (Figure 1A). We confirmed the activity of THZ1, which specifically inhibits CDK7, CDK12 and CDK13,31 by the disappearance in western blots of paused RNAPII phospho-Ser5 (pS5) and, consequently, elongating RNAPII phospho-Ser2 (pS2) (Figure S1E). We confirmed the activity of DRB, which preferentially targets the catalytic CDK9 subunit of P-TEFb,32 by the loss of only elongating RNAPII(pS2) (Figure S1E). Neither inhibitor altered the level of RNAPII (Figure S1E). Strikingly, the co-IP of CBP80 and CBP20 with PGC-1α, like the reciprocal co-IP of PGC-1α with CBP80, was inhibited by THZ1, which prevents the establishment of PPP, but was enhanced by DRB, which stalls RNAPII at PPP sites (Figure 1B, C). As controls, the co-IP of MEF2, ERα or ERRα with PGC-1α, and the co-IP of CBP20 with CBP80, were not impacted by either THZ1 or DRB (Figure 1B, C). We conclude that PGC-1α binding to the CBC occurs during RNAPII PPP.
Figure 1. PGC-1α complexes with the CBC, Mediator, p-TEFb, ERRα and RNAPII during PPP.
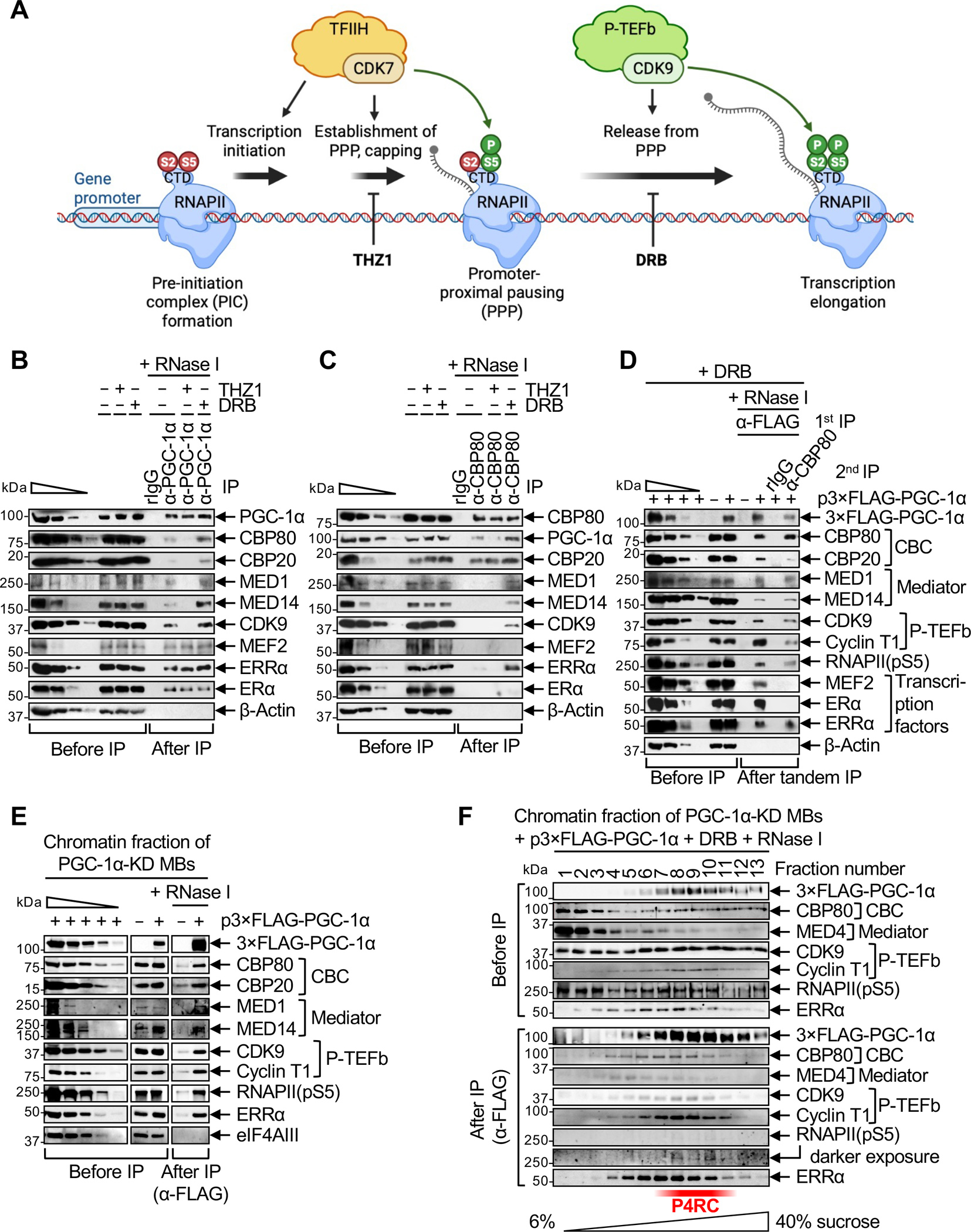
(A) Schematic illustrating the effect of culturing cells in the presence of the CDK inhibitors THZ1 or DRB on early steps of gene transcription, i.e. establishment of promoter-proximal pausing (PPP) and release of RNAPII from PPP into transcription elongation, respectively.
(B) Western blots (WBs) of lysates of C2C12-MBs that were (+) or were not (−) treated with THZ1 or DRB, before or after IP in the presence of RNase I using anti(α)-PGC-1α or, as a control, rabbit (r)IgG. In this WB and others, β-Actin serves to control for variations in loading and IP specificity, the wedge denotes 3-fold serial dilutions of samples to provide semi-quantitative comparisons, and n = 2–3 biological replicates. For this and all other IPs, cell equivalents in IP lanes relative to before IP lanes are described in Table S1.
(C) As in B, but using anti-CBP80 in place of anti-PGC-1α.
(D) WBs of lysates of PGC-1α-KD MBs transiently transfected with a plasmid (p) producing 3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) (+) or FLAG alone (−) and subsequently treated with DRB, before IP, after a first IP in the presence of RNase I using anti-FLAG, or after a second IP on the eluates of the first IP in the presence of RNase I using anti-CBP80 or, as a control, rIgG. Samples were loaded so that the amounts of CBP80 in the first and second IPs are equivalent.
(E) WBs of the solubilized chromatin fraction of PGC-1α-KD MBs transiently expressing 3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) or FLAG alone (−), before or after IP in the presence of RNase I using anti-FLAG. eIF4AIII serves to control for variations in loading and to control for IP specificity.
(F) WBs of the solubilized chromatin fraction of PGC-1α-KD MBs transiently expressing 3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) and treated with DRB, after fractionation in 6–40% sucrose. Fractions were analyzed before or after anti-FLAG IP in the presence of RNase I.
PGC-1α forms a nexus with the CBC, Mediator, P-TEFb, ERRα and RNAPII during PPP
PGC-1α directly binds the MED1 subunit of Mediator,14,15 and Mediator directly binds and recruits P-TEFb to release RNAPII from PPP. 33–35 As evidence that PGC-1α functions with Mediator to recruit P-TEFb during RNAPII PPP, MED1, the Mediator scaffold subunit MED14, and CDK9 co-immunoprecipitated with PGC-1α in the presence of RNase I in a way that was inhibited by α-amanitin or THZ1, but was enhanced by DRB (Figures 1B, S1C). Moreover, MED1, MED14 and CDK9 detectably co-immunoprecipitated with CBP80 in DRB-treated MBs but not in untreated, α-amanitin-treated or THZ1-treated MBs (Figures 1C, S1D). Among the different PGC-1α-responsive transcription factors that we tested, only ERRα was present in anti-CBP80 IPs after DRB treatment (Figure 1C). Additionally, PGC-1α, the CBC (i.e. CBP80 and CBP20), Mediator (i.e. MED1 and MED14), P-TEFb (i.e. CDK9 and Cyclin T1) and RNAPII were detected in reciprocal anti-ERRα IPs performed in the presence of RNase I and TURBO DNase (Figure S1F). Together, our findings suggest the existence of a complex in which ERRα-bound PGC-1α tethers Mediator and P-TEFb at the cap of nascent transcripts to form a transient RNase I-resistant complex that induces transcription by overcoming PPP. We called this complex the PGC-1α Promoter-Proximal Pausing Release Complex (P4RC).
We used lysates of DRB-treated MBs in which PGC-1α was stably knock-downed (KD) using shRNA and that transiently expressed FLAG-PGC-1α(WT), i.e. 3xFLAG-tagged wild-type human PGC-1α1/-a, at near-normal levels, to support the existence of the P4RC (Figure S1G,H, which employed different anti-PGC-1α antibodies). IP of MB lysates using anti-FLAG followed by IP using anti-CBP80, both performed in the presence of RNase I, demonstrated that CBP20, Mediator, P-TEFb, transcriptionally engaged RNAPII(pS5), and ERRα form a complex with FLAG-PGC-1α and CBP80 in MBs in which RNAPII is paused by DRB (Figure 1D). As controls, MEF2 and ERα co-immunoprecipitated with FLAG-PGC-1α but were not part of the FLAG-PGC-1α- and CBP80-containing paused complex (Figure 1D). IPs using anti-FLAG and heparin-solubilized chromatin from PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) (Figure S1I) confirmed that these interactions exist on chromatin (Figure 1E) and are resistant to dissociation of nucleic acid-binding proteins from RNA and DNA by high concentrations of heparin.36 Supporting this conclusion, these interactions are largely resistant to micrococcal nuclease (Figure S1J), which is a relatively non-specific DNA and RNA endo-exonuclease.
Another line of evidence for the P4RC derived from sucrose gradient sedimentation of IPs using anti-FLAG in the presence of RNase I and heparin-solubilized chromatin from PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing FLAG-PGC-1α(WT). Our finding that PGC-1α, the CBC, P-TEFb and ERRα co-sedimented (Figure 1F) corroborated their co-existence in a complex. Mediator and RNAPII(pS5) likewise co-sedimented with the P4RC and were additionally present in lower and/or higher molecular-weight fractions (Figure 1F).
PGC-1α competes with Integrator for CBC binding during PPP
PGC-1α plays a central role in the formation of the P4RC, as evidenced by our finding that the co-IP of MED1, MED14, CDK9 and ERRα with CBP80 is impaired in PGC-1α-KD MBs relative to WT MBs (Figure 2A, where CBP20 exemplifies a PGC-1α-independent interaction). Given the functional competition between P-TEFb and Integrator,37 we tested if the loss of P-TEFb in CBP80 IPs upon the loss of PGC-1α was accompanied by recruitment of Integrator. In agreement with this idea, the co-IP of multiple subunits of Integrator with CBP80 was detected only in PGC-1α-KD MBs (Figure 2A): We detected the INTS11 subunit of the cleavage module, the INTS10 subunit of the RNA-binding module, and the INTS3 subunit. Importantly, we observed the same results using an independent functional knock-out (KO) of the PGC-1α CBM in primary MBs (see below). These findings provide the first evidence that PGC-1α not only promotes transcription elongation but also precludes early transcription termination by Integrator. They also provide the first evidence that the activity of Integrator on PPP termination can be regulated in a gene-specific mechanism.
Figure 2. ERRα mediates functional interactions of PGC-1α with CBP80, Mediator and P-TEFb, and is required for the P4RC to compete against Integrator for CBC binding.
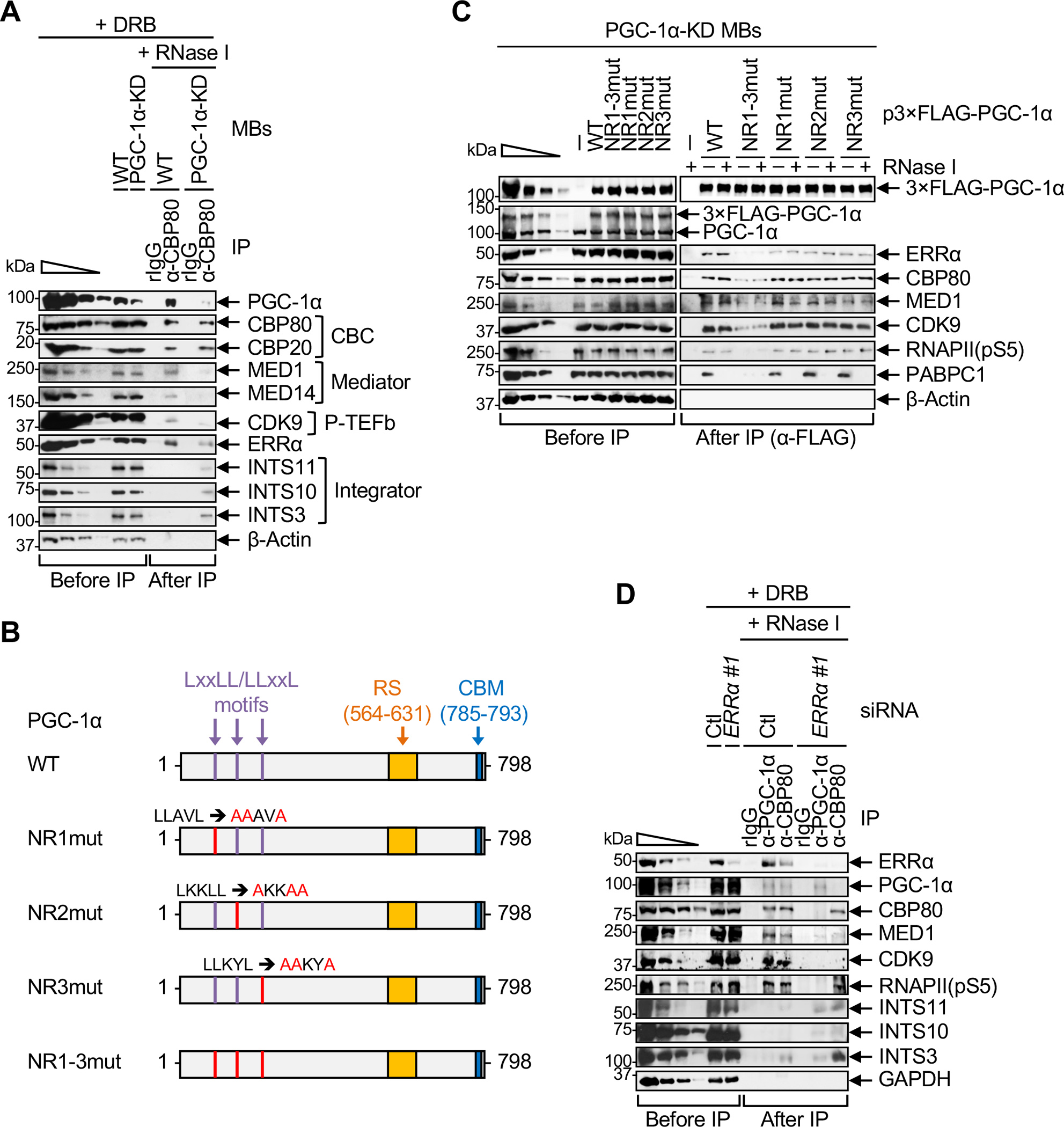
(A) WBs of lysates of WT or PGC-1α-KD MBs treated with DRB prior to lysis, before or after IP in the presence of RNase I using anti-CBP80 or, as a control, rIgG.
(B) Diagrams of human PGC-1α variants used in C, where red letters denote mutated amino acids in nuclear receptor (NR)-binding LxxLL/LLxxL motifs. RS, arginine- and serine-rich domain; CBM, CBP80-binding motif. Numbers specify amino acids.
(C) WBs of lysates of PGC-1α-KD MBs transiently transfected with the specified plasmid before or after IP in the presence (+) or absence (−) of RNase I using anti-FLAG. PABPC1 serves to control for RNase I-sensitive interactions.
(D) WBs of lysates of WT MBs that were transiently transfected with Errα or control (Ctl) siRNA and treated with DRB, before or after IP in the presence of RNase I using anti-PGC-1α, anti-CBP80 or, as a control, rIgG.
