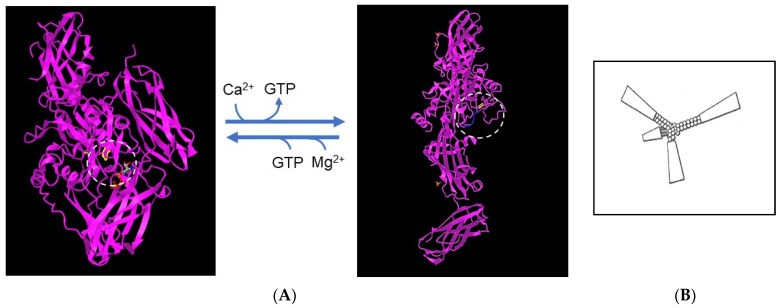
Figure 8.
Structures of transglutaminase 2. (A) The inactive, closed conformation (accession no. 3LY6) and (B) the fully open, active conformation (accession no. 2Q3Z). The catalytic site of the enzyme is circled and the position of the cysteine residue that forms the thioester linkage to the substrate in the first step in the reaction is highlighted. The closed conformation is stabilized by Mg2+ and a GTP molecule, shown in gray, that binds to β-barrel1 and covers the catalytic site. Calcium displaces Mg2+ and GTP and generates the open conformation, which is stabilized by an inactive derivative of the peptide substrate. As shown within the box at the right, the remainder of the tetravalent structure of svL4 and sv6D may restrict entry of an arm into the catalytic site of the closed or partially open conformation.