Fig. 6. resR, whiB2-fbiA and whiA mutants were associated with canonical drug resistance and relapse of drug-susceptible tuberculosis.
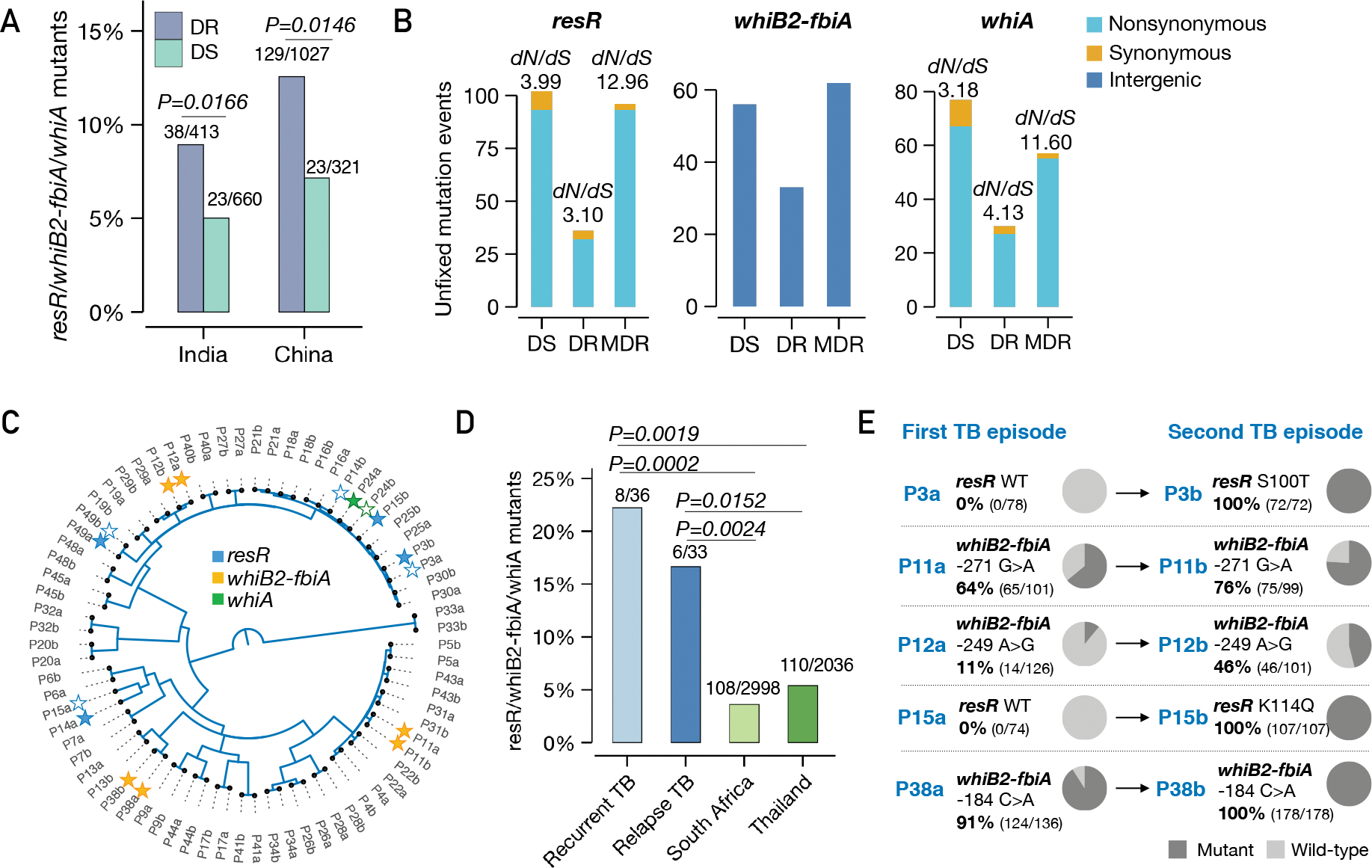
(A) The proportion of resR, whiB2-fbiA and whiA mutants in DR and DS strains sequenced from India and China, P values by Fisher’s exact test. (B) Unfixed mutations in DS, DR and MDR (resistant to RIF and INH) strains. (C) A phylogenetic tree of paired Mtb isolates from 36 recurrent TB patients. Solid stars indicate isolates in which mutations were detected while empty stars indicate absence of mutations in one of the paired isolates. (D) Percentage of isolates with mutations in resR/whiB2-fbiA/whiA. “Recurrent TB” includes 3 patients with Mtb isolates suggestive of re-infection. (E) Mutational trajectory in Mtb isolates from the first TB to second TB episodes in 5 pairs of isolates. The mutations in other three pairs: P14 (resR, D144N; 100% in P14a, 0% in P14b); P49 (resR, R95H; 8.7% in P49a, 0% in P49b); P24 (whiA, A131T; 11.6% in P24a, 0% in P24b).