PGC-1α binding to ERRα is a prerequisite for P4RC formation
To determine if PGC-1α binding to ERRα contributes to P4RC formation, we performed anti-FLAG IPs using PGC-1α-KD MBs transiently expressing FLAG alone, FLAG-PGC-1α(WT), or one of four FLAG-PGC-1α variants in which each of the three N-terminal α-helical Leucine-rich NR-binding motifs (LxxLL or LLxxL, where L is leucine, and x is any amino acid) was mutated individually or together using leucine-to-alanine substitutions (Figure 2B). We found that abolishing the co-IP of ERRα with FLAG-PGC-1α required that all three NR-binding motifs of PGC-1α be mutated (Figure 2C). This result is consistent with our observation that, compared to FLAG-PGC-1α(WT), a detectably smaller fraction of all mutated variants, especially the triply-mutated variant, localized to the chromatin fraction of MBs (Figure S2A). The co-IP of CBP80, MED1, CDK9 and paused RNAPII(pS5) with FLAG-PGC-1α was also strongly reduced with the triply-mutated variant (Figure 2C), as was the case when the cellular abundance of ERRα was reduced to ~10% using ERRα siRNA (Figures 2D, S2B). Moreover, the co-IP of PGC-1α, MED1 and CDK9 with CBP80 was impaired in ERRα-depleted cells (Figure 2D, where RNAPII(pS5) serves as a control for an ERRα-independent interaction). In contrast, ERRα KD promoted the co-IP of Integrator subunits INTS3, INTS11 and, to a lesser extent, INTS10 with CBP80 (Figure 2D). These results indicate that, in MBs, PGC-1α binding to NRs, and in particular ERRα, is a prerequisite for P4RC formation and for preventing Integrator from binding to the CBC, possibly via RNAPII.
Recruitment of P-TEFb to the P4RC requires PGC-1α binding to CBP80 and Mediator
To investigate how PGC-1α binding to CBP80 and MED1 contributes to P4RC formation, we performed additional anti-FLAG IPs using PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing previously characterized FLAG-PGC-1α variants:4 FLAG-PGC-1α(ΔCBM) lacks the CBM, FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) harbors 5-amino acid substitutions in the CBM that abolish CBP80 binding, and FLAG-PGC-1α(ΔRS) lacks the RS domain required to directly bind Mediator (Figure 3A).14,15
Figure 3. PGC-1α binding to CBP80 and Mediator promotes the recruitment of P-TEFb rather than Integrator to the CBC.
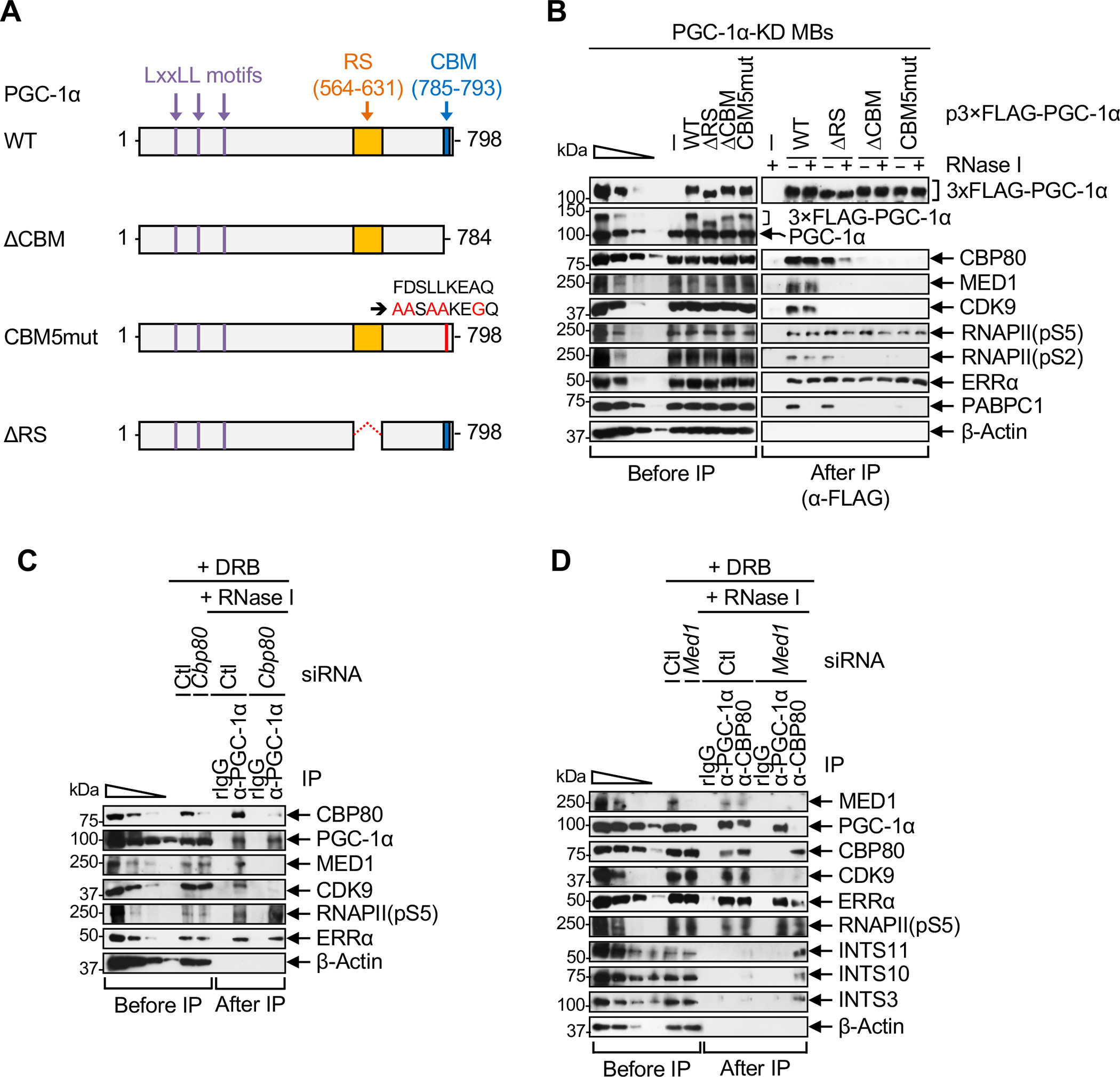
(A) Diagrams of human PGC-1α, as in Figure 2B but illustrating other PGC-1α variants used in B.
(B) WBs, essentially as in Figure 2C.
(C) WBs, essentially as in Figure 2D.
(D) WBs, essentially as in Figure 2D.
See also and Table S1.
The co-IP of MED1, CDK9 and elongating RNAPII(pS2), but not the co-IP of ERRα or paused RNAPII(pS5), was abolished by deleting or mutating the CBM of FLAG-PGC-1α, which abrogates FLAG-PGC-1α binding to CBP80 (Figure 3B). Corroborating the role of CBP80 in mediating these interactions, similar results were obtained in IPs of cellular PGC-1α after siRNA-mediated depletion of CBP80 (Figure 3C). We conclude that PGC-1α binding to CBP80 is required to nucleate P4RC formation in steps that occur after the binding of PGC-1α to ERRα and transcription initiation.
Consistent with previous reports that PGC-1α directly binds MED1 via its RS domain,14,15 MED1 failed to co-immunoprecipitate with FLAG-PGC-1α(ΔRS) (Figure 3B). Furthermore, consistent with the ability of Mediator to directly bind and recruit P-TEFb,33,34,38,39 CDK9 failed to co-immunoprecipitate with FLAG-PGC-1α(ΔRS) (Figure 3B). Intriguingly though, the co-IP of CBP80 and RNAPII(pS2) with FLAG-PGC-1α(ΔRS), unlike with FLAG-PGC-1α(WT), was RNase I-sensitive (Figure 3B), indicating that Mediator stabilizes P4RC formation in an RNA-dependent manner. We also found that ERRα and paused RNAPII(pS5) efficiently co-immunoprecipitated with FLAG-PGC-1α(ΔRS) (Figure 3B). Similar results were observed in IPs of PGC-1α after siRNA-mediated depletion of MED1 (Figure 3D, where ERRα and RNAPII(pS5) serve as controls for MED1-independent interactions), indicating that the loss of P4RC integrity following deletion of the PGC-1α RS domain (Figure 3B) reflects the inability of PGC-1α to bind MED1. Additionally, depletion of MED1 prevented efficient co-IP of PGC-1α, CDK9 and ERRα with CBP80, but enhanced the co-IP of Integrator subunits with CBP80 (Figure 3D, where RNAPII(pS5) serves as a control for a MED1-independent interaction). Together, our results indicate that Mediator stabilizes the binding of PGC-1α and ERRα to the CBC and is required for the subsequent recruitment of P-TEFb to form the P4RC and exclude Integrator.
From these data, we conclude that P4RC formation is dynamic and competes against Integrator recruitment: (i) PGC-1α binds via its LxxLL/LLxxL motifs to ERRα, which ensures association with paused RNAPII(pS5); (ii) PGC-1α binds via its CBM to the CBC; and (iii) PGC-1α binds via its RS domain to Mediator, which stabilizes the complex formed at step ii in an RNA-dependent manner and promotes P-TEFb recruitment.
The PGC-1α CBM activates gene transcription by favoring transcription elongation over early transcription termination
Inherent to the conclusions presented above is that PGC-1α binding via its CBM to CBP80, via its RS domain to Mediator, and via its three NR motifs to ERRα contribute to gene transcription by shifting RNAPII dynamics at PPP sites of PGC-1α target genes toward elongation rather than early termination. To test this hypothesis, we first used precision run-on sequencing (PRO-seq)23 to map transcribing RNAPII at single-nucleotide resolution in control (CTL) MBs (i.e. WT MBs stably expressing a control shRNA that targets GFP mRNA) transiently expressing FLAG alone and in PGC-1α-KD MBs transiently expressing FLAG alone, or either FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) or FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) at near-normal PGC-1α levels (Figure S3A). Comparison of PRO-seq counts across active genes identified 125 genes whose transcription was downregulated after PGC-1α KD and largely restored after expression of FLAG-PGC-1α(WT), i.e. genes that are bona fide targets of PGC-1α (Figure 4A, Table S2). Remarkably, however, expression of FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) failed to restore PRO-seq counts to normal for 124 out of the 125 genes, demonstrating that the CBM is a pivotal contributor to the transcriptional activity of PGC-1α at most if not all of its target genes. Moreover, results from RNA-seq showed that PGC-1α(CBM)-dependent activation of gene transcription led to increased levels of mRNA (Figure 4B, Table S2) that are specific to the PGC-1α targets defined by PRO-seq (Figure 4C).
Figure 4. PGC-1α binding to CBP80, MED1 and ERRα promotes gene transcription by promoting PPP release and preventing early transcription termination.
(A) Heatmap representation of raw-scaled full-gene PRO-seq log2-fold changes in the specified MBs, for genes whose levels are significantly (P ≤ 0.01) downregulated at least 1.3-fold after PGC-1α-KD and upregulated at least 1.3-fold after re-expression of FLAG-PGC-1α(WT). Genes are ranked by CBM-dependency, where the least efficient rescue of PRO-seq signal after re-expression of FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) relative to FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) is at the top. Results are means (n = 2 biological replicates). Genes indicated with arrows are used in subsequent experiments. TSS, transcription start site; TES, transcription end site.
(B) As in A, but representing RNA-seq log2-fold changes. Results are means (n = 3 biological replicates).
(C) Differential cumulative distribution of the average (n = 3 biological replicates) changes in the abundance of mRNAs measured by RNA-seq in PGC-1α KD MBs transiently expressing FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) relative to FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut). ****, P < 0.0001 comparing PRO-seq PGC-1α-responsive genes (red line) with non-target genes (blue line) using a Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.
(D) As in A, but representing raw-scaled log2-fold changes in pausing indices. Results are means (n = 2 biological replicates).
(E) Scatter plot representation of gene-scaled log2-fold changes in pausing indices for the specified MBs. Horizontal bars indicate mean values. P-values compare the indicated conditions using a nonparametric Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. ****, P < 0.0001.
(F) Average distribution of PRO-seq signal (n = 2 biological replicates) at and around the TSS of the 125 PGC-1α-responsive genes identified in A. Read counts are summed in non-overlapping 25-nucleotide bins.
(G) Histogram representations of CUT&RUN qPCR quantitations of INTS11 binding, in the specified MBs, to the promoter (left) or PPP site (right) of three PGC-1α CBM-activated genes, where values were normalized to binding values obtained for the corresponding locations in the Gapdh gene. Results are means ± S.D. (n = 4 biological replicates). Here and in histograms below, P-values compare the specified MBs using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; no asterisks, P ≥ 0.05. Asterisk color corresponds to gene color.
(H) Histogram representations of RT-qPCR quantitations of pre-mRNA (top) and mRNA (bottom) from three PGC-1α(CBM)-responsive genes, normalized to the geometric mean of Hprt and Gapdh mRNA levels using lysates of the specified MBs. Results are means ± S.E.M. (n = 3 biological replicates). P-values are as shown in G.
Next, we quantitated PRO-seq signals that resided immediately downstream of promoters, i.e. at PPP sites, and within gene bodies to calculate pausing indices for the 125 PGC-1α-responsive genes (Table S2) and, as negative control, a set of 120 randomly selected expression-matched genes. Comparison of pausing indices demonstrated that either downregulating PGC-1α or mutating its CBM reduced the release of RNAPII from PPP (Figure 4D) in a way that is specific to PGC-1α target genes (Figure S3B). Importantly, direct comparisons of average pausing indices demonstrated that mutating the CBM of FLAG-PGC-1α almost completely abolished its ability to release RNAPII from pausing at its target genes (Figure 4E). This agrees with our biochemical data showing that the PGC-1α CBM is required for the recruitment of P-TEFb to the CBC (Figures 2 and 3).
Additional comparisons of PRO-seq signal distributions at PGC-1α-responsive genes (Figure 4F) and expression-matched control genes (Figure S3C) showed that PGC-1α KD decreased RNAPII densities at PPP sites and within bodies of target genes in a way that was largely rescued by FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) expressed at near-normal PGC-1α levels (Figure S3D–G). This observation, combined to our finding that FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) inhibits recruitment of the catalytic subunit of Integrator, INTS11, at PPP sites but not at the promoter of CBM-responsive genes (Figure 4G), supports our biochemical data (Figures 2 and 3) indicating that, in addition to promoting RNAPII release from PPP, the P4RC also prevents early transcription termination by competing against Integrator recruitment to the CBC during PPP. Notably, recruitment of INTS11 at PPP sites of control genes was not PGC-1α-dependent (Figure S3H). Consistent with this, expression of FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) in PGC-1α-KD MBs failed to restore the PRO-seq signal to the same extent as did FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) for PGC-1α target genes (Figures 4F and S3D–G,I,J). Our finding that FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) partially restored normal RNAPII densities at sites of PPP and in the bodies of PGC-1α target genes may reflect CBM-independent activity of PGC-1α on transcription initiation. This interpretation is supported by our observation that mutating the CBM prevents association of FLAG-PGC-1α with RNAPII(pS2) but not with RNAPII(pS5) (Figure 3B).
P4RC formation activates the expression of genes in the interferon-signaling pathway
Term enrichment analyses indicated that more than half of PGC-1α(CBM)-dependent genes are involved in the cellular response to stress (75 genes were annotated with GO:0006950, response to stress, Padj = 2.82×10−34). In particular, 51 of PGC-1α(CBM)-dependent genes are annotated as functioning in interferon (IFN)-signaling pathways (Table S3). We randomly selected CBM-dependent IFN-pathway genes for further analyses. These genes included IFN-stimulated gene 15 (Isg15), Bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 (Bst2), and Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase family member 10 (Parp10). RT-qPCR quantitations of pre-mRNA and mRNA levels deriving from these genes showed that, similar to FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut), expression of FLAG-PGC-1α(ΔRS) or FLAG-PGC-1α(NR1-3mut) at near-normal PGC-1α levels in PGC-1α-KD cells (Figure S3A) failed to restore gene expression to the same extent as did FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) (Figures 4H, S3K). Furthermore, siRNA-mediated knock-down of MED1 or ERRα in CTL MBs transiently expressing FLAG likewise reduced pre-mRNA levels of five randomly selected PGC-1α-CBM-responsive genes (Figure S3L). Together, our results demonstrate that PGC-1α, via its interactions that are required for P4RC formation, promotes the transcription of stress-associated genes by preventing early transcription termination and by inducing the release of RNAPII from PPP into productive transcription elongation.
