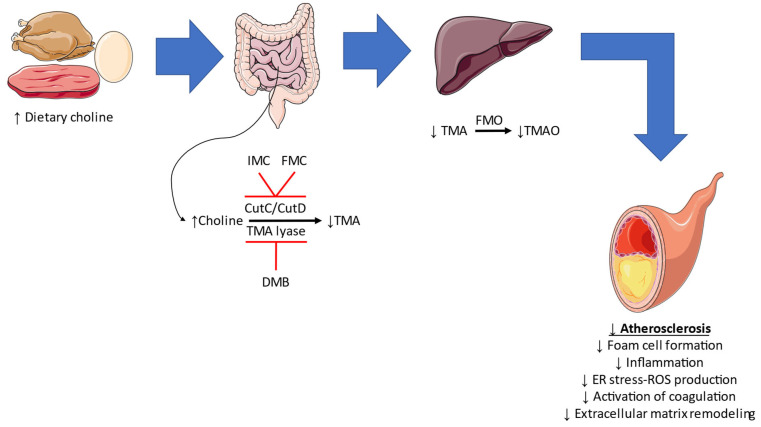
Figure 4.
The effect of TMAO inhibition in atherosclerosis. Consumption of a high-choline diet leads to its conversion to trimethylamine (TMA) in the gut, with the aid of CutC/CutD and TMA-lyase. Inhibition of these enzymes by iodomethylcholine (IMC)/fluoromethylcholine (FMC) and 3,3-dimethyl-1-butanol (DMB) leads to lower trimethylamine N-Oxide (TMAO) production in the liver. As a result, atherosclerosis may be attenuated through multiple mechanisms. FMO: flavin-containing monooxygenase, ER: endoplasmic reticulum, ROS: reactive oxygen species.