Dear Editor,
Silicone oil is a vitreous substitute used in treating complex retinal detachments. 1 Pupillary block secondary to silicone oil is common in aphakic patients 2 but can also occur in pseudophakic patients if there is zonular laxity or significant inflammation. 3,4 Therefore, a surgical peripheral iridectomy (PI) via a posterior approach is commonly made in pseudophakic and aphakic patients requiring silicone oil. In dark irides this can be a blind approach and localization of the vitreous cutter can be difficult. We present a guided approach to creating a PI that allows for ease and precision of placement.
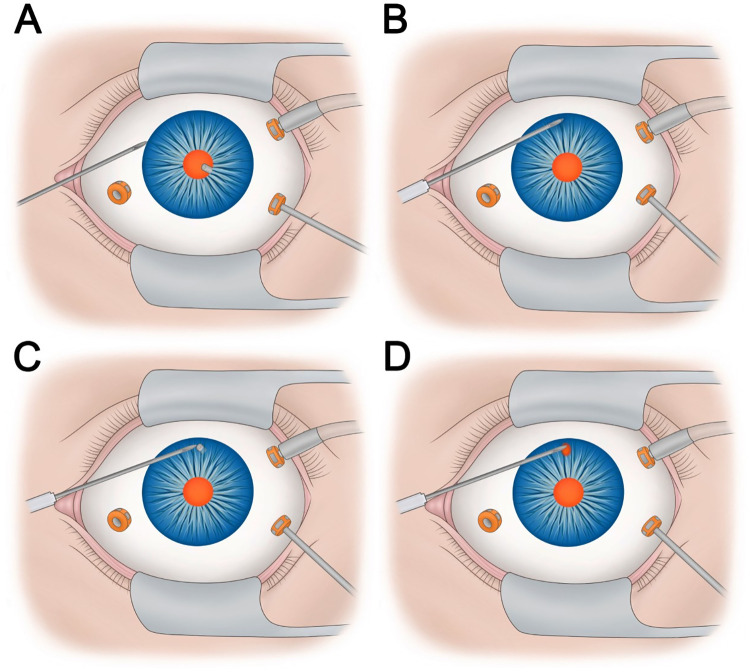
The vitreous cutter is introduced through the superotemporal pars plana port and visualized in the pupil. Next, a 30-gauge needle is introduced into the anterior chamber via the surgical limbus at approximately the 4 o’clock position (Figure 1A). The needle is on a syringe with its plunger, creating a closed system and preventing the anterior chamber from collapsing. The needle is advanced across the anterior chamber to the desired site of the iridectomy at the 6 o’clock position. The vitreous cutter is positioned posterior to the iris at the desired iridectomy site. The 30-gauge needle is then used to “feed” the peripheral iris at the 6 o’clock position into the mouth of the vitreous cutter (Figure 1B). The immediate tactile and visual feedback allow for precise localization of the PI (Figure 1C). The vitreous cutter is then used to create the PI of the appropriate size (Figure 1D). Silicone oil may next be injected as per the surgeon’s typical approach.
Figure 1.
Intraoperative view from the head of the bed of the right eye. The step-wise illustration shows creation of a peripheral iridectomy at the 6 o’clock position. (A) The vitreous cutter is inserted through the superotemporal pars plana vitrectomy port. A 30-gauge needle is inserted through the limbus into the anterior chamber and (B) advanced to the 6 o’clock position. (C) The needle is gently manipulated to help localize the cutting mouth of the vitrector. (D) Once it is confirmed that the vitrector is in the correct location, a surgical peripheral iridectomy is created.
We present a technique for surgical PI in the setting of retinal surgery. This procedure is useful in pseudophakic and aphakic patients in whom silicone oil will be instilled as a vitreous substitute, and a PI has been suggested to protect against significant increases in intraocular pressure. 5 Our technique can be especially beneficial in dark irides where visualization of the vitreous cutter may be more difficult.
Footnotes
Ethical Approval: Ethical approval was not required.
Statement of Informed Consent: Informed consent was not required.
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
References
- 1. Riedel KG, Gabel VP, Neubauer L, Kampik A, Lund OE. Intravitreal silicone oil injection: complications and treatment of 415 consecutive patients. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 1990;228(1):19–23. doi:10.1007/BF02764284 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Beekhuis WH, Ando F, Zivojnović R, Mertens DA, Peperkamp E. Basal iridectomy at 6 o’clock in the aphakic eye treated with silicone oil: prevention of keratopathy and secondary glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 1987;71(3):197–200. doi:10.1136/bjo.71.3.197 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Yusuf IH, Fung TH, Salmon JF, Patel CK. Silicone oil pupil block glaucoma in a pseudophakic eye. BMJ Case Rep. 2014;2014:bcr2014205018. doi:10.1136/bcr-2014-205018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Jackson TL, Thiagarajan M, Murthy R, Snead MP, Wong D, Williamson TH. Pupil block glaucoma in phakic and pseudophakic patients after vitrectomy with silicone oil injection. Am J Ophthalmol. 2001;132(3):414–416. doi:10.1016/s0002-9394(01)00991-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Fisk MJ, Cairns JD. Silicone oil insertion. A review of 127 consecutive cases. Aust NZ J Ophthalmol. 1995;23(1):25-32. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9071.1995.tb01641.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]