P4RC function requires PGC-1α CBM binding to CBP80 at the 5´-end of nascent transcripts
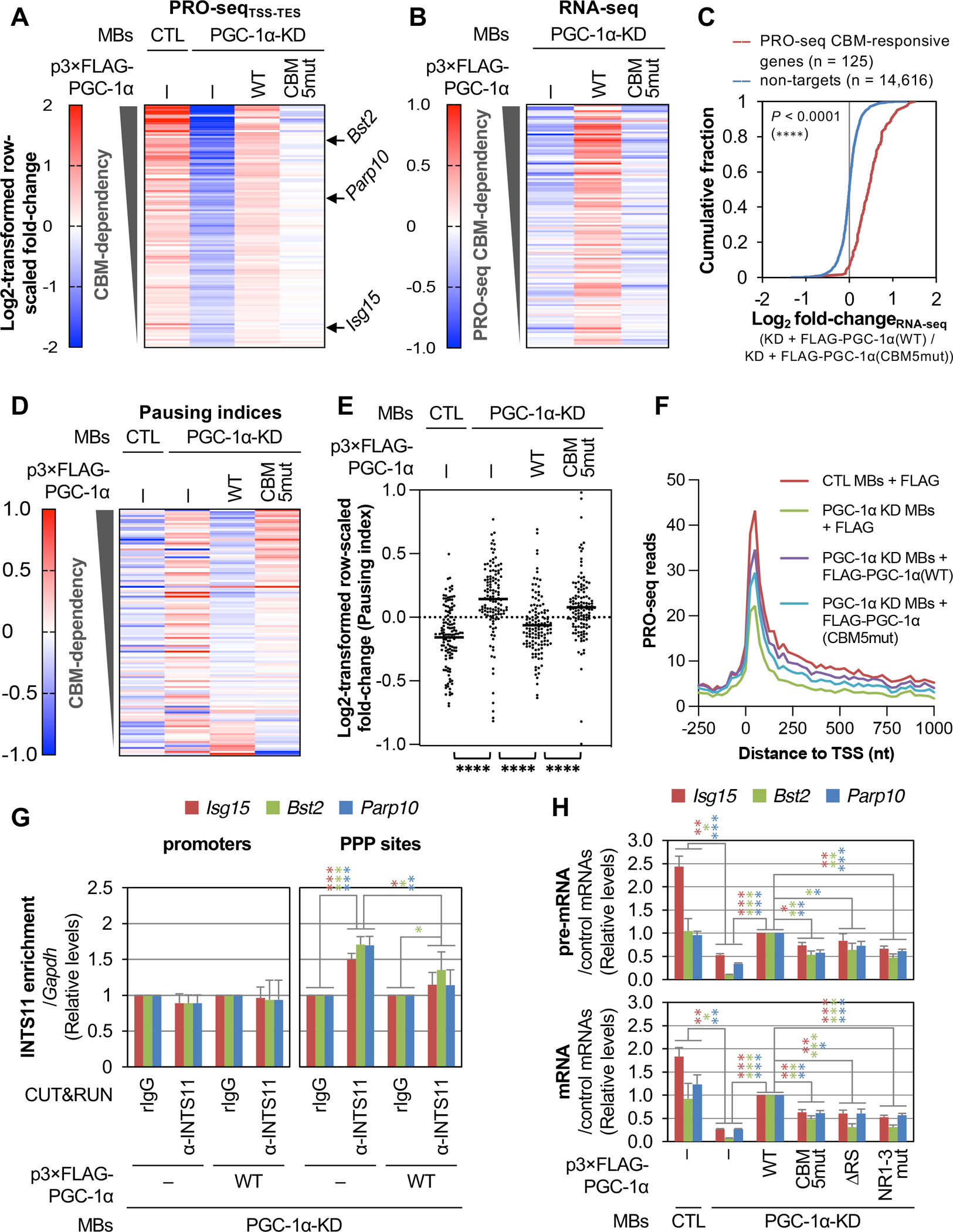
We next used native RNA IP coupled to sequencing (RIP-seq) (Figure S4A) to determine genome-wide if the PGC-1α CBM binds transcripts that the P4RC upregulates. Briefly, we prepared cDNA libraries using RNA purified from anti-FLAG IPs of lysates of PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing either FLAG, FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) or FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut). We then mapped Illumina sequencing reads to either exons or introns. Results revealed that FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) binds both exon-containing transcripts (i.e. pre-mRNAs and/or mRNAs) and intron-containing transcripts (i.e. pre-mRNAs) deriving from the 125 PGC-1α-dependent PRO-seq target-genes in a CBM-dependent manner (Figure 5A, Table S2). CBM-dependent binding was largely specific to PRO-seq targets (Figures 5B, S4B). Thus, PGC-1α binds its target RNAs co-transcriptionally and via its CBM. RT-qPCR analyses validated that the CBM significantly contributes to the relative enrichment of Isg15, Bst2 and Parp10 pre-mRNAs and mRNAs, but not control Hprt pre-mRNA and mRNA, in FLAG-PGC-1α IPs (Figures 5C), showing that PGC-1α remains associated with its target transcripts after introns are removed by splicing.
Figure 5. PGC-1α CBM and NR motifs positively regulate PPP dynamics via binding to CBP80 at the 5´ end of transcripts and to ERRα at gene promoters, respectively.
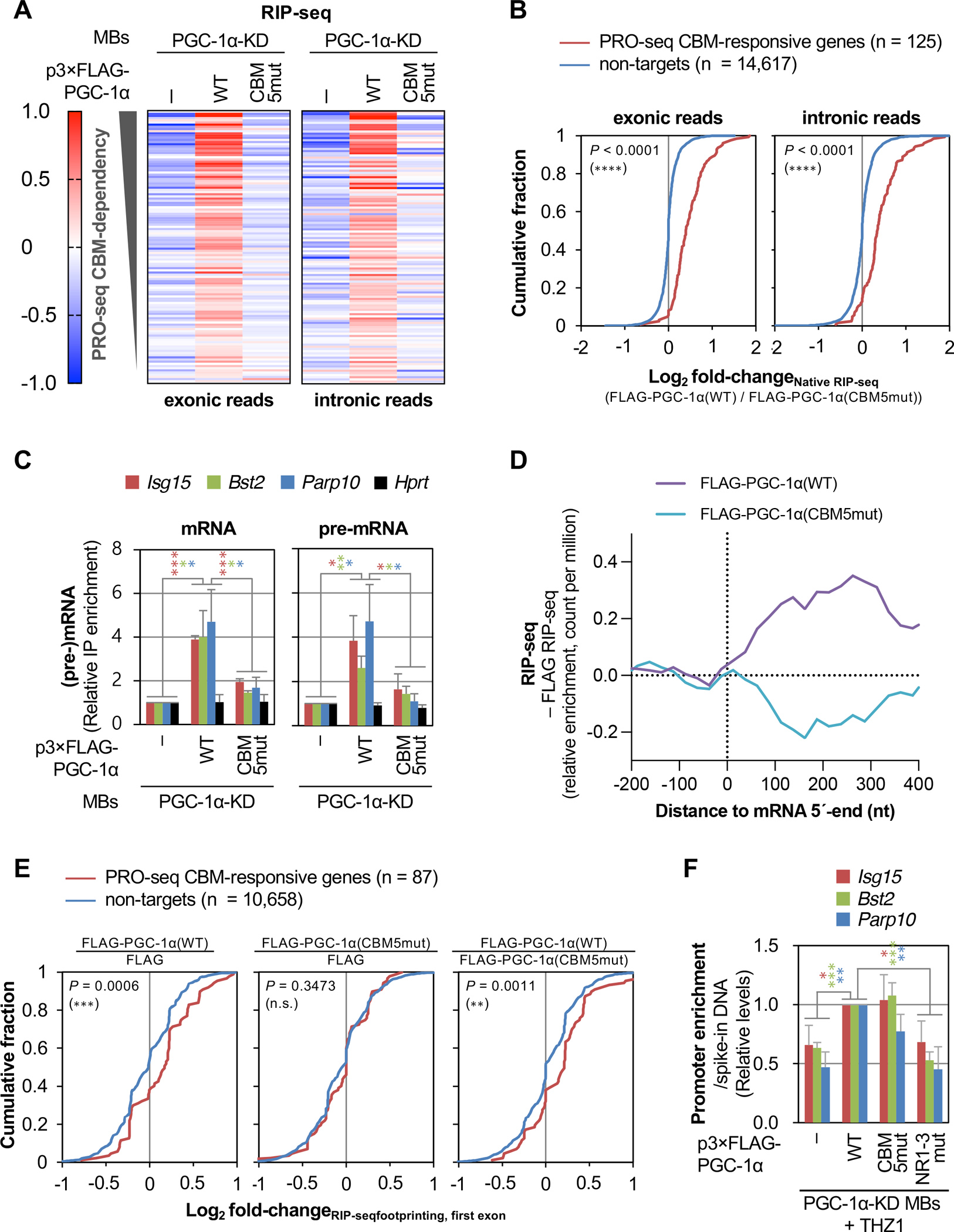
(A) Heatmap representation of raw-scaled RNA-seq log2-fold changes in anti-FLAG IPs (i.e. native RIP-seq) using lysates of the specified MBs and exonic (left) or intronic (right) Illumina reads mapped to transcripts from genes shown in Figure 4A. Results are means (n = 3 biological replicates).
(B) Differential cumulative distribution of the average (n = 3 biological replicates) relative enrichment of exonic (left) or intronic (right) Illumina reads in anti-FLAG IPs (native RIP-seq) in lysates of PGC-1α KD MBs transiently expressing FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) relative to FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut). Here and in differential cumulative distributions below, P-values compare PRO-seq CBM-responsive genes (red) or non-target genes (blue) using a Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.
(C) Histogram representations of RT-qPCR quantitations of mRNA (left) and pre-mRNA (right) from three PGC-1α(CBM)-responsive genes and control gene Hprt, after anti-FLAG IP relative to before IP using lysates of the specified MBs, where values for PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing FLAG were set to 1. Here and in histograms below, results are means ± S.D. (n = 3 biological replicates), P-values compare the indicated conditions using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test., P < 0.05;, P < 0.01;, P < 0.001; no asterisks, P ≥ 0.05. Asterisk color corresponds to gene color.
(D) Average distribution (n = 3 biological replicates) of the relative enrichment of Illumina reads in anti-FLAG IPs using lysates of PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) or FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut), relative to PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing FLAG alone, for the 5ʹ-region of transcripts from genes shown in A. Relative read counts are summed in non-overlapping 25-nucleotide bins.
(E) As B, but showing the average (n = 3 biological replicates) relative enrichment of Illumina reads mapping to first exons in RNase I-treated anti-FLAG IPs (i.e. RIP-seq footprinting) from PGC-1α KD cells transiently expressing the specified constructs. Only genes for which first-exon footprints were identified in each IP are included.
(F) Histogram representations of CUT&RUN-qPCR quantitations of FLAG or the specified FLAG-PGC-1α variant binding to the promoter of three PGC-1α CBM-activated genes in THZ1-treated PGC-1α KD MBs. Values for PGC-1α KD MBs expressing FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) are set to 1. P-values are as shown in C.
See also Figure S4.
Since our IPs of FLAG-PGC-1α were performed in the absence of RNase inhibitors, and immunoprecipitated RNA fragments were 200–1000 nucleotides (Figure S4C), we reasoned that RIP-seq Illumina reads derived primarily from RNA regions bound by FLAG-PGC-1α. In keeping with this idea, reads that mapped within the first 400 nucleotides of transcripts deriving from PGC-1α-target genes were enriched, relative to the control IP of FLAG alone, in the IP of FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) but not the IP of FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) (Figure 5D). In contrast, comparable reads of transcripts deriving from control genes were not enriched in the IP of either FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) or FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) relative to FLAG alone (Figure S4D). To test our reasoning further, we sequenced 20–100-nucleotide RNA fragments, i.e. “footprints”, protected by FLAG-PGC-1α from on-bead RNase I digestion (Figure S4A,E). As predicted, when compared to non-targets, RNA footprints that mapped to the first exon of PGC-1α(CBM) PRO-seq targets were enriched in the IP of FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) relative to the IP of either FLAG alone or FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) (Figure 5E). We conclude that PGC-1α association via its CBM with the 5ʹ-region of its target pre-mRNAs is functionally linked to its ability to activate gene transcription in a CBM-dependent manner.
Evidence that intron-binding-mediated activation of energy metabolism genes by PGC-1α does not depend on the PGC-1α1/-a CBM
Tavares et al. (2020) showed using primary hepatocytes that PGC-1α directly binds introns of pre-mRNAs deriving from genes that are functionally linked to glucose energy metabolism and are activated by PGC-1α.19 In particular, two genes, Gfra1 and 4833422C13Rik, whose expression was downregulated by siRNA-mediated KD of PGC-1α in unstimulated hepatocytes, were identified.19 We detected a robust PRO-seq signal for Gfra1, but not 4833422C13Rik, in unstimulated C2C12 MBs, and we observed that Gfra1 was transcriptionally downregulated after PGC-1α KD (Figure S4F,G). However, relative to P4RC-responsive IFN-pathway genes, e.g. Bst2, (i) no PPP was observed for Gfra1 (Figure S4F), (ii) Gfra1 transcription was not restored to levels close to normal after expression of FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) (Figure S4G), and (iii) neither exon- nor intron-containing Gfra1 RNAs co-immunoprecipitated with FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) (Figure S4H). We conclude that a non-canonical isoform of PGC-1α (see Limitations of the study) regulates the expression of Gfra1 in a mechanism that is distinct from P4RC-dependent release of RNAPII from PPP. However, we cannot ascertain that this is true for all PGC-1α-responsive energy metabolism genes that encode pre-mRNAs whose introns are bound directly by PGC-1α.
PGC-1α binds the promoter of P4RC-dependent genes independently of its CBM
Our integrated analyses of PRO-seq and RIP-seq experiments demonstrate, genome-wide, that the PGC-1α CBM promotes the release of RNAPII pausing at genes whose pre-mRNAs it binds, i.e. that PGC-1α regulates these genes directly. We next used anti-FLAG CUT&RUN coupled to qPCR and PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing a FLAG-PGC-1α variant or FLAG alone to validate that PGC-1α is present at the promoter of target genes and, if so, to test whether the CBM contributes to binding. In these experiments, MBs were treated with the transcription initiation inhibitor THZ1 to quantitate PGC-1α binding to chromatin independently of P4RC formation during PPP.
Consistent with the CBM not being required for either ERRα or paused RNAPII(pS5) to co-immunoprecipitate with FLAG-PGC-1α (Figure 3B), results showed that mutating the CBM did not significantly reduce the recruitment of FLAG-PGC-1α to target-gene promoters (Figure 5F). In contrast, as a control, mutating the ERRα-interacting LxxLL/LLxxL motifs prevented recruitment of FLAG-PGC-1α to target-gene promoters (Figure 5F). Thus, while PGC-1α binding to ERRα is required for the recruitment of PGC-1α to the promoter of genes whose PPP it overcomes, PGC-1α binding to the CBC is not required.
Evidence for P4RC function in primary MBs
To evaluate PGC-1α function in the context of a living organism, we utilized CRISPR-Cas9 to edit into the mouse genome the five amino acid changes to the PGC-1α CBM that preclude CBP80 binding (Figures 6A, S5A). Crossing mice heterozygous for the PGC-1α(CBM) mutations yielded the expected Mendelian ratio (1×PGC-1α(CBM)wt/wt : 2×PGC-1α(CBM)wt/5mut : 1×PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut) of live-born pups that reached weaning age (Figure S5B), indicating that the PGC-1α CBM mutations do not cause embryonic or postnatal lethality. Furthermore, PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut mice that were fed a normal diet did not manifest any growth delays during their first 10-weeks after birth (Figure S5C). Taken together, these observations agree with the finding that PGC-1α is not required for embryonic-to-pubertal myogenesis 40 but does not exclude the possibility that the PGC-1α CBM, while not required for survival and growth in basal conditions, may contribute to known functions of the full-length protein as a regulator of cellular adaption in response to stress.
Figure 6. The P4RC is conserved in mouse skeletal muscle tissues and mediates the differentiation of primary MBs and muscle regeneration.
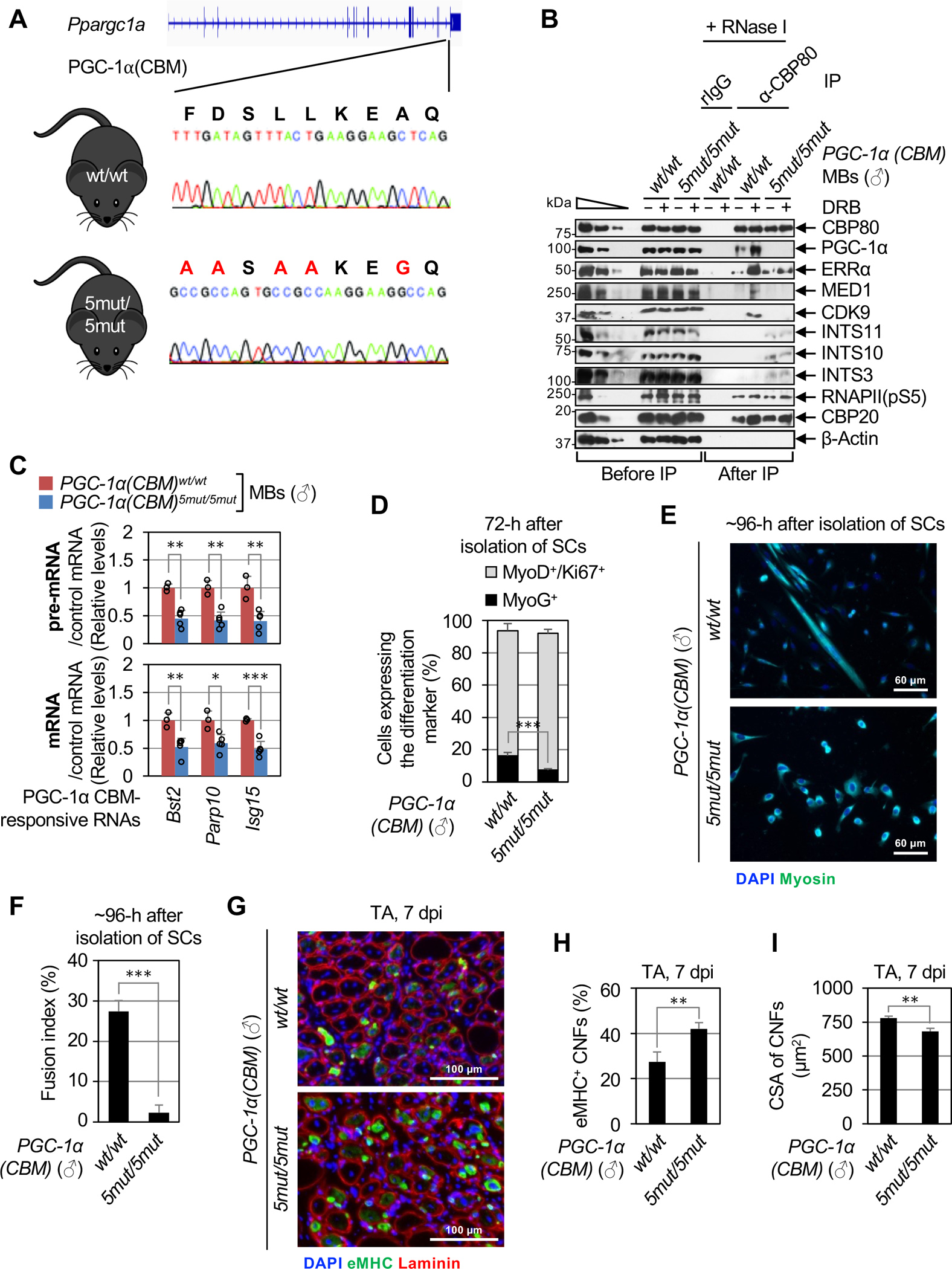
(A) Location of the CRISPR-Cas9-induced point-mutations inserted into both alleles of the mouse Ppargc1a gene to generate the PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut mouse line. Large red letters above the gene sequence indicate changes in CBM residues that were made.
(B) WBs of lysates of primary MBs derived from male (♂) PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut or PGC-1α(CBM)wt/wt mice, that were (+) or were not (−) treated with DRB, before or after IP in the presence of RNase I using α-CBP80 or, as a control, rIgG.
(C) As Figure 4H, but using lysates of primary MBs derived from male PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut or PGC-1α(CBM)wt/wt mice. Here and for histograms below, results are means ± S.D. (n ≥ 3 biological replicates), P-values compare PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut and PGC-1α(CBM)wt/wt using a two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; no asterisks, P ≥ 0.05.
(D) Histogram representations of the percentage of proliferating primary MBs (MyoD+/Ki67+, gray bars) and myocytes (MyoG+, black bars) derived from male PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut or PGC-1α(CBM)wt/wt, 72-hours post-isolation of SCs (n = 4 mice).
(E) Representative images of immunofluorescence staining of Myosin (green) and nuclei (DAPI, blue) in SC cultures derived from male PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut or PGC-1α(CBM)wt/wt, 96-hours post-isolation.
(F) Histogram representations of the fusion index, i.e. the percentage of cells having ≥ 3 nuclei, of SCs isolated and cultured as in E (n = 4 mice).
(G) Representative images of immunofluorescence staining of eMHC (green), Laminin (red), and nuclei (DAPI, blue) in transverse sections of injured tibialis anterior (TA) muscles from male PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut or PGC-1α(CBM)wt/wt mice, isolated 7-days post BaCl2-induced injury (7 dpi).
(H) Histogram representations of the percentage of eMHC-positive centrally nucleated fibers (CNFs) in transverse sections of regenerating TA muscles (n =3 mice).
(I) As in H but for the cross-sectional area (CSA) of CNFs (n = 3 mice).
See also Figures S5,6 and Table S1.
To address this possibility in the context of skeletal muscle biology, we first tested if the PGC-1α CBM functions in primary MBs as it does in C2C12 MBs. We isolated PAX7-positive satellite cells (SCs) from the skeletal muscle of young adult PGC-1α(CBM)wt/wt and PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut mice and subsequently induced SC differentiation to MBs ex vivo (Figure S5D). At 72-hours post-isolation, PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut SCs activated normally into MBs, as evidenced by the appearance of the MyoD MB marker in the same percentage (~80–85%) of WT and CBM mutant cells (Figure S5E). Consistent with our demonstrating that PGC-1α promotes release of RNAPII from PPP in C2C12 MBs via the P4RC (Figures 1–3), the co-IP of PGC-1α, ERRα, MED1 and CDK9 with CBP80 in WT primary MBs cultured ex vivo was evident during DRB-mediated PPP and strongly reduced, if not totally lost, in CBM mutant primary MBs (Figure 6B). Furthermore, each Integrator subunit co-immunoprecipitated with CBP80 in lysates of CBM mutant but not WT primary MBs (Figure 6B). This was true with or without DRB treatment, indicating that CBM-mediated exclusion of Integrator is not due to the catalytic inactivation of P-TEFb. As controls, the expression levels of PGC-1α, as well as the co-IP of paused RNAPII(pS5) and CBP20 with CBP80, were the same for CBM mutant and WT primary MBs (Figure 6B). Additionally, when the P4RC cannot form, CBM mutant MBs expressed abnormally reduced levels of pre-mRNAs and mRNAs from CBM-responsive IFN-pathway genes (Figure 6C).
The PGC-1α CBM mediates primary MB differentiation ex vivo and timely skeletal muscle regeneration in vivo
Both the commitment of proliferating primary MBs (MyoD+/Ki67+) to form myocytes (MyoG+) (Figures 6D, S5F) and the subsequent fusion of myocytes into multinucleated myofibers (Figures 6E–F and S5G,H) were impaired in cells deriving from PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut mice relative to WT littermates. In addition to coordinating the inflammatory response during skeletal muscle regeneration, IFN-ɣ promotes MB differentiation both ex vivo and after injury in vivo (reviewed in Tidball, 201741). Supporting the idea of functional crosstalk between the CBM-dependent and IFN-dependent activation of gene transcription and differentiation of MBs, the CBM was required for efficient IFN-ɣ-dependent induction of PGC-1α target genes when primary MBs were cultured ex vivo with different IFN-ɣ concentrations (as low as 50–500 pg/ml, Figure S5I) and for different times (as early as 3 hours, Figure S5J). We found that IFN-ɣ-mediated activation of gene expression occurred in bursts of transcription that, considering at least ISG15 promotes secretion of cellular IFN-ɣ,42 may reflect autocrine and/or paracrine IFN-mediated signaling. Nonetheless, IFN-ɣ stimulation did not detectably increase the levels of P4RC in DRB-treated WT MBs (Figure S5K). This observation most likely results from the ability of DRB, which is required for P4RC detection using IP, to pile-up P4RC levels in untreated cells.
Our results raise the possibility that the PGC-1α CBM contributes to adult myogenesis in vivo during skeletal muscle regeneration. To test this, we experimentally injured the tibialis anterior (TA) muscle of WT or mutant mice through intramuscular injection of BaCl2 and analyzed regenerating myofibers. Immunostaining TA-muscle cross-sections 7-days post injury (dpi) demonstrated sustained expression of embryonic myosin heavy chain (eMHC), a marker of immature muscle fibers, in a larger fraction of centrally nucleated, i.e. regenerating, fibers (CNFs) in CBM mutant mice compared to WT littermates (Figures 6G,H and S6A,B). The cross-sectional area (CSA) of CNFs was smaller in the TA of CBM mutants compared to WT animals at 7 dpi but no longer at 28 dpi (Figures 6G,I and S6A,C–E). Considering that regenerative myogenesis is typically completed within 10 days in WT mice,43 these observations demonstrate that, like knocking-out ERRα,44 mutating the CBM delays regeneration of skeletal fibers following injury in a way that can be overcome with sufficient time. The same number of SCs was observed in regenerated muscles of mutant and WT animals (Figure S6F), indicating that regeneration delays in mutant mice are not linked to impaired self-renewal of SCs. Finally, consistent with PGC-1α inducing fiber switching in a MEF2-dependent manner,5 and MEF2 not being part of the P4RC (Figure 1D), the distribution of muscle fiber types post-regeneration was not altered in CBM mutant animals (Figure S6G,H). Notably, mutating the CBM impaired ex vivo and in vivo myogenesis both in male (Figure 6D–I) and female (Figures S5F–H,S6A–C) animals, indicating that this mechanism is not sex-specific.
In summary, our observations demonstrate that PGC-1α binding via its CBM to CBP80 at the cap of nascent transcripts sustains normal expression of IFN-pathway genes in skeletal muscle progenitor cells through the formation of the P4RC to support progenitor-cell differentiation ex vivo and muscle regeneration in vivo. As evidenced by the loss of CBP80, MED1, CDK9 and elongating RNAPII(pS2) in IPs of PGC-1α from lysates of PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut livers (Figure S6I), CBM-dependent formation of the P4RC is not limited to MBs, opening up new research avenues in search of biological roles for the P4RC in other tissues.
DISCUSSION
An unanticipated pre-mRNP surveillance mechanism by which PGC-1α activates gene expression
Transcriptional control of gene expression by PGC-1α has been reported to involve chromatin remodeling through the recruitment of histone acetyltransferases, assembly and/or function of the PIC through recruitment of Mediator,14,15 and by direct recruitment, stabilization and/or activation of CDK7.16 Here, we describe the choreographed series of steps that define an unanticipated mechanism, i.e. subsequent to transcription initiation, in which PGC-1α binding to the CBC at the 5´-end of nascent pre-mRNAs promotes the transcription of stress-associated genes by overcoming PPP (each step is numbered as illustrated in the Graphical Abstract): ① PGC-1α is initially recruited to promoters via specific transcription factors, in particular ERRα in the case of mouse MBs (Figures 1, 2, 5); ② the 5´-end of nascent pre-mRNAs synthesized by RNAPII is capped and subsequently bound by the CBC during PPP (reviewed in Rambout and Maquat, 202017) ③ as the CBC becomes physically accessible, PGC-1α binds CBP80 at the cap of transcripts via its CBM and, concomitantly or subsequently, the Mediator subunit MED1 via its RS domain (Figures 1, 3, 5); and ④ the ERRα–PGC-1α–CBC–Mediator–RNAPII complex then recruits P-TEFb to form the P4RC (Figures 1–3), ⑤ thereby releasing RNAPII from PPP and promoting transcript elongation (Figure 4).
We previously provided evidence that the PGC-1α CBM prevents cytoplasmic accumulation of intron 1-containing pre-mRNAs by promoting intron 1 splicing and/or activating nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD).45 Data presented here indicate that PGC-1α also regulates gene expression in a second RNA quality-control pathway: PGC-1α activates the elongation of target-gene transcription provided that the nascent pre-mRNA is properly capped and bound by the CBC, i.e. provided that the pre-mRNA 5ʹ-end is equipped to ensure efficient co- and post-transcriptional maturation of newly synthesized mRNAs as well as their nuclear export and pioneer round(s) of translation.17 To our knowledge, no other transcription factor or coactivator is known to activate gene transcription in a pre-mRNA quality-control pathway.
P4RC competition against Integrator defines a mechanism by which Integrator achieves gene-specific attenuation of transcription
Under conditions where the P4RC cannot form, e.g. when the CBM is mutated, ③ʹ Mediator and P-TEFb are replaced by Integrator (Figures 2,3,4 and 6), ④ʹ which attenuates gene expression by triggering promoter-proximal transcription termination.25,26 In agreement with our view that the P4RC competes against Integrator in a quality-control pathway, Integrator has also been described as an attenuator of non-productive transcription.46
Since Integrator preferentially represses a subset of protein-coding genes, one important and unanswered question has been how Integrator achieves gene-specificity.47 To our knowledge, our data provide the first indication that gene-specificity can derive from transcriptional activators, e.g. PGC-1α and the P4RC, which prevent the promiscuous binding of Integrator to PPP sites and/or nascent pre-mRNAs. This is in contrast to the rixosome, another RNA endonuclease and pausing termination complex, for which gene specificity was recently shown to be achieved through recruitment to specific promoters via binding to promoter-bound Polycomb.48
Do transcription factors define the step of gene transcription regulated by PGC-1α binding to Mediator?
Our data show that, when cooperating with ERRα in MBs, Mediator binding to PGC-1α requires and stabilizes PGC-1α binding to CBP80 to activate gene transcription by overcoming PPP. This is in strong contrast to long-standing studies showing that PGC-1α and Mediator cooperate with CBP/p300 to activate PPARɣ or thyroid hormone receptor α (TRα) in conjunction with retinoid X receptor alpha (RXRα) by augmenting transcription initiation.14,15 Importantly, these latter conclusions derived from in vitro transcription assays, i.e. using conditions in which PPP is not observed.24 On another note, unlike ERRα, which is not known to bind Mediator, PPARɣ, TRα and RXRα each directly bind different Mediator subunits.49 Such interactions may induce structural changes in Mediator that affect its function in gene transcription.35 Therefore, it would not be surprising if PGC-1α-dependent recruitment of Mediator to promoters via ERRα would influence gene transcription differently than when Mediator is recruited to promoters via PPARɣ, TRα or RXRα.
Limitations of the study
Multiple PGC-1α isoforms have been characterized in skeletal muscle cells.50 Using two different antibodies, one of which was raised against the N-terminus of PGC-1α1/-a, we characterized in C2C12 and primary MBs a PGC-1α isoform of ~100 kDa, i.e. the molecular weight of PGC-1α1/-a in primary myotubes.51 Our PRO-seq analyses revealed that 714 genes are transcriptionally downregulated in PGC-1α-KD cells, while only 125 of them are largely reactivated after expression of FLAG-PGC-1α1/-a. Our IP experiments demonstrate that, like cellular PGC-1α in WT cells, FLAG-PGC-1α1/-a is a key constituent of the P4RC in PGC-1α-KD cells. Thus, it is likely that exogenous FLAG-PGC-1α1/-a largely if not fully replaces its corresponding cellular PGC-1α isoform. However, it is possible that PRO-seq targets that are not responsive to FLAG-PGC-1α1/-a are activated by an alternative CBM-containing PGC-1α isoform, such as PGC-1α-b, -c, or a yet-to-be characterized MB-specific isoform.
STAR★METHODS
RESOURCE AVAILABILITY
Lead contact
Further information and requests for resources and reagents should be directed to and will be fulfilled by the lead contact, Lynne E. Maquat (lynne_maquat@urmc.rochester.edu).
Material availability
All materials and reagents will be made available upon request directed to the lead contact, Lynne E. Maquat (lynne_maquat@urmc.rochester.edu), and installation of a material transfer agreement (MTA).
Data and code availability
All sequencing datasets generated in this study (PRO-seq, RNA-seq, native RIP-seq, RIP-seq footprinting) have been submitted to the GEO database (GSE197312). Unprocessed and uncompressed imaging data are available in Mendeley Data (doi:10.17632/39mxxdfkdn.1).
This paper does not report original code.
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.
EXPERIMENTAL MODEL AND SUBJECT DETAILS
Culture of C2C12 and HEK293T cell lines
Mouse C2C12 myoblast (MB) (ATCC, CRL-1772™) and human HEK293T (ATCC, CRL-3216™) cell lines were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM; Gibco) containing 15% fetal bovine serum (VWR) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco). C2C12 MBs in which PGC-1α or, as a negative control, GFP was stably knocked-down (i.e. PGC-1α-KD and CTL C2C12 MBs, respectively) were newly generated as described4 and cultured in medium (see above) supplemented with 1 μg/ml puromycin (Gibco).
To inhibit transcription, C2C12 MBs were cultured for 48 hours with 5 μg/ml of α-amanitin (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), 4 hours with 0.75 μM THZ1 (APExBIO), or 2 hours with 100 μM 5,6-Dichlorobenzimidazole 1-β-D-ribofuranoside (DRB, Sigma-Aldrich). Cell viability was assayed using Trypan blue (Gibco) prior to harvesting.
Isolation and culture of primary skeletal muscle progenitor cells
Primary satellite cells (SCs) were isolated from total-body skeletal muscles of adult mice (see Animal studies) as described52. SCs derived from mouse limb muscles (avoiding the quadriceps) were activated to form MBs in “basal” medium, and MBs were differentiated into myofibers in “differentiation” medium, as described52 except that FGF2 was omitted. Primary MBs were maintained in culture dishes coated with Matrigel® Basement Membrane Matrix (Corning, 37.5 μl/150 cm2) in F10 medium (Gibco) supplemented with 20% FBS (Gibco), 1× GlutaMAX (Gibco), 100 μg/ml Primocin (Invivogen), and 2.5 ng/ml Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor, Human Recombinant (Corning).
Animal studies
After validation of scientific merit by the University of Rochester Dean’s Research Advisory Committee (DRAC), all experiments using mice were approved and authorized by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at the University of Rochester, known as the University Committee on Animal Resources (UCAR). Experiments used adult (age 2–4 months) PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut or PGC-1α(CBM)wt/wt littermates deriving from heterozygous intercrosses. Male and female animals were studied separately, as described in the text, figures, and figure legends.
Founder C57BL/6J PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut mice were generated using 3-component CRISPR-Cas9 editing of the PGC-1α CBM-coding region in the Ppargc1a mouse gene.53 First, the CRISPOR algorithm54 was used to define a protospacer (5´-GGATTTTGATAGTTTACTGA-3´), i.e. a 20-bp sequence within the CBM of Ppargc1a starting with a G and directly preceding an AGG protospacer-adjacent motif (PAM). This protospacer has specificity scores of 72 (MIT; a specificity score) and 87 (CFD; cutting frequency determination, an off-target score) with 0, 0, 2, 25, and 126 predicted off-targets having 0, 1, 2, 3, or 4 mismatches, respectively. Purified Cas9 protein and the single guide RNA (sgRNA, proprietary sequence using the provided protospacer sequence) were obtained from Synthego Corp. (Menlo Park, CA). An ultramer single-strand oligodeoxynucleotide (ssODN) repair template (TTTCAGATACCAACTCAGACGATTTTGACCCTGCTTCCACCAAGAGCAAGTATGACT CTCTGGATGCCGCCAGTGCCGCCAAGGAAGGCCAGAGAAGCTTGCGCAGGTAACGT GTTCCCAGGCTGAGGAATGACAGAGAGATGGTCAATACCTC) carrying codon-optimized substitutions (underlined) within the CBM was obtained from Integrated DNA Technologies.
Cas9 protein (3 pmol) and sgRNA (3pmol) were complexed, combined with the ssODN repair template (10 pmol) in microinjection buffer (100 mM NaCl; 10 mM Tris-HCl [pH, 7.5]; 0.1 mM EDTA), and microinjected into the pronucleus of C57BL/6J mouse zygotes. Founder mice were identified using a duplex PCR assay(see Figure S5A, PCR oligodeoxynucleotides (oligos) are listed in Table S4).53 On-target sequence fidelity was confirmed using Sanger sequencing (Figure 6A). Further, Sanger sequencing around the predicted off-target sites in the Ppargc1a CBM vicinity (i.e. ± 5 million bp from the edited site) and at the Cdk14, Slit2, and Stim2 loci revealed no detectable indels or substitutions (data not shown).
The mouse colony was maintained by backcrossing PGC-1α(CBM)wt/5mut animals with WT C57BL/6J mice (The Jackson Laboratory) at each generation. The PGC-1α(CBM) genotype of each mouse was performed using PCR amplification of the PGC-1α(CBM)wt or PGC-1α(CBM)5mut alleles and ear-punch lysates, a set of three DNA oligonucleotides (Figure S5A and Table S4), and AccuStart II GelTrack PCR SuperMix (Quantabio).
METHOD DETAILS
Plasmid constructions
The following constructs have been previously reported: pcDNA3×FLAG, pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT), pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(ΔRS), pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(ΔCBM), pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut), and pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(NR2mut) (previously referred to as pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(NR mut).4 These constructs were derived from cDNA encoding the canonical 798-amino acid isoform of human PGC-1α, also known as PGC-1α-a, or PGC-1α–1 (Q9UBK2-1).
To construct pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(NR1mut), which encodes full-length human PGC-1α harboring a leucine-to-alanine substitution at residues 88, 89, and 92, (i) a 5´-fragment of PGC-1α cDNA was PCR-amplified using pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) and the primer pair 5´-AAAGGATCCATGGCGTGGG-3´ (sense) and 5´-TGTCTCTGTGGCGACTGCTGCCGCGTTTGCCTC-3´ (antisense), and (ii) a 3´-fragment of PGC-1α cDNA was PCR-amplified using pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) and the primer pair 5´-GAGGCAAACGCGGCAGCAGTCGCCACAGAGACAC-3´ (sense) and 5´-TCCATGAATTCTCAGTCTTAACAATTGCAGGGTTTG-3´ (antisense), where underlined nucleotides specify BamHI and EcoRI sites, respectively, and italicized nucleotides specify NR1 mutations. The resulting two PCR fragments were mixed and PCR-amplified using the sense primer used to amplify the 5´-fragment and the antisense primer used to amplify the 3´-fragment. The resulting PCR product was digested with BamHI and EcoRI and ligated to replace the corresponding region of pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT).
To construct pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(NR3mut), which encodes full-length human PGC-1α harboring a leucine-to-alanine substitution at residues 210, 211, and 214, (i) a 5´-fragment of PGC-1α cDNA was PCR-amplified using pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) and the primer pair 5´-GTTAAGACTGAGAATTCATGGAGCAATAAAG-3´ (sense) and 5´-GTTTGTGGTCGCATATTTGGCAGCCTCCGAGCAG-3´ (antisense), and (ii) a 3´-fragment of PGC-1α cDNA was PCR-amplified using pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) and the primer pair 5´-CTGCTCGGAGGCTGCCAAATATGCGACCACAAAC-3´ (sense) and 5´-GTTCCACACTTAAGGTGCGTTCAATAG-3´ (antisense), where underlined nucleotides specify EcoRI and AflII sites, respectively, and italicized nucleotides specify NR3 mutations. The resulting two PCR fragments were mixed and PCR-amplified using the sense primer used to amplify the 5´-fragment and the antisense primer used to amplify the 3´-fragment. The resulting PCR product was digested with EcoRI and AflII and ligated to replace the corresponding region of pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT).
To construct pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α NR(1-2mut), which encodes full-length human PGC-1α harboring a leucine-to-alanine substitution at residues 88, 89, 92, 144, 147, and 148, (i) a 5´-fragment of PGC-1α cDNA was PCR amplified using pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(NR2mut) and the primer pair 5´-AAAGGATCCATGGCGTGGG-3´ (sense) and 5´-TGTCTCTGTGGCGACTGCTGCCGCGTTTGCCTC-3´ (antisense), and (ii) a 3´-fragment of PGC-1α cDNA was PCR-amplified using pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) and the primer pair 5´-GAGGCAAACGCGGCAGCAGTCGCCACAGAGACAC-3´ (sense) and 5´-TCCATGAATTCTCAGTCTTAACAATTGCAGGGTTTG-3´ (antisense), where underlined nucleotides specify BamHI and EcoRI sites, respectively, and italicized nucleotides specify NR1-2 mutations. The resulting two PCR fragments were mixed and PCR-amplified using the sense primer used to amplify the 5´-fragment and the antisense primer used to amplify the 3´-fragment. The resulting PCR product was digested with BamHI and EcoRI and ligated to replace the corresponding region of pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT).
To construct pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(NR1-3mut), which encodes full-length human PGC-1α harboring a leucine-to-alanine substitution at residues 88, 89, 92, 144, 147, 148, 210, 211 and 214, pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(NR1-2mut) was digested with EcoRI and AflII and ligated to an EcoRI–AflII fragment of pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(NR3mut).
Transient transfections of C2C12 MBs
C2C12 MBs were transiently transfected per 6-cm diameter dish with 2 μg of plasmid DNA using 10 μl of Lipofectamine™ 2000 (Invitrogen), 60 pmol of siRNA using 9 μl of Lipofectamine™ RNAiMAX (Invitrogen), or 2 μg of plasmid DNA and 60 pmol of siRNA using 13 μl of Lipofectamine™ 2000 (Invitrogen). These relative amounts were scaled up or down, depending on needs. Manufacturer’s guidelines were followed except that: cells that had reached 50% confluency were washed with warm PBS (Gibco) and covered with 2 ml of either DMEM (for transfections using plasmid DNA alone or plasmid DNA and siRNA together) or OPTI-MEM™ I Reduced Serum Medium (Gibco) (for transfections using siRNA alone). The transfection mix was then added within 20 minutes. Four-hours post-transfection, 2 ml of DMEM (Gibco) containing 30% FBS (Gibco) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco) were added. Cells were harvested 32–48-hours post-transfection. Control siRNA was purchased from Ambion, and custom siRNAs were purchased from Dharmacon (see KEY RESOURCES TABLE and Table S4).
KEY RESOURCES TABLE.
| REAGENT or RESOURCE | SOURCE | IDENTIFIER |
|---|---|---|
| Antibodies | ||
| Anti-PGC-1α | Novus | NBP1-04676 |
| Anti-PGC-1α1/-a | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-518025 |
| Anti-FLAG-HRP | Sigma | A8592 |
| Anti-FLAG | Sigma-Aldrich | F1804 |
| Anti-CBP80 | Bethyl Laboratories or gift from Yoon Ki Kim | A301-793A N/A |
| Anti-CBP20 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-48793 |
| Anti-MED1 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-5334 |
| Anti-MED4 | Abcam | ab129170 |
| Anti-MED14 | Invitrogen | PA5-44864 |
| Anti-CDK9 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-484 or sc-13130 |
| Anti-Cyclin T1 | Cell Signaling | 81464 |
| Anti-MEF2 (MEF2A + MEF2C) | Abcam | ab64644 |
| Anti-ERRα | Cell Signaling | 13826 |
| Anti-ERα | Proteintech | 21244-1-AP |
| Anti-RNAPII (total) | Millipore | 05-623 |
| Anti-RNAPII(pS5) | Abcam | ab5131 |
| Anti-RNAPII(pS2) | Abcam | ab5095 |
| Anti-eIF4AIII | Bethyl Laboratories or Santa Cruz Biotechnology | A302-981A sc-33632 |
| Anti-MAGOH | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-56724 |
| Anti-INTS3 | Proteintech | 16620-1-AP |
| Anti-INTS10 | Proteintech | 15271-1-AP |
| Anti-INTS11 | Sigma-Aldrich | HPA029025 |
| Anti-PABPC1 | Abcam | ab21060 |
| Anti-β-Actin | Sigma-Aldrich | A2228 |
| Anti-α-Tubulin | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | sc-58666 |
| Anti-GAPDH | Cell Signaling | 2118 |
| Anti-Calnexin | Enzo | ADI-SPA-865 |
| Anti-NONO | Bethyl or Santa Cruz Biotechnology | A300-582A sc-46220 |
| Anti-Histone H3 | Abcam | ab1791 |
| Goat anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Poly-HRP Secondary Antibody, HRP | Invitrogen | 32230 |
| Goat anti-Rabbit IgG (H+L) Secondary Antibody [HRP] (Pre-adsorbed) | Novus | NBP1-75318 |
| Peroxidase IgG Fraction Monoclonal Mouse Anti-Rabbit IgG, light chain specific | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 211-032-171 |
| Clean-Blot™ IP Detection Reagent (HRP) | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 21230 |
| Anti-PAX7 | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | AB_528428 |
| Anti-MyoD | BD Biosciences | 554130 |
| Anti-Ki67(Alexa 488) | Cell Signaling | 11882S |
| Anti-MyoG | Abcam | ab124800 |
| Anti-Skeletal muscle myosin | Sigma Aldrich | HPA1239 |
| Anti-eMHC | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | BF-45 and F1.652 |
| Anti-Myosin heavy chain Type I | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | BA-D5 |
| Anti-Myosin heavy chain Type IIA | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | SC-71 |
| Myosin heavy chain Type IIB | Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank | BF-F3 |
| Anti-Laminin | Sigma-Aldrich | L0663 |
| Goat anti-Mouse IgG2b Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor™ 568 | Invitrogen | A-21144 |
| Goat anti-Mouse IgG1 Cross-Adsorbed Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor™ 633 | Invitrogen | A-21126 |
| Goat anti-Mouse IgG, IgM (H+L) Secondary Antibody, Alexa Fluor™ 488 | Invitrogen | A-10680 |
| Bacterial and virus strains | ||
| One Shot™ MAX Efficiency™ DH5α-T1R Competent Cells | Invitrogen | 12297016 |
| Biological samples | ||
| N/A | ||
| Chemicals, peptides, and recombinant proteins | ||
| DMEM, high glucose, pyruvate | Gibco | 11995-065 |
| Ham’s F-10 Nutrient Mix | Gibco | 11550-043 |
| Trypsin-EDTA (0.25%), phenol red | Gibco | 25200-056 |
| Avantor Seradigm Premium Grade Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) | VWR | 97068-085 |
| Horse Serum, New Zealand origin | Gibco | 16050-114 |
| Penicillin-Streptomycin (10,000 U/mL) | Gibco | 15140-122 |
| Hexadimethrine bromide (Polybrene) | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | SC134220 |
| Puromycin | Gibco | A11138-03 |
| Hepes | Gibco | 15630-106 |
| Collagenase Type II | Gibco | 17101-015 |
| Dispase | Gibco | 17105-041 |
| GlutaMAX™ Supplement | Gibco | 35050-061 |
| Primocin | InvivoGen | ant-pm-1 |
| Basic Fibroblast Growth Factors (bFGF), Human Recombinant | Corning | 354060 |
| Matrigel® Basement Membrane Matrix | Coming | 354234 |
| α-amanitin | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | CAS 23109-05-9 |
| THZ1 | APExBIO | A8882 |
| 5,6-Dichlorobenzimidazole 1-β-D-ribofuranoside (DRB) | Sigma-Aldrich | D1916 |
| Trypan Blue Stain (0.4%) | Gibco | 15250-061 |
| Lipofectamine™ 2000 | Invitrogen | 11668019 |
| Lipofectamine™ RNAiMAX | Invitrogen | 13778075 |
| Opti-MEM™ I Reduced Serum Medium | Gibco | 31985070 |
| PBS, pH 7.4 | Gibco | 10010023 |
| Halt™ Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail | Thermo Fisher Scientific | 78442 |
| N-ethylmaleimide | Alpha Aesar | 40526 |
| Protein A-Agarose | Roche | 10037256 |
| Dynabeads™ Protein A | Invitrogen | 10002D |
| ANTI-FLAG® M2 Affinity Gel | Sigma-Aldrich | A2220 |
| Anti-FLAG® M2 Magnetic Beads | Millipore | M8823 |
| Mouse IgG–Agarose | Sigma-Aldrich | A0919 |
| Ambion™ RNase I, cloned, 100 U/μL | Ambion | AM2295 |
| RNase A, DNase and protease-free | Thermo Fisher Scientific | EN0531 |
| TURBO™ DNase | Invitrogen | AM2238 |
| Micrococcal Nuclease (MNase) | Cell Signaling | 10011 |
| 3×FLAG® peptide | Sigma-Aldrich | F4799 |
| Heparin sodium salt from porcine intestinal mucosa | Sigma-Aldrich | H3393 |
| TRIzol™ Reagent | Invitrogen | 15596018 |
| Maxima™ H Minus cDNA Synthesis Master Mix | Thermo Fisher Scientific | M1662 |
| Superscript™ III Reverse Transcriptase | Invitrogen | 18080093 |
| dNTP Mixture | Omega | S123315 |
| Random Primers | Invitrogen | 58875 |
| RNase OUT™ Recombinant Ribonuclease Inhibitor | Invitrogen | 10777019 |
| SUPERase·In™ RNase Inhibitor | Invitrogen | AM2696 |
| PerfeCTa SYBR Green SuperMix, ROX™ | Quantabio | 95055-02K |
| PerfeCTa SYBR Green SuperMix, Low ROX™ | Quantabio | 95056-02K |
| T4 RNA ligase 2, truncated KQ | New England Biolabs | M0373 |
| RNA 5′ pyrophosphohydrolase (RppH) | New England Biolabs | M0356S |
| T4 polynucleotide kinase (T4 PNK) | New England Biolabs | M0201L |
| NEBNext® Ultra™ II Q5® Master Mix | New England Biolabs | M0544 |
| SYBR™ Gold Nucleic Acid Gel Stain | Thermo Fisher Scientific | S11494 |
| RQ1 RNase-free DNase | Promega | M6101 |
| Shrimp Alkaline Phosphatase (rSAP) | New England Biolabs | M0371L |
| Cas9 2NLS Nuclease | Synthego | N/A |
| AccuStart II GelTrack PCR SuperMix | Quantabio | 95136 |
| Cas9 2NLS Nuclease | Synthego | N/A |
| Recombinant Murine IFN-ɣ | Prepotech | 50-813-665 |
| Critical commercial assays | ||
| Satellite Cell Isolation Kit, mouse | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-104-268 |
| Anti-Integrin α-7 MicroBeads, mouse | Miltenyi Biotec | 130-104-261 |
| miRNeasy Mini Kit | Qiagen | 217004 |
| RNase-Free DNase Set | Qiagen | 79254 |
| RiboMinus™ Eukaryote Kit v2 | Thermo Fisher Scientific | A15020 |
| 5′ DNA Adenylation Kit | New England Biolabs | E2610 |
| Monarch® RNA Cleanup | New England Biolabs | T2040 |
| Gel Cassettes, Pippin HT, 2% agarose | Sage Science | HTC2010 |
| NEBNext® Multiplex Small RNA Library Prep Set for Illumina® | New England Biolabs | E7560 |
| TruSeq RNA Library Prep Kit v2 | Illumina | RS-122-2001/2 |
| CUTANA™ ChIC/CUT&RUN Kit | EpiCypher | 14-1048 |
| NucleoBond® Xtra Maxi EF | Macherey-Nagel | 740424.50 |
| Deposited data | ||
| PRO-seq, RNA-seq, native RIP-seq, and RIP-seq footprinting from C2C12 MBs | This paper | GSE197312 |
| Original imaging data | This paper | doi:10.17632/39mxxdfkdn.1 |
| Experimental models: Cell lines | ||
| C2C12 MBs | ATCC | CRL-1772™ |
| HEK293T cells | ATCC | CRL-3216™ |
| CTL C2C12 MBs | This paper | N/A |
| PGC-1α-KD C2C12 MBs | This paper | N/A |
| Experimental models: Organisms/strains | ||
| C57BL/6J mice | The Jackson Laboratory | 000664 |
| PGC-1α(CBM)5mut/5mut C57BL/6J mice | This paper | N/A |
| Oligonucleotides | ||
| PCR primers for the generation of constructs: see Table S4 | This paper | see Table S4 |
| Gene-specific shRNA and siRNA sequences: see Table S4 | This paper | see Table S4 |
| SilencerTM Negative Control No.1 siRNA | Ambion | N/A |
| RT-qPCR primers: see Table S4 | This paper | see Table S4 |
| CUT&RUN-qPCR primers: see Table S4 | This paper | see Table S4 |
| CUT&RUN Spike-in DNA sequence: see Table S4 | This paper | see Table S4 |
| Protospacer sequence used to generate CBM sgRNA: see Table S4 | This paper | see Table S4 |
| Single-stranded oligodeoxynucleotide repair template to introduce 5 point mutations in the CBM of the mouse Ppargc1a gene: see Table S4 | This paper | see Table S4 |
| Recombinant DNA | ||
| pcDNA3×FLAG | Cho et al., 2018 | N/A |
| pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) | Cho et al., 2018 | N/A |
| pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(NR1mut) | This paper | N/A |
| pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(NR2mut) | This paper | N/A |
| pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(NR3mut) | This paper | N/A |
| pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(NR1-3mut) | This paper | N/A |
| pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(ΔRS) | Cho et al., 2018 | N/A |
| pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(ΔCBM) | Cho et al., 2018 | N/A |
| pcDNA3×FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) | Cho et al., 2018 | N/A |
| VSV-G plasmid | Addgene | 8454 |
| pCG-gag-pol plasmid | Cho et al., 2018 | N/A |
| MISSION shRNA pLKO.1-puro plasmid | Cho et al., 2018 | N/A |
| pRetroSuper-GFP-shRNA plasmid | Cho et al., 2018 | N/A |
| Software and algorithms | ||
| CRISPOR | Haeussler et al., 2016 | N/A |
| ImageJ | Schneider et al., 2012 | N/A |
| Integrative Genomics Viewer (v2.9.2) | Robinson et al., 2017 | N/A |
| Prism9 | GraphPad | N/A |
| Custom PRO-seq analysis scripts | AdelmanLab GitHub | DOI 10.5281/zenodo.5519915 |
| fastP (v0.20.0) | Chen et al., 2018 | N/A |
| STAR (v2.7.2c) | Dobin et al., 2013 | N/A |
| featureCounts (v2.0.3) | Liao et al., 2014 | N/A |
| DESeq2 | Love et al., 2014 | N/A |
| Other | ||
| N/A | ||
Western blotting
Cell lysates were prepared using Hypotonic Gentle Lysis Buffer (10 mM Tris [pH 7.4], 10 mM NaCl, 10 mM EDTA, 1% [w/w] Triton X-100, 1× Halt™ Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail EDTA-free (Thermo Fisher Scientific)) and two 30-second rounds of sonication (Branson Sonifier 250, duty cycle 30%, output control = 3). Protein was analyzed after adding NaCl to a final concentration of 150 mM. Cell lysates were electrophoresed in 8%, 10%, or 12% polyacrylamide gels, and proteins were transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane (Amersham Biosciences) by electroblotting (Bio-Rad). Antibodies used are listed in the KEY RESOURCES TABLE.
Immunoprecipitations of MB lysates
Total C2C12-cell lysates were prepared as for Western blotting. For anti-ERRα IPs, the concentration of Triton X-100 in the Hypotonic Gentle Lysis Buffer was reduced to 0.1 % [v/v]. The NaCl concentration was adjusted to 150 mM, and insoluble debris was pelleted by centrifugation at 16,000g for 10 minutes. After setting aside a fraction of each lysate for analyses before IP, IPs using the rest were performed as previously described,4 except that Dynabeads™ Protein A (Invitrogen) were used in place of Protein A-Agarose (Roche) for the anti-ERRα IPs. When specified, antibody-bound beads were incubated with cell lysates, washed twice with NET2 Buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.4], 150 mM NaCl, 0.05% NP-40, 1× Halt™ Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail EDTA-Free), treated for 15 minutes at 37°C with RNase I (Ambion), TURBO™ DNase (Invitrogen), and/or Micrococcal nuclease (Cell Signaling), and washed again five-times with NET2 buffer prior to adding 2×Laemmli Buffer and analysis by western blotting. RNase I was incubated in the manufacturer’s buffer supplemented with 1× Halt™ Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail EDTA-Free. TURBO DNase or Micrococcal nuclease was incubated in 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 100 mM NaCl, 0.05% (v/v) Triton X-100, 10 mM CaCl2, 0.5 mM MgCl2, 1× Halt™ Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail EDTA-Free.
For tandem IPs, FLAG-containing complexes were affinity-eluted from antibody-bound beads using NET2 Buffer supplemented with 200 μg/mL 3×FLAG peptide (Sigma) and 5% glycerol (v/v). Elution was overnight at 4°C with rocking.
Immunoprecipitations of MB chromatin fractions
Fractionation of C2C12 MBs was optimized from a previously published protocol,55 and performed on ice using freshly prepared RNase-free and 0.2 μm-filtered ice-cold buffers. All centrifugations were performed at 4°C. Four 15-cm dishes of PGC-1α-KD C2C12 MBs transiently expressing FLAG or FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) were rinsed with ice-cold PBS, and scraped in ice-cold PBS containing 5 μM α-amanitin to stall engaged RNAPII on chromatin. Cells were pelleted at 500g for 5 minutes, and pellets were resuspended in 500 μl of ice-cold HLB+N Buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 10 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.5% [v/v] NP-40, 20 μM α-amanitin, 1× Halt™ Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail EDTA-Free, 2.5 mg/ml N-ethylmaleimide (Alpha Aesar)) and incubated for 5 minutes on ice to break cell membranes. Samples were underlaid with 250 μl of ice-cold HLB+NS Buffer (HLB+N supplemented with 10% [w/v] sucrose) and centrifuged at 3,500g for 5 minutes to pellet nuclei (P1). The supernatant was collected (S1), cleared of any contaminating nuclei by centrifugation at 16,000g for 5 minutes, and the cleared cytoplasmic fraction (S2, typically 700 μl) was stored at −80 °C.
Nuclei (P1) were cleared of any remaining cytoplasmic contamination using a second centrifugation at 3,500g for 5 minutes. Cleared nuclei (P2) were resuspended by pipetting up and down in 375 μl of ice-cold NUN1 Buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl [pH 8.0], 75 mM NaCl, 0.5 mM EDTA, 50% [v/v] glycerol, 20 μM α-amanitin, 1× Halt™ Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail EDTA-Free, 2.5 mg/ml N-ethylmaleimide, 1 mM DTT, 300 U RNase OUT™ (Invitrogen)). Samples were supplemented with 375 μl of NUN2 Buffer (20 mM HEPES-KOH [pH 7.5], 300 mM NaCl, 0.2 mM EDTA, 7.5 mM MgCl2, 1% [v/v] NP-40, 1 M urea, 20 μM α-amanitin, 1× Halt™ Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail EDTA-Free, 2.5 mg/ml N-ethylmaleimide, 1 mM DTT, 300 U RNase OUT™), and nuclei were lysed using five one-second vortex pulses every two minutes for 10 minutes. Samples were centrifuged at 16,000g for 5 minutes to pellet chromatin (P3). The resulting supernatant (S3) was cleared of any chromatin contamination at 16,000g for 5 minutes, and the cleared nucleoplasmic fraction (S4, typically 700 μl) was stored at −80 °C.
Major modifications of the fractionation protocol55 pertain to solubilizing the chromatin fraction prior to IP. Chromatin pellets (P3) were washed two times with 750 μl of Chromatin Washing Buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.4], 10 mM NaCl, 10 mM EDTA, 0.1% [w/v] Triton X-100), resuspended in 750 μl of Chromatin Lysis Buffer (Chromatin Washing Buffer supplemented with 20 μM α-amanitin, 1× Halt™ Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail EDTA-Free, and 2.5 mg/ml N-ethylmaleimide), and sheared on ice by passage through a 26-gauge needle ten times followed by two successive 30-second rounds of sonication (Branson Sonifier 250, duty cycle 30%, output control = 3). NaCl concentration was adjusted to 150 mM, and lysates were treated with 100 μg/ml RNase A (Thermo Fisher Scientific) for 15 minutes at room temperature and under gentle rotation. Chromatin was further solubilized by adding 2 mg heparin (Sigma) per mg of chromatin proteins and gentle rotation for 1 hour at 4°C. Insoluble debris was pelleted by centrifugation at 16,000g for 10 minutes (P5). The supernatant was collected (S5), cleared of any contaminating nuclei by centrifugation at 16,000g for 5 minutes, and the cleared solubilized chromatin fraction (S6, typically 700 μl) was pre-cleared using mouse IgG-Agarose beads (Sigma) for 1 hour at 4°C with gentle rotation. Anti-FLAG IPs were performed overnight using pre-cleared samples as described.4 FLAG-containing complexes were eluted in three successive steps that each added 200 μg/mL 3×FLAG peptide (Sigma) in a volume of Chromatin Elution Buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 100 mM NaCl, 0.1% [w/v] Triton X-100, 2.5% glycerol [v/v]) made 1× in Protease and Phosphatase Inhibitor Cocktail EDTA-Free supplemented. The volume was equal to the volume of beads, after which beads were pelleted, and the supernatants were collected and pooled.
To assess fractionation efficacy, cell-equivalent volumes of each fraction were boiled in 1×Laemmli Buffer and analyzed by western blotting.
Immunoprecipitations of mouse tissues
Flash-frozen mouse tissues (~20 mg) were lysed in a 2-ml Tissue homogenizing CKMix tube (Precellys) using 500 μl of Hypotonic Gentle Lysis Buffer (see above) and 30-seconds in a Bead Ruptor 4 Bead Mill Homogenizer (Omni International). Samples were centrifuged for 10 minutes at 4°C and 12,000g. Supernatants were collected and sonicated, and IPs were performed as described above.
Sucrose gradient analyses
Using DRB-treated PGC-1α-KD MBs transiently expressing FLAG-PGC-1α(WT), total solubilized chromatin fractions, or eluates after anti-FLAG IP of chromatin fractions, were prepared as described above. Samples were loaded onto 6–40% (w/v) sucrose gradients prepared with Chromatin Elution Buffer and centrifuged for 90 minutes at 4°C and 41,000 rpm in an SW41 Ti rotor (Beckman Coulter). Gradients were fractionated into 13 ~0.9-ml aliquots using a Density Gradient Fractionation system (Brandel). In the case of aliquots deriving from anti-FLAG IPs, sucrose concentrations were adjusted to ~30%, and proteins were precipitated by adding 1/25 volume of 5% (w/v) sodium deoxycholate salt followed by incubation for 10 minutes at room temperature. Then, 1/10 volume of a solution of 50 g trichloroacetic acid in 22.7 ml water was added, and samples were incubated overnight on ice in a 4°C cold room. Proteins were pelleted for 10 minutes at 4°C and 21,000g. The resulting pellets were washed two times with 1 ml of ice-cold acetone, air-dried, resuspended in 1×Laemmli Buffer in 100 mM Tris (pH 8.0), boiled, and analyzed by western blotting.
RT-qPCR
Total-cell RNA (including small RNAs) was extracted from cell pellets or anti-FLAG immunoprecipitates using TRIzol™ reagent and purified either using a miRNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, including the Optional On-Column DNase Digestion) for C2C12 MB pellets, or using ethanol precipitation for anti-FLAG IPs and primary MB pellets. RNA was reverse-transcribed using SuperScript™ III Reverse Transcriptase (Invitrogen) and random primers (Invitrogen) (Figure 5C), or Maxima™ H Minus cDNA Synthesis Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific) (Figures 4H, 6C, S3K,L, and S5I,J). RT-qPCR was undertaken using PerfeCTa SYBR Green SuperMix (Quantabio) and either the 96-well 7500 Fast Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems) or the 384-well QuantStudio 5 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems). RT-qPCR oligos are listed in Table S4.
PRO-seq library preparation and sequencing
Two biological replicates of 2–4 × 106 CTL MBs expressing FLAG, or PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing either FLAG, FLAG-PGC-1α(WT), or FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut), were permeabilized as described25 with the following modifications. Pellets of PBS-washed trypsinized cells were resuspended in 200 μl of Buffer W, permeabilized in 6 mL of Buffer P for 2 minutes on ice, washed one time with 6 mL of Buffer W, and resuspended at a concentration of 6 × 106 permeabilized cells/mL in Buffer F. Each centrifugation was performed at 500g for 5 minutes.
PRO-seq libraries from permeabilized MBs were generated and sequenced by the Nascent Transcriptomics Core at Harvard University as described elsewhere56 with the following modifications. For each run-on reaction, 0.8 × 106 permeabilized MBs were spiked with 4 × 104 Drosophila S2 cells as a normalization control. Run-on reactions were performed at 37°C in 2× Nuclear Run-on Buffer (10 mM Tris [pH 8], 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 300 mM KCl, 20 μM of each biotin-11-NTP (Perkin Elmer), 0.8 U/μL SuperaseIN (Thermo Fisher Scientific), 1% sarkosyl). Both 5ʹ and 3ʹ adapters have the same sequences as used in Reimer et al. (2021),56 except that random hexanucleotide unique molecular identifier (UMI) sequences were added to the 3ʹ end of the 5ʹ adapter and 5ʹ end of 3ʹ adapter. Adenylated 3’-adapter was prepared using the 5ʹ DNA Adenylation Kit (New England Biolabs) and ligated using T4 RNA Ligase 2, truncated KQ (New England Biolabs) per manufacturer’s instructions in a final concentration of 15% PEG-8000, and incubated overnight at 16°C. Ligations were mixed with 180 μL of Betaine Buffer (1.42 g of betaine brought to 10 mL with Binding Buffer) and incubated for 5 minutes at 65°C and then 2 minutes on ice before adding streptavidin beads. After T4 polynucleotide kinase (New England Biolabs) treatment, beads were washed once each with High Salt Buffer, Low Salt Buffer, and Blocking Oligo Wash (0.25× T4 RNA Ligase Buffer (New England Biolabs) and 0.3 μM blocking oligo), and resuspended in 5ʹ Adapter Mix (10 pmol 5ʹ adapter and 30 pmol blocking oligo). 5ʹ adapter ligation was per Reimer et al. (2021),56 but made 15% in PEG-8000. Eluted cDNA was amplified using five PCR cycles in NEBNext Ultra II Q5 Master Mix (New England Biolabs) and Illumina TruSeq PCR primers RP-1 and RPI-X following the manufacturer’s suggested cycling protocol for library construction. A portion of samples prior to PCR amplification was serially diluted to determine optimal amplification conditions for final library constructions. Pooled libraries were sequenced using the Illumina NovaSeq platform.
RNA-seq library preparation and sequencing
RNA was extracted from three biological replicates of PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing either FLAG, FLAG-PGC-1α(WT), or FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) using TRIzol™ reagent, purified by ethanol precipitation, diluted in 2× Alkaline Fragmentation Solution (12 mM Na2CO3, 88 mM NaHCO3), incubated for 2–5-minutes at 95°C to generate ~20–100-nucleotide RNA fragments, and precipitated using ethanol. Note that fragmentation times need to be optimized for each batch of alkaline-fragmentation solution. Contaminating genomic DNA was degraded using RQ1 RNase-free DNase (Promega) in the presence of 0.4 U/μl of RNase OUT (Invitrogen). RNA was purified by phenol extraction and precipitated using ethanol. DNA-free RNA (500 ng) was decapped using RNA 5´ pyrophosphohydrolase (RppH; New England Biolabs), purified using TRIzol extraction, and precipitated overnight at 4°C using isopropanol. RNA 5´ and 3´ ends were dephosphorylated using recombinant Shrimp Alkaline Phosphatase (rSAP) (New England Biolabs), rSAP was heat-inactivated, and RNA 5énds were re-phosphorylated using T4 polynucleotide kinase (T4 PNK, New England Biolabs) in the presence of RNase OUT. RNA with repaired ends was purified using Monarch® RNA Cleanup Kit (New England Biolabs). cDNA libraries were prepared using a NEBNext® Multiplex Small RNA Library Prep Set for Illumina® (New England Biolabs, Version 8.0_10/20 protocol). PCR products of 140–300-bp were size-selected using Pippin HT (Sage Science). Libraries were sequenced using Illumina NextSeq 550 System High-Output (2 × 75 bp).
Native RNA-immunoprecipitation (RIP-seq) and RIP-seq footprinting library preparation and sequencing
Lysates of three biological replicates of PGC-1α-KD C2C12 MBs expressing either FLAG, FLAG-PGC-1α(WT), or FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) were subjected to IP using anti-FLAG as previously described 4 with the following modifications. IPs utilized Anti-FLAG® M2 Magnetic Beads (Millipore), immunoprecipitates were washed twice with NET2 Buffer supplemented to 150 mM NaCl, twice with NET2 Buffer supplemented to 300 mM NaCl, and once with NET2 Buffer supplemented to 150 mM NaCl.
For native RIP-seq, contaminating genomic DNA was degraded using RQ1 RNase-free DNase in the presence of 0.4 U/μl of RNase OUT, and RNA was purified by phenol extraction and precipitated using ethanol. cDNA libraries were prepared using a TruSeq RNA Library Prep Kit v2 (Illumina) with the following modification: 20 ng of immunoprecipitated RNA was not subjected to poly(A)+ enrichment but rather directly fragmented, shortening the fragmentation time to 4 min. Libraries were sequenced using NovaSeq 6000 Illumina Sequencer (2 × 75 bp).
For RIP-seq footprinting, washed immunoprecipitates were digested on-bead using 2 U/μL RNase I for 30 minutes at 4°C to generate ~20–100-nucleotide RNP fragments, i.e. PGC-1α or control RNA footprints (Figure S4E). Immunoprecipitated RNA fragments were purified using TRIzol™ and precipitated using ethanol. Then, RNA was treated, and cDNA libraries were prepared and sequenced as described for RNA-seq.
Cleavage under targets and release using nuclease (CUT&RUN) coupled to qPCR
Cleavage under targets and release using nuclease (CUTANA™ pAG-MNase for ChiC/CUT&RUN, EpiCypher) was performed using manufacturer instructions (v1.5.2) with some modifications. For anti-INTS11 CUT&RUN, (i) cells were cross-linked with 1% formaldehyde in PBS at room temperature for 10 minutes, and crosslinking was quenched at room temperature for 5 minutes using glycine at a final concentration of 125 mM (after step 7); (ii) bead-bound cells where blocked with washing buffer supplemented with 2 mM EDTA (after step 11); (iii) cell–bead suspensions were incubated, at room temperature for 60 minutes, instead of 10 minutes, after adding pAG-MNase (at step 20); (iv) solubilized chromatin fragments were reverse-crosslinked at 65°C overnight after the addition of SDS (0.1% final), NaCl (200 mM final), and Proteinase K (20 mg/ml final) (after step 28); and (v) reverse-crosslinked DNA was extracted using Phenol[pH 8]:Chloroform:Isoamyl Alcohol (25:24:1, v/v) and purified by ethanol precipitation, instead of using the NEB Monarch DNA Cleanup Kit (at steps 30–31). For anti-FLAG-PGC-1α CUT&RUN, (i) bead–cell suspensions were incubated at room temperature for 30 minutes, instead of 10 minutes, after adding pAG-MNase (at step 20); and (ii) yeast spike-in DNA was added to a final concentration of 100 pg/ml (at step 27, yeast spike-in DNA sequence and qPCR oligos can be found in Table S4).
Immunocytochemistry staining
Immunocytochemistry staining of cultures of primary SCs was performed as described.52
Skeletal muscle injury, tissue sectioning and immunohistochemistry
Skeletal muscle injury using injection of BaCl2 into the tibialis anterior (TA) muscle of WT or mutant mice was performed as described.52 Isolation of injured muscles 7 days post-injury, sectioning and immunohistochemistry were performed as described.52
Microscopy
Immunocytochemistry and immunohistochemistry stainings were imaged using an Echo Revolve Microscope, and images were processed and analyzed using ImageJ.57 Sample analysis was conducted in a double-blind manner.
Illustrations
The graphical abstract and the schematics in Figure 1A were created using BioRender.com. PRO-seq and RNA-seq signal densities were generated using Integrative Genomics Viewer (v2.9.2).58
QUANTIFICATION AND STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
Statistical analyses of results represented as histograms or differential cumulative distributions
For experiments with results represented as histograms or broken lines with error bars (where results are means ± S.D./S.E.M., and n ≥ 3), statistical significance for comparisons was assessed using the unpaired two-tailed Studentś t-test or, in the case of Figures S5I,J, the ratio paired two-tailed Studentś t-test using Prism (v9.3.1). For results represented as differential cumulative distributions (where results are means, n = 3), statistical significance for comparisons was assessed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. ∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01; ∗∗∗, P < 0.001; ∗∗∗∗, P < 0.001; no asterisks, P ≥ 0.05. Statistical significance for comparisons between the observed numbers and expected Mendelian numbers of live-born pups, by genotype, derived from heterozygous intercrosses and reached weaning age was assessed using the χ2 test.
PRO-seq data analysis
All custom scripts described herein are available on the AdelmanLab GitHub (https://github.com/AdelmanLab/NIH_scripts). Dual, 6-nucleotide UMIs were extracted from read pairs using UMI-tools.59 Read pairs were then trimmed using cutadapt 1.14 to remove adapter sequences and low-quality 3ʹ bases (--match-read-wildcards -m 20 -q 10).60 The paired-end reads were then mapped to a combined genome index, including both the spike (dm6) and primary (mm10) genomes, using BWA-MEM (-L 100,5).61 Inserts shorter than 25 nucleotides were removed. The remaining read pairs were then separated based on the genome (i.e. spike-in vs primary) to which they mapped. Both spike-in and primary reads were independently deduplicated, again using UMI-tools. Reads mapping to the Mus Musculus mm10 reference genome were separated according to whether they were R1 or R2, sorted via samtools 1.3.1 (-n),62 and subsequently converted to bedGraph format using a custom script (bowtie2stdBedGraph.pl). We note that this script counts each read once at the exact 3ʹ end of the nascent RNA. Because R1 in PRO-seq reveals the position of the RNA 3ʹ end, the “+” and “−” strands were swapped to generate bedGraphs representing 3ʹ end positions at single-nucleotide resolution. Samples displayed highly comparable recovery of spike-in reads. Thus, samples were normalized based on sequencing depth. Combined bedGraphs were generated by summing counts per nucleotide of both replicates for each condition.
| Sample | Total reads | Uniquely mapped reads (Percentage of total) | Agreement between replicates (Spearman’s rho) |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTL MBs + FLAG | 116,116,729 | 60.33% | 0.97 |
| PGC-1α-KD MBs + FLAG | 113,517,396 | 60.14% | 0.98 |
| PGC-1α-KD MBs + FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) | 128,610,850 | 60.85% | 0.97 |
| PGC-1α-KD MBs + FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) | 90,848,827 | 63.12% | 0.97 |
Refinement of gene annotation (GGA)
To select gene-level features for differential expression analysis and pairing with PRO-seq data, we assigned a single, dominant transcription start site (TSS) and transcription end site (TES) to each active gene. This was accomplished using a custom script, get_gene_annotations.sh (available at https://github.com/AdelmanLab/GetGeneAnnotation_GGA), which uses RNA-seq read abundance and PRO-seq R2 reads (RNA 5ʹ ends) to identify dominant TSSs, and RNA-seq profiles to define most commonly used TESs. RNA-seq and PRO-seq data from all conditions were used for this analysis to comprehensively capture gene activity in these samples.
PRO-seq differential expression
Read counts from the dominant transcription start site (TSS) to the dominant transcription end site (TES) of each gene were calculated, in a strand-specific manner. Differentially expressed genes were identified using DESeq2.63 Size factors were determined using DESeq2 (for CTL MBs + FLAG: 1.061, 1.010; PGC-1α-KD MBs + FLAG: 1.229, 1.117; PGC-1α-KD MBs + FLAG-PGC-1α(WT): 0.9720, 1.060; PGC-1α-KD MBs + FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut): 1.077, 0.6196).
| DEseq2 size factors | ||
|---|---|---|
| Sample | Replicate 1 | Replicate 2 |
| CTL MBs + FLAG | 1.0611648 | 1.01078469 |
| PGC-1α-KD MBs + FLAG | 1.22958216 | 1.11771848 |
| PGC-1α-KD MBs + FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) | 0.97209693 | 1.06009376 |
| PGC-1α-KD MBs + FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) | 1.07704874 | 0.6196903 |
At P-value threshold of < 0.001 and fold-change > 1.3, 125 genes were identified as both downregulated in PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing FLAG relative to CTL MBs expressing FLAG, and upregulated in PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) relative to PGC-1α-KD MBs expressing FLAG.
PRO-seq control genes
Unchanged genes were selected based on having |log2FC| ≤ log2(1.3) and Padj > 0.1 across all comparisons made in the PRO-seq differential expression analyses. Subsequent filtering included retaining only protein-coding genes at least 1 kbp in length. These unchanged genes, alongside the 125 differentially expressed genes of interest, were subjected to expression-matching (https://github.com/AdelmanLab/Expression-Matching) to generate a list of control genes (n = 120) matched with the genes of interest in terms of counts/kbp in the CTL MBs expressing FLAG alone.
PRO-seq upstream antisense RNAs
Upstream antisense RNA (uaRNA) TSSs were determined for any gene having a divergent partner as called by GGA refinement (63/125 genes of interest, 82/120 control genes).
PRO-seq metagene plots and pausing indices
Read-count matrices were created around the dominant TSSs (described above) from −500 to +2500 in 25-bp bins (50-bp for uaRNAs) (all windows herein relative to TSS) using the custom script, make_heatmap. Binned signal in each condition was averaged across gene lists. To calculate pausing indices, PRO-seq read counts were summed in the window from the TSS to +150 nt (sense strand) for each gene, and also from +250 nt to +2250 nt, using the refined annotations described above. The ratio of signal density in the promoter-proximal region (TSS to +150) relative to the gene-body region (+250 to +2250) is defined as the pausing index.
RNA-seq and RIP-seq data analysis
Sequencing quality and adapter contamination were assessed using FastQC v0.10.1.64 Adapter sequences were trimmed using fastp v0.20.065 with a minimum length of 25 nucleotides and a mean quality of 13 nucleotides at 5ʹ and 3ʹ ends. Processed reads were aligned to the mouse reference genome GRCm38 using STAR v2.7.2c,66 and this genome was indexed using STAR by setting --runMode to genomeGenerat. Raw FASTA sequences and annotations were downloaded from the GENCODE portal. Parameters outFilterScoreMinOverLread and outFilterMatchNminOverLread were set to 0.3 and 0.5 for RIP-seq footprinting or RNA-seq, and native RIP-seq datasets respectively. Gene expression values were quantified using featureCounts v2.0.367 and the TSS-TES annotations as described above. Exonic reads were quantified using featureCounts with parameters -t exon, --fracOverlap 1 and GRCm38v24 annotations. Intronic reads were quantified as the difference in total gene and exonic reads. Genes with exonic reads ≥ total reads were excluded. Raw read counts were size factor-normalized using DESeq2.63
Native RIP-seq metagene plots
Bam files of native RIP-seq replicates were merged using samtools merge.62 Pooled read counts for anti-FLAG-PGC-1α(WT) IPs and for FLAG-PGC-1α(CBM5mut) IPs were individually normalized to pooled read counts for anti-FLAG IPs and converted to bigwig files using deeptools bamCompare subtract operation.68 Enrichment read-count matrices were computed around the 5´-end of PGC-1α PRO-seq mRNA targets, or expression-matched control mRNAs (see above), using deeptools computeMatrix as described elsewhere.69
Term enrichment analysis
Term enrichment analysis was performed using g:Profiler (version e105_eg52_p16_e84549f) online tool, selecting the Ensembl ID with the most GO annotations for each given mouse gene, and otherwise using standard parameters (https://biit.cs.ut.ee/gplink/l/GjfICSh0RT).
Supplementary Material
Cell equivalents in after IP relative to before IP samples, related to Figures 1, 2, 3, 6, S1, S5 and S6.
PRO-seq, RNA-seq, and RIP-seq values for the 125 PGC-1α-responsive genes, related to Figures 4, 5, S3 and S4.
Term enrichment analysis of PGC-1α CBM-responsive genes identified by PRO-seq, related to Figure 4.
Oligonucleotide sequences, related to STAR Methods.
Highlights.
Complexes of PGC-1α reconfigure during transcription initiation and early elongation
PGC-1α binding to ERRα, CBP80 and MED1 nucleates P4RC formation during RNAPII pausing
P4RC recruits P-TEFb and also prevents Integrator binding to promote pause release
Skeletal muscle regeneration in mice is promoted by the PGC-1α CBP80-binding motif
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank Alex Hewko for technical help, Yoon Ki Kim for anti-CBP80, Xin Zhiguo Li lab-members for help with sucrose-gradient fractionations, Seth Goldman and the Harvard Nascent Transcriptomics Core for constructing PRO-seq libraries, Jeffrey Malik and the University of Rochester Medical Center Genomics Research Center for help with RIP-seq library constructions and sequencing of the RNA-seq and RIP-seq libraries, Michelle Dias for help with the RIP-seq analyses, and Eric Wagner for anti-Integrator antibodies and helpful discussions. Research was supported by NIH R01 GM59514 to L.E.M., NIH R01 HL147476 to J.M.M., NIH R01 AG051456 and R01 CA220467 to J.V.C, and NIH R01 GM134539 to K.A. H.K.Y was supported by USDA/ARS funding under Cooperative Agreement No. 58-3092-0-001 and a NRI Zoghbi Scholar Award. X.R. was partially supported by an AHA Postdoctoral Fellowship (18POST33960339), an AHA Career Development Award (854100), and NIH R21 AG075368. H.C. was partially supported by an AHA Postdoctoral Fellowship (16POST27260273).
Footnotes
DECLARATION OF INTERESTS
K.A. is a member of the Advisory Board of Molecular Cell.
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
REFERENCES
- 1.Villena JA (2015). New insights into PGC-1 coactivators: redefining their role in the regulation of mitochondrial function and beyond. FEBS J. 282, 647–672. 10.1111/febs.13175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chambers JM, and Wingert RA (2020). PGC-1alpha in disease: recent renal insights into a versatile metabolic regulator. Cells 9, 2234. 10.3390/cells9102234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rius-Perez S, Torres-Cuevas I, Millan I, Ortega AL, and Perez S (2020). PGC-1alpha, inflammation, and oxidative stress: an integrative view in metabolism. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 1452696. 10.1155/2020/1452696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cho H, Rambout X, Gleghorn ML, Nguyen PQT, Phipps CR, Miyoshi K, Myers JR, Kataoka N, Fasan R, and Maquat LE (2018). Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha contains a novel CBP80-binding motif that orchestrates efficient target gene expression. Genes Dev. 32, 555–567. 10.1101/gad.309773.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lin J, Wu H, Tarr PT, Zhang CY, Wu Z, Boss O, Michael LF, Puigserver P, Isotani E, Olson EN, et al. (2002). Transcriptional co-activator PGC-1 alpha drives the formation of slow-twitch muscle fibres. Nature 418, 797–801. 10.1038/nature00904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Calvo JA, Daniels TG, Wang X, Paul A, Lin J, Spiegelman BM, Stevenson SC, and Rangwala SM (2008). Muscle-specific expression of PPARgamma coactivator-1alpha improves exercise performance and increases peak oxygen uptake. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 104, 1304–1312. 10.1152/japplphysiol.01231.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ruas JL, White JP, Rao RR, Kleiner S, Brannan KT, Harrison BC, Greene NP, Wu J, Estall JL, Irving BA, et al. (2012). A PGC-1alpha isoform induced by resistance training regulates skeletal muscle hypertrophy. Cell 151, 1319–1331. 10.1016/j.cell.2012.10.050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dinulovic I, Furrer R, Beer M, Ferry A, Cardel B, and Handschin C (2016). Muscle PGC-1alpha modulates satellite cell number and proliferation by remodeling the stem cell niche. Skelet. Muscle 6, 39. 10.1186/s13395-016-0111-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wang YX, and Rudnicki MA (2011). Satellite cells, the engines of muscle repair. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 127–133. 10.1038/nrm3265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Puigserver P, Wu Z, Park CW, Graves R, Wright M, and Spiegelman BM (1998). A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell 92, 829–839. 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Michael LF, Wu Z, Cheatham RB, Puigserver P, Adelmant G, Lehman JJ, Kelly DP, and Spiegelman BM (2001). Restoration of insulin-sensitive glucose transporter (GLUT4) gene expression in muscle cells by the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 3820–3825. 10.1073/pnas.061035098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Ichida M, Nemoto S, and Finkel T (2002). Identification of a specific molecular repressor of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma Coactivator-1 alpha (PGC-1alpha). J. Biol. Chem. 277, 50991–50995. 10.1074/jbc.M210262200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Puigserver P, Adelmant G, Wu Z, Fan M, Xu J, O’Malley B, and Spiegelman BM (1999). Activation of PPARgamma coactivator-1 through transcription factor docking. Science 286, 1368–1371. Available at: http://science.sciencemag.org/content/sci/286/5443/1368.full.pdf. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wallberg AE, Yamamura S, Malik S, Spiegelman BM, and Roeder RG (2003). Coordination of p300-mediated chromatin remodeling and TRAP/mediator function through coactivator PGC-1alpha. Mol. Cell 12, 1137–1149. 10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00391-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chen W, Yang Q, and Roeder RG (2009). Dynamic interactions and cooperative functions of PGC-1alpha and MED1 in TRalpha-mediated activation of the brown-fat-specific UCP-1 gene. Mol. Cell 35, 755–768. 10.1016/j.molcel.2009.09.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sano M, Izumi Y, Helenius K, Asakura M, Rossi DJ, Xie M, Taffet G, Hu L, Pautler RG, Wilson CR, et al. (2007). Menage-a-trois 1 is critical for the transcriptional function of PPARgamma coactivator 1. Cell Metab. 5, 129–142. 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rambout X, and Maquat LE (2020). The nuclear cap-binding complex as choreographer of gene transcription and pre-mRNA processing. Genes Dev. 34, 1113–1127. 10.1101/gad.339986.120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mihaylov SR, Castelli LM, Lin Y-H, Gül A, Soni N, Hastings C, Flynn HR, Dickman MJ, Snijders AP, Bandmann O, et al. (2021). The master energy homeostasis regulator PGC-1α couples transcriptional co-activation and mRNA nuclear export. bioRxiv, 2021.2009.2019.460961. 10.1101/2021.09.19.460961. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tavares CDJ, Aigner S, Sharabi K, Sathe S, Mutlu B, Yeo GW, and Puigserver P (2020). Transcriptome-wide analysis of PGC-1alpha-binding RNAs identifies genes linked to glucagon metabolic action. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 117, 22204–22213. 10.1073/pnas.2000643117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Olson CM, Liang Y, Leggett A, Park WD, Li L, Mills CE, Elsarrag SZ, Ficarro SB, Zhang T, Düster R, et al. (2019). Development of a selective CDK7 covalent inhibitor reveals predominant cell-cycle phenotype. Cell Chem. Biol. 26, 792–803.e710. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.02.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Parua PK, and Fisher RP (2020). Dissecting the Pol II transcription cycle and derailing cancer with CDK inhibitors. Nat. Chem. Biol. 16, 716–724. 10.1038/s41589-020-0563-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Doamekpor SK, Sanchez AM, Schwer B, Shuman S, and Lima CD (2014). How an mRNA capping enzyme reads distinct RNA polymerase II and Spt5 CTD phosphorylation codes. Genes Dev. 28, 1323–1336. 10.1101/gad.242768.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kwak H, Fuda NJ, Core LJ, and Lis JT (2013). Precise maps of RNA polymerase reveal how promoters direct initiation and pausing. Science 339, 950–953. 10.1126/science.1229386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Core L, and Adelman K (2019). Promoter-proximal pausing of RNA polymerase II: a nexus of gene regulation. Genes Dev. 33, 960–982. 10.1101/gad.325142.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Elrod ND, Henriques T, Huang KL, Tatomer DC, Wilusz JE, Wagner EJ, and Adelman K (2019). The Integrator complex attenuates promoter-proximal transcription at protein-coding genes. Mol. Cell 76, 738–752 e737. 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.10.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tatomer DC, Elrod ND, Liang D, Xiao MS, Jiang JZ, Jonathan M, Huang KL, Wagner EJ, Cherry S, and Wilusz JE (2019). The Integrator complex cleaves nascent mRNAs to attenuate transcription. Genes Dev. 33, 1525–1538. 10.1101/gad.330167.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Meininghaus M, and Eick D (1999). Requirement of the carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II for the transcriptional activation of chromosomal c-fos and hsp70A genes. FEBS Lett. 446, 173–176. 10.1016/s0014-5793(99)00184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Nilson KA, Guo J, Turek ME, Brogie JE, Delaney E, Luse DS, and Price DH (2015). THZ1 reveals roles for Cdk7 in co-transcriptional capping and pausing. Mol. Cell 59, 576–587. 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.06.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sampathi S, Acharya P, Zhao Y, Wang J, Stengel KR, Liu Q, Savona MR, and Hiebert SW (2019). The CDK7 inhibitor THZ1 alters RNA polymerase dynamics at the 5’ and 3’ ends of genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, 3921–3936. 10.1093/nar/gkz127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nechaev S, and Adelman K (2011). Pol II waiting in the starting gates: regulating the transition from transcription initiation into productive elongation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1809, 34–45. 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.11.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kwiatkowski N, Zhang T, Rahl PB, Abraham BJ, Reddy J, Ficarro SB, Dastur A, Amzallag A, Ramaswamy S, Tesar B, et al. (2014). Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor. Nature 511, 616–620. 10.1038/nature13393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Baumli S, Endicott JA, and Johnson LN (2010). Halogen bonds form the basis for selective P-TEFb inhibition by DRB. Chem. Biol. 17, 931–936. 10.1016/j.chembiol.2010.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang W, Yao X, Huang Y, Hu X, Liu R, Hou D, Chen R, and Wang G (2013). Mediator MED23 regulates basal transcription in vivo via an interaction with P-TEFb. Transcription 4, 39–51. 10.4161/trns.22874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Takahashi H, Parmely TJ, Sato S, Tomomori-Sato C, Banks CA, Kong SE, Szutorisz H, Swanson SK, Martin-Brown S, Washburn MP, et al. (2011). Human mediator subunit MED26 functions as a docking site for transcription elongation factors. Cell 146, 92–104. 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Allen BL, and Taatjes DJ (2015). The Mediator complex: a central integrator of transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 155–166. 10.1038/nrm3951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Courvalin JC, Dumontier M, and Bornens M (1982). Solubilization of nuclear structures by the polyanion heparin. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 456–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Huang KL, Jee D, Stein CB, Elrod ND, Henriques T, Mascibroda LG, Baillat D, Russell WK, Adelman K, and Wagner EJ (2020). Integrator recruits protein phosphatase 2A to prevent pause release and facilitate transcription termination. Mol Cell. 80, 345–358.e349. 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.08.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Galbraith MD, Allen MA, Bensard CL, Wang X, Schwinn MK, Qin B, Long HW, Daniels DL, Hahn WC, Dowell RD, and Espinosa JM (2013). HIF1A employs CDK8-mediator to stimulate RNAPII elongation in response to hypoxia. Cell 153, 1327–1339. 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Yang Z, Yik JH, Chen R, He N, Jang MK, Ozato K, and Zhou Q (2005). Recruitment of P-TEFb for stimulation of transcriptional elongation by the bromodomain protein Brd4. Mol. Cell 19, 535–545. 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.06.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Arany Z, He H, Lin J, Hoyer K, Handschin C, Toka O, Ahmad F, Matsui T, Chin S, Wu PH, et al. (2005). Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1 alpha controls the energy state and contractile function of cardiac muscle. Cell metabolism 1, 259–271. 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.03.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Tidball JG (2017). Regulation of muscle growth and regeneration by the immune system. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 17, 165–178. 10.1038/nri.2016.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Perng YC, and Lenschow DJ (2018). ISG15 in antiviral immunity and beyond. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 16, 423–439. 10.1038/s41579-018-0020-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Forcina L, Cosentino M, and Musarò A (2020). Mechanisms regulating muscle regeneration: Insights into the interrelated and time-dependent phases of tissue healing. Cells 9. 10.3390/cells9051297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.LaBarge S, McDonald M, Smith-Powell L, Auwerx J, and Huss JM (2014). Estrogen-related receptor-alpha (ERRalpha) deficiency in skeletal muscle impairs regeneration in response to injury. FASEB J. 28, 1082–1097. 10.1096/fj.13-229211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rambout X, Cho H, and Maquat LE (2019). Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1α binding to newly synthesized RNA via CBP80: a nexus for co- and posttranscriptional gene regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 84, 47–54. 10.1101/sqb.2019.84.040212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lykke-Andersen S, Žumer K, Molska E, Rouvière JO, Wu G, Demel C, Schwalb B, Schmid M, Cramer P, and Jensen TH (2021). Integrator is a genome-wide attenuator of non-productive transcription. Mol. Cell 81, 514–529.e516. 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Mendoza-Figueroa MS, Tatomer DC, and Wilusz JE (2020). The Integrator complex in transcription and development. Trends Biochem Sci. 45, 923–934. 10.1016/j.tibs.2020.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Zhou H, Stein CB, Shafiq TA, Shipkovenska G, Kalocsay M, Paulo JA, Zhang J, Luo Z, Gygi SP, Adelman K, and Moazed D (2022). Rixosomal RNA degradation contributes to silencing of Polycomb target genes. Nature 604, 167–174. 10.1038/s41586-022-04598-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Das J, and Yu H (2012). HINT: high-quality protein interactomes and their applications in understanding human disease. BMC Syst. Biol. 6, 92. 10.1186/1752-0509-6-92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Martínez-Redondo V, Pettersson AT, and Ruas JL (2015). The hitchhiker’s guide to PGC-1alpha isoform structure and biological functions. Diabetologia 58, 1969–1977. 10.1007/s00125-015-3671-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Martínez-Redondo V, Jannig PR, Correia JC, Ferreira DM, Cervenka I, Lindvall JM, Sinha I, Izadi M, Pettersson-Klein AT, Agudelo LZ, et al. (2016). Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha isoforms selectively regulate multiple splicing events on target genes. J. Biol. Chem. 291, 15169–15184. 10.1074/jbc.M115.705822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Blanc RS, Kallenbach JG, Bachman JF, Mitchell A, Paris ND, and Chakkalakal JV (2020). Inhibition of inflammatory CCR2 signaling promotes aged muscle regeneration and strength recovery after injury. Nat. Commun. 11, 4167. 10.1038/s41467-020-17620-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Miano JM, Zhu QM, and Lowenstein CJ (2016). A CRISPR path to engineering new genetic mouse models for cardiovascular research. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 36, 1058–1075. 10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.304790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Haeussler M, Schonig K, Eckert H, Eschstruth A, Mianne J, Renaud JB, Schneider-Maunoury S, Shkumatava A, Teboul L, Kent J, et al. (2016). Evaluation of off-target and on-target scoring algorithms and integration into the guide RNA selection tool CRISPOR. Genome Biol. 17, 148. 10.1186/s13059-016-1012-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Nojima T, Gomes T, Carmo-Fonseca M, and Proudfoot NJ (2016). Mammalian NET-seq analysis defines nascent RNA profiles and associated RNA processing genome-wide. Nat. Protoc. 11, 413–428. 10.1038/nprot.2016.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Reimer KA, Mimoso CA, Adelman K, and Neugebauer KM (2021). Co-transcriptional splicing regulates 3’ end cleavage during mammalian erythropoiesis. Mol. Cell 81, 998–1012 e1017. 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Schneider CA, Rasband WS, and Eliceiri KW (2012). NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 9, 671–675. 10.1038/nmeth.2089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Robinson JT, Thorvaldsdottir H, Wenger AM, Zehir A, and Mesirov JP (2017). Variant review with the integrative genomics viewer. Cancer Res. 77, e31–e34. 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Smith T, Heger A, and Sudbery I (2017). UMI-tools: modeling sequencing errors in Unique Molecular Identifiers to improve quantification accuracy. Genome Res. 27, 491–499. 10.1101/gr.209601.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Martin M (2011). Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 17, 3. 10.14806/ej.17.1.200. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Li H (2013). Aligning sequence reads, clone sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv:1303.3997v2. [Google Scholar]
- 62.Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T, Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G, and Durbin R (2009). The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25, 2078–2079. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Love MI, Huber W, and Anders S (2014). Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15, 550. 10.1186/s13059-014-0550-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Andrews S (2010). FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data. Available online at: http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/.
- 65.Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y, and Gu J (2018). fastp: an ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 34, i884–i890. 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, Batut P, Chaisson M, and Gingeras TR (2013). STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29, 15–21. 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Liao Y, Smyth GK, and Shi W (2014). featureCounts: an efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 30, 923–930. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Ramírez F, Ryan DP, Grüning B, Bhardwaj V, Kilpert F, Richter AS, Heyne S, Dündar F, and Manke T (2016). deepTools2: a next generation web server for deep-sequencing data analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, W160–165. 10.1093/nar/gkw257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Ito-Ishida A, Yamalanchili HK, Shao Y, Baker SA, Heckman LD, Lavery LA, Kim JY, Lombardi LM, Sun Y, Liu Z, and Zoghbi HY (2018). Genome-wide distribution of linker histone H1.0 is independent of MeCP2. Nat. Neurosci. 21, 794–798. 10.1038/s41593-018-0155-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Cell equivalents in after IP relative to before IP samples, related to Figures 1, 2, 3, 6, S1, S5 and S6.
PRO-seq, RNA-seq, and RIP-seq values for the 125 PGC-1α-responsive genes, related to Figures 4, 5, S3 and S4.
Term enrichment analysis of PGC-1α CBM-responsive genes identified by PRO-seq, related to Figure 4.
Oligonucleotide sequences, related to STAR Methods.
Data Availability Statement
All sequencing datasets generated in this study (PRO-seq, RNA-seq, native RIP-seq, RIP-seq footprinting) have been submitted to the GEO database (GSE197312). Unprocessed and uncompressed imaging data are available in Mendeley Data (doi:10.17632/39mxxdfkdn.1).
This paper does not report original code.
Any additional information required to reanalyze the data reported in this paper is available from the lead contact upon request.


